Sea Anemone-Derived Toxin Avd3i Inhibited Sodium Channel Nav1.4
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Structural Analysis of Avd3i
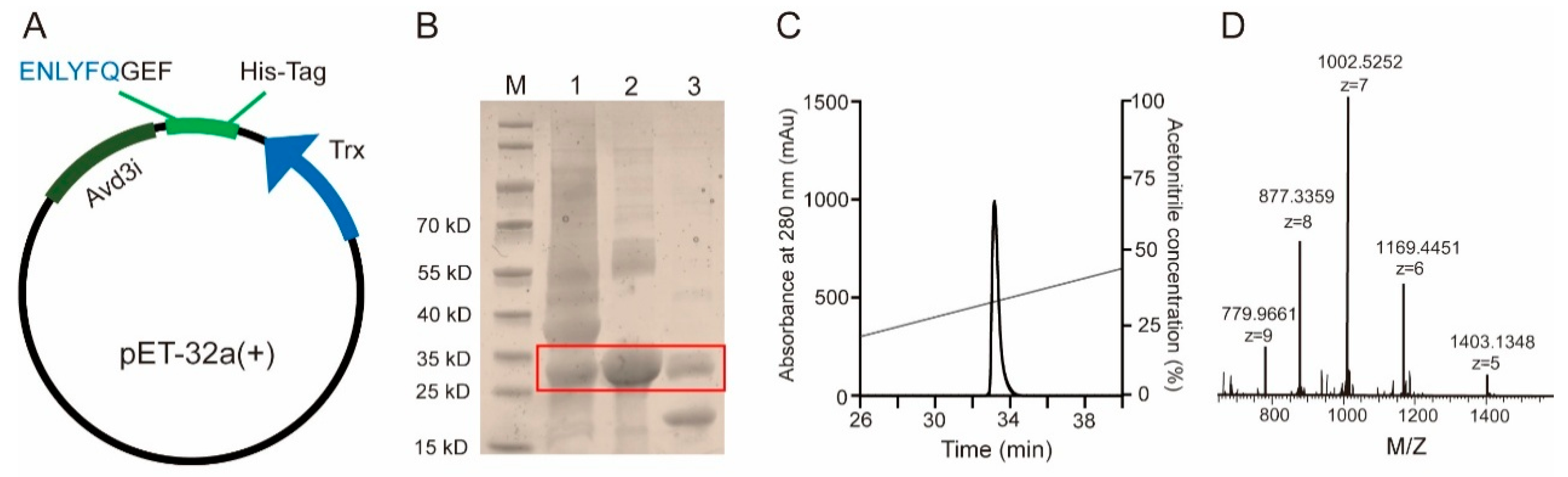
2.2. Prokaryotic Expression and Purification of Avd3i
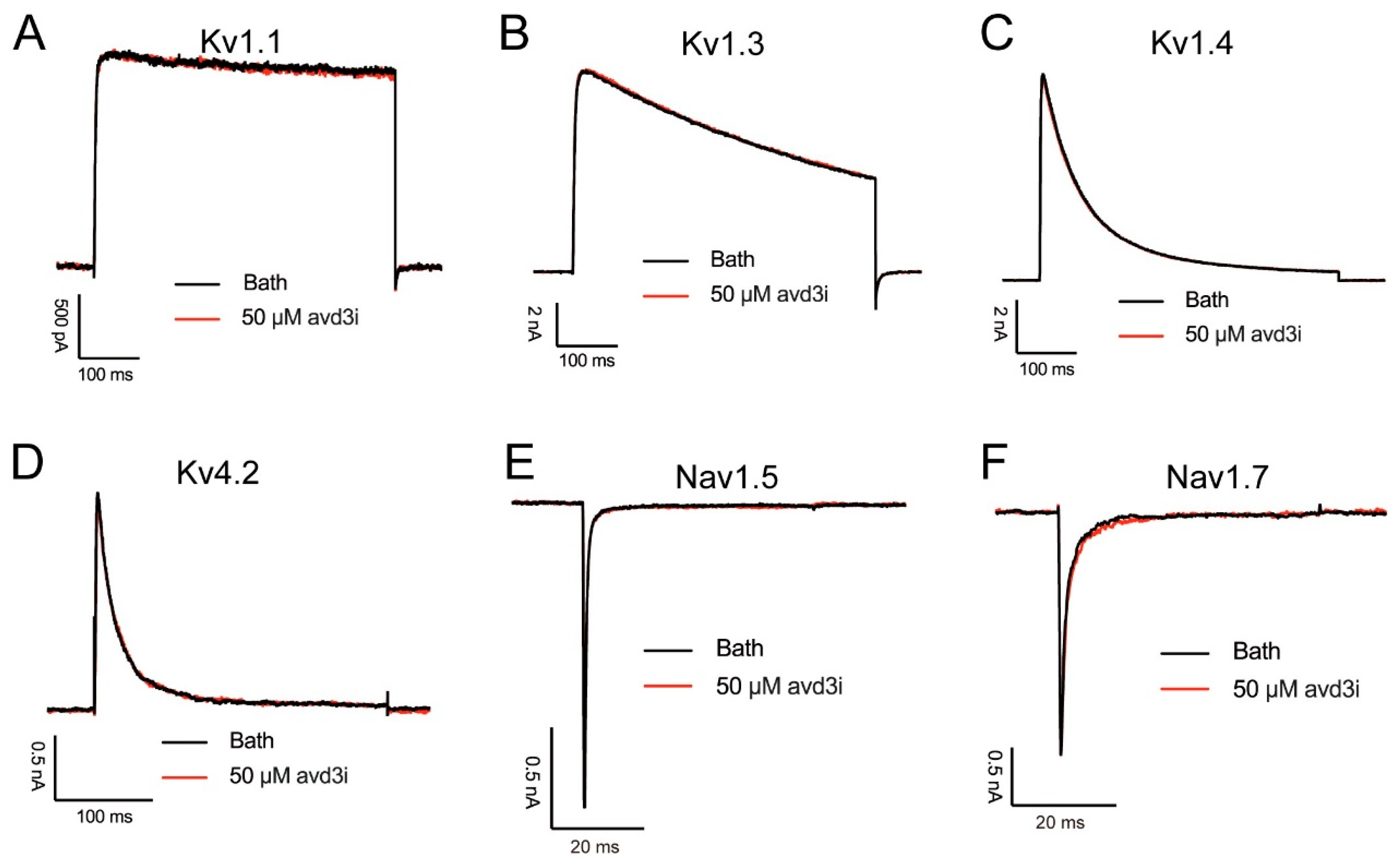
2.3. Peptide Avd3i Had No Effect on Some Ion Channels
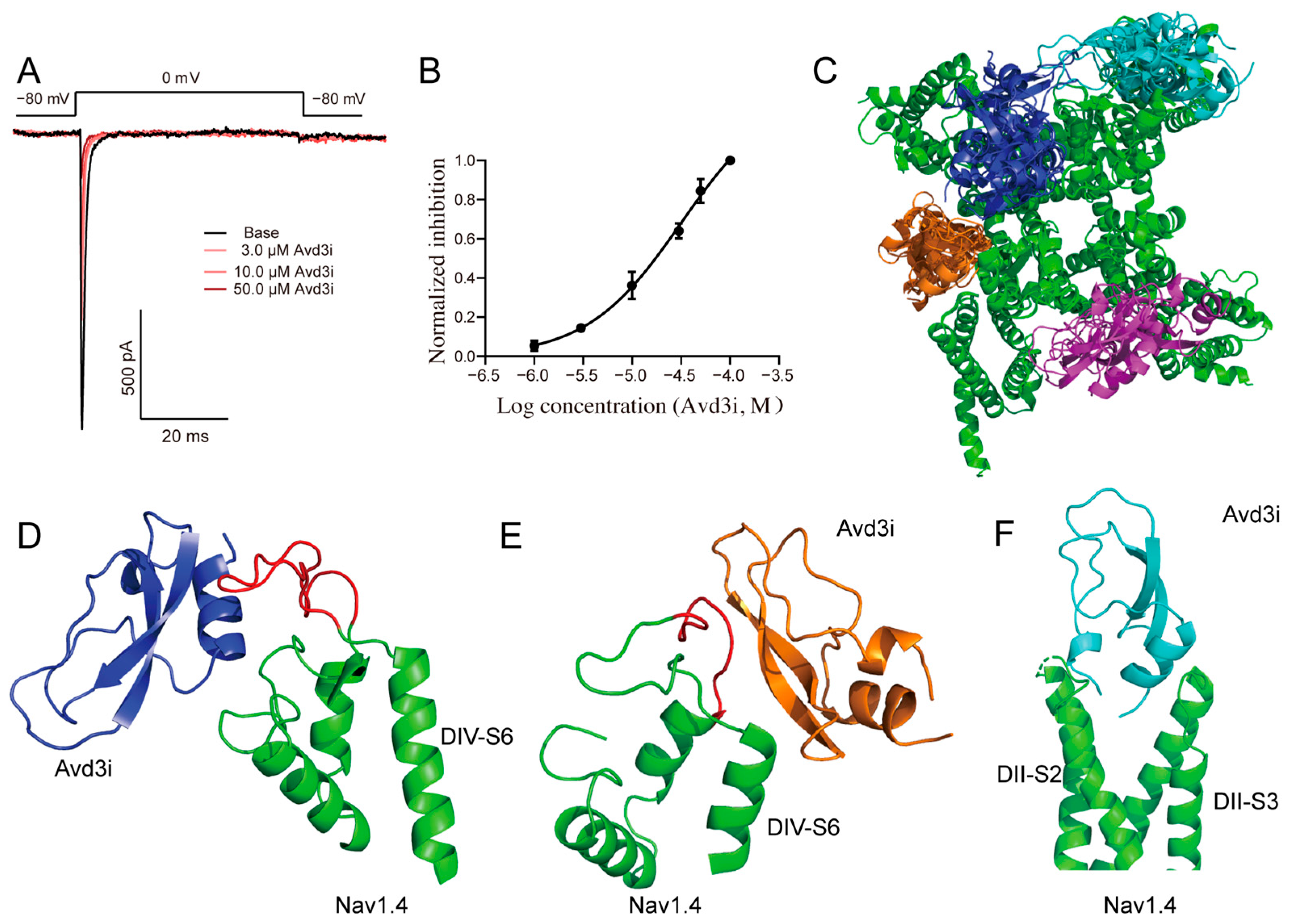
2.4. Peptide Avd3i Inhibited Nav1.4 Channel
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Experimental Procedures and Materials
5.1. Sequence Alignment and Homologous Modeling
5.2. Recombinant Expression and Purification of Avd3i
5.3. Electrophysiological Recording
5.4. Molecular Docking
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhao, W.; Pan, L.; Chen, Y. Functional effects of drugs and toxins interacting with NaV1.4. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1378315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groome, J.R.; Lehmann-Horn, F.; Fan, C.; Wolf, M.; Winston, V.; Merlini, L.; Jurkat-Rott, K. NaV1.4 mutations cause hypokalaemic periodic paralysis by disrupting IIIS4 movement during recovery. Brain 2014, 137, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sukharev, S.I.; Blount, P.; Martinac, B.; Kung, C. Mechanosensitive channels of Escherichia coli: The MscL gene, protein, and activities. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1997, 59, 633–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Pan, X.; Yan, N. Structural biology and molecular pharmacology of voltage-gated ion channels. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 904–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monastyrnaya, M.M.; Kalina, R.S.; Kozlovskaya, E.P. The Sea Anemone Neurotoxins Modulating Sodium Channels: An Insight at Structure and Functional Activity after Four Decades of Investigation. Toxins 2023, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, H.; Wu, K.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Lei, J.; et al. Structure of the human voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.4 in complex with β1. Science 2018, 362, eaau2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loussouarn, G.; Sternberg, D.; Nicole, S.; Marionneau, C.; Le Bouffant, F.; Toumaniantz, G.; Barc, J.; Malak, O.A.; Fressart, V.; Péréon, Y.; et al. Physiological and Pathophysiological Insights of Nav1.4 and Nav1.5 Comparison. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 6, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bellis, M.; Boccanegra, B.; Cerchiara, A.G.; Imbrici, P.; De Luca, A. Blockers of Skeletal Muscle Na(v)1.4 Channels: From Therapy of Myotonic Syndrome to Molecular Determinants of Pharmacological Action and Back. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madio, B.; King, G.F.; Undheim, E.A.B. Sea Anemone Toxins: A Structural Overview. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazão, B.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Sea anemone (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Actiniaria) toxins: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1812–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashevsky, D.; Deuis, J.R.; Vetter, I.; Huynh, T.; Hodgson, W.C.; Tan, C.H.; Nouwens, A.; Fry, B.G. Novel Neurotoxic Activity in Calliophis intestinalis Venom. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, O.; Harvey, A.L. Discovery and characterization of cnidarian peptide toxins that affect neuronal potassium ion channels. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peigneur, S.; Billen, B.; Derua, R.; Waelkens, E.; Debaveye, S.; Béress, L.; Tytgat, J. A bifunctional sea anemone peptide with Kunitz type protease and potassium channel inhibiting properties. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flight, S.M.; Johnson, L.A.; Du, Q.S.; Warner, R.L.; Trabi, M.; Gaffney, P.J.; Lavin, M.F.; de Jersey, J.; Masci, P.P. Textilinin-1, an alternative anti-bleeding agent to aprotinin: Importance of plasmin inhibition in controlling blood loss. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millers, E.K.; Trabi, M.; Masci, P.P.; Lavin, M.F.; de Jersey, J.; Guddat, L.W. Crystal structure of textilinin-1, a Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor from the venom of the Australian common brown snake (Pseudonaja textilis). FEBS J. 2009, 276, 3163–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, R.; Peigneur, S.; Pons, T.; Alvarez, C.; González, L.; Chávez, M.A.; Tytgat, J. The Kunitz-Type Protein ShPI-1 Inhibits Serine Proteases and Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels. Toxins 2016, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitz, H.; Bruhn, T.; Guillemare, E.; Moinier, D.; Lancelin, J.M.; Béress, L.; Lazdunski, M. Kalicludines and kaliseptine. Two different classes of sea anemone toxins for voltage sensitive K+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25121–25126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, L.; Bonanno, S.; Altamura, C.; Desaphy, J.F. Ion Channel Gene Mutations Causing Skeletal Muscle Disorders: Pathomechanisms and Opportunities for Therapy. Cells 2021, 10, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, B. Muscle channelopathies and related diseases. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 113, pp. 1433–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokunai, Y.; Dalle, C.; Vicart, S.; Sternberg, D.; Pouliot, V.; Bendahhou, S.; Fournier, E.; Chahine, M.; Fontaine, B.; Nicole, S. A204E mutation in Na(v)1.4 DIS3 exerts gain- and loss-of-function effects that lead to periodic paralysis combining hyper- with hypo-kalaemic signs. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.X.; Yu, M.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. Sequence CLCN1 and SCN4A genes in patients with nondystrophic myotonia in Chinese people. Medicine 2022, 101, e29591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereb, N.; Montagnese, F.; Gläser, D.; Schoser, B. Non-dystrophic myotonias: Clinical and mutation spectrum of 70 German patients. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavel-Greant, D.; Lehmann-Horn, F.; Jurkat-Rott, K. The impact of permanent muscle weakness on quality of life in periodic paralysis: A survey of 66 patients. Acta Myol. 2012, 31, 126–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kroncke, B.M.; Glazer, A.M.; Smith, D.K.; Blume, J.D.; Roden, D.M. SCN5A (Na(V)1.5) Variant Functional Perturbation and Clinical Presentation: Variants of a Certain Significance. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2018, 11, e002095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djillani, A.; Mazella, J.; Heurteaux, C.; Borsotto, M. Role of TREK-1 in Health and Disease, Focus on the Central Nervous System. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djillani, A.; Pietri, M.; Mazella, J.; Heurteaux, C.; Borsotto, M. Fighting against depression with TREK-1 blockers: Past and future. A focus on spadin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 194, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flucher, B.E. Skeletal muscle Ca(V)1.1 channelopathies. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2020, 472, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geron, M.; Hazan, A.; Priel, A. Animal Toxins Providing Insights into TRPV1 Activation Mechanism. Toxins 2017, 9, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.C.; Sun, F.D.; Zhang, L.; Huang, B.; An, H.L.; Rong, M.Q.; Du, C.W. General mechanism of spider toxin family I acting on sodium channel Nav1.7. Zool. Res. 2022, 43, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niklas, B.; Jankowska, M.; Gordon, D.; Béress, L.; Stankiewicz, M.; Nowak, W. Interactions of Sea Anemone Toxins with Insect Sodium Channel-Insights from Electrophysiology and Molecular Docking Studies. Molecules 2021, 26, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, T.; Rohou, A.; Arthur, C.P.; Tzakoniati, F.; Wong, E.; Estevez, A.; Kugel, C.; Franke, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Structural Basis of Nav1.7 Inhibition by a Gating-Modifier Spider Toxin. Cell 2019, 176, 702–715.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, Z.; He, Z.; Liu, G.; Hou, W.; Deng, M.; Liu, C.; Rong, M. Spider-derived peptide LCTx-F2 suppresses ASIC channels by occupying the acidic pocket. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 108286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Chen, L.; Liu, G.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Rong, M.; Mo, G.; Liu, C. Tick-Derived Peptide Blocks Potassium Channel TREK-1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetterlin, K.J.; Bugiardini, E.; Kaski, J.P.; Morrow, J.M.; Matthews, E.; Hanna, M.G.; Fialho, D. Long-term Safety and Efficacy of Mexiletine for Patients With Skeletal Muscle Channelopathies. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1531–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statland, J.M.; Bundy, B.N.; Wang, Y.; Rayan, D.R.; Trivedi, J.R.; Sansone, V.A.; Salajegheh, M.K.; Venance, S.L.; Ciafaloni, E.; Matthews, E.; et al. Mexiletine for symptoms and signs of myotonia in nondystrophic myotonia: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2012, 308, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denaro, C.P.; Benowitz, N.L. Poisoning Due to Class 1B Antiarrhythmic Drugs. Med. Toxicol. Advers. Drug Exp. 1989, 4, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desaphy, J.F.; De Luca, A.; Didonna, M.P.; George, A.L., Jr.; Camerino Conte, D. Different flecainide sensitivity of hNav1.4 channels and myotonic mutants explained by state-dependent block. J. Physiol. 2004, 554 Pt 2, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echt, D.S.; Ruskin, J.N. Use of Flecainide for the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2020, 125, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droctové, L.; Ciolek, J.; Mendre, C.; Chorfa, A.; Huerta, P.; Carvalho, C.; Gouin, C.; Lancien, M.; Stanajic-Petrovic, G.; Braco, L.; et al. A new Kunitz-type snake toxin family associated with an original mode of interaction with the vasopressin 2 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3470–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcio, R.; Di Matteo, F.; Capolupo, I.; Ciaglia, T.; Musella, S.; Di Chio, C.; Stagno, C.; Campiglia, P.; Bertamino, A.; Ostacolo, C. Voltage-Gated K+ Channel Modulation by Marine Toxins: Pharmacological Innovations and Therapeutic Opportunities. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Xu, J.; Bao, W.; Xu, F.; Qi, J.; Tan, Z.; Li, C.; Luo, X.; You, X.; Rong, M.; et al. Pore blocking mechanisms of centipede toxin SsTx-4 on the inwardly rectifying potassium channels. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 988, 177213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, P.; Kong, X.; Hu, H.; Liang, S.; Tang, C.; Liu, Z. Molecular mechanisms of centipede toxin SsTx-4 inhibition of inwardly rectifying potassium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, H.; Peng, S.; Si, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, M.; Xie, Q.; He, X.; et al. Inherent fast inactivation particle of Nav channels as a new binding site for a neurotoxin. EMBO J. 2025, 44, 3180–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.J.; Berecki, G. Mechanisms of conotoxin inhibition of N-type (Cav2.2) calcium channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.S.; Fuentes-Silva, D.; King, G.F. Development of a rational nomenclature for naming peptide and protein toxins from sea anemones. Toxicon 2012, 60, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Li, S.; Huang, B.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Peng, Y.; Du, C.; Rong, M. Molecular mechanism by which spider-driving peptide potentiates coagulation factors. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; He, Q.; Liao, Q.; Du, C. Sea Anemone-Derived Toxin Avd3i Inhibited Sodium Channel Nav1.4. Toxins 2025, 17, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090461
Gao J, Liu G, Liu Y, Zhang D, He Q, Liao Q, Du C. Sea Anemone-Derived Toxin Avd3i Inhibited Sodium Channel Nav1.4. Toxins. 2025; 17(9):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090461
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jiaxin, Guohao Liu, Yan Liu, Dezhao Zhang, Qinyi He, Qiong Liao, and Canwei Du. 2025. "Sea Anemone-Derived Toxin Avd3i Inhibited Sodium Channel Nav1.4" Toxins 17, no. 9: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090461
APA StyleGao, J., Liu, G., Liu, Y., Zhang, D., He, Q., Liao, Q., & Du, C. (2025). Sea Anemone-Derived Toxin Avd3i Inhibited Sodium Channel Nav1.4. Toxins, 17(9), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090461




