Structure, Toxicity, Prevalence, and Degradation of Six Understudied Freshwater Cyanopeptides
Abstract
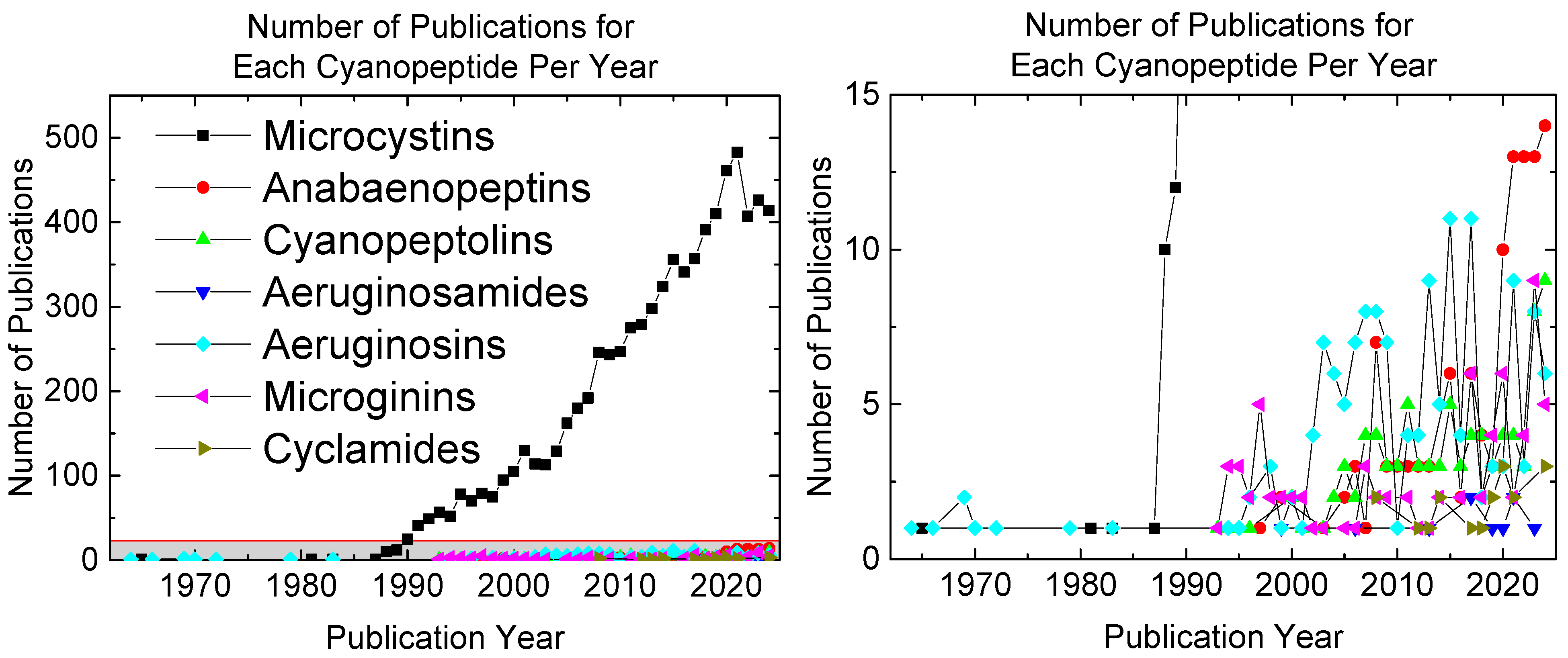
1. Introduction
2. Cyanopeptide Structure, Toxicity, and Prevalence
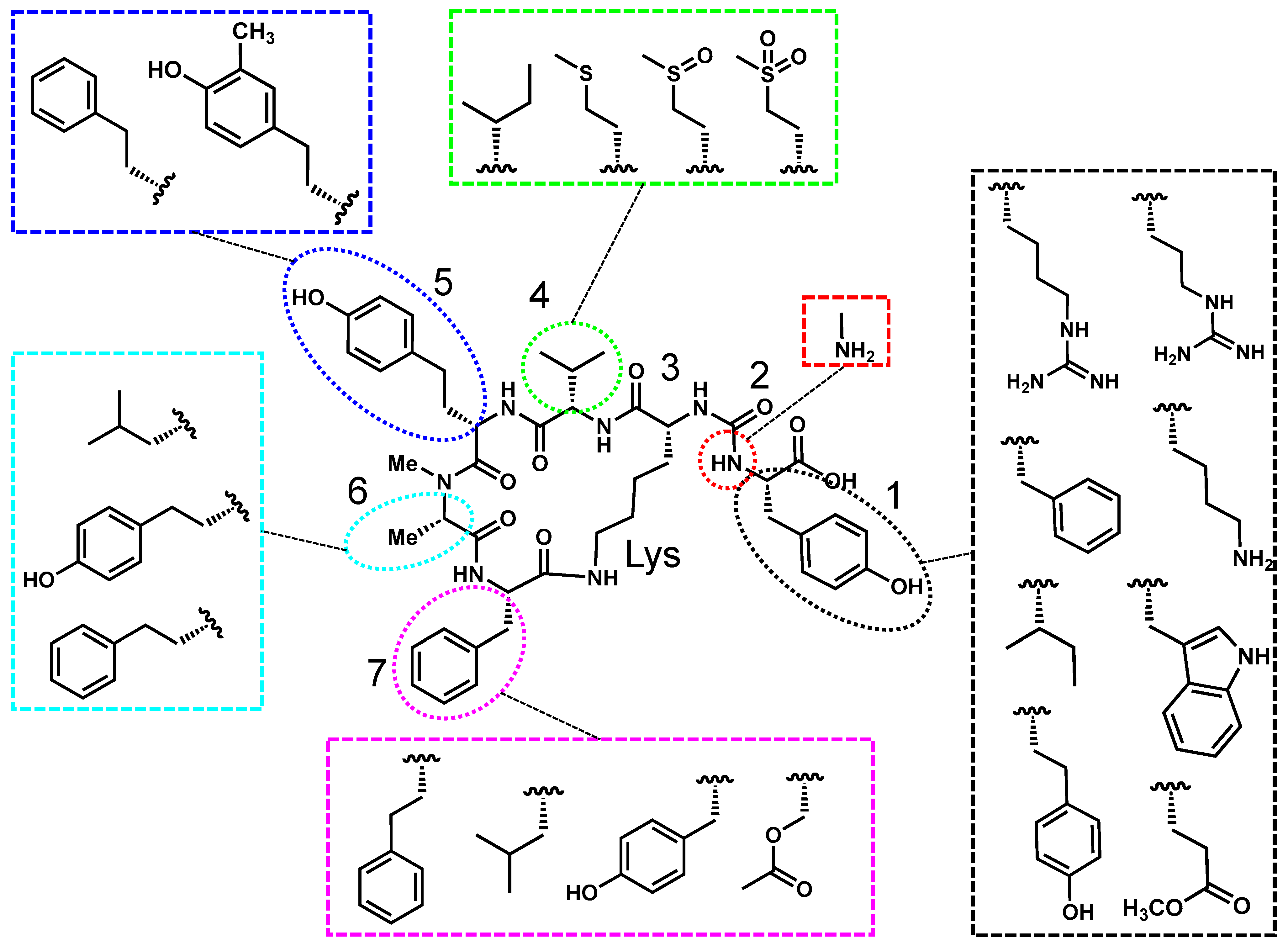
2.1. Anabaenopeptin’s Structure, Toxicity, and Prevalence
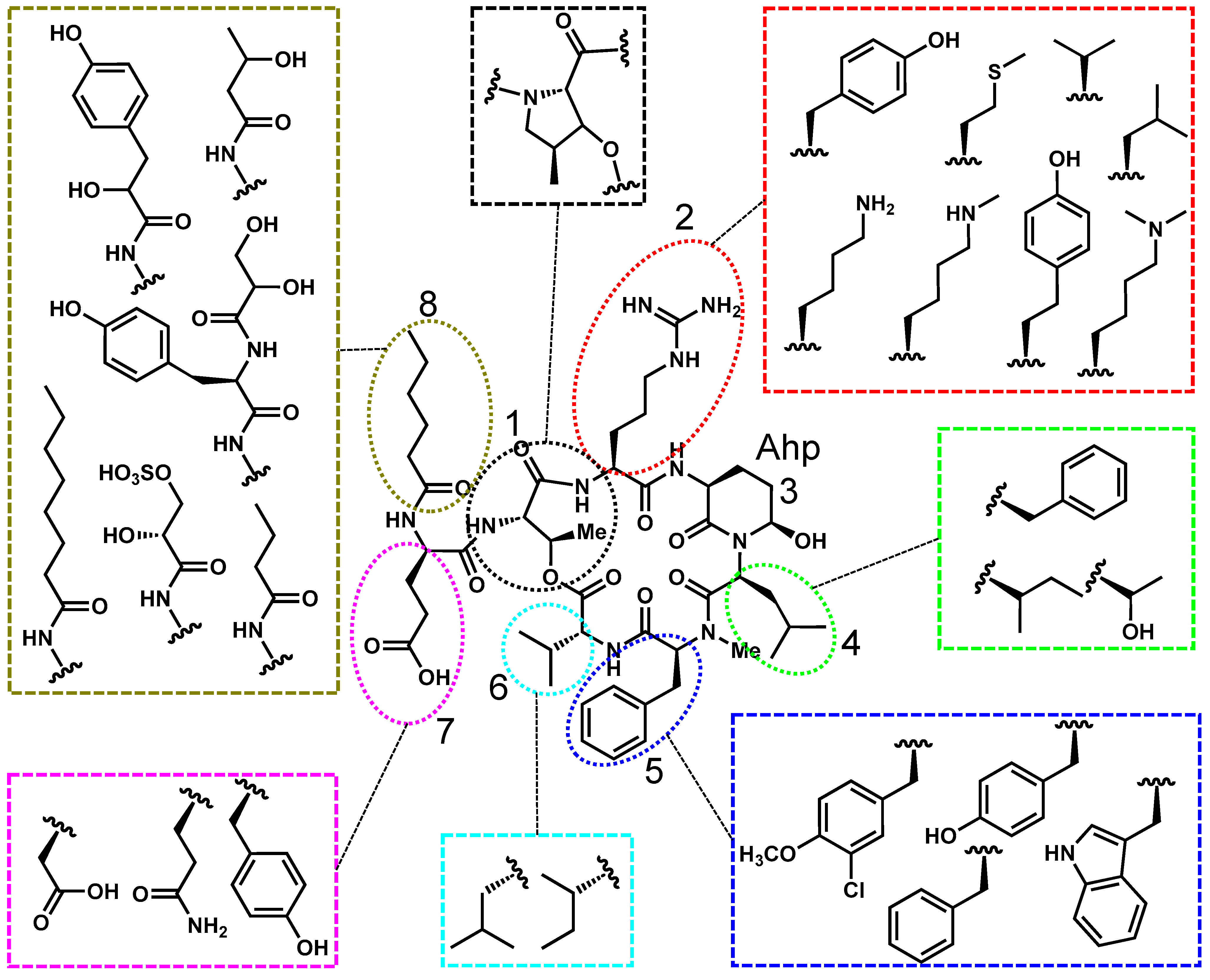
2.2. Cyanopeptolin’s Structure, Toxicity, and Prevalence
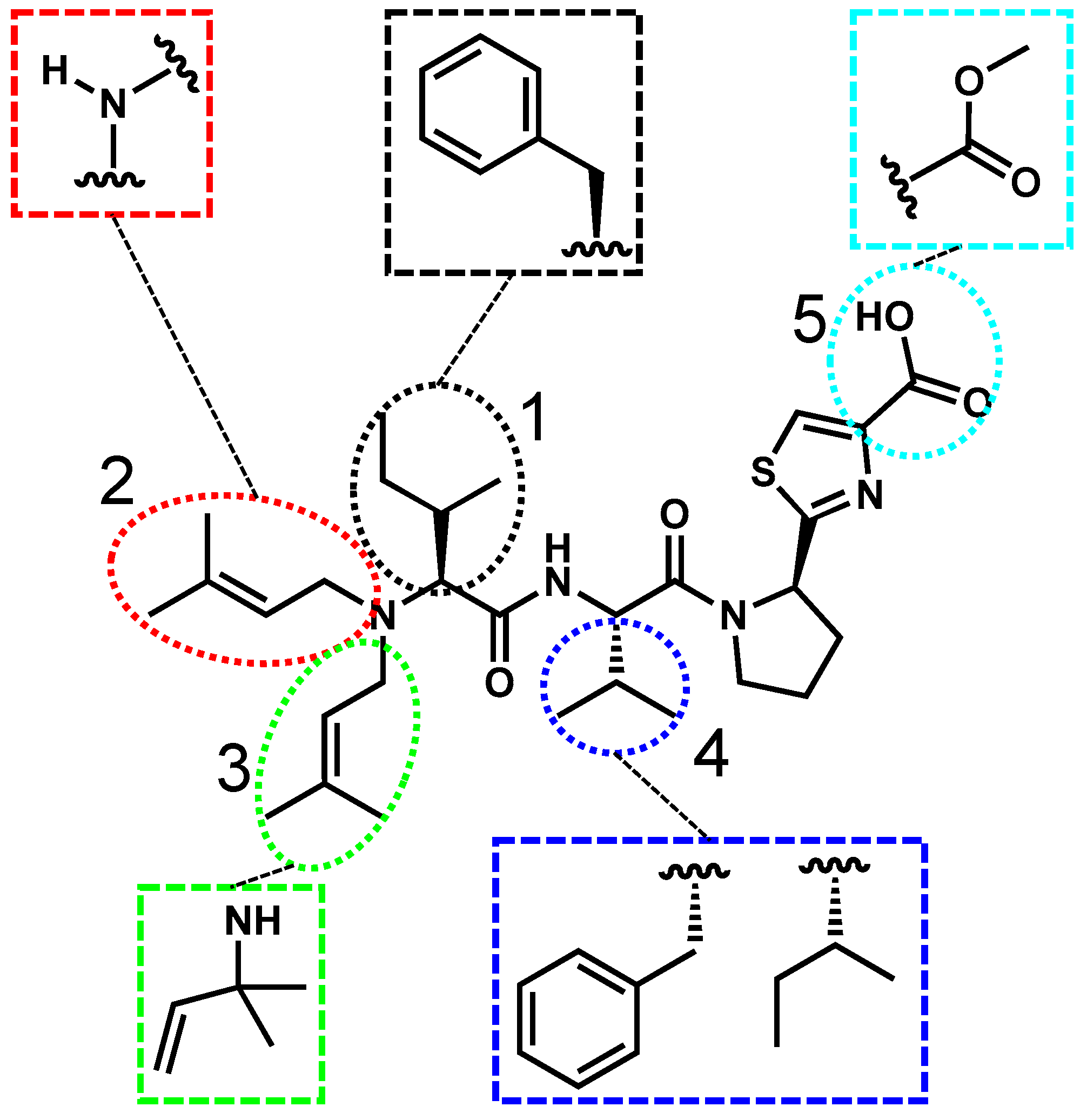
2.3. Aeruginosamide’s Structure, Toxicity, and Prevalence
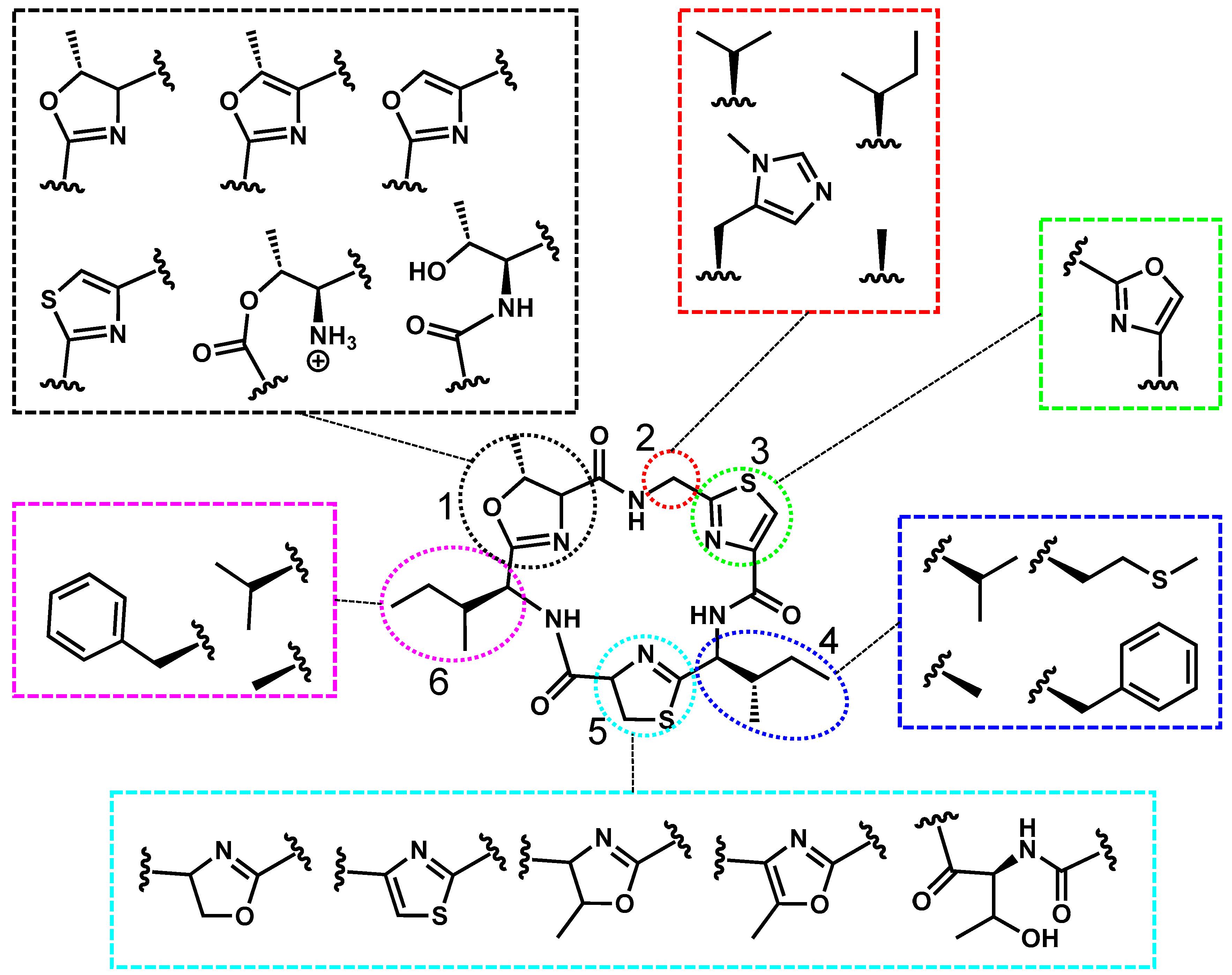
2.4. Aeruginosin’s Structure, Toxicity, and Prevalence
2.5. Microginin’s Structure, Toxicity, and Prevalence
2.6. Cyclamide’s Structure, Toxicity, and Prevalence
3. Degradation of Cyanopeptides
3.1. Degradation of Anabaenopeptins
3.2. Degradation of Cyanopeptolins
3.3. Degradation of Aeruginosamides
3.4. Degradation of Aeruginosins
3.5. Degradation of Microginins
3.6. Degradation of Cyclamides
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cHAB | Cyanobacterial Harmful Algae Blooms |
| DWTP | Drinking Water Treatment Plant |
| MC | Microcystin |
| CPA | Carboxypeptidase A |
| CPB | Carboxypeptidase B |
| PP1 | Protein Phosphatase 1 |
| PP2A | Protein Phosphatase 2A |
| ACE | Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme |
| Ahp | 3-amino-6-hydroxy-piperidone |
| Choi | 2-carboxy-6-hydroxyoctahydroindole |
| Adda | (2S,3S,4E,6E,8S,9S)-3-amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyldeca-4,6-dienoic acid |
| Mdha | N-methyldehydroalanine |
| Adha | 3-amino-(2-hydroxy)-decenoic acid |
References
- Hallegraeff, G. Harmful algal blooms: A global overview. Man. Harmful Mar. Microalgae 2003, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen, K.; Jones, G. Cyanobacterial toxins. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 1999; Volume 1, pp. 43–112. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, W.W. The toxins of cyanobacteria. Sci. Am. 1994, 270, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, R.M. The toxicology of microcystins. Toxicon 1998, 36, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.B.; Borges, R.M.; Sullivan, P.; Domingues, J.P.; da Silva, F.H.; Trindade, V.G.; Luo, S.; Orjala, J.; Crnkovic, C.M. Chemical diversity of cyanobacterial natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2025, 42, 6–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkelis, S.; Papadimitriou, T.; Zaoutsos, N.; Leonardos, I. Anthropogenic and climate-induced change favors toxic cyanobacteria blooms: Evidence from monitoring a highly eutrophic, urban Mediterranean lake. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.; Zeng, J.; Chabi, K.; Song, W.; Xian, X.; Yu, X. Impact of chlorination on cell inactivation, toxin release and degradation of cyanobacteria of development and maintenance stage. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drikas, M.; Chow, C.W.; House, J.; Burch, M.D. Using coagulation, flocculation, and settling to remove toxic cyanobacteria. J.-Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2001, 93, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnegar, M.; Berndt, N.; Kong, S.M.; Lee, E.Y.C.; Zhang, L.F. In Vivo and in Vitro Binding of Microcystin to Protein Phosphatase 1 and 2A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 216, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouria, S.; de Andrade, A.; Barbosa, J.; Cavalcanti, R.; Barreto, V.; Ward, C.; Preiser, W.; Poon, G.K.; Neild, G.; Codd, G. Fatal microcystin intoxication in haemodialysis unit in Caruaru, Brazil. Lancet 1998, 352, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Figueiredo, D.R.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Esteves, S.M.; Gonçalves, F.J.; Pereira, M.J. Microcystin-producing blooms—A serious global public health issue. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.-i. Production of Secondary Metabolites by Freshwater Cyanobacteria. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Giesy, J.P.; Adamovsky, O.; Svirčev, Z.; Meriluoto, J.; Codd, G.A.; Mijovic, B.; Shi, T.; Tuo, X.; Li, S.-C.; et al. Challenges of using blooms of Microcystis spp. in animal feeds: A comprehensive review of nutritional, toxicological and microbial health evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, E.M.-L. Cyanobacterial peptides beyond microcystins–A review on co-occurrence, toxicity, and challenges for risk assessment. Water Res. 2019, 151, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik-Skowrońska, B.; Bownik, A. Cyanobacterial anabaenopeptin-B, microcystins and their mixture cause toxic effects on the behavior of the freshwater crustacean Daphnia magna (Cladocera). Toxicon 2021, 198, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Adamczuk, M.; Pawlik-Skowrońska, B. Behavioral disturbances induced by cyanobacterial oligopeptides microginin-FR1, anabaenopeptin-A and microcystin-LR are associated with neuromotoric and cytotoxic changes in Brachionus calyciflorus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik-Skowrońska, B.; Bownik, A.; Pogorzelec, M.; Kulczycka, J.; Sumińska, A. First report on adverse effects of cyanobacterial anabaenopeptins, aeruginosins, microginin and their mixtures with microcystin and cylindrospermopsin on aquatic plant physiology: An experimental approach. Toxicon 2023, 236, 107333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Adamczuk, M.; Pawlik-Skowrońska, B.; Mieczan, T. Cyanobacterial metabolites: Aeruginosin 98A, microginin-FR1, anabaenopeptin-A, cylindrospermopsin and their mixtures affect behavioral and physiological responses of Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 100, 104161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Pawlik-Skowrońska, B.; Wlodkowic, D.; Mieczan, T. Interactive effects of cyanobacterial metabolites aeruginosin-98B, anabaenopeptin-B and cylindrospermopsin on physiological parameters and novel in vivo fluorescent indicators in Chironomus aprilinus larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaïcha, N.; Miles, C.O.; Beach, D.G.; Labidi, Z.; Djabri, A.; Benayache, N.Y.; Nguyen-Quang, T. Structural diversity, characterization and toxicology of microcystins. Toxins 2019, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, M.; Luu, H.A.; McCready, T.L.; Holmes, C.F.; Williams, D.; Andersen, R.J. Molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction of motuporin and microcystins with type-1 and type-2A protein phosphatases. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 74, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.R.; Vasconcelos, V.M.; Antunes, A. Computational study of the covalent bonding of microcystins to cysteine residues–a reaction involved in the inhibition of the PPP family of protein phosphatases. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagu, J.R.; Sykes, B.D.; Craig, M.M.; Holmes, C.B. A molecular basis for different interactions of marine toxins with protein phosphatase-1: Molecular models for bound motuporin, microcystins, okadaic acid, and calyculin A. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 5087–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, P.R.; do Amaral, S.C.; Siqueira, A.S.; Xavier, L.P.; Santos, A.V. Anabaenopeptins: What we know so far. Toxins 2021, 13, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckesser, J.; Martin, C.; Jakobi, C. Cyanopeptolins, depsipeptides from cyanobacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 19, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, L.A.; Morris, L.A.; Jaspars, M. A bioactive modified peptide, aeruginosamide, isolated from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 5329–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Okita, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Okino, T.; Murakami, M. Aeruginosins, protease inhibitors from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 10971–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Kato, T.; Murakami, M.; Watanabe, M.; Watanabe, M.F. Microginins, zinc metalloproteases inhibitors from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 8643–8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttner, F.; Todorova, A.K.; Walch, N.; Von Philipsborn, W. Nostocyclamide M: A cyanobacterial cyclic peptide with allelopathic activity from Nostoc 31. Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, T.; Sano, T.; Kaya, K. Micropeptin T-20, a novel phosphate-containing cyclic depsipeptide from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 2379–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Usui, T.; Ueda, K.; Osada, H.; Kaya, K. Isolation of new protein phosphatase inhibitors from two cyanobacteria species, Planktothrix spp. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itou, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Ishida, K.; Murakami, M. Anabaenopeptins G and H, potent carboxypeptidase A inhibitors from the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria agardhii (NIES-595). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 1243–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiv, S.; Aharonv-Nadborny, R.; Carmeli, S. Micropeptins from Microcystis aeruginosa collected in Dalton reservoir, Israel. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 7429–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastepa, A.; Westrick, J.A.; Liang, A.; Birbeck, J.A.; Furr, E.; Watson, L.C.; Stockdill, J.L.; Ramakrishna, B.S.; Crevecoeur, S. Broad screening of toxic and bioactive metabolites in cyanobacterial and harmful algal blooms in Lake of the Woods (Canada and USA), 2016–2019. J. Great Lakes Res. 2023, 49, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathane Nunes de Freitas, P.; Kinoshita Teramoto, K.; Ossanes de Souza, A.; Pinto, E. Evaluation of the Toxicity of Microcyclamide Produced by Microcystis aeruginosa in Danio rerio Embryos. Toxics 2023, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, C.; Caixach, J. High Levels of Anabaenopeptins Detected in a Cyanobacteria Bloom from NE Spanish Sau-Susqueda-El Pasteral Reservoirs System by LC–HRMS. Toxins 2020, 12, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ju, F. Cyanopeptides restriction and degradation co-mediate microbiota assembly during a freshwater cyanobacterial harmful algal bloom (CyanoHAB). Water Res. 2022, 220, 118674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafrir-Ilan, E.; Carmeli, S. Eight novel serine proteases inhibitors from a water bloom of the cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 9194–9202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoof, L.; Błaszczyk, A.; Meriluoto, J.; Cegłowska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Structures and activity of new anabaenopeptins produced by Baltic Sea cyanobacteria. Mar. Drugs 2015, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatova, D.; Jones, M.R.; Haley, J.A.; Núñez, O.; Farré, M.; Janssen, E.M.-L. Cyanobacteria and their secondary metabolites in three freshwater reservoirs in the United Kingdom. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halland, N.; Brönstrup, M.; Czech, J.; Czechtizky, W.; Evers, A.; Follmann, M.; Kohlmann, M.; Schiell, M.; Kurz, M.; Schreuder, H.A.; et al. Novel Small Molecule Inhibitors of Activated Thrombin Activatable Fibrinolysis Inhibitor (TAFIa) from Natural Product Anabaenopeptin. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4839–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobi, C.; Rinehart, K.L.; Neuber, R.; Mez, K.; Weckesser, J. Cyanopeptolin SS, a disulphated depsipeptide from a water bloom: Structural elucidation and biological activities. Phycologia 1996, 35, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beversdorf, L.J.; Rude, K.; Weirich, C.A.; Bartlett, S.L.; Seaman, M.; Kozik, C.; Biese, P.; Gosz, T.; Suha, M.; Stempa, C.; et al. Analysis of cyanobacterial metabolites in surface and raw drinking waters reveals more than microcystin. Water Res. 2018, 140, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, B.; Murakami, M.; Clardy, J. Atomic Structure of the Trypsin−Aeruginosin 98-B Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 595–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstvedt, C.B.; Rohrlack, T.; Ptacnik, R.; Edvardsen, B. On the effect of abiotic environmental factors on production of bioactive oligopeptides in field populations of Planktothrix spp. (Cyanobacteria). J. Plankton Res. 2008, 30, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifshits, M.; Zafrir-Ilan, E.; Raveh, A.; Carmeli, S. Protease inhibitors from three fishpond water blooms of Microcystis spp. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 4017–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervou, S.-K.; Moschandreou, K.; Paraskevopoulou, A.; Christophoridis, C.; Grigoriadou, E.; Kaloudis, T.; Triantis, T.M.; Tsiaoussi, V.; Hiskia, A. Cyanobacterial toxins and peptides in Lake Vegoritis, Greece. Toxins 2021, 13, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beversdorf, L.J.; Weirich, C.A.; Bartlett, S.L.; Miller, T.R. Variable Cyanobacterial Toxin and Metabolite Profiles across Six Eutrophic Lakes of Differing Physiochemical Characteristics. Toxins 2017, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okino, T.; Matsuda, H.; Murakami, M.; Yamaguchi, K. Microginin, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor from the blue-green alga Microcystis aeruginosa. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafrir-Ilan, E.; Carmeli, S. Two new microcyclamides from a water bloom of the cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 6602–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, J.; Lantvit, D.D.; Swanson, S.M.; Orjala, J. Lyngbyaureidamides A and B, two anabaenopeptins from the cultured freshwater cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. (SAG 36.91). Phytochemistry 2012, 74, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur-Marzec, H.; Kaczkowska, M.J.; Blaszczyk, A.; Akcaalan, R.; Spoof, L.; Meriluoto, J. Diversity of peptides produced by Nodularia spumigena from various geographical regions. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Kaya, K. Oscillamide Y, a chymotrypsin inhibitor from toxic Oscillatoria agardhii. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 5933–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Matsuda, H.; Murakami, M.; Yamaguchi, K. Anabaenopeptins E and F, Two New Cyclic Peptides from the Cyanobacterium Oscillatoria agardhii (NIES-204). J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Craig, M.; Holmes, C.F.B.; Andersen, R.J. Ferintoic Acids A and B, New Cyclic Hexapeptides from the Freshwater Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, H.S.; Philmus, B.; Portmann, C.; Hemscheidt, T.K. Homotyrosine-Containing Cyanopeptolins 880 and 960 and Anabaenopeptins 908 and 915 from Planktothrix agardhii CYA 126/8. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honkanen, R.E.; Zwiller, J.; Moore, R.; Daily, S.L.; Khatra, B.; Dukelow, M.; Boynton, A. Characterization of microcystin-LR, a potent inhibitor of type 1 and type 2A protein phosphatases. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 19401–19404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, L.A.; Crosbie, N.D.; Neilan, B.A. Distribution and conservation of known secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters in the genomes of geographically diverse Microcystis aeruginosa strains. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 71, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Sivonen, K.; Naganawa, E.; Harada, K.-I. Non-Toxic Peptides from Toxic Cyanobacteria, Oscillatoria agardhii. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnshaw, C.D.; McMullin, D.R. Cyanopeptolins and Anabaenopeptins Are the Dominant Cyanopeptides from Planktothrix Strains Collected in Canadian Lakes. Toxins 2024, 16, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Sivonen, K.; Nakano, T.; Harada, K.-I. Structural elucidation of cyanobacterial peptides encoded by peptide synthetase gene in Anabaena species. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 6863–6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy-Lachapelle, A.; Duy, S.V.; Munoz, G.; Dinh, Q.T.; Bahl, E.; Simon, D.F.; Sauvé, S. Analysis of multiclass cyanotoxins (microcystins, anabaenopeptins, cylindrospermopsin and anatoxins) in lake waters using on-line SPE liquid chromatography high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 5289–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Oh, S.K.; Yih, W.; Chin, J.; Kang, H.; Rho, J.-R. Cyanopeptoline CB071: A Cyclic Depsipeptide Isolated from the Freshwater Cyanobacterium Aphanocapsa sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 1191–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gademann, K.; Portmann, C.; Blom, J.F.; Zeder, M.; Jüttner, F. Multiple Toxin Production in the Cyanobacterium Microcystis: Isolation of the Toxic Protease Inhibitor Cyanopeptolin 1020. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bister, B.; Keller, S.; Baumann, H.I.; Nicholson, G.; Weist, S.; Jung, G.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Jüttner, F. Cyanopeptolin 963A, a chymotrypsin inhibitor of Microcystis PCC 7806. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1755–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elert, E.; Oberer, L.; Merkel, P.; Huhn, T.; Blom, J.F. Cyanopeptolin 954, a Chlorine-Containing Chymotrypsin Inhibitor of Microcystis aeruginosa NIVA Cya 43. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1324–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, K.A.; Miller, T.R.; Ma, H. Anabaenopeptins and cyanopeptolins induce systemic toxicity effects in a model organism the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltermann, S.; Zucchi, S.; Kohler, E.; Blom, J.F.; Pernthaler, J.; Fent, K. Molecular effects of the cyanobacterial toxin cyanopeptolin (CP1020) occurring in algal blooms: Global transcriptome analysis in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 149, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.d.A.; Dax, A.; Grand, I.; vom Berg, C.; Pinto, E.; Janssen, E.M.-L. Lethal and behavioral effects of semi-purified microcystins, Micropeptin and apolar compounds from cyanobacteria on freshwater microcrustacean Thamnocephalus platyurus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 273, 106983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegłowska, M.; Kwiecień, P.; Szubert, K.; Brzuzan, P.; Florczyk, M.; Edwards, C.; Kosakowska, A.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Biological activity and stability of aeruginosamides from cyanobacteria. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leikoski, N.; Liu, L.; Jokela, J.; Wahlsten, M.; Gugger, M.; Calteau, A.; Permi, P.; Kerfeld, C.A.; Sivonen, K.; Fewer, D.P. Genome Mining Expands the Chemical Diversity of the Cyanobactin Family to Include Highly Modified Linear Peptides. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, M.A.; van der Donk, W.A. New Insights into the Biosynthetic Logic of Ribosomally Synthesized and Post-translationally Modified Peptide Natural Products. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Okita, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Okino, T.; Yamaguchi, K. Aeruginosin 298-A, a thrombin and trypsin inhibitor from the blue-green alga Microcystis aeruginosa (NIES-298). Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 3129–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Ishida, K.; Okino, T.; Okita, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Yamaguchi, K. Aeruginosins 98-A and B, trypsin inhibitors from the blue-green alga Microcystis aeruginosa (NIES-98). Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 2785–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Matsuda, H.; Murakami, M.; Yamaguchi, K. Aeruginosins 205A and -B, Serine Protease Inhibitory Glycopeptides from the Cyanobacterium Oscillatoria agardhii (NIES-205). J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 1810–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, E.; Grundler, V.; Häussinger, D.; Kurmayer, R.; Gademann, K.; Pernthaler, J.; Blom, J.F. The toxicity and enzyme activity of a chlorine and sulfate containing aeruginosin isolated from a non-microcystin-producing Planktothrix strain. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, M.; Bezold, D.; Gademann, K. Investigating the toxicity of the aeruginosin chlorosulfopeptides by chemical synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9427–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodin-Friedman, A.; Carmeli, S. Microginins from a Microcystis sp. Bloom Material Collected from the Kishon Reservoir, Israel. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.M.; Kronenberger, T.; de Almeida, É.C.; Sampaio, J.; Terra, C.F.; Pinto, E.; Trossini, G.H.G. Inhibition of Porcine Aminopeptidase M (pAMP) by the Pentapeptide Microginins. Molecules 2019, 24, 4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.K.; Ravindra, R.; Van Wagoner, R.M.; Wright, J.L.C. Metabolomics-Guided Discovery of Microginin Peptides from Cultures of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, R.L.; Dörr, F.A.; Dörr, F.; Bortoli, S.; Delherbe, N.; Vasquez, M.; Pinto, E. Co-occurrence of microcystin and microginin congeners in Brazilian strains of Microcystis sp. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 82, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabro, K.; Genta-Jouve, G.g.; Thomas, O.P. Structure Revision of Microginins 674 and 690 from the Cultured Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bober, B.; Bialczyk, J. Determination of the toxicity of the freshwater cyanobacterium Woronichinia naegeliana (Unger) Elenkin. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Kaya, K. A 3-amino-10-chloro-2-hydroxydecanoic acid-containing tetrapeptide from Oscillatoria agardhii. Phytochemistry 1997, 44, 1503–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rounge, T.B.; Rohrlack, T.; Nederbragt, A.J.; Kristensen, T.; Jakobsen, K.S. A genome-wide analysis of nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene clusters and their peptides in a Planktothrix rubescens strain. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bober, B.; Lechowski, Z.; Bialczyk, J. Determination of some cyanopeptides synthesized by Woronichinia naegeliana (Chroococcales, Cyanophyceae). Phycol. Res. 2011, 59, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portmann, C.; Blom, J.F.; Gademann, K.; Jüttner, F. Aerucyclamides A and B: Isolation and synthesis of toxic ribosomal heterocyclic peptides from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portmann, C.; Blom, J.F.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Jüttner, F.; Gademann, K. Isolation of aerucyclamides C and D and structure revision of microcyclamide 7806A: Heterocyclic ribosomal peptides from Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806 and their antiparasite evaluation. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1891–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, K.; DesRochers, N.; Renaud, J.B.; Sumarah, M.W.; McMullin, D.R. Metabolomics Reveals Strain-Specific Cyanopeptide Profiles and Their Production Dynamics in Microcystis aeruginosa and M. flos-aquae. Toxins 2023, 15, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natumi, R.; Janssen, E.M.L. Cyanopeptide Co-Production Dynamics beyond Mirocystins and Effects of Growth Stages and Nutrient Availability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6063–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westrick, J.A.; Szlag, D.C.; Southwell, B.J.; Sinclair, J. A review of cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins removal/inactivation in drinking water treatment. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, K.; Watanuki, T.; Kondo, F.; Watanabe, M.F.; Nakazawa, H.; Suzuki, M.; Uchida, H.; Harada, K.-I. Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria—IV. Effect of chlorination on decomposition. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, J.L.; Rodriguez, E.; Meriluoto, J. Kinetics of reactions between chlorine and the cyanobacterial toxins microcystins. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merel, S.; LeBot, B.; Clément, M.; Seux, R.; Thomas, O. Ms identification of microcystin-LR chlorination by-products. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Stanford, B.D.; Adams, C.; Rosenfeldt, E.J.; Wert, E.C. Varied influence of microcystin structural difference on ELISA cross-reactivity and chlorination efficiency of congener mixtures. Water Res. 2017, 126, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natumi, R.; Dieziger, C.; Janssen, E.M.L. Cyanobacterial Toxins and Cyanopeptide Transformation Kinetics by Singlet Oxygen and pH-Dependence in Sunlit Surface Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15196–15205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bober, B.; Bialczyk, J.; Chrapusta-Srebrny, E. Effect of abiotic factors on the stability of chosen oligopeptides isolated from the freshwater cyanobacterium Woronichinia naegeliana. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 7057–7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Imanishi, S.Y.; Tsuji, K.; Harada, K.-i. Microbial degradation of cyanobacterial cyclic peptides. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.A.; Soldatou, S.; de Magalhães, V.F.; Azevedo, S.M.; Camacho-Muñoz, D.; Lawton, L.A.; Edwards, C. Degradation of multiple peptides by Microcystin-Degrader Paucibacter toxinivorans (2C20). Toxins 2021, 13, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.; Pattison, D.; Davies, M. Hypochlorite-induced oxidation of amino acids, peptides and proteins. Amino Acids 2003, 25, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantouch, A.; Ardel-Fattah, S. Action of sodium hypochlorite on a-amino acids. Chem. Zvesti 1971, 25, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Na, C.; Olson, T.M. Relative reactivity of amino acids with chlorine in mixtures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3220–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, E.; Humbert, J.F.; Tambosco, K.; Bormans, M.; Gerwick, W.H. Role of bacteria in the production and degradation of Microcystis cyanopeptides. Microbiologyopen 2016, 5, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, X.; Manzi, H.P.; Kiki, C.; Lin, L.; Hong, J.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Zeng, Q. Chlorination of microcystin-LR in natural water: Kinetics, transformation products, and genotoxicity. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 338, 117774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kull, T.P.J.; Sjövall, O.T.; Tammenkoski, M.K.; Backlund, P.H.; Meriluoto, J.A.O. Oxidation of the Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxin Microcystin-LR by Chlorine Dioxide: Influence of Natural Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1504–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natumi, R.; Marcotullio, S.; Janssen, E.M.-L. Phototransformation kinetics of cyanobacterial toxins and secondary metabolites in surface waters. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltermann, S.; Hutter, S.; Christen, V.; Hettich, T.; Fent, K. Anti-inflammatory activity of cyanobacterial serine protease inhibitors aeruginosin 828A and cyanopeptolin 1020 in human hepatoma cell line Huh7 and effects in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxins 2016, 8, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bober, B.; Kaminski, A.; Chrapusta, E.; Bialczyk, J. Stability of some microginins synthesized by the cyanobacterium W oronichinia naegeliana (U nger) E lenkin. Phycol. Res. 2014, 62, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cyanopeptide | Mode of Action | IC50 (µM) | Environmental Concentrations (ppb) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anabaenopeptin | Serine Proteases (Chymotrypsin, Elastase) | 45, 14.3 | 1.5–1100 | [40] |
| Phosphatases (Protein Phosphatase 1A, 2A) | 0.9, 1.3 | [33,36,38,41,42] | ||
| Carboxypeptidases (Carboxypeptidase A, B) | 0.002, 0.0002 | [34,43] | ||
| Cyanopeptolin | Serine Proteases (Trypsin, Chymotrypsin) | 0.00067, 0.0025 | 7.1–22 | [32] |
| Phosphatases (Protein Phosphatase 1A, 2A) | >10, >10 | [39,42,44,45] | ||
| Peptidases (Aminopeptidase N, Cytosolic) | 4.2, 4.7 | [35] | ||
| Aeruginosamide | Cytotoxicity (human ovarian cancer, human K562 leukemia cells) | 2.9, 5.2 | 0.893 *–9.4 * | [28,36] |
| Aeruginosin | Serine Protease (Trypsin, Thrombin, Plasmin) | 0.4, 0.03, 0.02 | 0.2 | [42,46,47] |
| Microginin | Peptidases (Aminopeptidase N, M) | 7.7, 1.2 | 2.2–1324 | [39,48,49,50] |
| Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme | 9.8 | [51] | ||
| Cyclamide | Serine Proteases (Chymotrypsin) | 75 | N/A | [52] |
| Antiparasitic (Plasmodium falciparum K1, Trypanosoma cruzi) | 0.7, 1.1 | [37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stringer, B.B.; Szlag Silva, R.G.; Kodanko, J.J.; Westrick, J.A. Structure, Toxicity, Prevalence, and Degradation of Six Understudied Freshwater Cyanopeptides. Toxins 2025, 17, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050233
Stringer BB, Szlag Silva RG, Kodanko JJ, Westrick JA. Structure, Toxicity, Prevalence, and Degradation of Six Understudied Freshwater Cyanopeptides. Toxins. 2025; 17(5):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050233
Chicago/Turabian StyleStringer, Blake B., Regina G. Szlag Silva, Jeremy J. Kodanko, and Judy A. Westrick. 2025. "Structure, Toxicity, Prevalence, and Degradation of Six Understudied Freshwater Cyanopeptides" Toxins 17, no. 5: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050233
APA StyleStringer, B. B., Szlag Silva, R. G., Kodanko, J. J., & Westrick, J. A. (2025). Structure, Toxicity, Prevalence, and Degradation of Six Understudied Freshwater Cyanopeptides. Toxins, 17(5), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050233







