Metabolomics of the Bio-Degradation Process of Aflatoxin B1 by Actinomycetes at an Initial pH of 6.0
Abstract
:1. Introduction
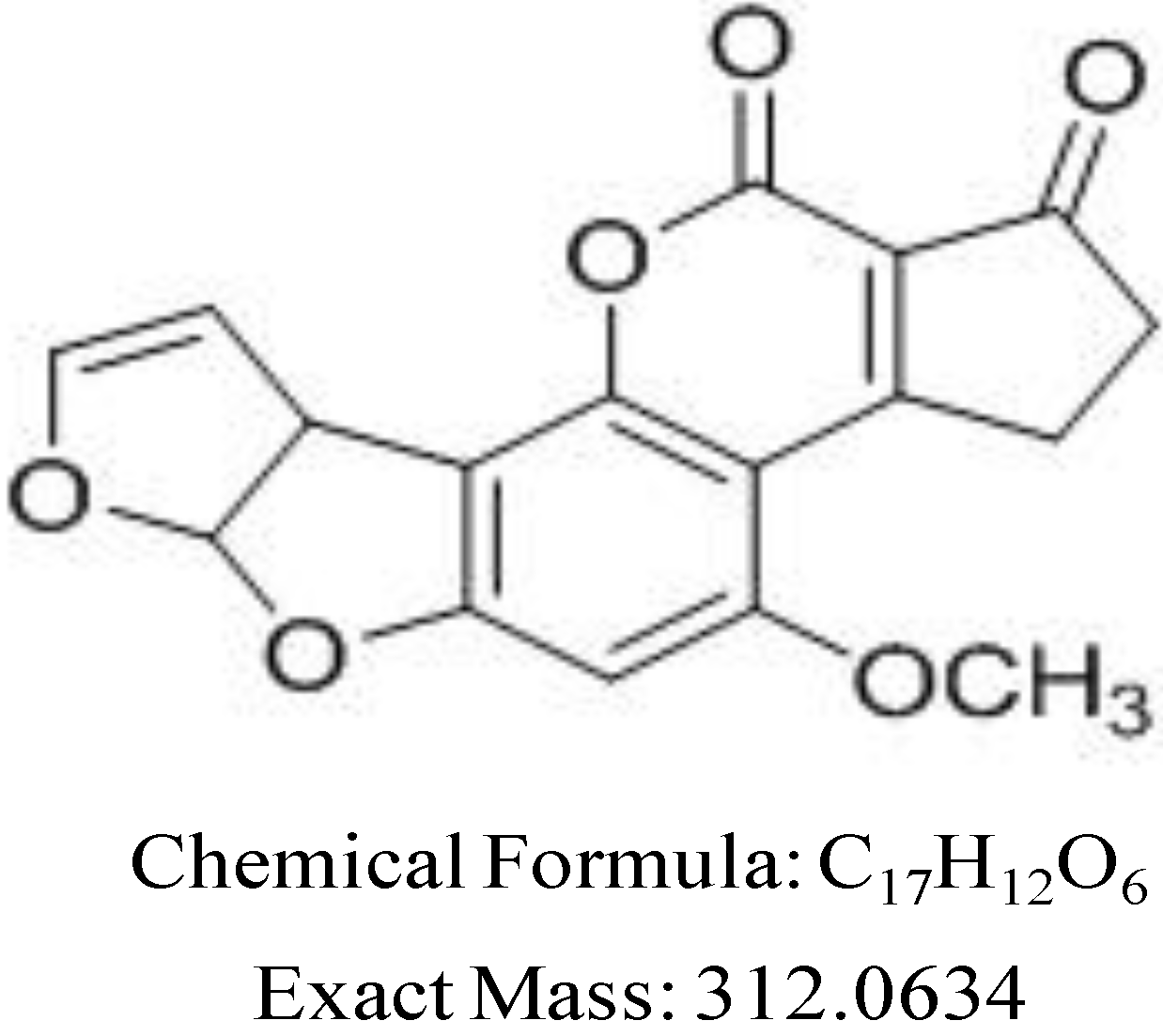
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. AFB1 Degradation by Actinomyces in Liquid Culture

2.2. Optimising AFB1 Degradation Conditions
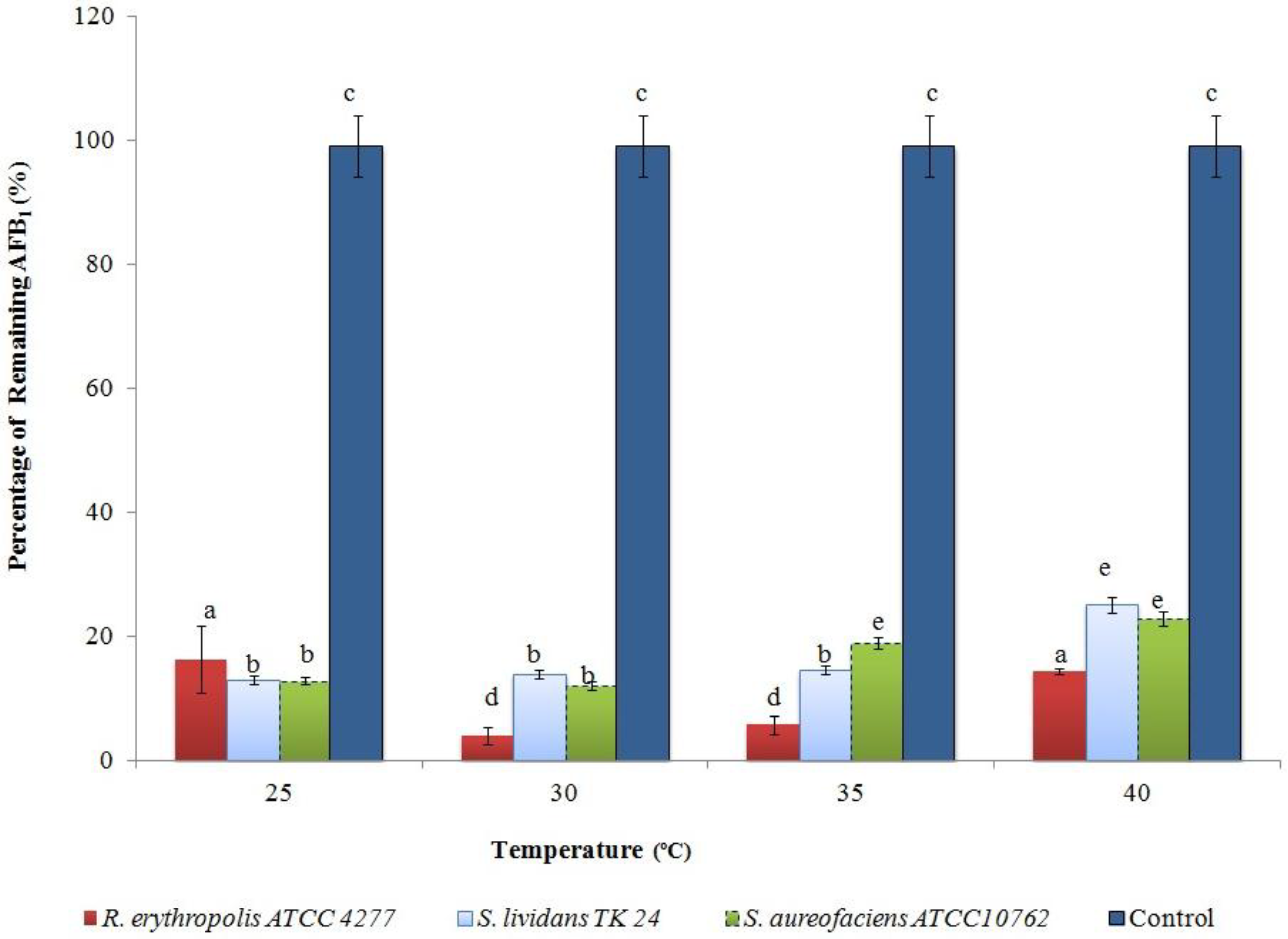

2.3. Confirmation of AFB1 Degradation
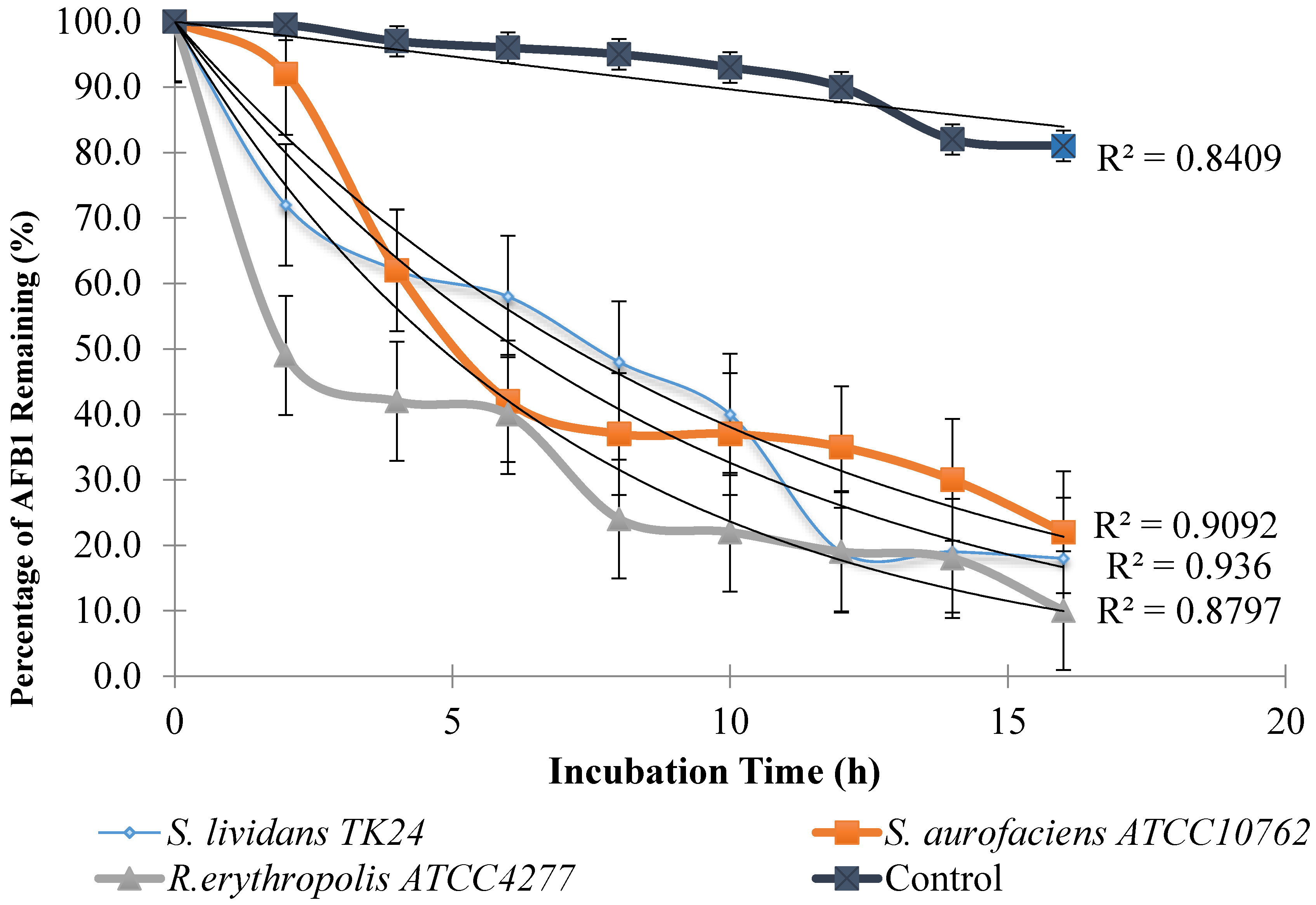
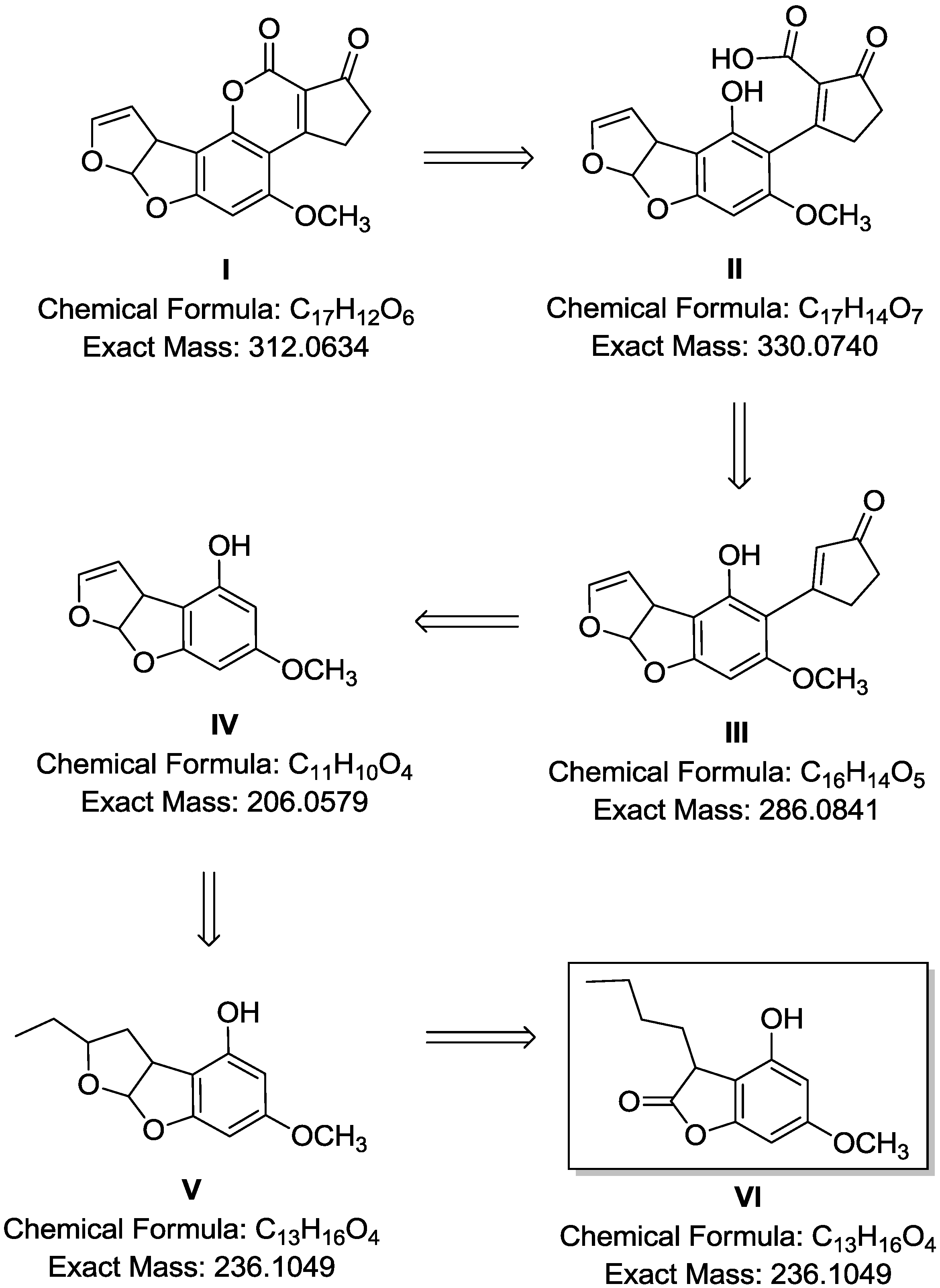
2.4. Breakdown Product Identification and AFB1 Degradation Hypothesis

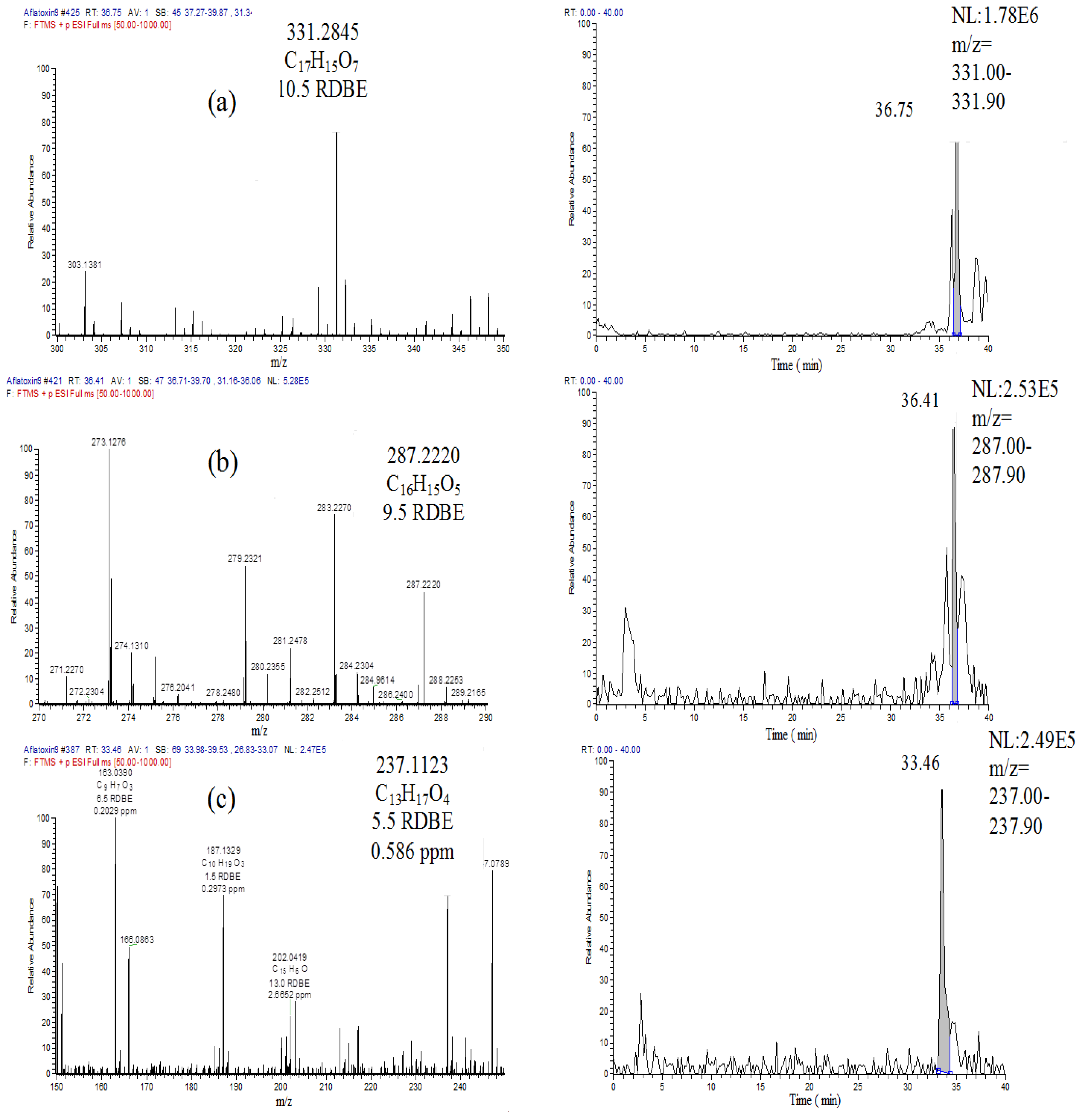

| m/z | Peak area | Correlation | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 331.2845 | 782442 | −0.921 | 0.254 |
| 297.2428 | 2418033 | −0.546 | 0.633 |
| 299.2584 | 117588 | 0.809 | 0.400 |
| 287.2219 | 115295 | −0.645 | 0.263 |
| 269.2477 | 1488 | 0.916 | 0.554 |
| 237.1121 | 31685 | −0.998 | 0.041 |

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Microbial Strains and Cultivation
3.2. AFB1 Degradation by Actinomycetes in Liquid Culture
3.3. Optimization of the Degradation Conditions
3.4. Quantification of AFB1 and Its Degradants
3.4.1. TLC
3.4.2. Reversed phase HPLC
3.4.3. LCMS
3.4.4. LTQ-Orbitrap
4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, F.H.V.D.; Martins, S.J.; Zucchi, T.D.; Melo, I.S.D.; Batista, L.R.; Machado, J.D.C. Biological control of mycotoxin-producing molds. Ciênc. Agrotecnol. 2012, 36, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognani, F.; Rumney, C.J.; Rowland, I.R. Influence of carcinogen binding by lactic acid-producing bacteria on tissue distribution and in vivo mutagenicity of dietary carcinogens. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1997, 35, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabak, B. The fate of mycotoxins during thermal food processing. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nezami, H.; Kankaanpaa, P.; Salminen, S.; Ahokas, J. Ability of dairy strains of lactic acid bacteria to bind a common food carcinogen, aflatoxin B-1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.L.; Yao, D.S.; Liang, R.; Ma, L.; Cheng, W.Q.; Gu, L.Q. Detoxification of aflatoxin B-1 by enzymes isolated from Armillariella tabescens. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumaningtyas, E.; Widiastuti, R.; Maryam, R. Reduction of aflatoxin B1 in chicken feed by using Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Rhizopus oligosporus and their combination. Mycopathologia 2006, 162, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Jezkova, A.; Yuan, Z.; Pavlikova, L.; Dohnal, V.; Kuca, K. Biological degradation of aflatoxins. Drug Metab. Rev. 2009, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.L.; Ma, L.; Gu, L.Q.; Liang, R.; Yao, D.S.; Chen, W.Q. Armillariella Tabescen Enzymatic detoxification of aflatoxin B1: Part III. Immobilized enzymatic detoxification. In Proceedings of the 14th International Enzyme Engineering Conference, Beijing, China, 12–17 October 1997; Laskin, A.I., Li, G.X., Yu, Y.T., Eds.; Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 592–599. [Google Scholar]
- Martinkova, L.; Uhanakova, B.; Patek, M.; Nesvera, J.; Kren, V. Biodegradation potential of genus Rhodococcus. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motomura, M.; Toyomasu, T.; Mizuno, K. Shinozawa Purification and chracterization of an aflatoxin degrdation enzyme from Pleurotus ostreatus. Microbiol. Res. 2003, 158, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, J.; Toth, B. Novel strategies to control mycotoxins in feeds: A review. Acta Vet. Hung. 2005, 53, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shantha, T. Fungal degradation of aflatoxin B1. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, P.H.; Jespersen, L. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and lactic acid bacteria as potential mycotoxin decontaminating agents. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, D.J.; Casale, C.H.; Pizzolitto, R.P.; Salano, M.A.; Olivier, G. Physical Adsorption of Aflatoxin B1 by lactic acid bacteria and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A theoretical model. J. Food Prot. 2006, 7, 2148–2154. [Google Scholar]
- El-Nezami, H.; Mykkanen, H.; Kankaanpaa, P.; Salminen, S.; Ahokas, J. Ability of Lactobacillus and Propionibacterium strains to remove aflatoxin B-1 from the chicken duodenum. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elgerbi, A.M.; Aidoo, K.E.; Candlish, A.A.G.; Williams, A.G. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria on levels of aflatoxin M-1 in milk and phosphate buffer. Milchwiss.-Milk Sci. Int. 2006, 61, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- El-Nezami, H.; Kankaanpaa, P.; Salminen, S.; Ahokas, J. Physicochemical alterations enhance the ability of dairy strains of lactic acid bacteria to remove aflatoxin from contaminated media. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Teniola, O.D.; Addo, P.A.; Brost, I.M.; Farber, P.; Jany, K.D.; Alberts, J.F.; van Zyl, W.H.; Steyn, P.S.; Holzapfel, W.H. Degradation of aflatoxin B-1 by cell-free extracts of Rhodococcus erythropolis and Mycobacterium fluoranthenivorans sp. nov. DSM44556(T). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 105, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cserháti, M.; Kriszt, B.; Krifaton, C.; Szoboszlay, S.; Háhn, J.; Tóth, S.; Nagy, I.; Kukolya, J. Mycotoxin-degradation profile of Rhodococcus strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.; Ji, C.; Zhou, T.; Li, J.X.; Ma, Q.G.; Niu, T.G. Aflatoxin B-1 degradation by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and other microbes selected using coumarin medium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 1489–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Zhai, C.; Guan, B.; Li, C.; Shan, S.; Yu, J. Mathematic modeling for optimum conditions on aflatoxin B1 degradation by the aerobic bacterium Rhodococcus erythropolis. Toxins 2012, 4, 1181–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.Q.; Zhang, C.G.; Li, B.; Wei, D.Z.; Tong, W.Y. New Microbiological Transformations of Steroids by Streptomyces virginiae IBL-14. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5967–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogell, B.M. oremediation of pesticides and herbicides by Streptomycetes. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Environmental Biotechnology, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 4–8 July 1994; MooYoung, M., Anderson, W.A., Chakrabarty, A.M., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publ: Waterloo, ON, Canada, 1994; pp. 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ciegler, A.; Lillehoj, E.B.; Peterson, R.E.; Hall, H.H. Microbial detoxification of Aflatoxin. Appl. Microbiol. 1966, 14, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.L. Some major mycotoxins and their mycotoxicoses—An overview. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiley, R.D.; Draughon, F.A. Preliminary evidence that degradation of aflatoxin B1 by Flavobacterium aurantiacum is enzymatic. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.S.; Dunn, J.J.; DeLucca, A.J.; Ciegler, A. Role of lactone ring of aflatoxin B1 in toxicity and mutagenicity. Experientia 1981, 37, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez-Albores, A.; Arambula-Villa, G.; Loarea-Pina, M.G.F.; Castano-Tostado, E.; Moreno-Martinez, E. Safety and efficacy evaluation of aqueous citric acid to degrade B-aflatoxins in maize. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez-Albores, A.; Veles-Medina, J.; Urbina-Alvarez, E.; Martinez-Bustos, F.; Moreno-Martinez, E. Effect of citric acid on aflatoxin degradation and on functional and textural properties of extruded sorghum. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 150, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttajit, M. Mycotoxin prevention and control in foodgrains—Prevention and control of mycotoxins. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/X5036E/x5036E0q.htm (accessed on 2 January 2015).
- Alberts, J.F.; Engelbrecht, Y.; Steyn, P.S.; Holzapfel, W.H.; van Zyl, W.H. Biological degradation of aflatoxin B1 by Rhodococcus erythropolis cultures. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 109, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapalikar, G.V.; Taylor, M.C.; Warden, A.C.; Scott, C.; Russell, R.J.; Oakeshott, J.G. F420H2-dependent degradation of aflatoxin and other furanocoumarins is widespread throughout the Actinomycetales. PLoS One 2012, 7, e30114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eshelli, M.; Harvey, L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; McNeil, B. Metabolomics of the Bio-Degradation Process of Aflatoxin B1 by Actinomycetes at an Initial pH of 6.0. Toxins 2015, 7, 439-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7020439
Eshelli M, Harvey L, Edrada-Ebel R, McNeil B. Metabolomics of the Bio-Degradation Process of Aflatoxin B1 by Actinomycetes at an Initial pH of 6.0. Toxins. 2015; 7(2):439-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7020439
Chicago/Turabian StyleEshelli, Manal, Linda Harvey, RuAngelie Edrada-Ebel, and Brian McNeil. 2015. "Metabolomics of the Bio-Degradation Process of Aflatoxin B1 by Actinomycetes at an Initial pH of 6.0" Toxins 7, no. 2: 439-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7020439
APA StyleEshelli, M., Harvey, L., Edrada-Ebel, R., & McNeil, B. (2015). Metabolomics of the Bio-Degradation Process of Aflatoxin B1 by Actinomycetes at an Initial pH of 6.0. Toxins, 7(2), 439-456. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7020439







