Oral Exposure to Chlorella sorokiniana Detoxifies Deoxynivalenol, Ochratoxin A, and Fumonisin B1 In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
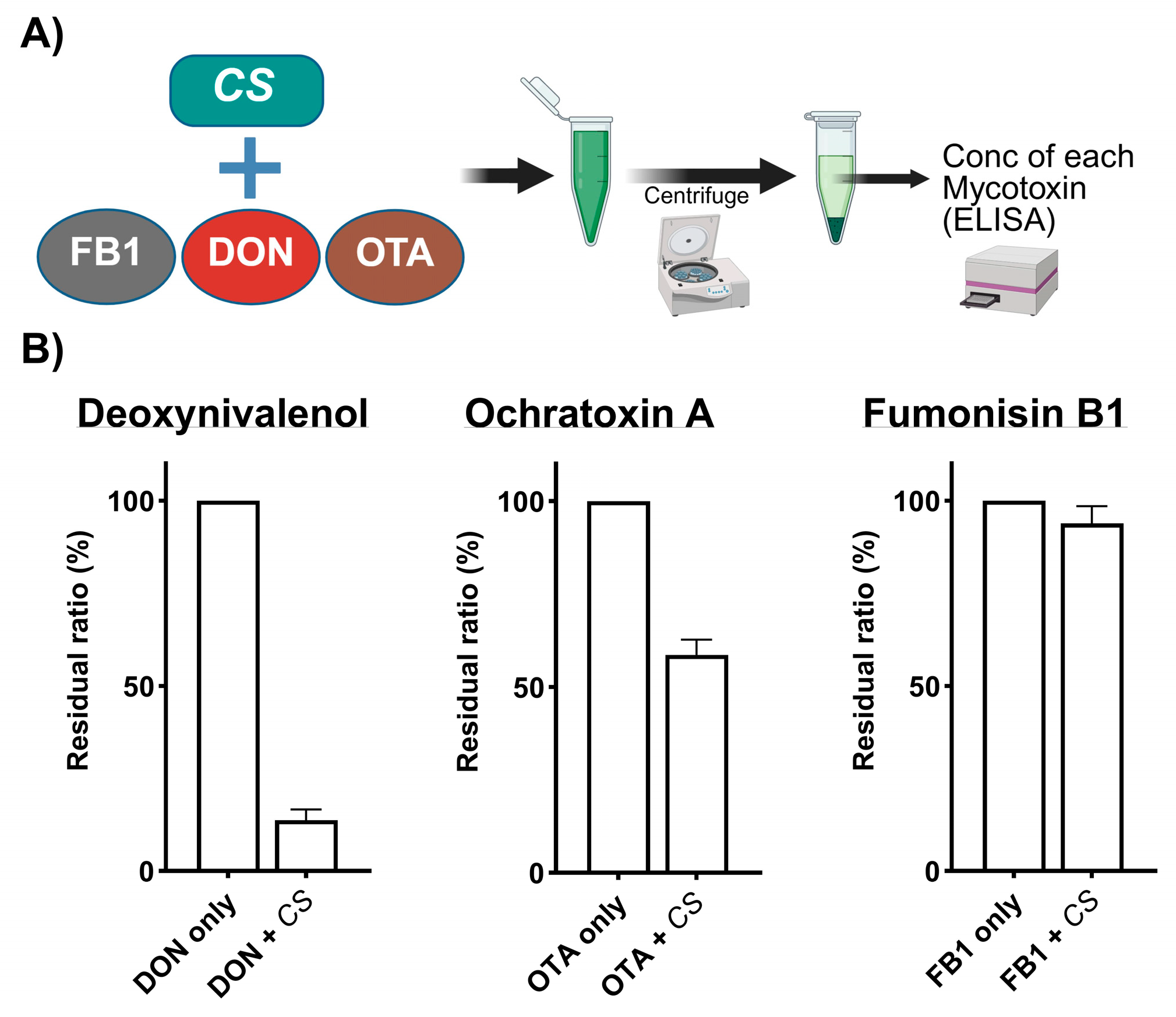
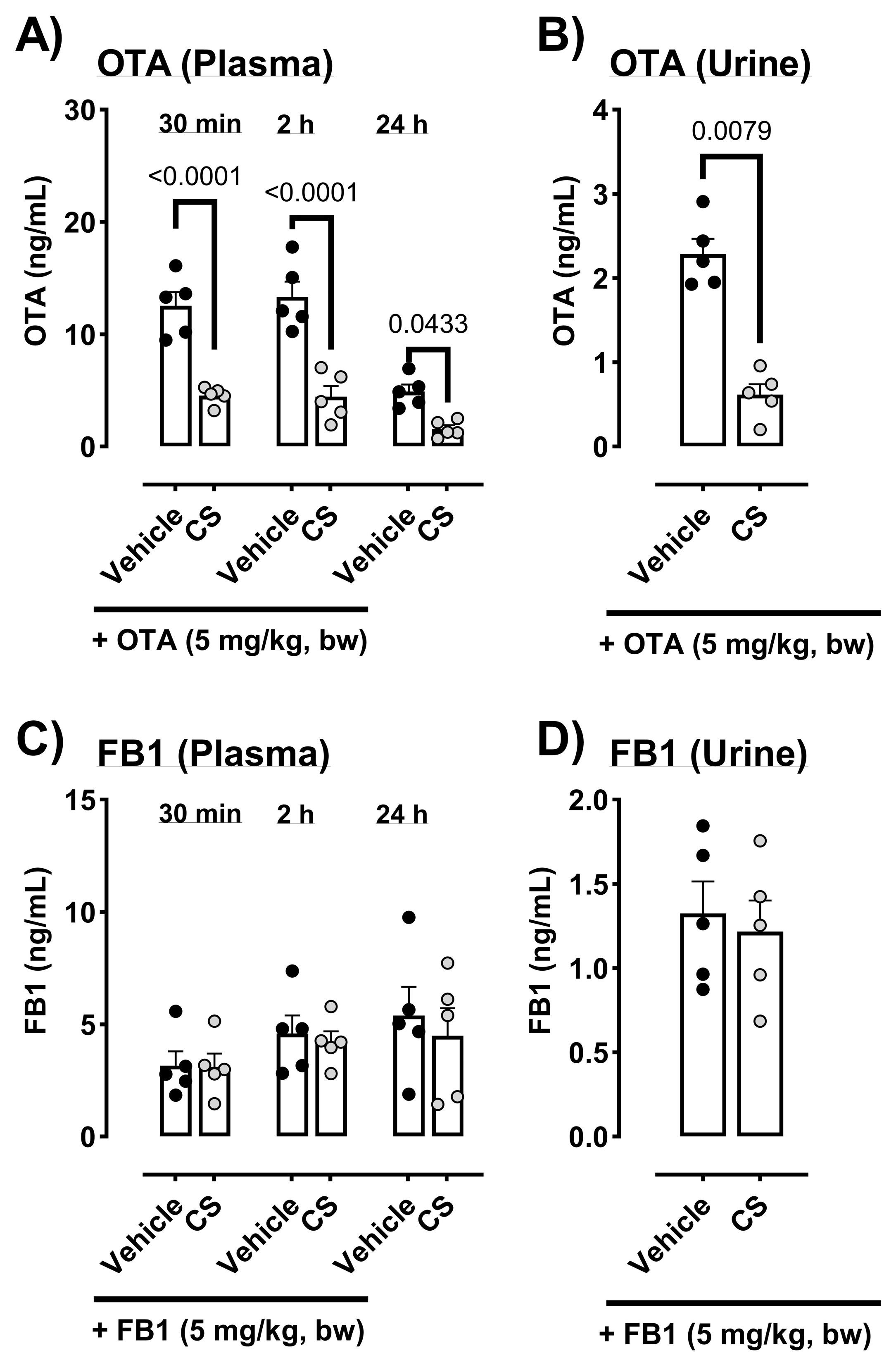
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Binding Property of CS to DON, OTA, and FB1
5.2. Mycotoxin Concentrations in Plasma and Urine Samples After Oral Exposure to 5 mg/kg Body Weight of DON, OTA, or FB1 in Male ICR Mice
5.3. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DON | deoxynivalenol |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FB1 | fumonisin B1 |
| LC/MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry |
| OTA | ochratoxin A |
| SEM | standard error of the mean |
References
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huybrechts, I.; Jacobs, I.; Biessy, C.; Aglago, E.K.; Jenab, M.; Claeys, L.; Zavadil, J.; Casagrande, C.; Nicolas, G.; Scelo, G.; et al. Associations between dietary mycotoxins exposures and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a European cohort. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0315561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, R.; Ookawara, T.; Morimoto, A.; Iwashita, N.; Takagi, Y.; Miyasaka, A.; Kushiro, M.; Miyake, S.; Fukuyama, T. Acute and subacute oral administration of mycotoxin deoxynivalenol exacerbates the pro-inflammatory and pro-pruritic responses in a mouse model of allergic dermatitis. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 4197–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Iwashita, N.; Takagi, Y.; Yoshinari, T.; Fukuyama, T. Oral Exposure to Low Concentration of Fumonisin B2, but Not Fumonisin B1, Significantly Exacerbates the Pathophysiology of Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Morimoto, A.; Iwashita, N.; Takagi, Y.; Nagane, M.; Yoshinari, T.; Fukuyama, T. Chronic oral exposure to low-concentration fumonisin B2 significantly exacerbates the inflammatory responses of allergies in mice via inhibition of IL-10 release by regulatory T cells in gut-associated lymphoid tissue. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2707–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ookawara, T.; Aihara, R.; Morimoto, A.; Iwashita, N.; Kurata, K.; Takagi, Y.; Miyasaka, A.; Kushiro, M.; Miyake, S.; Fukuyama, T. Acute and Subacute Oral Toxicity of Deoxynivalenol Exposure in a Dermatophagoides farinae-Induced Murine Asthma Model. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 179, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, F.; Ottoboni, M.; Pinotti, L.; Cheli, F. Integrated Mycotoxin Management System in the Feed Supply Chain: Innovative Approaches. Toxins 2021, 13, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojati, M.; Norouzian, M.A.; Assadi Alamouti, A.; Afzalzadeh, A. In vitro evaluation of binding capacity of different binders to adsorb aflatoxin. Vet. Res. Forum 2021, 12, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgbeahuruike, A.C.; Ejiofor, T.E.; Ashang, M.U.; Ojiako, C.; Obasi, C.C.; Ezema, C.; Okoroafor, O.; Mwanza, M.; Karlsson, M.; Chah, K.F. Reduction of the Adverse Impacts of Fungal Mycotoxin on Proximate Composition of Feed and Growth Performance in Broilers by Combined Adsorbents. Toxins 2021, 13, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bito, T.; Okumura, E.; Fujishima, M.; Watanabe, F. Potential of Chlorella as a Dietary Supplement to Promote Human Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, S.; Noguchi, T.; Takekoshi, H.; Suzuki, G.; Nakano, M. Maternal-fetal distribution and transfer of dioxins in pregnant women in Japan, and attempts to reduce maternal transfer with Chlorella (Chlorella pyrenoidosa) supplements. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, K.; Ogata, M.; Hasegawa, T. Chlorophyll derived from Chlorella inhibits dioxin absorption from the gastrointestinal tract and accelerates dioxin excretion in rats. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbasuni, S.S.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Elsabagh, R.; Nada, M.O.; Elshemy, M.A.; Ismail, A.K.; Mansour, H.M.; Ghamry, H.I.; Ibrahim, S.F.; Alsaati, I.; et al. The Preferential Therapeutic Potential of Chlorella vulgaris against Aflatoxin-Induced Hepatic Injury in Quail. Toxins 2022, 14, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, S.; Robben, N.; Burghart, R.; Cote, P.; Greenway, S.; Thakkar, R.; Upreti, D.; Nakashima, A.; Suzuki, K.; Comer, J.; et al. Cell Wall Membrane Fraction of Chlorella sorokiniana Enhances Host Antitumor Immunity and Inhibits Colon Carcinoma Growth in Mice. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1534735419900555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, S.; Roth, M.; Welti, R.; Loyd, M.; Thakkar, R.; Phillips, M.; Robben, N.; Upreti, D.; Nakashima, A.; Suzuki, K.; et al. A Water Extract from Chlorella sorokiniana Cell Walls Stimulates Growth of Bone Marrow Cells and Splenocytes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, T.; Komuro, M.; Aihara, R.; Ohira, C.; Kaneki, M.; Iwashita, N.; Takagi, Y.; Miyasaka, A.; Kushiro, M.; Miyake, S.; et al. Short-Term Oral Administration of 1.5 mug/kg bw/day of Deoxynivalenol Significantly Exacerbates Inflammatory and Itching Symptoms in a Mouse Model of Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis. Toxins 2025, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Khoury, A.; Atoui, A. Ochratoxin a: General overview and actual molecular status. Toxins 2010, 2, 461–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, R.; Kamarozaman, N.S.; Ab Dullah, S.S.; Aziz, M.Y.; Aziza, H.B.A. Health risks evaluation of mycotoxins in plant-based supplements marketed in Malaysia. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penalva-Olcina, R.; Juan, C.; Fernandez-Franzon, M.; Juan-Garcia, A. Neurotoxic implications of gliotoxin and ochratoxin A in SH-SY5Y cells: ROS-induced apoptosis and genotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2025, 405, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, C.; Borchers, J.; Brode, J.; Lambeck, P.; Mally, A. Replication stress: An early key event in ochratoxin a genotoxicity? Arch. Toxicol. 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.S.; Ryu, D. Summary of the ACS Symposium on Public Health Perspectives of Mycotoxins in Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7017–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber-Dorninger, C.; Jenkins, T.; Schatzmayr, G. Global Mycotoxin Occurrence in Feed: A Ten-Year Survey. Toxins 2019, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missmer, S.A.; Suarez, L.; Felkner, M.; Wang, E.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Rothman, K.J.; Hendricks, K.A. Exposure to fumonisins and the occurrence of neural tube defects along the Texas-Mexico border. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.J.; Hungerford, N.L.; Laycock, B.; Fletcher, M.T. A review on Pimelea poisoning of livestock. Toxicon 2020, 186, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.M.; Rohandel, G.; Roudbarmohammadi, S.; Roudbary, M.; Sohanaki, H.; Ghiasian, S.A.; Taherkhani, A.; Semnani, S.; Aghasi, M. Fumonisin B1 contamination of cereals and risk of esophageal cancer in a high risk area in northeastern Iran. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 2625–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, S.; Grande, P.M.; Blank, L.M.; Klose, H. Insights into cell wall disintegration of Chlorella vulgaris. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.R.; Spinola, M.P.; Lordelo, M.; Prates, J.A.M. Impact of Chlorella vulgaris Intake Levels on Performance Parameters and Blood Health Markers in Broiler Chickens. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koszegi, T.; Poor, M. Ochratoxin A: Molecular Interactions, Mechanisms of Toxicity and Prevention at the Molecular Level. Toxins 2016, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestka, J.J.; Clark, E.S.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Berthiller, F. Sex Is a Determinant for Deoxynivalenol Metabolism and Elimination in the Mouse. Toxins 2017, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; He, X.; Matsuo, Y.; Singh, P.K.; Kushiro, M. Analysis of the Masked Metabolite of Deoxynivalenol and Fusarium Resistance in CIMMYT Wheat Germplasm. Toxins 2017, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamaguchi, H.; Ando, M.; Ohira, C.; Magami, T.; Kaneki, M.; Sugita, K.; Ogawa, T.; Nakashima, A.; Fukuyama, T. Oral Exposure to Chlorella sorokiniana Detoxifies Deoxynivalenol, Ochratoxin A, and Fumonisin B1 In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxins 2025, 17, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070318
Yamaguchi H, Ando M, Ohira C, Magami T, Kaneki M, Sugita K, Ogawa T, Nakashima A, Fukuyama T. Oral Exposure to Chlorella sorokiniana Detoxifies Deoxynivalenol, Ochratoxin A, and Fumonisin B1 In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxins. 2025; 17(7):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070318
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamaguchi, Hiroki, Mana Ando, Chiharu Ohira, Tensei Magami, Mao Kaneki, Kazutoshi Sugita, Taro Ogawa, Ayaka Nakashima, and Tomoki Fukuyama. 2025. "Oral Exposure to Chlorella sorokiniana Detoxifies Deoxynivalenol, Ochratoxin A, and Fumonisin B1 In Vitro and In Vivo" Toxins 17, no. 7: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070318
APA StyleYamaguchi, H., Ando, M., Ohira, C., Magami, T., Kaneki, M., Sugita, K., Ogawa, T., Nakashima, A., & Fukuyama, T. (2025). Oral Exposure to Chlorella sorokiniana Detoxifies Deoxynivalenol, Ochratoxin A, and Fumonisin B1 In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxins, 17(7), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070318





