A Review on Toxic and Harmful Algae in Greek Coastal Waters (E. Mediterranean Sea)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sampling Areas and Data Collection
3. Results and Discussion
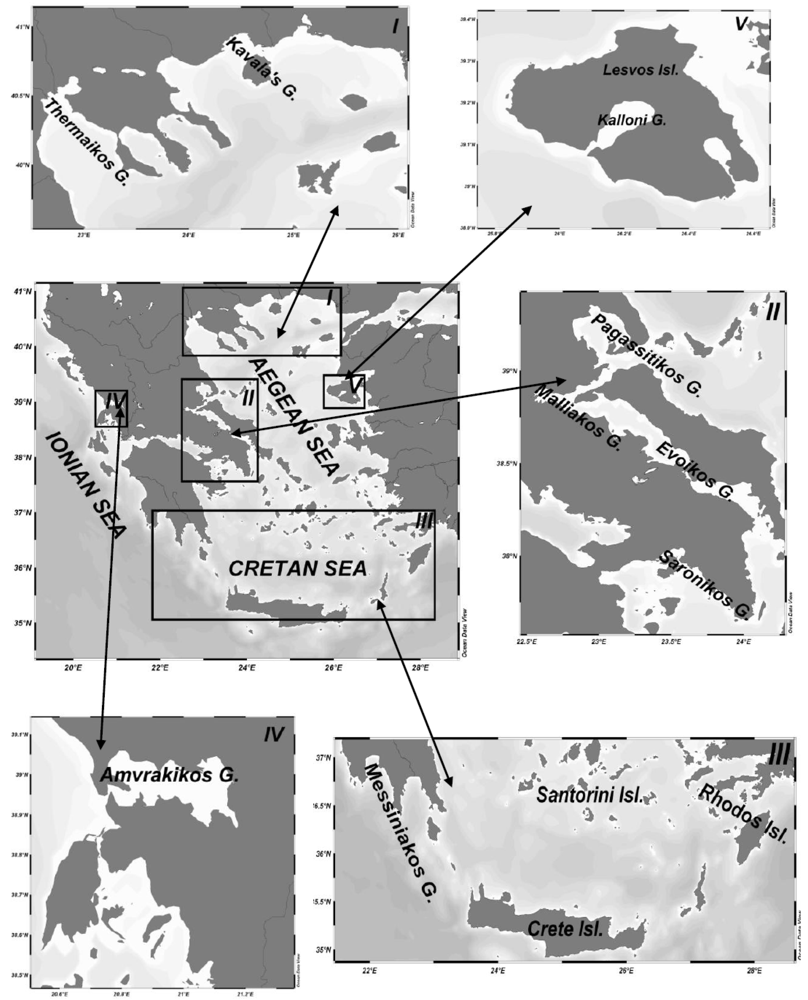
3.1. Taxonomy and toxic properties of detected HAB species in Greek coastal waters
3.1.1. Class Bacillariophyceae (Diatoms)
3.1.1.1. Order Thalassiophysales
3.1.1.2. Order Bacillarialles
3.1.2. Class Dinophyceae (Dinoflagellates)
3.1.2.1. Order Peridiniales
3.1.2.2. Order Prorocentrales
3.1.2.3. Order Dinophysiales
3.1.2.4. Order Gymnodiniales
3.1.2.5. Order Noctilucales
3.1.3. Class Prymnesiophyceae (Haptophytes)
3.1.3.1. Order Phaeocystales
3.1.3.2. Order Prymnesiales
3.1.4. Class Rhaphidophyceae (Chloromonadophytes)
3.1.5. Class Cyanophyceae (Cyanobacteria)
3.1.5.1. Order Chroococales
3.1.5.2. Order Nostocalles
| Species | Toxins | Category | Area | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diatoms | ||||
| Amphora coffeaeformis (C. Agardh) Kützing | Domoic acid | (PT) | V | [29] |
| Pseudo-nitzschia calliantha, Lundholm, Moestrup et Hasle | Domoic acid | (PT) | V | [29] |
| Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima (Cleve) Heiden | Domoic acid | (PT) | I, II, III | [73,77] |
| Pseudo-nitschia pseudodelicatissima (Hasle) Hasle | Domoic acid | (PT) | I, II, IV, V | [43,78,79] |
| Pseudo-nitzschia pungens (Grunow ex Cleve) Hasle | Domoic acid | (PT) | I, II, III, IV, V | [29,43,73] |
| Pseudo-nitzschia seriata (Cleve) H. Peragallo | Domoic acid | (PT) | I, II, III, V | [78,80,81] |
| Dinoflagellates | ||||
| Alexandrium balechii (Steidinger) Balech | Unknown toxicity | (PT) | II | [82] |
| Alexandrium catenella (Whedon et Kofoid) Balech | Saxitoxin, Gonyautoxin, c1-c4 toxins | (PT) | I, II | [82] |
| Alexandrium insuetum Balech | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | IV, V | [29,43] |
| Alexandrium minutum Halim | Gonyautoxins (1-4) | (PT) | I, II, IV, V | [43,64,83] |
| Alexandrium tamarense (Lebour) Balech | Gonyautoxins (1-4) | (PT) | I, II | [82,84] |
| Alexandrium taylori Balech | Gonyautoxin-4, Gonyautoxin-6 | (PT) | I, II | [82] |
| Amphidinium carterae Hulburt | Maitotoxin | (PT) | IV, V | [29,85] |
| Ceratium furca (Ehrenberg) Claparède et Lachmann | Unknown toxicity | (PT) | I, II, III, IV, V | [29,73,78,80] |
| Ceratium fusus (Ehrenberg) Dujardin | Unknown toxicity | (PT) | I, II, III, IV, V | [29,73,78,80] |
| Ceratium lineatum (Ehrenberg) Cleve | Unknown toxicity | (PT) | IV, V | [29,79] |
| Ceratium tripos (Müller) Nitzsch | Unknown toxicity | (PT) | I, II, III, IV, V | [29,73,78,79,80] |
| Coolia monotis Meunier | Cooliatoxin | (PT) | I, III, IV | [79,86,87] |
| Dinophysis acuminata Claparède et Lachmann | Okadaic acid, Dinophysistoxin-2 | (TX) | I, II, IV | [42,43,71,85] |
| Dinophysis acuta Ehrenberg | Okadaic acid, Dinophysistoxin-2 | (PT) | I | [88] |
| Dinophysis caudata Saville-Kent | Okadaic acid, Palytoxin | (PT) | I, II, IV, V | [29,42,43] |
| Dinophysis fortii Pavillard | Okadaic acid, Dinophysistoxin-1, Palytoxin | (PT) | I | [42] |
| Dinophysis rotundata Claparède et Lachmann | Dinophysistoxin-1 | (PT) | I, IV | [42,79] |
| Dinophysis sacculus Stein | Okadaic acid | (PT) | I, II, III, IV, V | [29,43,73] |
| Dinophysis tripos Gourret | Dinophysistoxin-1 | (PT) | I, II | [82,88] |
| Diplopsalis lenticula Bergh | Unknown toxicity | (PT) | I, V | [29,88] |
| Gambierdiscus sp. | Ciguatoxin, Maitotoxine | (PT) | III | [87] |
| Gymnodinium catenatum Graham | Gonyautoxins (1-4), Saxitoxin | (PT) | I | [84,88] |
| Gyrodinium aureolum Hulburt | 1-acyl-3-digalactosyl glycerol, Octadeca- pentaenoic acid | (TX) | I, II | [46,88] |
| Gyrodinium impudicum Fraga et Bravo | Unkown toxicity | (PT) | I, IV | [79,84] |
| Heterocapsa circularisquama Horiguchi | hemolytic toxin2-a, hemolytic toxin 3-a | (PT) | V | [29] |
| Karenia brevis(Gymnodinium breve) (Davis) G. Hansen et Moestrup | Brevetoxin-1, Brevetoxin-2, Brevetoxin-3 | (TX) | I, II, III | [46,70,73,78] |
| Karenia mikimotoi (Miyake et Kominami ex Oda) Hansen et Moestrup | Gymnocin-A | (PT) | IV | [79] |
| Karlodinium veneficum (Ballantine) J. Larsen | Karlotoxin-1, Karlotoxin-2 | (PT) | V | [29] |
| Noctiluca scintillans (Macartney) Kofoid et Swezy | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | I | [43] |
| Ostreopsis ovata Fukuyo | Putative Palytoxin, Ovatoxin-a | (PT) | I, III, V | [29,86,87] |
| Ostreopsis siamensis Schmidt | Putative Palytoxin | (PT) | I, III | [86,87] |
| Peridinium quinquecornen Abé | Unknown toxicity | (PT) | V | [29] |
| Prorocentrum arcuatum Issel | Unknown toxicity | (PT) | V | [29] |
| Prorocentrum borbonicum Ten-Hage, Turquet, Quod, Puiseux-Dao et Couté | Borbotoxins | (PT) | I, III | [87,89] |
| Prorocentrum dentatum Stein | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | I, II | [46] |
| Prorocentrum emarginatum Fukuyo | Unknown toxicity | (PT) | I, III, IV | [79,87,89] |
| Prorocentrum levis M.A. Faust, Kibler, Vandersea, P.A. Tester & Litaker | Okadaic acid, Dinophysistoxin-2 | (PT) | I | [89] |
| Prorocentrum lima (Ehrenberg) Stein | Okadaic acid, Dinophysistoxin-1, Dinophysistoxin-2 | (PT) | I, II, III, V | [29,73,87,89] |
| Prorocentrum micans Ehrenberg | Putative Palytoxin, Ovatoxin-a | (PT) | I, II, III, IV | [73,77,78,79] |
| Prorocentrum minimum (Pavillard) Schiller | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | I, II, IV, V | [29,43,46] |
| Prorocentrum obtusidens Schiller | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | I | [42,43] |
| Prorocentrum redfeldii Bursa | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | I, IV | [43,79] |
| Prorocentrum rhathymum Loeblich III, Sherley et Schmidt | Okadaic acid | (PT) | I, III, IV | [85,87,89] |
| Protoceratium reticulatum (Claparède et Lachmann) Bütschli | Yessotoxin | (PT) | I | [84] |
| Protoperidinium crassipes (Kofoid) Balech | Azaspiracid toxin-1 Azaspiracid toxin-2 Azaspiracid toxin-3 | (PT) | V | [29] |
| Scrippsiella trochoidea (Stein) Loeblich | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | I, II, III, IV, V | [29,46,73,78,79] |
| Prymnesiophytes | ||||
| Phaeocystis pouchetii (M.P. Hariot) G. Lagerheim | Polyunsaturated aldehydes | (HB) | I, II, III | [46,62,73] |
| Prymnesium parvum N. Carter | Prymnesin-1, Prymnesin-2 | (PT) | I, IV | [85,88] |
| Rhaphidophytes | ||||
| Chattonella globosa Y. Hara et Chihara | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | I, IV | [42,43] |
| Chattonella verucolosa Y. Hara et Chihara | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | I, IV | [42,43] |
| Cyanobacteria | ||||
| Microcystis aeruginosa (Kützing) Kützing | Microcystin-LR | (TX) | II | [62] |
| Lyngbya agardhii P.L.Crouan & H.M.Crouan ex Gomont | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | II | [62] |
| Chroococcus gelatinosus Geitler | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | II | [62] |
| Synechocystis sallensis Skuja | Unknown toxicity | (HB) | II | [62] |
| Trichodesmium erythraeum Ehrenberg | Saxitoxin | (TX) | II | [62] |
3.2. The ecological role of toxic, potentially toxic and bloom forming species in Greek coastal waters
| Species | Feeding mechanism | Food type | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alexandrium catenella | Osmotrophy | Urea, dextrans | [90] |
| Alexandrium minutum | Osmotrophy-Phagotrophy | Urea, Cyanobacteria | [91,92] |
| Alexandrium tamarense | Osmotrophy-Phagotrophy | Urea, Cyanobacteria, Cryptophytes | [92,93,94] |
| Ceratium furca | Phagotrophy | Ciliates | [95] |
| Dinophysis acuminata | Phagotrophy | Ciliates | [96] |
| Gambierdiscus sp. | Phagotrophy | Unknown pray | [8] |
| Gymnodinium catenatum | Phagotrophy | Cyanobacteria | [92] |
| Gyrodinium impudicum | Phagotrophy | Cyanobacteria, Algae | [94,97] |
| Karenia brevis | Osmotrophy-Phagotrophy | Urea, Cyanobacteria | [92,98] |
| Karlodinium veneficum | Osmotrophy-Phagotrophy | Urea, Cryptophytes | [99,100] |
| Noctiluca scintillans | Phagotrophy | Algae | [101] |
| Ostreopsis ovata | Phagotrophy | Unknown pray | [8] |
| Ostreopsis siamensis | Phagotrophy | Unknown pray | [8] |
| Prorocentrum micans | Phagotrophy | Cyanobacteria, Algae | [92,94] |
| Prorocentrum minimum | Osmotrophy-Phagotrophy | Urea, Cyanobacteria, Algae | [92,99,102] |
| Protoperidinium crassipes | Phagotrophy | Algae | [103] |
| Scrippsiella trochoidea | Phagotrophy | Cyanobacteria, Algae | [92,94] |
| Prymnesium parvum | Phagotrophy | Algae | [104] |
| Microcystis aeruginosa | Osmotrophy | Leucine | [69] |
| Species | Season/year of max. abundance (Cells.L−1) | Gulf | Impact | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexandrium insuetum | April 2003 (2.5 × 106 ) | Amvrakikos | Water discoloration | [43] |
| May 2004 (4.7 × 105) | ||||
| Dinophysis acuminata | Jan. 2000 (8.5 × 104) | Thermaikos | Diarrhetic shellfish toxins | [42,71] |
| Feb. 2002 (3.7 × 104) | ||||
| March 2003 (2.2 × 103) | ||||
| May 2004 (1.1 × 104 ) | ||||
| Karenia brevis | Sept. 1977 (1.0 × 107) | Saronikos | Massive fish kill | [70,105] |
| Sept. 1978 (5.0 × 107) | ||||
| Oct. 1987 (2.7 × 107) | ||||
| Noctiluca scintillans | February-March 2000-2004 (>1.0 × 106) | Thermaikos | Water discoloration | [43] |
| March 1978 (1.1 × 105) | Kavalas | Water discoloration | [105] | |
| Prorocentrum micans | April 1994 (3.7 × 107) | Thermaikos | Water discoloration Water discoloration | [43] |
| May 1993 (1.1 × 106) | Saronikos | [46] | ||
| Prorocentrum minimum | April 2003 (1.2 × 105) | N. Aegean coastal area, Saronikos, Amvrakikos | Water discoloration | [43] |
| April 2003 (1.1 × 105) | ||||
| Autumn 2003 (1.0 × 105) | ||||
| Prorocentrum obtusidens | Jan. 2000 (1.2 × 106) | Thermaikos | Water discoloration | [43] |
| Jan. 2001 (1.2 × 106) | ||||
| Prorocentrum redfeldii | Winter 2000 (1.2 × 106) | Thermaikos | Water discoloration | [43] |
| Winter 2001 (6.0 × 106) | ||||
| Phaeocystis pouchetii | March 1989 (2.5 × 106) | Saronikos | Water discoloration | [46] |
| August 1993 (3.5 × 107) | Evoikos | Mucilage | [62] | |
| Sept. 1999 (2.7 × 106) | ||||
| Chattonella globosa | Spring 2001 (>104) | Thermaikos | Water discoloration | [43] |
| Spring 2002 (>104) | ||||
| Spring 2003 (>104) | ||||
| Chattonella verucolosa | Dec. 1998 (Massive presence) | Amvrakikos | Mass finfish mortality | [43] |
| Microcystis aeruginosa | Sept. 1999 (9.9 × 105) | Evoikos | Mucilage | [62] |
| Lyngbya agardhii | Sept. 1999 (4.8 × 103 filaments.L−1) | Evoikos | Mucilage | [62] |
| Chroococcus gelatinosus | Sept. 1999 (8.2 × 105) | Evoikos | Mucilage | [62] |
| Synechocystis sallensis | Sept. 1999 (8.9 × 104) | Evoikos | Mucilage | [62] |
| Trichodesmium erythraeum | Sept. 1999 (7.1 × 104 trichomes.L−1) | Evoikos | Mucilage | [62] |
4. Conclusions
References
- Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Ignatiades, L. Distribution of chlorophyll α in the Aegean and Ionian Sea. In State of the Hellenic Fisheries; Papaconstantinou, C., Zenetos, A., Vassilopoulou, V., Tserpes, G., Eds.; HCMR: Athens, Greece, 2007; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Codd, G.A. Cyanobacterial toxins: Their occurrence in aquatic environments and significance to health. In Marine Cyanobacteria; Charpy, L., Larkum, A.W.D., Eds.; Bulletin De L'Institut Oceanographique: Paris, France, 1999; pp. 483–500. [Google Scholar]
- Vershinin, A.O.; Orlova, T.Y. Toxic and harmful algae in the coastal waters of Russia. Mar. Biol. 2008, 48, 524–537. [Google Scholar]
- Akselman, R.; Cronberg, G.; Elbraechter, M.; Fraga, S.; Halim, Y.; Hansen, G.; Hoppenrath, M.; Larsen, J.; Lundholm, N.; Nguyen, L.N.; Zingone, A. IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae (HABs). Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org/hab/,accessed 3 March 2010.
- Anonymous. EUROHAB Science Initiative Part B: Research and Infrastructural Need. In National European and International Programmes.; Granéli, E., Lipiatou, E., Eds.; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sournia, A. Atlas du Phytoplankton Marin. Cyanophycees, Dictyochophycees, Dinophycees, Raphidophycees; Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique: Paris, France, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Zingone, A.; Evenoldsen, H.O. The diversity of algal blooms: A challenge for science and management. Ocean Coast. Manage. 2000, 43, 725–748. [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder, J.M.; Gilbert, P.M.; Skelton, H.M. Mixotrophy, a major mode of nutrition for harmful algal species in eutrophic waters. HarmfulAlgae 2008, 8, 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sala, S.E.; Sar, E.A.; Ferrario, M.E. Review of materials reported as containing Amphora coffeaeformis (Agardh) Kützing in Argentina. Diatom Res. 1998, 13, 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, M.; Coccia, A.; Volterra, L. Ecology of mucilage production by Amphora coffeaeformis var. perpusilla blooms of Adriatic Sea. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1993, 69, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, E.C.D. Amnestic shellfish poisoning-a new seafood toxin syndrome. In Toxic Marine Phytoplankton; Granéli, E., Sundström, B., Edler, L., Anderson, D.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 1990; pp. 504–508. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarska, I.; LeGresley, M.M.; Martin, J.L.; Ehrman, J. Diversity of the diatom genus Pseudo-nitzschia Peragallo in the Quoddy region of the Bay of Fundy, Canada. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, N.; Skov, J.; Pocklington, R.; Moestrup, Ø. Domoic acid, the toxic amino acid responsible for amnesic shellfish poisoning, now in Pseudo-nitzschia seriata (Bacillariophyceae) in Europe. Phycologia 1994, 33, 475–478. [Google Scholar]
- Codd, G.A.; Elbrächter, M.; Faust, M.A.; Fraga, S.; Fukuyo, Y.; Cronberg, G.; Halim, Y.; Taylor, F.J.R.; Zingone, A. IOC Taxonomic Reference List of Toxic Algae. Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO. 2004. Available online: http://www.ioc.unesco.org/hab/data.htm (accessed on 18 March 2009).
- Thessen, A.E.; Stoecker, D.K. Distribution, abundance and domoic acid analysis of the toxic diatom genus Pseudo-nitzschia from the Chesapeake Bay. Estuar. Coast. 2008, 31, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, M.A.; Gulledge, R.A. Identifying harmful marine dinoflagellates. Contr. US Nat. Herb. 2002, 42, 1–144. [Google Scholar]
- Krock, B.; Seguel, C.G.; Cembella, A.D. Toxin profile of Alexandrium catenella from the Chilean coast as determined by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection and liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangopoulos, M.; Guisande, C.; de Blas, E.; Maneiro, I. Toxin production and competitive abilities under phosphorus limitation of Alexandrium species. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.T.; Usup, G.; Leaw, C.P.; Ogata, T. First report of Alexandrium taylori and Alexandrium peruvianum (Dinophyceae) in Malaysia waters. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congestri, R.; Bianko, I.; Albertano, P. Potentially toxic thecate dinoflagellates of middle Tyrrhenian coastal waters (Mediterranean Sea). In Harmful Algae; Steidinger, K.A., Landsberg, J.H., Tomas, C.R., Vargo, G.A., Eds.; Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, Florida Institute of Oceanography, and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, 2002; pp. 332–334. [Google Scholar]
- Durand-Clement, M. Study of production and toxicity of cultured Gambierdiscus toxicus. Biol. Bull. 1987, 172, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Jones, A.; Hoy, A.W. Cooliatoxin, the first toxin from Coolia monotis (Dinophyceae). Nat. Toxins 1995, 3, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Nakashima, T.; Iwashita, T.; Fujita, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Odaa, T. Purification and characterization of photosensitizing haemolytic toxin from harmful red tide phytoplankton, Heterocapsa circularisquama. Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 73, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aligizaki, K.; Katikou, P.; Nikolaidis, G.; Panou, A. First episode of shellfish contamination by palytoxin-like compounds from Ostreopsis species (Aegean Sea, Greece). Toxicon 2008, 51, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, F.; Pezzolesi, L.; Feller, A.; Riccardi, M.; Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Tartaglione, L.; Lacovo, E.D.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Pistocchi, R. Comparative growth and toxin profile of cultured Ostreopsis ovata from the Tyrrhenian and Adriatic Seas. Toxicon 2009, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, L.; Towers, N.; Briggs, L.; Munday, R.; Adamson, J. Uptake of palytoxin-like compounds by shellfish fed Ostreopsis siamensis (Dinophyceae). N.Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 36, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, M.D.A.; Smith, G.J.; Kudela, R.M. Phylogenetic relationships of yessotoxin-producing dinoflagellates, based on the large subunit and internal transcribed spacer ribosomal DNA domains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Gárate-Lizárraga, I.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Lopez-Cortés, D.J.; Muneton-Gomez, M.D. Bloom of Scrippsiella trochoidea (Gonyaulacaceae) in a shrimp pond in the southwestern Gulf of California, Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatharis, S.; Dolapsakis, N.P., Economou-Amilli; Tsirtsis, G.; Danielidis, D.B. Dynamics of potentially harmful microalgae in a confined Mediterranean Gulf-Assessing the risk of bloom formation. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalena, A.B.; Lehane, M.; Krys, S.; Fernández, M.L.F.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. The first identification of azaspiracids in shellfish from France and Spain. Toxicon 2003, 42, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gárate-Lizárraga, I.; Muneton-Gomez, M.D. Bloom of Peridinium quinquecorne Abé in La Ensenada de La Paz, Gulf of California (July 2003). Acta Bot. Mex. 2008, 83, 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.H.; Shimode, S.; Han, M.S.; Kikuchi, T. Population development of the dinoflagellates Ceratium furca and Ceratium fusus during spring and early summer in Iwa Harbor, Sagami Bay, Japan. Ocean Sci. J. 2008, 43, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Landsberg, J.H.; Evans, J.J.; Al-Sarawi, M.A.; Faraj, M.; Al-Jarallah, M.A.; Haywood, A.; Ibrahem, S.; Klesius, P.; Powell, K.; Shoemaker, C. A. Fish kill of massive proportion in Kuwait Bay, Arabian Gulf, 2001: the roles of bacterial disease, harmful algae, and eutrophication. Harmful Algae 2002, 1, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoue, Y. Massive fish kills by a Ceratium fusus red tide in Kagoshima Bay, Japan. Red Tide Newslett. 1990, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Rost, B.; Richter, K.U.; Riebesell, U.; Hansen, P.J. Inorganic carbon acquisition in red tide dinoflagellates. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.S. Ceratium in Fire Island Inlet, Long-Island New-York (1971-1977). Limnol. Oceanogr. 1979, 24, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten-Hage, L.; Turquet, J.; Quod, J.P.; Puiseux-Da, S.; Couté, A. Prorocentrum borbonicum sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a new toxic benthic dinoflagellate from southwestern Indian Ocean. Phycologia 2000, 39, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, M.A.; Vandersea, M.W.; Kibler, S.R.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W. Prorocentrum levis, a new benthic species (Dinophyceae) from a mangrove island, Twin Cays, Belize. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Veloso, V.; Amorim, A. Toxin composition of Prorocentrum lima strain isolated from the Portuguese coast. Toxicon 2009, 54, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianying, A.; Winshell, J.; Scorzetti, G.; Fell, J.W.; Rein, K.S. Identification of okadaic acid production in the marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum rhathymumfrom Florida Bay. Toxicon 2009, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Baric, A.; Grbec, B.; Kuspilic, G.; Marasovic, I.; Nincevic, Z.; Grubelic, I. Mass mortality event in a small saline lake (Lake Rogoznica) caused by unusual holomictic conditions. Sci. Mar. 2003, 67, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Koukaras, K.; Nikolaidis, G. Dinophysis blooms in Greek coastal waters (Thermaikos Gulf, NW Aegean Sea). J. Plankton Res. 2004, 26, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaidis, G.; Koukaras, K.; Aligizaki, K.; Heracleous, A.; Kalopesa, E.; Moschandreou, K.; Tsolaki, E.; Mantoudis, A. Harmful microalgal episodes in Greek coastal waters. J. Biol. Res.-Thessal. 2005, 3, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Lassus, P.; Berthome, J.P. Status of 1987 algal blooms in IFREMER. ICES/annex III C.M. 1988, 33A, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Berden-Zrimec, M.; Flander-Putrle, V.; Drinovec, L.; Zrimec, A.; Monti, M. Growth, delayed fluorescence and pigment composition of four Prorocentrum minimum strains growing at two salinities. Biol. Res. 2008, 41, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Moncheva, S.; Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Pagou, K.; Krastev, A. Phytoplankton blooms in Black Sea and Mediterranean coastal ecosystems subjected to anthropogenic eutrophication: Similarities and differences. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 53, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, M.A. Morphologic details of six benthic species of Prorocentrum (Pyrrhophyta) from a mangrove island, Twin Cays, Belize, including two new species. J. Phycol. 1990, 26, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.L.C.; Cembella, A.D. Ecophysiology and biosynthesis of polyether marine biotoxins. In Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 427–451. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; lgarashi, T.; Fraga, S.; Dahl, E.; Hovgaard, P.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in various dinoflagellate species. J. Appl. Phycol. 1989, 1, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, S.; Bravo, I.; Delgado, M.; Franco, J.M.; Zapata, M. Gymnodinium impudicum sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a non-toxic, chain forming red tide dinoflagellate. Phycologia 1995, 34, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessard, V.; Diogène, G.; Dubreuil, A; Quod, J.P.; Durand-Clément, M.; Legay, C.; Puiseux-Dao, S. Selection of cytotoxic responses to maitotoxin and okadaic acid and evaluation of toxicity of dinoflagellate extracts. Nat. Toxins 2006, 2, 322–328. [Google Scholar]
- Smolowitz, R.; Shumway, S.A. Possible cytotoxic effects of the dinoflagellate, Gyrodinium aureolum, on juvenile bivalve molluscs. Aquac. Int. 1997, 5, 29–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, R.H.; Henry, M.S. Harmful algal toxins of the Florida red tide (Karenia brevis): Natural chemical stressors in South Florida coastal ecosystems. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Shoji, M.; Oshima, Y.; Naoki, H.; Fujita, T.; Yasumoto, T. Gymnocin-A, a cytotoxic polyether from the noxious red tide dinoflagellate, Gymnodinium mikimotoi. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 5829–5832. [Google Scholar]
- Gárate-Lizárraga, I.; Bustillos-Guzmán, J.J.; Alonso-Rodríguez, R.; Luckas, B. Comparative paralytic shellfish toxin profiles in two marine bivalves during outbreaks of Gymnodinium catenatum (Dinophyceae) in the Gulf of California. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimany, E.; Place, A.R.; Ramón, M.; Jutson, M.; Pipe, R.K. The effects of feeding Karlodinium veneficum (PLY # 103; Gymnodinium veneficum Ballantine) to the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.Z.; Mesaad, I. First report on Noctiluca scintillans in the Red Sea off the coasts of Soudi Arabia: Consequencies of eutrophication. Oceanologia 2007, 49, 337–351. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, E.; Ernstsen, A.; Eilertsen, H.C. Isolation and characterization of a cytotoxic polyunsaturated aldehyde from the marine phytoplankter Phaeocystis puchettii (Hariot) Lagerheim. Toxicology 2004, 199, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, T.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. Structures and partial stereochemical assignments for prymnesin-1 and prymnesin-2: potent hemolytic and ichthyotoxic glycosides isolated from the red tide alga Prymnesium parvum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 8499–8511. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, H.A. Taxonomy of toxic haptophytes (prymnesiophytes). In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae, 2nd; Hallegraeff, G.M., Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Eds.; IOC-UNESCO: Paris, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Raabergh, C.M.I.; Bylund, G.; Eriksson, J.E. Hystopathological effects of microcystin-LR a cyclic peptide toxin from the cyanobacterium (blue-green alga) Microcystis aeruginosa on common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquat. Toxicol. 1991, 20, 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- Metaxatos, A.; Panagiotopoulos, C.; Ignatiades, L. Monosaccharide and aminoacid composition of mucilage material produced from a mixture of four phytoplanktonic taxa. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 294, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, A.P.; Bunter, O.; Jones, B.; Llewllyn, L. Effects of the bloom-forming alga Trichodesmium erythraeum on the pearl oyster Pinctada maxima. Aquaculture 2004, 232, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiades, L.; Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Metaxatos, A. Field and culture studies on the ecophysiology of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum (Halim) grown in Greek coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smayda, T.J. Harmful algal blooms: Their ecotoxicology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1137–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D. Chemical ecology of eukaryotic microalgae in marine ecosystems. Phycologia 2003, 42, 420–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegman, R.; Colijin, F.; Malschaert, J.F.P.; Klooosterhuis, H.T.; Cadee, G.C. Assessment of growth rate limiting nutrients in the North Sea by the use of nutrient-uptake kinetics. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1990, 26, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, M.A. Mixotrophy in tropical benthic dinoflagellates. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernandez, M.L., Watt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and IOC-UNESCO: Paris, France, 1998; pp. 390–393. [Google Scholar]
- Kamjunke, N.; Tittel, J. Utilisation of leucine by several phytoplankton species. Limnologica 2008, 38, 360–366. [Google Scholar]
- Pagou, K.; Ignatiades, L. The periodicity of Gymnodinium breve (Davis) in Saronicos Gulf, Aegean Sea. In Toxic Marine Phytoplankton; Granéli, E., Sundström, B., Edler, L., Anderson, D.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 1990; pp. 206–208. [Google Scholar]
- Reizopoulou, S.; Strogyloudi, E.; Giannakourou, A.; Pagou, K.; Chatzianestis, I.; Pyrgaki, C.; Granéli, E. Okadaic acid accumulation in macrofilter feeders subjected to natural blooms of Dinophysis acuminata. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiades, L. Annual cycle, species diversity and succession of phytoplankton in lower Saronikos Gulf, Aegean Sea. Mar. Biol. 1969, 3, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiades, L.; Georgopoulos, D.; Karydis, M. Description of phytoplanktonic community of the oligotrophic waters of S. E. Aegean Sea. Mar. Ecol. 1995, 16, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiades, L. Scaling the trophic status of the Aegean Sea, Eastern Mediterranean. J. Sea Res. 2005, 54, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F. Endemic and Indo-Pacific plankton in the Mediterranean Sea: a study based on dinoflagellate records. J. Biogeogr. 2006, 33, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granéli, E.; Codd, G.A.; Dale, B.; Lipiatou, E.; Maestrini, S.Y.; Rosenthal, H. Harmful Algal Blooms in European Marine and Brackish Waters.; European Commission: Belgium, 1999; EUR 18592. [Google Scholar]
- Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Ignatiades, L. Phytoplankton in pelagic and coastal waters. In State of the Hellenic Marine Environment; Papathanassiou, E., Zenetos, A., Eds.; HCMR: Athens, Greece, 2005; pp. 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Friligos, N. Contribution to eutrophication and phytoplankton ecology in the Thermaikos Gulf. Thalassographica 1990, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaidis, G.; Koukaras, K.; Aligizaki, K.; Kalopesa, E.; Moschandreou, K.; Tsolaki, E. Phytoplankton. In Monitoring of Water Quality in the Coastal Area of Kalamitsi-Preveza (2nd phase); Final Report, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (A.U.Th.): Thessaloniki, Greece, 2006; pp. 90–106. [Google Scholar]
- Friligos, N.; Gotsis-Skretas, O. Relationships of phytoplankton with certain environmental factors in the South Euboikos Gulf (Greece). P.S.Z.N.I.: Mar. Ecol. 1987, 8, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Spatharis, S.; Mouillot, D.; Danielidis, D.B.; Karydis, M.; Chi, T.D.; Tsirtsis, G. Influence of terrestrial runoff on phytoplankton species richness-biomass relationships: A double stress hypothesis. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 362, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Ignatiades, L.; Pavlidou, A.; Metaxatos, A.; Papadopoulos, A.; Pappas, G. Alexandrium spatio-temporal distribution in the STRATEGY areas (WP1) March 2002-October 2002): Greek Area. In Second Year Report of the EU Project ‘‘STRATEGY’’ New Strategy of Monitoring and Management of HABs in the Mediterranean Sea; 2003; pp. 1–14. Annex III. [Google Scholar]
- Spatharis, S.; Dolapsakis, N.P.; Danielidis, D.B.; Tsirtsis, G. Dynamics of a HAB developed after an episodic rainfall event in a coastal area. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer. Medit. 2007, 38, 396. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakourou, A.; Orlova, T.; Assimakopoulou, G.; Pagou, K. Dinoflagellate cysts in recent marine sediments from Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Possible implications of resuspension events on the onset of phytoplankton blooms. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolapsakis, N.P.; Tzovenis, I.; Kantourou, P.; Bitis, I.; Economou-Amilli, A. Potentially harmful microalgae from lagoons of the NW Ionian Sea, Greece. J. Biol. Res.-Thessalon. 2008, 9, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Aligizaki, K.; Nikolaidis, G. The presence of the potentially toxic genera Ostreopsis and Coolia (Dinophyceae) in the North Aegean Sea, Greece. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aligizaki, K.; Nikolaidis, G. Morphological identification of two tropical dinoflagellates of the genera Gambierdiscus and Sinophysis in the Mediterranean. J. Biol. Res.-Thessalon. 2008, 9, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaidis, G.; Moustaka-Gouni, M. The structure and dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages from the inner part of the Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. I. Phytoplankton composition and biomass from May 1988 to April 1989. Helgolander Meeresunters 1990, 44, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aligizaki, K.; Nikolaidis, G.; Katikou, P.; Baxevanis, A.D.; Abatzopoulos, T.J. Potentially toxic epiphytic Prorocentrum (Dinophyceae) species in Greek coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyhrman, S.T.; Anderson, D.M. Urease activity in cultures and field populations of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.H.; McClean, M. Growth responses of Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae) as a function of three different nitrogen sources and irradiance. N.Z. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 1997, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Park, J.Y.; Nho, J.H.; Park, M.O.; Ha, J.H.; Seong, K.A.; Jeng, C.; Seong, C.N.; Lee, K.Y.; Yih, W.H. Feeding by red tide dinoflagellates on the cyanobacterium Synechococcus. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 41, 1331–2143. [Google Scholar]
- Leong, S.C.Y.; Murata, A.; Nagashima, Y.; Taguchi, S. Variability in toxicity of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarence in response to different nitrogen sources and concentrations. Toxicon 2004, 43, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Yoo, D.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, S.T.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Yih, W.H. Feeding by phototrophic red-tide dinoflagellates: five species newly revealed and six species previously known to be mixotrophic. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 40, 133–150.
- Smalley, G.W.; Coats, D.W. Ecology of the red- tide Dinoflagellate Ceratium furca: distribution, mixotrophy and grazing impact on ciliate populations of Chesapeake Bay. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2002, 49, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, D.M.; Anderson, D.M. Widespread phagocytosis of ciliates and other protists by marine mixotrophic and heterotrophic thacate dinoflagellates. J. Phycol. 1996, 32, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Yoo, D.Y.; Seong, K.A.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Ha, J.H.; Yih, W.H. Feeding by the mixotrophic red-tide dinoflagellate Gonyaulax polygramma: mechanisms, prey species, effects of prey concentration and grazing impact. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 38, 133–150. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, G.; Kamykowski, D.; Glibert, P.M. Growth, uptake, and assimilation of ammonium, nitrate, and urea, by three starins of Karenia brevis grown under low light. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, C.M.; Glibert, P.M. Urease activity in five phytoplankton species. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 52, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, J.E.; Bachvaroff, T.; Place, A.R. Can Cryptophyte abundance trigger toxic Karlodinium veneficum blooms in eutrophic estuaries? Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.J.; Miranda, L.; Azanza, R. Green Noctiluca scintillans: a dinoflagellate with its own greenhouse. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 275, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecker, D.K.; Li, A.; Coats, D.W.; Gustafson, D.E.; Nannen, M.K. Mixotrophy in the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 152, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Latz, M.I. Growth ang grazing rates of the heterotrophic dinoflagellates Protoperidinium spp. on red tide dinoflagellates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 106, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U. Kill and eat your predator: a winning strategy of the plankton flagellate Prynmesium parvum. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 32, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satsmadjis, J.; Friligos, N. Red tide in Greek waters. Vie et Milieu 1983, 33, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ignatiades, L.; Gotsis-Skretas, O. A Review on Toxic and Harmful Algae in Greek Coastal Waters (E. Mediterranean Sea). Toxins 2010, 2, 1019-1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2051019
Ignatiades L, Gotsis-Skretas O. A Review on Toxic and Harmful Algae in Greek Coastal Waters (E. Mediterranean Sea). Toxins. 2010; 2(5):1019-1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2051019
Chicago/Turabian StyleIgnatiades, Lydia, and Olympia Gotsis-Skretas. 2010. "A Review on Toxic and Harmful Algae in Greek Coastal Waters (E. Mediterranean Sea)" Toxins 2, no. 5: 1019-1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2051019
APA StyleIgnatiades, L., & Gotsis-Skretas, O. (2010). A Review on Toxic and Harmful Algae in Greek Coastal Waters (E. Mediterranean Sea). Toxins, 2(5), 1019-1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2051019




