Biodegradation of Microcystins by Aquatic Bacteria Klebsiella spp. Isolated from Lake Kasumigaura
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
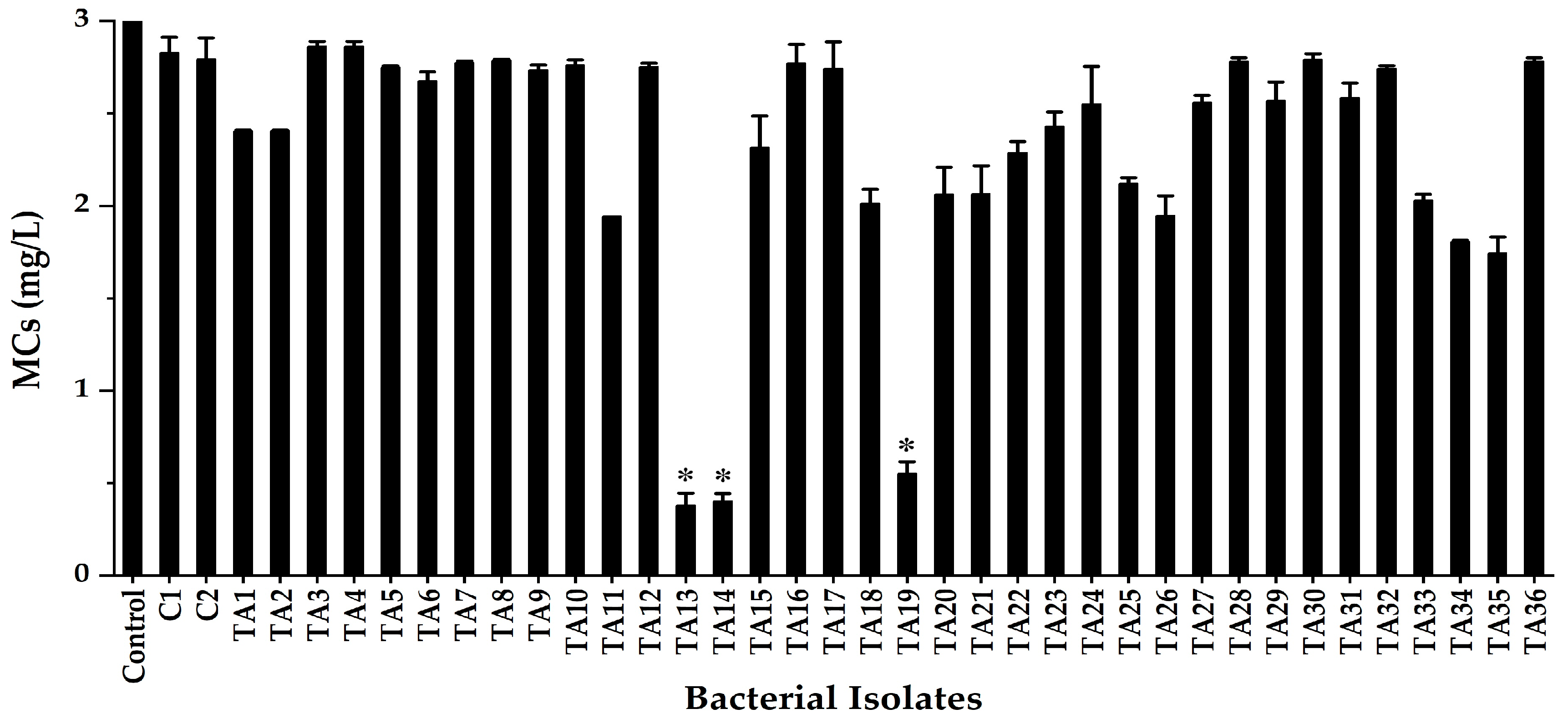
2.1. Isolation of MC-Degrading Bacteria from Lake Kasumigaura
2.2. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis
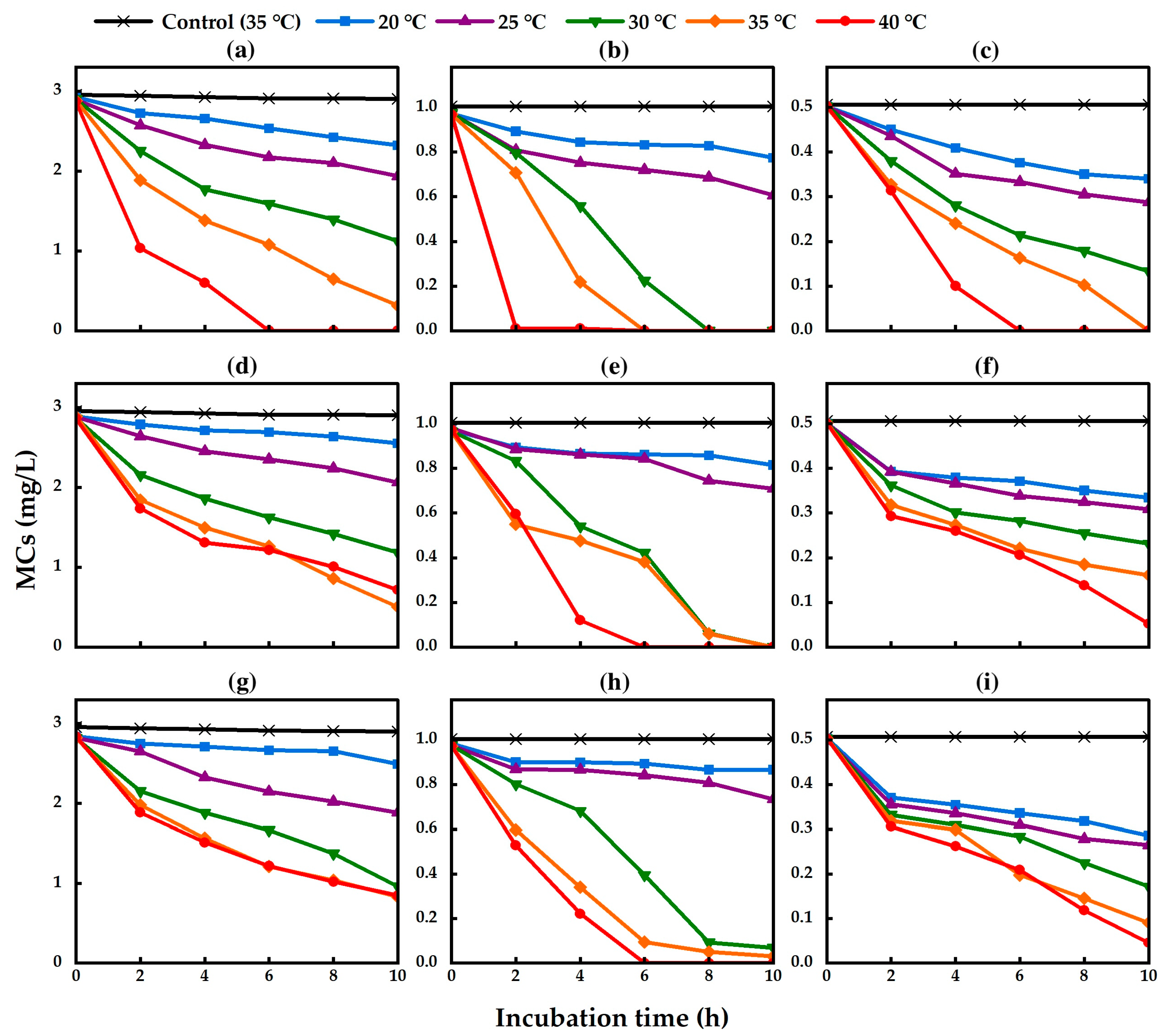
2.3. Effect of Temperature on the Biodegradation of MCs
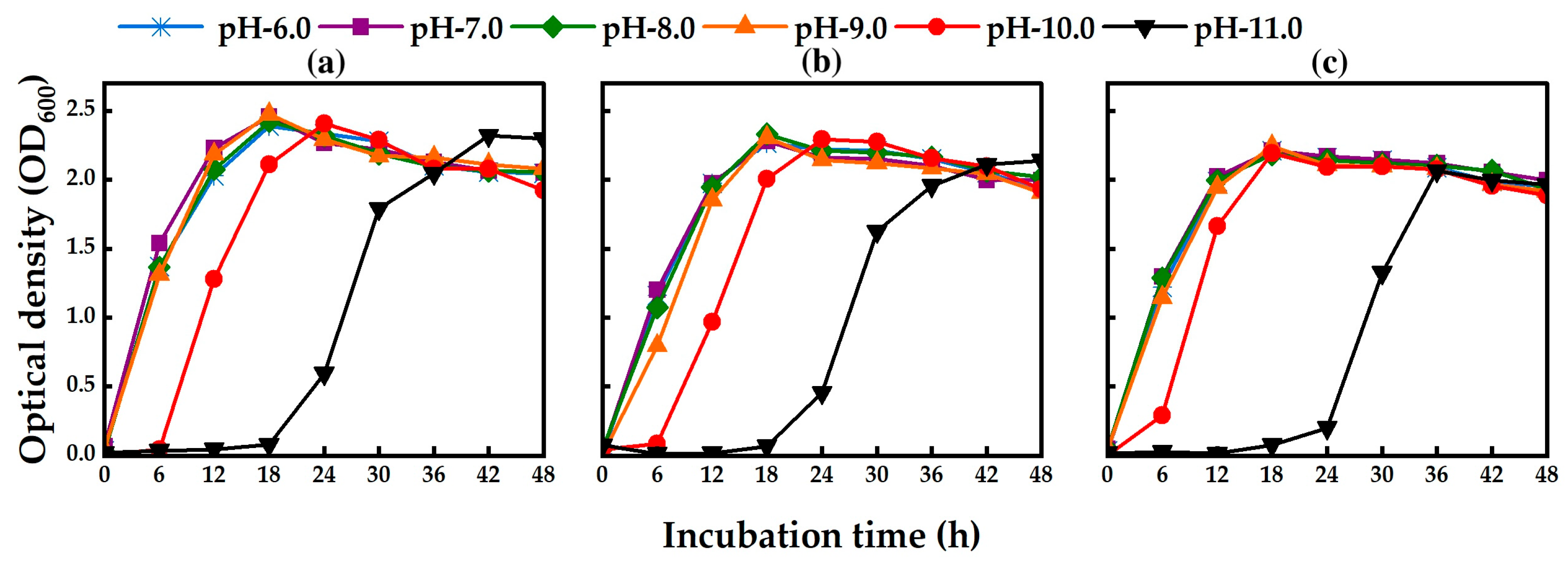
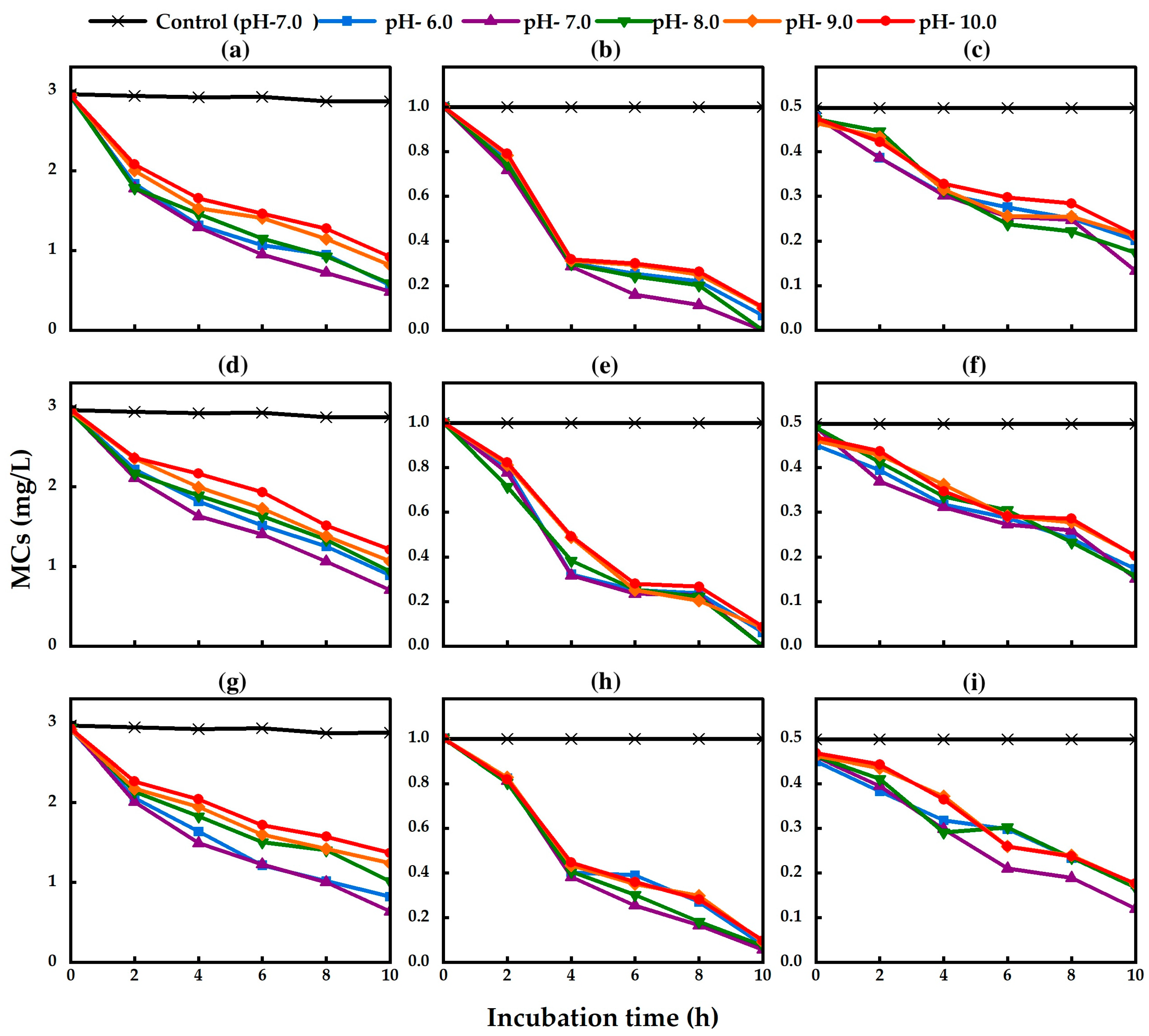
2.4. Effect of pH on Bacterial Growth and Biodegradation of MCs
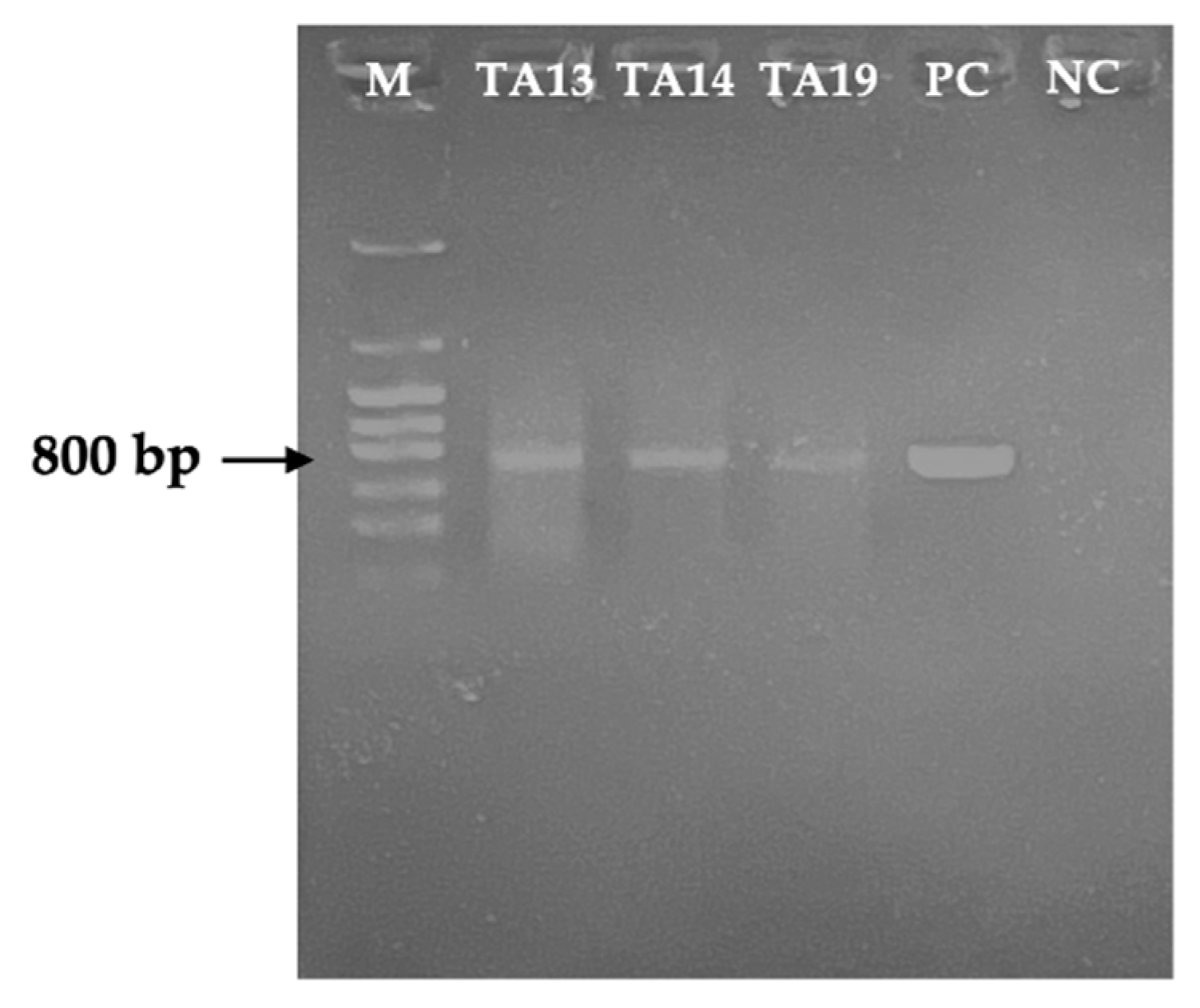
2.5. Detection of the mlrA Gene by PCR
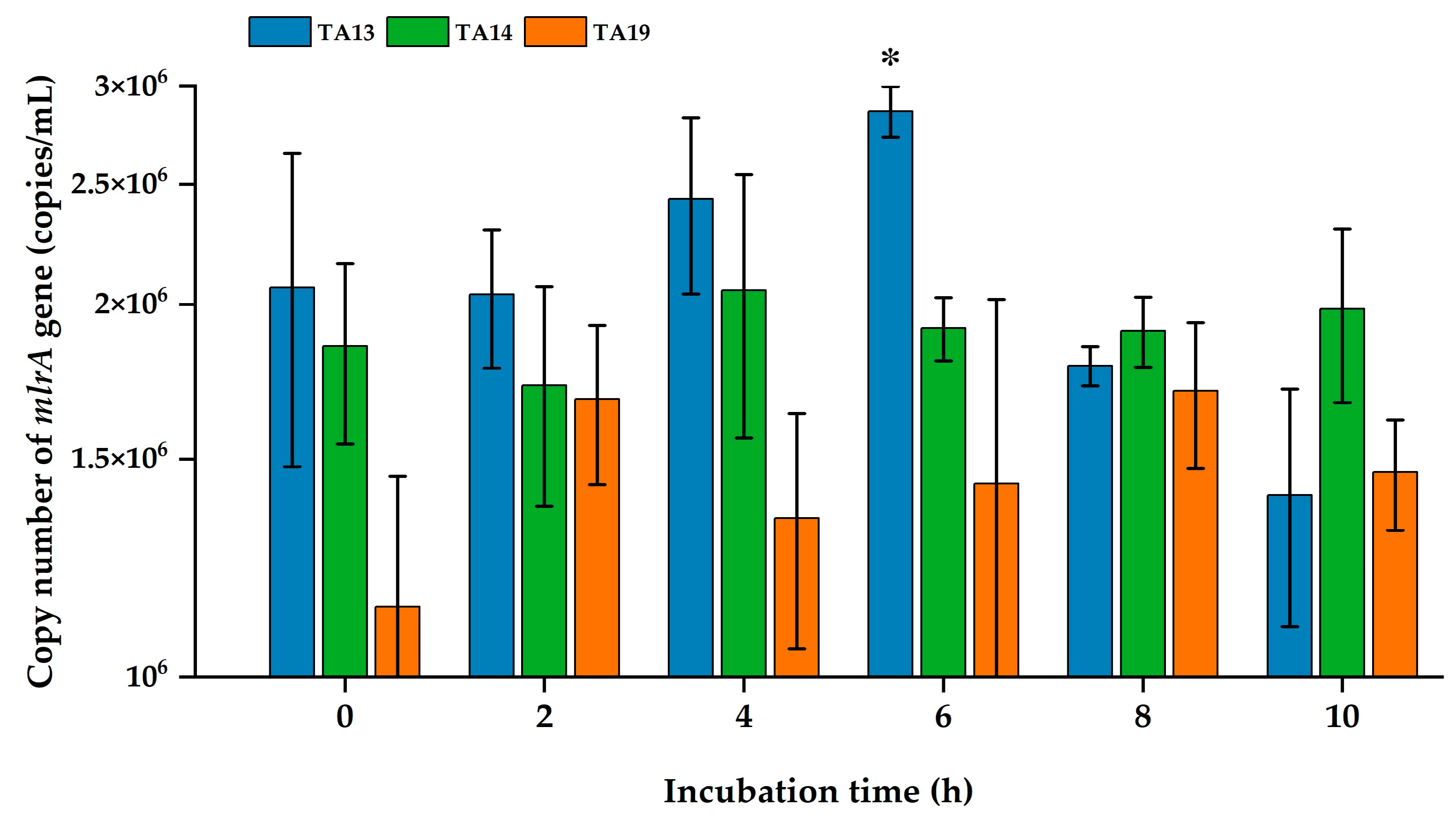
2.6. Quantification of the mlrA Gene by Real-Time PCR (qPCR) Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Water Sample Collection
5.2. Isolation of MC-Degrading Bacteria from Water Samples
5.3. Identification of Isolated MC-Degrading Bacteria
5.4. Purification and Analysis of MCs
5.5. Effect of Temperature on MC Biodegradation
5.6. Effect of pH on Growth of the Isolated Bacteria
5.7. Effect of pH on MC Biodegradation
5.8. Detection of the mlrA Gene in MC-Degrading Bacteria
5.9. Quantification of the mlrA Gene During MC Degradation
5.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, E.A.; Blanchard, P.B.; Bargu, S. Education and public outreach concerning freshwater harmful algal blooms in Southern Louisiana. Harmful Algae 2014, 35, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Beasley, V.R.; Bunner, D.L.; Eloff, J.N.; Falconer, I.R.; Gorham, P.; Harada, K.; Krishnamurthy, T.; Yu, M.J.; Moore, R.E.; et al. Naming of cyclic heptapeptide toxins of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). Toxicon 1988, 26, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivonen, K.; Namikoshi, M.; Evans, W.R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Sun, F.; Rouhiainen, L.; Luukkainen, R.R.; Rinehart, K.L. Isolation and characterization of a variety of microcystins from seven strains of the cyanobacteria genus Anabaena. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, K.; Rapala, J.; Fardig, M.; Niemela, M.; Sivonen, K. Persistence of cyanobacterial hepatotoxin, microcystin-LR in particulate material and dissolved in lake water. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.G.; Yang, X.; Yang, L.L.; Xiao, B.G.; Wu, X.Q.; Wang, J.T. An effective pathway for the removal of microcystin-LR via anoxic biodegradation in lake sediments. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareli, K.; Jaeger, W.; Touka, A.; Frillingos, S.; Briasoulis, E.; Sainis, I. Hepatotoxic seafood poisoning (HSP) due to microcystins: A threat from the ocean? Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2751–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins: Information for Drinking Water Systems. EPA-810F11001; 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2019-07/documents/cyanobacteria_and_cyanotoxins_fact_sheet_for_pws_final_06282019.pdf.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2019).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Drinking Water Health Advisory for the Cyanobacterial Microcystin Toxins; EPA-820R15100; Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Health Effects Support Document for Cyanobacterial Toxin Microcystins; EPA-820R15102; Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Okano, K.; Maseda, H.; Sugita, K.; Saito, T.; Utsumi, M.; Maekawa, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Sugiura, N. Biochemical characteristics of microcystin LR degradation by typical protease. Jpn. J. Water Treat. Biol. 2006, 42, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Somdee, T.; Thunders, M.; Ruck, J.; Lys, I.; Allison, M.; Page, R. Degradation of MC-LR by a microcystin degrading bacterium isolated from Lake Rotoiti, New Zealand. J. Toxicol. 2013, 2013, 596429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, Q.; Ding, Q.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. A novel and native microcystin-degrading bacterium of Sphingopyxis sp. isolated from Lake Taihu. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Yan, H.; Wang, J.; Wei, W.; Ning, J.; Pan, G. Microcystin-LR biodegradation by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2011, 5, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Liu, K.; Xu, K.; Sun, R.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. Further understanding of degradation pathways of microcystin-LR by an indigenous Sphingopyxis sp. in environmentally relevant pollution concentrations. Toxins 2018, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Massey, I.Y.; Guo, J.; Yang, S.; Pu, Y.; Zeng, W.; Tan, H. Microcystin-LR degradation utilizing a novel effective indigenous bacterial community YFMCD1 from Lake Taihu. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2018, 81, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; He, X.; Wu, P.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, S.; Song, X.; He, Y.; Wei, Y.; Ding, P.; et al. Biodegradation of microcystin-RR and nutrient pollutants using Sphingopyxis sp. YF1 immobilized activated carbon fibers-sodium alginate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10811–10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, S.A. Biodegradation of microcystin by a new Bacillus sp. isolated from a Saudi freshwater lake. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 6552–6559. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto, N.; Ohno, N.; Tanaka, K.; Narahara, I.; Ohnishi, A.; Suzuki, M.; Iwami, N.; Mizuochi, M.; Inamori, Y. Degradation of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin by bacteria isolated from a monoxenic culture of the flagellate Monas guttula. Jpn. J. Water Treat. Biol. 2007, 43, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, T.; Sugiura, N.; Itayama, T.; Inamori, Y.; Matsumura, M. Degradation characteristics of microcystins by isolated bacteria from Lake Kasumigaura. J. Water Suppl. Res. Technol. Aqua. 2003, 52, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobac, D.; Tokodi, N.; Simeunovic, J.; Baltic, V.; Stanic, D.; Svircev, Z. Human exposure to cyanotoxins and their effects on health. Arh. Indust. Hig. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivonen, K.; Jones, G. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; E and FN Spon: London, UK, 1999; pp. 41–111. [Google Scholar]
- Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F.; Ding, Z.; Yang, S.; Guo, J.; Tezi, C.; Al-Osman, M.; Kamegni, R.B.; Zeng, W. Exposure routes and health effects of microcystins on animals and humans: A mini-review. Toxicon 2018, 151, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Massey, I.Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, F.; Gao, R.; Ding, M.; Xiang, L.; He, C.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Identification and characterization of a novel indigenous algicidal bacterium Chryseobacterium species against Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2019, 82, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.; Ahmed, Z.; Bakr, A.; Hashem, M.; Alamri, S. Detection of free and bound microcystins in tilapia fish from Egyptian fishpond farms and its related public health risk assessment. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2020, 15, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochimsen, E.M.; Carmichael, W.W.; An, J.S.; Cardo, D.M.; Cookson, S.T.; Holmes, C.E.; Antunes, M.B.; de Melo Filho, D.A.; Lyra, T.M.; Barreto, V.S.; et al. Liver failure and death after exposure to microcystins at a hemodialysis center in Brazil. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.J.; Bourne, D.G.; Blakeley, R.L.; Doelle, H. Degradation of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin by aquatic bacteria. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramani, A.; Rein, K.; Shetty, K.G.; Jayachandran, K. Microbial degradation of microcystin in Florida’s freshwaters. Biodegradation 2012, 23, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hu, L.B.; Zhou, W.; Yan, S.H.; Yang, J.D.; Xue, Y.F.; Shi, Z.Q. Degradation of microcystin-LR and RR by a Stenotrophomonas sp. strain EMS isolated from Lake Taihu, China. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 896–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagala, I.; Mankiewicz-Boczek, J. The natural degradation of microcystins (cyanobacterial hepatotoxins) in fresh water-the future of modern treatment systems and water quality improvement. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 1125–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Kenefick, S.L.; Hrudey, S.E.; Peterson, H.G.; Prepas, E.E. Toxin release from Microcystis aeruginosa after chemical treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.J.; Orr, P.T. Release and degradation of microcystin following algicide treatment of a Microcystis aeruginosa bloom in a recreational lake, as determined by HPLC and protein phosphatase inhibition assay. Water Res. 1994, 28, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, I.T.; Bealing, D.J.; James, H.A.; Sutton, A. Biodegradation of microcystin-LR by indigenous mixed bacterial populations. Water Res. 1996, 30, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F. A mini review on microcystins and bacterial degradation. Toxins 2020, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, K.; Shimizu, K.; Kawauchi, Y.; Maseda, H.; Utsumi, M. Characteristics of a microcystin-degrading bacterium under alkaline environmental conditions. J. Toxicol. 2009, 2009, 954291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shimizu, K.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Utsumi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N. Comparative study for the effects of variable nutrient conditions on the biodegradation of microcystin-LR and concurrent dynamics in microcystin-degrading gene abundance. Biores. Technol. 2011, 102, 9509–9517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; Jones, G.J.; Blakeley, R.L.; Jones, A.; Negri, A.P.; Riddles, P. Enzymatic pathway for the bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin-LR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4086–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Imanishi, S.; Kato, H.; Mizuno, M.; Ito, E.; Tsuji, K. Isolation of Adda from microcystin-LR by microbial degradation. Toxicon 2004, 44, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeria, A.M.; Ricardo, E.J.; Stephan, P.; Alberto, W.D. Degradation of microcystin-RR by Sphingomonas sp. CBA4 isolated from San Roque reservoir (Cordoba-Argentina). Biodegradation 2006, 17, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, L.; Hoefel, D.; Saint, C.P.; Newcombe, G. Isolation and identification of a novel microcystin-degrading bacterium from a biological sand filter. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4685–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Maseda, H.; Okano, K.; Kurashima, T.; Kawauchi, Y.; Xue, Q.; Utsumi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N. Enzymatic pathway for biodegrading microcystin-LR in Sphingopyxis sp. C-1. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, S.A. Biodegradation of microcystin-RR by Bacillus flexus isolated from a Saudi freshwater lake. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 19, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; Riddles, P.; Jones, G.J.; Smith, W.; Blakeley, R.L. Characterization of a gene cluster involved in bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-LR. Environ. Toxicol. 2001, 16, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseda, H.; Shimizu, K.; Doi, Y.; Inamori, Y.; Utsumi, M.; Sugiura, N.; Kobayashi, M. MlrA located in the inner membrane is essential for initial degradation of microcystin in Sphingopyxis sp. C-1. Jpn. J. Water Treat. Biol. 2012, 48, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saito, T.; Okano, K.; Park, H.D.; Itayama, T.; Inamori, Y.; Neilan, B.A.; Burns, B.P.; Sugiura, N. Detection and sequencing of the microcystin LR-degrading gene, mlrA, from new bacteria isolated from Japanese lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 229, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, L.; Zhu, G.; Liang, G.; Pu, Y. Microcystin-degrading activity of an indigenous bacterial strain Stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila MC- LTH2 isolated from Lake Taihu. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for drinking-water quality. In Health Criteria and Other Supporting Information, 2nd ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998; Volume 2, pp. 95–110. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.D.; Sasaki, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Yanagisawa, E.; Hiraishi, A.; Kato, K. Degradation of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin by a new bacterium isolated from a hypertrophic lake. Environ. Toxicol. 2001, 16, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, R.; Wei, H.; Li, Y.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. Biodegradation of microcystin-LR and -RR by a novel microcystin-degrading bacterium isolated from Lake Taihu. Biodegradation 2014, 25, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, C.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y. Simultaneous degradation of tetracycline and denitrification by a novel bacterium, Klebsiella sp. SQY5. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, M.; Qu, J.; Ying Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Characterization and mechanism analysis of tylosin biodegradation and simultaneous ammonia nitrogen removal with strain Klebsiella pneumoniae TN-1. Biores. Technol. 2021, 336, 125342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Li, C.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Chen, R.; Yin, X.; Li, T.; Wu, S. Biodegradation of phthalate isomers by newly isolated Klebsiella variico SY1 and its functional genomic analysis. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2023, 178, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Zhang, Y.; Mou, X. Isolation and characterization of microcystin-degrading bacteria from Lake Erie. Bull. Environ. Contami. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Maseda, H.; Okano, K.; Itayama, T.; Kawauchi, Y.; Chen, R.; Utsumi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N. How microcystin-degrading bacteria express microcystin degradation activity. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2011, 16, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Shen, M.; Bai, P.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Gan, N.; Li, T.; Zhao, J. Microcystin-LR degradation and gene regulation of microcystin-degrading Novosphingobium sp. THN1 at different carbon concentrations. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, N.; Watanabe, M.M. Seasonal changes in the biomass of four species of Microcystis in Lake Kasumigaura. Jpn. J. Limnol. 1987, 48, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, K.; Watanabe, M.M. Microcystin composition of an axenic clonal strain of Microcystis viridis and Microcystis viridis-containing water blooms in Japanese freshwaters. J. Appl. Phycol. 1990, 2, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, T.; Yagi, O.; Takamura, Y.; Sudo, R. Isolation of bacteria-free Microcystis aeruginosa from Lake Kasumigaura. J. Jpn. Socie. Water Environ. 1984, 7, 437–442. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, K.I.; Matsuura, K.; Suzuki, M.; Oka, H.; Watanabe, M.F.; Oishi, S.; Dahlem, A.M.; Beasley, V.R.; Carmichael, W.W. Analysis and purification of toxic peptides from cyanobacteria by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1988, 448, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoefel, D.; Adriansen, C.M.M.; Bouyssou, M.A.C.; Saint, C.P.; Newcombe, G.; Ho, L. Development of an mlrA gene-directed TaqMan PCR assay for quantitative assessment of microcystin-degrading bacteria within water treatment plant sand filter biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5167–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, G.; Shao, J.; Tan, W. Establishment and field applications of real-time PCR methods for the quantification of potential MIB-producing cyanobacteria in aquatic systems. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
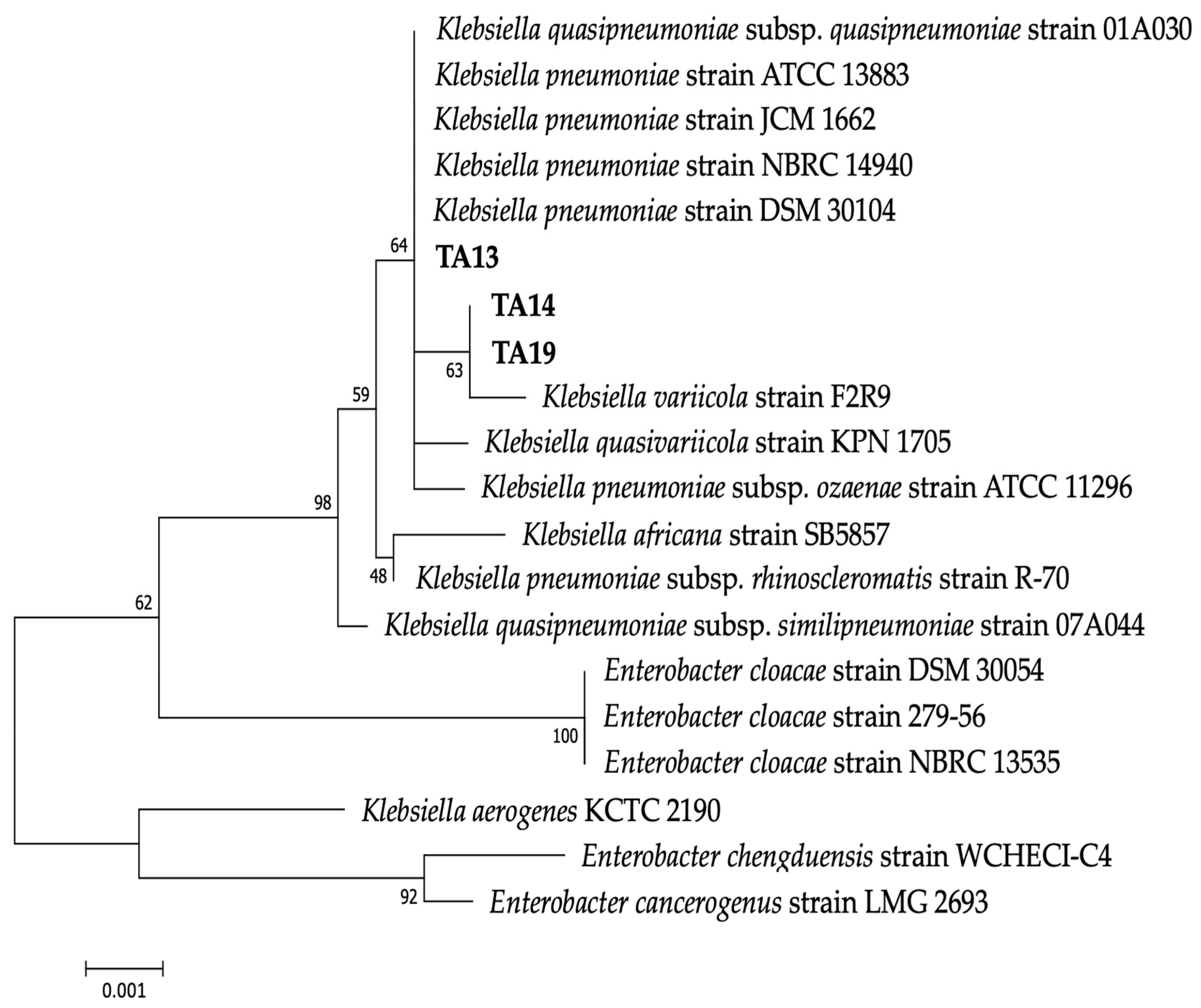
| Strain | Gene Bank Accession No. | Closely Related sp. | Strain No. | Sequence (bp) | Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA13 | LC791357 | Klebsiella pneumoniae (NR_117683.1) | DSM 30104 | 1454/1459 | 99.7 |
| TA14 | LC791358 | Klebsiella variicola (NR_025635.1) | F2R9 | 1408/1412 | 99.7 |
| TA19 | LC791359 | Klebsiella variicola (NR_025635.1) | F2R9 | 1408/1412 | 99.7 |
| Strain | Degradation Rate (mg L−1 h−1) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | 25 °C | 30 °C | 35 °C | 40 °C | |||||||||||
| MC-RR | MC-YR | MC-LR | MC-RR | MC-YR | MC-LR | MC-RR | MC-YR | MC-LR | MC-RR | MC-YR | MC-LR | MC-RR | MC-YR | MC-LR | |
| TA13 | 0.064 a | 0.020 a | 0.016 a | 0.110 ab | 0.037 a | 0.021 ab | 0.194 bc | 0.122 b | 0.037 bc | 0.293 c | 0.161 b | 0.050 c | 0.494 d | 0.484 c | 0.126 d |
| TA14 | 0.047 a | 0.016 a | 0.019 a | 0.099 ab | 0.027 a | 0.019 a | 0.175 bc | 0.109 b | 0.027 ab | 0.229 c | 0.109 b | 0.034 b | 0.239 c | 0.243 c | 0.045 c |
| TA19 | 0.046 a | 0.012 a | 0.022 a | 0.104 ab | 0.024 a | 0.024 a | 0.196 bc | 0.103 ab | 0.033 ab | 0.207 bc | 0.107 ab | 0.041 b | 0.227 c | 0.142 b | 0.046 b |
| Strain | Degradation Rate (mg L−1 h−1) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 6.0 | pH 7.0 | pH 8.0 | pH 9.0 | pH 10.0 | |||||||||||
| MC-RR | MC-YR | MC-LR | MC-RR | MC-YR | MC-LR | MC-RR | MC-YR | MC-LR | MC-RR | MC-YR | MC-LR | MC-RR | MC-YR | MC-LR | |
| TA13 | 0.236 ab | 0.094 a | 0.028 a | 0.247 b | 0.100 a | 0.035 a | 0.235 ab | 0.100 a | 0.030 a | 0.213 ab | 0.090 a | 0.026 a | 0.203 a | 0.090 a | 0.026 a |
| TA14 | 0.205 ab | 0.094 a | 0.032 a | 0.224 b | 0.100 a | 0.034 a | 0.200 ab | 0.100 a | 0.033 a | 0.188 ab | 0.092 a | 0.029 a | 0.176 a | 0.092 a | 0.029 a |
| TA19 | 0.209 a | 0.092 a | 0.032 a | 0.229 a | 0.095 a | 0.037 a | 0.192 a | 0.093 a | 0.032 a | 0.167 a | 0.091 a | 0.032 a | 0.156 a | 0.091 a | 0.031 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, T.; Shimizu, K.; Liu, T.; Li, Q.; Utsumi, M. Biodegradation of Microcystins by Aquatic Bacteria Klebsiella spp. Isolated from Lake Kasumigaura. Toxins 2025, 17, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070346
Lin T, Shimizu K, Liu T, Li Q, Utsumi M. Biodegradation of Microcystins by Aquatic Bacteria Klebsiella spp. Isolated from Lake Kasumigaura. Toxins. 2025; 17(7):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070346
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Thida, Kazuya Shimizu, Tianxiao Liu, Qintong Li, and Motoo Utsumi. 2025. "Biodegradation of Microcystins by Aquatic Bacteria Klebsiella spp. Isolated from Lake Kasumigaura" Toxins 17, no. 7: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070346
APA StyleLin, T., Shimizu, K., Liu, T., Li, Q., & Utsumi, M. (2025). Biodegradation of Microcystins by Aquatic Bacteria Klebsiella spp. Isolated from Lake Kasumigaura. Toxins, 17(7), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070346





