Effect of PKC-β Signaling Pathway on Expression of MCP-1 and VCAM-1 in Different Cell Models in Response to Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. AGEs Characterization

2.2. Endotoxin Levels in AGEs
2.3. Effect of AGEs on Cell Viability
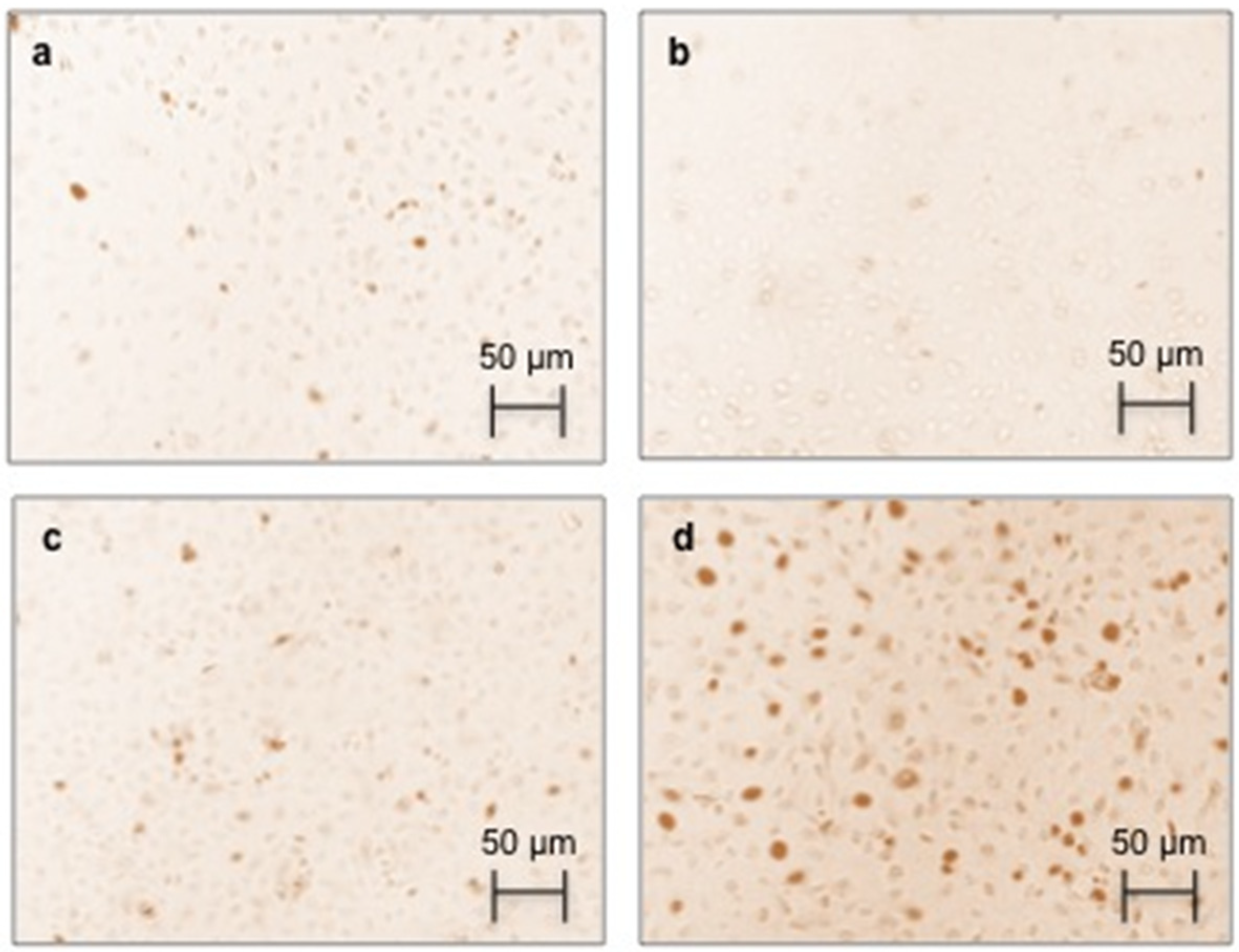
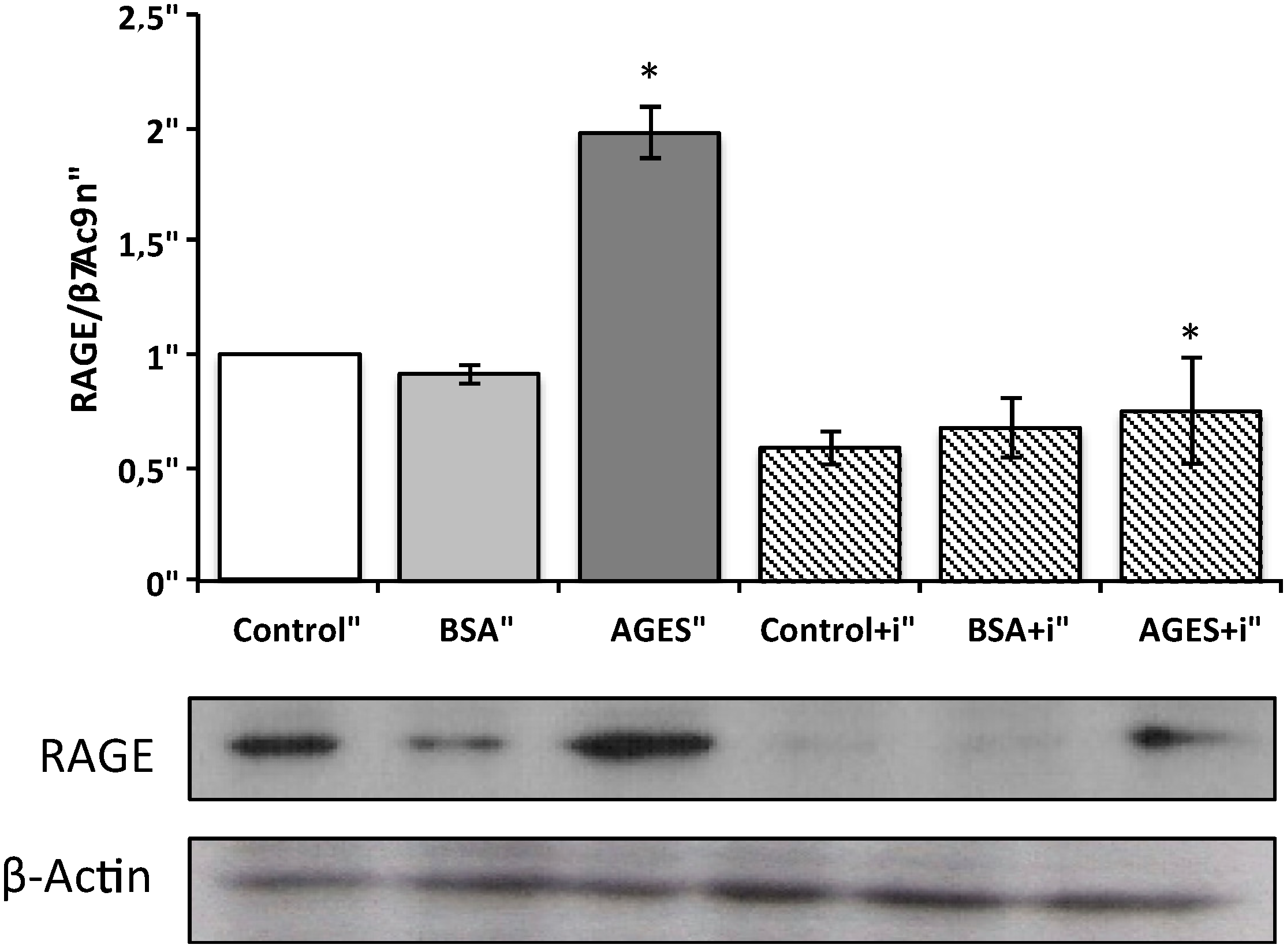
2.4. Effect of AGEs on RAGE Immunostaining and Protein Expression
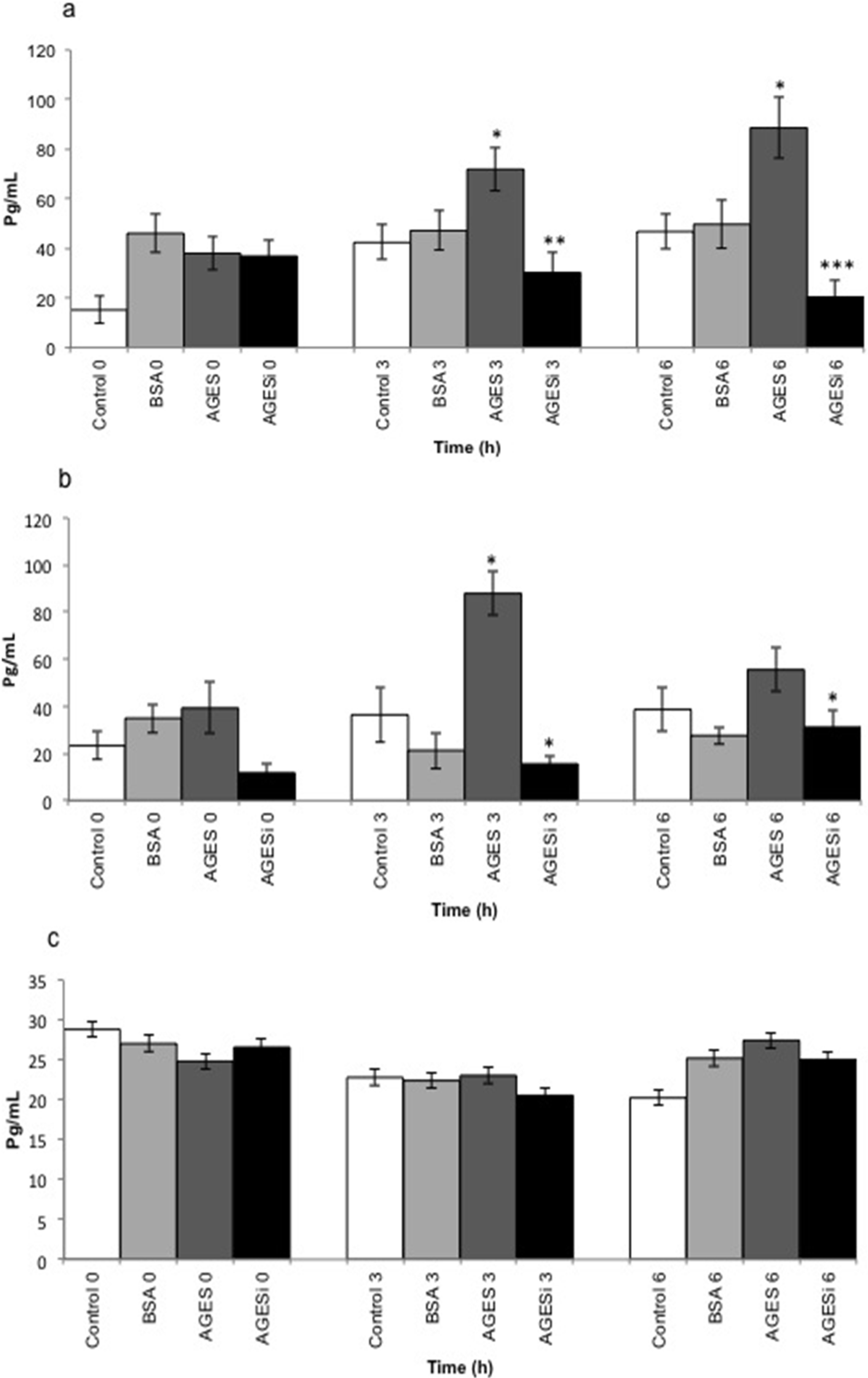
2.5. Effect of AGEs on MCP-1 Expression and Inhibition of the PKC-β Pathway
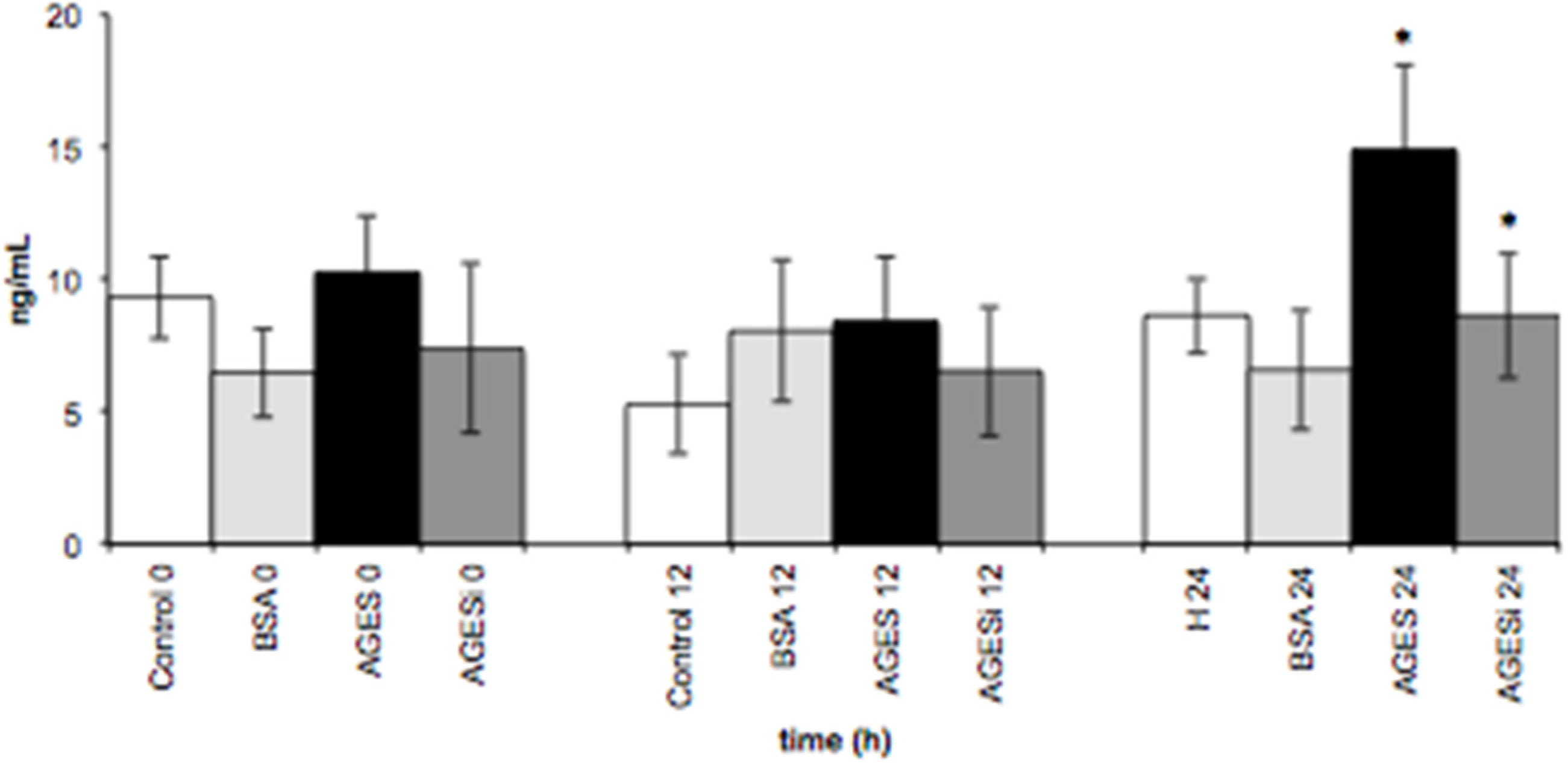
2.6. Effect of AGEs on VCAM-1 Expression and Inhibition of the PKC-β Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Preparation and Characterization of AGEs
4.2. Endotoxin Assay
4.3. Isolation, Culturing, and Characterization of Endothelial Cells
4.4. U-937 Cell Culture
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Treatment of HUVECs, U937 Cells, and Cocultured HUVEC–U937 Cells with AGEs
4.7. RAGE Immunostaining
4.8. RAGE Western Blot Analysis
4.9. MCP-1 and VCAM-1 Supernatant Levels
4.10. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meijers, B.K.; de Preter, V.; Verbeke, K.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Evenepoel, P. P-cresyl sulfate serum concentrations in haemodialysis patients are reduced by the prebiotic oligofructose-enriched inulin. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 25, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Nahas, M. Cardio-Kidney-Damage: A unifying concept. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinghen, A.E.M.; Pecoits-Filho, R. Vascular damage in kidney disease: Beyond hypertension. Int. J. Hypertens. 2011, 2011, 232683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinghen, A.E.M.; Goncalves, S.M.; Martines, E.G.; Nakao, L.S.; Riella, M.C.; Aita, C.A.; Pecoits-Filho, R. Increased plasma and endothelial cell expression of chemokines and adhesion molecules in chronic kidney disease. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2009, 111, c117–c126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwedler, S.; Schinzel, R.; Vaith, P.; Wanner, C. Inflammation and advanced glycation end products in uremia: Simple coexistence, potentiation or causal relationship? Kidney Int. 2001, 59, S32–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semba, R.D.; Nicklett, E.J.; Ferruci, L. Does accumulation of advanced glycation end products contribute to the aging phenotype? J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010, 65, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piperi, C.; Adamopoulos, C.; Dalagiorgou, G.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Crosstalk between advanced glycation and endoplasmic reticulum stress: Emerging therapeutic targeting for metabolic diseases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 2231–2242. [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley, P.J.; Rabbani, N. Highlights and hotspots of protein glycation in end-stage renal disease. Semin. Dial. 2009, 22, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhamdani, M.S.; Al-Azzawie, H.F.; Abbas, F.K. Decreased formation of advanced glycation end-products in peritoneal fluid by carnosine and related peptides. Perit. Dial. Int. 2007, 27, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Woodward, M.; Poretsky, L.; Vlassara, H.; Striker, G.E. Effects of sevelamer carbonate on advanced glycation end products and antioxidant/pro-oxidant status in patients with diabetic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerwaldt, R.; Zeebregts, C.J.; Navis, G.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Lefrandt, J.D.; Smit, A.J. Accumulation of advanced glycation end products and chronic complications in ESRD treated by dialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieman, S.; Kass, D. Advanced glycation end product cross-linking: Pathophysiologic role and therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Congest. Heart Fail. 2004, 10, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, E.; Cai, W.; He, J.C.; Xue, C.; Liz, Z.; Winston, J.; Vlassara, H.; Uribarri, J. Endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease results from advanced glycation end products (AGE)-mediated inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase through RAGE activation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanji, N.; Markowitz, G.S.; Fu, C.; Kislinger, T.; Taguchi, A.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Stern, D.; Schmidt, A.M.; D’Agati, V.D. Expression of advanced glycation end products and their cellular receptor RAGE in diabetic nephropathy and nondiabetic renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Huang, K.; Cai, G.Y.; Chen, X.M.; Yang, J.R.; Lin, L.R.; Yang, J.; Huo, B.G.; Zhan, J.; He, Y.N. Receptor for advanced glycation end-products promotes premature senescence of proximal tubular epithelial cells via activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress dependent p21 signaling. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumur, Z.; Shimizu, H.; Enomoto, A.; Miyazaki, H.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate upregulates expression of ICAM-1 and MCP-1 by oxidative stress-induced NF-kappaB activation. Am. J. Nephrol. 2010, 31, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongor, S.; Ulrich, P.C.; Bencsath, F.A.; Cerami, A. Aging of proteins: Isolation and identification of a fluorescent chromophore from the reaction of polypeptides with glucose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 2684–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recio-Mayoral, A.; Banerjee, D.; Streather, C.; Kaski, J.C. Endothelial dysfunction, inflammation and atherosclerosis in chronic kidney disease a cross-sectional study of predialysis, dialysis and kidney-transplantation patients. Atherosclerosis 2011, 216, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaipersad, A.S.; Lip, G.Y.; Silverman, S.; Shantsila, E. The role of monocytes in angiogenesis and atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, R.J.; Bourassa, P.A.; Lindsey, S.; Weng, W.; Natoli, E.; Rollins, B.J.; Milos, P.M. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 accelerates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Chibber, R.; Ruggiero, D.; Kohner, E.; Ritter, J.; Ferro, A. Impairment of vascular endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity by advanced glycation end products. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1289–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, M.; Bucciarelli, L.; Hwang, Y.C.; Lee, L.; Yan, S.F.; Schmidt, A.M.; Ramasamy, R. Aldose reductase and AGE-RAGE pathways: Key players in myocardial ischemic injury. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R. Advanced glycation end products accelerate ischemia/reperfusion injury through receptor of advanced end product/nitrative thioredoxin inactivation in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal-Pizzol, F.; Pasquali, M.; Quevedo, J.; Gelain, D.P.; Moreira, J.C. Is there a role for high mobility group box 1 and the receptor for advanced glycation end products in the genesis of long-term cognitive impairment in sepsis survivors? Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 1357–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Feng, L.; Zhu, Q.; Xiang, P.; He, B. Blockade of PKC-beta protects HUVEC from advanced glycation end products induced inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukami, K.; Yamagishi, S.; Okuda, S. Role of AGEs-RAGE system in cardiovascular disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basta, G.; Lazzerini, G.; Del Turco, S.; Ratto, G.M.; Schimidt, A.M.; de Catarina, R. At least 2 distinct pathways generating reactive oxygen species mediate vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 induction by advanced glycation end products. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, D.X.; Rai, V.; Shen, X.; Rosario, R.; Lu, Y.; D’Agati, V.; Yan, S.F.; Friedman, R.A.; Nuglozeh, E.; Schimidt, A.M. Activation of the ROCK1 branch of the transforming growth factor-beta pathway contributes to RAGE-dependent acceleration of atherosclerosis in diabetic ApoE-null mice. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, B.; Li, Q.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Huang, Q. RhoA/ROCK-dependent moesin phosphorylation regulates AGE-induced endothelial cellular response. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matasui, T.; Nishino, Y.; Maeda, S.; Takeuchi, M.; Yamagishi, S. Irbesartan inhibits advanced glycation end product (AGE)-induced up-regulation of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) mRNA levels in glomerular endothelial cells. Microvasc. Res. 2011, 81, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramli, J.; Calderon Artero, P.; Block, R.C.; Mousa, S.A. Novel therapeutic targets for preserving a healthy endothelium: Strategies for reducing the risk of vascular and cardiovascular disease. Cardiol. J. 2011, 18, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bordoni, V.; de Cal, M.; Rassu, M.; Cavvavillan, S.; Segala, C.; Bonello, M.; Ranishta, R.; Andrikos, E.; Yavuz, A.; Salvatori, G.; et al. Protective effect of urate oxidase on uric acid induced-monocyte apoptosis. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2005, 2, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Buxo, J.A.; Woods, H.F. Protecting the endothelium: A new focus for management of chronic kidney disease. Hemodial. Int. 2006, 10, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.S.; Fortheringham, A.K.; Cooper, M.E.; Forbes, J.M. Targeting advanced glycation endproducts and mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.M.; Hori, O.; Chen, J.X.; Li, J.F.; Crandall, J.; Zhang, J.; Cao, R.; Yan, S.D.; Brett, J.; Stern, D. Advanced glycation endproducts interacting with their endothelial receptor induce expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in cultured human endothelial cells and in mice. A potential mechanism for the accelerated vasculopathy of diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucciarelli, L.G.; Wendt, T.; Rong, L.; Lalla, E.; Hofmann, M.A.; Goova, M.T.; Taquchi, A.; Yan, S.F.; Stern, D.M.; Schmidt, A.M. RAGE is a multiligand receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily: Implications for homeostasis and chronic disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naum, M.H.; Lee, H.S.; Seomun, Y.; Lee, Y.; Lee, K.W. Monocyte-endothelium-smooth muscle cell interaction in co-culture: Proliferation and cytokine productions in response to advanced glycation end products. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1810, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukacs, N.W.; Strieter, R.M.; Elner, V.; Evanoff, H.L.; Burdick, M.D.; Kunkel, S.L. Production of chemokines, interleukin-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, during monocyte: Endothelial cell interactions. Blood 1995, 86, 2767–2773. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iwashima, Y.; Eto, M.; Horiuchi, S.; Sano, H. Advanced glycation end product-induced peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma gene expression in the cultured mesangial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 264, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, E.A.; Nachman, R.L.; Becker, C.G.; Minick, C.R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J. Clin. Investig. 1973, 52, 2745–2756. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rempel, L.C.T.; Finco, A.B.; Maciel, R.A.P.; Bosquetti, B.; Alvarenga, L.M.; Souza, W.M.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Stinghen, A.E.M. Effect of PKC-β Signaling Pathway on Expression of MCP-1 and VCAM-1 in Different Cell Models in Response to Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs). Toxins 2015, 7, 1722-1737. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7051722
Rempel LCT, Finco AB, Maciel RAP, Bosquetti B, Alvarenga LM, Souza WM, Pecoits-Filho R, Stinghen AEM. Effect of PKC-β Signaling Pathway on Expression of MCP-1 and VCAM-1 in Different Cell Models in Response to Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs). Toxins. 2015; 7(5):1722-1737. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7051722
Chicago/Turabian StyleRempel, Lisienny C. T., Alessandra B. Finco, Rayana A. P. Maciel, Bruna Bosquetti, Larissa M. Alvarenga, Wesley M. Souza, Roberto Pecoits-Filho, and Andréa E. M. Stinghen. 2015. "Effect of PKC-β Signaling Pathway on Expression of MCP-1 and VCAM-1 in Different Cell Models in Response to Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)" Toxins 7, no. 5: 1722-1737. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7051722
APA StyleRempel, L. C. T., Finco, A. B., Maciel, R. A. P., Bosquetti, B., Alvarenga, L. M., Souza, W. M., Pecoits-Filho, R., & Stinghen, A. E. M. (2015). Effect of PKC-β Signaling Pathway on Expression of MCP-1 and VCAM-1 in Different Cell Models in Response to Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs). Toxins, 7(5), 1722-1737. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7051722






