Pathways for Diagnosis and Multimodal Management, Including Botulinum Neurotoxin Therapy, in Shoulder Conditions Following Acquired Central Nervous System Lesions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Diagnosis
Clinical Evaluation and Investigation
- What is the impact on passive and active function, including posture at rest and in gait?
- Is there pain with passive or active movement, or at rest?
- What are the neural and musculoskeletal contributing factors?
- Is the etiology neurological or non-neurological?
- For neurological causes, what are the patterns of pathological movement and posture?
- Is the movement pattern hypo- or hyperkinetic?
- -
- If it is hyperkinetic, is it tonic or phasic?
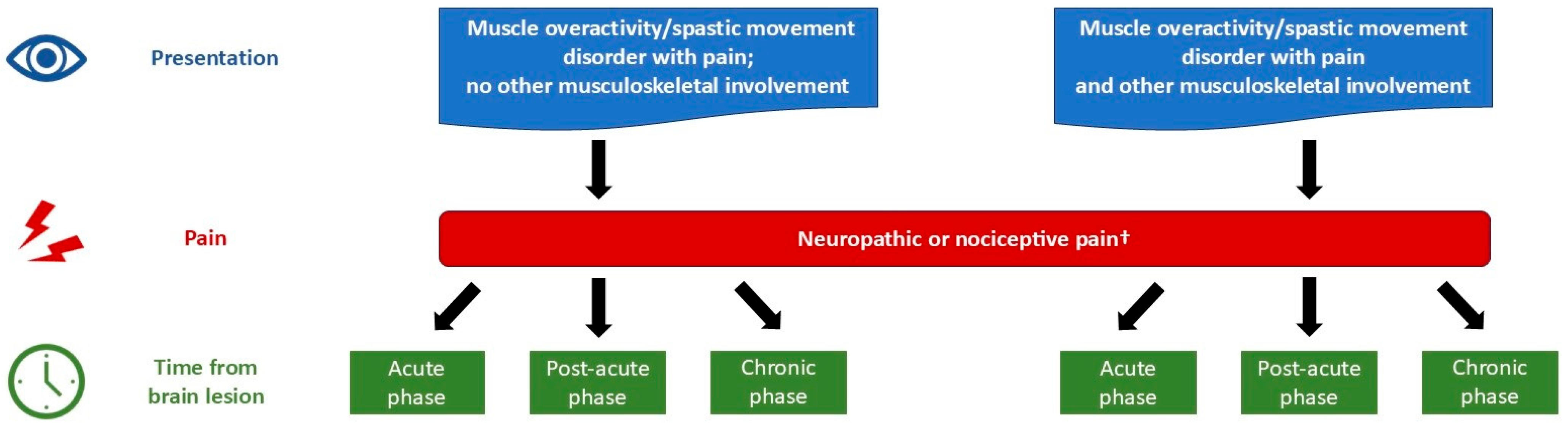
2.2. Management Strategies
2.2.1. Pain
2.2.2. Multimodal Treatment
2.2.3. Goal Setting
2.2.4. Case Study
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ArmA | Arm Activity Measure |
| BoNT-A | Botulinum neurotoxin type A |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CP | Cerebral palsy |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| GAS-eous | Goal Attainment Scaling-Evaluation of Outcomes for Upper Limb Spasticity |
| MAS | Modified Ashworth Scale |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| ViVe | Victoria Verona |
References
- Jacinto, J.; Camões-Barbosa, A.; Carda, S.; Hoad, D.; Wissel, J. A practical guide to botulinum neurotoxin treatment of shoulder spasticity 1: Anatomy, physiology, and goal setting. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1004629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnasabapathy, Y.; Broad, J.; Baskett, J.; Pledger, M.; Marshall, J.; Bonita, R. Shoulder pain in people with a stroke: A population-based study. Clin. Rehabil. 2003, 17, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, I.; Jönsson, A.C.; Norrving, B.; Lindgren, A. Shoulder pain after stroke: A prospective population-based study. Stroke 2007, 38, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.D.; Chae, J. Hemiplegic shoulder pain. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 26, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaess-Leistner, S.; Ri, S.J.; Audebert, H.J.; Wissel, J. Early clinical predictors of post stroke spasticity. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2021, 28, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhao, Y. Post-stroke upper limb spasticity incidence for different cerebral infarction site. Open Med. 2018, 13, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner-Stokes, L.; Jacinto, J.; Fheodoroff, K.; Brashear, A.; Maisonobe, P.; Lysandropoulos, A.; ULIS-III study group. Longitudinal goal attainment with integrated upper limb spasticity management including repeat injections of botulinum toxin A: Findings from the prospective, observational Upper Limb International Spasticity (ULIS-III) cohort study. J. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 53, jrm00157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitterer, J.W.; Picelli, A.; Winston, P. A novel approach to new-onset hemiplegic shoulder pain with decreased range of motion using targeted diagnostic nerve blocks: The ViVe algorithm. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 668370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, Q.V.; Brashear, A.; Gillard, P.J.; Varon, S.F.; Vandenburgh, A.M.; Turkel, C.C.; Elovic, E.P. Relationship between disability and health-related quality of life and caregiver burden in patients with upper limb poststroke spasticity. PMR 2012, 4, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adey-Wakeling, Z.; Liu, E.; Crotty, M.; Leyden, J.; Kleinig, T.; Anderson, C.S.; Newbury, J. Hemiplegic shoulder pain reduces quality of life after acute stroke: A prospective population-based study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 95, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.J.; Jarrett, L.; Lockley, L.; Marsden, J.; Stevenson, V.L. Clinical management of spasticity. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biering-Sørensen, B.; Stevenson, V.L.; Bensmail, D.; Grabljevec, K.; Martínez Moreno, M.; Pucks-Faes, E.; Wissel, J.; Zampolini, M. European expert consensus on improving patient selection for the management of disabling spasticity with intrathecal baclofen and/or botulinum toxin type A. J. Rehabil. Med. 2022, 53, jrm00236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Stroke Rehabilitation in Adults; NICE guideline (NG236); NICE: London, UK, 2023; Available online: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng236 (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Cerebral Palsy in Adults; NICE Guideline (NG119); NICE: London, UK, 2019; Available online: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng119 (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Gracies, J.M.; Brashear, A.; Jech, R.; McAllister, P.; Banach, M.; Valkovic, P.; Walker, H.; Marciniak, C.; Deltombe, T.; Skoromets, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of abobotulinumtoxinA for hemiparesis in adults with upper limb spasticity after stroke or traumatic brain injury: A double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracies, J.M.; O’Dell, M.; Vecchio, M.; Hedera, P.; Kocer, S.; Rudzinska-Bar, M.; Rubin, B.; Timerbaeva, S.L.; Lusakowska, A.; Boyer, F.C.; et al. Effects of repeated abobotulinumtoxinA injections in upper limb spasticity. Muscle Nerve 2018, 57, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissel, J.; Bensmail, D.; Scheschonka, A.; Flatau-Baqué, B.; Simon, O.; Althaus, M.; Simpson, D. Post hoc analysis of the improvement in shoulder spasticity and safety observed following treatment with incobotulinumtoxinA. J. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 52, jrm00028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fheodoroff, K.; Kossmehl, P.; Wissel, J. Validity and reliability of the Spasticity-Associated Arm Pain Scale. J. Pain Manage Med. 2017, 3, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto, J.; Varriale, P.; Pain, E.; Lysandropoulos, A.; Esquenazi, A. Patient perspectives on the therapeutic profile of botulinum neurotoxin type A in spasticity. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Fahey, M.; Finch-Edmondson, M.; Galea, C.; Hines, A.; Langdon, K.; Mc Namara, M.; Paton, M.C.; Popat, H.; et al. State of the evidence traffic lights 2019: Systematic review of interventions for preventing and treating children with cerebral palsy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centorame, D.; Rawicki, B.; Hennel, S.; Hoare, B. Upper limb onabotulinumtoxin A injections in children under 2 years with cerebral palsy: A retrospective chart review. J. Child Neurol. 2022, 37, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoad, D.; Ashford, S.; Bavikatte, G.; Farrell, R.; Robertson, A.; Wissel, J. A concise practical clinical guide to identifying spasticity in neurological shoulder dysfunction. Front. Neurol. 2025, 15, 1440955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissel, J.; Camões-Barbosa, A.; Carda, S.; Hoad, D.; Jacinto, J. A practical guide to botulinum neurotoxin treatment of shoulder spasticity 2: Injection techniques, outcome measurement scales, and case studies. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1022549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boublik, M.; Hawkins, R.J. Clinical examination of the shoulder complex. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 1993, 18, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fugl-Meyer, A.R.; Jääskö, L.; Leyman, I.; Olsson, S.; Steglind, S. The post-stroke hemiplegic patient. 1. a method for evaluation of physical performance. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1975, 7, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiowetz, V.; Volland, G.; Kashman, N.; Weber, K. Adult norms for the Box and Block Test of manual dexterity. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1985, 39, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yozbatiran, N.; Der-Yeghiaian, L.; Cramer, S.C. A standardized approach to performing the action research arm test. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2008, 22, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.B.; Wilcox, R.B., III; Katz, J.N.; Higgins, L.D. Clinical examination of the rotator cuff. PMR 2013, 5, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissel, J.; Müller, J.; Dressnandt, J.; Heinen, F.; Naumann, M.; Topka, H.; Poewe, W. Management of spasticity associated pain with botulinum toxin A. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2000, 20, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trompetto, C.; Marinelli, L.; Mori, L.; Puce, L.; Avanti, C.; Saretti, E.; Biasotti, G.; Amella, R.; Cotellessa, F.; Restivo, D.A.; et al. Effectiveness of botulinum toxin on pain in stroke patients suffering from upper limb spastic dystonia. Toxins 2022, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.M.; Guo, T.T.; Sun, X.; Ge, H.X.; Chen, X.D.; Zhao, K.J.; Zhang, L.N. Effectiveness of botulinum toxin A in treatment of hemiplegic shoulder pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 102, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; Jia, L. Ultrasound-guided BoNT-A [botulinum toxin A] injection into the subscapularis for hemiplegic shoulder pain: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Stroke 2021, 52, 3759–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.V.; Hung, C.Y.; Wu, W.T.; Han, D.S.; Yang, R.S.; Lin, C.P. Comparison of the effectiveness of suprascapular nerve block with physical therapy, placebo, and intra-articular injection in management of chronic shoulder pain: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 1366–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.; Moisset, X.; Ferraro, M.C.; de Andrade, D.C.; Baron, R.; Belton, J.; Bennett, D.L.H.; Calvo, M.; Dougherty, P.; Gilron, I.; et al. Pharmacotherapy and non-invasive neuromodulation for neuropathic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2025, 24, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reebye, R.; Jacinto, L.J.; Balbert, A.; Biering-Sørensen, B.; Carda, S.; Draulans, N.; Molteni, F.; O’dEll, M.W.; Picelli, A.; Santamato, A.; et al. Multimodal therapy and use of adjunctive therapies to BoNT-A in spasticity management: Defining terminology to help enhance spasticity treatment. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1432330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reebye, R.; Balbert, A.; Bensmail, D.; Walker, H.; Wissel, J.; Deltombe, T.; Francisco, G.E. Module 2: Nonsurgical management of spasticity. J. Int. Soc. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2022, 5 (Suppl. S1), S23–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.; Singer, B.J.; Ashford, S.; Hoare, B.; Hastings-Ison, T.; Fheodoroff, K.; Berweck, S.; Sutherland, E.; Hill, B. A synthesis and appraisal of clinical practice guidelines, consensus statements and Cochrane systematic reviews for the management of focal spasticity in adults and children. Disabil. Rehabil. 2022, 44, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, J.; Hayward, K.S.; Kwakkel, G.; Ward, N.S.; Wolf, S.L.; Borschmann, K.; Krakauer, J.W.; Boyd, L.A.; Carmichael, S.T.; Corbett, D.; et al. Agreed definitions and a shared vision for new standards in stroke recovery research: The Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Roundtable Taskforce. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2017, 31, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, M.B.; Coster, W.J.; Figueiredo, P.R.P.; Amaral, M.F.; Gordon, A.M.; Mancini, M.C. Assisting hand use and self-care bimanual performance of children with unilateral spastic cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2023, 65, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliasson, A.C.; Nordstrand, L.; Backheden, M.; Holmefur, M. Longitudinal development of hand use in children with unilateral spastic cerebral palsy from 18 months to 18 years. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2023, 65, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gils, A.; Meyer, S.; Van Dijk, M.; Thijs, L.; Michielsen, M.; Lafosse, C.; Truyens, V.; Oostra, K.; Peeters, A.; Thijs, V.; et al. The Adult Assisting Hand Assessment Stroke: Psychometric properties of an observation-based bimanual upper limb performance measurement. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, C.; Rauchenzauner, M.; Staudt, M.; Berweck, S. Activities of daily living in children with hemiparesis: Influence of cognitive abilities and motor competence. Neuropediatrics 2014, 45, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacinto, J.; Balbert, A.; Bensmail, D.; Carda, S.; Draulans, N.; Deltombe, T.; Ketchum, N.; Molteni, F.; Reebye, R. Selecting goals and target muscles for botulinum toxin A injection using the Goal Oriented Facilitated Approach to Spasticity Treatment (GO-FAST) tool. Toxins 2023, 15, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashford, S.; Turner-Stokes, L. Management of shoulder and proximal upper limb spasticity using botulinum toxin and concurrent therapy interventions: A preliminary analysis of goals and outcomes. Disabil. Rehabil. 2009, 31, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner-Stokes, L.; Ashford, S.; Jacinto, J.; Maisonobe, P.; Balcaitiene, J.; Fheodoroff, K. Impact of integrated upper limb spasticity management including botulinum toxin A on patient-centred goal attainment: Rationale and protocol for an international prospective, longitudinal cohort study (ULIS-III). BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashford, S.; Fheodoroff, K.; Jacinto, J.; Turner-Stokes, L. Common goal areas in the treatment of upper limb spasticity: A multicentre analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2016, 30, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, F.; Wissel, J.; Fheodoroff, K.; Munin, M.C.; Patel, A.T.; Althaus, M.; Comes, G.; Dekundy, A.; Pulte, I.; Scheschonka, A.; et al. Improvement in quality-of-life-related outcomes following treatment with incobotulinumtoxinA in adults with limb spasticity: A pooled analysis. Toxins 2024, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, T.; Khatkova, S.; Turner-Stokes, L.; Picaut, P.; Maisonobe, P.; Balcaitiene, J.; Boyer, F.C. AbobotulinumtoxinA injections in shoulder muscles to improve adult upper limb spasticity: Results from a phase 4 real-world study and a phase 3 open-label trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 52, jrm00068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoisili, O.E.; Chung, A.; Tong, X.; Hayes, D.K.; Loustalot, F. Prevalence of stroke—behavioral risk factor surveillance system, United States, 2011–2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2024, 73, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgetts, C.J.; Leboeuf-Yde, C.; Beynon, A.; Walker, B.F. Shoulder pain prevalence by age and within occupational groups: A systematic review. Arch. Physiother. 2021, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunis, T.; Lubberts, B.; Reilly, B.T.; Ring, D. A systematic review and pooled analysis of the prevalence of rotator cuff disease with increasing age. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014, 23, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.N.; Cǎpet, C.; Beiu, C.; Berteanu, M. The Elias University Hospital Approach: A visual guide to ultrasound-guided botulinum toxin injections in spasticity: Part II- proximal upper limb muscles. Toxins 2025, 17, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbinati, P.; Bemporad, J.; Massimiani, A.; Bianchini, E.; Mazzoli, D.; Glorioso, D.; della Vecchia, G.; De Luca, A.; De Blasiis, P. Lateral pectoral nerve identification through ultrasound-guided methylene blue injection during selective peripheral neurectomy for shoulder spasticity: Proposal for a new procedure. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, S.; David, R.; Speirs, A.; Hashemi, M.; Winston, P. A case report illustrating the combined use of cryoneurolysis and percutaneous needle tenotomy in the treatment of longstanding spastic shoulder contractures after stroke. Arch. Rehabil. Res. Clin. Transl. 2023, 5, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampacchia, G.; Gerini, A.; Morganti, R.; Felzani, G.; Marani, M.; Massone, A.; Onesta, M.P.; Capeci, W.; Andretta, E.; Giuliana Campus, G.; et al. Pain characteristics in Italian people with spinal cord injury: A multicentre study. Spinal Cord. 2022, 60, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.; Eun, S.D.; Kang, D. Effectiveness of exercise programs for alleviation of upper body pain in patients with spinal cord injury: A systematic review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwah, L.K.; Harvey, L.A.; Diong, J.H.; Herbert, R.D. Half of the adults who present to hospital with stroke develop at least one contracture within six months: An observational study. J. Physiother. 2012, 58, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakra, C.; Cohen, H. A clinical review of the use of Botulinum Toxin type A in managing central neuropathic pain in patients with spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord. Med. 2022, 45, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
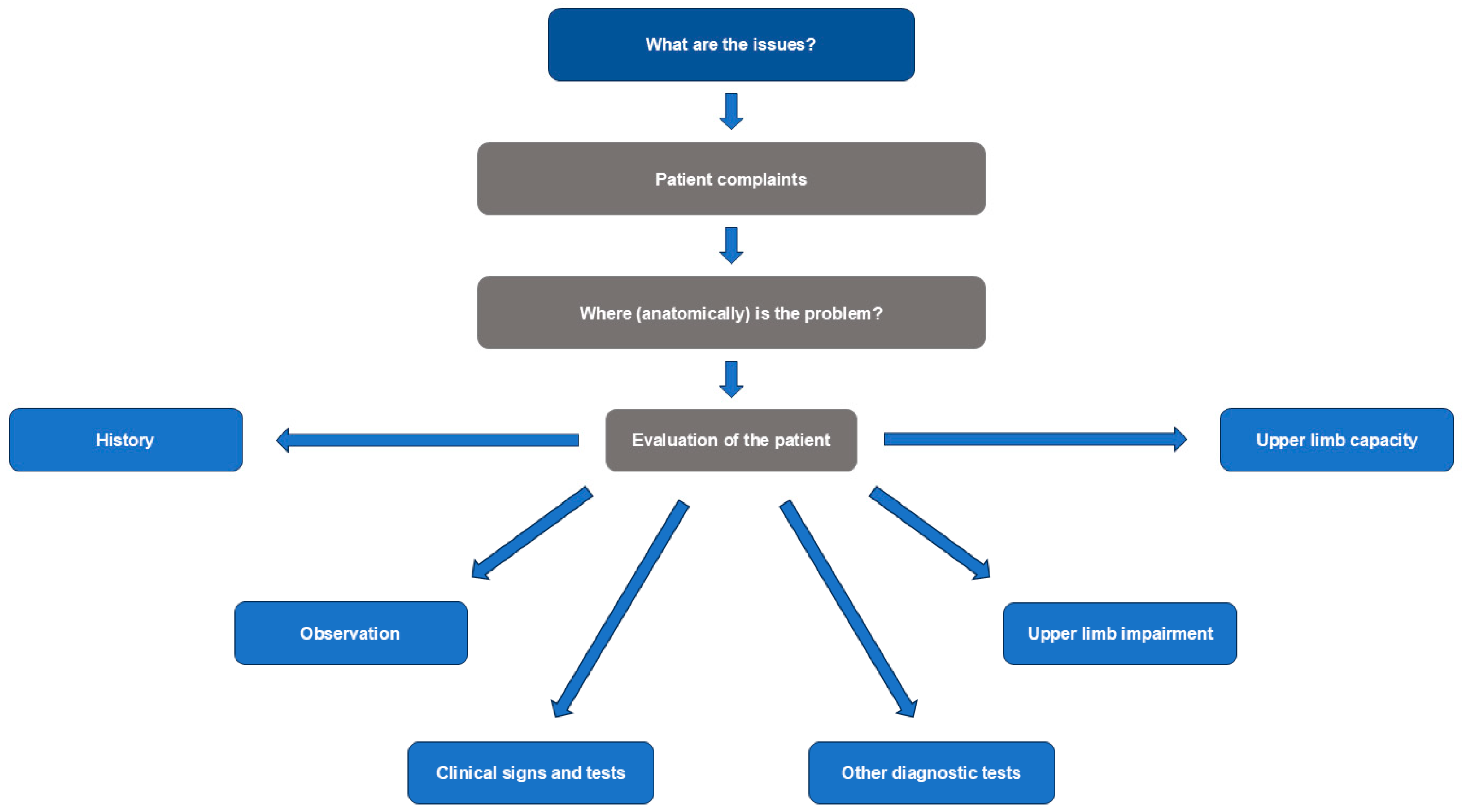
| Diagnostic Component | Tools and Approaches |
|---|---|
| Patient history, including interpretation of reported symptoms | Assess:
|
| Observation of postures and pain responses | Check presence and impact of:
|
| Clinical examination with targeted tests for specific signs | Examine:
|
| Diagnostic tests | Consider the following diagnostic tests:
Assess upper limb capacity with functional tests, for example: |
| Phase 2 | Management Strategies to Consider |
|---|---|
| Acute | |
| Muscle overactivity and no other musculoskeletal involvement |
|
| Muscle overactivity with other musculoskeletal involvement | As above, plus:
|
| Post-acute | |
| Muscle overactivity and no other musculoskeletal involvement |
|
| Muscle overactivity with other musculoskeletal involvement | As above, plus:
|
| Chronic | |
| Muscle overactivity and no other musculoskeletal involvement |
|
| Muscle overactivity with other musculoskeletal involvement | As above, plus:
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biering-Sørensen, B.; Cordero-García, C.; Boulias, C.; Hoad, D.; Bensmail, D.; Molteni, F.; Genêt, F.; Wissel, J.; Jacinto, J.; Marque, P.; et al. Pathways for Diagnosis and Multimodal Management, Including Botulinum Neurotoxin Therapy, in Shoulder Conditions Following Acquired Central Nervous System Lesions. Toxins 2025, 17, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080385
Biering-Sørensen B, Cordero-García C, Boulias C, Hoad D, Bensmail D, Molteni F, Genêt F, Wissel J, Jacinto J, Marque P, et al. Pathways for Diagnosis and Multimodal Management, Including Botulinum Neurotoxin Therapy, in Shoulder Conditions Following Acquired Central Nervous System Lesions. Toxins. 2025; 17(8):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080385
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiering-Sørensen, Bo, Carlos Cordero-García, Chris Boulias, Damon Hoad, Djamel Bensmail, Franco Molteni, François Genêt, Jörg Wissel, Jorge Jacinto, Philippe Marque, and et al. 2025. "Pathways for Diagnosis and Multimodal Management, Including Botulinum Neurotoxin Therapy, in Shoulder Conditions Following Acquired Central Nervous System Lesions" Toxins 17, no. 8: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080385
APA StyleBiering-Sørensen, B., Cordero-García, C., Boulias, C., Hoad, D., Bensmail, D., Molteni, F., Genêt, F., Wissel, J., Jacinto, J., Marque, P., & Berweck, S. (2025). Pathways for Diagnosis and Multimodal Management, Including Botulinum Neurotoxin Therapy, in Shoulder Conditions Following Acquired Central Nervous System Lesions. Toxins, 17(8), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080385





