A Comprehensive Review of Detection Methods for Staphylococcus aureus and Its Enterotoxins in Food: From Traditional to Emerging Technologies
Abstract
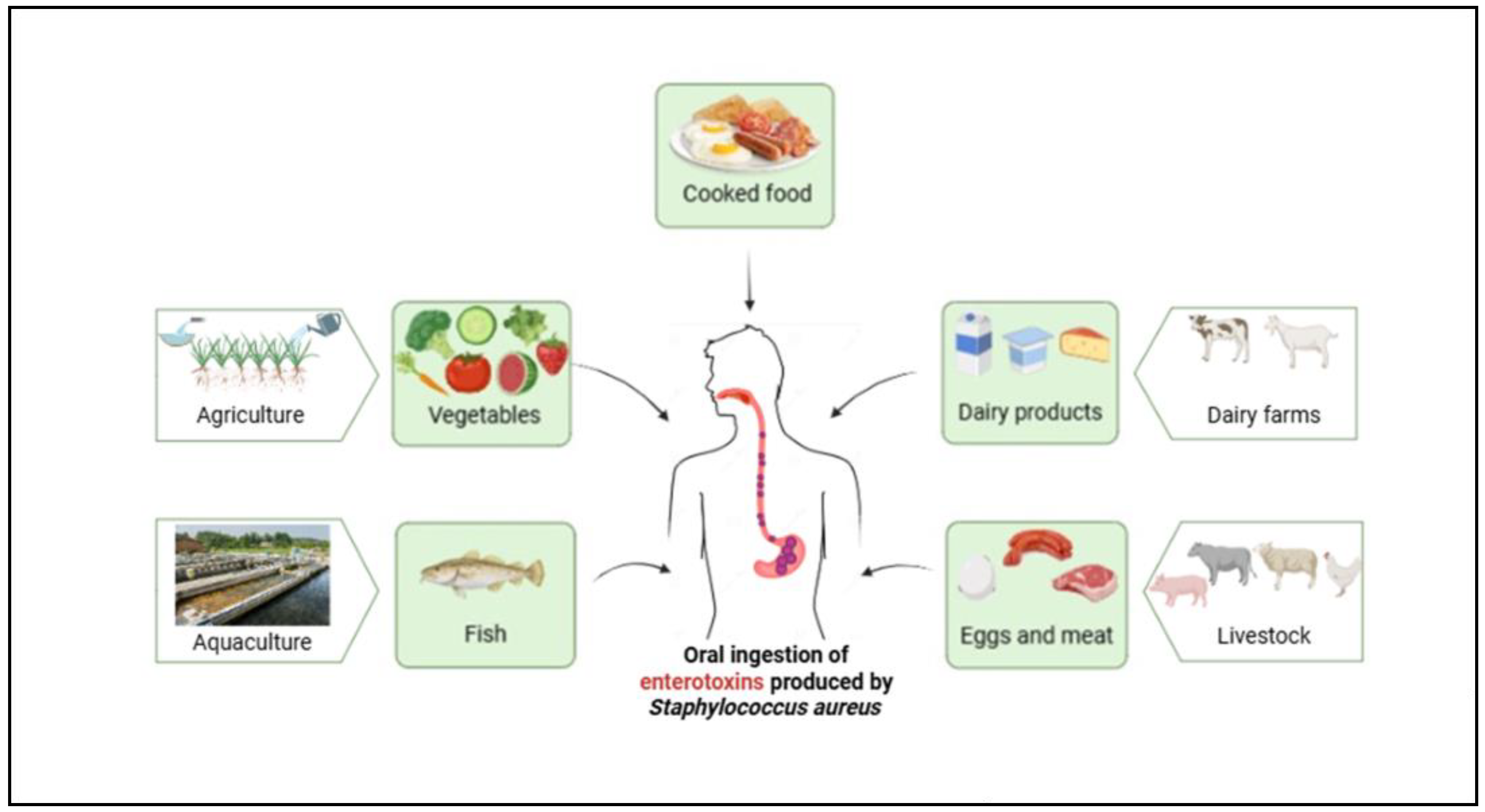
1. Introduction
2. Sample Preparation and Pretreatment Methods for Staphylococcus aureus and Detection of Its Toxin in Food Matrices
3. Microbiological Methods
3.1. Objective and Methodology
3.2. Performance
3.3. Limitations/Challenges
4. Biochemical Methods
4.1. Objective and Methodology
4.2. Performance
4.3. Limitations/Challenges
5. Mass Spectrometry-Based Methods
5.1. Objective and Methodology
5.2. Performance
5.3. Limitations/Challenges
6. Immunological Methods for Detecting Staphylococcus aureus and Its Enterotoxins in Foodborne Intoxication Epidemics
6.1. Objective and Methodology
6.2. Performance
6.3. Limitations and Challenges
7. PCR-Based Methods
7.1. Objective and Methodology
7.2. Performance
7.3. Limitations/Challenges
8. Isothermal Amplification-Based Methods
8.1. Objective and Methodology
8.2. Performance
8.3. Limitations/Challenges
9. Sequencing-Based Methods
9.1. Objective and Methodology
9.2. Performance
9.3. Limitations/Challenges
10. Sequence-Based Typing Methods
10.1. Objective and Methodology
10.2. Performance
10.3. Limitations/Challenges
11. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis-Based Methods
11.1. Objective and Methodology
11.2. Performance
11.3. Limitations/Challenges
12. Other Molecular-Based Methods
12.1. NAuRA (Nice Automatic Research of Alleles)
12.1.1. Objective and Methodology
12.1.2. Performance
12.1.3. Limitations/Challenges
12.2. CCB-Detection
12.2.1. Objective and Methodology
12.2.2. Performance
12.2.3. Limitations/Challenges
12.3. DNA Microarray
12.3.1. Objective and Methodology
12.3.2. Performance
12.3.3. Limitations/Challenges
12.4. PCR-SSCP (Polymerase Chain Reaction–Single-Strand Conformation Polymorphism)
12.4.1. Objective and Methodology
12.4.2. Performance
12.4.3. Limitations/Challenges
12.5. Plasmid Profiling
12.5.1. Objective and Methodology
12.5.2. Performance
12.5.3. Limitations/Challenges
12.6. RAPD (Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA)
12.6.1. Objective and Methodology
12.6.2. Performance
12.6.3. Limitations/Challenges
12.7. Rep-PCR (Repetitive Sequence-Based PCR)
12.7.1. Objective and Methodology
12.7.2. Performance
12.7.3. Limitations/Challenges
12.8. MLVA (Multiple-Locus Variable-Number Tandem Repeat Analysis)
12.8.1. Objective and Methodology
12.8.2. Performance
12.8.3. Limitations/Challenges
13. Biosensor-Based Methods
13.1. Objective and Methodology
13.2. Performance
13.3. Limitations/Challenges
14. AI-Based Methods
14.1. Objective and Methodology
14.2. Performance
14.3. Limitations/Challenges
15. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denayer, S.; Delbrassinne, L.; Nia, Y.; Botteldoorn, N. Food-Borne Outbreak Investigation and Molecular Typing: High Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus Strains and Importance of Toxin Detection. Toxins 2017, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennekinne, J.-A.; De Buyser, M.-L.; Dragacci, S. Staphylococcus aureus and Its Food Poisoning Toxins: Characterization and Outbreak Investigation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.; Boost, M.V.; O’Donoghue, M.M. Tracking Sources of Staphylococcus aureus Hand Contamination in Food Handlers by Spa Typing. Am. J. Infect. Control 2015, 43, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, R.A.C.; Ferreira, F.A.; Rubio Cieza, M.Y.; Silva, N.C.C.; Miotto, M.; Carvalho, M.M.; Bazzo, B.R.; Botelho, L.A.B.; Dias, R.S.; De Dea Lindner, J. Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Traditional Artisanal Raw Milk Cheese from Southern Brazil: Diversity, Virulence, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile. J. Food Prot. 2024, 87, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mairi, A.; Touati, A.; Pantel, A.; Zenati, K.; Martinez, A.Y.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.-P. Distribution of Toxinogenic Methicillin-Resistant and Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus from Different Ecological Niches in Algeria. Toxins 2019, 11, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Féraudet Tarisse, C.; Goulard-Huet, C.; Nia, Y.; Devilliers, K.; Marcé, D.; Dambrune, C.; Lefebvre, D.; Hennekinne, J.-A.; Simon, S. Highly Sensitive and Specific Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxins SEA, SEG, SEH, and SEI by Immunoassay. Toxins 2021, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Dou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, H.; Wen, K.; Yu, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. A Comprehensive Review on the Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins in Food Samples. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncarevic, S.; Jørgensen, H.J.; Løvseth, A.; Mathisen, T.; Rørvik, L.M. Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxin Types within Single Samples of Raw Milk and Raw Milk Products. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouharova, M.; Rysanek, D. Multiplex PCR and RPLA Identification of Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxigenic Strains from Bulk Tank Milk. Zoonoses Public Health 2008, 55, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Park, Y.K.; Koo, H.C.; Park, Y.H. Spa Typing and Enterotoxin Gene Profile of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bovine Raw Milk in Korea. J. Vet. Sci. 2010, 11, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Deepak, S.J.; Kannan, P.; Savariraj, W.R.; Ayyasamy, E.; Tuticorin Maragatham Alagesan, S.K.; Ravindran, N.B.; Sundaram, S.; Mohanadasse, N.Q.; Kang, Q.; Cull, C.A.; et al. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Milk Samples for Their Virulence, Biofilm, and Antimicrobial Resistance. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiśniewski, P.; Gajewska, J.; Zadernowska, A.; Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W. Identification of the Enterotoxigenic Potential of Staphylococcus Spp. from Raw Milk and Raw Milk Cheeses. Toxins 2023, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Sun, B.; Jiang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Shang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Lv, C.; Guo, C.; et al. Genetic Diversity, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus from Raw Milk over 10 Years in Shanghai. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 401, 110273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostyn, A.; Guillier, F.; Prufer, A.-L.; Papinaud, I.; Messio, S.; Krys, S.; Lombard, B.; Hennekinne, J.-A. Intra-Laboratory Validation of the Ridascreen® SET Total Kit for Detecting Staphylococcal Enterotoxins SEA to SEE in Cheese. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleny, R.; Nia, Y.; Schimmel, H.; Mutel, I.; Hennekinne, J.-A.; Emteborg, H.; Charoud-Got, J.; Auvray, F. Certified Reference Materials for Testing of the Presence/Absence of Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxin A (SEA) in Cheese. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 5457–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Yamada, K.; Ikami, M.; Kaji, N.; Tokeshi, M.; Atsumi, Y.; Mizutani, M.; Murai, A.; Okamoto, A.; Namikawa, T.; et al. Application of IgY to Sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays, Lateral Flow Devices, and Immunopillar Chips for Detecting Staphylococcal Enterotoxins in Milk and Dairy Products. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 92, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, A.; Ahari, H.; Shahbazzadeh, D. Designing a Direct ELISA Kit for the Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxin A in Raw Milk Samples. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrada, H.; Soriano, J.M.; Mañes, J.; Picó, Y. Real-Time Quantitative PCR of Staphylococcus aureus and Application in Restaurant Meals. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararaj, N.; Kalagatur, N.K.; Mudili, V.; Krishna, K.; Antonysamy, M. Isolation and Identification of Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Indian Food Samples: Evaluation of in-House Developed Aptamer Linked Sandwich ELISA (ALISA) Method. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwe, Y.H.; Mohan, R.D.; Lim, S.J.; Lai, W.C.; Sim, K.H.; Leyau, Y.L.; Lew, K.; Chua, J.M.C.; Aung, K.T.; Chng, K.R.; et al. Occurrence & Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus from Ready-to-Eat (RTE), and Cooked Food in Singapore: A Retrospective Analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 436, 111213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Vittal, R.; Raj, J.M.; Chakraborty, G. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): A Sensitive Molecular Tool for Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Meat and Dairy Product. Braz. J. Microbiol. Publ. Braz. Soc. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, R.; Johler, S.; Sihto, H.-M.; Stephan, R.; Zweifel, C. Microarray-Based Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Obtained from Chicken Carcasses. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Larsen, J.; Kjeldgaard, J.; Andersen, P.S.; Skov, R.; Ingmer, H. Methicillin-Resistant and -Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus from Retail Meat in Denmark. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 249, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manukumar, H.M.; Umesha, S. MALDI-TOF-MS Based Identification and Molecular Characterization of Food Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, A.; Wang, K.; Mao, Y.; Yuan, L.; Ye, Y.; Chen, L.; Zou, Y.; Huang, T. First Report on the Rapid Detection and Identification of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Viable but Non-Culturable (VBNC) Under Food Storage Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 615875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Cui, J.Y.; Sun, L.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.L. Cross-priming Amplification Targeting the Coagulase Gene for Rapid Detection of Coagulase-positive Staphylococci. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhme, K.; Morandi, S.; Cremonesi, P.; Fernández No, I.C.; Barros-Velázquez, J.; Castiglioni, B.; Brasca, M.; Cañas, B.; Calo-Mata, P. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Italian Dairy Products by MALDI-TOF Mass Fingerprinting. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulajic, S.; Colovic, S.; Misic, D.; Djordjevic, J.; Savic-Radovanovic, R.; Asanin, J.; Ledina, T. Enterotoxin Production and Antimicrobial Susceptibility in Staphylococci Isolated from Traditional Raw Milk Cheeses in Serbia. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2017, 52, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonacini, J.; Stephan, D.; Vogel, G.; Avondet, M.-A.; Kalman, F.; Crovadore, J.; Lefort, F.; Schnyder, B. Intact Staphylococcus Enterotoxin SEB from Culture Supernatant Detected by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2019, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léguillier, V.; Pinamonti, D.; Chang, C.-M.; Gunjan; Mukherjee, R.; Himanshu; Cossetini, A.; Manzano, M.; Anba-Mondoloni, J.; Malet-Villemagne, J.; et al. A Review and Meta-Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Prevalence in Foods. Microbe 2024, 4, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissong, M.E.A.; Tahnteng, B.F.; Ateba, C.N.; Akoachere, J.-F.T.K. Pathogenic Potential and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Staphylococcus aureus in Milk and Beef from the Northwest and Southwest Regions of Cameroon. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6015283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Dong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Zheng, N. Antimicrobial Susceptibility, and Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Different Raw Milk Samples in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 840670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basanisi, M.G.; La Bella, G.; Nobili, G.; Franconieri, I.; La Salandra, G. Genotyping of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolated from Milk and Dairy Products in South Italy. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Oh, D.H.; Song, B.R.; Heo, E.J.; Lim, J.S.; Moon, J.S.; Park, H.J.; Wee, S.H.; Sung, K. Molecular Characterization, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Factors of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Imported and Domestic Meat in Korea. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.A.; Shah, S.H.H.; Sherafzal, Y.; Shafi-Ur-Rehman, S.; Khan, M.A.; Barrett, J.B.; Woodley, T.A.; Jamil, B.; Abbasi, S.A.; Jackson, C.R. Detection and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Table Eggs in Haripur, Pakistan. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiimwe, B.B.; Baldan, R.; Trovato, A.; Cirillo, D.M. Prevalence and Molecular Characteristics of Staphylococcus Aureus, Including Methicillin Resistant Strains, Isolated from Bulk Can Milk and Raw Milk Products in Pastoral Communities of South-West Uganda. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, V.; Vergara, J.L.; Bonilla, A.M.; Muñoz, J.; Mallea, A.; Vallejos, D.; Quezada-Aguiluz, M.; Campos, J.; Rojas-García, P. Prevalence and Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Strains in the Pork Chain Supply in Chile. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xie, S. Genotypes, Enterotoxin Gene Profiles, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Associated with Foodborne Outbreaks in Hangzhou, China. Toxins 2019, 11, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derke, R.E.; Rahimi, E.; Shakerian, A.; Khamesipour, F. Prevalence, Virulence Factors, and Antibiotic Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus in Seafood Products. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; et al. Prevalence and Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Pasteurized Milk in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencardino, D.; Vitali, L.A.; Petrelli, D. High Prevalence of Clonally Diverse Spa Type T026 Staphylococcus aureus Contaminating Rural Eggshells. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroning, I.S.; Iglesias, M.A.; Mendonça, K.S.; Lopes, G.V.; Silva, W.P. Presence of Classical Enterotoxin Genes, Agr Typing, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Genetic Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus from Milk of Cows with Mastitis in Southern Brazil. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Miao, X.; Zhou, L.; Cui, B.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, C.; Peng, X.; Wang, X. Characterization of Oxacillin-Susceptible mecA-Positive Staphylococcus aureus from Food Poisoning Outbreaks and Retail Foods in China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehramuz, B.; Taghizadeh, S.; Kafil, H.S.; Zonouzaq, G.Y.; Khiabani, M.S.; Sheikhsaran, E.; Mokarram, R.R.; Dehghani, L. High Rate of Contamination with Staphylococcus aureus in Traditional Koozeh Cheeses. A Molecular Typing Approach. Ann. Ig. Med. Prev. E Comunita 2020, 32, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkuraythi, D.M.; Alkhulaifi, M.M.; Binjomah, A.Z.; Alarwi, M.; Mujallad, M.I.; Alharbi, S.A.; Alshomrani, M.; Gojobori, T.; Alajel, S.M. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Patients and Retail Meat. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1339339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegegne, H.A.; Florianová, M.; Gelbíčová, T.; Karpíšková, R.; Koláčková, I. Detection and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bulk Tank Milk of Cows, Sheep, and Goats. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, E.; Terzi Gulel, G. Detection of Enterotoxin Genes and Methicillin-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Water Buffalo Milk and Dairy Products. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1716–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.-L.; Ono, H.K.; Isayama, S.; Okada, R.; Okamura, M.; Lei, L.C.; Liu, Z.S.; Zhang, X.-C.; Liu, M.Y.; Cui, J.C.; et al. Biological Characteristics of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Q and Its Potential Risk for Food Poisoning. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaalal, W.; Chaalal, N.; Bourafa, N.; Kihal, M.; Diene, S.M.; Rolain, J.-M. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Food Products in Western Algeria. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, N.; Kumar, M.; Kanaujia, P.K.; Virdi, J.S. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: An Emerging Technology for Microbial Identification and Diagnosis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, D.; Blanco-Valle, K.; Feraudet-Tarisse, C.; Merda, D.; Simon, S.; Fenaille, F.; Hennekinne, J.-A.; Nia, Y.; Becher, F. Quantitative Determination of Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins Types A to I and Variants in Dairy Food Products by Multiplex Immuno-LC-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.C.; Huang, S.H. An Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Rapid Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Processed Foods. J. Food Prot. 1994, 57, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraj, S.; Ramlal, S.; Kingston, J.; Batra, H.V. Development of IgY Based Sandwich ELISA for the Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin G (SEG), an Egc Toxin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 237, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendimann, L.; Merda, D.; Berger, T.; Denayer, S.; Feraudet-Tarisse, C.; Kläui, A.J.; Messio, S.; Mistou, M.Y.; Nia, Y.; Hennekinne, J.A.; et al. Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Gene Cluster: Prediction of Enterotoxin (SEG and SEI) Production and of the Source of Food Poisoning on the Basis of vSaβ Typing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0266220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macori, G.; Bellio, A.; Bianchi, D.M.; Gallina, S.; Adriano, D.; Zuccon, F.; Chiesa, F.; Acutis, P.L.; Casalinuovo, F.; Decastelli, L. Molecular Typing of Staphylococcus aureus Isolate Responsible for Staphylococcal Poisoning Incident in Homemade Food. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2016, 5, 5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciupescu, L.-M.; Auvray, F.; Nicorescu, I.M.; Meheut, T.; Ciupescu, V.; Lardeux, A.-L.; Tanasuica, R.; Hennekinne, J.-A. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Strains and Evidence for the Involvement of Non-Classical Enterotoxin Genes in Food Poisoning Outbreaks. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragina, V.A.; Znoyko, S.L.; Orlov, A.V.; Pushkarev, A.V.; Nikitin, M.P.; Nikitin, P.I. Analytical Platform with Selectable Assay Parameters Based on Three Functions of Magnetic Nanoparticles: Demonstration of Highly Sensitive Rapid Quantitation of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B in Food. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 9852–9857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, M.; Scatassa, M.L.; Cardamone, C.; Oliveri, G.; Piraino, C.; Alduina, R.; Napoli, C. Staphylococcal Food Poisoning Case and Molecular Analysis of Toxin Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Food in Sicily, Italy. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johler, S.; Sihto, H.-M.; Macori, G.; Stephan, R. Sequence Variability in Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Genes Seb, Sec, and Sed. Toxins 2016, 8, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercoli, L.; Gallina, S.; Nia, Y.; Auvray, F.; Primavilla, S.; Guidi, F.; Pierucci, B.; Graziotti, C.; Decastelli, L.; Scuota, S. Investigation of a Staphylococcal Food Poisoning Outbreak from a Chantilly Cream Dessert, in Umbria (Italy). Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macori, G.; Bellio, A.; Bianchi, D.M.; Chiesa, F.; Gallina, S.; Romano, A.; Zuccon, F.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Cauquil, A.; Merda, D.; et al. Genome-Wide Profiling of Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus Strains Used for the Production of Naturally Contaminated Cheeses. Genes 2019, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, K.; Nakamura, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Nishina, N.; Yasufuku, K.; Hirai, Y.; Hirayama, T.; Goto, K.; Hase, A.; Ogasawara, J. Molecular and Epidemiological Characterization of Staphylococcal Foodborne Outbreak of Staphylococcus aureus Harboring Seg, Sei, Sem, Sen, Seo, and Selu Genes without Production of Classical Enterotoxins. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 256, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Zou, G.; Huang, Q.; Meng, X.; Pei, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, R.; Hu, D.; et al. Prevalence and Virulence Determinants of Staphylococcus aureus in Wholesale and Retail Pork in Wuhan, Central China. Foods 2022, 11, 4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, F.; Duranti, A.; Gallina, S.; Nia, Y.; Petruzzelli, A.; Romano, A.; Travaglini, V.; Olivastri, A.; Calvaresi, V.; Decastelli, L.; et al. Characterization of A Staphylococcal Food Poisoning Outbreak in A Workplace Canteen during the Post-Earthquake Reconstruction of Central Italy. Toxins 2018, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oniciuc, E.-A.; Ariza-Miguel, J.; Bolocan, A.-S.; Diez-Valcarce, M.; Rovira, J.; Hernández, M.; Fernández-Natal, I.; Nicolau, A.I.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D. Foods from Black Market at EU Border as a Neglected Route of Potential Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Transmission. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 209, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalrahman, L.S.; Stanley, A.; Wells, H.; Fakhr, M.K. Isolation, Virulence, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) Strains from Oklahoma Retail Poultry Meats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 6148–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Ye, C.; Chen, L.; Liang, Y.; Huang, T.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J. “One-Step” Characterization Platform for Pathogenic Genetics of Staphylococcus Aureus. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekhloufi, O.A.; Chieffi, D.; Hammoudi, A.; Bensefia, S.A.; Fanelli, F.; Fusco, V. Prevalence, Enterotoxigenic Potential and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolated from Algerian Ready to Eat Foods. Toxins 2021, 13, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ashmawy, M.A.; Sallam, K.I.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Elhadidy, M.; Tamura, T. Prevalence, Molecular Characterization, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Milk and Dairy Products. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johler, S.; Macori, G.; Bellio, A.; Acutis, P.L.; Gallina, S.; Decastelli, L. Short Communication: Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated along the Raw Milk Cheese Production Process in Artisan Dairies in Italy. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2915–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemiri, M.; Abbassi, M.S.; Elghaieb, H.; Zouari, M.; Dhahri, R.; Pomba, C.; Hammami, S. High Occurrence of Enterotoxigenic Isolates and Low Antibiotic Resistance Rates of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Raw Milk from Cows and Ewes. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titouche, Y.; Hakem, A.; Houali, K.; Meheut, T.; Vingadassalon, N.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Salmi, D.; Chergui, A.; Chenouf, N.; Hennekinne, J.A.; et al. Emergence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ST8 in Raw Milk and Traditional Dairy Products in the Tizi Ouzou Area of Algeria. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 6876–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elolu, S.; Oloo, B.O.; Opiyo, A.M.; Huyskens-Keil, S. Microbial Food Safety Aspects Along the Supply Chain of African Indigenous Vegetables. A Case Study of Leaf Amaranth (Amaranthus Spp.) in Kenya. J. Food Prot. 2025, 88, 100485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.; Gaglio, S.; Galluzzo, P.; Cascone, G.; Piraino, C.; Di Marco Lo Presti, V.; Alduina, R. Antibiotic Resistance Profiling, Analysis of Virulence Aspects and Molecular Genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated in Sicily, Italy. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yan, W.; Niu, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. The Distribution of 18 Enterotoxin and Enterotoxin-Like Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Strains from Different Sources in East China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.D. Distribution of Food-Borne Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxin Genes. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, gmr.15016084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, G.; Bao, G.; Cao, Y.; Yan, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Y. Prevalence and Diversity of Enterotoxin Genes with Genetic Background of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Different Origins in China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 211, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, K.; Yan, M.; Ye, Q.; Lin, X.; Chen, L.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Huang, T. Pathogenic and Virulence Factor Detection on Viable but Non-Culturable Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 630053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qian, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Fan, G.; Li, Y. A Multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid Detection of Bacillus Cereus and Staphylococcus aureus. Biosci. Trends 2020, 13, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.Y.; Fang, T.J.; Wen, H.W. Combined Multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Lateral Flow Assay to Detect Sea and Seb Genes of Enterotoxic Staphylococcus aureus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 63, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylova, Y.; Shelenkov, A.; Chernyshkov, A.; Tyumentseva, M.; Saenko, S.; Egorova, A.; Manzeniuk, I.; Akimkin, V. Whole-Genome Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Ready-to-Eat Food in Russia. Foods 2022, 11, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, F.; Chieffi, D.; Cho, G.-S.; Schubert, J.; Mekhloufi, O.A.; Bania, J.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Fusco, V. First Genome-Based Characterisation and Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Production Ability of Methicillin-Susceptible and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Ready-to-Eat Foods in Algiers (Algeria). Toxins 2022, 14, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Xu, W.; Huang, Y.; Lei, G.; Huang, W.; Lv, H.; Yang, X. Molecular Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Form Food-Poisoning Outbreaks (2011–2022) in Sichuan, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2024, 21, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, Y. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Staphylococcus Aureus. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2069, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, G.; Yang, W.; Chen, F.; Qi, Y.; Lou, Z. Investigation into the Prevalence of Enterotoxin Genes and Genetic Background of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Retain Foods in Hangzhou, China. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keisam, S.; Tuikhar, N.; Ahmed, G.; Jeyaram, K. Toxigenic and Pathogenic Potential of Enteric Bacterial Pathogens Prevalent in the Traditional Fermented Foods Marketed in the Northeast Region of India. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 296, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merda, D.; Felten, A.; Vingadassalon, N.; Denayer, S.; Titouche, Y.; Decastelli, L.; Hickey, B.; Kourtis, C.; Daskalov, H.; Mistou, M.-Y.; et al. NAuRA: Genomic Tool to Identify Staphylococcal Enterotoxins in Staphylococcus aureus Strains Responsible for FoodBorne Outbreaks. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normanno, G.; Dambrosio, A.; Lorusso, V.; Samoilis, G.; Di Taranto, P.; Parisi, A. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Slaughtered Pigs and Abattoir Workers in Italy. Food Microbiol. 2015, 51, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Shi, C.; Xu, X.; Shi, X. Molecular Typing and Virulence Gene Profiles of Enterotoxin Gene Cluster (Egc)-Positive Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Obtained from Various Food and Clinical Specimens. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraj, R.; Ramadan, H.; Bentum, K.E.; Alkaraghulli, B.; Woube, Y.; Hassan, Z.; Samuel, T.; Adesiyun, A.; Jackson, C.R.; Abebe, W. Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Gene Profiling, and Spa Typing of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Retail Chicken Meat in Alabama, USA. Pathogens 2025, 14, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, S.; Luo, W.; Su, Y.; Luan, Y.; Wang, X. Staphylococcus aureus ST6-T701 Isolates from Food-Poisoning Outbreaks (2006–2013) in Xi’an, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairat, S.; Gharsa, H.; Lozano, C.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Gómez, P.; Zarazaga, M.; Boudabous, A.; Torres, C.; Ben Slama, K. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus from Raw Meat Samples in Tunisia: Detection of Clonal Lineage ST398 from the African Continent. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jans, C.; Merz, A.; Johler, S.; Younan, M.; Tanner, S.A.; Kaindi, D.W.M.; Wangoh, J.; Bonfoh, B.; Meile, L.; Tasara, T. East and West African Milk Products Are Reservoirs for Human and Livestock-Associated Staphylococcus Aureus. Food Microbiol. 2017, 65, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalrahman, L.S.; Fakhr, M.K. Incidence, Antimicrobial Susceptibility, and Toxin Genes Possession Screening of Staphylococcus aureus in Retail Chicken Livers and Gizzards. Foods 2015, 4, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendani Chadi, Z.; Arcangioli, M.-A. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Analysis of Bovine Associated Staphylococcus aureus: A Review. Pathogens 2023, 12, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingadassalon, N.; Merda, D.; Felten, A.; Chesnais, V.; Kourtis, C.; Van Nieuwenhuysen, T.; Nia, Y.; Hennekinne, J.-A.; Cavaiuolo, M. Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus Food Isolates: Comparison of Conventional Methods with Whole Genome Sequencing Typing Methods. Food Microbiol. 2025, 125, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Heu, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.-P.; Roh, E. Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Leaf Vegetables in Korea. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, M1526-1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Man, S. CRISPR-Cas13a-Based Bacterial Detection Platform: Sensing Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus in Food Samples. In CRISPR-Cas Methods: Volume 3; Islam, M.T., Molla, K., Bhowmik, P., Xie, K., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 107–115. ISBN 978-1-07-164358-7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Yin, L.; Dong, Y.; Peng, L.; Liu, G.; Man, S.; Ma, L. CRISPR-Cas13a Based Bacterial Detection Platform: Sensing Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus in Food Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1127, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morach, M.; Käppeli, N.; Hochreutener, M.; Johler, S.; Julmi, J.; Stephan, R.; Etter, D. Microarray Based Genetic Profiling of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Abattoir Byproducts of Pork Origin. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achek, R.; El-Adawy, H.; Hotzel, H.; Hendam, A.; Tomaso, H.; Ehricht, R.; Neubauer, H.; Nabi, I.; Hamdi, T.M.; Monecke, S. Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Human and Food Samples in Northern Algeria. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, A.; Stephan, R.; Johler, S. Genotyping and DNA Microarray Based Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Rabbit Carcasses. Meat Sci. 2016, 112, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaizar, J.; Rementeria, A.; Porwollik, S. DNA Microarray Technology: A New Tool for the Epidemiological Typing of Bacterial Pathogens? FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 47, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangavai, C. Molecular Characterization of Food Borne Staphylococcus aureus and Designing of Novel Anti Biofilm: Understanding and Controlling Food-Borne Staphylococcus aureus Infections. J. Adv. Sch. Res. Allied Educ. 2019, 16, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshed, S.; Jabeen, S.; Mir, H.; Yousufi, A.H.; Ahmad, H.; Waqar, M.; Ullah, I.; Akbar, M.; Wajid, W.; Mudasser. Rapd Based Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Poultry Meat and Workers in the Local Market of Peshawar. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 31, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi Alni, R.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Mahmoodi, P.; Alikhani, M.Y. RAPD-PCR Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Different Sources. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 26, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandka, D.K.; Tuna, M.; Tal, M.; Nejidat, A.; Golan-Goldhirsh, A. Variability in the Pattern of Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2852–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.N.; Sheeja, T.E.; Minoo, D.; Rajesh, M.K.; Samsudeen, K.; Suraby, E.J.; Kumar, I.P.V. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and Derived Techniques. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2222, 219–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, S.; Derakhshandeh, A.; Haghkhah, M.; Naziri, Z.; Broujeni, A.M. Molecular Typing of Staphylococcus aureus from Different Sources by RAPD-PCR Analysis. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogiel, T.; Mikucka, A.; Kanarek, P. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis-Based RAPD-PCR—An Optimization of the Conditions to Rapidly Detect Similarity of the Alert Pathogens for the Purpose of Epidemiological Studies. Gels 2022, 8, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zee, A.; Verbakel, H.; van Zon, J.C.; Frenay, I.; van Belkum, A.; Peeters, M.; Buiting, A.; Bergmans, A. Molecular Genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus Strains: Comparison of Repetitive Element Sequence-Based PCR with Various Typing Methods and Isolation of a Novel Epidemicity Marker. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, P.A.; McCulloch, J.A.; Oliveira, G.A.; Mamizuka, E.M. Molecular Techniques for MRSA Typing: Current Issues and Perspectives. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Braz. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2003, 7, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.B.; Rossatto, F.C.P.; Martins, P.D.; Frazzon, A.P.G. Genetic Relationships and Virulence Factors in Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Raw Poultry in South Brazil. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabestani, M.R.; Kamarehei, F.; Dini, M.; Aziz Jalilian, F.; Moradi, A.; Shokoohizadeh, L. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Pastry Samples by Rep-PCR and Phage Typing. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2022, 14, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldy-Chudzik, K. Rep-PCR--a Variant to RAPD or an Independent Technique of Bacteria Genotyping? A Comparison of the Typing Properties of Rep-PCR with Other Recognised Methods of Genotyping of Microorganisms. Acta Microbiol. Pol. 2001, 50, 189–204. [Google Scholar]
- Sobral, D.; Schwarz, S.; Bergonier, D.; Brisabois, A.; Feßler, A.T.; Gilbert, F.B.; Kadlec, K.; Lebeau, B.; Loisy-Hamon, F.; Treilles, M.; et al. High Throughput Multiple Locus Variable Number of Tandem Repeat Analysis (MLVA) of Staphylococcus aureus from Human, Animal and Food Sources. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, P.; Price, L.; Klevytska, A.; Smith, K.; Schupp, J.; Okinaka, R.; Jackson, P.; Hugh-Jones, M. Multiple-Locus Variable-Number Tandem Repeat Analysis Reveals Genetic Relationships Within. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2928–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Belkum, A. Tracing Isolates of Bacterial Species by Multilocus Variable Number of Tandem Repeat Analysis (MLVA). FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 49, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haguenoer, E.; Baty, G.; Pourcel, C.; Lartigue, M.-F.; Domelier, A.-S.; Rosenau, A.; Quentin, R.; Mereghetti, L.; Lanotte, P. A Multi Locus Variable Number of Tandem Repeat Analysis (MLVA) Scheme for Streptococcus Agalactiae Genotyping. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadon, C.A.; Trees, E.; Ng, L.K.; Nielsen, E.M.; Reimer, A.; Maxwell, N.; Kubota, K.A.; Gerner-Smidt, P. Development and Application of MLVA Methods as a Tool for Inter-Laboratory Surveillance. Euro Surveill. Bull. Eur. Sur Mal. Transm. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2013, 18, 20565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D. Multiple-Locus VNTR Analyses of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Jamaica. Infect. Dis. 2015, 8, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubab, M.; Shahbaz, H.M.; Olaimat, A.N.; Oh, D.-H. Biosensors for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Food. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 105, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inês, A.; Cosme, F. Biosensors for Detecting Food Contaminants—An Overview. Processes 2025, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, T.; Feng, X.; Liu, D.; Zhong, Q.; Fang, X.; Liao, Z.; Wang, J.; Xiao, M.; Wang, L. A Micro-Carbon Nanotube Transistor for Ultra-Sensitive, Label-Free, and Rapid Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin C in Food. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 449, 131033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Li, H.; Qian, S.; Fu, P.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y. An Emerging Fluorescent Carbon Nanobead Label Probe for Lateral Flow Assays and Highly Sensitive Screening of Foodborne Toxins and Pathogenic Bacteria. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 11514–11520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, C.; Qian, S.; Li, H.; Fu, P.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, J. An Ultrasensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay Platform for Foodborne Biotoxins and Pathogenic Bacteria Based on Carbon-Dots Embedded Mesoporous Silicon Nanoparticles Fluorescent Reporter Probes. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, P.; Ruan, F.; Chang, G.; Zhou, T.; Chen, D.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Construction of a Colorimetric and Fluorescence Dual-Mode Immunoassay Detection of Alpha-Hemolysin in Milk. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2025, 22, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaifan, G.A.R.Y.; Alhogail, S.; Zourob, M. Rapid and Low-Cost Biosensor for the Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Duan, N.; Wu, S.; Xu, B.; Wang, Z. A Multicolor Time-Resolved Fluorescence Aptasensor for the Simultaneous Detection of Multiplex Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins in the Milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Wan, N.; Shi, L.; Wang, C.; Sun, Z.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. Dual-Recognition Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering(SERS)Biosensor for Pathogenic Bacteria Detection by Using Vancomycin-SERS Tags and Aptamer-Fe3O4@Au. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1077, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, W. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Quantification of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Food by Color-Encoded Multiplex Hydrogel Digital LAMP. Food Chem. 2025, 468, 142304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, R.; Jiang, F.; Chen, M.; Kutsanedzie, F.Y.H.; Jiao, T.; Wei, J.; Chen, X.-M.; Chen, Q. Nanogap-Assisted SERS/PCR Biosensor Coupled Machine Learning for the Direct Sensing of Staphylococcus aureus in Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Luo, Y. Machine Learning Supported Single-Stranded DNA Sensor Array for Multiple Foodborne Pathogenic and Spoilage Bacteria Identification in Milk. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Baker, M.; Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.; Maciel-Guerra, A.; Xue, N.; Li, H.; Yan, S.; Li, M.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Machine Learning Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus from Multiple Heterogeneous Sources in China Reveals Common Genetic Traits of Antimicrobial Resistance. mSystems 2021, 6, e01185-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Wang, S.; Xi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, Y. Deep Learning Enhanced Multiplex Detection of Viable Foodborne Pathogens in Digital Microfluidic Chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 245, 115837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.-U.; Sikder, R.; Tripathi, M.; Zahan, M.; Ye, T.; Gnimpieba, Z.E.; Jasthi, B.K.; Dalton, A.B.; Gadhamshetty, V. Machine Learning-Assisted Raman Spectroscopy and SERS for Bacterial Pathogen Detection: Clinical, Food Safety, and Environmental Applications. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Bao, H.; Li, H.; Wu, T.; Qi, X.; Zhu, C.; Tan, W.; Jia, D.; Zhou, D.; Qi, Y. Microscopic Identification of Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens Based on Deep Learning Method. Food Control 2024, 161, 110413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idhmad, A.; Kaicer, M.; Chentoufi, J.A. Food Quality Detection by Identification of Bacterial Contaminants: A Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Predictive Models. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 2023, 11, 789–800. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Pei, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Lu, S.; Li, B.; Dong, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Ji, H. Construction of a Dynamic Model to Predict the Growth of Staphylococcus aureus and the Formation of Enterotoxins during Kazak Cheese Maturation. Food Microbiol. 2023, 112, 104234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mairi, A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Idres, T.; Touati, A. A Comprehensive Review of Detection Methods for Staphylococcus aureus and Its Enterotoxins in Food: From Traditional to Emerging Technologies. Toxins 2025, 17, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070319
Mairi A, Ibrahim NA, Idres T, Touati A. A Comprehensive Review of Detection Methods for Staphylococcus aureus and Its Enterotoxins in Food: From Traditional to Emerging Technologies. Toxins. 2025; 17(7):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070319
Chicago/Turabian StyleMairi, Assia, Nasir Adam Ibrahim, Takfarinas Idres, and Abdelaziz Touati. 2025. "A Comprehensive Review of Detection Methods for Staphylococcus aureus and Its Enterotoxins in Food: From Traditional to Emerging Technologies" Toxins 17, no. 7: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070319
APA StyleMairi, A., Ibrahim, N. A., Idres, T., & Touati, A. (2025). A Comprehensive Review of Detection Methods for Staphylococcus aureus and Its Enterotoxins in Food: From Traditional to Emerging Technologies. Toxins, 17(7), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070319




