Systematic Review on CyanoHABs in Central Asia and Post-Soviet Countries (2010–2024)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Collection Process
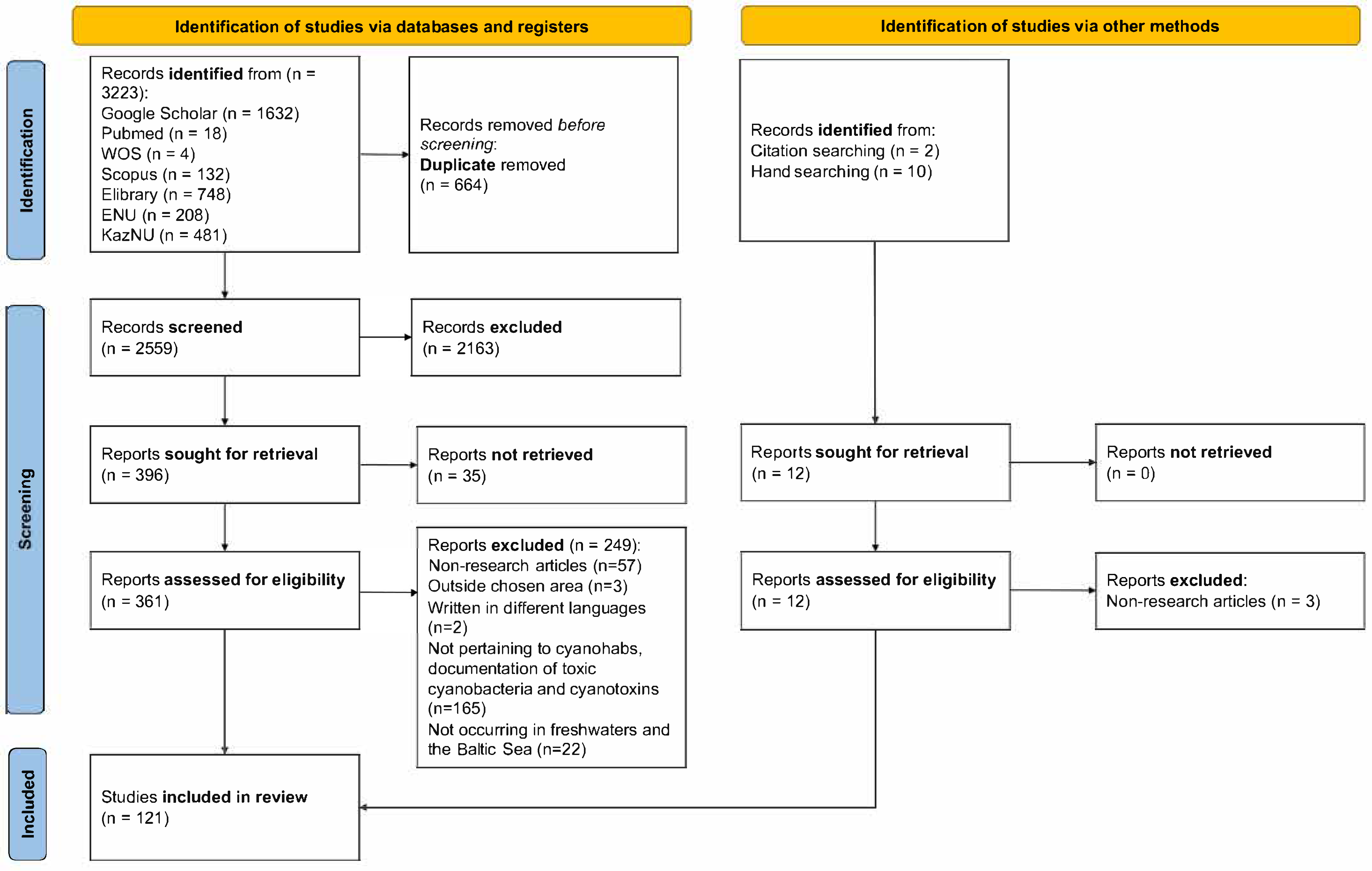
3. Results
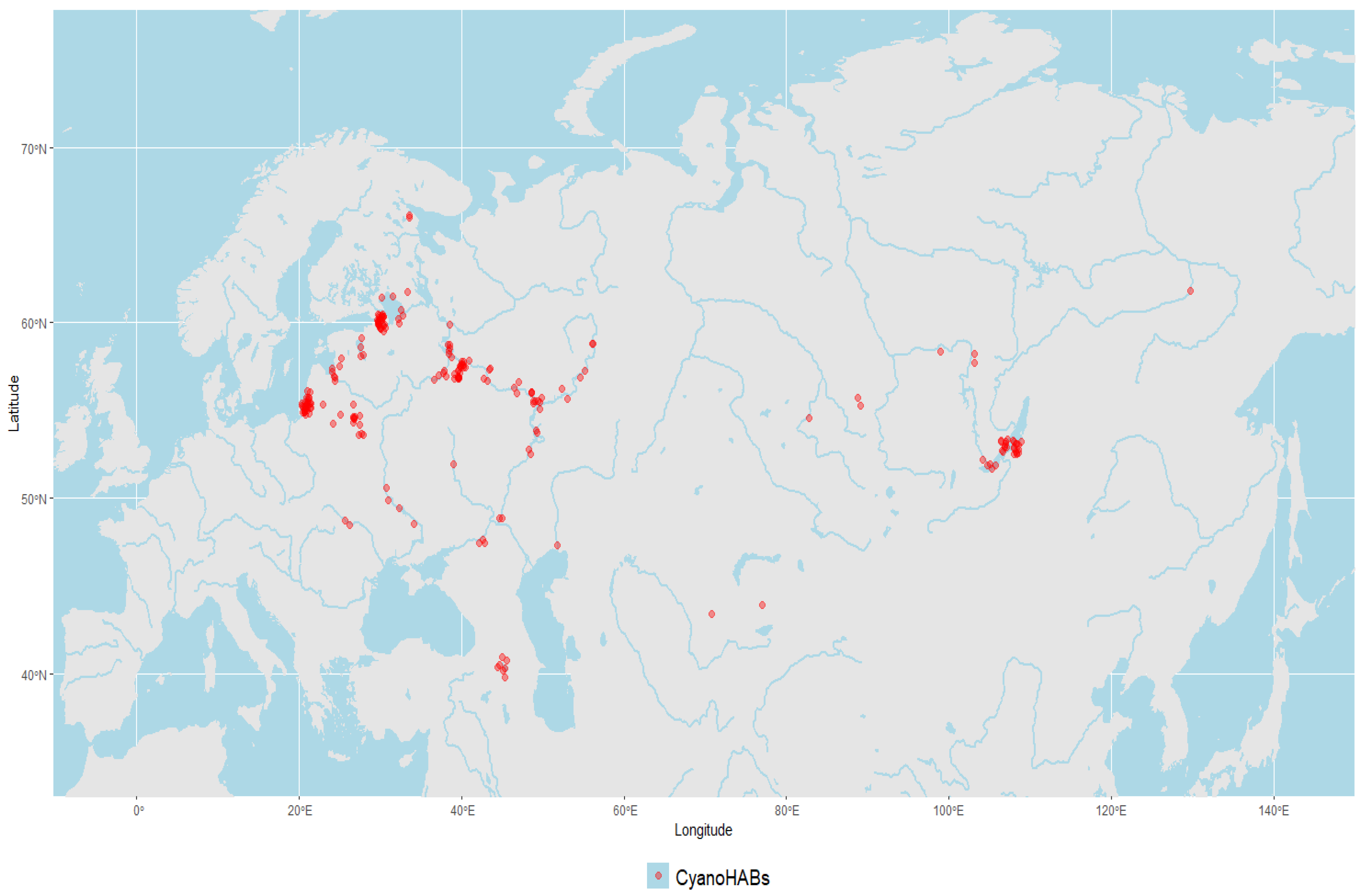
3.1. Overview on Local CyanoHAB Events
3.2. Documented Presence of Cyanotoxins and Their Detection Methods
| Location | Year/Period | Water Systems | Dominant Toxic Cyanobacterial Species | Cyanotoxin: Concentration (µg L−1, Unless Otherwise Specified) | Detection Method | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armenia | 2012 | Lake Yerevan | Microcystis spp., Dolichospermum spp., Planktothrix spp. | 12 cyanotoxins including 10 MC congeners (max MC-RR)—0.1–34.8 µg g−1 dw); ATX-a—0.1–2.3 µg g−1 dw; CYN—0.1–0.3 ng mg−1 dw. | LC-MS/MS; ELISA (MCs) | [69] |
| 2018 | Lake Sevan | Dolichospermum spp., Aphanizomenon spp., Anabaena spp., Microcystis spp. | 40 cyanopeptide congeners (aeruginosins, microginins, ana-baenopeptines, cyanopeptolines, and 10 MC congeners)— Up to 2.5 μg L−1 (total). | LC-MS | [74] | |
| 2020 | Lake Sevan | Microcystis spp., Aphanizomenon spp., Aphanothece spp., Dolichospermum spp., Anabaena spp. | Biological testing | [75] | ||
| Belarus | 2008–2010 | Svisloch River | Microcystis spp., Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Anabaena spp., Planktothrix agardhii Aphanotece clathrata | MCs (MC-LR, MC-VF)— 2.4 μg g−1 dw (total); Oscillamide Y—0.36 μg g−1 dw | LC/MS; ELISA, PCR (mcyE) | [76,77] |
| 2011–2012 | River Viliya (Neris) and two tributaries: the Smerdiya and Usha Rivers | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Dolichospermum spp., Microcystis spp., Planktothrix agardhii | MCs (MC-LR; MC-WR; MC-RR, dmMC-LR; dmMC-RR)— peaks identified. | MALDI-TOF | [78] | |
| 2012–2015 | Lake Bol’shie Shvakshty | Microcystis spp., Anabaena spp., Aphanizomenon flos-aquae | MCs (MC-LR; MC-YR; MC-RR; dmMC-LR; dmMC-RR)—peaks identified. | MALDI-TOF; PCR | [79] | |
| 2012–2016 | 35 fisheries | Aphanizomenon spp., Anabaena spp., Microcystis spp., Oscillatoria spp. | PCR (mcyE) | [80] | ||
| Estonia | 2014–2015 | Lake Peipsi | Aphanizomenon spp., Dolichospermum spp., Microcystis spp., Planktothrix spp. | Genus-specific qPCR (mcyE) | [81] | |
| Kazakhstan | 2016 | Lake Bilikol | Anabaena flos-aquae, Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Microcystis aeruginosa, Oscillatoria spp., Phormidium tenue, Nostoc spp. | MCs (MC-RR; 7-dmMC-RR; MC-LR)—peaks identified. | HPLC-MS; Daphnia test | [82] |
| 2019 | Ural River | Anabaena spp., Cuspidothrix issatschenkoi, Cylindrospermopsis ratiborskii, Dolichospermum spp., Pseudanabaena limnetica, Planktothrix spp. | MCs, NOD—peaks identified; STX—ND. | UHPLC-DAD; PCR (mcyE, sxtA) | [62] | |
| 2023 | Kapchagai Reservoir | MCs—peaks identified. | UHPLC-DAD | Unpubl. data | ||
| Lithuania | 2014–2015 | Lithuanian Lakes: Gauštvinis, Jieznas, and Širvys | Aphanizomenon spp., Cuspidothrix issatschenkoi, Sphaerospermopsis aphanizomenoides, Anabaenopsis cf.elenkinii, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, Dolichospermum spp. | STX (Lake Jieznas)—up to 1.06 μg L−1); ATX-a (Lake Širvys)—up to 0.31 μg L−1; neoSTX, GTXs— peaks identified. | LC-MS/MS; PCR (sxtA) | [83] |
| Lithuania, | 2014 | Curonian Lagoon (southeastern Baltic Sea) | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Microcystis spp., Planktothrix agardhii | 10 MC congeners— 0.52–153.60 μg L−1 (total); STX, ATX-a, and CYN—ND. | LC-MS/MS | [84] |
| 2013–2017 | Curonian Lagoon (southeastern Baltic Sea) | Aphanizomenon spp., Planktothrix spp., Microcystis spp., Dolichospermum spp., Woronichinia spp. | 27–34 cyano- metabolites at different sample stations; including 10 MC congeners, NOD, and ATX-a (detailed quantitative analysis). | LC-MS | [85] | |
| 2018 | Curonian Lagoon (southeastern Baltic Sea) | Planktothrix agardhii, Microcystis spp., Aphanizomenon flos-aquae | MCs confirmed. | Microcystin Strip test | [86] | |
| 2018 | Curonian Lagoon (southeastern Baltic Sea) | Microcystis spp., Aphanizomenon spp., Dolichospermum spp., Planktothrix agardhii, Nodularia spumigena, Aphanocapsa spp., Limnococcus limneticus | 8 MC congeners—0.002–12.13 μg L−1; NOD—0.003–0.05 μg L−1; ATX-a—0.01–2.23 μg L−1. | LC-MS/MS | [87] | |
| 2018–2020 | Curonian Lagoon (southeastern Baltic Sea) | Microcystis spp., Aphanizomenon flosaquae, Dolichospermum spp., Woronichinia compacta | 20 MC congeners—peaks identified. | LC-MS/MS; PCR (mcyE) | [72] | |
| Russia | 1999–2004 and 2005–2007 | Lake Nero | Planktothrix agardhii, Microcystis spp. | MCs (MC-LR; MC-RR)— 0.55–12.91 μg L−1. | MALDI-TOF MS; HPLC-DAD | [88] |
| 2010–2011 | Lake Nero | Raphidiopsis raciborskii, Aphanizomenon gracile | CYN—0.01–0.36 μg L−1. | LC-MS/MS; PCR (CYN biosynthesis genes) | [73] | |
| 2000s | 4 water reservoirs of Leningrad | Planktothrix agardhii, Microcystis aeruginosa | 9 MC congener peaks identified. | HPLC | [89] | |
| 2002–2008 | Curonian Lagoon (southeastern Baltic Sea) | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Anabaena spp., Microcystis spp., Planktothrix agardhii | PCR (mcyE) | [90] | ||
| 2004–2005 | Red Lake | Anabaena spp., Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Gloeotrichia echinulata, Microcystis spp. | 4 MC congener peaks identified. | HPLC-UV-MS; PCR (mcyE) | [91] | |
| 2004–2005 | Lake Ladoga | Aphanizomenon spp., Anabaena spp., Anabaena affine, Microcystis spp., Woronichinia naegeliana | 5 MC congeners (MC-LR and others); 7 cytotoxins (anabaenopeptins and planktopeptin BL). | HPLC; biological tests (Daphnia) | [92] | |
| 2004–2006 | Beryozovskayartificial reservoir | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Microcystis aeruginosa | PCR (mcyE) | [93] | ||
| 2005–2012 | Lake Baikal and water reservoirs of Angara water | Anabaena spp., Aphanizomenon spp., Gloeotrichia echinulata, Microcystis spp. | MCs; STX; neoSTX; GTX— 0.14–1.37 μg L−1 (total). | ELISA, LC-MS; PCR (mcyE and sxtA) | [94,95,96,97,98,99] | |
| 2006 | Curonian Lagoon (southeastern Baltic Sea) | Microcystis spp., Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Woronichinia compacta | MCs—NA. | PCR (mcyA, mcyE, mcyD, ana C, anaA, anaB, sxtA, and sxtI) | [100,101] | |
| 2006–2007 | The Gulf of Finland (Baltic Sea) | Microcystis spp., Anabaena spp., Woronichinia naegeliana, Gloeotrichia echinulata | MC-LR; [DMAdda5]MC-LR; anabenopeptin F; micropeptin 88A; aerunogenosin 298A; anabaenopeptins; oscillapeptilid 97A; oscyllamid Y— peaks identified. | HPLC; biological tests | [102] | |
| 2008–2010 | Lakes Sestroretsky Razliv, Suzdal, Shchuchy, and the Gulf of Finland | Planktothrix agardhii | 2010—MC-LR: 1.2–53.8 μg gr−1; MC-RR: 1.2–10.3 μg gr−1, ATX-a: <0.6 μg L−1. | LC-MS | [103] | |
| 2008–2011 | Sestroretsky Razliv | Planktothrix agardhii, Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Microcystis spp. | MCs (MC-LR—0.02–0.2 μg L−1; dmMC-LR—0.02 μg L−1; MC-RR—0.01–0.09 μg L−1; dmMC-RR—0.01–0.04 μg L−1; MC-YR—0.01–0.02 μg L−1);—0.01–0.341 μg L−1 (total); ATX-a—0.8–5.0 μg L−1. | LC-MS | [104] | |
| 2014–2018 | Lakes Sestroretsky Razliv and Nizhny Suzdalskoye and the Gulf of Finland | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Planktothrix agardhii, Microcystis spp., Planktolyngbya limnetica, Aphanocapsa spp., Woronichinia compacta, Dolichospermum spp., Aphanocapsa spp. | 20 MC congeners (detailed analysis by years/locations)— Up to 8.2 μg L−1 (Lakes); >40 μg L−1 (Gulf of Finland); ATX-a— 0.01–1.7 μg L−1. | HPLC-MS-HR | [105] | |
| 2009–2011 | Lake Nero and Upper Volga | Planktothrix agardhii, Microcystis spp., Anabaena spp. | MCs—NA. | ELISA; PCR (mcyE) | [106,107] | |
| 2010 | Lake Nero | Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, Planktothrix agardhii, Pseudoanabaena limnetica, Limnotrix redekei | CYN—0.12–0.36 μg L−1. | LC-MS/MS | [60] | |
| 2010 | Rybinsk, Gorky, and Cheboksary reservoirs | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Microcystis aeruginosa, Anabaena scheremetievi, Anabaena flos-aquae, Planktothrix agardhii | 9 MC congeners 0.079–8.375 μg L−1 (total). | LC-MS | [108] | |
| 2010 and 2012 | Kotokelskoe Lake | Aphanocapsa spp., Anabaena spp., Microcystis spp. | 8 MC congeners— 13.8–76 μg L−1 (ELISA). | LC-MS; ELISA PCR (mcyE) | [109] | |
| 2010–2012 | Lakes of Saint Petersburg: Sestroretsky Razliv Lake (Razliv) and Lower Suzdal Lake (Suzdal) | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Microcystis spp., Planktothrix agardhii | 14 MC congeners (Razliv)— 0.11–41.37 μg L−1; 9 MC congeners (Suzdal)— 0.01–2.89 μg L−1; ATX-a (Suzdal)—<0.54 μg L−1. | LC-MS | [110] | |
| 2010–2012 | Sestroretsky Razliv and Nizhny Suzdalskoye lakes | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Anabaena spp., Microcystis spp., Limnothrix planctonica, Planktothrix agardhii | MCs (MC-LR; MC-YR; MC-RR; D-Asp3-MC-RR; demethyl-MC-RR; MC-yR)—ext up to 0.211 μg L−1 ATX-a—ND. | LC-MS | [111] | |
| 2011 | Kuibyshev Reservoir and Rivers Kama and Mesha | MCs— 0.45–5.72 μg L−1. | ELISA | [112] | ||
| 2011 | Kuibyshev reservoirs, River Mesha and Lake Nijnij Kaban | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Microcystis aeruginosa, Anabaena spp. | MCs (total)— 0.5–5.72 μg L−1. | ELISA | [113] | |
| 2011–2013 | Curonian Lagoon (southeastern Baltic Sea) | Microcystis spp., Planktothrix agardhii, Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Anabaena flos-aquae | MCs—identified. | ELISA | [114] | |
| 2012–2015 | Sestroretsky Razliv | Dolichospermum flos-aquae, Dolichospermum lemmermannii, Planktothrix agardhii, Aphanizomenon flos-aquae | ATX-a—ND; STX, neoSTX, and GTXs—ND. | LC-MS; thiol-sensitive biosensors | [115] | |
| 2012–2017 | The Gulf of Finland (Baltic Sea) | Aphanizomenon flosaquae, Planktothrix agardhii, Microcystis aeruginosa, Dolichospermum spp. | 9 MC congeners— Komarovo: ext up to 49 μg L−1; intra 466 μg g−1; ATX-a—ext 1.4 μg L−1. | HPLC-HRMS; genus-specific PCR (mcyE and anaC) | [116] | |
| 2013 | Rybinsk Reservoir | Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis viridis, Planktothrix agardhii, Dolichospermum spp. | MCs—1.7–5.8 μg L−1; STX—0.02–0.05 μg L−1; CYN, ATX-a—ND. | ELISA; PCR (mcyE, anaA, anaC and sxtA) | [117] | |
| 2013 | 4 water reservoirs of Yaroslavl | Microcystis spp., Aphanizomenon flos-aquae | MCs—0.2–9.5 μg L−1. | ELISA; PCR (mcyE, mcyD, anaA, anaC, and sxtA) | [118] | |
| 2013–2015 | Sestroretsky Razliv Lake, Lower Suzdal Lake, Nero Lake, Rumnikovo Lake, Gorky Reservoir, Novosibirsk Reservoir | Aphanizomenon spp., Microcystis aeruginosa, Limnothrix redekei, Dolichospermum spp., Planktothrix agardhii | STX—intra 1.3–26.0 μg L−1, ext 174–1386 μg g−1 dw; ATX-a—3.0–35 μg g−1 dw. | LC-MS/MS; PCR (sxtA, sxtI and anaC) | [119] | |
| 2013–2017 | Volga River reservoirs, Curonian Lagoon (southeastern Baltic Sea), and lakes in the European part of the RF | Microcystis spp. | MCs—highly variable; 0.1–32.0 μg L−1 (total) | HPLC-HRMS; LC-MS/MS; ELISA; PCR (mcyE and mcyD) | [120] | |
| 2017 | Voronezhskoye Reservoir | Microcystis spp. | MCs (MC-LR; MC-RR; MC-YR)—19.73–88.68 µg L−1 (total). | HPLC-MS-MS | [121] | |
| 2016 | Mukhor Bay (Lake Baikal) | Dolichospermum spp., Planktothrix spp., Aphanocapsa spp. | MCs (MC-LA; MC-YR; MC-LF; MC-YM(O); dmMC-LR)— ext—1.2–3.39 μg L−1; intra 0.66–4 μg g−1 dw. | ELISA; LC-MS | [122] | |
| 2016 | Boguchansk water reservoir | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Dolichospermum spp. | MCs—0.3 μg L−1. | ELISA; PCR (mcyE and sxtA) | [123] | |
| 2016 | Lake Baikal | Anabaena spp., Gloeotrichia echinulata | MCs—0.11–6.2 μg g−1 dw. | ELISA | [124] | |
| 2016 and 2018 | Volga–Kama–Don water cascade | Microcystis spp., Dolichospermum spp., Planktothrix agardhii, Aphanizomenon spp., Cuspidothrix issatschenkoi, Oscillatoria spp. | 14 MCs (MC-RR; MC-LR; MC-YR; dmMCs and others)— 0.1–16.4 μg L−1; ATX-a— 0.01 μg L−1. | LC-MS; HPLC-HRMS; PCR (mcyE and anaC) | [125,126] | |
| 2017 | Irkutsk Reservoir, 50 × 30 m water patch near hydroelectric dam | Dolichospermum lemmermannii | STX: HPLC-MS 600 ± 100 μg L−1; ELISA—2900 ± 900 μg L−1. | HPLC-MS; ELISA; PCR (sxtA) | [127] | |
| 2017 | Curonian Lagoon (southeastern Baltic Sea) | MCs—1–10 μg L−1. | Microcystin strip test | [128] | ||
| 2019 | Lake Baikal | Dolichospermum lemmermannii | STX—ext 0.45 ± 0.05 μg L−1; Intra 7.900 ± 200 μg g−1 dw. | ELISA; PCR (sxtA) | [129] | |
| 2018 | Saint Petersburg water reservoirs | MC-RR and MC-LR peaks detected (NA). | HPLC-UV/MS | [130] | ||
| 2019 | Svyatozero Lake | Microcystis spp., Woronichinia naegeliana | 8 MC congeners— 6.22–6.34 μg L−1. | HPLC–HRMS | [131] | |
| 2019–2020 | Lakes Krivoe and Krugloe | Dolichospermum lemmermannii | 4 MCs (MC-LR; MC-RR; 2 demethylated MC congeners) MC-LR—ext up to 78 ng L−1, intra—2 mg g−1 dw. | HPLC-HRMS | [132] | |
| Ukraine | 2017 | Reservoir for Kasperivtsi Hydrothermal Power Plant, River Seret, and pond of Khmelnytsky Atomic Power Plant | Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, Aphanizomenon gracile, Dolichospermum flos-aquae, Planktothrix agardhii, Microcystis aeruginosa, Cuspidothrix issatschenkoi | MC-LR; MC-YR; MC-RR; CYN; ATX-a—ND. | HPLC-DAD; Biological test | [65] |
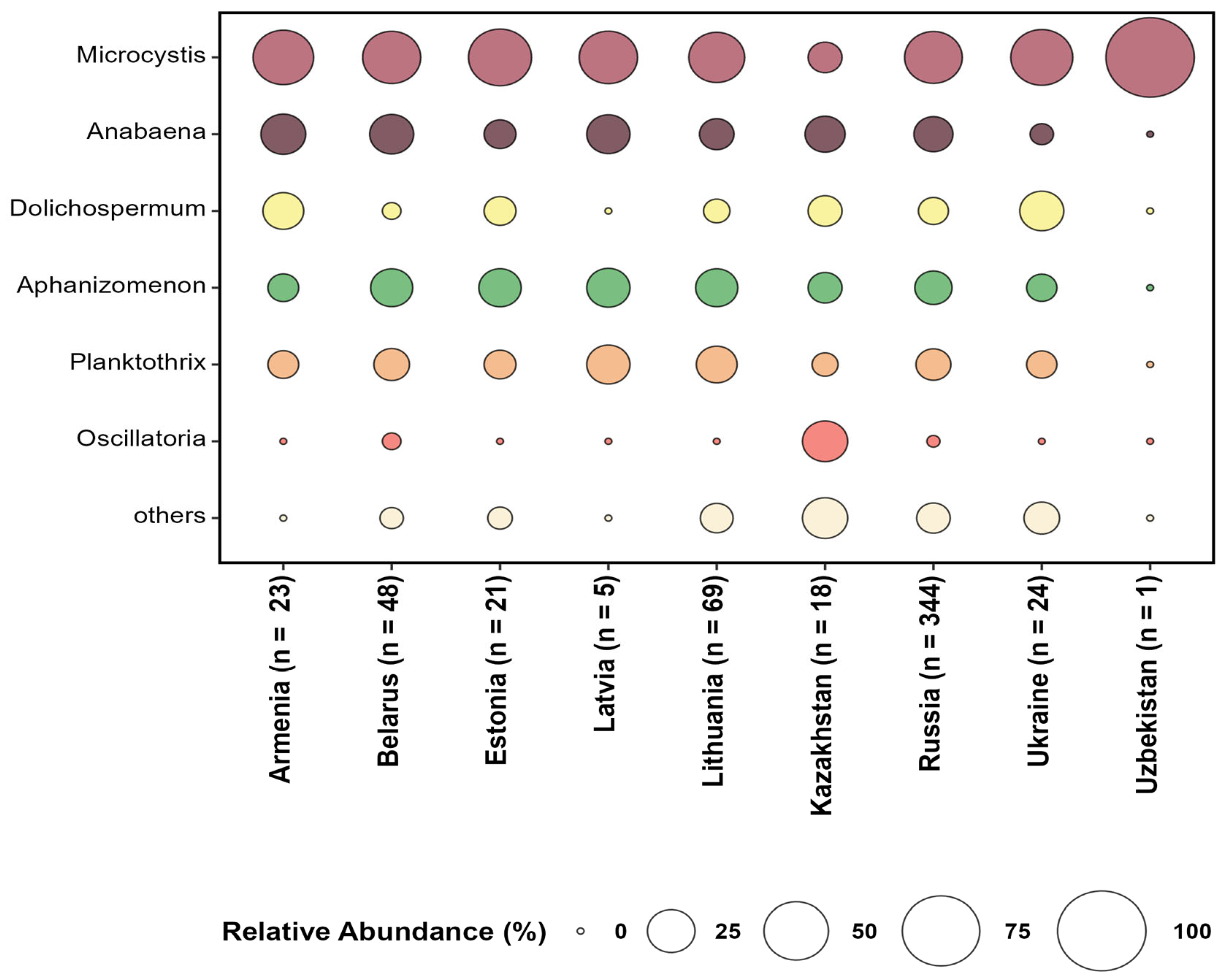
3.3. Dominant and Recurrent Potentially Toxic Cyanobacteria Genera
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopez, C.B.; Jewett, E.B.; Dortch, Q.T.W.B.; Walton, B.T.; Hudnell, H.K. Scientific Assessment of Freshwater Harmful Algal Blooms; Interagency Working Group on Harmful Algal Blooms, Hypoxia, and Human Health of the Joint Subcommittee on Ocean Science and Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Boyer, G.L. Health impacts from cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Implications for the North American Great Lakes. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, V.G.; Khan, E. Freshwater neurotoxins and concerns for human, animal, and ecosystem health: A review of anatoxin-a and saxitoxin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugumanova, G.; Ponomarev, E.D.; Askarova, S.; Fasler-Kan, E.; Barteneva, N.S. Freshwater cyanobacterial toxins, cyanopeptides and neurodegenerative diseases. Toxins 2023, 15, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeger, S.J.; Hitzfeld, B.C.; Dietrich, D.R. Occurrence and elimination of cyanobacterial toxins in drinking water treatment plants. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.P.; Wood, S.A.; Dietrich, D.R.; Puddick, J. Costs of harmful blooms of freshwater cyanobacteria. In Cyanobacteria: An Economic Perspective; Sharma, N.K., Rai, A.K., Stal, L.J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Sanseverino, I.; Conduto, D.; Pozzoli, L.; Dobricic, S.; Lettieri, T. Algal Bloom and Its Economic Impact; JRC Technical Reports; European Commission, JRC Institute for Environment and Sustainability: Ispra, Italy, 2016; pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ash, A.K.; Patterson, S. Reporting of freshwater cyanobacterial poisoning in terrestrial wildlife: A systematic map. Animals 2022, 12, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornabene, B.J.; Smalling, K.L.; Hossack, B.R. Effects of harmful algal blooms on amphibians and reptiles are under-reported and under-represented. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 1936–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W. A Status Report on Planktonic Cyanobacteria (Blue Green Algae) and Their Toxins; US Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinatti, OH, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Brittain, S.M.; Wang, J.; Babcock-Jackson, L.; Carmichael, W.W.; Rinehart, K.L.; Culver, D.A. Isolation and characterization of microcystins, cyclic heptapeptide hepatotoxins from a Lake Erie strain of Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Great Lakes Res. 2000, 26, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKindles, K.; Frenken, T.; McKay, R.M.L.; Bullerjahn, G.S. Binational efforts addressing cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in the Great Lakes. In Contaminants of the Great Lakes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 109–133. [Google Scholar]
- Gorney, R.M.; June, S.G.; Stainbrook, K.M.; Smith, A.J. Detections of Cyanobacteria Harmful Algal Blooms (cyanoHABs) in New York State, United States (2012–2020). Lake Reserv. Manag. 2023, 39, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy-Lachapelle, A.; Duy, S.V.; Munoz, G.; Dinh, Q.T.; Bahl, E.; Simon, D.F.; Sauvé, S. Analysis of multiclass cyanotoxins (microcystins, anabaenopeptins, cylindrospermopsin and anatoxins) in lake waters using on-line SPE liquid chromatography high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 5289–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Eggleston, E.; Howard, M.D.A.; Ryan, S.; Gichuki, J.; Kennedy, K.; Tyler, A.; Beck, M.; Huie, S.; Caron, D.A. Historic and recent trends of cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms and environmental conditions in Clear Lake, California: A 70-Year perspective. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2023, 11, 00115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Jia, Y.; Qin, B.; Li, R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Gan, N.; Xu, H.; Shan, K.; Sukenik, A. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Biological traits, mechanisms, risks, and control strategies. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2023, 48, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M.; Pahlevan, N. Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature 2019, 574, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftin, K.A.; Graham, J.L.; Hilborn, E.D.; Lehmann, S.C.; Meyer, M.T.; Dietze, J.E.; Griffith, C.B. Cyanotoxins in inland lakes of the United States: Occurrence and potential recreational health risks in the EPA National Lakes Assessment 2007. Harmful Algae 2016, 56, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harke, M.J.; Steffen, M.M.; Gobler, C.J.; Otten, T.G.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Wood, S.A.; Paerl, H.W. A review of the global ecology, genomics, and biogeography of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis spp. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorus, I. Introduction: Cyanotoxins—Research for environmental safety and human health. In Cyanotoxins: Occurrence, Causes, Consequences; Chorus, I., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 1–4. ISBN 978-3-642-59514-1. [Google Scholar]
- Plaas, H.E.; Paerl, H.W. Toxic cyanobacteria: A growing threat to water and air quality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svirčev, Z.; Lalić, D.; Bojadžija Savić, G.; Tokodi, N.; Drobac Backović, D.; Chen, L.; Meriluoto, J.; Codd, G.A. Global geographical and historical overview of cyanotoxin distribution and cyanobacterial poisonings. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 2429–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R. Acute animal and human poisonings from cyanotoxin exposure—A review of the literature. Environ. Intern. 2016, 91, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svirčev, Z.; Drobac, D.; Tokodi, N.; Mijović, B.; Codd, G.A.; Meriluoto, J. Toxicology of Microcystins with reference to cases of human intoxications and epidemiological investigations of exposures to Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 621–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegura, B.; Straser, A.; Filipič, M. Genotoxicity and potential carcinogenicity of cyanobacterial toxins—A review. Mutat. Researc 2011, 727, 16–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caban-Holt, A.; Mattingly, M.; Cooper, G.; Schmitt, F.A. Neurodegenerative memory disorders: A potential role of environmental toxins. Neurol. Clin. 2005, 23, 485–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.A.; Höglinger, G.U. Neurodegenerative diseases: Neurotoxins as sufficient etiologic agents? Neuromolecular Med. 2008, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caller, T.A.; Doolin, J.W.; Haney, J.F.; Murby, A.J.; West, K.G.; Farrar, H.E.; Ball, A.; Harris, B.T.; Stommel, E.W. A Cluster of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in New Hampshire: A possible role for toxic Cyanobacteria blooms. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2009, 10 (Suppl. S2), 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banack, S.A.; Caller, T.; Henegan, P.; Haney, J.; Murby, A.; Metcalf, J.S.; Powell, J.; Cox, P.A.; Stommel, E. Detection of cyanotoxins, β-N-Methylamino-l-Alanine and microcystins, from a lake surrounded by cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Toxins 2015, 7, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbick, N.; Ziniti, B.; Stommel, E.; Linder, E.; Andrew, A.; Caller, T.; Haney, J.; Bradley, W.; Henegan, P.L.; Shi, X. Assessing cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms as risk factors for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurotox. Res. 2018, 33, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, F.J.; Preece, E.; Backer, L. Status of state cyanoHAB outreach and monitoring efforts, United States. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2021, 37, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, N.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Guertault, L.; Nelson, N.G. Satellite and in situ cyanobacteria monitoring: Understanding the impact of monitoring frequency on management decisions. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, L.C.; Manassaram-Baptiste, D.; LePrell, R.; Bolton, B. Cyanobacteria and algae blooms: Review of health and environmental data from the harmful algal bloom-related illness surveillance system (HABISS) 2007–2011. Toxins 2015, 7, 1048–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Stumpf, R.P.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Werdell, P.J.; Loftin, K.A.; Meredith, A. Measurement of cyanobacterial bloom magnitude using satellite remote sensing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Cao, M.; Tang, P.; Deng, S.; Chen, L.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Shen, M.; et al. Microcystins exposure associated with blood lipid profiles and dyslipidemia: A cross-sectional study in Hunan Province, China. Toxins 2023, 15, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuellar-Martinez, T.; Ruiz-Fernández, A.C.; Alonso-Hernández, C.; Amaya-Monterrosa, O.; Quintanilla, R.; Carrillo-Ovalle, H.L.; Arbeláez, M.N.; Díaz-Asencio, L.; Méndez, S.M.; Vargas, M.; et al. Addressing the problem of harmful algal blooms in Latin America and the Caribbean—A regional network for early warning and response. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . Buratti, F.M.; Manganelli, M.; Vichi, S.; Stefanelli, M.; Scardala, S.; Testai, E.; Funari, E. Cyanotoxins: Producing organisms, occurrence, toxicity, mechanism of action and human health toxicological risk evaluation. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1049–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barteneva, N.S.; Meirkhanova, A.; Malashenkov, D.; Vorobjev, I.A. To Die or Not to Die—Regulated cell death and survival in cyanobacteria. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, A.; Almanza, V.; Haakonsson, S.; Palacio, H.; Benitez Rodas, G.A.; Barros, M.U.G.; Capelo-Neto, J.; Urrutia, R.; Aubriot, L.; Bonilla, S. Cyanobacterial bloom monitoring and assessment in Latin America. Harmful Algae 2023, 125, 102429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Lim, W.A.; Lu, D.; Dai, X.; Orlova, T.; Iwataki, M. Harmful algal blooms and associated fisheries damage in East Asia: Current status and trends in China, Japan, Korea and Russia. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, A.A.; Komova, A.V.; Namsaraev, Z.B. Trends and driving forces of cyanobacterial blooms in Russia in the 20th and early 21st Centuries. Microbiology 2022, 91, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkes, B.; Löptien, U.; Dietze, H. Cyanobacteria blooms in the Baltic Sea: A review of models and facts. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 2347–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finni, T.; Kononen, K.; Olsonen, R.; Wallström, K. The history of cyanobacterial blooms in the Baltic Sea. AMBIO A J. Hum. Environ. 2001, 30, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, B.; Andersen, P.; Arneborg, L.; Cembella, A.; Eikrem, W.; John, U.; West, J.J.; Klemm, K.; Kobos, J.; Lehtinen, S.; et al. Harmful Algal Blooms and their effects in coastal seas of Northern Europe. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Gan, N.; Geng, R.; Cao, Q.; Song, L.; Yu, G.; Li, R. Cyanobacterial blooms in China: Diversity, distribution, and cyanotoxins. Harmful Algae 2021, 109, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libert, B.; Lipponen, A. Challenges and opportunities for transboundary water cooperation in Central Asia: Findings from UNECE’s regional assessment and project work. Inter. J. Water Resour. Develop. 2012, 28, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Pi, Y.; Yu, X.; Ta, Z.; Sun, L.; Disse, M.; Zeng, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, R. Climate change, water resources and sustainable development in the arid and semi-arid lands of Central Asia in the past 30 years. J. Arid. Land 2019, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fang, G.; Wang, F.; Hao, H. Water resources management and dynamic changes in water politics in the transboundary river basins of Central Asia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 3281–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthe, D.; Chalov, S.; Borchardt, D. Water resources and their management in central Asia in the early twenty first century: Status, challenges and future prospects. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhupankhan, A.; Tussupova, K.; Berndtsson, R. Water in Kazakhstan, a key in Central Asian water management. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Gojenko, B.; Yu, J.; Wei, L.; Luo, D.; Xiao, T. A review of water pollution arising from agriculture and mining activities in Central Asia: Facts, causes and effects. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU. Water in Central Asia: An Increasingly Scarce Resource. Think Tank. European Parliament. 2018. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/thinktank/en/document/EPRS_BRI(2018)625181 (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Oad, R.; Wichelns, D.; Patterson, T.; Parsons, S. Developing Water Resources: Sector Strategies in Central and West Asia—Azerbaijan: Final Report. Available online: https://www.adb.org/projects/documents/developing-water-resources-sector-strategies-cwa-azerbaijan-tacr (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Betsiavili, M.; Ubilava, M. Water quality and wastewater treatment systems in Georgia. In Dangerous Pollutants (Xenobiotics) in Urban Water Cycle; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; pp. 35–44.
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatziefthimiou, A.D.; Banack, S.A.; Metcalf, J.S. Harmful algal and cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in the Arabian seas: Current status, implications, and future directions. In The Arabian Seas: Biodiversity, Environmental Challenges and Conservation Measures; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2021; pp. 1083–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Belykh, O.; Gladkikh, A.; Sorokovikova, E.; Tikhonova, I.; Potapov, S.; Fedorova, G. Microcystin-producing Cyanobacteria in water reservoirs of Russia, Belarus and Ukraine. Chem. Sustain. Develop. 2013, 21, 347–361. [Google Scholar]
- Babanazarova, O.V.; Sidelev, S.I.; Fastner, J. Northern Expansion of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanoprokaryota) observed in shallow highly eutrophic Lake Nero (Russia). IJA 2015, 17, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namsaraev, Z.; Melnikova, A.; Komova, A.; Ivanov, V.; Rudenko, A.; Ivanov, E. Algal bloom occurrence and effects in Russia. Water 2020, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirasbekov, Y.; Abdimanova, A.; Sarkytbayev, K.; Samarkhanov, K.; Abilkas, A.; Potashnikova, D.; Arbuz, G.; Issayev, Z.; Vorobjev, I.A.; Malashenkov, D.V.; et al. Combining imaging flow cytometry and molecular biological methods to reveal presence of potentially toxic algae at the Ural River in Kazakhstan. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 680482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulabhusan, P.K.; Campbell, K. Recent trends in the detection of freshwater cyanotoxins with a critical note on their occurrence in Asia. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 32, e00150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, I.Y.; Wu, P.; Wei, J.; Luo, J.; Ding, P.; Wei, H.; Yang, F. A mini-review on detection methods of microcystins. Toxins 2020, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzymski, P.; Horyn, O.; Budzyńska, A.; Jurczak, T.; Kokociński, M.; Niedzielski, P.; Klimaszyk, P.; Falfushynska, H. A report of Cylindrospermopsis Raciborskii and other Cyanobacteria in the water reservoirs of power plants in Ukraine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15245–15252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaravadivelu, D.; Sanan, T.T.; Venkatapathy, R.; Mash, H.; Tettenhorst, D.; DAnglada, L.; Frey, S.; Tatters, A.O.; Lazorchak, J. Determination of cyanotoxins and prymnesins in water, fish tissue, and other matrices: A review. Toxins 2022, 14, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying small molecules via high resolution mass spectrometry: Communicating confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardo, M.; Sanchís, J.; Núñez, O.; Farré, M. Suspect screening of natural toxins in surface and drinking water by high performance liquid chromatography and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasyan, A.; Christophoridis, C.; Wilson, A.E.; Zervou, S.-K.; Kaloudis, T.; Hiskia, A. Diversity of Cyanobacteria and the presence of cyanotoxins in the epilimnion of Lake Yerevan (Armenia). Toxicon 2018, 150, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, A.T. Environmental mass spectrometry. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2013, 6, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabyshev, V.A.; Sidelev, S.I.; Chernova, E.N.; Gabysheva, O.I.; Voronov, I.V.; Zhakovskaya, Z.A. Limnological characterization and first data on the occurrence of toxigenic cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in the plankton of some lakes in the permafrost zone (Yakutia, Russia). Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2023, 16, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overlingė, D.; Toruńska-Sitarz, A.; Kataržytė, M.; Pilkaitytė, R.; Gyraitė, G.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Characterization and diversity of microcystins produced by cyanobacteria from the Curonian Lagoon (SE Baltic Sea). Toxins 2021, 13, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidelev, S.; Koksharova, O.; Babanazarova, O.; Fastner, J.; Chernova, E.; Gusev, E. Phylogeographic, toxicological and ecological evidence for the global distribution of Raphidiopsis raciborskii and its northernmost presence in Lake Nero, Central Western Russia. Harmful Algae 2020, 98, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevorgyan, G.; Rinke, K.; Schultze, M.; Mamyan, A.; Kuzmin, A.; Belykh, O.; Sorokovikova, E.; Hayrapetyan, A.; Hovsepyan, A.; Khachikyan, T.; et al. First report about toxic cyanobacterial bloom occurrence in Lake Sevan, Armenia. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2020, 105, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrovyan, A.; Avalyan, R.; Atoyants, A.; Aghajanyan, E.; Hambaryan, L.; Aroutiounian, R.; Gabrielyan, B. Tradescantia-based test systems can be used for the evaluation of the toxic potential of harmful algal blooms. Water 2023, 15, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheyeva, T.M.; Belykh, O.I.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Potapov, S.A. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in plankton of regulated reservoirs and in the urban section of the Svisloch River (Belarus). Ecol. Bull. 2011, 4, 30–37. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mikheyeva, T.M.; Belykh, O.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Luk’yanova, E.V.; Potapov, S.A.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Fedorova, G.A.; Korneva, E.S.; Kuzmin, A.V. Detection of microcystin producing cyanobacteria in the Svisloch River, Belarus. Balt. Coast. Zone J. Ecol. Prot. Coastline 2012, 16, 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- Adamovich, B.; Mikheeva, T.; Sorokovikova, E.; Belykh, O.; Paskauskas, R.; Zhukava, H.; Kuzmin, A.; Fedorova, G.; Karosienė, J. Phytoplankton of the transboundary river Viliya (Neris): Community structure and toxic cyanobacterial blooms. Baltica 2021, 34, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheyeva, T.M.; Adamovich, B.V.; Zhukova, T.V.; Savich, I.V.; Belykh, O.I.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Kuzmin, A.V.; Fedorova, G.A.; Kovalevskaya, R.Z.; Selivonchik, I.N.; et al. Phytoplankton of Lake Bol’shie Shvakshty (Belarus) during the shift of the ecosystem from a macrophyte–weakly eutrophic to a phytoplankton–hypereutrophic State. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2018, 11, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizevskiy, S.V.; Adamovich, B.V.; Degtyarik, S.M.; Savich, I.V.; Voronova, G.P.; Kurchenko, V.P.; Mikheeva, T.M. Detection of potentially toxic cyanobacteria in water bodies of Belarus using polymerase chain reaction. Proceed. Belarusian State Univ. Ser. Physiol. Biochem. Mol. Found. Biosyst. Funct. 2016, 11, 368–372. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Agasild, H.; Panksep, K.; Tõnno, I.; Blank, K.; Kõiv, T.; Freiberg, R.; Laugaste, R.; Jones, R.I.; Nõges, P.; Nõges, T. Role of potentially toxic cyanobacteria in crustacean zooplankton diet in a eutrophic lake. Harmful Algae 2019, 89, 101688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolatkhan, K.; Akmuhanova, N.R.; Sadvakasova, A.K.; Bauenova, M.O.; Zayadan, B.K. Toxins produced by Cyanobacteria during blooms in Bilikol Lake. Bull. Kazn. Ser. Ecol. 2016, 47, 14–22. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Karosienė, J.; Savadova-Ratkus, K.; Toruńska-Sitarz, A.; Koreivienė, J.; Kasperovičienė, J.; Vitonytė, I.; Błaszczyk, A.; Mazur-Marzec, H. First report of saxitoxins and anatoxin-a production by Cyanobacteria from Lithuanian lakes. Eur. J. Phycol. 2020, 55, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šulčius, S.; Pilkaitytė, R.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Kasperovičienė, J.; Ezhova, E.; Błaszczyk, A.; Paškauskas, R. Increased risk of exposure to microcystins in the scum of the filamentous cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae accumulated on the western shoreline of the Curonian Lagoon. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkaitytė, R.; Overlingė, D.; Gasiūnaitė, Z.R.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Spatial and temporal diversity of cyanometabolites in the eutrophic Curonian Lagoon (SE Baltic Sea). Water 2021, 13, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerb, M.; Ezhova, E.; Lange, E.; Volodina, A.; Kocheshkova, O.; Rodionova, N.; Smirnova, M. Characterization of the state of the biota of the littoral zone of the Curonian Lagoon in the Curonian Spit National Park in 2018. In Problems of Study and Preservation of the Natural and Cultural Heritage of the “Curonian Spit”; National Park: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 82–108. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Overlingė, D.; Kataržytė, M.; Vaičiūtė, D.; Gyraite, G.; Gečaitė, I.; Jonikaitė, E.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Are there concerns regarding cHAB in coastal bathing waters affected by freshwater-brackish continuum? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 159, 111500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babanazarova, O.V.; Karmayer, R.; Sidelev, S.I.; Aleksandrina, E.M.; Sakharova, E.G. Structure of phytoplankton and microcystin content in the highly eutrophic Lake Nero. Water Resour. 2011, 38, 223–231. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshko, L.N. Cyanobacterial Toxins and the Other Bioactive Compounds in Water Bodies of the Leningrad Region; Astrakhansky Vestnik Ekologicheskogo Obrazovaniya: Astrakhan, Russia, 2016; pp. 28–35. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Belykh, O.; Dmitrieva, O.; Gladkikh, A.; Sorokovikova, E. Identification of toxigenic cyanobacteria of Microcystis genus in the Curonian Lagoon of the Baltic Sea. Oceanology 2013, 53, 78–87. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshko, L.N.; Kopetsky, I.; Hrouzek, P. Toxic Cyanobacterial Blooms in the Krasnoe Lake (Leningrad Region, Russia); Astrakhansky Vestnik Ekologicheskogo Obrazovaniya: Astrakhan, Russia, 2014; pp. 24–36. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Safronova, T.V.; Voloshko, L.N. The Study of Cyanobacteria Producing Biologically Active Substances in Lake Ladoga; Astrakhansky Vestnik Ekologicheskogo Obrazovaniya: Astrakhan, Russia, 2018; Volume 6, pp. 103–109. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gaevsky, N.A.; Kolmakov, V.I.; Belykh, O.I.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Joung, Y.; Ahn, T.S.; Nabatova, V.A.; Gladkikh, A.S. Ecological development and genetic diversity of Microcystis Aeruginosa from artificial reservoir in Russia. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, O.I.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Fedorova, G.A.; Kaluzhnaya, O.V.; Korneva, E.S.; Sakirko, M.V.; Sherbakova, T.A. Presence and genetic diversity of microcystin-producing Cyanobacteria (Anabaena and Microcystis) in Lake Kotokel (Russia, Lake Baikal Region). Hydrobiologia 2011, 671, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, O.I.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Potapov, S.A. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Lake Baikal. Izv. Irkutsk. State Univ. Ser. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 6, 27–34. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Belykh, O.; Gladkikh, A.; Sorokovikova, E.; Tikhonova, I.; Butina, T. Identification of toxic Cyanobacteria in Lake Baikal. Rep. Acad. Sci. 2015, 463, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belykh, O.; Gladkikh, A.; Sorokovikova, E.; Tikhonova, I.; Potapov, S.; Butina, T. Saxitoxin-producing Cyanobacteria in Lake Baikal. Sib. J. Ecol. 2015, 2, 229–237. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, O.; Gladkikh, A.; Tikhonova, I.; Kuzmin, A.; Mogilnikova, T.; Fedorova, G.; Sorokovikova, E. Identification of Cyanobacteria producing paralytic shellfish toxins in Lake Baikal and reservoirs of the Angara River. Microbiology 2015, 84, 98–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, O.I.; Fyodorova, G.A.; Kuzmin, A.V.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Timoshkin, O.A.; Sorokovikova, E.G. Detection of microcystins in cyanobacterial mats on various substrates in the coastal zone of lake Baikal. Mosc. Univ. Bull. Ser. 16 Biol. 2017, 72, 262–269. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Semenova, A.S.; Sidelev, S.I.; Dmitrieva, O.A. Experimental investigation of natural populations of Daphnia galeata G.O. Sars from the Curonian Lagoon feeding on potentially toxigenic cyanobacteria. Biol. Bull. 2017, 44, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, A.S.; Dmitrieva, O.A. Spatial and temporal aspects of toxic effect of harmful algae on zooplankton in the Curonian Lagoon (the Baltic Sea). AtlantNIRO Proc. 2017, 1, 56–69. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Voloshko, L.N.; Safronova, T.V. Water Blooms Produced by Cyanobacteria in the Finnish Bay of Baltic Sea; Astrakhansky Vestnik Ekologicheskogo Obrazovaniya: Astrakhan, Russia, 2015; pp. 65–73. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Russkikh, Y.; Chernova, E.; Nekrasova, L.; Voyakina, E.; Nikiforov, V.; Zhakovskaya, Z. First results of determining new ecotoxins in water bodies of Northwestern Russia. Reg. Ecol. 2011, 1–2, 82–87. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Russkikh, Y.V.; Chernova, E.N.; Voyakina, E.Y.; Nikiforov, V.A.; Zhakovskaya, Z.A. Determination of cyanotoxins in water matrix by high-performance liquid chromatography—High-resolution mass spectrometry. Proceed. St. Petersburg State Inst. Technol. Tech. Univ. 2012, 17, 61–66. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Voyakina, E.Y.; Russkih, Y.V.; Chernova, E.N.; Zhakovskaya, Z.A. Toxic cyanobacteria and their metabolites in the lakes of the Russian Northwest. Theor. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 1, 124–129. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidelev, S.I.; Babanazarova, O.V.; Zubishina, A.A.; Fomichev, A.A. Detection of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria in the Upper Volga reservoirs. Microbiology 2013, 82, 370. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidelev, S.; Zubishina, A.A.; Babanazarova, O.; Kutuzova, V.Y.; Martianov, O.V. Monitoring of the content of microcystin cyanotoxins in reservoirs of the Upper Volga: Molecular-genetic and analytical approaches. Water Chem. Ecol. 2014, 8, 88–94. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Korneva, L.G.; Solovyova, V.V.; Jackowskaya, Z.A.; Russkikh, Y.V.; Chernova, E.N. Phytoplankton and content of cyanotoxins in Rybinsk, Gorky and Cheboksary reservoirs during the anomalously hot summer of 2010. Water Chem. Ecol. 2014, 8, 24–29. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sorokovikova, E.; Belykh, O.; Gladkikh, A.; Mogilnikova, T.; Fedorova, G.; Kuzmin, A.; Mikheyeva, T. Toxic cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Kotokelskoye (Buryatia): Current state of the problem. Water Chem. Ecol. 2014, 2, 29–35. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chernova, E.; Russkikh, Y.; Vojakina, E.; Zhakovskaya, Z. Occurrence of microcystins and anatoxin-a in eutrophic lakes of Saint Petersburg, Northwestern Russia. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2016, 45, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernova, E.N.; Russkih, Y.A.V.; Vojakina, E.J.U.; Zhakovskaya, Z.A. Investigation of natural ecotoxicants—Metabolites of blue-green algae—In various water bodies of the north-west of Russia. Reg. Ecol. 2014, 1–2, 88–95. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nikitin, O.V.; Stepanova, N.Y.; Mukminov, M.N. Indication of cyanotoxins in natural waters of the Republic of Tatarstan. Sci. Rep. N. E. Bauman Kazan State Acad. Vet. Med. 2012, 212, 341–344. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Stepanova, N.Y.; Khalilullina, L.Y.; Nikitin, O.V.; Latypova, V.Z. Structure and toxicity of cyanobacteria in recreational zones of water bodies in the Kazan region. Water Chem. Ecol. 2012, 11, 67–72. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Yezhova, E.E.; Gerb, M.A.; Lange, E.K.; Rodionova, N.V.; Kochetshkova, O.V.; Volodina, A.A.; Chibisova, N.V.; Sukhoruk, V.I. Results of comprehensive ecological monitoring of the coastal zone of the Curonian Lagoon within the National Park “Curonian Spit” for 2013. Probl. Stud. Prot. Nat. Cult. Herit. Natl. Park Curonian Spit 2014, 10, 98–127. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pilip, A.G.; Russkikh, Y.V.; Zigel’, V.V.; Zhakovskaia, Z.A.; Eremenko, A.V.; Kurochkin, I.N. Using of thiol-sensitive sensors to determine the overall neurotoxicity of cyanobacterial biomass of Lake Sestroretskii Razliv. Water Chem. Ecol. 2016, 7, 64–71. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chernova, E.; Sidelev, S.; Russkikh, I.; Voyakina, E.; Zhakovskaya, Z. First observation of microcystin- and anatoxin-a-producing Cyanobacteria in the easternmost part of the Gulf of Finland (the Baltic Sea). Toxicon 2019, 157, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidelev, S.I.; Korneva, L.G.; Solovyeva, V.V.; Zubishina, A.A.; Pligin, D.N. Molecular genetic identification and seasonal succession of toxigenic Cyanobacteria in phytoplankton of the Rybinsk Reservoir (Russia). Inland Water Biol. 2016, 9, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidelev, S.I.; Babanazarova, O.V. Detection of cyanobacterial toxins in water supply sources and tap water in some Russian cities: Searching producers and testing removal methods. Water Resour. 2020, 47, 218–229. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernova, E.; Sidelev, S.; Russkikh, I.; Voyakina, E.; Babanazarova, O.; Romanov, R.; Kotovshchikov, A.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Dolichospermum and Aphanizomenon as neurotoxins producers in some Russian freshwaters. Toxicon 2017, 130, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidelev, S.; Zubishina, A.; Chernova, E. Distribution of microcystin-producing genes in Microcystis colonies from some Russian freshwaters: Is there any correlation with morphospecies and colony size? Toxicon 2020, 184, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosyan, V.S.; Antsiferova, G.A.; Akimov, L.M.; Kulnev, V.V.; Shevyrev, S.L.; Akimov, E.L. Valuation and prognosis of ecologic-sanitary state for the Voronezh water basin in 2018–2019. Ecol. Ind. Russ. 2019, 23, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, I.; Kuzmin, A.; Fedorova, G.; Sorokovikova, E.; Krasnopeev, A.; Tsvetkova, A.; Shtykova, Y.; Potapov, S.; Ivacheva, M.; Zabortzeva, T.; et al. Toxic Cyanobacteria blooms of Mukhor Bay (Lake Baikal, Russia) during a period of intensive anthropogenic pressure. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2022, 25, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokovikova, E.G.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Podlesnaya, G.V.; Belykh, O.I. Evaluation and prediction of toxic cyanobacterial blooming in phytoplankton of the Boguchany Reservoir. Water Ecol. Probl. Solut. 2019, 1, 86–93. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtykova, Y.R.; Drucker, V.V.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Zhuchenko, N.A.; Zimens, E.A.; Belykh, O.I. Sanitary-microbiological and toxicological monitoring of lake Baikal. part 1: Water area of the Maloe more in 2016. Monit. Syst. Environ. 2018, 1, 110–114. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneva, L.G.; Solovyova, V.V.; Sidelev, S.I.; Chernova, E.N.; Russkich, Y.V. Ecology and metabolic activity of cyanobacteria in large different types of lowland reservoirs in the European part of Russia. Issues Mod. Algol. 2021, 2, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernova, E.; Sidelev, S.; Russkikh, I.; Korneva, L.; Solovyova, V.; Mineeva, N.; Stepanova, I.; Zhakovskaya, Z. Spatial distribution of cyanotoxins and ratios of microcystin to biomass indicators in the reservoirs of the Volga, Kama and Don Rivers, the European part of Russia. Limnologica 2020, 84, 125819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grachev, M.; Zubkov, I.; Tikhonova, I.; Ivacheva, M.; Kuzmin, A.; Sukhanova, E.; Sorokovikova, E.; Fedorova, G.; Galkin, A.; Suslova, M.; et al. Extensive contamination of water with saxitoxin near the dam of the Irkutsk hydropower station reservoir (East Siberia, Russia). Toxins 2018, 10, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, M.M. Presence of microcystins in the littoral zone of the Curonian lagoon by the data of immunochromatographic analysis in 2017. Mar. Biol. J. 2019, 4, 109–111. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, N.A.; Tomberg, I.V.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Belykh, O.I.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Fedorova, G.A.; Netsvetaeva, O.G.; Eletskaya, E.V.; Timoshkin, O.A. Dolichospermum lemmermannii (Nostocales) bloom in world’s deepest Lake Baikal (East Siberia): Abundance, toxicity and factors influencing growth. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 1, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhachyov, E.V.; Mikhailova, K.A.; Markina, M.V.V.; Al-Shehadat, R.I.; Yudina, N.S.; Kuchaev, A.V.; Akhmatovich, N.A.; Yugantsev, A.V. Pathological and toxicological studies of the causes of mass mortality of mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) in water bodies of St. Petersburg. Appl. Probl. Saf. Technol. Biotechn. Syst. 2019, 1, 32–35. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, V.S.; Tekanova, E.V.; Kalinkina, N.M.; Chernova, E.N. Phytoplankton state and cyanotoxins in the Svyatozero lake bloom spot (Onega lake basin, Russia). Water Ecol. 2021, 26, 50–60. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinchuk, L.F.; Sharov, A.N.; Chernova, E.N.; Smirnov, V.V.; Berezina, N.A. Mutual links between microcystins-producing cyanobacteria and plankton community in clear and brown northern lakes. Food Webs 2023, 35, e00279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Cho, K.H.; Recknagel, F. Bibliometric network analysis of scientific research on early warning signals for cyanobacterial blooms in lakes and rivers. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Gardner, W.S.; Havens, K.E.; Joyner, A.R.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Qin, B.; Scott, J.T. Mitigating cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in aquatic ecosystems impacted by climate change and anthropogenic nutrients. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Stumpf, R.P.; Schaeffer, B.; Werdell, P.J.; Loftin, K.A.; Meredith, A. Evaluation of a satellite-based cyanobacteria bloom detection algorithm using field-measured microcystin data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.L.; Loftin, K.A.L.; Kamman, N. Monitoring recreational freshwaters. Lakelines 2009, 29, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Almuhtaram, H.; Kibuye, F.A.; Ajjampur, S.; Glover, C.M.; Hofmann, R.; Gaget, V.; Owen, C.; Wert, E.C.; Zamyadi, A. State of knowledge on early warning tools for cyanobacteria detection. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments. Coastal and Fresh Waters; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; pp. 1–219. [Google Scholar]
- Chorus, I. (Ed.) Current Approaches to Cyanotoxin Risk Assessment, Risk Management and Regulation in Different Countries; Federal Environmental Agency (Umweltbundesamt): Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–147. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M. Challenges in tracking harmful algal blooms: A synthesis of evidence from Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzouki, E.; Lürling, M.; Fastner, J.; de Senerpont Domis, L.; Wilk-Woźniak, E.; Koreivienė, J.; Seelen, L.; Teurlincx, S.; Verstijnen, Y.; Krztoń, W.; et al. Temperature effects explain continental scale distribution of cyanobacterial toxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, I.; Welker, M. (Eds.) Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; 858p. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Cyanobacterial Toxins: Microcystins Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality and Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/338066 (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Feng, L.; Wang, Y.; Hou, X.; Qin, B.; Kuster, T.; Qu, F.; Chen, N.; Paerl, H.W.; Zheng, C. Harmful algal blooms in inland waters. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.; Kutser, T.; Hunter, P.D. Remote sensing of inland waters: Challenges, progress and future directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.M.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Darling, J.A.; Urquhart, E.A.; Johnston, J.M.; Ignatius, A.R.; Myer, M.H.; Loftin, K.A.; Werdell, P.J.; Stumpf, R.P. Satellite monitoring of cyanobacterial harmful algal bloom frequency in recreational waters and drinking water sources. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 80, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Li, J.; Hu, R.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, F. Landsat-satellite-based analysis of spatial–temporal dynamics and drivers of CyanoHABs in the plateau Lake Dianchi. Inter. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 8552–8571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatius, A.R.; Purucker, S.T.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Wolfe, K.; Urquhart, E.; Smith, D. Satellite-derived cyanobacteria frequency and magnitude in headwaters & near-dam reservoir surface waters of the Southern US. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153568. [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Davis, T.W.; Wynne, T.T.; Graham, J.L.; Loftin, K.A.; Johengen, T.H.; Gossiaux, D.; Palladino, D.; Burtner, A. Challenges for mapping cyanotoxin patterns from remote sensing of cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumway, S.E.; Allen, S.M.; Boersma, P.D. Marine birds and harmful algal blooms: Sporadic victims or under-reported events? Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciponte, D.N.; Bough, M.W.; Seidler, D.; Carroll, J.L.; Ashare, A.; Andrew, A.S.; Tsongalis, G.J.; Vaickus, L.J.; Henegan, P.L.; Butt, T.H.; et al. Identifying aerosolized cyanobacteria in the human respiratory tract: A proposed mechanism for cyanotoxin-associated diseases. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaas, H.E.; Paerl, R.W.; Baumann, K.; Karl, C.; Popendorf, K.J.; Barnard, M.A.; Chang, N.Y.; Curtis, N.P.; Huang, H.; Mathieson, O.L.; et al. Harmful cyanobacterial aerosolization dynamics in the airshed of a eutrophic estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejerano, E.P.; Ahn, J.; Scott, G.I. Aerosolized algal bloom toxins are not inert. Environ. Sci. Atmos. 2024, 4, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.C.; Yoon, J.; Reynolds, K.; Gerald, L.B.; Ault, A.P.; Heo, S.; Bell, M.L. Harmful algal bloom aerosols and human health. EBioMedicine 2023, 93, 104604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalf, J.S.; Banack, S.A.; Cox, P.A. Cyanotoxin Analysis of Air Samples from the Great Salt Lake. Toxins 2023, 15, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, W. A world overview—One-hundred-twenty-seven years of research on toxic cyanobacteria—Where do we go from here? In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Hudnell, H.K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 105–125. [Google Scholar]
- Codd, G.A.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Bagchi, S.N.; Burch, M.D.; Carmichael, W.W.; Harding, W.R.; Kaya, K.; Utkilen, H.C. Cyanonet: A global network for cyanobacterial bloom and toxin risk management. Initial situation assessment and recommendations. Int. Hydrol. Program VI Unesco Tech. Doc. Hydrol. 2005, 76, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, D.R.; Kumar, A.; Ramaswamy, L.; Boddula, V.K.; Das, M.C.; Page, B.P.; Weber, S.J. CyanoTRACKER: A cloud-based integrated multi-platform architecture for global observation of cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms. Harmful Algae 2020, 96, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messineo, V.; Bruno, M.; De Pace, R. The role of Cyano-HAB (Cyanobacteria Harmful Algal Blooms) in the One Health approach to global health. Hydrobiology 2024, 3, 238–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka-Krawczyk, P.; Żelazna-Wieczorek, J.; Skrobek, I.; Ziułkiewicz, M.; Adamski, M.; Kaminski, A.; Żmudzki, P. Persistent cyanobacteria blooms in artificial water bodies—An effect of environmental conditions or the result of anthropogenic change. Inter. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.T.; Gu, V.X. Global Dam Tracker: A database of more than 35,000 dams with location, catchment, and attribute information. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, W.B.; Hay, C.C.; Mitrovica, J.X.; Kopp, R.E. A spatially variable time series of sea level change due to artificial water impoundment. Earths Future 2020, 8, e2020EF001497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaičiūtė, D.; Sokolov, Y.; Bučas, M.; Dabulevičienė, T.; Zotova, O. Earth observation-based cyanobacterial bloom index testing for ecological status assessment in the open, coastal and transitional waters of the Baltic and Black seas. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahn, I.-A.; Kangro, K.; Jaanus, A.; Alikas, K. Application of satellite-derived summer bloom indicators for estonian coastal waters of the Baltic Sea. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzouki, E.; Visser, P.M.; Bormans, M.; Ibelings, B.W. Understanding the key ecological traits of cyanobacteria as a basis for their management and control in changing lakes. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.; Audet, J.; Davidson, T.A.; De Meester, L.; Hilt, S.; Kosten, S.; Liu, Z.; Mazzeo, N.; Paerl, H.; Scheffer, M.; et al. Feedback between climate change and eutrophication: Revisiting the allied attack concept and how to strike back. Inland Waters 2022, 12, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Q.; Tian, H. Temperature changes in Central Asia from 1979 to 2011 based on multiple datasets. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 1143–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ji, M.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Ran, J. Global semi-arid climate change over last 60 years. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 1131–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fang, G.; Li, W. Large hydrological processes changes in the transboundary rivers of Central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 5059–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, I.; Shah, A.R.; Salik, K.M.; Ismail, M. Annual, seasonal and monthly trend analysis of temperature in Kazakhstan during 1970–2017 using non-parametric statistical methods and GIS technologies. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 5, 575–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, S.; Aguilera, A.; Aubriot, L.; Huszar, V.; Almanza, V.; Haakonsson, S.; Izaguirre, I.; O’Farrell, I.; Salazar, A.; Becker, V.; et al. Nutrients and not temperature are the key drivers for cyanobacterial biomass in the Americas. Harmful Algae 2023, 121, 102367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehob, M.M.; Pennino, M.J.; Handler, A.M.; Compton, J.E.; Lee, S.S.; Sabo, R.D. Estimates of lake nitrogen, phosphorus, and chlorophyll-a concentrations to characterize harmful algal bloom risk across the United States. Earths Future 2024, 12, e2024EF004493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormans, M.; Ford, P.W.; Fabbro, L. Spatial and temporal variability in cyanobacterial populations controlled by physical processes. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate change: A catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haakonsson, S.; Rodríguez-Gallego, L.; Somma, A.; Bonilla, S. Temperature and precipitation shape the distribution of harmful cyanobacteria in subtropical lotic and lentic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, J.S.; Chatziefthimiou, A.D.; Souza, N.R.; Cox, P.A. Desert dust as a vector for cyanobacterial toxins. In The Arabian Seas: Biodiversity, Environmental Challenges and Conservation Measures; Jawad, L.A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 161–178. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, E.S.; Hilt, S. Impact of water-level fluctuations on cyanobacterial blooms: Options for management. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlibayev, M.; Volchek, A.; Kalinin, M. Hydrological natural phenomena (world trends, chronicle of Belarus and Kazakhstan). In Proceedings of the Water Resources of Central Asia and Their Use, Aktobe, Kazakhstan, 22–24 September 2016; pp. 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Coccia, G.; Ceresa, P.; Bussi, G.; Denaro, S.; Bazzurro, P.; Martina, M.; Fagà, E.; Avelar, C.; Ordaz, M.; Huerta, B.; et al. Large-scale flood risk assessment in data scarce areas: An application to Central Asia. In Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Discussions; European Geosciences Union: Munich, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. The dilemma of controlling cultural eutrophication of lakes. Proceed. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 4322–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenenbaev, S.B.; Ramazanova, S.B.; Gusev, V.N. State and prospects of mineral fertilizers use in agriculture of Kazakhstan. Sabrao J. Breed. Genet. 2023, 55, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djanibekov, N.; Bobojonov, I.; Lamers, J.P. Farm reform in Uzbekistan. Cotton, Water, Salts and Soums: Economic and Ecological Restructuring in Khorezm, Uzbekistan; Martius, C., Rudenko, I., Lamers, J.P.A., Vlek, P.L.G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 95–112. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Sun, W.; Xue, J. Selection of China’s imported grain distribution centers in the context of the Belt and Road Initiative. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2018, 120, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, T.; Paltan, H.; Sternberg, T.; Wheeler, K. Evaluating vulnerability of Central Asian water resources under uncertain climate and development conditions: The case of the Ili-Balkhash Basin. Water 2021, 13, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueppke, S.G.; Zhang, Q.; Nurtazin, S.T. Irrigation in the Ili River basin of Central Asia: From ditches to dams and diversion. Water 2018, 10, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasser, I.; Khomutovska, N.; Sandzewicz, M.; Łach, Ł.; Hisoriev, H.; Chmielewska, M.; Suska-Malawska, M. High altitude may limit production of secondary metabolites by cyanobacteria. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2024, 24, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomutovska, N.; Sandzewicz, M.; Łach, Ł.; Suska-Malawska, M.; Chmielewska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Cegłowska, M.; Niyatbekov, T.; Wood, S.A.; Puddick, J.; et al. Limited microcystin, anatoxin and cylindrospermopsin production by cyanobacteria from microbial mats in cold deserts. Toxins 2020, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, H.S.; Makhlough, A.; Pourgholam, R.; Vahedi, F.; Qanqermeh, A.; Foong, S.Y. The study of Nodularia spumigena bloom event in the southern Caspian Sea. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2011, 9, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, K.; Moradi, M.; Kabiri, K.; Rahimzadegan, M. The effects of cyanobacterial blooms on MODIS-L2 data products in the southern Caspian Sea. Oceanologia 2018, 60, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modabberi, A.; Noori, R.; Madani, K.; Ehsani, A.H.; Mehr, A.D.; Hooshyaripor, F.; Kløve, B. Caspian Sea is eutrophying: The alarming message of satellite data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 124047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrova, O.Y.; Kostianoy, A.G.; Bocharova, T.Y.; Strochkov, A.Y. Spatio-temporal variability of algal bloom in the Caspian Sea. Ecol. Montenegrina 2024, 76, 14–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkonen, T.; Harding, K.C.; Wilson, S.; Baimukanov, M.; Dmitrieva, L.; Svensson, C.J.; Goodman, S.J. Collapse of a marine mammal species driven by human impacts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadereev, E.; Lipka, O.; Karimov, B.; Krylenko, M.; Elias, V.; Pinto, I.S.; Alizade, V.; Anker, Y.; Feest, A.; Kuznetsova, D.; et al. Overview of past, current, and future ecosystem and biodiversity trends of inland saline lakes of Europe and Central Asia. Inland Waters 2020, 10, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodini, A.; Pereira, D.; Scotti, M. The decline of kilkas, sturgeons and seals in the Caspian Sea: The potential of qualitative loop analysis for the cumulative assessment of multiple drivers of stress. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 200, 116091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.C.; Eybatov, T.M.; Amano, M.; Jepson, P.D.; Goodman, S.J. The role of canine distemper virus and persistent organic pollutants in mortality patterns of Caspian seals (Pusa caspica). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrieva, L.; Kondakov, A.A.; Oleynikov, E.; Kydyrmanov, A.; Karamendin, K.; Kasimbekov, Y.; Baimukanov, M.; Wilson, S.; Goodman, S.J. Assessment of Caspian seal by-catch in an illegal fishery using an interview-based approach. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.C.; Trukhanova, I.; Dmitrieva, L.; Dolgova, E.; Crawford, I.; Baimukanov, M.; Baimukanov, T.; Ismagambetov, B.; Pazylbekov, M.; Jüssi, M.; et al. Assessment of impacts and potential mitigation for icebreaking vessels transiting pupping areas of an ice-breeding seal. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 214, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamendin, K.; Goodman, S.J.; Kasymbekov, Y.; Kumar, M.; Nuralibekov, S.; Kydyrmanov, A. Viral metagenomic survey of Caspian seals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1461135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadwater, M.H.; Van Dolah, F.M.; Fire, S.E. Vulnerabilities of marine mammals to harmful algal blooms. In Harmful Algal Blooms: A Compendium Desk Reference; Shumway, S.E., Burkholder, J.A.M., Morton, S.L., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 191–222. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dolah, F.M.; Doucette, G.J.; Gulland, F.M.; Bossart, T.L.R.G.D. Impacts of algal toxins on marine mammals. In Toxicology of Marine Mammals; Vos, J.G., Bossart, G.D., Fournier, M., O’Shea, T.G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 259–281. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, S.K.; Lacaze, J.P.; Hermann, G.; Kershaw, J.; Brownlow, A.; Turner, A.; Hall, A. Detection and effects of harmful algal toxins in Scottish harbour seals and potential links to population decline. Toxicon 2015, 97, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogomolni, A.L.; Bass, A.L.; Fire, S.; Jasperse, L.; Levin, M.; Nielsen, O.; Waring, G.; De Guise, S. Saxitoxin increases phocine distemper virus replication upon in-vitro infection in harbor seal immune cells. Harmful Algae 2016, 51, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, T.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Zabka, T.S.; Langlois, G.; Colegrove, K.M.; Silver, M.; Bargu, S.; Van Dolah, F.; Leighfield, T.; Conrad, P.A.; et al. Novel symptomatology and changing epidemiology of domoic acid toxicosis in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus): An increasing risk to marine mammal health. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargu, S.; Goldstein, T.; Roberts, K.; Li, C.; Gulland, F. Pseudo-nitzschia blooms, domoic acid, and related California sea lion strandings in Monterey Bay, California. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2012, 28, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollerup, I.M.; Bjørneset, J.; Krock, B.; Jensen, T.H.; Galatius, A.; Dietz, R.; Teilmann, J.; van den Brand, J.M.; Osterhaus, A.; Kokotovic, B.; et al. Did algal toxin and Klebsiella infections cause the unexplained 2007 mass mortality event in Danish and Swedish marine mammals? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, S.; Khatib, S.; Yeok, F.S. Changes in near-shore phytoplankton community and distribution, southwestern Caspian Sea. Limnology 2024, 25, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vostokov, S.V.; Pautova, L.A.; Sahling, I.V.; Vostokova, A.S.; Gadzhiev, A.A.; Petherbridge, G.; Lobachev, E.N.; Abtahi, B.; Shojaei, M.G. Seasonal and long-term phytoplankton dynamics in the Middle Caspian according to satellite data and in situ observations in the first decades of the 21st century. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautova, L.A.; Kravchishina, M.D.; Silkin, V.A.; Klyuvitkin, A.A.; Artemiev, V.A.; Vazyulya, S.V.; Burenkov, V.I. Alien diatom species of the autumn phytoplankton in the Caspian Sea: Their role in the formation of the total biomass and the distribution along the salinity gradient. Russ. J. Biol. Invasions 2022, 13, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaee, S.; Omidzahir, S.; Sayyad Shirazic, A.; Akhoundian, M. Seasonal distribution and some biological parameters of the Caspian seal (Pusa caspica) in the southeastern region of the Caspian Sea. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2020, 19, 2464–2474. [Google Scholar]
- Gadzhiev, A.; Petherbridge, G.; Sharshov, K.; Sobolev, I.; Alekseev, A.; Gulyaeva, M.; Litvinov, K.; Boltunov, I.; Teymurov, A.; Zhigalin, A.; et al. Pinnipeds and avian influenza: A global timeline and review of research on the impact of highly pathogenic avian influenza on pinniped populations with particular reference to the endangered Caspian seal (Pusa caspica). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1325977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kydyrmanov, A.; Karamendin, K.; Kassymbekov, Y.; Kumar, M.; Mazkirat, S.; Suleimenova, S.; Baimukanov, M.; Carr, I.M.; Goodman, S.J. Exposure of wild Caspian seals (Pusa caspica) to parasites, bacterial and viral pathogens, evaluated via molecular and serological assays. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1087997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.; Klemm, K.; John, U.; Karlson, B.; Arneborg, L.; Clarke, D.; Yamanaka, T.; Cusack, C.; Naustvoll, L.; Bresnan, E.; et al. Emerging phylogeographic perspective on the toxigenic diatom genus Pseudo-nitzschia in coastal northern European waters and gateways to eastern Arctic seas: Causes, ecological consequences and socio-economic impacts. Harmful Algae 2023, 129, 102496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D. Chemical ecology of eukaryotic microalgae in marine ecosystems. Phycologia 2003, 42, 420–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Frame, E.R.; Kendrick, P.S. Domoic acid and fish behavior: A review. Harmful Algae 2012, 13, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Huang, J.; Luo, J.; Xiao, Q.; Shen, M.; Xiao, P.; Peng, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Duan, H. Monitoring, simulation and early warning of cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms: An upgraded framework for eutrophic lakes. Environ. Res. 2025, 264, 120296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamyadi, A.; Romanis, C.; Mills, T.; Neilan, B.; Choo, F.; Coral, L.A.; Gale, D.; Newcombe, G.; Crosbie, N.; Stuetz, R.; et al. Diagnosing water treatment critical control points for cyanobacterial removal: Exploring benefits of combined microscopy, next-generation sequencing, and cell integrity methods. Water Res. 2019, 152, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casero, M.C.; Velázquez, D.; Medina-Cobo, M.; Quesada, A.; Cirés, S. Unmasking the identity of toxigenic cyanobacteria driving a multi-toxin bloom by high-throughput sequencing of cyanotoxins genes and 16S rRNA metabarcoding. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiazi, V.; De La Cruz, A.; Mishra, S.; Shanov, V.; Heineman, W.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. A comprehensive review: Development of electrochemical biosensors for detection of cyanotoxins in freshwater. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1151–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirkhanova, A.; Marks, S.; Feja, N.; Vorobjev, I.A.; Barteneva, N.S. Spectral algal fingerprinting and long sequencing in synthetic algal–microbial communities. Cells 2024, 13, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhumakhanova, A.; Mirasbekov, Y.; Meirkhanova, A.; Malashenkov, D.V.; Davidson, T.A.; Levi, E.E.; Jeppesen, E.; Barteneva, N.S. From colonial clusters to colonial sheaths: Imaging flow cytometry analysis of Microcystis morphospecies dynamics in mesocosm and links to CyanoHABs management. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, F.; Jiang, J.L.; Atrache, R.; Paschos, A.; Edge, T.A.; Schellhorn, H.E. Cyanobacterial algal bloom monitoring: Molecular methods and technologies for freshwater ecosystems. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filatova, D.; Núñez, O.; Farré, M. Ultra-trace analysis of cyanotoxins by liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. Toxins 2020, 12, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.B.F.; Guedes, I.A.; Azevedo, S.M. Is qPCR a reliable indicator of cyanotoxin risk in freshwater? Toxins 2016, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.V.; Beyer, J.E.; Xiao, X.; Hambright, K.D. Ground-based remote sensing provides alternative to satellites for monitoring cyanobacteria in small lakes. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Dai, Y.; Hu, C.; Gibson, L.; Tang, J.; Lee, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Global mapping reveals increase in lacustrine algal blooms over the past decade. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torremorell, A.; Hegoburu, C.; Brandimarte, A.L.; Rodrigues, E.H.C.; Pompêo, M.; da Silva, S.C.; Moschini-Carlos, V.; Caputo, L.; Fierro, P.; Mojica, J.I.; et al. Current and future threats for ecological quality management of South American freshwater ecosystems. Inland Waters 2021, 11, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kastuganova, K.; Nugumanova, G.; Barteneva, N.S. Systematic Review on CyanoHABs in Central Asia and Post-Soviet Countries (2010–2024). Toxins 2025, 17, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050255
Kastuganova K, Nugumanova G, Barteneva NS. Systematic Review on CyanoHABs in Central Asia and Post-Soviet Countries (2010–2024). Toxins. 2025; 17(5):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050255
Chicago/Turabian StyleKastuganova, Kakima, Galina Nugumanova, and Natasha S. Barteneva. 2025. "Systematic Review on CyanoHABs in Central Asia and Post-Soviet Countries (2010–2024)" Toxins 17, no. 5: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050255
APA StyleKastuganova, K., Nugumanova, G., & Barteneva, N. S. (2025). Systematic Review on CyanoHABs in Central Asia and Post-Soviet Countries (2010–2024). Toxins, 17(5), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050255





