Research Progress on the Detection Methods of Botulinum Neurotoxin
Abstract
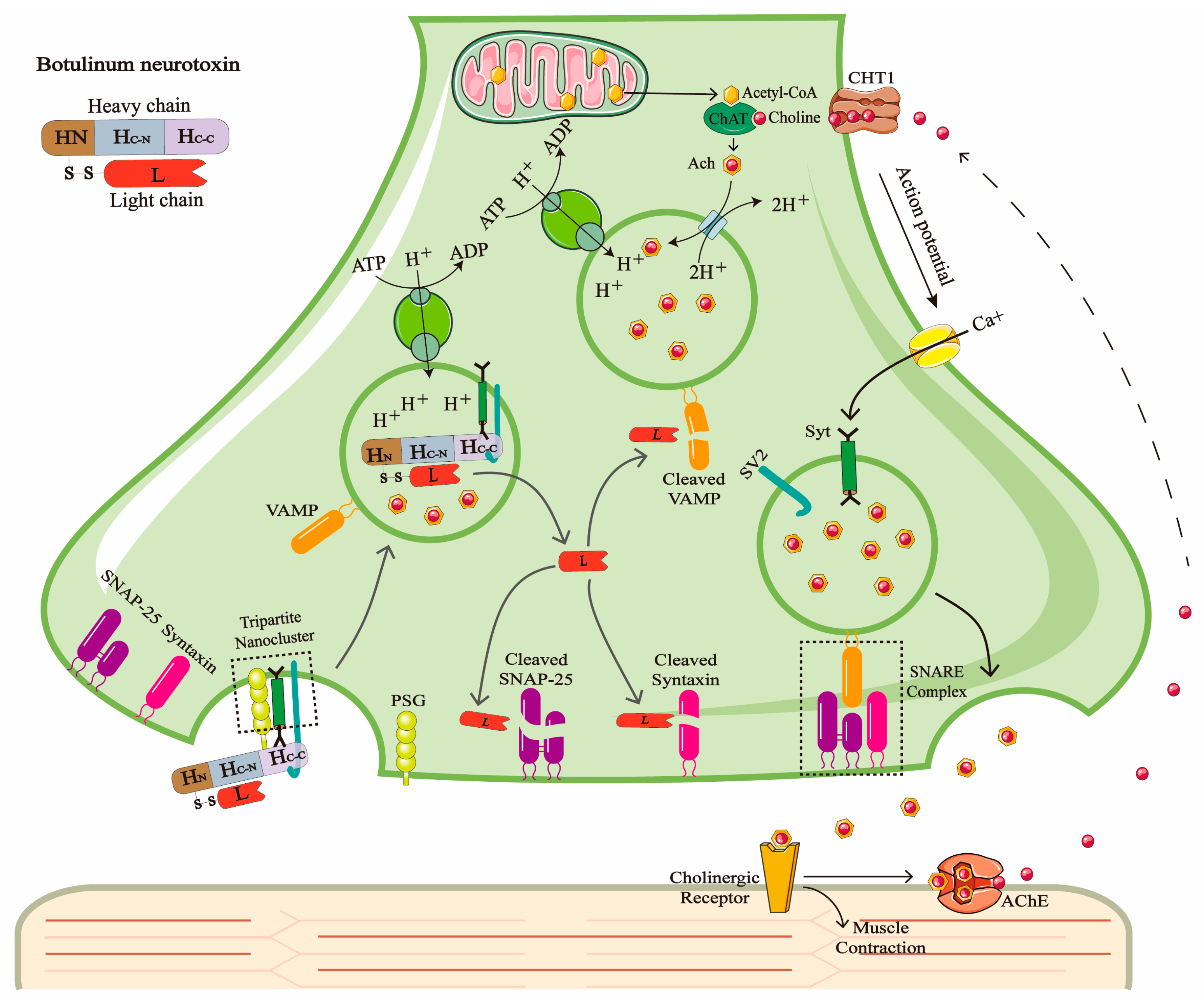
1. Introduction
2. Mouse Bioassay
3. Cell-Based Assay
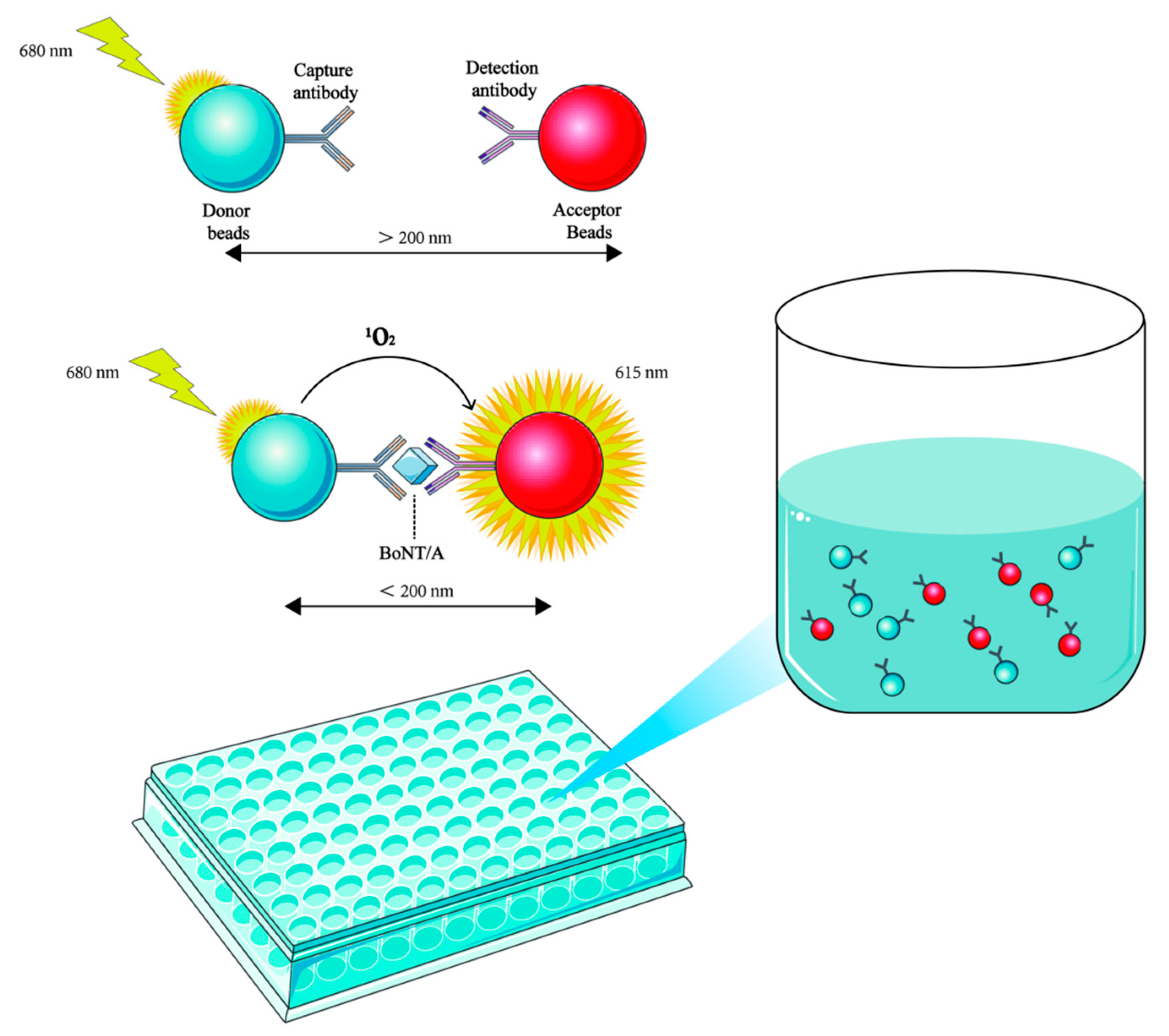
4. Immunological Methods
5. Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry
6. Endopeptidase–Mass Spectrometry
7. Biosensors
8. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, M.; Masuyer, G.; Stenmark, P. Botulinum and Tetanus Neurotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 811–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, R.J.; Thomas, C.A.; Halliwell, J.; Gwenin, C.D. Rapid Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxins-A Review. Toxins 2019, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montal, M. Botulinum neurotoxin: A marvel of protein design. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 591–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensuu, M.; Syed, P.; Saber, S.H.; Lanoue, V.; Wallis, T.P.; Rae, J.; Blum, A.; Gormal, R.S.; Small, C.; Sanders, S.; et al. Presynaptic targeting of botulinum neurotoxin type A requires a tripartite PSG-Syt1-SV2 plasma membrane nanocluster for synaptic vesicle entry. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e112095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Richards, D.A.; Goodnough, M.C.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Chapman, E.R. Synaptotagmins I and II mediate entry of botulinum neurotoxin B into cells. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Yeh, F.; Tepp, W.H.; Dean, C.; Johnson, E.A.; Janz, R.; Chapman, E.R. SV2 is the protein receptor for botulinum neurotoxin A. Science 2006, 312, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovsepian, S.V.; O’Leary, V.B.; Ayvazyan, N.M.; Al-Sabi, A.; Ntziachristos, V.; Dolly, J.O. Neurobiology and therapeutic applications of neurotoxins targeting transmitter release. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 193, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Fan, F.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, S.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Q.W.; Dong, M.Q.; Yao, J.; et al. Mechanistic insights into the SNARE complex disassembly. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau8164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centurioni, D.A.; Egan, C.T.; Perry, M.J. Current Developments in Diagnostic Assays for Laboratory Confirmation and Investigation of Botulism. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, e0013920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Jiang, D.; Li, R.; Sun, L. Food-borne botulism from homemade sauce leading to cardiac arrest: A family case series with literature review. Toxicon 2023, 235, 107326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.A.; Tchao, C.; Prystajecky, N.; Weedmark, K.; Tcholakov, Y.; Lefebvre, M.; Austin, J.W. Foodborne Botulism, Canada, 2006–2021(1). Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonati, D.; Schicchi, A.; Crevani, M.; Buscaglia, E.; Scaravaggi, G.; Maida, F.; Cirronis, M.; Petrolini, V.M.; Locatelli, C.A. Foodborne Botulism: Clinical Diagnosis and Medical Treatment. Toxins 2020, 12, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, N.T.; Klein, G. Microbiology and foodborne pathogens in honey. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1852–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabritz, H.A.; Chung, C.H.; Read, J.S.; Khouri, J.M. Global Occurrence of Infant Botulism: 2007–2021. Pediatrics 2025, 155, e2024068791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, B.; Danino, D.; Levinsky, Y.; Levy, I.; Straussberg, R.; Dabaja-Younis, H.; Guri, A.; Almagor, Y.; Tasher, D.; Elad, D.; et al. Infant Botulism, Israel, 2007-2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxins: Genetic, structural and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myllykoski, J.; Lindström, M.; Bekema, E.; Pölönen, I.; Korkeala, H. Fur animal botulism hazard due to feed. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrera-Figallo, M.A.; Ruiz-de-León-Hernández, G.; Torres-Lagares, D.; Castro-Araya, A.; Torres-Ferrerosa, O.; Hernández-Pacheco, E.; Gutierrez-Perez, J.L. Use of Botulinum Toxin in Orofacial Clinical Practice. Toxins 2020, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, E.; Diotallevi, F.; Radi, G.; Campanati, A.; Offidani, A. Therapeutic Use of Botulinum Neurotoxins in Dermatology: Systematic Review. Toxins 2021, 13, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Lansiaux, E.; Yucel, U.; Huenermund, S.; Goeschl, S.; Schlagenhauf, P. Outbreaks of iatrogenic botulism in Europe: Combating off-label medical use of Botulinum Neurotoxin (BoNT) in bariatric procedures. New Microbes New Infect. 2023, 53, 101152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertow, D.S.; Tan, E.T.; Maslanka, S.E.; Schulte, J.; Bresnitz, E.A.; Weisman, R.S.; Bernstein, J.; Marcus, S.M.; Kumar, S.; Malecki, J.; et al. Botulism in 4 adults following cosmetic injections with an unlicensed, highly concentrated botulinum preparation. JAMA 2006, 296, 2476–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerttler, T.; Dorner, M.B.; van der Linden, C.; Kienitz, R.; Petrik, S.; Blechinger, S.; Spickschen, J.; Betz, I.R.; Hinrichs, C.; Steindl, D.; et al. Iatrogenic botulism after intragastric botulinum neurotoxin injections—A major outbreak. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2024, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Tian, T.; Guo, W.; Liu, C.; Liang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Fu, P. Epidemiological Analysis of Foodborne Botulism Outbreaks—China, 2004-2020. China CDC Wkly. 2022, 4, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, M.; Guerrero-Vadillo, M.; Valdezate, S.; Zamora, M.J.; Leon-Gomez, I.; Flores-Cuéllar, Á.; Carrasco, G.; Díaz-García, O.; Varela, C. Botulism in Spain: Epidemiology and Outcomes of Antitoxin Treatment, 1997-2019. Toxins 2022, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellett, S.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A. Critical Analysis of Neuronal Cell and the Mouse Bioassay for Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxins. Toxins 2019, 11, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.K.; Sobel, J.; Chatham-Stephens, K.; Luquez, C. Clinical Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Botulism, 2021. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2021, 70, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrin, G.; Cai, S.; Singh, B.R. Critical analysis in the advancement of cell-based assays for botulinum neurotoxin. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 49, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliskan, C.; Simsek, D.; Leese, C.; Doran, C.; Seward, E.; Peden, A.A.; Davletov, B. A sensitive cell-based assay for testing potency of botulinum neurotoxin type A. Altex 2024, 41, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, N.; Rajagopal, S.; Stickings, P.; Sesardic, D. SiMa Cells for a Serotype Specific and Sensitive Cell-Based Neutralization Test for Botulinum Toxin A and E. Toxins 2017, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgeman, A.; Diamant, E.; Levin, L.; David, A.B.; Epstein, E.; Girshengorn, M.; Mazor, O.; Rosenfeld, R.; Zichel, R. An in vitro cell-based potency assay for pharmaceutical type A botulinum antitoxins. Vaccine 2017, 35, 7213–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Datta, S.; Sachdeva, A.; Maslanka, S.; Dykes, J.; Skinner, G.; Burr, D.; Whiting, R.C.; Sharma, S.K. Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit for the detection of botulinum neurotoxins A, B, E, and F in selected food matrices. Health Secur. 2015, 13, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenko, K.L.; Zhang, Y.; Kostenko, Y.; Fan, Y.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Lou, J.; Marks, J.D.; Varnum, S.M. Development of an ELISA microarray assay for the sensitive and simultaneous detection of ten biodefense toxins. Analyst 2014, 139, 5093–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M. Immunosensors for Assay of Toxic Biological Warfare Agents. Biosensors 2023, 13, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, R.; Ding, D.; Ma, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhi, D.; et al. EGFP/RFP-based FRET sensors for botulinum neurotoxin A biological activity detection and methodological validation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1337, 343546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.P.; Chuang, H.S. Rapid and Sensitive Nano-Immunosensors for Botulinum. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Hashemi, P.; Bagheri, H.; Salimian, J.; Ahmadi, A.; Madrakian, T. Impedimetric immunosensor for the label-free and direct detection of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A using Au nanoparticles/graphene-chitosan composite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesardic, D.; Leung, T.; Gaines Das, R. Role for standards in assays of botulinum toxins: International collaborative study of three preparations of botulinum type A toxin. Biologicals 2003, 31, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.; Gericke, C.; Alvarez, L.R. Botulinum toxin testing on animals is still a Europe-wide issue. Altex 2019, 36, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, K.; Das, R.E.; Ekong, T.A.; Sesardic, D. Therapeutic botulinum type A toxin: Factors affecting potency. Toxicon 1996, 34, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasetti-Escargueil, C.; Jones, R.G.; Liu, Y.; Sesardic, D. Measurement of botulinum types A, B and E neurotoxicity using the phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm: Improved precision with in-bred mice. Toxicon 2009, 53, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.G.; Alsop, T.A.; Hull, R.; Tierney, R.; Rigsby, P.; Holley, J.; Sesardic, D. Botulinum type A toxin neutralisation by specific IgG and its fragments: A comparison of mouse systemic toxicity and local flaccid paralysis assays. Toxicon 2006, 48, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilder-Kofie, T.D.; Lúquez, C.; Adler, M.; Dykes, J.K.; Coleman, J.D.; Maslanka, S.E. An alternative in vivo method to refine the mouse bioassay for botulinum toxin detection. Comp. Med. 2011, 61, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Broide, R.S.; Rubino, J.; Nicholson, G.S.; Ardila, M.C.; Brown, M.S.; Aoki, K.R.; Francis, J. The rat Digit Abduction Score (DAS) assay: A physiological model for assessing botulinum neurotoxin-induced skeletal muscle paralysis. Toxicon 2013, 71, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, S.P.; Grandgirard, D.; Heidemann, M.; Tscherter, A.; Avondet, M.A.; Leib, S.L. Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Neurons Grown on Multi-Electrode Arrays as a Novel In vitro Bioassay for the Detection of Clostridium botulinum Neurotoxins. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamotte, J.D.; Roqueviere, S.; Gautier, H.; Raban, E.; Bouré, C.; Fonfria, E.; Krupp, J.; Nicoleau, C. hiPSC-Derived Neurons Provide a Robust and Physiologically Relevant In Vitro Platform to Test Botulinum Neurotoxins. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 617867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, E.; Gong, Y.; Al Saleem, F.H.; Ancharski, D.M.; Joshi, S.G.; Simpson, L.L. An initial assessment of the systemic pharmacokinetics of botulinum toxin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenke, M.; Schjeide, B.M.; Püschel, G.P.; Seeger, B. Analysis of Motor Neurons Differentiated from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for the Use in Cell-Based Botulinum Neurotoxin Activity Assays. Toxins 2020, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonfria, E.; Marks, E.; Foulkes, L.M.; Schofield, R.; Higazi, D.; Coward, S.; Kippen, A. Replacement of the Mouse LD(50) Assay for Determination of the Potency of AbobotulinumtoxinA with a Cell-Based Method in Both Powder and Liquid Formulations. Toxins 2023, 15, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, A.; Doran, C.; Hart, R.; Binz, T.; Stickings, P.; Sesardic, D.; Peden, A.A.; Davletov, B. A Cell Line for Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type B. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamant, E.; Torgeman, A.; Epstein, E.; Mechaly, A.; David, A.B.; Levin, L.; Schwartz, A.; Dor, E.; Girshengorn, M.; Barnea, A.; et al. A cell-based alternative to the mouse potency assay for pharmaceutical type E botulinum antitoxins. Altex 2022, 39, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkiss, J.R.; Friis, L.M.; Doward, S.; Quinn, C.P. Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins act with a wide range of potencies on SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Neurotoxicology 2001, 22, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasetti-Escargueil, C.; Popoff, M.R. Recent Developments in Botulinum Neurotoxins Detection. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Salas, E.; Wang, J.; Molina, Y.; Nelson, J.B.; Jacky, B.P.; Aoki, K.R. Botulinum neurotoxin serotype A specific cell-based potency assay to replace the mouse bioassay. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, A.M.; Ruthel, G.; Torres-Melendez, E.; Kenny, T.A.; Panchal, R.G.; Bavari, S. Primary cultures of embryonic chicken neurons for sensitive cell-based assay of botulinum neurotoxin: Implications for therapeutic discovery. J. Biomol. Screen. 2007, 12, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenke, M.; Prause, H.C.; Bergforth, W.; Przykopanski, A.; Rummel, A.; Klawonn, F.; Seeger, B. Human-Relevant Sensitivity of iPSC-Derived Human Motor Neurons to BoNT/A1 and B1. Toxins 2021, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisemann, J.; Stern, D.; Mahrhold, S.; Dorner, B.G.; Rummel, A. Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A Recognizes Its Protein Receptor SV2 by a Different Mechanism than Botulinum Neurotoxin B Synaptotagmin. Toxins 2016, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, B.J.; Atmaramani, R.; Pancrazio, J.J. Spontaneous and Evoked Activity from Murine Ventral Horn Cultures on Microelectrode Arrays. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, L.; Yu, F.; Roqueviere, S.; Duchesne de Lamotte, J.; Krupp, J.; Dong, M.; Nicoleau, C. Split luciferase-based assay to detect botulinum neurotoxins using hiPSC-derived motor neurons. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, L.; Wang, S.; Ma, X. A Validation of the Equivalence of the Cell-Based Potency Assay Method with a Mouse LD50 Bioassay for the Potency Testing of OnabotulinumtoxinA. Toxins 2024, 16, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfulian, M.; Hatheway, C.L.; Yolken, R.H.; Bartlett, J.G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Clostridium botulinum type A and type B toxins in stool samples of infants with botulism. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1984, 20, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressler, D.; Gessler, F.; Tacik, P.; Bigalke, H. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of botulinum toxin-antibodies. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1322–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doellgast, G.J.; Triscott, M.X.; Beard, G.A.; Bottoms, J.D.; Cheng, T.; Roh, B.H.; Roman, M.G.; Hall, P.A.; Brown, J.E. Sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins A, B, and E using signal amplification via enzyme-linked coagulation assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, J.W.; Gu, J.; Jaroszewski, L.; Schwarzenbacher, R.; Hanson, M.A.; Lebeda, F.J.; Stevens, R.C. The structure of the neurotoxin-associated protein HA33/A from Clostridium botulinum suggests a reoccurring beta-trefoil fold in the progenitor toxin complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 346, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Razai, A.; Geren, I.N.; Lou, J.; Conrad, F.; Wen, W.H.; Farr-Jones, S.; Smith, T.J.; Brown, J.L.; Skerry, J.C.; et al. A Three Monoclonal Antibody Combination Potently Neutralizes Multiple Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype E Subtypes. Toxins 2018, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benecke, R. Clinical relevance of botulinum toxin immunogenicity. Biodrugs 2012, 26, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.Y.; Schaff, U.Y.; Piccini, M.E.; Stanker, L.H.; Cheng, L.W.; Ravichandran, E.; Singh, B.R.; Sommer, G.J.; Singh, A.K. Centrifugal microfluidic platform for ultrasensitive detection of botulinum toxin. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöhlmann, C.; Elßner, T. Multiplex Immunoassay Techniques for On-Site Detection of Security Sensitive Toxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lv, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, S.; Huang, W.; Liu, P.; Kong, D.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Rapid and sensitive detection of botulinum toxin type A in complex sample matrices by AlphaLISA. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 987517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozanich, R.M., Jr.; Bruckner-Lea, C.J.; Warner, M.G.; Miller, K.; Antolick, K.C.; Marks, J.D.; Lou, J.; Grate, J.W. Rapid multiplexed flow cytometric assay for botulinum neurotoxin detection using an automated fluidic microbead-trapping flow cell for enhanced sensitivity. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5783–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohrabi, H.; Majidi, M.R.; Khaki, P.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, A.; de la Guardia, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. State of the art: Lateral flow assays toward the point-of-care foodborne pathogenic bacteria detection in food samples. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1868–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. Highly sensitive detection of three protein toxins via SERS-lateral flow immunoassay based on SiO(2)@Au nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2022, 41, 102522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalb, S.R.; Baudys, J.; Smith, T.J.; Smith, L.A.; Barr, J.R. Characterization of Hemagglutinin Negative Botulinum Progenitor Toxins. Toxins 2017, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, J.R.; Moura, H.; Boyer, A.E.; Woolfitt, A.R.; Kalb, S.R.; Pavlopoulos, A.; McWilliams, L.G.; Schmidt, J.G.; Martinez, R.A.; Ashley, D.L. Botulinum neurotoxin detection and differentiation by mass spectrometry. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, H.; Kanda, M.; Hayashi, H.; Matsushima, Y.; Yoshikawa, S.; Ohba, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Nagano, C.; Sekimura, K.; Otsuka, K.; et al. Development of an alternative approach for detecting botulinum neurotoxin type A in honey: Analysis of non-toxic peptides with a reference labelled protein via liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2020, 37, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazuet, C.; Ezan, E.; Volland, H.; Popoff, M.R.; Becher, F. Toxin detection in patients' sera by mass spectrometry during two outbreaks of type A Botulism in France. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 4091–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, B.; Perobelli, R.F.; Walter, M.E.; da Silva, F.S.; Dalmora, S.L. Content/Potency Assessment of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type-A by Validated Liquid Chromatography Methods and Bioassays. Toxins 2019, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalb, S.R.; Baudys, J.; Barr, J.R. Detection of the HA-33 protein in botulinum neurotoxin type G complex by mass spectrometry. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rasooly, R.; Do, P.M. Development of an in vitro activity assay as an alternative to the mouse bioassay for Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type A. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4309–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J. Serotype Features of 17 Suspected Cases of Foodborne Botulism in China 2019–2022 Revealed by a Multiplex Immuno-Endopep-MS Method. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 869874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, O.; Feldberg, L.; Gura, S.; Zichel, R. A new peptide substrate for enhanced botulinum neurotoxin type B detection by endopeptidase-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry/multiple reaction monitoring assay. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 473, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, K.M.; Barr, J.R.; Hopkins, A.O.; Dykes, J.K.; Lúquez, C.; Kalb, S.R. Validation of a clinical assay for botulinum neurotoxins through mass spectrometric detection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2024, 62, e0162923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalb, S.R.; Baudys, J.; Wang, D.; Barr, J.R. Recommended mass spectrometry-based strategies to identify botulinum neurotoxin-containing samples. Toxins 2015, 7, 1765–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalb, S.R.; Krilich, J.C.; Dykes, J.K.; Lúquez, C.; Maslanka, S.E.; Barr, J.R. Detection of Botulinum Toxins A, B, E, and F in Foods by Endopep-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, M.M.; Cornelissen, J.C.; van der Wal, F.J.; Bergervoet, J.H.W.; Koene, M. Single-Domain Antibody Multimers for Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotypes C, D, and Their Mosaics in Endopep-MS. Toxins 2023, 15, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, O.; Feldberg, L.; Dor, E.; Gura, S.; Zichel, R. Optimization of SNAP-25-derived peptide substrate for improved detection of botulinum A in the Endopep-MS assay. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 528, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, O.; Feldberg, L.; Yamin, T.S.; Dor, E.; Barnea, A.; Weissberg, A.; Zichel, R. Development of a multiplex Endopep-MS assay for simultaneous detection of botulinum toxins A, B and E. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Baudys, J.; Hoyt, K.; Barr, J.R.; Kalb, S.R. Sensitive detection of type G botulinum neurotoxin through Endopep-MS peptide substrate optimization. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5489–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Baudys, J.; Hoyt, K.M.; Barr, J.R.; Kalb, S.R. Further optimization of peptide substrate enhanced assay performance for BoNT/A detection by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4779–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Baudys, J.; Kalb, S.R.; Barr, J.R. Improved detection of botulinum neurotoxin type A in stool by mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 412, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.C.; Flannery, A.R.; Cheng, L.W. A Rapid, Sensitive, and Portable Biosensor Assay for the Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A in Complex Food Matrices. Toxins 2018, 10, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subekin, A.; Alieva, R.; Kukushkin, V.; Oleynikov, I.; Zavyalova, E. Rapid SERS Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvin, S.; Hashemi, P.; Afkhami, A.; Ghanei, M.; Bagheri, H. Simultaneous determination of BoNT/A and /E using an electrochemical sandwich immunoassay based on the nanomagnetic immunosensing platform. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.N.; Baider, Z.; Elad, D.; Blum, S.E.; Shtenberg, G. Botulinum Neurotoxin C Dual Detection through Immunological Recognition and Endopeptidase Activity Using Porous Silicon Interferometers. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 5927–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.; Nhiem, L.T. Facile detection of botulinum neurotoxin using LSPR nanosensor based on Langmuir-Blodgett films of gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 31176–31181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Schill, K.M.; Fry, H.C.; Duncan, T.V. A Quantum Dot Nanobiosensor for Rapid Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype E. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caratelli, V.; Fillo, S.; D’Amore, N.; Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Moccia, M.; Avitabile, C.; Moscone, D.; Lista, F.; Arduini, F. Paper-based electrochemical peptide sensor for on-site detection of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A and C. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 183, 113210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabka, M.; Jasek, K.; Witkiewicz, Z. Surface Acoustic Wave Immunosensor for Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin. Sensors 2023, 23, 7688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yan, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Cui, D.; Xin, W.; Gao, S.; Jin, H. Wearable Temperature Sensor Enhanced Volatilomics Technique for Swift and Convenient Detection of Latrogenic Botulism. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2411738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessler, F.; Pagel-Wieder, S.; Avondet, M.A.; Böhnel, H. Evaluation of lateral flow assays for the detection of botulinum neurotoxin type A and their application in laboratory diagnosis of botulism. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 57, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, J.; Sharma, M.K.; Ponmariappan, S.; Sarita; Shaik, M.; Upadhyay, S. Electrochemical immunosensor for botulinum neurotoxin type-E using covalently ordered graphene nanosheets modified electrodes and gold nanoparticles-enzyme conjugate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 69, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohanka, M. Current Trends in the Biosensors for Biological Warfare Agents Assay. Materials 2019, 12, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, W.; Lindo, P.; Singh, B.R. Type A botulinum neurotoxin complex proteins differentially modulate host response of neuronal cells. Toxicon 2014, 82, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.B.; Cai, S.; Adler, M.; Singh, B.K.; Parmar, V.S.; Singh, B.R. Natural Compounds and Their Analogues as Potent Antidotes against the Most Poisonous Bacterial Toxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01280–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Stenmark, P. The Structure and Classification of Botulinum Toxins. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 263, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslanka, S.E.; Lúquez, C.; Dykes, J.K.; Tepp, W.H.; Pier, C.L.; Pellett, S.; Raphael, B.H.; Kalb, S.R.; Barr, J.R.; Rao, A.; et al. A Novel Botulinum Neurotoxin, Previously Reported as Serotype H, Has a Hybrid-Like Structure With Regions of Similarity to the Structures of Serotypes A and F and Is Neutralized With Serotype A Antitoxin. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, M.W.; Smith, T.J.; Anniballi, F.; Austin, J.W.; Bano, L.; Bradshaw, M.; Cuervo, P.; Cheng, L.W.; Derman, Y.; Dorner, B.G.; et al. Historical Perspectives and Guidelines for Botulinum Neurotoxin Subtype Nomenclature. Toxins 2017, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Xue, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, L. Research Progress on the Detection Methods of Botulinum Neurotoxin. Toxins 2025, 17, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090453
Wang S, Zhang H, Xue Y, Yang Y, Yuan L. Research Progress on the Detection Methods of Botulinum Neurotoxin. Toxins. 2025; 17(9):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090453
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuo, Huajie Zhang, Yanhua Xue, Yingchao Yang, and Liyong Yuan. 2025. "Research Progress on the Detection Methods of Botulinum Neurotoxin" Toxins 17, no. 9: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090453
APA StyleWang, S., Zhang, H., Xue, Y., Yang, Y., & Yuan, L. (2025). Research Progress on the Detection Methods of Botulinum Neurotoxin. Toxins, 17(9), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090453




