Immunoinformatics Design and Identification of B-Cell Epitopes from Vespa affinis PLA1 Allergen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Structural Modeling of Ves a 1 and Its B-Cell Epitope Regions Area Analysis
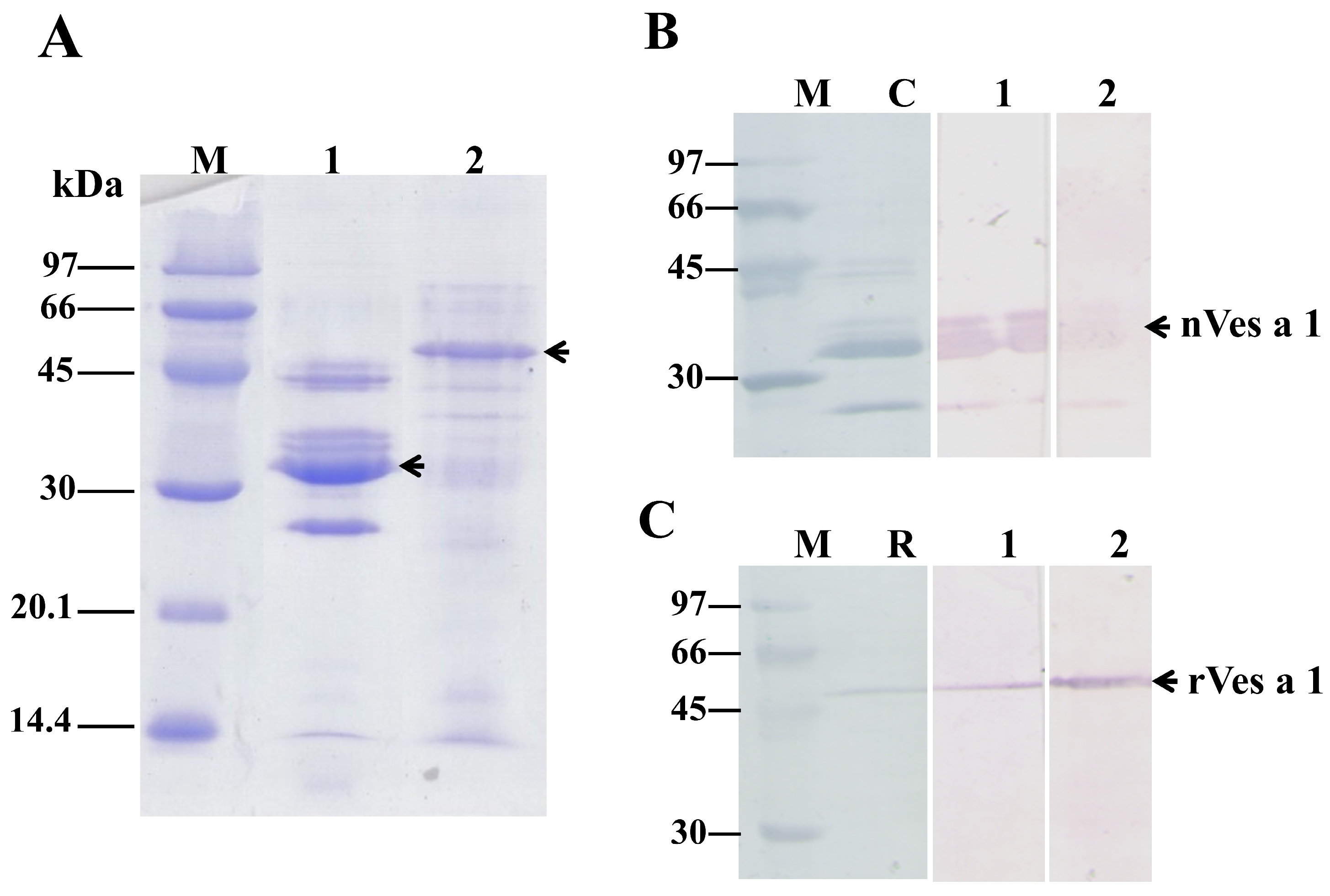
2.2. Production of the nVes a 1 and rVes a 1-Specific Polyclonal Antibodies
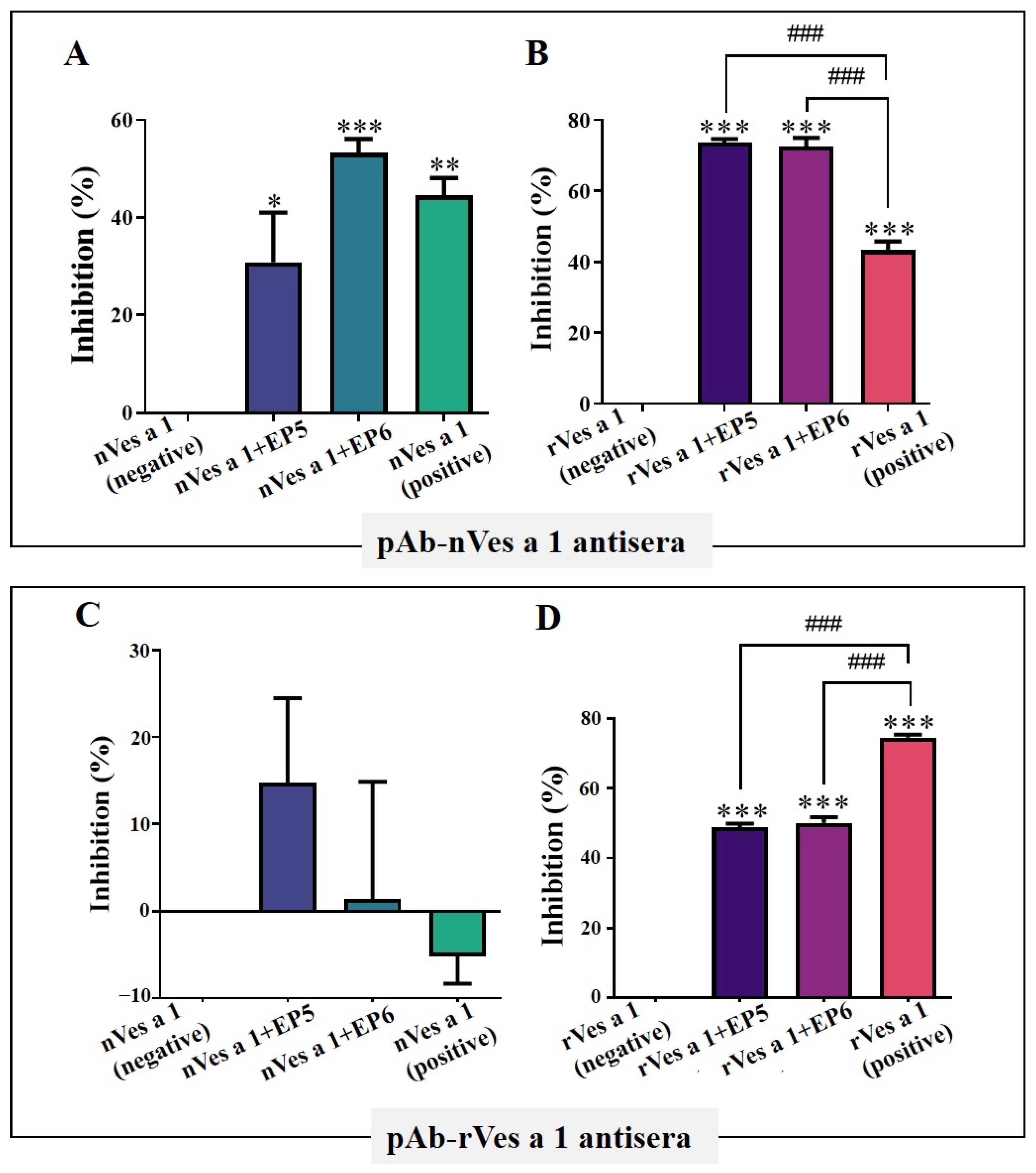
2.3. Inhibition Assay of Synthetic B-Cell Linear Epitope Peptides
2.3.1. Inhibitory Activity by ELISA
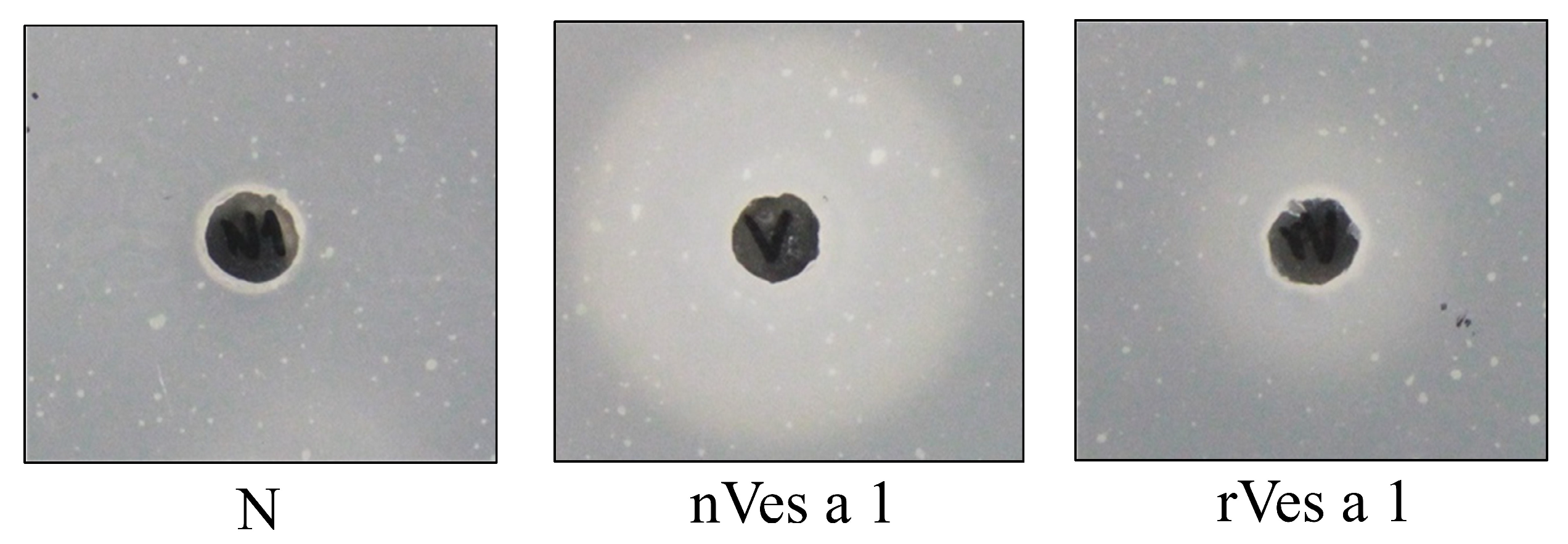
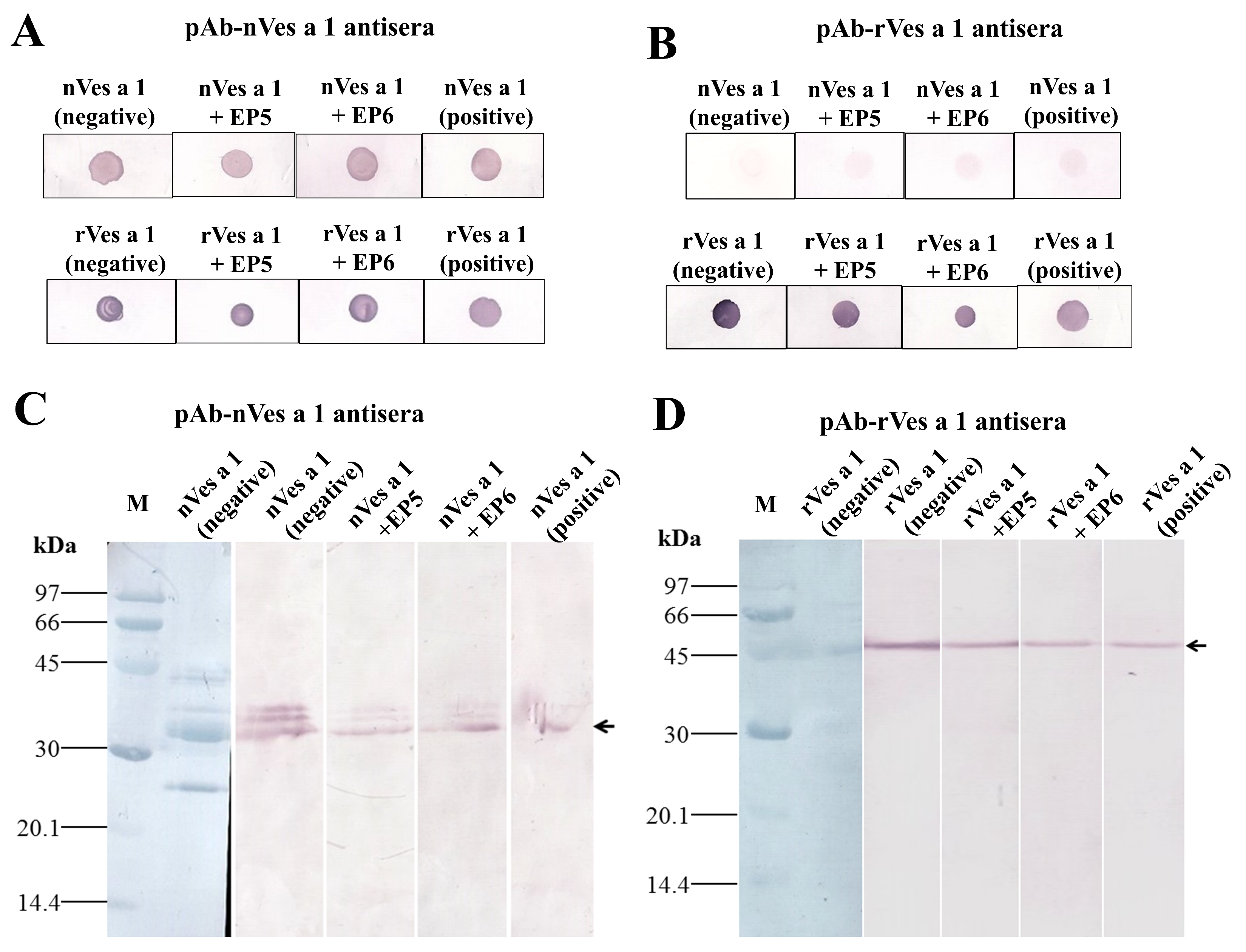
2.3.2. Inhibitory Activity of Synthetic Peptides EP5 and EP6 on the Binding of Polyclonal Antibodies to Native or Recombinant Antigens Evaluated by Dot Blotting and Western Blotting
2.4. Enzymatic Activity
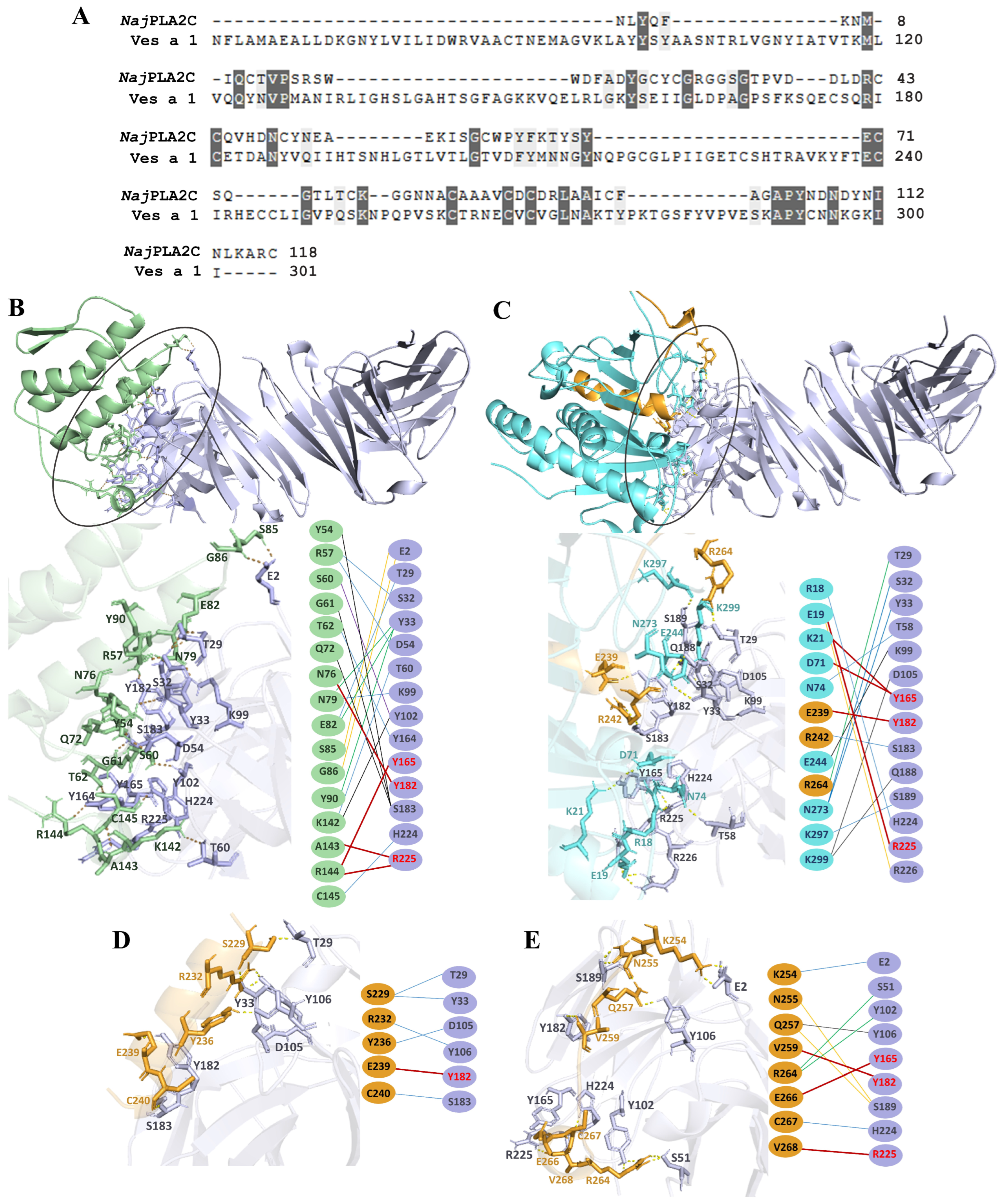
2.5. Molecular Docking
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Ves a 1
5.2. Three-Dimensional Structure Modeling of Ves a 1
5.3. B-Cell Epitope Determinant Prediction and Peptide Synthesis
5.4. One-Dimensional Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
5.5. Mouse Immunizations
5.6. Evaluation of Ves a 1 Antigenicity by ELISA
5.7. Immunoblot Inhibition Assay by ELISA, Dot Blot and Western Blot
5.8. Enzymatic Activity Assay
5.9. Molecular Docking of Ves a 1 and Epitopes with scFv Antibody
5.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EP5 | Synthetic linear epitope peptide of Ves a 1 |
| EP6 | Synthetic linear epitope peptide of Ves a 1 |
| PLA1 | Phospholipase A1 |
| PLA2 | Phospholipase A2 |
| vPLA1 | Vespid phospholipase A1 |
| Ves a 1 | Phospholipase A1 from Vespa affinis venom |
| nVes a 1 | Ves a 1 from crude venom protein |
| rVes a 1 | recombinant Ves a 1 expressed by E. coli |
| pAb-Ves a 1 | Polyclonal antibodies produced by nVes a 1 band from crude venom protein |
| pAb-rVes a 1 | Polyclonal antibodies produced by rVes a 1 band |
| scFv | Single-chain variable fragment antibody |
References
- Das, R.N.; Mukherjee, K. Asian wasp envenomation and acute renal failure: A report of two cases. McGill J. Med. 2008, 11, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, D.R. Allergen in Hymenoptera venom XIV: IgE binding activities of venom proteins from three species of vespids. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1985, 75, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, D.R.; Jacobson, R.S. Allergens in Hymenoptera venom. XII. How much protein in a sting? Ann. Allergy 1984, 52, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- King, T.P.; Alagon, A.C.; Kuan, J.; Sobotka, A.K.; Lichtenstein, L.M. Immunochemical studies of Yellow jacket venom proteins. Mol. Immunol. 1983, 20, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos-Pinto, J.R.A.; dos Santos, L.D.; Arcuri, H.A.; da Silva Menegasso, A.R.; Pego, P.N.; Santos, K.S.; Castro, F.M.; Kalil, J.E.; De-Simone, S.G.; Palma, M.S. B-cell linear epitopes mapping of antigen-5 allergen from Polybia paulista wasp venom. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, M.; Akdis, C.A. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy: Multiple suppressor factors at work in immune tolerance to allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haka, J.; Niemi, M.H.; Mattila, P.; Söderlund, H.; Laukkanen, M.L.; Taivainen, A.; Rytkönen-Nissinen, M.; Virtanen, T. Development of hypoallergenic variants of the major horse allergen Equ c 1 for immunotherapy by rational structure-based engineering. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenner, C.; Mach, L.; Glössl, J.; März, L. The antigenicity of the carbohydrate moiety of an insect glycoprotein, honey-bee (Apis mellifera) venom phospholipase A2. The role of alpha 1,3-fucosylation of the asparagine-bound N-acetylglucosamine. Biochem. J. 1992, 284, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.L.; Hwang, L.L. Local edema induced by the black-bellied hornet (Vespa basalis) venom and its components. Toxicon 1991, 29, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.L.; Hwang, L.L.; Chen, C.T. Edema-inducing activity of a lethal protein with phospholipase A1 activity isolated from the black-bellied hornet (Vespa basalis) venom. Toxicon 1993, 31, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.L.; Lin, Y.L.; Li, S.F. Three toxins with phospholipase activity isolated from the yellow-legged hornet (Vespa velutina) venom. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.P.; Lu, G.; Gonzalez, M.; Qian, N.; Soldatova, L. Yellow jacket venom allergens, hyaluronidase and phospholipase: Sequence similarity and antigenic cross-reactivity with their hornet and wasp homologs and possible implications for clinical allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.D.; Santos, K.S.; de Souza, B.M.; Arcuri, H.A.; Cunha-Neto, E.; Castro, F.M.; Kalil, J.E.; Palma, M.S. Purification, sequencing and structural characterization of the phospholipase A1 from the venom of the social wasp Polybia paulista (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Toxicon 2007, 50, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.P.; Jim, S.Y.; Wittkowski, K.M. Inflammatory role of two venom components of yellow jackets (Vespula vulgaris): A mast cell degranulating peptide mastoparan and phospholipase A1. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2003, 131, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, X.; Ma, D.; Zhang, K.; Lai, R. A phospholipase A1 platelet activator from the wasp venom of Vespa magnifica (Smith). Toxicon 2008, 51, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, M.H.; Chuang, C.Y.; Ko, T.P.; Hu, N.J.; Chou, C.C.; Shih, Y.P.; Ho, C.L.; Wang, A.H.J. Crystal structure of vespid phospholipase A1 reveals insights into the mechanism for cause of membrane dysfunction. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 68, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moein, P.; Zand, R. Cerebral infarction as a rare complication of wasp sting. J. Vasc. Interv. Neurol. 2017, 9, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perez-Riverol, A.; Campos Pereira, F.D.; Musacchio Lasa, A.; Romani Fernandes, L.G.; Santos-Pinto, J.R.; Justo-Jacomini, D.L.; Oliveira de Azevedo, G.; Bazon, M.L.; Palma, M.S.; Zollner, R.L.; et al. Molecular cloning, expression and IgE-immunoreactivity of phospholipase A1, a major allergen from Polybia paulista (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) venom. Toxicon 2016, 124, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odorico, M.; Pellequer, J.L. BEPITOPE: Predicting the location of continuous epitopes and patterns in proteins. J. Mol. Recognit. 2003, 16, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’antonia, F.; Pavkov-Keller, T.; Zangger, K.; Keller, W. Structure of allergens and structure-based epitope predictions. Methods 2014, 66, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Hauser, M.; Himly, M.; Wopfner, N.; Wallner, M.; Ferreira, F. Development of recombinant allergens for diagnosis and therapy. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2009, 1, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Sukprasert, S.; Rungsa, P.; Uawonggul, N.; Incamnoi, P.; Thammasirirak, S.; Daduang, J.; Daduang, S. Purification and structural characterisation of phospholipase A1 (Vespapase, Ves a 1) from Thai banded tiger wasp (Vespa affinis) venom. Toxicon 2013, 61, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungsa, P.; Incamnoi, P.; Sukprasert, S.; Uawonggul, N.; Klaynongsruang, S.; Daduang, J.; Patramanon, R.; Roytrakul, S.; Daduang, S. Comparative proteomic analysis of two wasps venom, Vespa tropica and Vespa affinis. Toxicon 2016, 119, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookrung, N.; Wong-din-Dam, S.; Tungtrongchitr, A.; Reamtong, O.; Indrawattana, N.; Sakolvaree, Y.; Visitsunthorn, N.; Manuyakorn, W.; Chaicumpa, W. Proteome and allergenome of Asian wasp, Vespa affinis, venom and IgE reactivity of the venom components. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haste Andersen, P.; Nielsen, M.; Lund, O. Prediction of residues in discontinuous B-cell epitopes using protein 3D structures. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 2558–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Regenmortel, M.H.V. Mapping epitope structure and activity: From one-dimensional prediction to four-dimensional description of antigenic specificity. Methods 1996, 9, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarvmeili, J.; Baghban Kohnehrouz, B.; Gholizadeh, A.; Shanehbandi, D.; Ofoghi, H. Immunoinformatics design of a structural proteins driven multi-epitope candidate vaccine against different SARS-CoV-2 variants based on fynomer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davarinejad, H. Quantifications of western blots with ImageJ. Univ. York 2015, 854, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Madni, Z.K.; Chaturvedi, S.; Salunke, D.M. Recombinant human scFv antibody fragments against phospholipase A2 from Naja naja and Echis carinatus snake venoms: In vivo neutralization and mechanistic insights. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 165, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermann, E. Bee and wasp venoms. Science 1972, 177, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, D.B.K. Insect sting anaphylaxis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2007, 27, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.R. Allergens in hymenoptera venom: Protein families and structural characteristics. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1993, 100, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bilo, M.B.; Bonifazi, F. Hymenoptera venom immunotherapy. Immunotherapy 2011, 3, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, P.; Handunnetti, S.M.; Premawansa, S.; Kaluarachchi, P.; Karunatilake, C.; Ratnayake, I.P.; Dias, R.K.S.; Premakumara, G.A.S.; Dasanayake, W.M.D.K.; Seneviratne, S.L.; et al. Diagnosis of Vespa affinis venom allergy: Use of immunochemical methods and a passive basophil activation test. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, R.; Niederberger, V. Recombinant allergens for immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, A.; Lasa, A.M.; Santos-Pinto, J.R.A.; Palma, M.S. Insect venom phospholipases A1 and A2: Roles in the envenoming process and allergy. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 105, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonica, G.W.; Cox, L.; Pawankar, R.; Baena-Cagnani, C.E.; Blaiss, M.; Bonini, S.; Bousquet, J.; Calderón, M.; Compalati, E.; Durham, S.R.; et al. Sublingual immunotherapy: World Allergy Organization position paper. World Allergy Organ. J. 2014, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.E.P.; Lund, O.; Nielsen, M. Improved method for predicting linear B-cell epitopes. Immunome Res. 2006, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kringelum, J.V.; Lundegaard, C.; Lund, O.; Nielsen, M. Reliable B cell epitope predictions: Impacts of method development and improved benchmarking. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buus, S.; Rockberg, J.; Forsström, B.; Nilsson, P.; Uhlén, M.; Schafer-Nielsen, C. High-resolution mapping of linear antibody epitopes using ultradense peptide microarrays. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2012, 11, 1790–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wang, Q.; Qi, J.; Shi, Y.; Yan, J.; Gao, G.F. Molecular basis of antibody-mediated neutralization and protection against flavivirus. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, E.; Lane, D. Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Lequin, R.M. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 2415–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chávez-Olórtegui, C.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Diniz, C.R.; Amaral, C.F.S. Clinical and experimental aspects of venom allergy and venom immunotherapy. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 1999, 17, 215–239. [Google Scholar]
- Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Phospholipases A2 from Viperidae snake venoms: How do they induce skeletal muscle damage? Acta Chim. Slov. 2003, 50, 647–662. [Google Scholar]
- De la Rosa, G.; Olvera, F.; Archundia, I.G.; Lomonte, B.; Alagón, A.; Corzo, G. Immunological and toxinological properties of a recombinant phospholipase A1 from Vespa affinis venom. Toxicon 2019, 158, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Arimori, T.; Kitago, Y.; Umitsu, M.; Fujii, Y.; Asaki, R.; Tamura-Kawakami, K.; Takagi, J. Fv-clasp: An artificially designed small antibody fragment with improved production compatibility, stability, and crystallizability. Structure 2017, 25, 1611–1622.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jespersen, M.C.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M.; Marcatili, P. BepiPred-2.0: Improving sequence-based B-cell epitope prediction using conformational epitopes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W24–W29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielkopf, C.L.; Bauer, W.; Urbatsch, I.L. Bradford assay for determining protein concentration. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2020, pdb.prot102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Liang, M.H.; Leu, S.J.; Lin, L.T.; Chiang, J.R.; Yang, Y.Y. Antibodies against venom of the snake Deinagkistrodon acutus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 82, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsch-Ozcürümez, M.; Kischel, N.; Priebe, H.; Splettstösser, W.; Finke, E.J.; Grunow, R. Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Western blotting, microagglutination, indirect immunofluorescence assay, and flow cytometry for serological diagnosis of tularemia. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2004, 11, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, T.; Yang, P.C. Western blot: Technique, theory, and troubleshooting. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 4, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Desta, I.T.; Kotelnikov, S.; Jones, G.; Vajda, S. The ClusPro AbEMap web server for the prediction of antibody epitopes. Nat. Protoc. 2023, 18, 1814–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
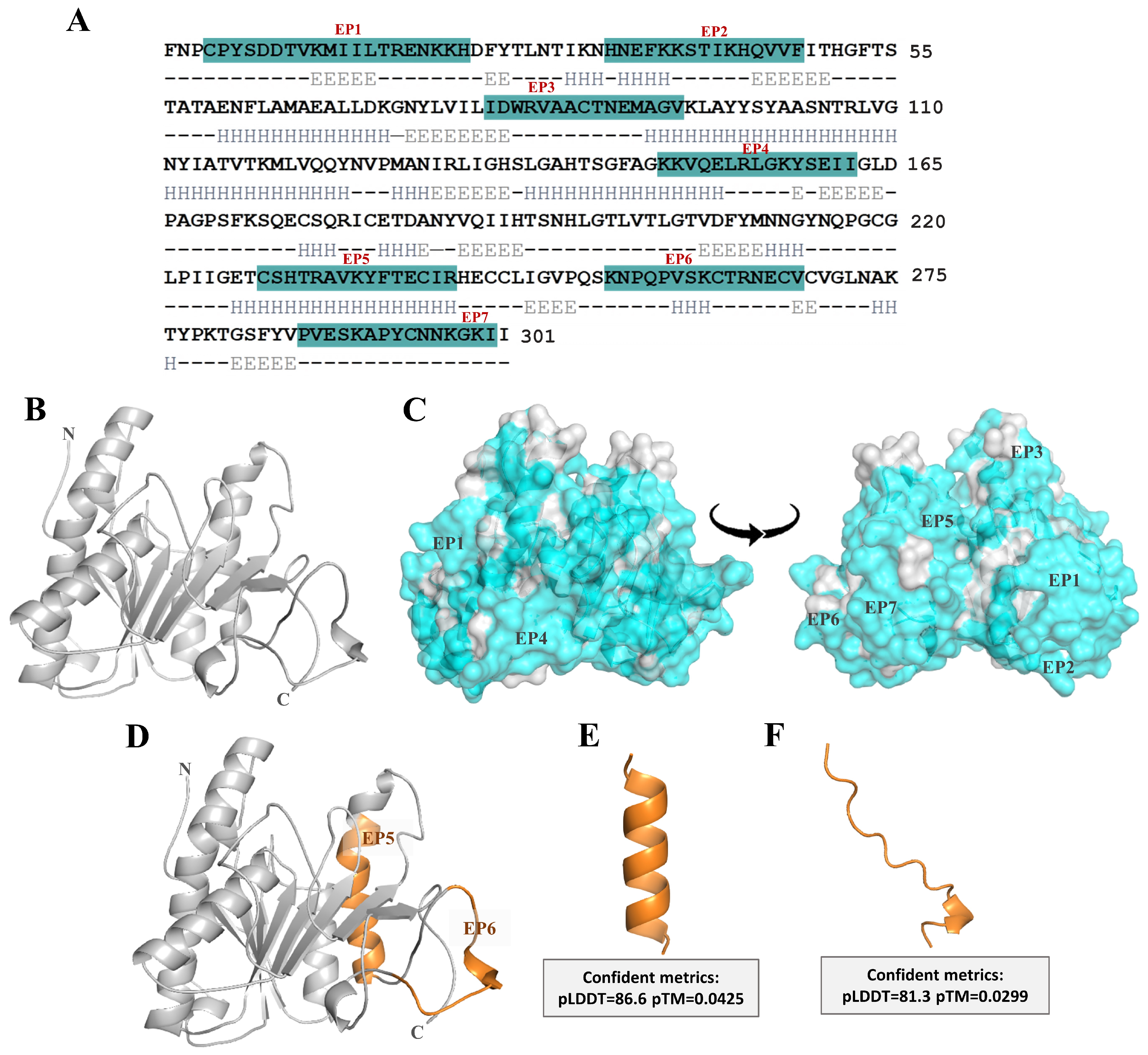

| Epitope | Sequence | Position | Length (Residue) | Probability Scale a | Net Charge | GRAVY b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1 | CPYSDDTVKMIILTRENKKH | 4–23 | 20 | 70.00 | 1.10 | −0.86 |
| EP2 | HNEFKKSTIKHQVVF | 34–48 | 15 | 69.19 | 2.20 | −0.77 |
| EP3 | IDWRVAACTNEMAGV | 80–94 | 15 | 69.34 | −1.00 | 0.38 |
| EP4 | KKVQELRLGKYSEII | 148–16 | 15 | 76.73 | 2.00 | −0.56 |
| EP5 | CSHTRAVKYFTECIR | 228–242 | 15 | 85.91 | 1.82 | −0.32 |
| EP6 | KNPQPVSKCTRNECV | 254–268 | 15 | 80.29 | 1.90 | −1.17 |
| EP7 | PVESKAPYCNNKGKII | 286–301 | 16 | 65.70 | 1.90 | −0.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sukprasert, S.; Nonkhwao, S.; Thanwiset, T.; Keller, W.; Daduang, S. Immunoinformatics Design and Identification of B-Cell Epitopes from Vespa affinis PLA1 Allergen. Toxins 2025, 17, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080373
Sukprasert S, Nonkhwao S, Thanwiset T, Keller W, Daduang S. Immunoinformatics Design and Identification of B-Cell Epitopes from Vespa affinis PLA1 Allergen. Toxins. 2025; 17(8):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080373
Chicago/Turabian StyleSukprasert, Sophida, Siriporn Nonkhwao, Thitijchaya Thanwiset, Walter Keller, and Sakda Daduang. 2025. "Immunoinformatics Design and Identification of B-Cell Epitopes from Vespa affinis PLA1 Allergen" Toxins 17, no. 8: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080373
APA StyleSukprasert, S., Nonkhwao, S., Thanwiset, T., Keller, W., & Daduang, S. (2025). Immunoinformatics Design and Identification of B-Cell Epitopes from Vespa affinis PLA1 Allergen. Toxins, 17(8), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080373





