Preclinical Evaluation of Botulinum Toxin Type E (TrenibotulinumtoxinE) Using the Mouse Digit Abduction Score (DAS) Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
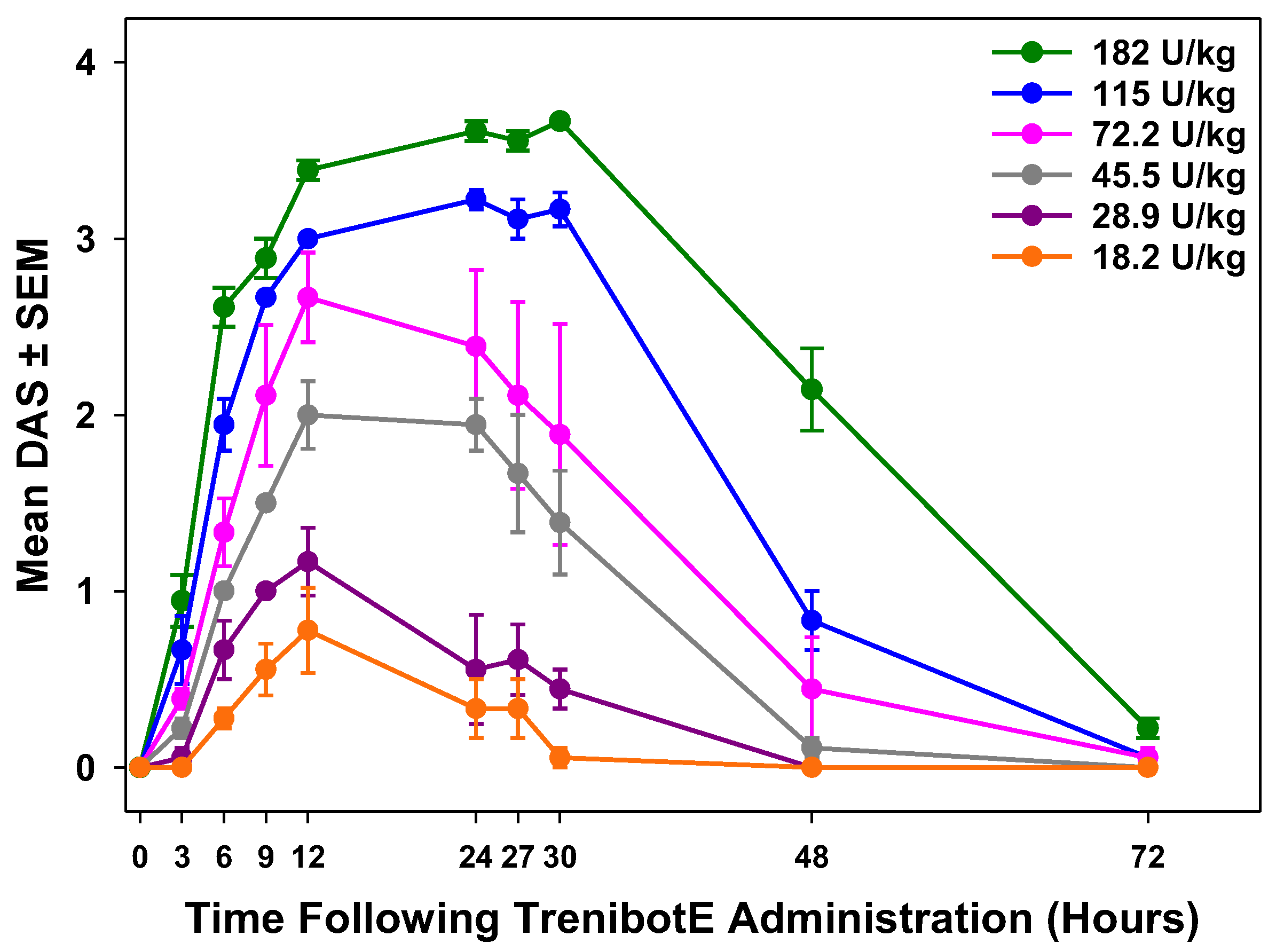
2.1. Dose-Dependent Peak Mouse DAS Response and Duration of Effect
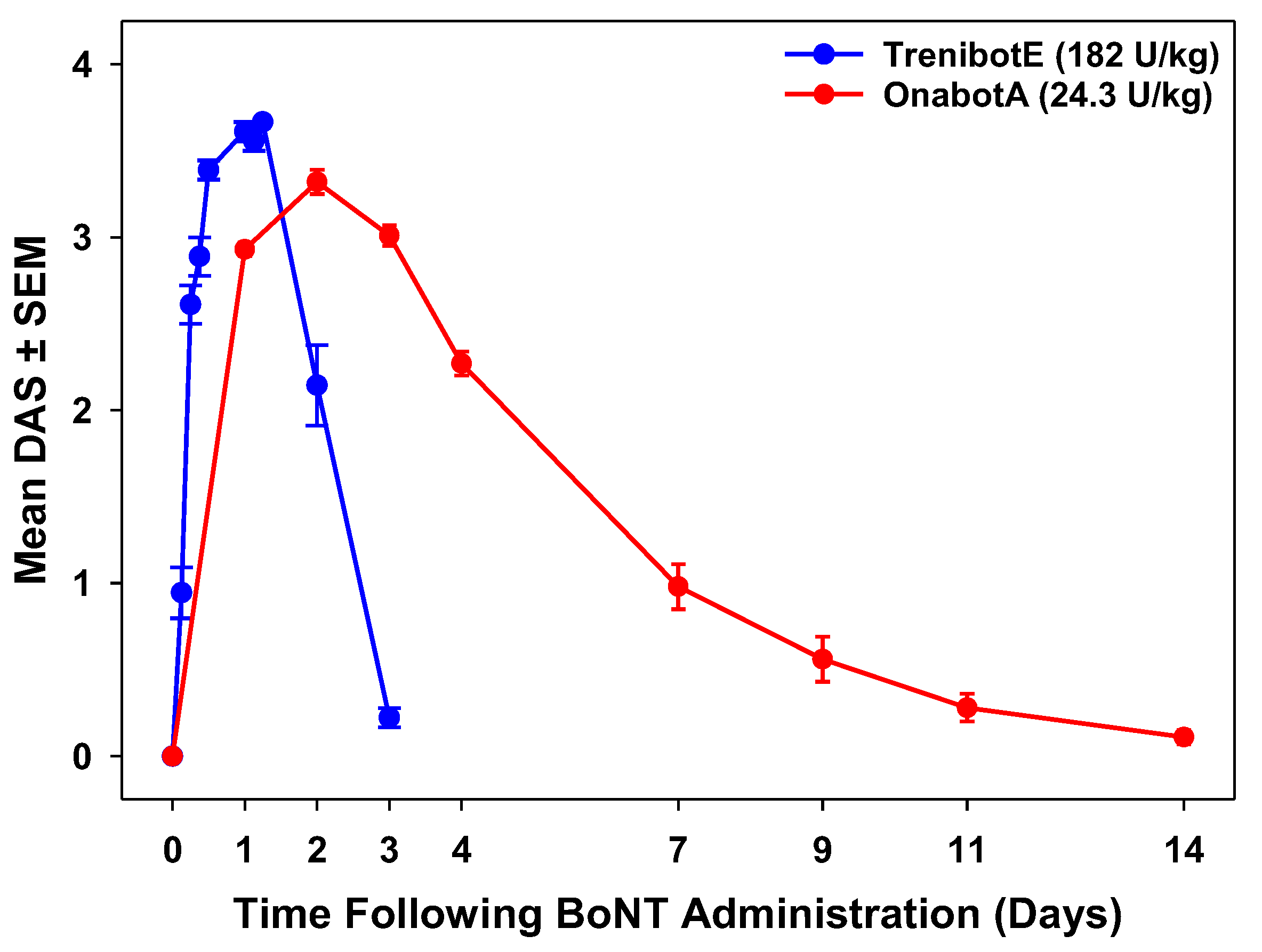
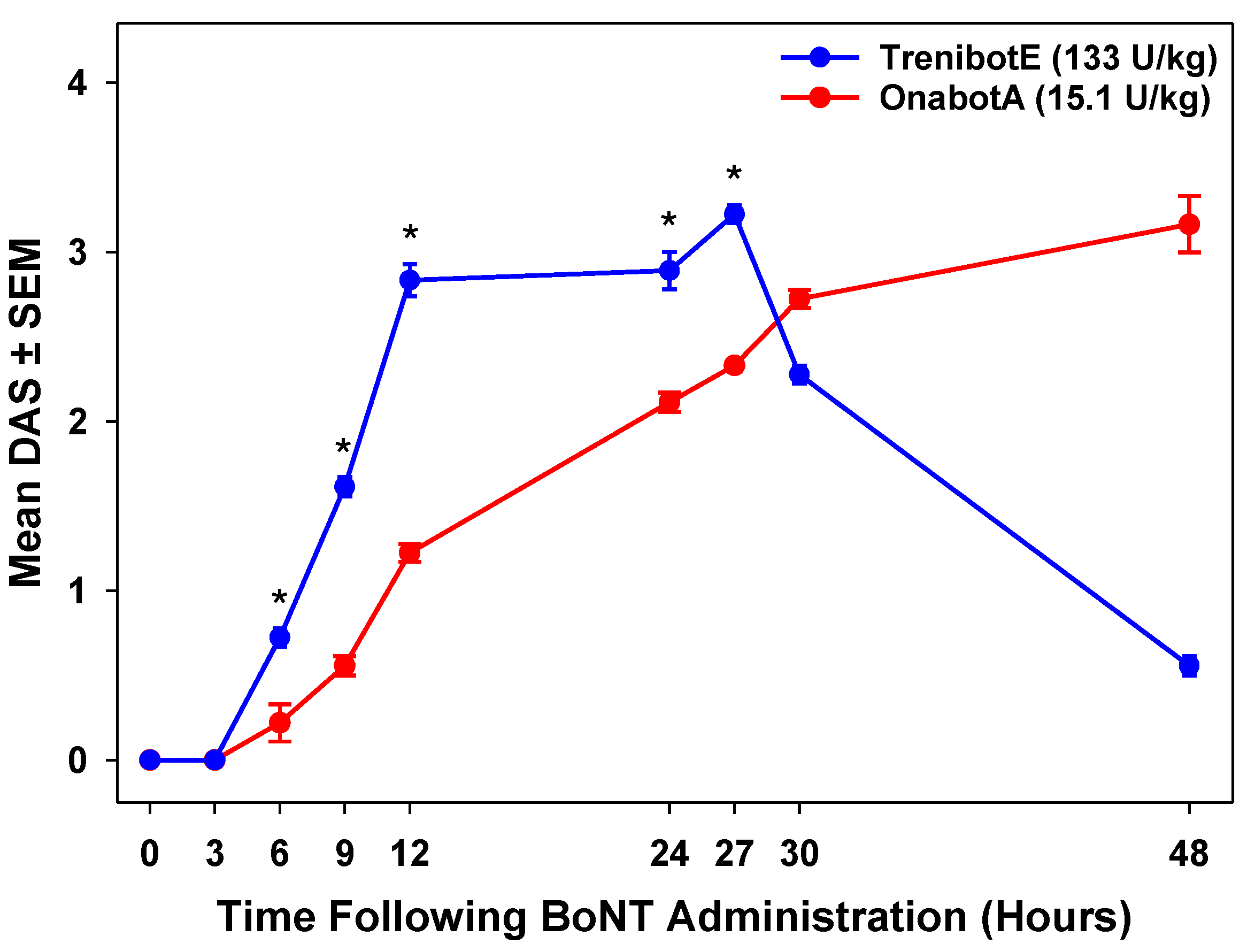
2.2. Comparative Analysis Between TrenibotE and OnabotA DAS Response
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. TrenibotE and OnabotA Preparation
5.2. Mice
5.3. Mouse DAS Assay
5.4. OnabotA Historical Data
5.5. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pirazzini, M.; Rossetto, O.; Eleopra, R.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxins: Biology, pharmacology, and toxicology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 200–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, M.F. Botulinum toxins: Pharmacology, immunology, and current developments. In Botulinum Toxins in Clinical Aesthetic Practice, 3rd ed.; Benedetto, A.V., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 6–20. [Google Scholar]
- Košenina, S.; Martínez-Carranza, M.; Davies, J.R.; Masuyer, G.; Stenmark, P. Structural analysis of botulinum neurotoxins type B and E by cryo-EM. Toxins 2021, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broide, R.S.; Rubino, J.; Nicholson, G.S.; Ardila, M.C.; Brown, M.S.; Aoki, K.R.; Francis, J. The rat Digit Abduction Score (DAS) assay: A physiological model for assessing botulinum neurotoxin-induced skeletal muscle paralysis. Toxicon 2013, 71, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, D.C.; Canty, D.; Rheaume, C.; Sondergaard, B.; Nino, C.; Broide, R.S.; Brideau-Andersen, A.D. A preclinical study comparing the activity and potency of onabotulinumtoxinA and prabotulinumtoxinA. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solish, N.; Rivers, J.K.; Humphrey, S.; Muhn, C.; Somogyi, C.; Lei, X.; Bhogal, M.; Caulkins, C. Efficacy and safety of onabotulinumtoxinA treatment of forehead lines: A multicenter, randomized, dose-ranging controlled trial. Dermatol. Surg. 2016, 42, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, A.; Carruthers, J.; Cohen, J. A prospective, double-blind, randomized, parallel- group, dose-ranging study of botulinum toxin type a in female subjects with horizontal forehead rhytides. Dermatol. Surg. 2003, 29, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Castaneda, J.; Jankovic, J. Long-term efficacy, safety, and side effect profile of botulinum toxin in dystonia: A 20-year follow-up. Toxicon 2014, 90, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, M.F.; Nelson, M.; Ashourian, N.; Brideau-Andersen, A.; Maltman, J. Update on non-interchangeability of botulinum neurotoxin products. Toxins 2024, 16, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleopra, R.; Tugnoli, V.; Rossetto, O.; De Grandis, D.; Montecucco, C. Different time courses of recovery after poisoning with botulinum neurotoxin serotypes A and E in humans. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 256, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehran, D.A.; Pirazzini, M. Novel botulinum neurotoxins: Exploring underneath the iceberg tip. Toxins 2018, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, F.A.; Lisk, G.; Sesardic, D.; Dolly, J.O. Dynamics of motor nerve terminal remodeling unveiled using SNARE-cleaving botulinum toxins: The extent and duration are dictated by the sites of SNAP-25 truncation. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2003, 22, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, M.; Keller, J.E.; Sheridan, R.E.; Deshpande, S.S. Persistence of botulinum neurotoxin A demonstrated by sequential administration of serotypes A and E in rat EDL muscle. Toxicon 2001, 39, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, S.; Elliott, M.; Gray, B.; Hornby, F.; Lewandowska, A.; Marlin, S.; Favre-Guilmard, C.; Périer, C.; Cornet, S.; Kalinichev, M.; et al. A comparison of biological activity of commercially available purified native botulinum neurotoxin serotypes A1 to F1 in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2018, 6, e00446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.; Carre, D.; Bilbault, H.; Oster, S.; Limana, L.; Sebal, F.; Favre-Guilmard, C.; Kalinichev, M.; Leveque, C.; Boulifard, V.; et al. Intramuscular botulinum neurotoxin serotypes E and A elicit distinct effects on SNAP25 protein fragments, muscular histology, spread and neuronal transport: An integrated histology-based study in the rat. Toxins 2024, 16, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, D.; Nicholson, G.; Canty, D.; Wang, J.; Rhéaume, C.; Le, L.; Steward, L.E.; Washburn, M.; Jacky, B.P.; Broide, R.S.; et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA displays greater biological activity compared to incobotulinumtoxinA, demonstrating non-interchangeability in both in vitro and in vivo assays. Toxins 2020, 12, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.R. Preclinical update on BOTOX (botulinum toxin type A)-purified neurotoxin complex relative to other botulinurn neurotoxin preparations. Eur. J. Neurol. 1999, 6 (Suppl. S4), s3–s10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoelin, S.G.; Dhawan, S.S.; Vitarella, D.; Ahmad, W.; Hasan, F.; Abushakra, S. Safety and efficacy of EB-001, a novel type E botulinum toxin, in subjects with glabellar frown lines: Results of a phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled, ascending-dose study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 847e–855e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, D.; Eswaramoorthy, S.; Furey, W.; Navaza, J.; Sax, M.; Swaminathan, S. Domain organization in Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type E is unique: Its implication in faster translocation. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lee, P.G.; Krez, N.; Lam, K.H.; Liu, H.; Przykopanski, A.; Chen, P.; Yao, G.; Zhang, S.; Tremblay, J.M.; et al. Structural basis for botulinum neurotoxin E recognition of synaptic vesicle protein 2. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, A.P.; Barbieri, J.T. Light chain diversity among the botulinum neurotoxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Salas, E.; Steward, L.E.; Ho, H.; Garay, P.E.; Sun, S.W.; Gilmore, M.A.; Ordas, J.V.; Wang, J.; Francis, J.; Aoki, K.R. Plasma membrane localization signals in the light chain of botulinum neurotoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washbourne, P.; Pellizzari, R.; Rossetto, O.; Bortoletto, N.; Tugnoli, V.; De Grandis, D.; Eleopra, R.; Montecucco, C. On the action of botulinum neurotoxins A and E at cholinergic terminals. J. Physiol. Paris. 1998, 92, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecucco, C.; Molgó, J. Botulinal neurotoxins: Revival of an old killer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecucco, C.; Schiavo, G.; Pantano, S. SNARE complexes and neuroexocytosis: How many, how close? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagin, O.; Tokhtaeva, E.; Garay, P.E.; Souda, P.; Bassilian, S.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Lewis, R.; Sachs, G.; Wheeler, L.; Aoki, R.; et al. Recruitment of septin cytoskeletal proteins by botulinum toxin A protease determines its remarkable stability. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127 Pt 15, 3294–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Kotiya, A.; Kiris, E.; Yang, M.; Bavari, S.; Tessarollo, L.; Oyler, G.A.; Weissman, A.M. Deubiquitinating enzyme VCIP135 dictates the duration of botulinum neurotoxin type A intoxication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5158–E5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, M.A.; Swope, D.M.; Grimes, D. Diffusion of botulinum toxins. Tremor Other Hyperkinet. Mov. 2012, 2, tre-02-85-417-411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carré, D.; Martin, V.; Kouidri, Y.; Morin, R.; Norlund, M.; Gomes, A.; Lagarde, J.M.; Lezmi, S. The distribution of neuromuscular junctions depends on muscle pennation, when botulinum neurotoxin receptors and SNAREs expression are uniform in the rat. Toxicon 2022, 212, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peker, T.; Gülekon, N.; Coşkun, Z.K.; Omeroğlu, S. Investigation of the nerve distribution pattern of leg muscles in rat. Anat. Sci. Int. 2013, 88, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppert, A.D.; Spirou, G.A.; Berrebi, A.S.; Garnett, J.D. Three-dimensional reconstruction of immunolabeled neuromuscular junctions in the human thyroarytenoid muscle. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 1973–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.H.; Lee, H.J.; Seo, K.K.; Kim, H.J. Intramuscular neural arborization of the latissimus dorsi muscle: Application of botulinum neurotoxin injection in flap reconstruction. Toxins 2022, 14, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicholson, G.S.; Canty, D.; Southern, A.; Whelan, K.; Brideau-Andersen, A.D.; Broide, R.S. Preclinical Evaluation of Botulinum Toxin Type E (TrenibotulinumtoxinE) Using the Mouse Digit Abduction Score (DAS) Assay. Toxins 2025, 17, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050230
Nicholson GS, Canty D, Southern A, Whelan K, Brideau-Andersen AD, Broide RS. Preclinical Evaluation of Botulinum Toxin Type E (TrenibotulinumtoxinE) Using the Mouse Digit Abduction Score (DAS) Assay. Toxins. 2025; 17(5):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050230
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicholson, Gregory S., David Canty, Annemarie Southern, Kevin Whelan, Amy D. Brideau-Andersen, and Ron S. Broide. 2025. "Preclinical Evaluation of Botulinum Toxin Type E (TrenibotulinumtoxinE) Using the Mouse Digit Abduction Score (DAS) Assay" Toxins 17, no. 5: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050230
APA StyleNicholson, G. S., Canty, D., Southern, A., Whelan, K., Brideau-Andersen, A. D., & Broide, R. S. (2025). Preclinical Evaluation of Botulinum Toxin Type E (TrenibotulinumtoxinE) Using the Mouse Digit Abduction Score (DAS) Assay. Toxins, 17(5), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050230



