Biodiversity-Driven Screening of Amphibian Skin Secretions for Inflammatory Modulation in Joint Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
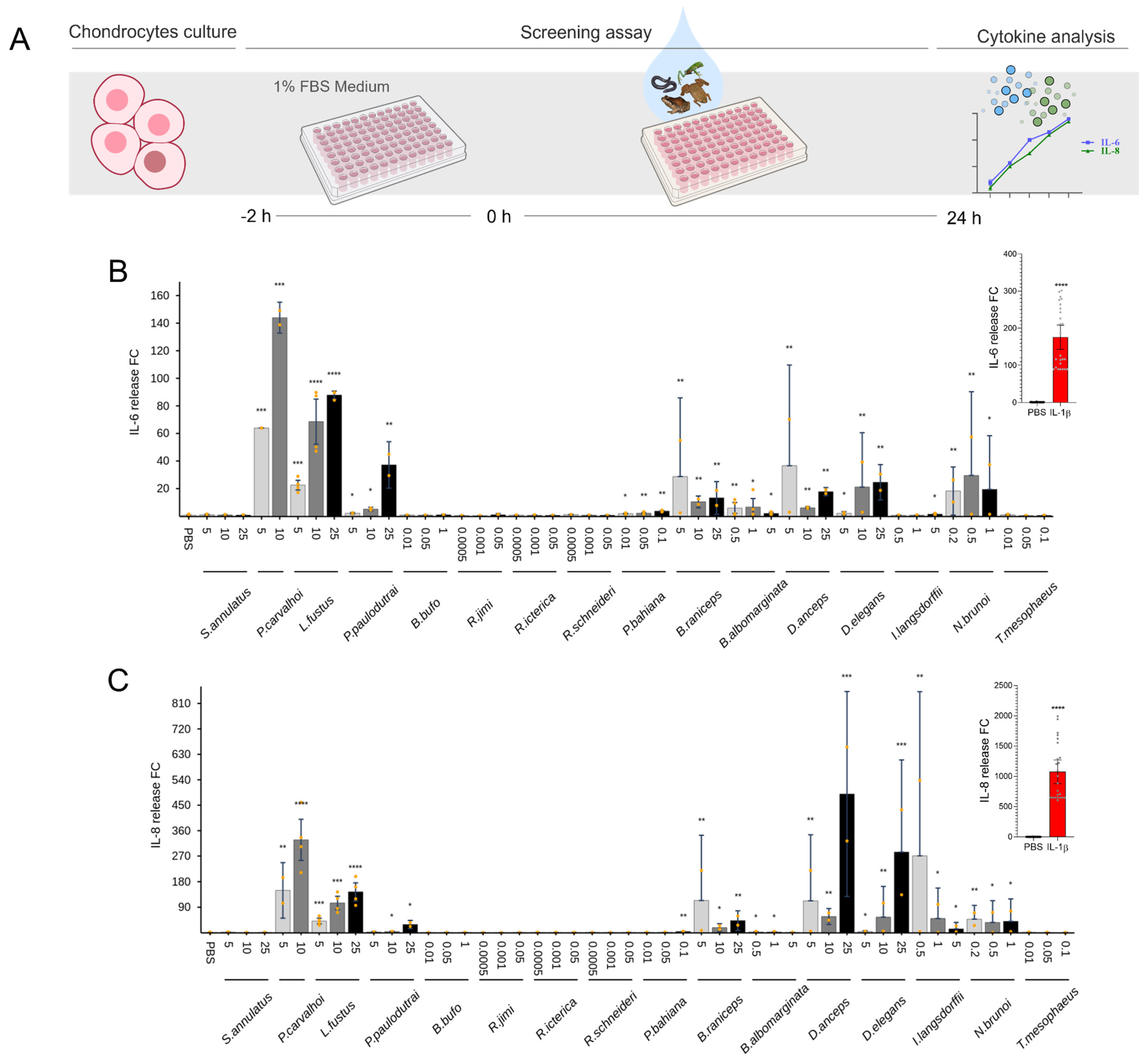
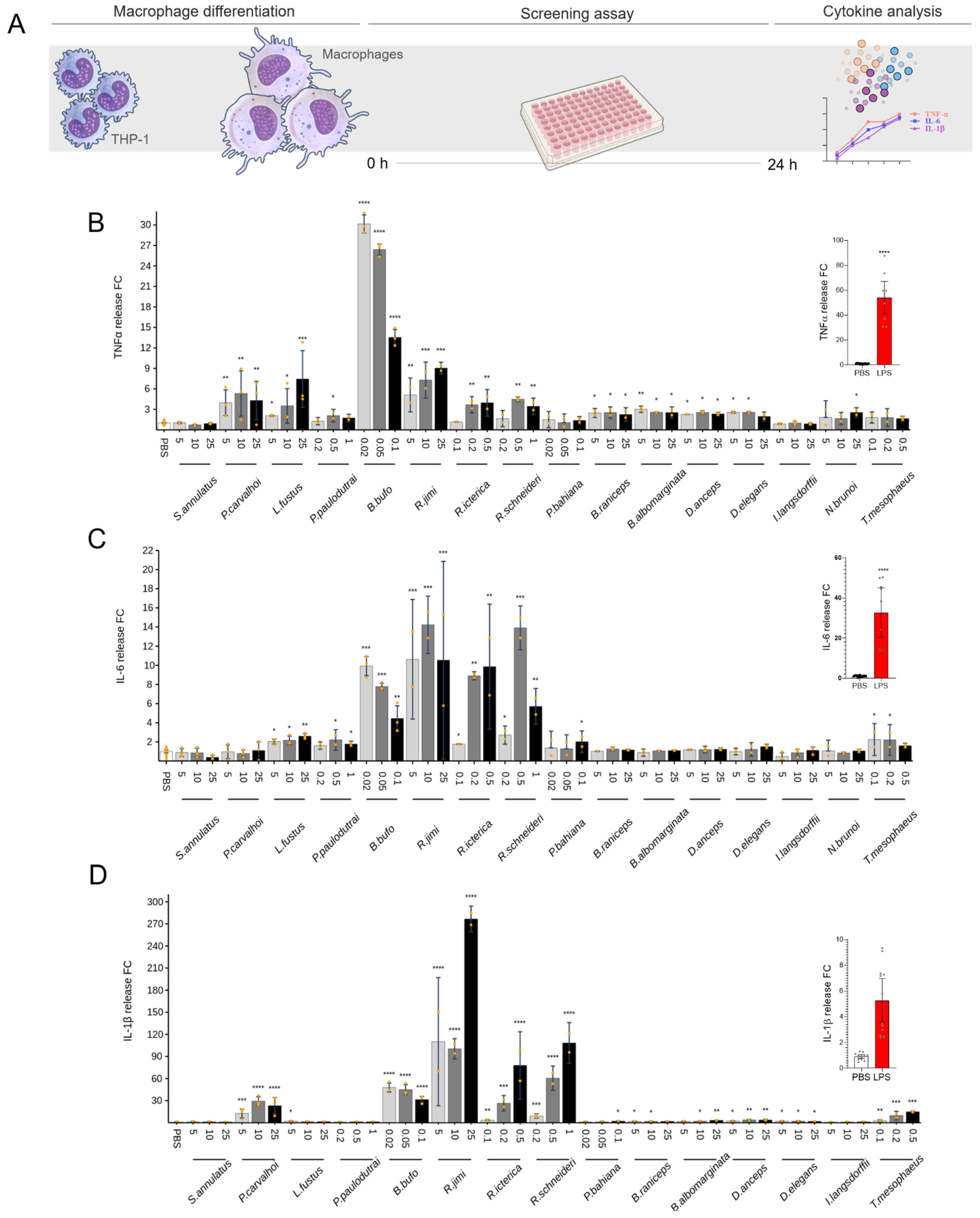
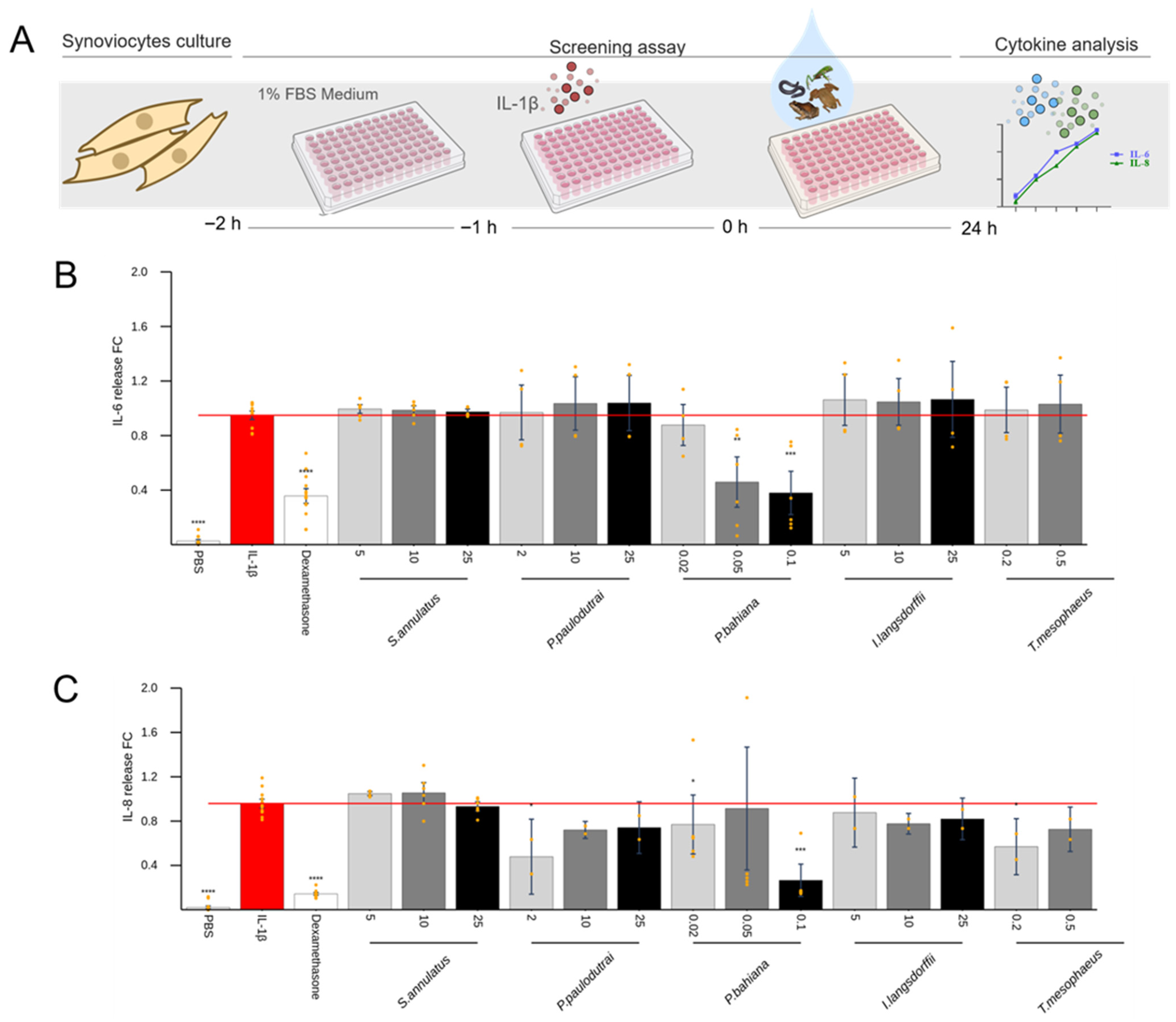
2. Results
2.1. Secretions’ Protein Profile
2.2. Cytotoxic Effect
2.3. Cytokine Release
2.4. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Skin Secretions
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Amphibian Skin Secretions
5.2. SDS-PAGE and HPLC Analyses
5.3. Cell Culture
5.3.1. Chondrocytes
5.3.2. Synoviocytes
5.3.3. THP-1 Macrophages
5.4. Screening Assays
5.5. Cell Viability
5.6. Evaluation of Cytokines Release
5.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frost, D.R. Amphibian Species of the World 6.2: An Online Reference; American Museum of Natural History: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Segalla, M.; Berneck, B.; Canedo, C.; Caramaschi, U.; Cruz, C.A.G.; Garcia, P.C.A.; Grant, T.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Lourenço, A.C.; Mangia, S.; et al. List of Brazilian Amphibians. Herpetol. Bras. 2021, 10, 121–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, R.C.; Jared, C. Cutaneous Granular Glands and Amphibian Venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1995, 111, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demori, I.; El Rashed, Z.; Corradino, V.; Catalano, A.; Rovegno, L.; Queirolo, L.; Salvidio, S.; Biggi, E.; Zanotti-Russo, M.; Canesi, L.; et al. Peptides for Skin Protection and Healing in Amphibians. Molecules 2019, 24, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huyen, T.T.; Anh, P.T.H.; Hong, N.T.A.; Duyen, N.N.; Quoc, L.P.T.; Thang, T.D. An Overview Bioactive Compounds on the Skin of Frogs (Anura). Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2023, 26, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, J.M.; Mechkarska, M.; Lukic, M.L.; Flatt, P.R. Potential Therapeutic Applications of Multifunctional Host-Defense Peptides from Frog Skin as Anti-Cancer, Anti-Viral, Immunomodulatory, and Anti-Diabetic Agents. Peptides 2014, 57, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, J.M.; Moffett, R.C.; Leprince, J.; Flatt, P.R. Identification of Components in Frog Skin Secretions with Therapeutic Potential as Antidiabetic Agents. In Peptidomics: Methods in Molecular Biology; Schrader, M., Fricker, L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1719, pp. 319–333. ISBN 978-1-4939-7536-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, P.; Ge, L.; Ma, R.; Wei, R.; McCrudden, C.M.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C.; Kwok, H.F. Identification and Pharmaceutical Evaluation of Novel Frog Skin-Derived Serine Proteinase Inhibitor Peptide–PE-BBI (Pelophylax Esculentus Bowman-Birk Inhibitor) for the Potential Treatment of Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, M.; Smith, E.; Hoy, D.; Carmona, L.; Wolfe, F.; Vos, T.; Williams, B.; Gabriel, S.; Lassere, M.; Johns, N.; et al. The Global Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.J.; Cross, M.; Haile, L.M.; Culbreth, G.T.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Hagins, H.; Kopec, J.A.; Brooks, P.M.; Woolf, A.D.; Ong, K.L.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis, 1990–2020, and Projections to 2050: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e594–e610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Advances. MedComm 2024, 5, e509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, K.D.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Kelmenson, L.B.; Kuhn, K.A.; Norris, J.M.; Holers, V.M. Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hong, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, C.; Wu, C.; Xu, G.; Bao, G.; Cui, Z. Role of Macrophage Polarization in Osteoarthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 24, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel-Pelletier, J.; Barr, A.J.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Conaghan, P.G.; Cooper, C.; Goldring, M.B.; Goldring, S.R.; Jones, G.; Teichtahl, A.J.; Pelletier, J.-P. Osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegertjes, R.; Van De Loo, F.A.J.; Blaney Davidson, E.N. A Roadmap to Target Interleukin-6 in Osteoarthritis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2681–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving Concepts of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gremese, E.; Tolusso, B.; Bruno, D.; Perniola, S.; Ferraccioli, G.; Alivernini, S. The Forgotten Key Players in Rheumatoid Arthritis: IL-8 and IL-17—Unmet Needs and Therapeutic Perspectives. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 956127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; De Andrés, M.C.; Hashimoto, K.; Itoi, E.; Oreffo, R.O.C. Epigenetic Regulation of Interleukin-8, an Inflammatory Chemokine, in Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, C. Nrf2-Mediated Anti-Inflammatory Polarization of Macrophages as Therapeutic Targets for Osteoarthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 967193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culemann, S.; Grüneboom, A.; Nicolás-Ávila, J.Á.; Weidner, D.; Lämmle, K.F.; Rothe, T.; Quintana, J.A.; Kirchner, P.; Krljanac, B.; Eberhardt, M.; et al. Locally Renewing Resident Synovial Macrophages Provide a Protective Barrier for the Joint. Nature 2019, 572, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Lee, A.-H.; Shin, H.-Y.; Song, H.-R.; Park, J.-H.; Kang, T.-B.; Lee, S.-R.; Yang, S.-H. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-α Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscitti, P.; Cipriani, P.; Carubbi, F.; Liakouli, V.; Zazzeroni, F.; Di Benedetto, P.; Berardicurti, O.; Alesse, E.; Giacomelli, R. The Role of IL-1 β in the Bone Loss During Rheumatic Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 782382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, V.; Matišić, V.; Kodvanj, I.; Bjelica, R.; Jeleč, Ž.; Hudetz, D.; Rod, E.; Čukelj, F.; Vrdoljak, T.; Vidović, D.; et al. Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Coras, R.; Torres, A.; Lane, N.E.; Guma, M. Synovial Inflammation in Osteoarthritis Progression. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narazaki, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kishimoto, T. The Role and Therapeutic Targeting of IL-6 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, X.; Eymard, F. Anti-IL-1 for the Treatment of OA: Dead or Alive? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlake, S.L.; Colebatch, A.N.; Baird, J.; Curzen, N.; Kiely, P.; Quinn, M.; Choy, E.; Ostor, A.J.K.; Edwards, C.J. Tumour Necrosis Factor Antagonists and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Literature Review. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahore, A.; Kamboj, P.; Kaleem, M.; Amir, M. Therapeutic Management of Arthritis: A Review on Structural and Target-based Approaches. Arch. Der Pharm. 2022, 355, 2200182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, M.C.; Cristiano, M.C.; Celia, C.; d’Avanzo, N.; Mancuso, A.; Paolino, D.; Wolfram, J.; Fresta, M. Injectable Drug Delivery Systems for Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19665–19690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conaghan, P.G.; Cook, A.D.; Hamilton, J.A.; Tak, P.P. Therapeutic Options for Targeting Inflammatory Osteoarthritis Pain. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C. Phylloseptin-PBa1, -PBa2, -PBa3: Three Novel Antimicrobial Peptides from the Skin Secretion of Burmeister’s Leaf Frog (Phyllomedusa burmeisteri). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 509, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo Calderon, L.D.; Silva, A.D.A.E.; Ciancaglini, P.; Stábeli, R.G. Antimicrobial Peptides from Phyllomedusa Frogs: From Biomolecular Diversity to Potential Nanotechnologic Medical Applications. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, K.; Miriane Bruni, F.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Jared, C.; Camargo, A.C.M.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Pimenta, D.C. Major Biological Effects Induced by the Skin Secretion of the Tree Frog Phyllomedusa hypochondrialis. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, C.; Mailho-Fontana, P.L.; Távora, B.C.L.F.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Jared, C. Defence Against Desiccation and Predation in Lophyohylini Casque-Headed Tree Frogs. Toxins 2025, 17, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.W. A Caution on Handling Trachycephalus venulosus (Anura: Hylidae); Toxic Effects of Skin Secretion on Human Eyes. Herpetol. Bull. 2020, 152, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, J.M.; Guilhaudis, L.; Leprince, J.; Coquet, L.; Mangoni, M.L.; Attoub, S.; Jouenne, T.; King, J.D. Peptidomic Analysis of Skin Secretions of the Mexican Burrowing Toad Rhinophrynus dorsalis (Rhinophrynidae): Insight into the Origin of Host-Defense Peptides within the Pipidae and Characterization of a Proline-Arginine-Rich Peptide. Peptides 2017, 97, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner, E.; Lemieszek, M.K.; Kwiecień, J.M.; Rajtar, G.; Rzeski, W.; Turski, W.A. Kynurenic Acid Induces Impairment of Oligodendrocyte Viability: On the Role of Glutamatergic Mechanisms. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dabrowski, W.; Kwiecien, J.M.; Rola, R.; Klapec, M.; Stanisz, G.J.; Kotlinska-Hasiec, E.; Oakden, W.; Janik, R.; Coote, M.; Frey, B.N.; et al. Prolonged Subdural Infusion of Kynurenic Acid Is Associated with Dose-Dependent Myelin Damage in the Rat Spinal Cord. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Zhou, M.; Gagliardo, R.; Walker, B.; Shaw, C. Elements of the Granular Gland Peptidome and Transcriptome Persist in Air-Dried Skin of the South American Orange-Legged Leaf Frog, Phyllomedusa hypocondrialis. Peptides 2006, 27, 2129–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiche, M.; Ladram, A.; Nicolas, P. A Consistent Nomenclature of Antimicrobial Peptides Isolated from Frogs of the Subfamily Phyllomedusinae. Peptides 2008, 29, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, K.; Konno, K.; Richardson, M.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Jared, C.; Daffre, S.; Camargo, A.C.M.; Pimenta, D.C. Isolation and Biochemical Characterization of Peptides Presenting Antimicrobial Activity from the Skin of Phyllomedusa hypochondrialis. Peptides 2006, 27, 3092–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Fang, Y.; Tan, X.; Jiang, H.; Gong, X.; Wang, X.; Hong, W.; Tu, J.; Wei, W. The Emerging Role of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes-mediated Synovitis in Osteoarthritis: An Update. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9518–9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-W.; Tang, C.-H. The Role of Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 142, 113056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, T.L.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Sasso-Cerri, E.; Egami, M.I.; Lima, C.; Rodrigues, M.T.; Jared, C. Carrying Progeny on the Back: Reproduction in the Brazilian Aquatic Frog Pipa carvalhoi. S. Am. J. Herpetol. 2011, 6, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, D.O.C.; Yamaguchi, L.F.; Jared, C.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Sciani, J.M.; Kato, M.J.; Pimenta, D.C. Pipa Carvalhoi Skin Secretion Profiling: Absence of Peptides and Identification of Kynurenic Acid as the Major Constitutive Component. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 167, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mándi, Y.; Stone, T.W.; Guillemin, G.J.; Vécsei, L.; Williams, R.O. Editorial: Multiple Implications of the Kynurenine Pathway in Inflammatory Diseases: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 860867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo, J.F.C.; Boaretto, A.G.; Santana, D.J.; Silva, D.B. Skin Secretions of Leptodactylidae (Anura) and Their Potential Applications. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 30, e20230042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha Filho, G.A.; Schwartz, C.A.; Resck, I.S.; Murta, M.M.; Lemos, S.S.; Castro, M.S.; Kyaw, C.; Pires, O.R.; Leite, J.R.S.; Bloch, C.; et al. Antimicrobial Activity of the Bufadienolides Marinobufagin and Telocinobufagin Isolated as Major Components from Skin Secretion of the Toad Bufo Rubescens. Toxicon 2005, 45, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Zehl, M.; Leitner, A.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Kopp, B. Comparison of Toad Venoms from Different Bufo Species by HPLC and LC-DAD-MS/MS. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Qi, F.; Tang, W.; Wang, F. Chemical Constituents and Bioactivities of the Skin of Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Wang, Q.; Chen, T.; Sang, D.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; He, F.; Li, Y.; He, L.; et al. Bufadienolides Originated from Toad Source and Their Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1044027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, T.; Su, W.; Jiang, C. Identification of Cinobufagin and Resibufogenin as Inhibitors of Enterovirus 71 Infection. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2014, 30, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seedi, H.R.; Yosri, N.; El-Aarag, B.; Mahmoud, S.H.; Zayed, A.; Du, M.; Saeed, A.; Musharraf, S.G.; El-Garawani, I.M.; Habib, M.R.; et al. Chemistry and the Potential Antiviral, Anticancer, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Cardiotonic Steroids Derived from Toads. Molecules 2022, 27, 6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjolette, F.A.P.; Leite, F.P.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Azzolini, A.E.C.S.; Pereira, J.C.; Pereira-Crott, L.S.; Arantes, E.C. Biological Characterization of Compounds from Rhinella schneideri Poison That Act on the Complement System. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erspamer, V.; Erspamer, G.F.; Severini, C.; Potenza, R.L.; Barra, D.; Mignogna, G.; Bianchi, A. Pharmacological Studies of ‘Sapo’ from the Frog Phyllomedusa bicolor Skin: A Drug Used by the Peruvian Matses Indians in Shamanic Hunting Practices. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, G.; Santos, R.; Arake, L.; Silva, V.; Veras, L.; Costa, V.; Costa, C.; Kuckelhaus, S.; Alexandre, J.; Feio, M.; et al. The Skin Secretion of the Amphibian Phyllomedusa nordestina: A Source of Antimicrobial and Antiprotozoal Peptides. Molecules 2013, 18, 7058–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechkarska, M.; Coquet, L.; Leprince, J.; Auguste, R.J.; Jouenne, T.; Mangoni, M.L.; Conlon, J.M. Peptidomic Analysis of the Host-Defense Peptides in Skin Secretions of the Trinidadian Leaf Frog Phyllomedusa trinitatis (Phyllomedusidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2018, 28, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantic, J.; Guilhaudis, L.; Musale, V.; Attoub, S.; Lukic, M.L.; Mechkarska, M.; Conlon, J.M. Immunomodulatory, Insulinotropic, and Cytotoxic Activities of Phylloseptins and plasticin-TR from the Trinidanian Leaf Frog Phyllomedusa trinitatis. J. Pept. Sci. 2019, 25, e3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorciapino, M.A.; Manzo, G.; Rinaldi, A.C.; Sanna, R.; Casu, M.; Pantic, J.M.; Lukic, M.L.; Conlon, J.M. Conformational Analysis of the Frog Skin Peptide, Plasticin-L1, and Its Effects on Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines by Macrophages. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 7231–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeager, J.; Zarling, A.; Rodríguez, C. Successful Multimodal Amphibian Defence in the Neotropical Frog Trachycephalus, Including Handling and Recovery Costs to Would-Be Predators. Herpetol. Notes 2019, 12, 279–280. [Google Scholar]
- Mailho-Fontana, P.L.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Coelho, G.R.; Pimenta, D.C.; Fernandes, L.P.; Kupfer, A.; Brodie, E.D.; Jared, C. Milk Provisioning in Oviparous Caecilian Amphibians. Science 2024, 383, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, D.S.; Alexandre, C.; Alvarez-Flores, M.P.; Villas-Boas, I.M.; Vigerelli, H.; Batista, I.d.F.C.; Bufalo, M.C.; Starobinas, N.; Lichtenstein, F.; Marques-Porto, R.; et al. Biodiversity-Driven Screening of Amphibian Skin Secretions for Inflammatory Modulation in Joint Diseases. Toxins 2025, 17, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090464
Oliveira DS, Alexandre C, Alvarez-Flores MP, Villas-Boas IM, Vigerelli H, Batista IdFC, Bufalo MC, Starobinas N, Lichtenstein F, Marques-Porto R, et al. Biodiversity-Driven Screening of Amphibian Skin Secretions for Inflammatory Modulation in Joint Diseases. Toxins. 2025; 17(9):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090464
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Douglas Souza, César Alexandre, Miryam Paola Alvarez-Flores, Isadora Maria Villas-Boas, Hugo Vigerelli, Isabel de Fátima Correia Batista, Michelle Cristiane Bufalo, Nancy Starobinas, Flávio Lichtenstein, Rafael Marques-Porto, and et al. 2025. "Biodiversity-Driven Screening of Amphibian Skin Secretions for Inflammatory Modulation in Joint Diseases" Toxins 17, no. 9: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090464
APA StyleOliveira, D. S., Alexandre, C., Alvarez-Flores, M. P., Villas-Boas, I. M., Vigerelli, H., Batista, I. d. F. C., Bufalo, M. C., Starobinas, N., Lichtenstein, F., Marques-Porto, R., Buri, M., Portas-Lopes, V., Mailho-Fontana, P. L., Antoniazzi, M. M., Tambourgi, D. V., Chudzinski-Tavassi, A. M., Teixeira, C., Jared, C., & Ibañez, O. M. (2025). Biodiversity-Driven Screening of Amphibian Skin Secretions for Inflammatory Modulation in Joint Diseases. Toxins, 17(9), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090464




