Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1-Mediated Toxicity Inhibited by Neutralizing Antibodies Late in the Course of Continual in Vivo and in Vitro Exposure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Multiple Dose Lethal Challenge and Protection by Neutralizing Antibody
| Antiserum raised against | Days of treatment | Survival (No. of animals that survived/total No. of animals challenged) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | 0/4 * | |
| Negative/irrelevant serum | 1–5 | 0/3 ++ | |
| TSST-1 variant | 2, 3 | 5/5 ** | p = 0.02 *** |
| TSST-1 variant | 3–5 | 5/5 ** | p = 0.02 |
| TSST-1wt | 3– 5 | 5/5 ** | p = 0.02 |
2.2. Inhibition of T-Cell Proliferation
2.3. Kinetics of Inhibition of Cytokine Expression after rTSST-1 wt Stimulation for Defined Time Periods
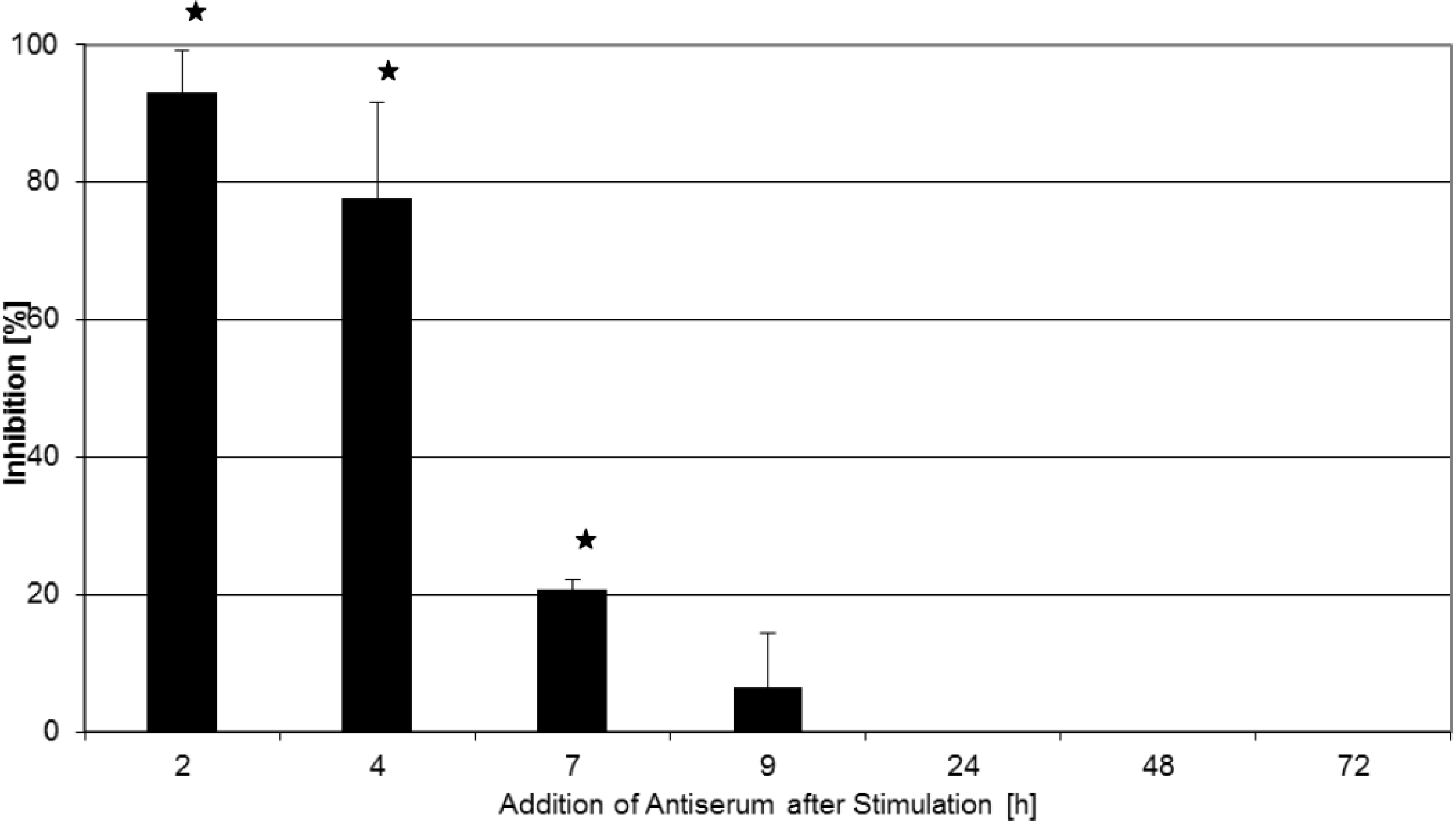

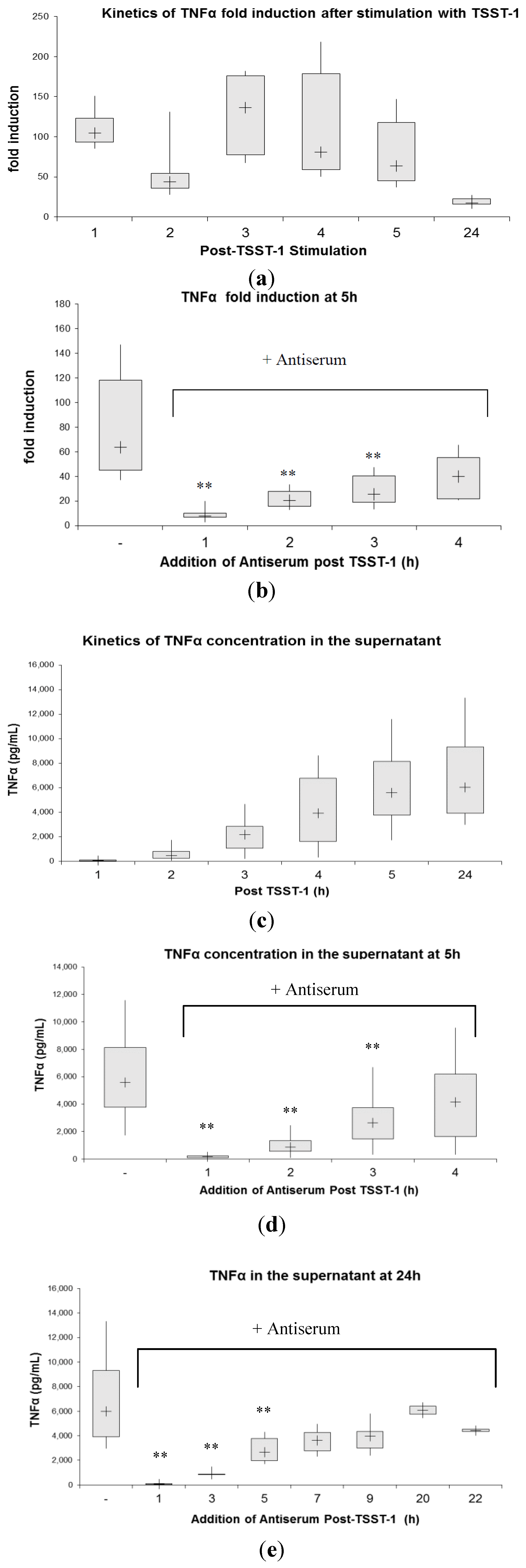
3. Experimental Section
3.1. In Vitro Cytokine Gene Expression Assay
3.2. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription
3.3. Primer Design
| IL-2-Forward: | 5'- AAACCTCTGGAGGAAGTG-3'; |
| IL-2-Reverse: | 5'- GTTCAGAAATTCTACAATGG-3'; |
| TNFα-Forward: | 5'- CTGTACCTCATCTACTCCC-3'; |
| TNFα-Reverse: | 5'- GAGAGGAGGTTGACCTTG-3'; |
| HPRT-Forward: | 5'- AGGCCATCACATTGTAGCCC-3'; |
| HPRT-Reverse: | 5'- GTTGAGAGATCATCTCCACCG-3'. |
3.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (QRT-PCR) and Quantification
3.5. Lymphocyte Proliferation Assay
3.6. Animals
3.7. Substances and Production of Antiserum
3.8. Multiple Dose Lethal Challenge
3.9. Neutralization of rTSST-1 wt by Pre-Incubation with Antiserum
3.10. Passive Immunization with Antiserum
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Disclosure
References
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Karl, I.E. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.J.; Agosti, J.M.; Opal, S.M. Treatment of septic shock with the tumor necrosis factor receptor: Fc fusion protein. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, K.; Karzai, W. Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in sepsis: Update on clinical trials and lessons learned. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, S121–S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, H.S.; Suffredini, A.F.; Eichacker, P.Q.; Munford, R.S. Risks and benefits of activated protein C treatment for severe sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedemann, N.C.; Guo, R.F.; Ward, P.A. The enigma of sepsis. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.J. Recombinant human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in the treatment of patients with sepsis syndrome: Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. JAMA 1994, 271, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedemann, N.C.; Guo, R.F.; Ward, P.A. Novel strategies for the treatment of sepsis. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Sakyr, Y.; Sprung, C.L.; Ranieri, V.M.; Reinhart, K.; Gerlach, H.; Moreno, R.; Carlet, J.; Le Gall, J.R.; Payen, D. Sepsis in European intensive care units: Results of the SOAP study. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.S.; Mannino, D.M.; Eaton, S.; Moss, M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetola, N.; Francis, J.S.; Nuermberger, E.L.; Bishai, W.R. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An emerging threat. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, W.E.; Rapp, R.P. Methicillin-resistant staphylococcal infections: An important consideration for orthopaedic surgeons. Orthopedics 2004, 27, 565–568. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado-Pabon, W.; Breshears, L.; Spaulding, A.R.; Merriman, J.A.; Stach, C.S.; Horswill, A.R.; Peterson, M.L.; Schlievert, P.M. Superantigens are critical for Staphylococcus aureus infective endocarditis, sepsis, and acute kidney injury. mBio 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, T. Therapeutic down-modulators of staphylococcal superantigen-induced inflammation and toxic shock. Toxins 2010, 2, 1963–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, T. Update on staphylococcal superantigen-induced signaling pathways and therapeutic interventions. Toxins 2013, 5, 1629–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar-Hari, M.; Spencer, J.; Sewel, W.A.; Rowan, K.M.; Singer, M. Bench-to-bedside review: Immunoglobulin therapy for sepsis- biological plausibility from a critical care perspective. Crit. Care 2012, 16, 206–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.L.; Omoe, K.; Sasaki, S.; Sashinami, H.; Sakuraba, H.; Yokomizo, Y.; Shinagawa, K.; Nakane, A. Vaccination with nontoxic mutant toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 protects against Staphylococcus aureus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, B.G.; Krakauer, T.; Bonventre, P.F. Biological activity of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 and a site-directed mutant, H135A, in a lipopolysaccharide-potentiated mouse lethality model. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Gampfer, J.; Thon, V.; Gulle, H.; Wolf, H.M.; Eibl, M.M. Double mutant and formaldehyde inactivated TSST-1 as vaccine candidates for TSST-1- induced toxic shock syndrome. Vaccine 2002, 20, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, T.; Buckley, M. Dexamethasone attenuates staphylococcal enterotoxin B- induced hypothermic response and protects mice from superantigen-induced toxic shock. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, M.L.; Margolin, S.B.; Krakauer, T.; Roy, C.J.; Stiles, B.G. Pirfenidone blocks in vitro and in vivo effects of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2989–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, T.; Buckley, M. Intransal rapamycin rescues mice from staphylococcal enterotoxin B-induced shock. Toxins 2012, 4, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, W.; Bernhagen, J.; Bucala, R. Cytokines in sepsis: Potent immunoregulators and potential therapeutic targets- an updated view. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 165974:1–165974:16. [Google Scholar]
- LeClaire, R.D.; Hunt, R.E.; Bavari, S. Protection against bacterial superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B by passive vaccination. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2278–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, E.A.; Stiles, B.G.; Ulrich, R.G. Inhibition of toxic shock by human monoclonal antibodies against staphylococcal enterotoxin B. PLos ONE 2010, 5, e13253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.L.; Han, D.P.; Burke, J.M.; Schlievert, P.M.; Wirostko, W.J.; Tarasewicz, D.G.; Skumatz, C.M.B. Intravitreally injected human immunoglobulin attenuates the effects of Staphylococcus aureus culture supernatant in a rabbit model of toxin-mediated endophthalmitis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonventre, P.F.; Heeg, H.; Cullen, C.; Lian, C.J. Toxicity of recombinant toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 and mutant toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus in a rabbit infection model of toxic shock syndrome. Inf. Immun. 1993, 61, 793–799. [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert, P.M. Cytolysins, superantigens, and pneumonia due to community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 676–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stich, N.; Waclavicek, M.; Model, N.; Eibl, M.M. Staphylococcal superantigen (TSST-1) mutant analysis reveals that T cell activation is required for the biological effects in the rabbit including the cytokine storm. Toxins 2010, 2, 2272–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaulding, A.R.; Salgado-Pabon, W.; Merriman, J.A.; Stach, C.S.; Ji, Y.; Gillman, A.N.; Peterson, M.L.; Schlievert, P.M. Vaccination against Staphylococcus aureus Pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaulding, A.R.; Ying-Chi, L.; Merriman, J.A.; Brosnahan, A.J.; Peterson, M.L.; Schlievert, P.M. Immunity to Staphylococcus aureus secreted proteins protects rabbits from serious illnesses. Vaccine 2012, 30, 5099–5109. [Google Scholar]
- LeClaire, R.D.; Bavari, S. Human Antibodies to bacterial superantigens and their ability to inhibit T cell activation and lethality. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2001, 45, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvanathan, K.; Charles, A.; Bannan, J.; Pugach, P.; Kashfi, K.; Zabriskie, J.B. Inhibition of bacterial superantigens by peptides and antibodies. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delsesto, D.; Opal, S.M. Future perspectives on regulating pro- and anti-inflammatory responses in sepsis. Contrib. Microbiol. 2011, 17, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waclavicek, M.; Stich, N.; Rappan, I.; Bergmeister, H.; Eibl, M.M. Analysis of the early response to TSST-1 reveals Vβ-unrestricted extravasation, compartmentalization of the response, and unresponsiveness but not anergy to TSST-1. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 44–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cheadle, C.; Fan, J.; Cho-Chung, Y.S.; Werner, T.; Ray, J.; Do, L.; Gorospe, M.; Becker, K.G. Control of gene expression during T cell activation: Alternate regulation of mRNA transcription and mRNA stability. BMC Genomics 2005, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khabar, K.S.A. Rapid transit in the immune cells: The role of mRNA turnover regulation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, A.; Bohjanen, P.R. Microarray-based analyses of mRNA decay in the regulation of mammalian gene expression. Brief. Funct. Genomics Proteomics 2004, 3, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, V.; Jakymiw, A.; van Tubergen, E.A.; D’Silva, N.J.; Kirkwood, K.L. Control of cytokine mRNA expression by RNA-binding proteins and microRNAs. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsten, T.; June, C.H.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Stella, G.; Thompson, C.B. Regulation of lymphokine messenger RNA stability by a surface-mediated T cell activation pathway. Science 1989, 244, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Rabenstein, H.L.; Behrendt, A.C.; Ellwart, J.W.; Naumann, R.; Horsch, M.; Beckers, J.; Obst, R.J. Differential kinetics of antigen dependency of CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3507–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, D.; Salmaso, S.; Mastrantonio, P.; Giuliano, M.; Tozzi, A.E.; Anemona, A.; Ciofi degli Atti, M.L.; Giammanco, A.; Panei, P.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Klein, D.L.; Wassilak, S.G. A controlled trial of two acellular vaccines and one whole-cell vaccine against pertussis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, R.G.; Flint, M.; Kalyan, N.; Johnson, E.; Witko, S.E.; Kotash, C.; Zhao, P.; Megati, S.; Yurgelonis, I.; Lee, P.K.; Matsuka, Y.V.; Severina, E.; Deatly, A.; Sidhu, M.; Jansen, K.U.; Minton, N.P.; Anderson, A.S. A novel approach to generate a recombinant toxoid vaccine against Clostridium difficile. Microbiology 2013, 159, 1254–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokori-Brown, M.; Hall, C.A.; Vance, C.; Fernandes da Costa, S.P.; Savva, C.G.; Naylor, C.E.; Cole, A.R.; Basak, A.K.; Moss, D.S.; Titball, R.W. Clostridium perfringens epsilon toxin mutant Y30A-Y196A as a recombinant vaccine candidate against enterotoxemia. Vaccine 2014, 32, 2682–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, J.W.; Pitt, M.L.; LeClaire, R.D.; Gibbs, P.H.; Torres, E.; Dyas, B.; Ulrich, R.G.; Bavari, S. Generation of protective immunity by inactivated recombinant staphylococcal enterotoxin B vaccine in nonhuman primates and identification of correlates of immunity. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 108, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Stich, N.; Model, N.; Samstag, A.; Gruener, C.S.; Wolf, H.M.; Eibl, M.M. Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1-Mediated Toxicity Inhibited by Neutralizing Antibodies Late in the Course of Continual in Vivo and in Vitro Exposure. Toxins 2014, 6, 1724-1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061724
Stich N, Model N, Samstag A, Gruener CS, Wolf HM, Eibl MM. Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1-Mediated Toxicity Inhibited by Neutralizing Antibodies Late in the Course of Continual in Vivo and in Vitro Exposure. Toxins. 2014; 6(6):1724-1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061724
Chicago/Turabian StyleStich, Norbert, Nina Model, Aysen Samstag, Corina S. Gruener, Hermann M. Wolf, and Martha M. Eibl. 2014. "Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1-Mediated Toxicity Inhibited by Neutralizing Antibodies Late in the Course of Continual in Vivo and in Vitro Exposure" Toxins 6, no. 6: 1724-1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061724
APA StyleStich, N., Model, N., Samstag, A., Gruener, C. S., Wolf, H. M., & Eibl, M. M. (2014). Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1-Mediated Toxicity Inhibited by Neutralizing Antibodies Late in the Course of Continual in Vivo and in Vitro Exposure. Toxins, 6(6), 1724-1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061724




