PhTX-II a Basic Myotoxic Phospholipase A2 from Porthidium hyoprora Snake Venom, Pharmacological Characterization and Amino Acid Sequence by Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Purification and Biochemical Characterization of PhTX-II

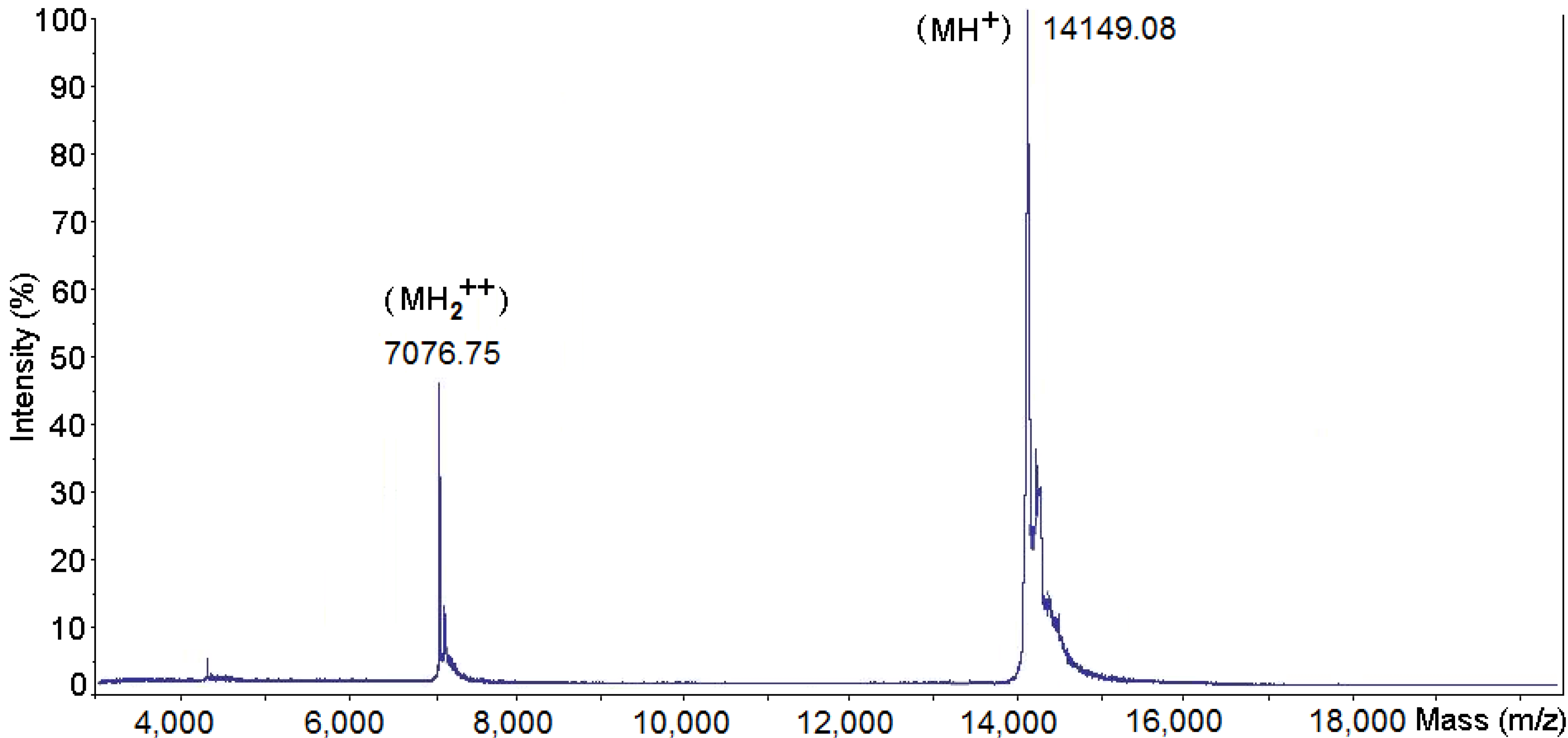
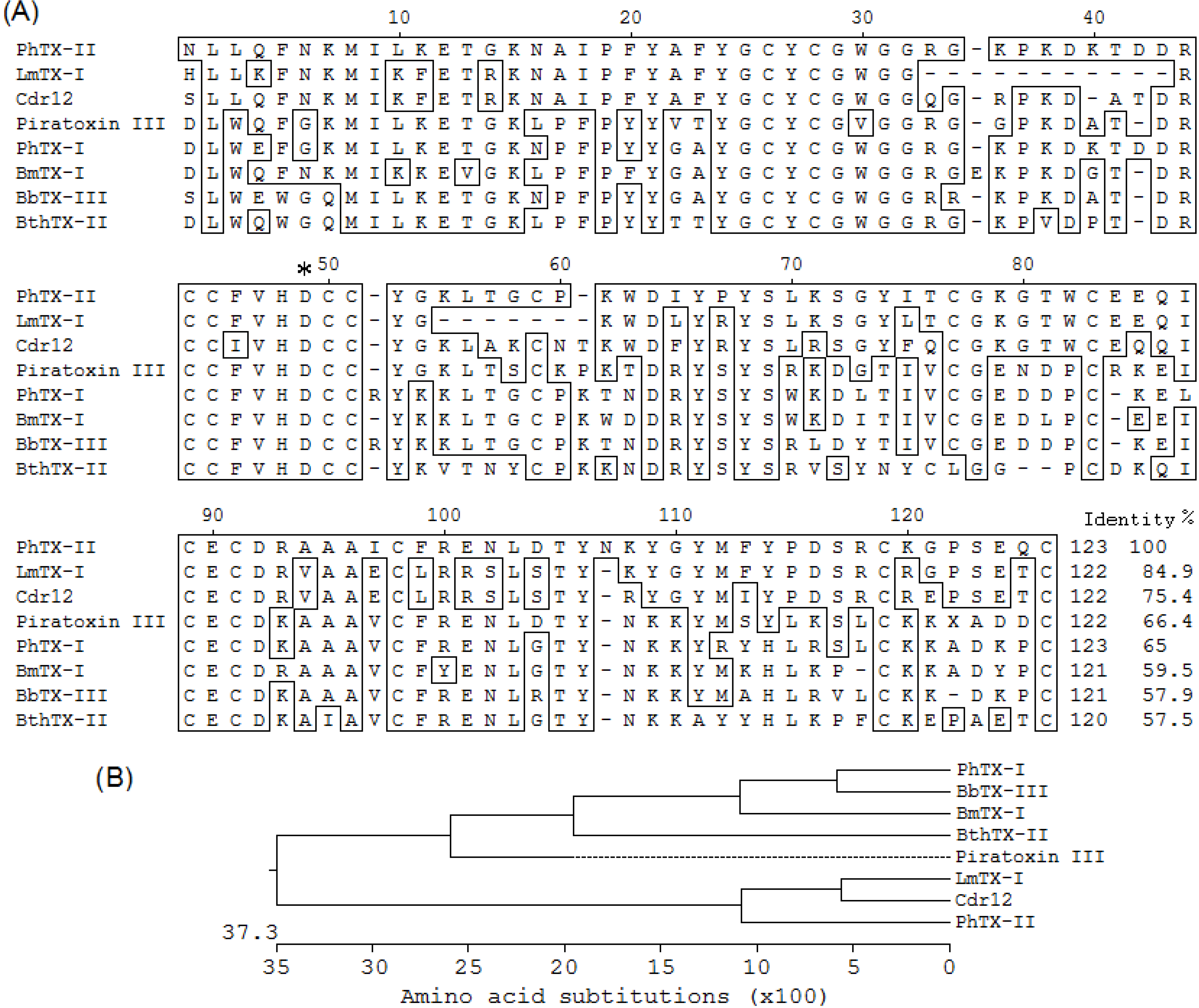
2.2. Determination of the Amino Acid Sequences of PhTX-II
| Start | End | Observed | Mr (Expected) | Mr (Calculated) | ∆ | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 438.731 | 875.449 | 875.486 | −0.037 | NL/IL/IQFNK(M) |
| 8 | 15 | 468.250 | 934.486 | 934.515 | −0.029 | (K)ML/IL/IKETGK(N) |
| 16 | 33 | 1079.967 | 2157.921 | 2157.918 | 0.002 | (K)NAL/IPFYAFYGCYCGWGGR(G) |
| 34 | 42 | 571.690 | 1140.521 | 1140.552 | −0.030 | (R)GKPKDKTDDR(C) |
| 43 | 53 | 753.247 | 1504.479 | 1504.535 | −0.055 | (R)CCFVHDCCYGK(L) |
| 54 | 60 | 300.403 | 599.304 | 599.310 | −0.005 | (K)L/ITGCPK(W) |
| 61 | 69 | 592.800 | 1183.586 | 1183.591 | −0.004 | (K)WDL/IYPYSL/IK(S) |
| 70 | 77 | 443.181 | 884.349 | 884.406 | −0.057 | (K)SGYL/ITCGK(G) |
| 78 | 90 | 871.806 | 1741.598 | 1741.649 | −0.051 | (K)GTWCEEQL/ICECDR(A) |
| 91 | 97 | 404.713 | 807.411 | 807.406 | 0.005 | (R)AAAL/ICFR(E) |
| 98 | 105 | 498.741 | 995.468 | 995.456 | 0.012 | (R)ENL/IDTYNK(Y) |
| 106 | 115 | 649.761 | 1297.508 | 1297.543 | −0.035 | (K)YGYMFYPDSR(C) |
| 116 | 123 | 483.172 | 964.330 | 964.374 | −0.043 | (R)CKGPSEQC- |

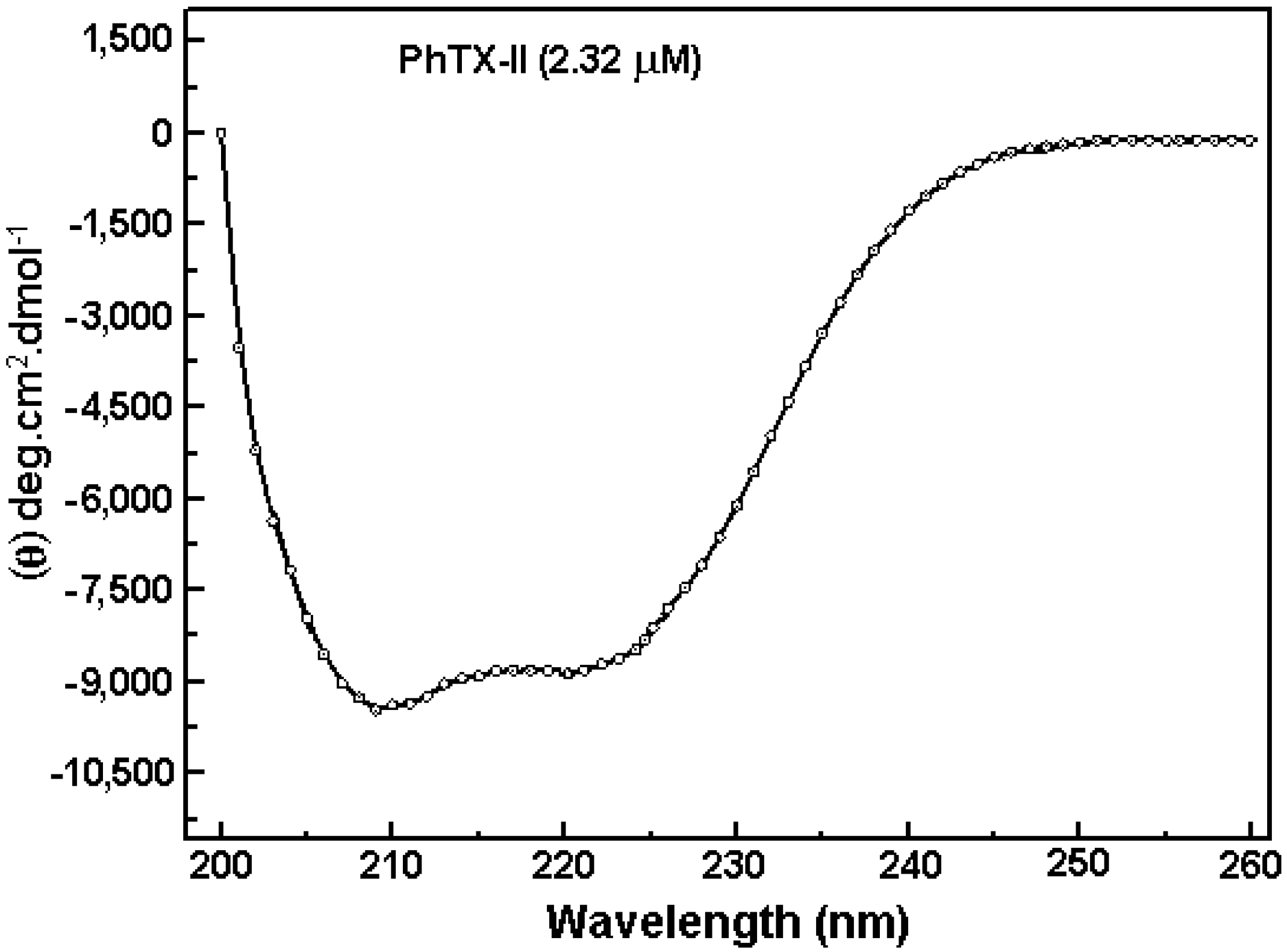
2.3. Activity Measurements of PhTX-II
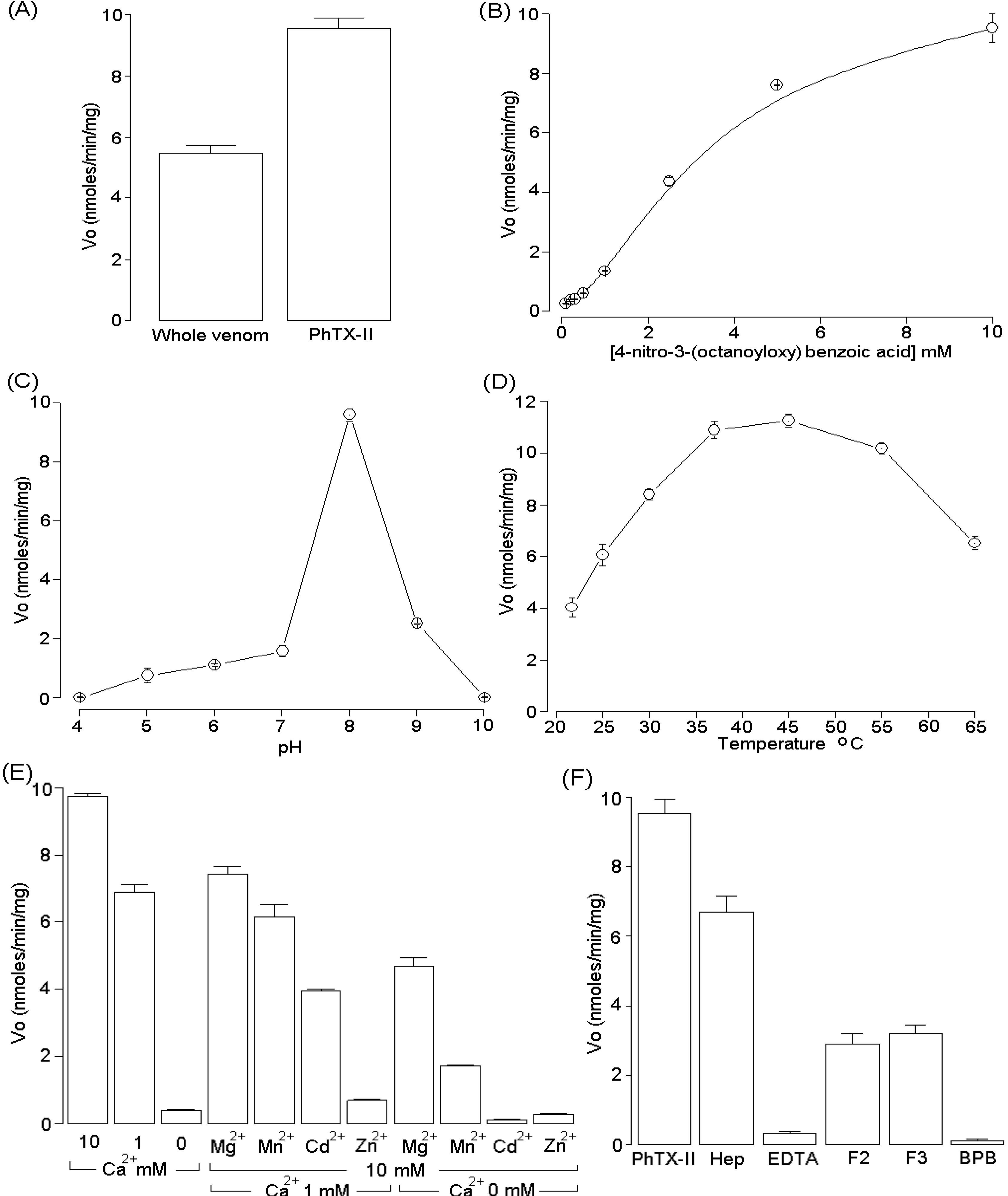
2.4. Pharmacological Activities of PhTX-II

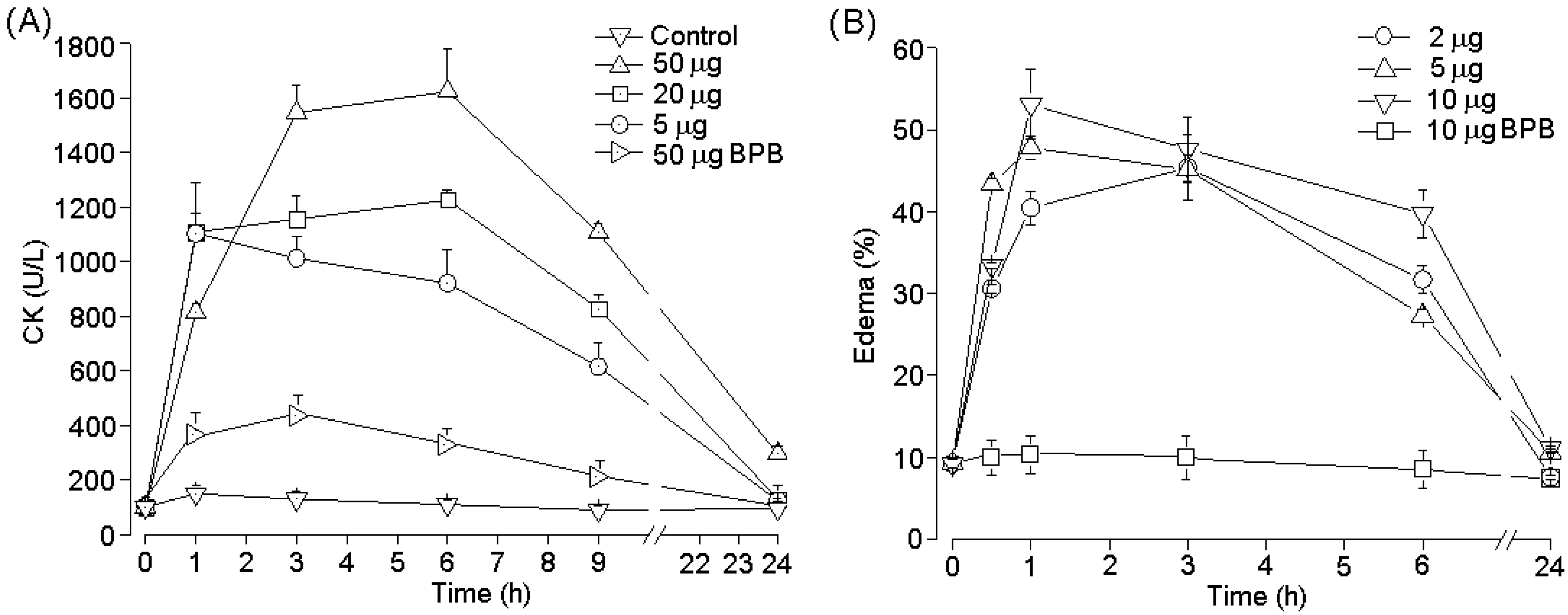
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Venom and Reagents
4.2. Purification of PhTX-II
4.3. Electrophoresis
4.4. Determination of the Molecular Mass of the Purified Protein by Mass Spectrometry
4.5. Analysis of Tryptic Digests
4.6. Circular Dichroism
4.7. Chemical Modifications
4.8. PLA2 Activity
4.9. Inhibition
4.10. Chick Biventer Cervicis Muscle Preparation (BCP)
4.11. Myotoxic Activity
4.12. Edema-Forming Activity
4.13. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albuquerque, P.L.; Silva Junior, G.B.; Jacinto, C.N.; Lima, C.B.; Lima, J.B.; Veras, M.S.; Daher, E.F. Epidemiological profile of snakebite accidents in a metropolitan area of northeast Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2013, 55, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.F.; Barros, R.; Pasquino, J.A.; Peixoto, L.R.; Sousa, J.A.; Leite Rde, S. Snakebite cases in the municipalities of the State of Paraíba, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2013, 46, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.A.; Lamar, W.W. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lomonte, B.; Rey-Suárez, P.; Tsai, W.C.; Angulo, Y.; Sasa, M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics of the pit vipers Porthidium nasutum, Porthidium ophryomegas, and Cerrophidion godmani from Costa Rica: Toxicological and taxonomical insights. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 1675–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón, M.E.; Estrella, A.; Sánchez, E.E.; Galán, J.; Tao, W.A.; Guerrero, B.; Salazar, A.M.; Rodríguez-Acosta, A. Purification and characterization of a metalloproteinase, Porthidin-1, from the venom of Lansberg’s hog-nosed pit vipers (Porthidium lansbergii hutmanni). Toxicon 2011, 57, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Martins-de-Souza, D.; Marangoni, S. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of PhTX-I a new myotoxic phospholipase A2 isolated from Porthidium hyoprora snake venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 154, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, E.A.; Cao, J.; Hsu, Y.H.; Magrioti, V.; Kokotos, G. Phospholipase A2 enzymes: Physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6130–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M. Excitement ahead: Structure, function and mechanism of snake venom phospholipase A2 enzymes. Toxicon 2003, 42, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B. Biochemistry and toxicology of toxins purified from the venom of the snake Bothrops asper. Toxicon 2009, 54, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Phospholipases A2: Unveiling the secrets of a functionally versatile group of snake venom toxins. Toxicon 2013, 62, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Corrêa, D.H.; Hollanda, L.M.; Lancellotti, M.; Ramos, C.H.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S. Chemical modifications of PhTX-I myotoxin from Porthidium hyoprora snake venom: Effects on structural, enzymatic, and pharmacological properties. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 103494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damico, D.C.; Lilla, S.; de Nucci, G.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Winck, F.V.; Novello, J.C.; Marangoni, S. Biochemical and enzymatic characterization of two basic Asp49 phospholipase A2 isoforms from Lachesis muta muta (Surucucu) venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1726, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Baldasso, P.A.; Romero-Vargas, F.F.; Winck, F.V.; Novello, J.C.; Marangoni, S. Biochemical, pharmacological and structural characterization of two PLA2 isoforms Cdr-12 and Cdr-13 from Crotalus durissus ruruima snake venom. Protein J. 2007, 26, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigden, D.J.; Hwa, L.W.; Marangoni, S.; Toyama, M.H.; Polikarpov, I. The structure of the D49 phospholipase A2 piratoxin III from Bothrops pirajai reveals unprecedented structural displacement of the calcium-binding loop: Possible relationship to cooperative substrate binding. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2003, 59, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calgarotto, A.K.; Damico, D.C.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Baldasso, P.A.; da Silva, S.L.; Souza, G.H.; Eberlin, M.N.; Marangoni, S. Biological and biochemical characterization of new basic phospholipase A2 BmTX-I isolated from Bothrops moojeni snake venom. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.F.; Novello, J.C.; Cintra, A.C.; Giglio, J.R.; Landucci, E.T.; Oliveira, B.; Marangoni, S. The amino acid sequence of bothropstoxin-II, an Asp-49 myotoxin from Bothrops jararacussu (Jararacucu) venom with low phospholipase A2 activity. J. Protein Chem. 1998, 17, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Martins-de-Souza, D.; Marangoni, S. Structural and functional characterization of brazilitoxins II and III (BbTX-II and -III), two myotoxins from the venom of Bothrops brazili snake. Toxicon 2009, 54, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, A.A.; Kayano, A.M.; Oliveira, G.A.; Setúbal, S.S.; Ribeiro, J.G.; Barros, N.B.; Nicolete, R.; Moura, L.A.; Fuly, A.L.; Nomizo, A.; et al. Purification and biochemical characterization of three myotoxins from Bothrops mattogrossensis snake venom with toxicity against Leishmania and tumor cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 195356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M. Phospholipase A2 a complex multifunctional protein puzzles. In Enzymes: Structure, Function and Mechanism; Kini, R.M., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1997; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Marangoni, F.A.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S.; Landucci, E.C. Unmasking snake venom of Bothrops leucurus: Purification and pharmacological and structural characterization of new PLA2 Bleu TX-III. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 941467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corasolla Carregari, V.; Stuani Floriano, R.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Winck, F.V.; Baldasso, P.A.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S. Biochemical, pharmacological, and structural characterization of new basic PLA2 Bbil-TX from Bothriopsis bilineata snake venom. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 612649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes Heleno, M.A.; Baldasso, P.A.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S. Biochemical characterization and pharmacological properties of new basic PLA2 BrTX-I isolated from Bothrops roedingeri (Roedinger’s Lancehead) Mertens, 1942, snake venom. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 591470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chijiwa, T.; Abe, K.; Ogawa, T.; Nikandrov, N.N.; Hattori, S.; Oda-Ueda, N.; Ohno, M. Amino acid sequence of a basic aspartate-49-phospholipase A2 from Trimeresurus flavoviridis venom and phylogenetic analysis of Crotalinae venom phospholipases A2. Toxicon 2005, 46, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, D.D.; Barbosa, C.M.B.; Bincoletto, C.; Chagas, J.R.; Magalhães, A.; Richardson, M.; Sanchez, E.F.; Pesquero, J.B.; Araújo, R.C.; Pesquero, J.L. Purification and partial characterization of two phospholipases A2 from Bothrops leucurus (white-tailed-jararaca) snake venom. Biochimie 2007, 89, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereañez, J.A.; Núñez, V.; Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Marangoni, S.; Ponce-Soto, L.A. Biochemical and biological characterization of a PLA2 from crotoxin complex of Crotalus durissus cumanensis. Toxicon 2009, 53, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulherkar, R.; Rao, R.S.; Wagle, A.S.; Patki, V.; Deo, M.G. Enhancing factor, a Paneth cell specific protein from mouse small intestines: Predicted amino acid sequence from RT-PCR amplified cDNA and its expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 195, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisne de Paula, R.; Castro, H.C.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Melo, P.A.; Fuly, A.L. Structural and pharmacological features of phospholipases A2 from snake venoms. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Gourinath, S.; Sharma, S.; Paramasivam, M.; Srinivasan, A.; Singh, T.P. Sequence and crystal structure determination of a basic phospholipase A2 from common krait (Bungarus caeruleus) at 2.4 A resolution: Identification and characterization of its pharmacological sites. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, A.J.; Fernandes, C.A.; dos Santos, J.I.; Fontes, M.R. Influence of quaternary conformation on the biological activities of the Asp49-phospholipases A2 from snake venoms. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arni, R.K.; Ward, R.J. Phospholipase A2 a structural review. Toxicon 1996, 34, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfim, V.L.; Toyama, M.H.; Novello, J.C.; Hyslop, S.; Oliveira, C.R.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Marangoni, S. Isolation and enzymatic characterization of a basic phospholipase A2 from Bothrops jararacussu snake venom. J. Protein Chem. 2001, 20, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, D.N.; Betzel, C.; Aleksiev, B.; Genov, N. Spectroscopic investigation of calcium binding sites in the neurotoxin vipoxin and its components-relation with the X-ray structure. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2000, 56, 2811–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landucci, E.C.; Toyama, M.; Marangoni, S.; Oliveira, B.; Cirino, G.; Antunes, E.; de Nucci, G. Effect of crotapotin and heparin on the rat paw oedema induced by different secretory phospholipases A2. Toxicon 2000, 38, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghini, D.G.; Toyama, M.H.; Hyslop, S.; Sodek, L.C.; Novello, C.; Marangoni, S. Enzymatic characterization of a novel phospholipase A2 from Crotalus durissus cascavella rattlesnake (Maracambóia) venom. J. Protein Chem. 2000, 19, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Oreiro, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Chemical modification of histidine and lysine residues of myotoxic phospholipases A2 isolated from Bothrops asper and Bothrops godmani snake venoms: Effects on enzymatic and pharmacological properties. Toxicon 1997, 35, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.M.; Andrião-Escarso, S.H.; Bortoleto, R.K.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Arni, R.K.; Ward, R.J.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Giglio, J.R. Dissociation of enzymatic and pharmacological properties of piratoxins-I and -III, two myotoxic phospholipases A2 from Bothrops pirajai snake venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 387, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrell, D.A. Snakebite. Lancet 2010, 375, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L.; Barfaraz, A.; Thomson, E.; Faiz, A.; Preston, S.; Harris, J.B. Screening of snake venoms for neurotoxic and myotoxic effects using simple in vitro preparations from rodents and chicks. Toxicon 1994, 32, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Vargas, F.F.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Martins-de-Souza, D.; Marangoni, S. Biological and biochemical characterization of two new PLA2 isoforms Cdc-9 and Cdc-10 from Crotalus durissus cumanensis snake venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 151, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floriano, R.S.; Carregari, V.C.; de Abreu, V.A.; Kenzo-Kagawa, B.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; da Cruz-Höfling, M.A.; Hyslop, S.; Marangoni, S.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L. Pharmacological study of a new Asp49 phospholipase A2 (Bbil-TX) isolated from Bothriopsis bilineata smargadina (forest viper) venom in vertebrate neuromuscular preparations. Toxicon 2013, 69, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, B.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Kaiser, I.I. Myotoxin II from Bothrops asper (Terciopelo) venom is a lysine-49 phospholipase A2. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1991, 284, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.A.; Comparetti, E.J.; Borges, R.J.; Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S.; Soares, A.M.; Fontes, M.R. Structural bases for a complete myotoxic mechanism: Crystal structures of two non-catalytic phospholipases A2-like from Bothrops brazili venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 2772–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.F.; Landucci, E.C.; Antunes, E.; Chacur, M.; Cury, Y. Inflammatory effects of snake venom myotoxic phospholipases A2. Toxicon 2003, 42, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.; Lomonte, B.; Vinolo, M.A.; Curi, R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Teixeira, C. An Asp49 phospholipase A2 from snake venom induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E2 production via activation of NF-κB, p38MAPK, and PKC in macrophages. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 105879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Novello, J.C.; Marangoni, S. Structural and functional properties of BaTX, a new Lys49 phospholipase A2 homologue isolated from the venom of the snake Bothrops alternatus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1770, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schagger, H.A.; von Jagow, G. Comassie blue-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for direct visualization of polypeptides during electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 166, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, D.H.A.; Ramos, C.H.I. The use of circular dichroism spectroscopy to study protein folding, form and function. Afr. J. Biochem. 2009, 3, 164–173. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, W.; Kezdy, F.J. Chromogenic substrates and assay of phospholipases A2. Methods Enzymol. 1991, 197, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Holzer, M.; Mackessy, S.P. An aqueous endpoint assay of snake venom phospholipase A2. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsborg, B.L.; Warriner, J. The isolated chick biventer cervicis nerve-muscle preparation. Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 1960, 15, 410–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S.; Lomonte, B. Systemic and local myotoxicity induced by snake venom group II phospholipases A2: Comparison between crotoxin, crotoxin B and a Lys49 PLA2 homologue. Toxicon 2008, 51, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damico, D.C.; da Cruz Höfling, M.A.; Cintra, M.; Leonardo, M.B.; Calgarotto, A.K.; da Silva, S.L.; Marangoni, S. Pharmacological study of edema and myonecrosis in mice induced by venom of the bushmaster snake (Lachesis muta muta) and its basic Asp49 phospholipase A2 (LmTX-I). Protein J. 2008, 27, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S. PhTX-II a Basic Myotoxic Phospholipase A2 from Porthidium hyoprora Snake Venom, Pharmacological Characterization and Amino Acid Sequence by Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2014, 6, 3077-3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6113077
Huancahuire-Vega S, Ponce-Soto LA, Marangoni S. PhTX-II a Basic Myotoxic Phospholipase A2 from Porthidium hyoprora Snake Venom, Pharmacological Characterization and Amino Acid Sequence by Mass Spectrometry. Toxins. 2014; 6(11):3077-3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6113077
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuancahuire-Vega, Salomón, Luis Alberto Ponce-Soto, and Sergio Marangoni. 2014. "PhTX-II a Basic Myotoxic Phospholipase A2 from Porthidium hyoprora Snake Venom, Pharmacological Characterization and Amino Acid Sequence by Mass Spectrometry" Toxins 6, no. 11: 3077-3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6113077
APA StyleHuancahuire-Vega, S., Ponce-Soto, L. A., & Marangoni, S. (2014). PhTX-II a Basic Myotoxic Phospholipase A2 from Porthidium hyoprora Snake Venom, Pharmacological Characterization and Amino Acid Sequence by Mass Spectrometry. Toxins, 6(11), 3077-3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6113077




