Unveiling the Neurotoxic Effects of Ochratoxin A and Its Impact on Neuroinflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Characteristics of Ochratoxin A and Its Relationship with the Nervous System
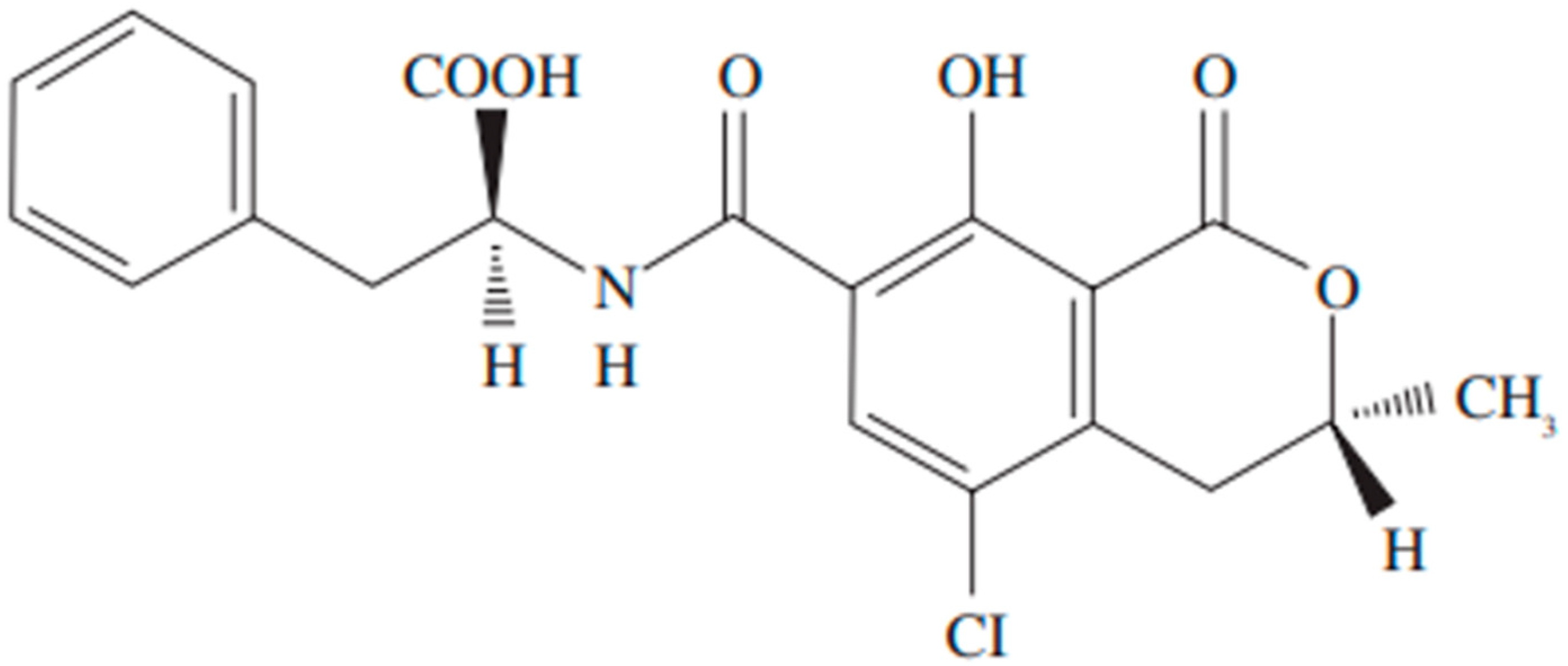
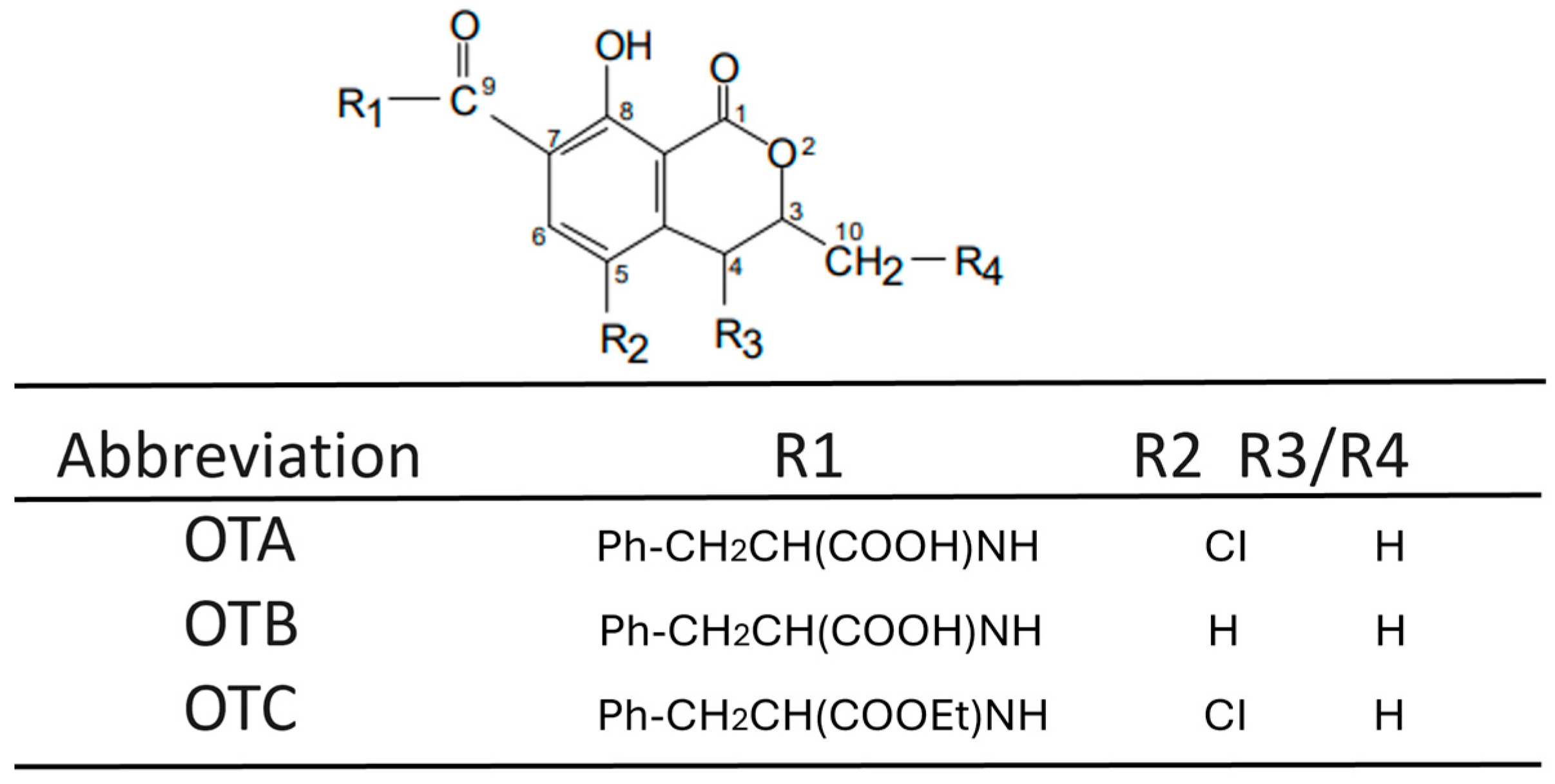
2.1. Origin, Contamination, and Characteristics of Ochratoxin A
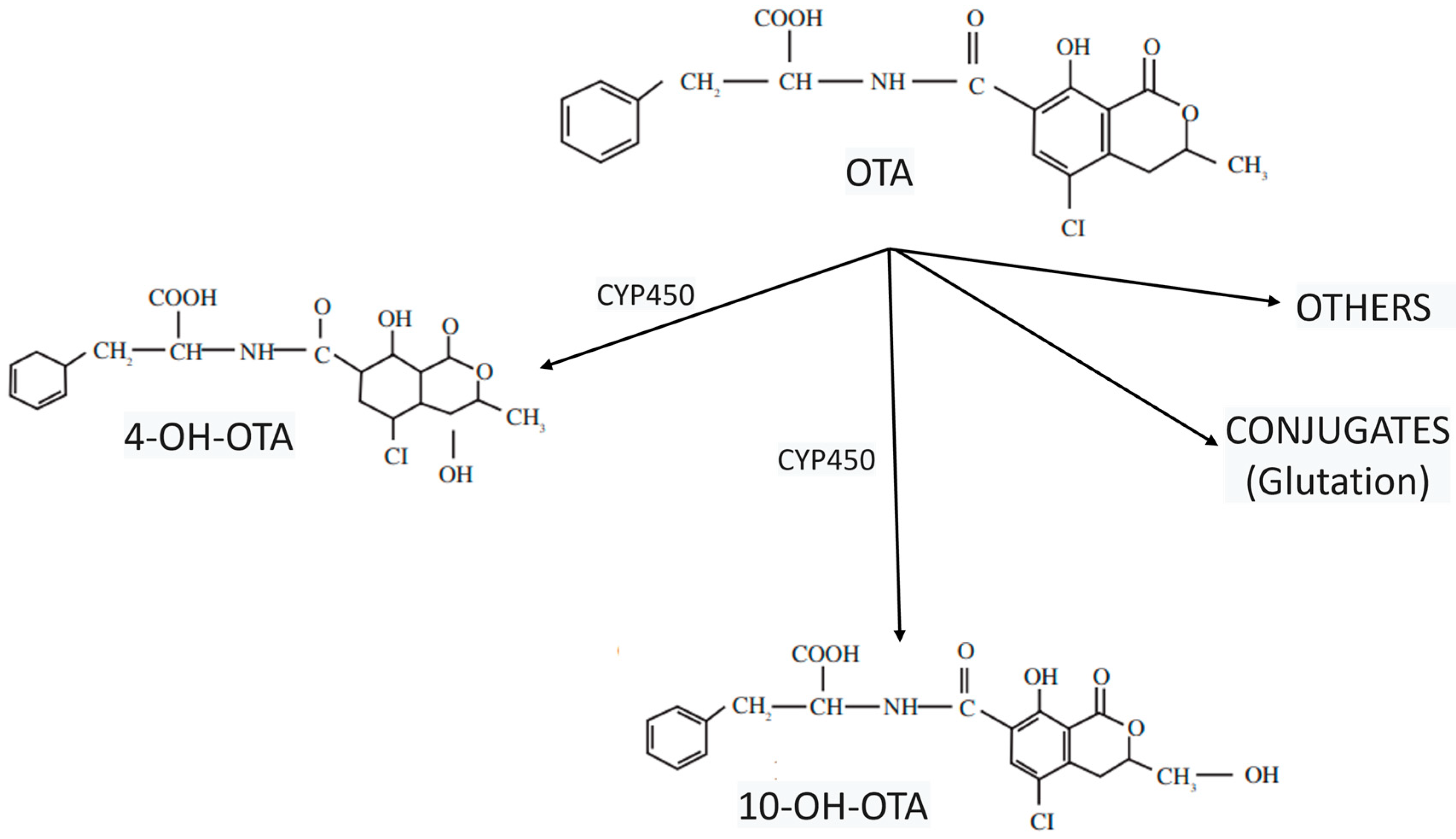
2.2. The Toxicokinetics of Ochratoxin A
3. Ochratoxin Crosses the Gastrointestinal and Blood–Brain Barrier
4. Cellular Effects of Ochratoxin A: An Insight into the Nervous System
5. Ochratoxin A, Mitochondrial Impairment, and Oxidative Stress: The Development of Neurological Diseases with Fatal Outcomes
6. The Role of Ochratoxin A in Neuroinflammation
6.1. The Astrocyte-Specific Effects of Ochratoxin A
6.2. Microglia Activation and the Effects of Ochratoxin A
6.3. Oligodendrocyte Markers Affected by Ochratoxin A Exposure
7. From Ochratoxin A-Induced Neuroinflammation to the Development of Neurodegenerative Diseases
8. Role of Antioxidants in Neuroprotection
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coffey, R.; Cummins, E.; Ward, S. Exposure assessment of mycotoxins in dairy milk. Food Control 2009, 20, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, S.; Ramos, A.J.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Sanchis, V. Mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, L.G.; Ross, P.F. Methods for Detection and Quantitation of Fumonisins in Corn, Cereal Products and Animal Excreta. J. Food Prot. 1994, 57, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization; United Nations Environment Programme (Eds.) Report of the Joint FAO/WHO/UNEP Conference on Mycotoxins Held in Nairobi, 17–19 September 1977; FAO food and nutrition paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1977; 107p. [Google Scholar]
- Paradells, S.; Rocamonde, B.; Llinares, C.; Herranz-Pérez, V.; Jimenez, M.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Zipancic, I.; Soria, J.M.; Garcia-Esparza, M.A. Neurotoxic effects of ochratoxin A on the subventricular zone of adult mouse brain. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, K.; Maekawa, M.; Katagiri, R.; Ueta, E.; Naruse, I. Genetic susceptibility in the neural tube defects induced by ochratoxin A in the genetic arhinencephaly mouse, Pdn/Pdn. Congenit. Anom. 2006, 46, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K.; Uetsuka, K. Mechanisms of mycotoxin-induced neurotoxicity through oxidative stress-associated pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5213–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmadani, A.; Steyn, P.S.; Tramu, G.; Betbeder, A.M.; Baudrimont, I.; Creppy, E.E. Selective toxicity of ochratoxin A in primary cultures from different brain regions. Arch. Toxicol. 1999, 73, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruinink, A.; Rasonyi, T.; Sidler, C. Differences in neurotoxic effects of ochratoxin A, ochracin and ochratoxin-alpha in vitro. Nat. Toxins 1998, 6, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; You, L.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Chrienova, Z.; Nepovimova, E.; Wu, Q.; Kuca, K. The neurotoxicity of trichothecenes T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol (DON): Current status and future perspectives. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, J.; Agrawal, M.; Gupta, N.; Rao, P.V.L. Alteration of blood brain barrier permeability by T-2 toxin: Role of MMP-9 and inflammatory cytokines. Toxicology 2011, 280, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, M.; Lenczyk, M.; Schwerdt, G.; Gekle, M.; Humpf, H.-U. Neurotoxic potential and cellular uptake of T-2 toxin in human astrocytes in primary culture. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerging Fusarium and Alternaria Mycotoxins: Occurrence, Toxicity and Toxicokinetics. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6651/9/7/228 (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Turner, P.C.; Flannery, B.; Isitt, C.; Ali, M.; Pestka, J. The role of biomarkers in evaluating human health concerns from fungal contaminants in food. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2012, 25, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mycotoxins: Emerging Toxic Mechanisms, and Unanswered Research Questions—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0278691523000753?via%3Dihub (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Nguyen, V.T.T.; König, S.; Eggert, S.; Endres, K.; Kins, S. The role of mycotoxins in neurodegenerative diseases: Current state of the art and future perspectives of research. Biol. Chem. 2022, 403, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, T.; Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz, M.; Pajarillo, E.; Rizor, A.; Soares, F.A.A.; Lee, E.; Aschner, M. Role of Astrocytes in Manganese Neurotoxicity Revisited. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 2449–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osemwegie, O.; Ramkumar, S.; Smith, E.E. Neurodegenerative Implications of Neuronal Cytoplasmic Protein Dysfunction in Response to Environmental Contaminants. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awogbindin, I.O.; Ikeji, C.N.; Adedara, I.A.; Farombi, E.O. Neurotoxicity of furan in juvenile Wistar rats involves behavioral defects, microgliosis, astrogliosis and oxidative stress. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 178, 113934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragulat, M.R.; Martínez, E.; Castellá, G.; Cabañes, F.J. Ochratoxin A and citrinin producing species of the genus Penicillium from feedstuffs. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 126, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabak, B.; Dobson, A.D.W.; Var, I. Strategies to prevent mycotoxin contamination of food and animal feed: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Shen, X.; Wei, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Z.; et al. Broad-Specificity Immunoassay for Simultaneous Detection of Ochratoxins A, B, and C in Millet and Maize. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4830–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mahato, D.K.; Sharma, B.; Borah, R.; Haque, S.; Mahmud, M.M.C.; Shah, A.K.; Rawal, D.; Bora, H.; Bui, S. Ochratoxins in food and feed: Occurrence and its impact on human health and management strategies. Toxicon 2020, 187, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Han, M.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y. Ochratoxin A: Overview of Prevention, Removal, and Detoxification Methods. Toxins 2023, 15, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Xie, S.; Xu, F.; Liu, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Pan, Y.; Huang, L.; Peng, D.; Wang, X.; et al. Ochratoxin A: Toxicity, oxidative stress and metabolism. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 112, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostry, V.; Malir, F.; Dofkova, M.; Skarkova, J.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Ruprich, J. Ochratoxin A Dietary Exposure of Ten Population Groups in the Czech Republic: Comparison with Data over the World. Toxins 2015, 7, 3608–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EU 2023/915. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32023R0915 (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Malir, F.; Ostry, V.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Malir, J.; Toman, J. Ochratoxin A: 50 Years of Research. Toxins 2016, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravelo Abreu, A.; Rubio Armendáriz, C.; Gutiérrez Fernández, A.J.; Hardisson de la Torre, A. La ocratoxina A en alimentos de consumo humano: Revisión. Nutr. Hosp. 2011, 26, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Studer-Rohr, I.; Schlatter, J.; Dietrich, D.R. Kinetic parameters and intraindividual fluctuations of ochratoxin A plasma levels in humans. Arch. Toxicol. 2000, 74, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojković, R.; Hult, K.; Gamulin, S.; Plestina, R. High affinity binding of ochratoxin A to plasma constituents. Biochem. Int. 1984, 9, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Samiee, F.; Kharazi, A.; Elaridi, J.; Taravati Javad, M.; Leili, M. An assessment of the occurrence and nutritional factors associated with aflatoxin M1, ochratoxin A, and zearalenone in the breast milk of nursing mothers in Hamadan, Iran. Toxicon 2020, 187, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, Z.; Hamzeh Pour, S.; Ezati, P.; Akrami-Mohajeri, F. Determination of aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A in breast milk in rural centers of Yazd, Iran: Exposure assessment and risk characterization. Mycotoxin Res. 2024, 40, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Trisha, A.; Hafsa, J.M.; Hasan, A.; Habib, A.; Tuba, H.R.; Degen, G.H.; Ali, N. Occurrence of ochratoxin A in breast milk and urine samples of nursing mothers in Bangladesh. Mycotoxin Res. 2024, 40, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Dohnal, V.; Huang, L.; Kuca, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Yuan, Z. Metabolic Pathways of Ochratoxin A. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simarro Doorten, A.Y.; Bull, S.; van der Doelen, M.M.; Fink-Gremmels, J. Metabolism-mediated cytotoxicity of ochratoxin A. Toxicol. Vitro 2004, 18, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knasmuller, S.; Cavin, C.; Chakraborty, A.; Darroudi, F.; Majer, B.J.; Huber, W.W.; Ehrlich, V.A. Structurally Related Mycotoxins Ochratoxin A, Ochratoxin B, and Citrinin Differ in Their Genotoxic Activities and in Their Mode of Action in Human-Derived Liver (HepG2) Cells: Implications for Risk Assessment. Nutr. Cancer 2004, 50, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, K.J.; Geueke, B.; Muncke, J. Food contact materials and gut health: Implications for toxicity assessment and relevance of high molecular weight migrants. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natividad, J.M.M.; Verdu, E.F. Modulation of intestinal barrier by intestinal microbiota: Pathological and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenwald, M.A.; Turner, J.R. The intestinal epithelial barrier: A therapeutic target? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crossing the Intestinal Barrier via Listeria Adhesion Protein and Internalin A: Trends in Microbiology. Available online: https://www.cell.com/trends/microbiology/abstract/S0966-842X(18)30283-X?_returnURL=https%3A%2F%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%2Fretrieve%2Fpii%2FS0966842X1830283X%3Fshowall%3Dtrue (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, A.; Shi, Z.; He, C.; Ding, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H. A mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathway induced by deoxynivalenol in human colon cancer cells. Toxicol. Vitro 2012, 26, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mariscal, L.; Betanzos, A.; Ávila-Flores, A. MAGUK proteins: Structure and role in the tight junction. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 11, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuse, M.; Hirase, T.; Itoh, M.; Nagafuchi, A.; Yonemura, S.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S. Occludin: A novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Meng, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. The Compromised Intestinal Barrier Induced by Mycotoxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, R.D. Mechanisms confining indigenous bacteria to the gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1980, 33 (Suppl. S11), 2472–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, S.; Epstein, M.D.; Alexander, J.W.; Trocki, O.; Jacobs, P.; Gura, P. Prevention of yeast translocation across the gut by a single enteral feeding after burn injury. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 1989, 13, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnason, I.; MacPherson, A.; Hollander, D. Intestinal permeability: An overview. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 1566–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoi, C.-S.; Chen, J.-H.; Lin, T.-Y.; Chiang, C.-K.; Hung, K.-Y. Ochratoxin A-Induced Nephrotoxicity: Up-to-Date Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresca, M.; Mahfoud, R.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Fantini, J. The mycotoxin ochratoxin A alters intestinal barrier and absorption functions but has no effect on chloride secretion. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 176, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Intestinal Barrier as an Emerging Target in the Toxicological Assessment of Mycotoxins|Archives of Toxicology. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00204-016-1794-8 (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- McLaughlin, J.; Padfield, P.J.; Burt, J.P.H.; O’Neill, C.A. Ochratoxin A increases permeability through tight junctions by removal of specific claudin isoforms. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 287, C1412–C1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Luo, C.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, N. Modulation of Intestinal Epithelial Permeability in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells Exposed to Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A Individually or Collectively. Toxins 2017, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Bao, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Modulation of intestinal epithelial permeability and mucin mRNA (MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC5B) expression and protein secretion in Caco-2/HT29-MTX co-cultures exposed to aflatoxin M1, ochratoxin A, and zearalenone individually or collectively. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 309, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, L.; Zhu, X.; Lv, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Selenomethionine attenuates ochratoxin A-induced small intestinal injury in rabbits by activating the Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting NF-κB activation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 256, 114837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Patabendige, A.A.K.; Dolman, D.E.M.; Yusof, S.R.; Begley, D.J. Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Tran, N.D.; Li, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhou, W.; Fisher, M.J. Brain endothelial hemostasis regulation by pericytes. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2006, 26, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.L.; Brites, D.; Brito, M.A. Looking at the blood-brain barrier: Molecular anatomy and possible investigation approaches. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 64, 328–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholesterol Metabolism in Neurons and Astrocytes—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0163782711000312?via%3Dihub (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Erceg, S.; Mateo, E.M.; Zipancic, I.; Rodríguez Jiménez, F.J.; Pérez Aragó, M.A.; Jiménez, M.; Soria, J.M.; Garcia-Esparza, M.Á. Assessment of Toxic Effects of Ochratoxin A in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Toxins 2019, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, E.; Tonino, R.P.B.; Canto, A.; Monroy Noyola, A.; Miranda, M.; Soria, J.M.; Garcia Esparza, M.A. The Neurotoxic Effect of Ochratoxin-A on the Hippocampal Neurogenic Niche of Adult Mouse Brain. Toxins 2022, 14, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayan, N.; Tadevosyan, G.; Khondkaryan, L.; Grigoryan, R.; Sarkisyan, N.; Haroutiounian, R.; Stopper, H. Ochratoxin A induces global DNA hypomethylation and oxidative stress in neuronal cells in vitro. Mycotoxin Res. 2020, 36, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sas, K.; Robotka, H.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Mitochondria, metabolic disturbances, oxidative stress and the kynurenine system, with focus on neurodegenerative disorders. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 257, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, Y.; Hoshino, K.; Kameyama, Y. Developmental abnormalities of mouse cerebellum induced by intracisternal injection of ochratoxin A in neonatal period. Exp. Neurol. 1987, 98, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, M.; Hüwel, S.; Galla, H.-J.; Humpf, H.-U. Efflux at the Blood-Brain Barrier Reduces the Cerebral Exposure to Ochratoxin A, Ochratoxin α, Citrinin and Dihydrocitrinone. Toxins 2021, 13, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Xiao, X.; Tang, S.; Li, D. Food-Origin Mycotoxin-Induced Neurotoxicity: Intend to Break the Rules of Neuroglia Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9967334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Napoli, C.; Marcotrigiano, V.; Pagliarone, C.N.; Montagna, M.T. Mycotoxins in food: Legislation and thresholds. Ig. E Sanita Pubblica 2009, 65, 607–620. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, P.V.; Pandareesh, M.; Khanum, F.; Tamatam, A. Cytotoxic Effects of Ochratoxin A in Neuro-2a Cells: Role of Oxidative Stress Evidenced by N-acetylcysteine. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Cong, W.-T.; Bang, Y.; Lee, S.N.; Yoon, C.S.; Kwack, S.J.; Kang, T.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Choi, J.-K.; Choi, H.J. Proteome response to ochratoxin A-induced apoptotic cell death in mouse hippocampal HT22 cells. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sava, V.; Velasquez, A.; Song, S.; Sanchez-Ramos, J. Adult hippocampal neural stem/progenitor cells in vitro are vulnerable to the mycotoxin ochratoxin-A. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 98, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, A.W.; Hood, R.D.; Lee, H.L. Teratogenic effects of ochratoxin A in mice. Teratology 1974, 9, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sava, V.; Reunova, O.; Velasquez, A.; Harbison, R.; Sánchez-Ramos, J. Acute neurotoxic effects of the fungal metabolite ochratoxin-A. Neurotoxicology 2006, 27, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sava, V.; Reunova, O.; Velasquez, A.; Sanchez-Ramos, J. Can low level exposure to ochratoxin-A cause parkinsonism? J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 249, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.T.; Park, K.L.; Han, S.Y.; Park, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Oh, S.D.; Lee, R.D.; Jang, S.J. Effects of ochratoxin A on cytotoxicity and cell differentiation in cultured rat embryonic cells. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2000, 61, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangikar, P.B.; Dwivedi, P.; Sinha, N. Effect in rats of simultaneous prenatal exposure to ochratoxin A and aflatoxin B1. I. Maternal toxicity and fetal malformations. Birth Defects Res. B. Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2004, 71, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niaz, K.; Shah, S.Z.A.; Khan, F.; Bule, M. Ochratoxin A-induced genotoxic and epigenetic mechanisms lead to Alzheimer disease: Its modulation with strategies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 44673–44700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnaseelan, A.M.; Tsilioni, I.; Theoharides, T.C. Effects of Mycotoxins on Neuropsychiatric Symptoms and Immune Processes. Clin. Ther. 2018, 40, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lim, W.; You, S.; Song, G. Ochratoxin A exerts neurotoxicity in human astrocytes through mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and intracellular calcium overload. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 313, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izco, M.; Vettorazzi, A.; Forcen, R.; Blesa, J.; de Toro, M.; Alvarez-Herrera, N.; Cooper, J.M.; Gonzalez-Peñas, E.; Lopez de Cerain, A.; Alvarez-Erviti, L. Oral subchronic exposure to the mycotoxin ochratoxin A induces key pathological features of Parkinson’s disease in mice six months after the end of the treatment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, P.V.; Anand, T.; Mohan Manu, T.; Khanum, F. Restorative effect of l-Dopa treatment against Ochratoxin A induced neurotoxicity. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 118, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, B.; Brera, C.; Mezzelani, A.; Soricelli, S.; Ciceri, F.; Moretti, G.; Debegnach, F.; Bonaglia, M.C.; Villa, L.; Molteni, M.; et al. Role of mycotoxins in the pathobiology of autism: A first evidence. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzelani, A.; Raggi, M.E.; Marabotti, A.; Milanesi, L. Ochratoxin A as possible factor trigging autism and its male prevalence via epigenetic mechanism. Nutr. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrenti, V.; Di Giacomo, C.; Acquaviva, R.; Barbagallo, I.; Bognanno, M.; Galvano, F. Toxicity of ochratoxin a and its modulation by antioxidants: A review. Toxins 2013, 5, 1742–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, J.C.; Holzhaeuser, D.; Markovic, J.; Gremaud, E.; Schilter, B.; Turesky, R.J. Oxidative damage and stress response from ochratoxin a exposure in rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mally, A.; Pepe, G.; Ravoori, S.; Fiore, M.; Gupta, R.C.; Dekant, W.; Mosesso, P. Ochratoxin a causes DNA damage and cytogenetic effects but no DNA adducts in rats. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbillaga, L.; Azqueta, A.; Ezpeleta, O.; López de Cerain, A. Oxidative DNA damage induced by Ochratoxin A in the HK-2 human kidney cell line: Evidence of the relationship with cytotoxicity. Mutagenesis 2007, 22, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Kuan, M.; Ehrlich, V.; Delatour, T.; Cavin, C.; Schilter, B. Evidence for a role of oxidative stress in the carcinogenicity of ochratoxin a. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 645361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.; Soni, M.; Kumar, V. Mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction in arsenic neurotoxicity: A review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, U.C.; Bhol, N.K.; Swain, S.K.; Samal, R.R.; Nayak, P.K.; Raina, V.; Panda, S.K.; Kerry, R.G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. Oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders: Mechanisms and implications. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 15, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uttara, B.; Singh, A.V.; Zamboni, P.; Mahajan, R.T. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.-H. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabe, Y.; Ando, K.; Hirao, S.; Yoshida, M.; Handa, H. Redox regulation of NF-kappaB activation: Distinct redox regulation between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battelli, M.G.; Polito, L.; Bolognesi, A. Xanthine oxidoreductase in atherosclerosis pathogenesis: Not only oxidative stress. Atherosclerosis 2014, 237, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, S.; Abramov, A.Y. Mechanism of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 428010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Ahn, D.-G.; Syed, G.H.; Siddiqui, A. The essential role of mitochondrial dynamics in antiviral immunity. Mitochondrion 2018, 41, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Esteves, A.R.; Silva, D.F.; Januário, C.; Cardoso, S.M. The Impact of Mitochondrial Fusion and Fission Modulation in Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaziz, C.; Sharaf El Dein, O.; El Golli, E.; Abid-Essefi, S.; Brenner, C.; Lemaire, C.; Bacha, H. Different apoptotic pathways induced by zearalenone, T-2 toxin and ochratoxin A in human hepatoma cells. Toxicology 2008, 254, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.H.; Lu, C.Y.; Lin, T.N.; Wei, R.D. Effect of ochratoxin A on rat liver mitochondrial respiration and oxidative phosphorylation. Toxicology 1985, 36, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, A. Ochratoxin A induces mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), leading to retinal damage in mice. Int. Ophthalmol. 2024, 44, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.-J.; Meng, N. Resveratrol acts via the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway to protect retinal ganglion cells from apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 4878–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilioni, I.; Theoharides, T.C. Ochratoxin A stimulates release of IL-1β, IL–18 and CXCL8 from cultured human microglia. Toxicology 2024, 502, 153738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, S.; Izzy, S.; Sen, P.; Morsett, L.; El Khoury, J. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpierre, A.D.; Wu, L.-J. How microglia sense and regulate neuronal activity. Glia 2021, 69, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streit, W.J.; Conde, J.R.; Fendrick, S.E.; Flanary, B.E.; Mariani, C.L. Role of microglia in the central nervous system’s immune response. Neurol. Res. 2005, 27, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, G.; Sharma, K.; Agyeah, G.; Krüger, R.; Grünewald, A.; Fitzgerald, J.C. Neurodegeneration and Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Self-Sustained Loop. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2022, 22, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnet-Tschudi, F.; Zurich, M.-G.; Honegger, P. Neurotoxicant-induced inflammatory response in three-dimensional brain cell cultures. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2007, 26, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, J.P.; Sriram, K.; Miller, D.B. Defining “neuroinflammation”. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1139, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.-È.; Lowery, R.L.; Majewska, A.K. Microglial interactions with synapses are modulated by visual experience. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellner, S.; Paricio-Montesinos, R.; Spieß, A.; Masuch, A.; Erny, D.; Harsan, L.A.; Elverfeldt, D.V.; Schwabenland, M.; Biber, K.; Staszewski, O.; et al. Microglial CX3CR1 promotes adult neurogenesis by inhibiting Sirt 1/p65 signaling independent of CX3CL1. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmerjahn, A.; Kirchhoff, F.; Helmchen, F. Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science 2005, 308, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnet-Tschudi, F.; Sorg, O.; Honegger, P.; Zurich, M.G.; Huggett, A.C.; Schilter, B. Effects of the naturally occurring food mycotoxin ochratoxin A on brain cells in culture. Neurotoxicology 1997, 18, 831–839. [Google Scholar]
- Zurich, M.-G.; Lengacher, S.; Braissant, O.; Monnet-Tschudi, F.; Pellerin, L.; Honegger, P. Unusual astrocyte reactivity caused by the food mycotoxin ochratoxin A in aggregating rat brain cell cultures. Neuroscience 2005, 134, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, L.F.; Ghirnikar, R.S.; Lee, Y.L. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969–2000). Neurochem. Res. 2000, 25, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, M. Structure and transcriptional regulation of the GFAP gene. Brain Pathol. 1994, 4, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramontina, F.; Leite, M.C.; Cereser, K.; de Souza, D.F.; Tramontina, A.C.; Nardin, P.; Andreazza, A.C.; Gottfried, C.; Kapczinski, F.; Gonçalves, C.-A. Immunoassay for glial fibrillary acidic protein: Antigen recognition is affected by its phosphorylation state. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 162, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumora, L.; Grubišić, T. A Journey Through Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and Ochratoxin A Interactions. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2009, 60, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumora, L.; Domijan, A.-M.; Žanić Grubišić, T.; Šegvić Klarić, M. Differential activation of MAPKs by individual and combined ochratoxin A and citrinin treatments in porcine kidney PK15 cells. Toxicon 2014, 90, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koistinaho, M.; Koistinaho, J. Role of p38 and p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinases in microglia. Glia 2002, 40, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chansawhang, A.; Phochantachinda, S.; Temviriyanukul, P.; Chantong, B. Corticosterone potentiates ochratoxin A-induced microglial activation. Biomol. Concepts 2022, 13, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penalva-Olcina, R.; Juan, C.; Fernández-Franzón, M.; Juan-García, A. Involvement of pro-inflammatory mediators and cell cycle disruption in neuronal cells induced by gliotoxin and ochratoxin A after individual and combined exposure. Toxicol. Lett. 2024, 393, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Tobel, J.S.; Antinori, P.; Zurich, M.-G.; Rosset, R.; Aschner, M.; Glück, F.; Scherl, A.; Monnet-Tschudi, F. Repeated exposure to Ochratoxin A generates a neuroinflammatory response, characterized by neurodegenerative M1 microglial phenotype. Neurotoxicology 2014, 44, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradl, M.; Lassmann, H. Oligodendrocytes: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, S.; Gritti, L.; Crooks, D.; Dombrowski, Y. Oligodendrocytes in Development, Myelin Generation and Beyond. Cells 2019, 8, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempuraj, D.; Dourvetakis, K.D.; Cohen, J.; Valladares, D.S.; Joshi, R.S.; Kothuru, S.P.; Anderson, T.; Chinnappan, B.; Cheema, A.K.; Klimas, N.G.; et al. Neurovascular unit, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration markers in brain disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1491952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilleux, S.; Hermans, E. Neuroinflammation and regulation of glial glutamate uptake in neurological disorders. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razafimanjato, H.; Garmy, N.; Guo, X.-J.; Varini, K.; Di Scala, C.; Di Pasquale, E.; Taïeb, N.; Maresca, M. The food-associated fungal neurotoxin ochratoxin A inhibits the absorption of glutamate by astrocytes through a decrease in cell surface expression of the excitatory amino-acid transporters GLAST and GLT-1. NeuroToxicology 2010, 31, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Key Molecule for Memory in the Healthy and the Pathological Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sferra, A.; Nicita, F.; Bertini, E. Microtubule Dysfunction: A Common Feature of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Gettings, S.M.; Hazell, G.; Bourbia, N. In vitro study of ochratoxin A in the expression of genes associated with neuron survival and viability. Toxicology 2023, 483, 153376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ascenzo, M.; Colussi, C. Oxidative Stress and the Central Nervous System. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magistretti, P.J.; Allaman, I. A cellular perspective on brain energy metabolism and functional imaging. Neuron 2015, 86, 883–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobley, J.N.; Fiorello, M.L.; Bailey, D.M. 13 reasons why the brain is susceptible to oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Cha, M.; Lee, B.H. Neuroprotective Effect of Antioxidants in the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabska-Kobyłecka, I.; Szpakowski, P.; Król, A.; Książek-Winiarek, D.; Kobyłecki, A.; Głąbiński, A.; Nowak, D. Polyphenols and Their Impact on the Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases and Development. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, T.; Burdeos, G.C.; Itaya, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyazawa, T. Vitamin E: Regulatory Redox Interactions. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha Germano, B.C.; de Morais, L.C.C.; Idalina Neta, F.; Fernandes, A.C.L.; Pinheiro, F.I.; do Rego, A.C.M.; Araújo Filho, I.; de Azevedo, E.P.; de Paiva Cavalcanti, J.R.L.; Guzen, F.P.; et al. Vitamin E and Its Molecular Effects in Experimental Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boothby, L.A.; Doering, P.L. Vitamin C and vitamin E for Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Pharmacother. 2005, 39, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorres, K.L.; Raines, R.T. Prolyl 4-hydroxylase. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 45, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muroyama, A. An alternative medical approach for the neuroprotective therapy to slow the progression of Parkinson’s disease. Yakugaku Zasshi 2013, 133, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.W.; Park, C.G.; Park, M.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.R.; Lim, J.; Paek, S.H.; Choy, Y.B. Intrastriatal administration of coenzyme Q10 enhances neuroprotection in a Parkinson’s disease rat model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korczowska-Łącka, I.; Słowikowski, B.; Piekut, T.; Hurła, M.; Banaszek, N.; Szymanowicz, O.; Jagodziński, P.P.; Kozubski, W.; Permoda-Pachuta, A.; Dorszewska, J. Disorders of Endogenous and Exogenous Antioxidants in Neurological Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Esparza, M.Á.; Mateo, E.M.; Robles, J.A.; Capoferri, M.; Jiménez, M.; Soria, J.M. Unveiling the Neurotoxic Effects of Ochratoxin A and Its Impact on Neuroinflammation. Toxins 2025, 17, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060264
García-Esparza MÁ, Mateo EM, Robles JA, Capoferri M, Jiménez M, Soria JM. Unveiling the Neurotoxic Effects of Ochratoxin A and Its Impact on Neuroinflammation. Toxins. 2025; 17(6):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060264
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Esparza, María Ángeles, Eva María Mateo, José Antonio Robles, Michela Capoferri, Misericordia Jiménez, and José Miguel Soria. 2025. "Unveiling the Neurotoxic Effects of Ochratoxin A and Its Impact on Neuroinflammation" Toxins 17, no. 6: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060264
APA StyleGarcía-Esparza, M. Á., Mateo, E. M., Robles, J. A., Capoferri, M., Jiménez, M., & Soria, J. M. (2025). Unveiling the Neurotoxic Effects of Ochratoxin A and Its Impact on Neuroinflammation. Toxins, 17(6), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060264




