Uncovering Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae) in South America: First Taxonomic and Toxicological Insights from Argentinean Coastal Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
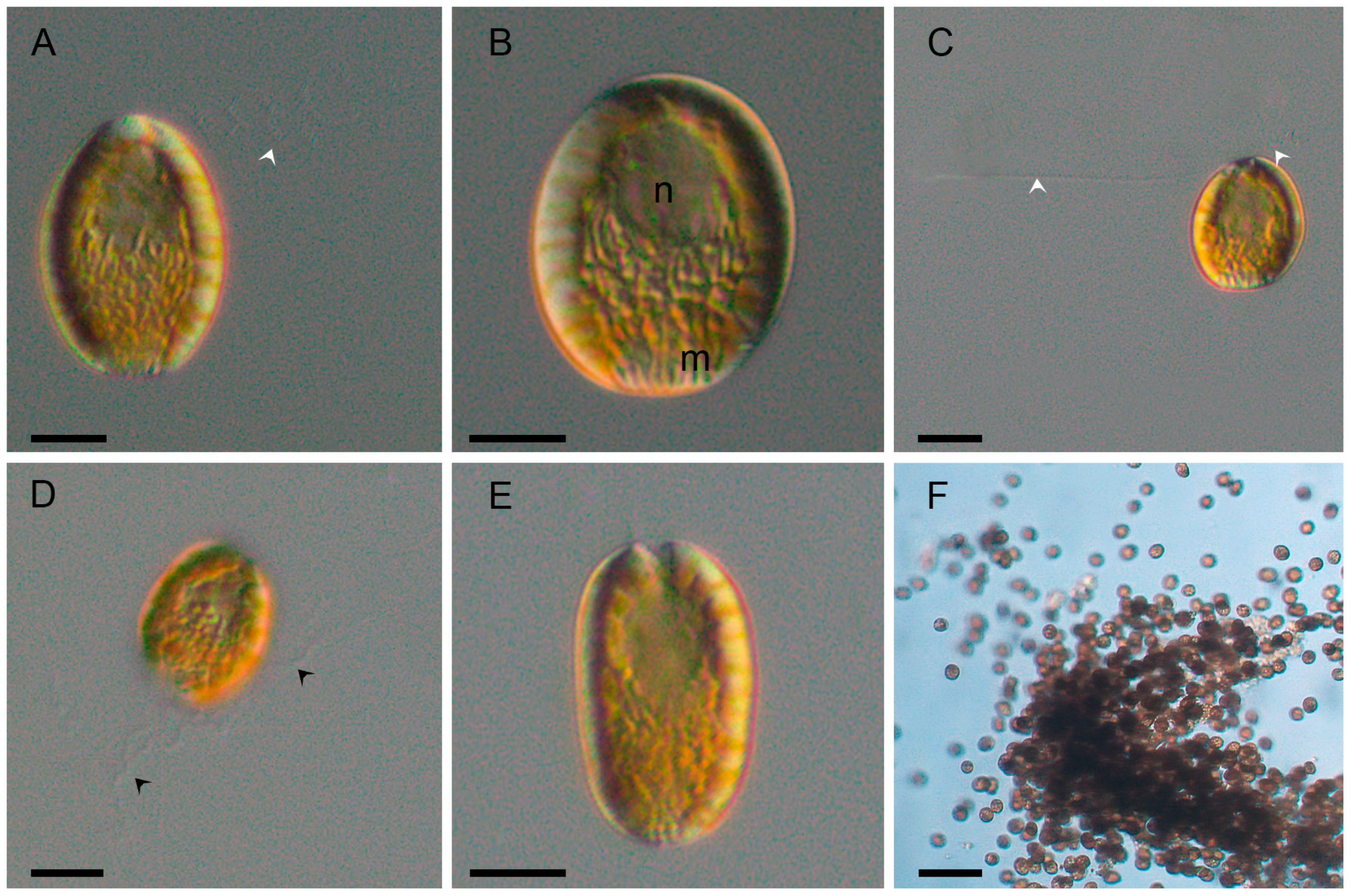
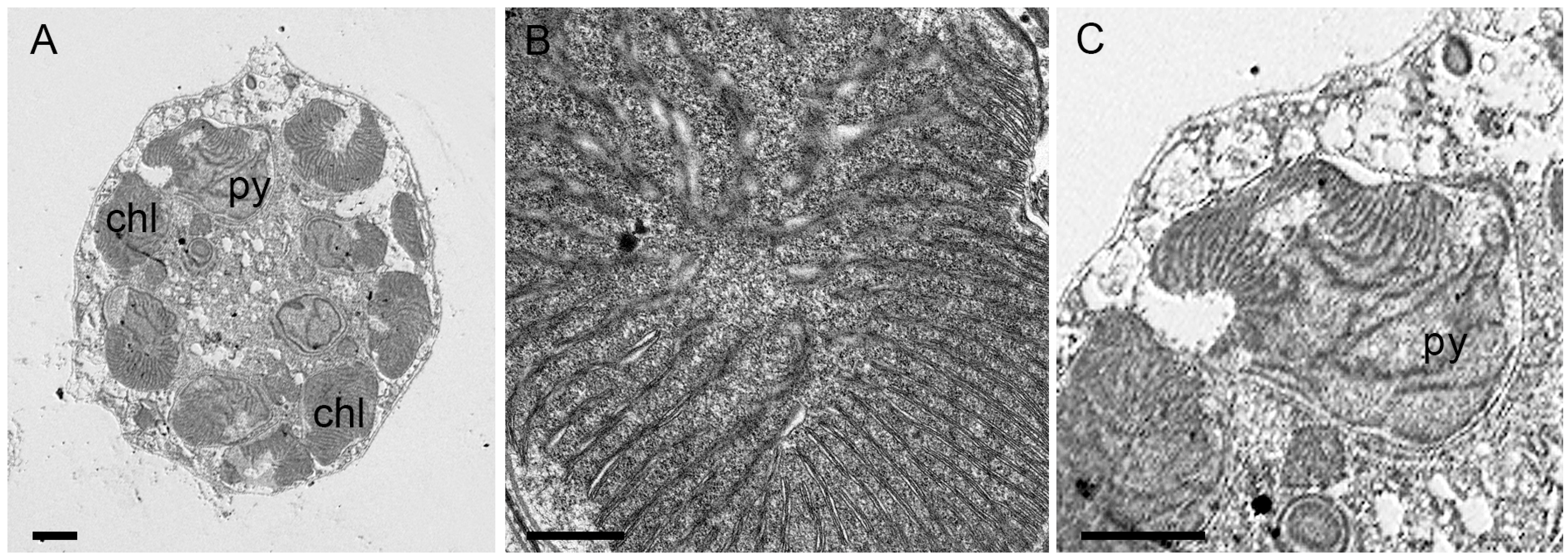
2.1. Morphological Analysis
2.2. Phylogeny
2.3. Pigment Signature
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assays
2.5. Brevetoxin Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Morphological Features and Taxonomic Identity
3.2. Phylogenetic Relationships
3.3. Pigment Composition
3.4. Toxicity and Potential Harmfulness
3.5. Ecological and Monitoring Implications
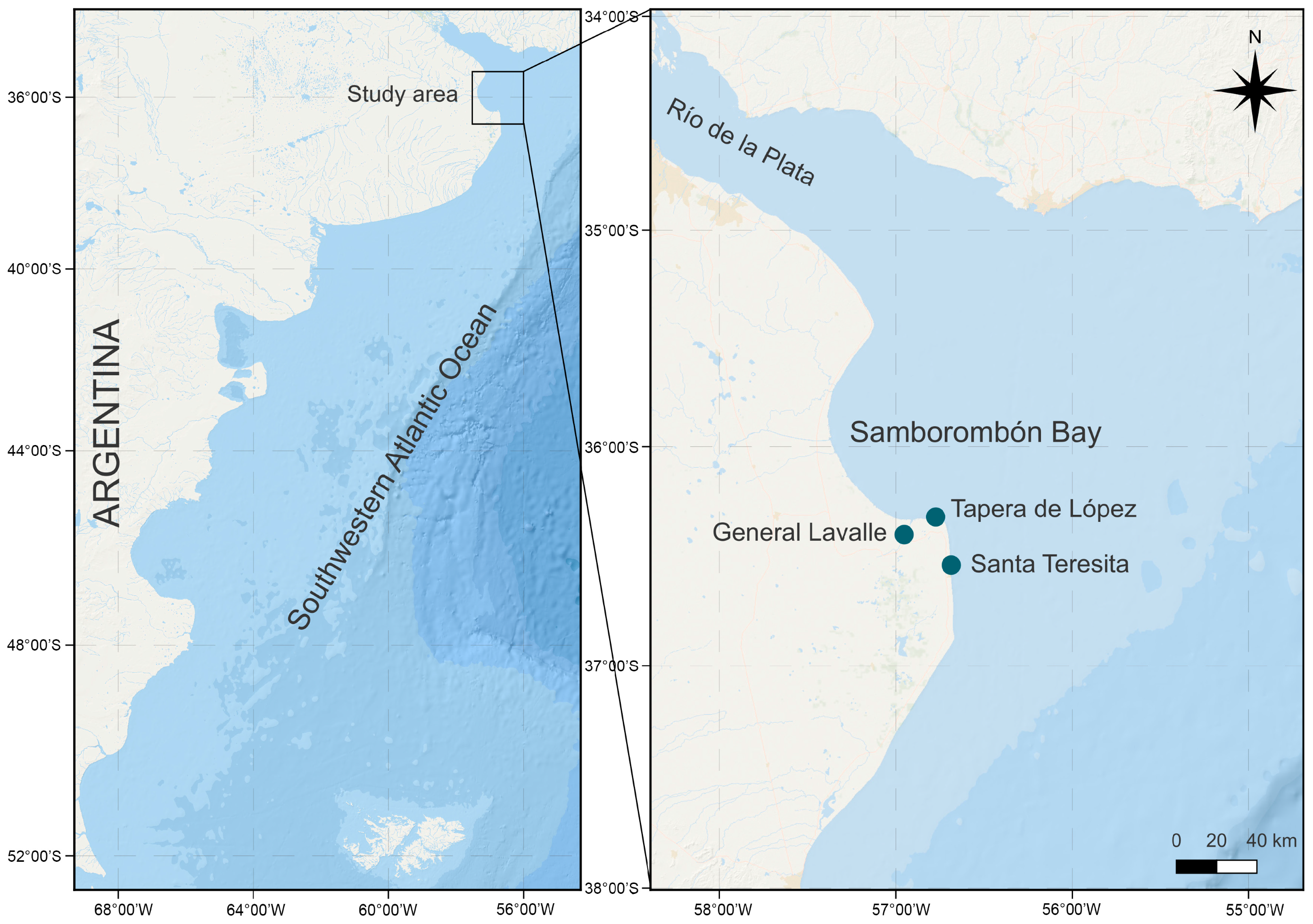
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Culture of Microalgae Strains
4.2. Microscopy
4.2.1. Light Microscopy
4.2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.3. DNA Extraction, Amplification, Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4. Pigment Analysis
4.5. Toxicity
4.5.1. Gill Cell Assay with Fibrocapsa Strains
4.5.2. Brevetoxin Screening
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horiguchi, T. Raphidophyceae (Raphidophyta). In Handbook of the Protists; Archibald, J.M., Simpson, A.G.B., Slamovits, C.H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hallegraeff, G.; Enevoldsen, H.; Zingone, A. Global Harmful Algal Bloom Status Reporting. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, Y.; Chihara, M. Ultrastructure and taxonomy of Fibrocapsa japonica (class Raphidophyceae). Arch. Protistenk. 1985, 130, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöpper, S.; John, U.; Cembella, A.D. A new Mediterranean genotype of Fibrocapsa sp. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2006; Moestrup, Ø., Ed.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae. Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008; pp. 259–261. [Google Scholar]
- Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Martínez-López, A.; Bustillos-Guzmán, J.J.; Carreón-Palau, L.; Morquecho, L.; Olguín-Monroy, N.O.; Zenteno-Savín, T.; Mendoza-Flores, A.; González-Acosta, B.; Hernández-Sandoval, F.H.; et al. Morphology, biochemistry, and growth of raphidophyte strains from the Gulf of California. Hydrobiologia 2012, 693, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, S.; Almeida, L.L.; Alves-de-Souza, C.; Oliveira, M.M.M.; Proença, L.A.O.; Menezes, M. Morphological and genetic characterization of bloom-forming raphidophyceae from Brazilian coast. Phycol. Res. 2019, 67, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooistra, W.H.C.F.; de Boer, M.K.; Vrieling, E.G.; Connell, L.B.; Gieskes, W.W.C. Variation along ITS markers across strains of Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae) suggests hybridisation events and recent range expansion. J. Sea Res. 2001, 46, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchiari, E.; Guerrini, F.; Penna, A.; Totti, C.; Pistocchi, R. Effect of salinity, temperature, organic and inorganic nutrients on growth of cultured Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae) from the Northern Adriatic Sea. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, K.M.; Tyl, M.R.; Vrieling, E.G.; van Rijssel, M. Effects of salinity and nutrient conditions on growth and haemolytic activity of Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 37, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, M.K.; Koolmees, E.M.; Vrieling, E.G.; Breeman, A.M.; Van Rijssel, M. Temperature responses of three Fibrocapsa japonica strains (Raphidophyceae) from different climate regions. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smayda, T.J.; Villareal, T. The 1985 ‘Brown Tide’ and the open phytoplankton niche in Narragansett Bay during summer. In Novel Phytoplankton Blooms: Causes and Impacts of Recurrent Brown Tides and Other Unusual Blooms; Cosper, E.M., Bricelj, V.M., Carpenter, E.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 165–187. [Google Scholar]
- Billard, C. Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae), planktonic marine alga reported for the first time in France. Cryptogam. Algol. 1992, 13, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, E.G.; Koeman, R.P.T.; Nagasaki, K.; Ishida, Y.; Pererzak, L.; Gieskes, W.W.C.; Veenhuis, M. Chattonella and Fibrocapsa (Raphidophyceae): First observation of, potentially harmful, red tide organisms in Dutch coastal waters. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1995, 33, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.H.; MacKenzie, L.; Till, D.; Hanna, D.; Rhodies, L. The first toxic shellfish outbreaks and the associated phytoplankton blooms in early 1993 in New Zealand. In Harmful Marine Algal Blooms: Technique et Documentation; Lassus, P., Arzul, G., Erard, E., Gentien, C., Marcaillou, C., Eds.; Lavoisier, Intercept Ltd.: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, L.L.; Haywood, A.J.; Ballantine, W.J.; MacKenzie, A.L. Algal blooms and climate anomalies in north-east New Zealand, August–December 1992. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 27, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Morquecho, L.; Hernández-Becerril, D.U.; Reyes-Salinas, A.; Bravo-Sierra, E. Raphidophyceans on the coasts of Mexico. Hydrobiologia 2004, 515, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeblich, A.R.; Fine, K. Marine Chloromonads: More widely distributed in nertic environments than previously thought. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1977, 90, 388–399. [Google Scholar]
- Okaichi, T. Red Tide Problems in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. In Red Tides: Biology, Environmental Science and Toxicology; Okaichi, T., Anderson, D.M., Nemoto, T., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Tomas, C.R. Harmful Algal Species Fact Sheet: Fibrocapsa japonica. In Harmful Algal Species Fact Sheets; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Odebrecht, C. Raphidophycean in Southern Brazil. Harmful Algae News 1995, 12, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Sunesen, I.; Méndez, S.M.; Mancera-Pineda, J.E.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.Y.; Enevoldsen, H. The Latin America and Caribbean HAB status report based on OBIS and HAEDAT maps and databases. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, S.; Akselman, R.; Tomas, C.R. First report of Heterosigma akashiwo, Fibrocapsa japonica and Chattonella marina var. antiqua in Uruguay. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Hersonissos, Greece, 1–5 November 2010; Pagou, K.A., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013; pp. 134–136. [Google Scholar]
- Toriumi, S.; Takano, H. Fibrocapsa, a new genus in Chloromonadophyceae from Atsumi Bay, Japan. Bull. Tokai Reg. Fish. Res. Lab. 1973, 76, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, M. Isolation and Characterisation of Toxins from Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oldenburg, Oldenburg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- de Boer, M.K.; Boerée, C.; Sjollema, S.B.; de Vries, T.; Rijnsdorp, A.D.; Buma, A.G.J. The toxic effect of the marine raphidophyte Fibrocapsa japonica on larvae of the common flatfish Sole (Solea solea). Harmful Algae 2012, 17, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Arakawa, O.; Onoue’, Y. Neurotoxin production by a Chloromonad Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae). J. World Aquac. Soc. 1996, 27, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgers, A.; McConell, E.; Naar, J.; Weidner, A.; Tomas, L.; Tomas, C. Comparision of regional clones of the genera Chattonella and Fibrocapsa for growth characteristics and potential toxin production. In Harmful Algae 2002; Steidinger, K.A., Landsberg, J.H., Tomas, C.R., Vargo, A., Eds.; Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission: Tallahassee, FL, USA; Florida Institute of Oceanography: Saint Petersburg, FL, USA; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 2004; pp. 405–407. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J.A.; De Salas, M.; Oda, T.; Hallegraeff, G. Superoxide production by marine microalgae: I. Survey of 37 species from 6 classes. Mar. Biol. 2005, 147, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Nakamura, A.; Shikayama, M.; Kawano, I.; Ishimatsu, A.; Muramatsu, T. Generation of reactive oxygen species by Raphidophycean phytoplankton. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 61, 1658–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.A.; Nichols, P.D.; Hamilton, B.; Lewis, R.J.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Ichthyotoxicity of Chattonella marina (Raphidophyceae) to damselfish (Acanthochromis polycanthus): The synergistic role of reactive oxygen species and free fatty acids. Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, M.K.; Tyl, M.R.; Fu, M.; Kulk, G.; Liebezeit, G.; Tomas, C.R.; Lenzi, A.; Naar, J.; Vrieling, E.G.; van Rijssel, M. Haemolytic activity within the species Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae). Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Seger, A.; Mardones, J.I.; Nichols, P.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Progress in understanding algal bloom-mediated fish kills: The role of superoxide radicals, phycotoxins and fatty acids. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar Juárez, D.; Mardones, J.I.; Flores-Leñero, A.; Norambuena, L.; Paredes-Mella, J.; Sar, E.A.; Sunesen, I. First description of the fish-killing raphidophyceae Chattonella marina complex in Argentina: From genetics to ichthyotoxicity unveiled. Harmful Algae 2025, 142, 102804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acha, M.E.; Mianzan, H.; Guerrero, R.A.; Carreto, J.I.; Giberto, D.; Montoya, N.G.; Carignan, M.O. An overview of physical and ecological processes in the Rio de la Plata Estuary. Cont. Shelf. Res. 2008, 28, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaert, A.S.; Karsten, U.; Hara, Y.; Watanabe, M.M. Pigments and fatty acids of marine raphidophytes: A chemotaxonomic re-evaluation. Phycol. Res. 1998, 46, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi-Rontani, C.; Maheswari, U.; Jabbari, K.; Bowler, C. Comparative ecophysiology and genomics of the toxic unicellular alga Fibrocapsa japonica. New Phytol. 2010, 185, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, J.I.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Nichols, P.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Fish gill damage by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella from Chilean Fjords: Synergistic action of ROS and PUFA. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.M.; Onoue, Y. Variation in toxin compositions of two harmful raphidophytes, Chattonella antiqua and Chattonella marina, at different salinities. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Khan, S.; Onoue, Y. Effects of temperature and light intensity on the growth and toxicity of Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae). Aquac. Res. 2000, 31, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzolesi, L.; Cucchiari, E.; Guerrini, F.; Pasteris, A.; Galletti, P.; Tagliavini, E.; Totti, C.; Pistocchi, R. Toxicity evaluation of Fibrocapsa japonica from the Northern Adriatic Sea through a chemical and toxicological approach. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, S. The cysts of Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae) found in bottom sediment in Harima-Nada, Eastern Inland Sea of Japan. Bull. Plankton Soc. Japan 1987, 34, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Sunesen, I.; Rodríguez Hernández, F.; Aguiar Juárez, D.; Tardivo Kubis, J.A.; Lavigne, A.S.; Rossignoli, A.; Riobó, P.; Sar, E.A. Morphology, genetics and toxin profile of Prorocentrum texanum (Dinophyceae) from Argentinian marine coastal waters. Phycologia 2020, 59, 634–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvardsen, B.; Shalchian-Tabrizi, K.; Jakobsen, K.S.; Medlin, L.K.; Dahl, E.; Brubak, S.; Paasche, E. Genetic variability and molecular phylogeny of Dinophysis species (Dinophyceae) from Norwegian waters inferred from single cell analyses of rDNA. J. Phycol. 2003, 39, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholin, C.A.; Herzog, M.; Sogin, M.; Anderson, D.M. Identification of group- and strain-specific genetic markers for globally distributed Alexandrium (Dinophyceae). II. Sequence analysis of a fragment of the LSU rRNA gene. J. Phycol. 1994, 30, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; Mcgettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X Version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian Inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bols, N.C.; Barlian, A.; Chirino-Trejo, M.; Caldwell, S.J.; Goegan, P.; Lee, L.E. Development of a cell line from primary cultures of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), gills. J. Fish. Dis. 1994, 17, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Waite, T.D.; Godrant, A.; Rose, A.L.; Tovar, C.D.; Woods, G.M.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Novel application of a fish gill cell line assay to assess ichthyotoxicity of harmful marine microalgae. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Leñero, A.; Vargas-Torres, V.; Paredes-Mella, J.; Norambuena, L.; Fuenzalida, G.; Lee-Chang, K.; Mardones, J.I. Heterosigma akashiwo in Patagonian fjords: Genetics, growth, pigment signature and role of PUFA and ROS in ichthyotoxicity. Toxins 2022, 14, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, C.; Baty, F.; Streibig, J.C.; Gerhard, D. Dose-response analysis using R. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0146021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihaka, R.; Gentleman, R. R: A language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riisberg, I.; Orr, R.J.S.; Kluge, R.; Schalchian-Tabrizi, K.; Bowers, H.A.; Patil, V.; Edvardsen, B.; Jakobsen, K.S. Seven gene phylogeny of Heterokonts. Protist 2009, 160, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, W.M.; Lim, H.C.; Lau, W.L.S.; Law, I.K.; Teng, S.T.; Benico, G.; Leong, S.C.Y.; Takahashi, K.; Gu, H.; Lirdwitayaprasit, T.; et al. Description of two new species Chattonella tenuiplastida sp. nov. and Chattonella malayana sp. nov. (Raphidophyceae) from South China Sea, with a report of wild fish mortality. Harmful Algae 2022, 118, 102322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, W.M.; Benico, G.; Doan-Nhu, H.; Furio, E.; Leaw, C.P.; Leong, S.C.Y.; Lim, P.T.; Lim, W.A.; Lirdwitayaprasit, T.; Lu, S.; et al. The harmful raphidophyte Chattonella (Raphidophyceae) in Western Pacific: Its red tides and associated fisheries damage over the past 50 years (1969–2019). Harmful Algae 2021, 107, 102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaran-Fariman, G.; Bolch, C.J.S. Morphology and genetic affinities of a novel Chattonella isolate (Raphidophyceae) isolated from Iran’s South Coast (Oman Sea). Turk. J. Botany 2014, 38, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engesmo, A.; Eikrem, W.; Seoane, S.; Smith, K.; Edvardsen, B.; Hofgaard, A.; Tomas, C.R. New insights into the morphology and phylogeny of Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae), with the description of Heterosigma minor sp. nov. Phycologia 2016, 55, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, J.V.; Bergquist, P.R.; Bergquist, P.L.; Scholin, C.A. Detection and enumeration of Heterosigma akashiwo and Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae) using rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Phycologia 2001, 40, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar Juárez, D. Dinámica Espacio-Temporal del Fitoplancton de la Bahía Samborombón y Caracterización Integral de Especies Ictiotóxicas. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, La Plata, Argentina, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Ki, J.S.; Han, M.S. Nuclear rDNA and chloroplast rbcL, rbcS and IGS sequence data, and their implications from the Japanese, Korean, and North American harmful algae, Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae). Environ. Res. 2007, 103, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ali, A.; De Baere, R.; De Wachter, R.; Van De Peer, Y. Evolutionary relationships among heterokont algae (the autotrophic Stramenopiles) based on combined analyses of small and large subunit ribosomal RNA. Protist 2002, 153, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| m/z Parent Ion | m/z Daughter Ion | Collision Energy [eV] | Compound Name | |
| 657.4 | 159.1 | 30 | Brevenal | |
| 657.4 | 255.2 | 30 | ||
| 657.4 | 603.4 | 30 | ||
| 657.4 | 621.4 | 30 | ||
| 657.4 | 639.4 | 30 | ||
| 867.1 | 385.2 | 15 | PbTx-1 | |
| 867.1 | 849.2 | 15 | ||
| 895.5 | 455.2 | 25 | PbTx-2 | |
| 895.5 | 877.2 | 15 | ||
| 897.5 | 725.2 | 25 | PbTx-3 | |
| 897.5 | 879.5 | 15 | ||
| 911.5 | 875.1 | 25 | PbTx-6 | |
| 911.5 | 893.2 | 14 | ||
| 869.5 | 851.5 | 30 | PbTx-7 | |
| 917.9 | 899.9 | 30 | PbTx-8 | |
| 899.5 | 881.5 | 25 | PbTx-9 | |
| 911.5 | 875.1 | 15 | ||
| 871.5 | 853.5 | 30 | PbTx-10 | |
| 985.5 | 967.5 | 30 | BTX-B1 | |
| 1034.6 | 753.0 | 30 | BTX-B2 | |
| 1034.6 | 929.0 | 30 | ||
| 1034.6 | 1016.6 | 30 |
| Strain | Sample Site and Herbarium Code | Water Temperature and Salinity | Date | Isolator | GenBank Accession Number | Cell Length (µm) | Cell Width (µm) |
| LPCc058 | Santa Teresita LPC 11471 | 23.0 °C 20.7 | 2 February 2017 | Sunesen I. | OR514481 | 23.4 ± 0.7 | 16.6 ± 0.9 |
| LPCc048 | Tapera de López LPC 13715 | 21.5 °C 18.9 | 15 March 2020 | Aguiar Juárez D. | OR498773 | 30.8 ± 1.2 | 22.4 ± 1.1 |
| LPCc049 | Tapera de López LPC 13727 | 23.6 °C 20.0 | 28 February 2021 | Aguiar Juárez D. | OR498774 | 27.5 ± 0.8 | 22.1 ± 1.0 |
| LPCc050 | General Lavalle LPC 13732 | 20.6 °C 15.9 | 29 March 2021 | Aguiar Juárez D. | OR498775 | 24.9 ± 0.8 | 18.0 ± 0.6 |
| LPCc051 | Tapera de López LPC 13734 | 23.0 °C 20.8 | 18 April 2021 | Aguiar Juárez D. | OR498776 | 30.3 ± 0.9 | 17.9 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguiar Juárez, D.; Sunesen, I.; Flores-Leñero, A.; Norambuena, L.; Krock, B.; Fuenzalida, G.; Mardones, J.I. Uncovering Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae) in South America: First Taxonomic and Toxicological Insights from Argentinean Coastal Waters. Toxins 2025, 17, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080386
Aguiar Juárez D, Sunesen I, Flores-Leñero A, Norambuena L, Krock B, Fuenzalida G, Mardones JI. Uncovering Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae) in South America: First Taxonomic and Toxicological Insights from Argentinean Coastal Waters. Toxins. 2025; 17(8):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080386
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguiar Juárez, Delfina, Inés Sunesen, Ana Flores-Leñero, Luis Norambuena, Bernd Krock, Gonzalo Fuenzalida, and Jorge I. Mardones. 2025. "Uncovering Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae) in South America: First Taxonomic and Toxicological Insights from Argentinean Coastal Waters" Toxins 17, no. 8: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080386
APA StyleAguiar Juárez, D., Sunesen, I., Flores-Leñero, A., Norambuena, L., Krock, B., Fuenzalida, G., & Mardones, J. I. (2025). Uncovering Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae) in South America: First Taxonomic and Toxicological Insights from Argentinean Coastal Waters. Toxins, 17(8), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080386





