Differential Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate and Inorganic Phosphate in a Murine Cerebral Endothelial Cell Line (bEnd.3)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
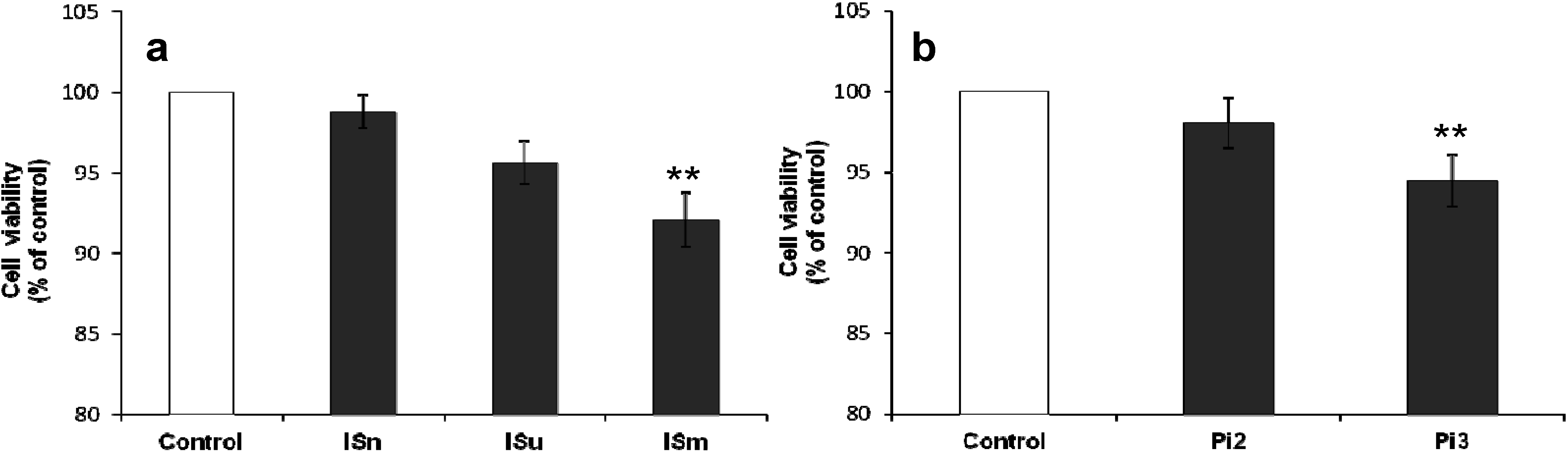
2.1.1. Effect of IS and Pi on Cell Viability
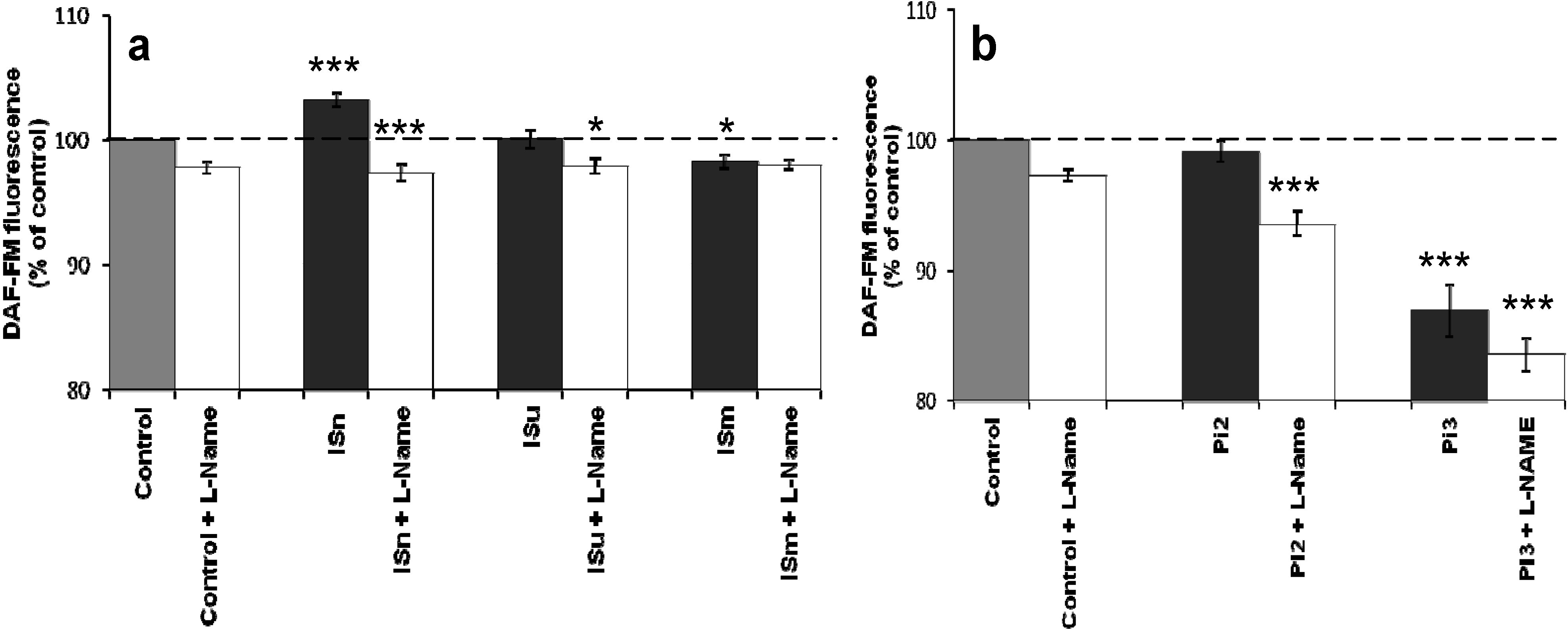
2.1.2. Effect of IS and Pi on NO Production
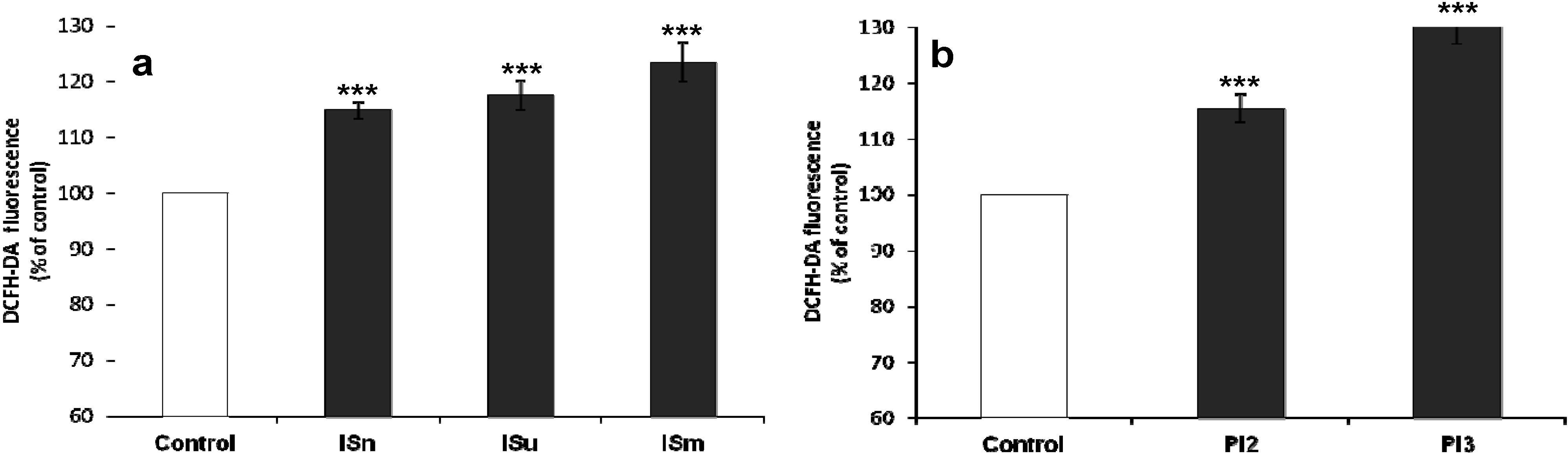
2.1.3. IS and Pi Induce ROS Production
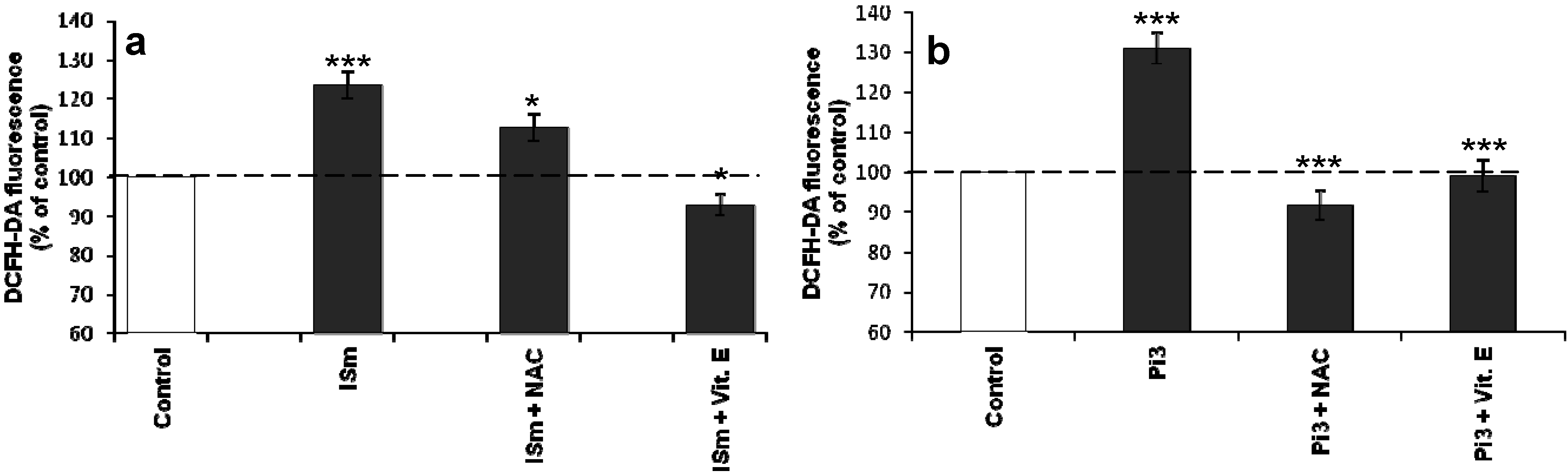
2.1.4. N-Acetylcysteine and α-Tocopherol Decrease Uremic Toxin-Induced ROS Production
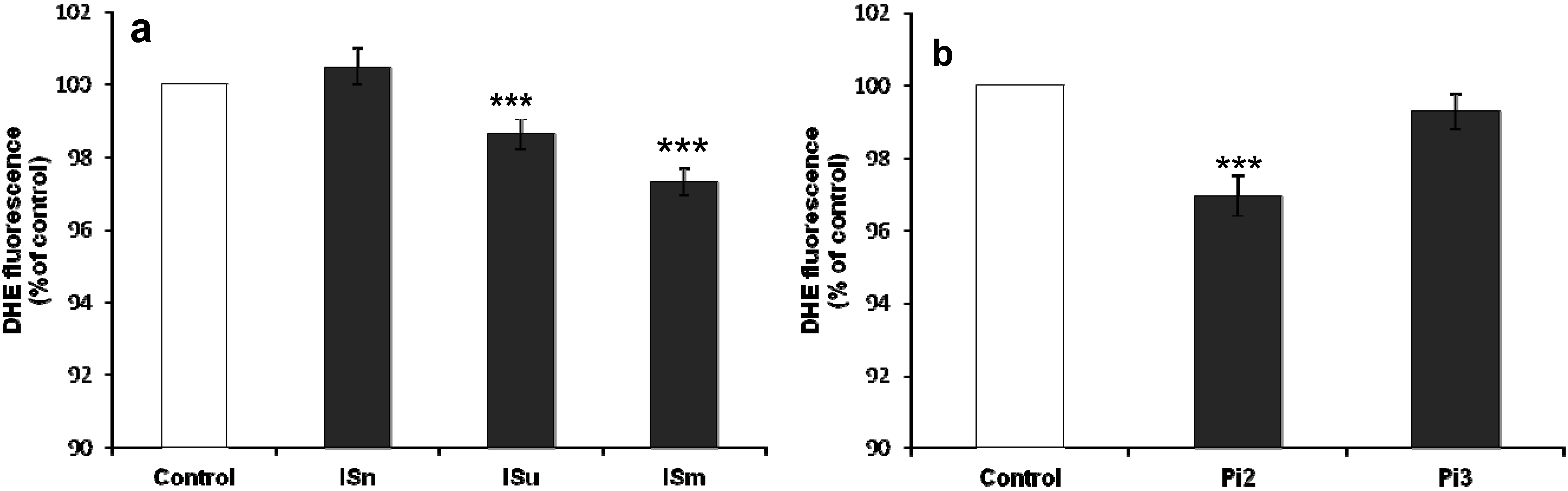
2.1.5. Effect of IS and Pi on O2•– Production
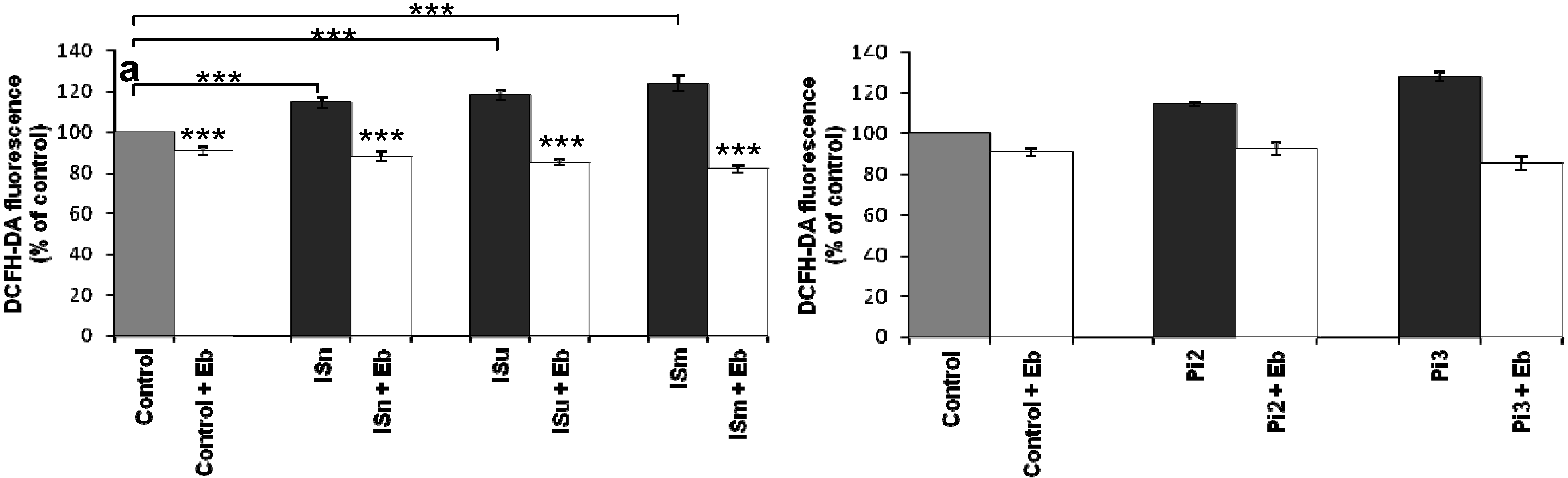
2.1.6. Effect of Antioxidants on IS- and Pi-Induced O2•– Production

2.1.7. Ebselen Reduces Uremic Toxin-Induced ROS Production
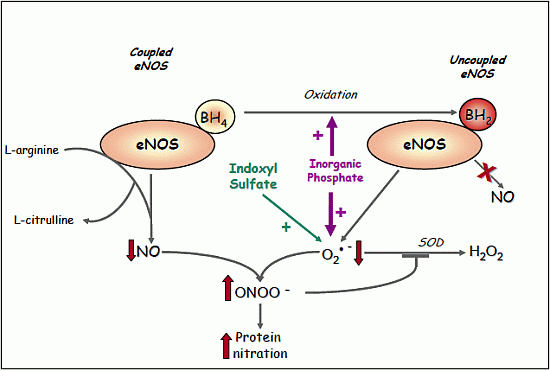
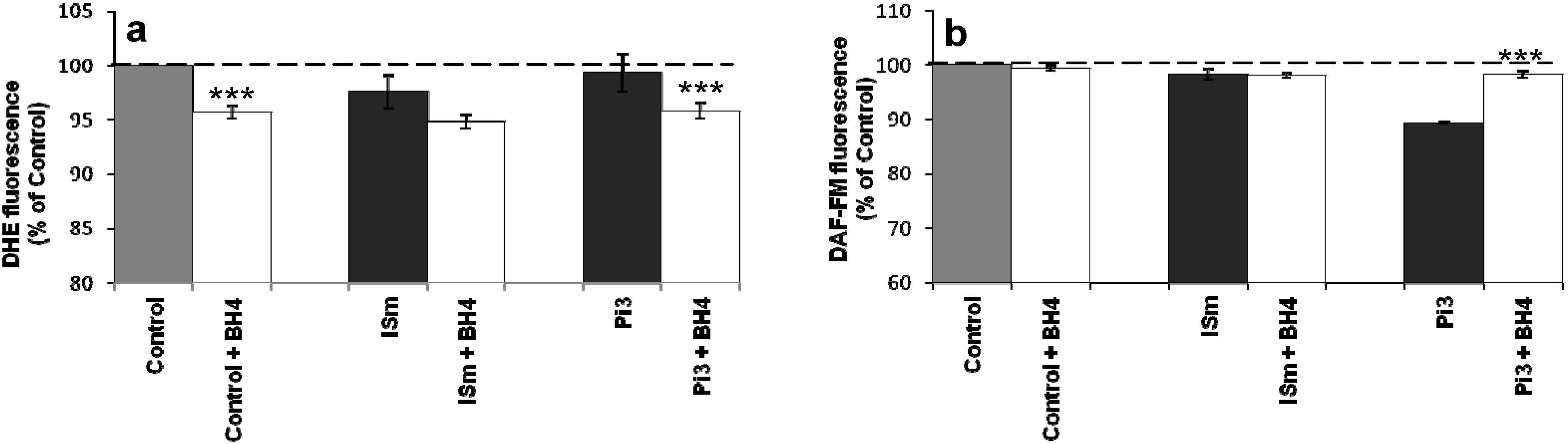
2.1.8. Evidence for eNOS Uncoupling
2.1.9. Nitrotyrosine (NT) Staining of Cells Treated with Uremic Toxins
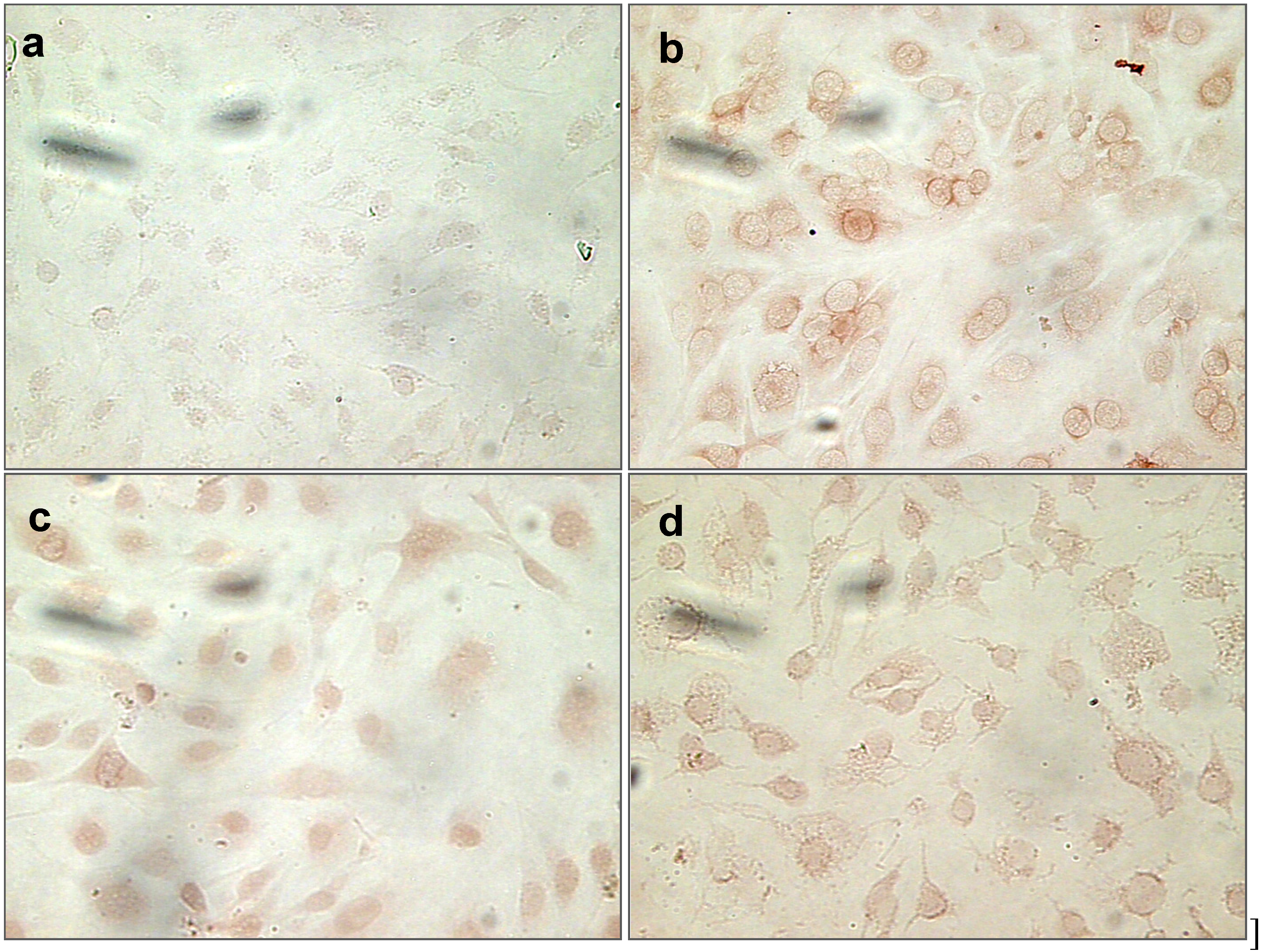
2.2. Discussions
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Material
3.2. Endothelial Cell Culture
3.3. Uremic Toxins Preparation
3.4. Cell Viability Assay
3.5. Measurement of NO Production
3.6. Measurement of ROS Production
3.7. Measurement of O2•− Production
3.8. Nitrotyrosine Immunostaining
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El Nahas, M. Cardio-kidney-damage: A unifying concept. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, R.N.; Parfrey, P.S.; Sarnak, M.J. Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 32, S112–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.; Argiles, A.; Spasovski, G.; Verbeke, F.; Lameire, N. Chronic kidney disease as cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2005, 20, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Seliger, S.L.; Gillen, D.L.; Tirschwell, D.; Wasse, H.; Kestenbaum, B.R.; Stehman-Breen, C.O. Risk factors for incident stroke among patients with end-stage renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, J.M.; Godefroy, O.; Chillon, J.M.; Choukroun, G.; Massy, Z.A. Cognitive disorders and dementia in ckd: The neglected kidney-brain axis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, A.S.; Tanne, D.; Boyle, P.A.; Shah, R.C.; Leurgans, S.E.; Bennett, D.A. Kidney function is associated with the rate of cognitive decline in the elderly. Neurology 2009, 73, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassal, S.K.; Kritz-Silverstein, D.; Barrett-Connor, E. A prospective study of albuminuria and cognitive function in older adults: The rancho bernardo study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 171, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etgen, T.; Sander, D.; Chonchol, M.; Briesenick, C.; Poppert, H.; Forstl, H.; Bickel, H. Chronic kidney disease is associated with incident cognitive impairment in the elderly: The invade study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 3144–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzilay, J.I.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Luchsinger, J.; Yasar, S.; Bernick, C.; Jenny, N.S.; Kuller, L.H. Albuminuria and dementia in the elderly: A community study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 52, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundelof, J.; Arnlov, J.; Ingelsson, E.; Sundstrom, J.; Basu, S.; Zethelius, B.; Larsson, A.; Irizarry, M.C.; Giedraitis, V.; Ronnemaa, E.; et al. Serum cystatin c and the risk of Alzheimer disease in elderly men. Neurology 2008, 71, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, C.; Bray, E.P.; Bryan, S.; Greenfield, S.M.; Haque, M.S.; Hobbs, F.R.; Jones, M.I.; Jowett, S.; Kaambwa, B.; Little, P.; et al. Targets and self-management for the control of blood pressure in stroke and at risk groups (tasmin-sr): Protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2013, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massy, Z.A.; Ivanovski, O.; Nguyen-Khoa, T.; Angulo, J.; Szumilak, D.; Mothu, N.; Phan, O.; Daudon, M.; Lacour, B.; Drueke, T.B.; et al. Uremia accelerates both atherosclerosis and arterial calcification in apolipoprotein e knockout mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bugnicourt, J.M.; da Silveira, C.; Bengrine, A.; Godefroy, O.; Baumbach, G.; Sevestre, H.; Bode-Boeger, S.M.; Kielstein, J.T.; Massy, Z.A.; Chillon, J.M. Chronic renal failure alters endothelial function in cerebral circulation in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H1143–H1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braam, B.; de Roos, R.; Dijk, A.; Boer, P.; Post, J.A.; Kemmeren, P.P.; Holstege, F.C.; Bluysen, H.A.; Koomans, H.A. Nitric oxide donor induces temporal and dose-dependent reduction of gene expression in human endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 287, H1977–H1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniades, C.; Shirodaria, C.; Leeson, P.; Antonopoulos, A.; Warrick, N.; Van-Assche, T.; Cunnington, C.; Tousoulis, D.; Pillai, R.; Ratnatunga, C.; et al. Association of plasma asymmetrical dimethylarginine (ADMA) with elevated vascular superoxide production and endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling: Implications for endothelial function in human atherosclerosis. Eur. Heart J. 2009, 30, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuillez, C.; Richard, V. Targeting endothelial dysfunction in hypertensive subjects. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2005, 19 (Suppl. 1), S21–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylis, C. Nitric oxide deficiency in chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2008, 294, F1–F9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, K.M. The role of nitric oxide in cardiovascular diseases. Mol. Asp. Med. 2005, 26, 33–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massy, Z.A.; Nguyen-Khoa, T. Oxidative stress and chronic renal failure: Markers and management. J. Nephrol. 2002, 15, 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Massy, Z.A.; Stenvinkel, P.; Drueke, T.B. The role of oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Semin. Dial. 2009, 22, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annuk, M.; Zilmer, M.; Lind, L.; Linde, T.; Fellstrom, B. Oxidative stress and endothelial function in chronic renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, 2747–2752. [Google Scholar]
- Enamoto, A.; Niwa, T. Roles of organic anion transporters in the progression of chronic renal failure. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2007, 11, S27–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki, S.; Asaba, H.; Takanaga, H.; Deguchi, T.; Hosoya, K.-I.; Otagiri, M.; Terasaki, T. Role of blood-brain barrier organic anion transporter 3 (OAT3) in the efflux of indoxyl sulphate, a uremic toxin: Its involvement in neurotransmitter metabolite clearance from the brain. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, K.; Tachikawa, M. Roles of organic anion/cation transporters at the blood-brain and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers involving uremic toxins. Clin. Exp. nephrol. 2011, 15, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, I.; Hernando, N.; Sorribas, V.; Werner, A. Phosphate transporters in renal, gastrointestinal, and other tissues. Adv. Chronic. Kidney Dis. 2011, 18, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davignon, J.; Ganz, P. Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004, 109, III27–III32. [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro, L.J.; Buga, G.M.; Wood, K.S.; Byrns, R.E.; Chaudhuri, G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 9265–9269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourde-Chiche, N.; Dou, L.; Cerini, C.; Dignat-George, F.; Brunet, P. Vascular incompetence in dialysis patients—Protein-bound uremic toxins and endothelial dysfunction. Semin. Dial. 2011, 24, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, F.; van Guldener, C.; Becker, A.; Dekker, J.M.; Heine, R.J.; Bouter, L.M.; Stehouwer, C.D. Endothelial dysfunction contributes to renal function-associated cardiovascular mortality in a population with mild renal insufficiency: The Hoorn study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizel, J.; Six, I.; Slama, M.; Tribouilloy, C.; Sevestre, H.; Poirot, S.; Giummelly, P.; Atkinson, J.; Choukroun, G.; Andrejak, M.; et al. Mechanisms of aortic and cardiac dysfunction in uremic mice with aortic calcification. Circulation 2009, 119, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannier, B.; Guerin, A.P.; Marchais, S.J.; Metivier, F.; Safar, M.E.; London, G.M. Postischemic vasodilation, endothelial activation, and cardiovascular remodeling in end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, S.L.; Gillen, D.L.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Kestenbaum, B.; Stehman-Breen, C.O. Elevated risk of stroke among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Faure, V.; Cerini, C.; Berland, Y.; Dignat-George, F.; Brunet, P. The uremic solute indoxyl sulfate induces oxidative stress in endothelial cells. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumur, Z.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate inhibits nitric oxide production and cell viability by inducing oxidative stress in vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Nephrol. 2009, 29, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Nie, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, T.; Guan, X.; Zhao, J. Amelioration of uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate-induced endothelial cell dysfunction by klotho protein. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 215, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, D.H. Indoxyl sulfate-induced endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease via an induction of oxidative stress. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.M.; Xu, M.J.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, G.; Guan, Y.; Kong, W.; Tang, C.; Wang, X. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote p65 nuclear translocation mediating high-phosphate-induced vascular calcification in vitro and in vivo. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.A.; Kowaltowski, A.J. Phosphate increases mitochondrial reactive oxygen species release. Free Radic. Res. 2004, 38, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, I.; Maizel, J.; Barreto, F.C.; Rangrez, A.Y.; Dupont, S.; Slama, M.; Tribouilloy, C.; Choukroun, G.; Maziere, J.C.; Bode-Boeger, S.; et al. Effects of phosphate on vascular function under normal conditions and influence of the uraemic state. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 96, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuto, E.; Taketani, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Harada, N.; Isshiki, M.; Sato, M.; Nashiki, K.; Amo, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Higashi, Y.; et al. Dietary phosphorus acutely impairs endothelial function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, G.S.; Hausberg, M.; Hillebrand, U.; Rustemeyer, P.; Wittkowski, W.; Lang, D.; Pavenstädt, H. Increased inorganic phosphate induces human endothelial cell apoptosis in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2008, 294, F1381–F1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevers, L.M.; Braam, B.; Post, J.A.; van Zonneveld, A.J.; Rabelink, T.J.; Koomans, H.A.; Verhaar, M.C.; Joles, J.A. Tetrahydrobiopterin, but not l-arginine, decreases no synthase uncoupling in cells expressing high levels of endothelial no synthase. Hypertension 2006, 47, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, A.; Alcaraz, O.; Arnao, M.B. Free radical-scavenging activity of indolic compounds in aqueous and ethanolic media. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Iwao, Y.; Tasaki, Y.; Sato, K.; Ishima, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Kadowaki, D.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M.; et al. The uremic solute indoxyl sulfate acts as an antioxidant against superoxide anion radicals under normal-physiological conditions. FEBS Lett. 2010, 2584, 2816–2820. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Otagari, M.; Maruyama, T. New insight into the redox properties of uremic solute indoxyl sulphate as a pro- and anti-oxidant. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2011, 15, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praschberger, M.; Hermann, M.; Wanner, J.; Jirovetz, L.; Exner, M.; Kapiotis, S.; Gmeiner, B.M.K.; Laggner, H. The uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate acts as a pro- or antioxidant on LDL oxidation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 48, 641–648. [Google Scholar]
- Zalba, G.; Fortuno, A.; Diez, J. Oxidative stress and atherosclerosis in early chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2006, 21, 2686–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.R.; Keller, J.N. Oxidative stress and cerebral endothelial cells: Regulation of the blood-brain-barrier and antioxidant based interventions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Canaud, B.; Eckardt, K.U.; Stenvinkel, P.; Wanner, C.; Zoccali, C. Oxidative stress in end-stage renal disease: An emerging threat to patient outcome. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2003, 18, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K.; Packer, L. Thiol homeostasis and supplements in physical exercise. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, S653–S669. [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa, M.; Ito, Y. N-acetylcysteine and neurodegenerative diseases: Basic and clinical pharmacology. Cerebellum 2007, 6, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massy, Z.A.; Borderie, D.; Nguyen-Khoa, T.; Drueke, T.B.; Ekindjian, O.G.; Lacour, B. Increased plasma s-nitrosothiol levels in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2003, 18, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakura, F.; Taka, H.; Fujimura, T.; Murayama, K. Inactivation of human manganese-superoxide dismutase by peroxynitrite is caused by exclusive nitration of tyrosine 34 to 3-nitrotyrosine. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14085–14089. [Google Scholar]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Ni, Z.; Oveisi, F.; Liang, K.; Pandian, R. Enhanced nitric oxide inactivation and protein nitration by reactive oxygen species in renal insufficiency. Hypertension 2002, 39, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilgen, G.; Werneck, M.L.; de Noronha, L.; Martins, A.P.; Varela, A.M.; Nakao, L.S.; Pecoits-Filho, R. Increased calcification and protein nitration in arteries of chronic kidney disease patients. Blood Purif. 2011, 32, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesano, R.; Pepper, M.S.; Mohle-Steinlein, U.; Risau, W.; Wagner, E.F.; Orci, L. Increased proteolytic activity is responsible for the aberrant morphogenetic behavior of endothelial cells expressing the middle t oncogene. Cell 1990, 62, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feine, I.; Pinkas, I.; Salomon, Y.; Scherz, A. Local oxidative stress expansion through endothelial cells—A key role for gap junction intercellular communication. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41633. [Google Scholar]
- EUToX Uremic Solutes Database. Available online: http://eutoxdb.odeesoft.com/index.php (Accessed on 30 April 2014).
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Stinghen, A.E.M.; Chillon, J.-M.; Massy, Z.A.; Boullier, A. Differential Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate and Inorganic Phosphate in a Murine Cerebral Endothelial Cell Line (bEnd.3). Toxins 2014, 6, 1742-1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061742
Stinghen AEM, Chillon J-M, Massy ZA, Boullier A. Differential Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate and Inorganic Phosphate in a Murine Cerebral Endothelial Cell Line (bEnd.3). Toxins. 2014; 6(6):1742-1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061742
Chicago/Turabian StyleStinghen, Andréa E. M., Jean-Marc Chillon, Ziad A. Massy, and Agnès Boullier. 2014. "Differential Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate and Inorganic Phosphate in a Murine Cerebral Endothelial Cell Line (bEnd.3)" Toxins 6, no. 6: 1742-1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061742
APA StyleStinghen, A. E. M., Chillon, J.-M., Massy, Z. A., & Boullier, A. (2014). Differential Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate and Inorganic Phosphate in a Murine Cerebral Endothelial Cell Line (bEnd.3). Toxins, 6(6), 1742-1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061742