A High-Throughput, Precipitating Colorimetric Sandwich ELISA Microarray for Shiga Toxins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preliminary Assay Development

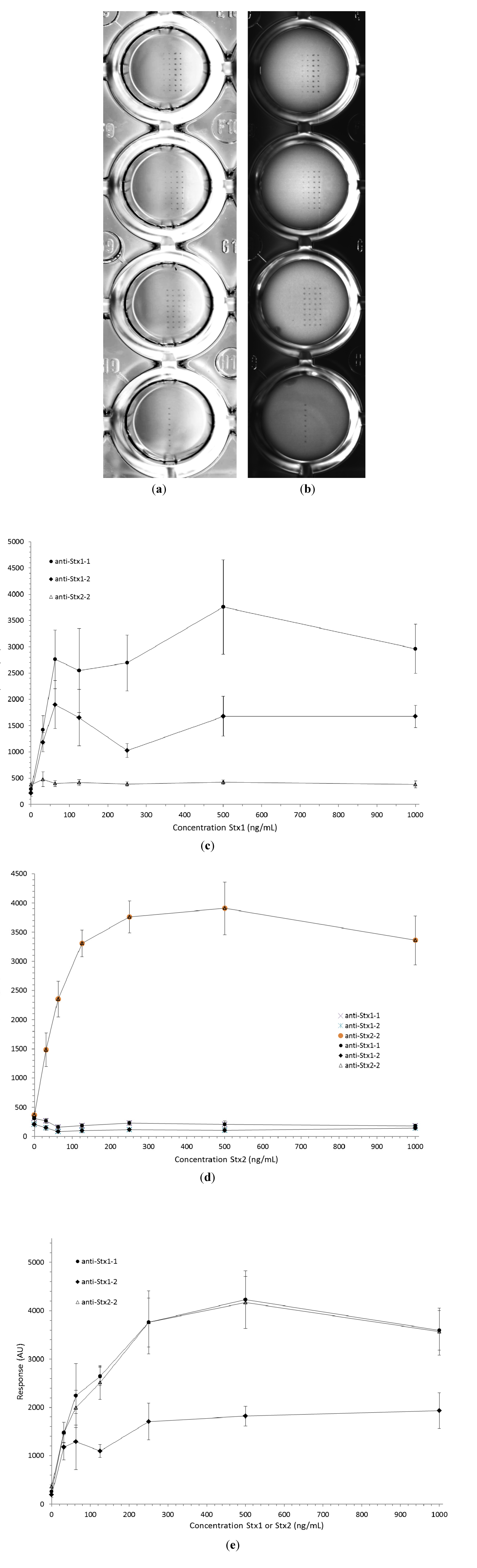
2.2. Stx Standard Curves with the Colorimetric ELISA Microarray Platform
2.3. Colorimetric ELISA Microarray Detection of Stx Generated from STEC Enrichment Cultures
| Strain | Serotype | −Mitomycin C | +Mitomycin C | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Stx monoclonal antibody | Final cell concentration (CFU/mL) | Anti-Stx monoclonal antibody | Final cell concentration (CFU/mL) | ||||||||||||||
| 1-1 | 1-2 | 2-2 | 1-1 | 1-2 | 2-2 | ||||||||||||
| (a) Colorimetric ELISA microarray detection responses for enriched axenic broth cultures | |||||||||||||||||
| (Stx1 producing) | |||||||||||||||||
| 05-6545 | O45:H2 | − | − | − | 1.26 × 109 | ? | − | − | 8.90 × 108 | ||||||||
| 96-3285 | O45:H2 | − | − | − | 1.10 × 109 | − | + | − | 1.78 × 108 | ||||||||
| TB352 | O26:NM | − | − | − | 7.10 × 108 | − | − | − | 2.21 × 108 | ||||||||
| (Stx2) | |||||||||||||||||
| 08023 | O121:H19 | − | − | + | 1.79 × 109 | − | − | + | 2.54 × 108 | ||||||||
| 94-0941 | O145:H− | − | − | − | 1.60 × 109 | − | − | − | 7.20 × 108 | ||||||||
| 94-0961 | O111:H− | − | − | − | 9.00 × 108 | − | − | + | 4.10 × 108 | ||||||||
| 96-1585 | O121:H19 | − | − | + | 1.76 × 109 | − | − | + | 3.39 × 108 | ||||||||
| (Stx1 and 2) | |||||||||||||||||
| 30-2C4 | O157:H7 | − | − | ? | 1.33 × 109 | − | + | + | 7.00 × 108 | ||||||||
| SJ2 | O26:H11 | − | − | − | 1.36 × 109 | − | − | + | 5.65 × 107 | ||||||||
| (non-Stx producing controls) | |||||||||||||||||
| B6-914 | O157:H7 | − | − | − | 1.06 × 109 | − | − | − | 1.72 × 108 | ||||||||
| K12 | n/a | − | − | − | 4.55 × 108 | − | − | − | 2.16 × 108 | ||||||||
| (b) Colorimetric ELISA microarray detection responses for enriched axenic broth cultures subsequently treated with B-PER (static reaction) | |||||||||||||||||
| (Stx1) | |||||||||||||||||
| 05-6545 | O45:H2 | − | − | − | 1.26 × 109 | − | + | − | 8.90 × 108 | ||||||||
| 96-3285 | O45:H2 | − | − | − | 1.10 × 109 | + | + | − | 1.78 × 108 | ||||||||
| TB352 | O26:NM | − | − | − | 7.10 × 108 | − | − | − | 2.21 × 108 | ||||||||
| (Stx2) | |||||||||||||||||
| 08023 | O121:H19 | − | − | + | 1.79 × 109 | − | − | ++ | 2.54 × 108 | ||||||||
| 94-0941 | O145:H− | − | − | − | 1.60 × 109 | − | − | − | 7.20 × 108 | ||||||||
| 94-0961 | O111:H− | − | − | − | 9.00 × 108 | − | − | ++ | 4.10 × 108 | ||||||||
| 96-1585 | O121:H19 | − | − | − | 1.76 × 109 | − | − | ++ | 3.39 × 108 | ||||||||
| (Stx1 and 2) | |||||||||||||||||
| 30-2C4 | O157:H7 | − | − | − | 1.33 × 109 | − | + | + | 7.00 × 108 | ||||||||
| SJ2 | O26:H11 | − | − | ? | 1.36 × 109 | + | + | + | 5.65 × 107 | ||||||||
| (non-Stx producing controls) | |||||||||||||||||
| B6-914 | O157:H7 | − | − | − | 1.06 × 109 | − | − | − | 1.72 × 108 | ||||||||
| K12 | n/a | − | − | − | 4.55 × 108 | − | − | − | 2.16 × 108 | ||||||||
| (c) Colorimetric ELISA microarray detection responses for enriched axenic broth cultures subsequently treated with B-PER (with shaking during reaction) | |||||||||||||||||
| (Stx1) | |||||||||||||||||
| 05-6545 | O45:H2 | − | − | − | 1.26 × 109 | − | + | − | 8.90 × 108 | ||||||||
| 96-3285 | O45:H2 | − | − | − | 1.10 × 109 | ++ | ++ | − | 1.78 × 108 | ||||||||
| TB352 | O26:NM | − | − | − | 7.10 × 108 | − | − | − | 2.21 × 108 | ||||||||
| (Stx2) | |||||||||||||||||
| 08023 | O121:H19 | − | − | + | 1.79 × 109 | − | − | + | 2.54 × 108 | ||||||||
| 94-0941 | O145:H− | − | − | − | 1.60 × 109 | − | − | − | 7.20 × 108 | ||||||||
| 94-0961 | O111:H− | − | − | − | 9.00 × 108 | − | − | + | 4.10 × 108 | ||||||||
| 96-1585 | O121:H19 | − | − | + | 1.76 × 109 | − | − | + | 3.39 × 108 | ||||||||
| (Stx1 and 2) | |||||||||||||||||
| 30-2C4 | O157:H7 | − | − | − | 1.33 × 109 | + | + | + | 7.00 × 108 | ||||||||
| SJ2 | O26:H11 | − | − | − | 1.36 × 109 | + | + | + | 5.65 × 107 | ||||||||
| (non-Stx controls) | |||||||||||||||||
| B6-914 | O157:H7 | − | − | − | 1.06 × 109 | − | − | − | 1.72 × 108 | ||||||||
| K12 | n/a | − | − | − | 4.55 × 108 | − | − | − | 2.16 × 108 | ||||||||
2.4. Colorimetric ELISA Microarray Detection of Stx in STEC-Inoculated Ground Beef Enrichments
| Strain | Serotype | −Mitomycin C | −Mitomycin C; +B-PER | ||||
| Anti-Stx monoclonal antibody | Anti-Stx monoclonal antibody | ||||||
| 1-1 | 1-2 | 2-2 | 1-1 | 1-2 | 2-2 | ||
| (a) Colorimetric ELISA microarray detection responses for enriched ground beef subsequently treated with B-PER | |||||||
| (Stx1 producing) | |||||||
| 00971 | O26:H11 | − | − | − | + | + | − |
| 04162 | O103:H8 | − | − | − | +++ | +++ | − |
| 98-8338 | O111:NM | + | + | − | ++ | ++ | − |
| (Stx2) | |||||||
| 08-023 | O121:H19 | − | − | ++ | − | − | +++ |
| 94-0961 | O111:H− | − | − | ? | − | − | + |
| 96-1585 | O121:H19 | − | − | ++ | − | − | +++ |
| (Stx1 and 2) | |||||||
| 00-4748 | O111:NM | − | − | + | + | + | + |
| 30-2C4 | O157:H7 | − | − | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ |
| SJ2 | O26:H11 | − | − | + | ++ | +++ | + |
| (non-Stx producing controls) | |||||||
| B6-914 | O157:H7 | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| K12 | n/a | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Ground beef | n/a | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Strain | Serotype | +Mitomycin C | +Mitomycin C; +B-PER | ||||
| Anti-Stx monoclonal antibody | Anti-Stx monoclonal antibody | ||||||
| 1-1 | 1-2 | 2-2 | 1-1 | 1-2 | 2-2 | ||
| (b) Colorimetric ELISA microarray detection responses for enriched ground beef containing mitomycin C and subsequently treated with B-PER | |||||||
| (Stx1) | |||||||
| 00971 | O26:H11 | − | − | − | + | + | − |
| 04162 | O103:H8 | − | − | − | ++ | ++ | − |
| 98-8338 | O111:NM | + | + | − | +++ | +++ | − |
| (Stx2) | |||||||
| 08-023 | O121:H19 | − | − | +++ | − | − | ++ |
| 94-0961 | O111:H− | − | − | + | − | − | + |
| 96-1585 | O121:H19 | − | − | +++ | − | − | +++ |
| (Stx1 and 2) | |||||||
| 00-4748 | O111:NM | − | − | − | ? | ? | ? |
| 30-2C4 | O157:H7 | + | + | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| SJ2 | O26:H11 | + | + | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| (non-Stx controls) | |||||||
| B6-914 | O157:H7 | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| K12 | n/a | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Ground beef | n/a | − | − | − | − | − | − |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Enrichment Growth of E. coli
3.4. Antibody Preparation and Microarray Printing
3.5. Antibody Microarray Detection of Shiga Toxin in Multiwell Plates
3.6. Microarray Scanning and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
- Materials: Charlie Barnett, Douglas Harris;
- Monoclonal antibodies: Xiaohua He, Craig Skinner;
- Bacterial strains: Pina Fratamico, Lori Bagi, George Paoli;
- Biophysics: Andrew Gehring, Jeffrey Brewster;
- Immunoassay: Andrew Gehring, Xiaohua He, Craig Skinner;
- Microbiology: Andrew Gehring, Xiaohua He, Pina Fratamico, Lori Bagi, George Paoli, Yiping He, Yanping Xie;
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—Major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Fratamico, P.M.; Gunther, N.W. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 86, 145–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesh, V.L.; Burris, J.A.; Owens, J.W.; Gordon, V.M.; Wadolkowski, E.A.; O’Brien, A.D.; Samuel, J.E. Comparison of the relative toxicities of Shiga-like toxins type I and type II for mice. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 3392–3402. [Google Scholar]
- Scheutz, F.; Teel, L.D.; Beutin, L.; Piérard, D.; Buvens, G.; Karch, H.; Mellmann, A.; Caprioli, A.; Tozzoli, R.; Morabito, S.; et al. Multicenter evaluation of a sequence-based protocol for subtyping Shiga toxins and standardizing Stx nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Ohta, Y.; Noda, M. Shiga toxin 2 is specifically released from bacterial cells by two different mechanisms. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGannon, C.M.; Fuller, C.A.; Weiss, A.A. Different classes of antibiotics differentially influence Shiga toxin production. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, A.E.; Acheson, D.W.K.; Echeverria, P.; Donohue-Rolfe, A.; Keusch, G.T. Mitomycin immunoblot colony assay for detection of Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli in fecal samples: Comparison with DNA probes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Kimmitt, P.T.; Harwood, C.R.; Barer, M.R. Toxin gene expression by Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli: The role of antibiotics and the bacterial SOS response. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljković-Selimović, B.; Kocić, B.; Babić, T.; Ristić, L. Bacterial typing methods. Acta Fac. Medicae Naissensis 2009, 26, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; He, Y.; Gehring, A.; Hu, Y.; Li, Q.; Tu, S.I.; Shi, X. Genotypes and toxin gene profiles of Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates from China. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corgier, B.P.; Mandon, C.A.; Le Goff, G.C.; Blum, L.J.; Marquette, C.A. Adhesive microarrays for multipurpose diagnostic tools. Lab ChipMiniat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 11, 3006–3010. [Google Scholar]
- Desmet, C.; Blum, L.J.; Marquette, C.A. Multiplex microarray ELISA versus classical ELISA, a comparison study of pollutant sensing for environmental analysis. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1876–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Customer Support; Toxin Technology, Inc., Sarasota, FL, USA. Personal Communication, 2011.
- Samuel, D.; Patt, R.J.; Abuknesha, R.A. A sensitive method of detecting proteins on dot and western blots using a monoclonal antibody to FITC. J. Immunol. Methods 1988, 107, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.P.; Caperna, T.J.; Elsasser, T.H.; Ashwell, C.M.; McMurtry, J.P. Design and application of a polyclonal peptide antiserum for the universal detection of leptin protein. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2000, 45, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, A.; Thomas, F.C.; Wright, P.F.; Shapiro, J.L.; Anderson, J.; Fulton, R.W. Blocking dot-ELISA, using a monoclonal antibody for detection of antibodies to bluetongue virus in bovine and ovine sera. J. Virol. Methods 1987, 18, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciewicz, R.A.; Knight, P.J. Transmission densitometry of stained nitrocellulose paper. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 175, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasiri Fernando, S.; Wilson, G.S. Multiple epitope interactions in the two-step sandwich immunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 1992, 151, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.I.; Uknalis, J.; Paoli, G.; He, Y.; Gehring, A. Production of Shiga-like toxins by Escherichia coli O157:H7: Effects of other bacteria and analogs of quorum sensing molecules. J. Rapid Meth. Aut. Mic. 2009, 17, 420–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, C.; Patfield, S.; Stanker, L.H.; Fratamico, P.; He, X. New high-affinity monoclonal antibodies against Shiga toxin 1 facilitate the detection of hybrid Stx1/Stx2 in vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; McMahon, S.; Skinner, C.; Merrill, P.; Scotcher, M.C.; Stanker, L.H. Development and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga toxin 2 and their application for toxin detection in milk. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 389, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Detection and isolation of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) from meat products and carcass and environmental sponges, chapter 5B.04. Microbiology Laboratory Guidebook, Food Safety and Inspection Service, 2013. Available online: http://www.fsis.usda.gov/wps/wcm/connect/7ffc02b5-3d33-4a79-b50c-81f208893204/MLG-5B.pdf?MOD=AJPERES (accessed on 16 December 2013).
- MacBeath, G.; Schreiber, S.L. Printing proteins as microarrays for high-throughput function determination. Science 2000, 289, 1760–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Gehring, A.G.; Albin, D.M.; Reed, S.A.; Tu, S.-I.; Brewster, J.D. An antibody microarray, in multiwell plate format, for multiplex screening of foodborne pathogenic bacteria and biomolecules. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Array-Pro Analyzer—Microarray analysis software and high-density array software. Available online: http://www.mediacy.com/index.aspx?page=ArrayPro (Accessed on 5 June 2014).
- He, X.; Patfield, S.; Hnasko, R.; Rasooly, R.; Mandrell, R.E. A polyclonal antibody based immunoassay detects seven subtypes of Shiga toxin 2 produced by Escherichia coli in human and environmental samples. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76368. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, M.; Sato, S.; Gondaira, F.; Sugiyama, J.-I. A rapid bioluminescent enzyme immunoassay (BLEIA) for the detection of Shiga toxin types 1 and 2. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 45, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, F.P.; Green, J.H.; Greene, K.; Strockbine, N.; Wells, J.G.; Wachsmuth, I.K. Development and evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detection of Shiga-like toxin I and Shiga-like toxin II. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Willford, J.; Mills, K.; Goodridge, L.D. Evaluation of three commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits for detection of shiga toxin. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 741–747. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, P.C.H.; Jinneman, K.; Scheutz, F.; Monday, S.R. Specificity of PCR and serological assays in the detection of Escherichia coli shiga toxin subtypes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6699–6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gehring, A.; He, X.; Fratamico, P.; Lee, J.; Bagi, L.; Brewster, J.; Paoli, G.; He, Y.; Xie, Y.; Skinner, C.; et al. A High-Throughput, Precipitating Colorimetric Sandwich ELISA Microarray for Shiga Toxins. Toxins 2014, 6, 1855-1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061855
Gehring A, He X, Fratamico P, Lee J, Bagi L, Brewster J, Paoli G, He Y, Xie Y, Skinner C, et al. A High-Throughput, Precipitating Colorimetric Sandwich ELISA Microarray for Shiga Toxins. Toxins. 2014; 6(6):1855-1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061855
Chicago/Turabian StyleGehring, Andrew, Xiaohua He, Pina Fratamico, Joseph Lee, Lori Bagi, Jeffrey Brewster, George Paoli, Yiping He, Yanping Xie, Craig Skinner, and et al. 2014. "A High-Throughput, Precipitating Colorimetric Sandwich ELISA Microarray for Shiga Toxins" Toxins 6, no. 6: 1855-1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061855
APA StyleGehring, A., He, X., Fratamico, P., Lee, J., Bagi, L., Brewster, J., Paoli, G., He, Y., Xie, Y., Skinner, C., Barnett, C., & Harris, D. (2014). A High-Throughput, Precipitating Colorimetric Sandwich ELISA Microarray for Shiga Toxins. Toxins, 6(6), 1855-1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061855





