Toxin Accumulation, Distribution, and Sources of Toxic Xanthid Crabs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Xanthid Crabs
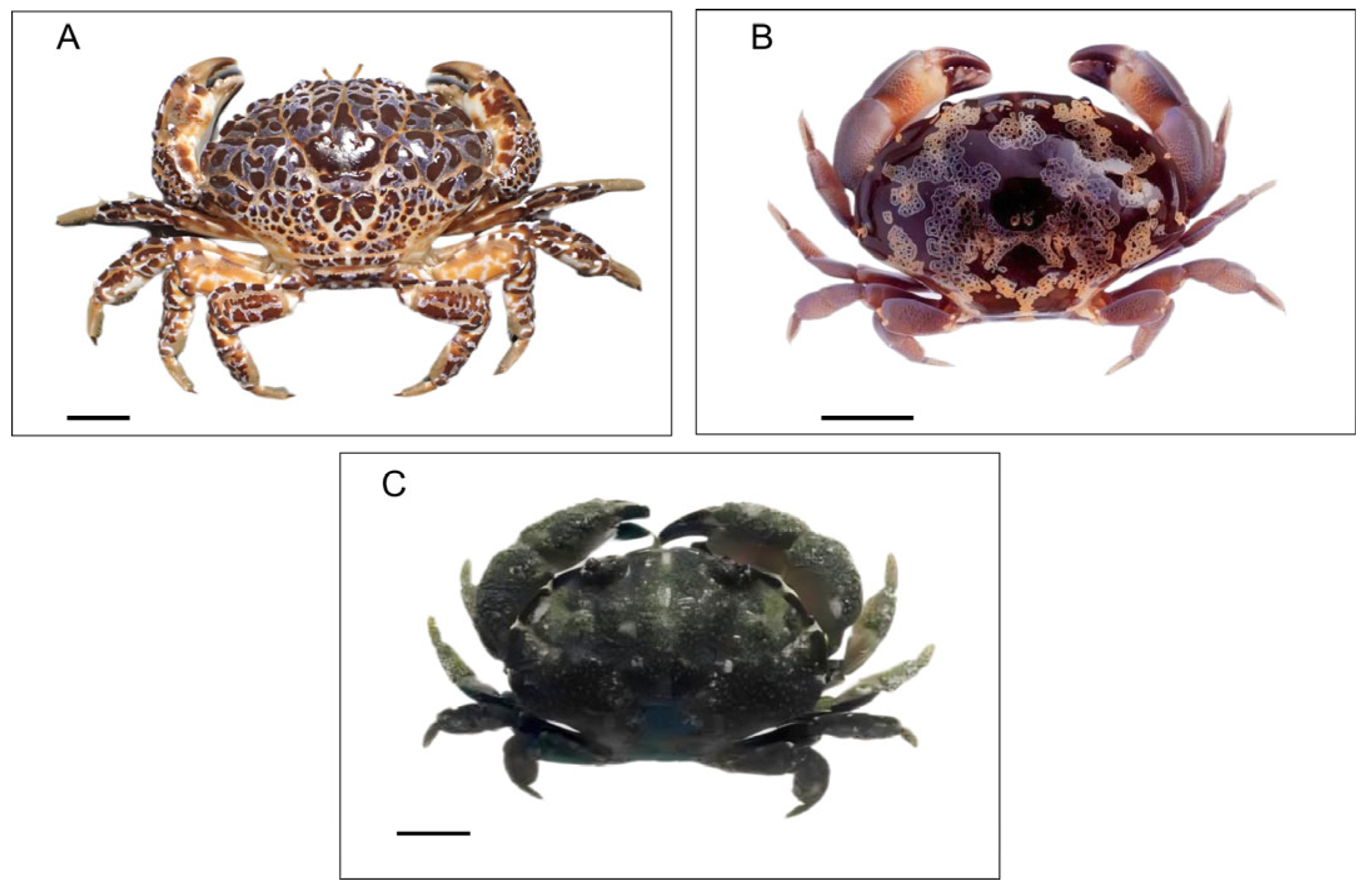
2.1. First Three Species Identified as Toxic
2.1.1. Zosimus aeneus
2.1.2. Atergatis floridus
| Species | Toxic Specimens/Tested Specimens | Toxin Profiles | Toxin Contents | Methods of Determination | Location | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zosimus aeneus | 81/112 | —— | NM | MBA3 | Ryukyu and Amami Islands, Japan | [3] |
| 77/107 | —— | ND-1580 MU/g | MBA | Kyonoura, Amami-Oshima Island, Ishigaki Island, and Tokunoshima Island, Japan | [4] | |
| 24/24 | —— | 30–1260 MU/g | MBA | Ishigaki Island, Japan | [5] | |
| 5/28 | —— | ND-30 MU/g | MBA | Marcus Island, Japan | ||
| 0/38 | —— | ND | MBA | Espiritu Santo, the Republic of Vanuatu | ||
| 0/2 | —— | ND | MBA | American Samoa | ||
| 9/9 | —— | 30–260 MU/g | MBA | Rangiroa, Tuamotu Island | ||
| 101/102 | —— | ND-16500 MU/g | MBA | Ishigaki Island, Japan | [33] | |
| 6/6 | —— | 2–220 MU/g | MBA | Hachijo Island and Bonin Islands, Japan | ||
| 11/11 | —— | 26–3000 MU/g | MBA | Cebu Island, the Philippines | ||
| 18/18 | PST | 2.2–33.8 MU/g | MBA, TLC | Fiji Island, Fiji | [34] | |
| 50/69 | PST and/or TTX | ND-259 MU/g | MBA, HPLC | Negros Island, the Philippines | [35] | |
| 53/75 | PST and/or TTX | ND-2300 MU | MBA, HPLC | Lanyu, Wanlitung, and Hsiaoliuchiu, Taiwan | [7] | |
| 14/15 | PST and/or TTX | ND-1258 MU | MBA, HPLC, LC-MS, GC-MS | Kenting National Park, Taiwan | [36] | |
| 9/16 | TTX | ND-11 MU/g | MBA, HPLC, LC-MS | Tokara Islands, Japan | [37] | |
| 52/53 | PST and/or TTX | ND-14700 MU/g (appendages) | HPLC, LC-MS | Ishigaki Island, Japan | [9] | |
| Atergatis floridus | 102/144 | —— | NM | MBA | Ryukyu Islands, Amami Islands, and the mainland of Japan, Japan | [3] |
| 66/96 | —— | NM | MBA | Nagasaki, Kaimon, Tosa, Minabe, Nagai, Awa-Shirahama, Hachijo Island, and Oshima Island, Japan | [4] | |
| 35/35 | PST | 3.4–717 MU/g | MBA, TLC | Fiji Island, Fiji | [34] | |
| 19/21 | PST and/or TTX | ND-1300 MU/g | MBA, TLC, HPLC | Ishigaki Island, Japan | [38] | |
| 25/25 | PST | 2.3–480 MU/g | MBA, HPLC | Negros Island, the Philippines | [35] | |
| 65/109 | PST | ND-108 MU/g | MBA, TLC | The Great Barrier Reef, Australia | [8] | |
| 8/8 | PST and/or TTX | 63–424 MU | MBA, TLC, HPLC | Keelung, Taiwan | [39] | |
| 32/32 | TTX | 3–237 MU/g (muscle of cheliped) | MBA | Kanagawa and Wakayama, Japan | [40] | |
| 15/15 | PST and/or TTX | 88 ± 40–1257 ± 607 MU/g (appendages Av. ± S.D.) | MBA, HPLC, GC-MS | Ishigaki Island, Japan | [41] | |
| 5/5 | PST and/or TTX | 221 ± 189 MU/g (appendages Av. ± S.D.) | MBA, HPLC, GC-MS | Cebu, the Philippines | [41] | |
| 9/9 | TTX | 2.73–206.64 MU/g | MBA, HPLC, GC-MS | Nagasaki, Japan | [42] | |
| 15/15 | TTX | 0.21–116.1 MU/g (appendages) | MBA, HPLC, GC-MS | Nagasaki, Japan | [42] | |
| Lophozozymus pictor | 4/4 | PLTX | 200–10,000 MU/g (viscera) 180–3000 MU/g (gill) | TLC, HPLC, FAB-MS | Negros Island, the Philippines | [43] |
| —— | PLTX | 5000 MU/g (extract) | MBA, TLC, HPLC | Sentosa Island, Singapore | [44] | |
| 21/21 | —— | 7840 ± 2254 MU/g (gut Av. ± S.D.) | MBA | Sentosa Island, Singapore | [45] | |
| 15/15 | PST | 386–3874 MU | MBA, TLC, HPLC | Keelung, Taiwan | [46] | |
| Platypodia granulosa | 12/38 | —— | NM | MBA | Ryukyu Islands, Japan | [3] |
| 11/35 | —— | NM | MBA | Miyako Island, and Ryukyu Islands, Japan | [4] | |
| Atergatopsis germaini | 17/17 | PST | 472–9045 MU | MBA, TLC, HPLC | Keelung, Taiwan | [47] |
| Atergatis integerrimus | 1/4 | TTX | ND-2 MU/g | MBA | Negros Island, the Philippines | [35] |
| Actaeodes tomentosus | 7/15 | TTX | ND-40 MU | MBA, HPLC, LC-MS, GC-MS | Kenting National Park, Taiwan | [36] |
| Carpilius maculatus | 1/2 | —— | ND-2 MU/g | MBA | Negros Island, the Philippines | [35] |
| Etisus rhynchophorus | 1/2 | —— | ND-2 MU/g | MBA | Negros Island, the Philippines | [35] |
| Etisus splendidus | 1/4 | —— | ND-2 MU/g | MBA | Negros Island, the Philippines | [35] |
| Eriphia sebana | 35/75 | PST | ND-9 MU/g | MBA, TLC | The Great Barrier Reef, Australia | [48] |
| Demania reynaudi | 7/7 | PST and/or TTX | 217–564 MU | MBA, TLC, HPLC | Keelung, Taiwan | [39] |
| 1/1 | PLTX-like toxin | 800 MU (two legs) | MBA, HPLC | Negros Island, the Philippines | [49] | |
| Demania cultripes | 7/7 | PST and/or TTX | 5.6–52.1 MU/g (viscera) | MBA, HPLC, GC-MS | Cebu Island, the Philippines | [50] |
| Demania alcalai | 2/2 | PLTX | 4000–5400 (viscera) 2400–16,000 (gill) | TLC, HPLC, FAB-MS | Negros Island, the Philippines | [43] |
| Leptodius sanguirreus | 3/3 | —— | 0.3–1.3 MU/g | MBA | Heron Island, Australia | [51] |
| Pilodius areolatus | 4/10 | —— | 1.5 MU/g (extract) | MBA | Heron Island, Australia | [51] |
| Phymodius angolalos | 6/9 | —— | 1.6–8.9 MU/g (three extracts) | MBA | Heron Island, Australia | [51] |
| Platypodiella spectabilis | 3/3 | PLTX | 20–50 HU/g | Hemolysis, HPLC | Santa Marta, Colombia | [52,53] |
| Xanthias lividu | 9/9 | PST and/or TTX | 118–430 MU | MBA, HPLC | Lanyu and Hsiaoliuchiu, Taiwan | [54] |
| 5/5 | PST and/or TTX | 11–118 MU | MBA, HPLC, LC-MS, GC-MS | Kenting National Park, Taiwan | [36] |
2.1.3. Platypodia granulosa
2.2. Species Subsequently Identified as Toxic
2.2.1. Lophozozymus pictor
2.2.2. Demania Species
3. Toxin Profiles and Contents in Toxic Crabs
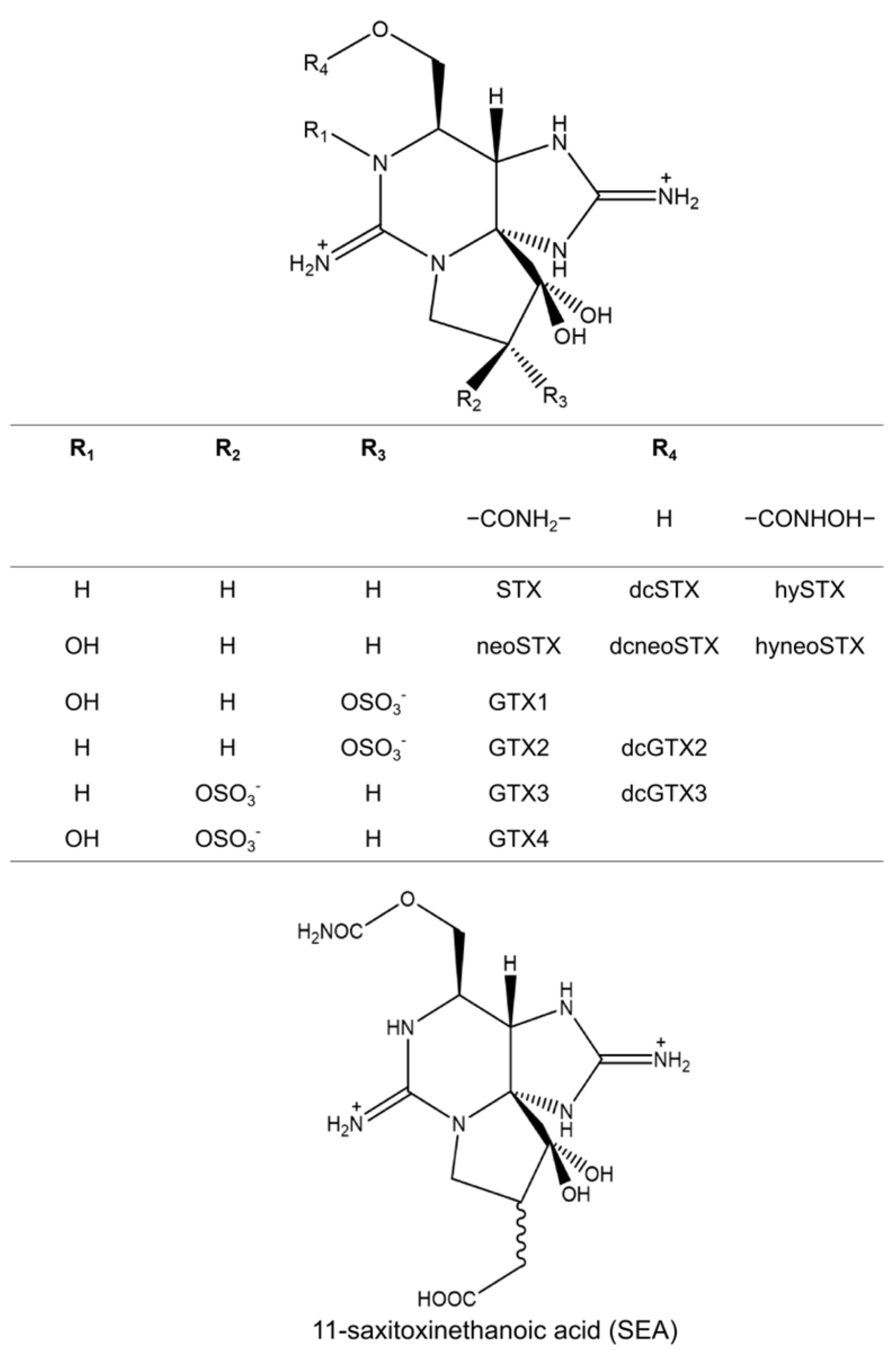
3.1. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins (PSTs)
3.2. Tetrodotoxin (TTX)
3.3. Palytoxins (PLTXs) and PLTX-like Compounds
4. Toxin Distribution in the Anatomy of Toxic Crabs
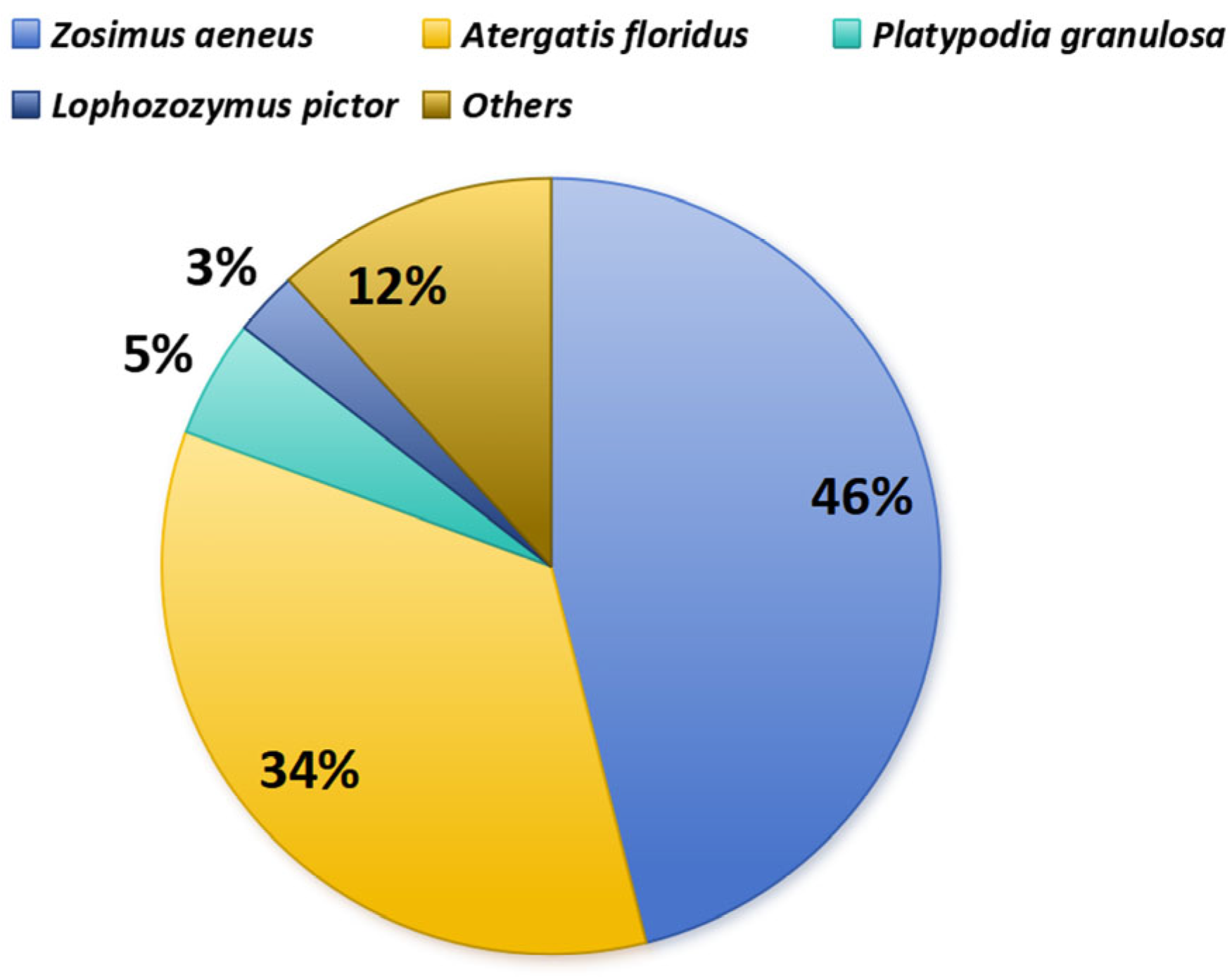
5. Geographic Distribution and Individual Variations in Toxins in Toxic Xanthid Crabs
5.1. Local and Individual Variations in Toxic Xanthid Crabs
5.2. Small-Scale Distribution of Toxin Profiles and Toxin Concentrations
6. Human Interactions and Risks
7. Hypotheses on the Origins of Toxin-Producing Organisms in Toxic Crabs
7.1. Red Algae Jania sp.
7.2. Ascidians
7.3. Zoanthid Genus Palythoa
7.4. Microorganisms
8. Resistibility and Defenses of Toxic Crabs
9. Ecological Role of Toxic Xanthid Crabs
10. Discussion
11. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashimoto, Y.; Konosu, S.; Yasumoto, T.; Inoue, A.; Noguchi, T. Occurrence of toxic crabs in Ryukyu and Amami Islands. Toxicon 1967, 5, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Daigo, K.; Oikawa, H.; Asakawa, M.; Miyazawa, K. Chapter 36—Different intoxication mechanism between paralytic shellfish toxin (PST)- and/or tetrodotoxin-contaminated xanthid crabs and PST-contaminated edible shore crabs in Japan and their food poisonings. In Handbook of Algal Science, Technology and Medicine; Konur, O., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 575–589. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, Y.; KoNosu, S.; Inoue, A.; Saisho, T.; Miyake, S. Screening of toxic crabs in the Ryukyu and Amami Islands. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1969, 35, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konosu, S.; Inoue, A.; Noguchi, T.; Hashimoto, Y. A further examination on the toxicity of three species of xanthid crab. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1969, 35, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konosu, S.; Noguchi, T.; Hashimoto, Y. Toxicity of a Xanthid Crab, Zosimus aeneus, and Several Other Species in the Pacific. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1970, 36, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcala, A.C. Recent cases of crab, cone shell, and fish intoxication on Southern Negros Island, Philippines. Toxicon 1983, 21, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Jeng, S.-S.; Hwang, D.-F. Seasonal and regional variations of toxicity in the xanthid crab Zosimus aeneus in Taiwan. Fish. Sci. 1997, 63, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, L.E.; Endean, R. Paralytic shellfish toxins in the xanthid crab Atergatis floridus collected from Australian coral reefs. J. Wilderness Med. 1991, 2, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tsutsui, H.; Yamawaki, N.; Morii, Y.; Nishihara, G.N.; Itoi, S.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T. Geographic Variations in the Toxin Profile of the Xanthid Crab Zosimus aeneus in a Single Reef on Ishigaki Island, Okinawa, Japan. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Du, L.; Zhu, P.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Wu, C.; Wang, P. Recent progress in micro/nano biosensors for shellfish toxin detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celio, L.; Ottaviani, M.; Cancelliere, R.; Di Tinno, A.; Panjan, P.; Sesay, A.M.; Micheli, L. Microfluidic Flow Injection Immunoassay System for Algal Toxins Determination: A Case of Study. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 6266320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, S. A novel screening on the specific peptides by molecular simulation and development of the highly-sensitive electrochemical sensor for saxitoxin. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charapata, P.; Bowers, E.K.; Hardison, D.R.; Kibler, S.; Anderson, D.M.; Fachon, E.; Lefebvre, K.A. Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Concentrations Measured in Alaskan Arctic Clams Using ELISA and HPLC Methods. Toxins 2025, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petropoulos, K.; Bodini, S.F.; Fabiani, L.; Micheli, L.; Porchetta, A.; Piermarini, S.; Volpe, G.; Pasquazzi, F.M.; Sanfilippo, L.; Moscetta, P.; et al. Re-modeling ELISA kits embedded in an automated system suitable for on-line detection of algal toxins in seawater. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, S.H.; Laura, M.; Giuseppe, P.; Compagnone, D. Development of an Electrochemical Immunosensor for Ochratoxin A. Anal. Lett. 2004, 37, 1545–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.-N.; Luo, L.; Wang, B.-Z.; Lei, H.-T.; Guan, T.; Shen, Y.-D.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.-L. Biosensors for detection of paralytic shellfish toxins: Recognition elements and transduction technologies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancelliere, R.; Di Tinno, A.; Cataldo, A.; Bellucci, S.; Kumbhat, S.; Micheli, L. Nafion-based label-free immunosensor as a reliable warning system: The case of AFB1 detection in cattle feed. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Konosu, S.; Hashimoto, Y. Identity of the crab toxin with saxitoxin. Toxicon 1969, 7, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Uzu, A.; Koyama, K.; Maruyama, j.; Nagashima, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin as the major toxin in a xanthid crab Atergatis floridus. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1983, 49, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, H.L.; Roy, C.J. History and Toxinology of Palytoxins. Toxins 2024, 16, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.A.; Naruse, T.; Reimer, J.D. Morphological and molecular investigation of some xanthid crabs from the Egyptian coast of the Red Sea. Thalass. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2023, 39, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Komatsu, H. A New and Some Rare Crabs of the Families Trapeziidae, Oziidae and Xanthidae (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura) from the Ogasawara Islands, Japan. Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci. Ser. A Zool. 2024, 50, 97–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.N.; Kim, M.H. A new record of the xanthid crab, Demania rotundata (Serène in Guinot, 1969) (Decapoda, Brachyura, Xanthioidea) from Korean waters. Crustaceana 2023, 96, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, E.; Christopher, J. Marine crabs new to Singapore, with a description of a new species of intertidal xanthid crab of the genus Macromedaeus Ward, 1942 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura). Raffles Bull. Zool. 2021, 69, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisho, T.; Noguchi, T.; Koyama, K.; Uzu, A.; Kikuta, T.; Hashimoto, K. Examination of stomach contents in xanthid crabs. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1983, 49, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.P. Observations on the Life Histories and the Distribution of the Xanthidae (Mud Crabs) of Chesapeake Bay. Am. Midl. Nat. 1956, 56, 138–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatfat, S.; Badreddine, A.; Aguilar, R. Expanding Boundaries: Documenting Two Xanthid Crabs (Atergatis integerrimus and Liomera rugipes) in the Mediterranean Sea from Lebanese Waters. J. Fish. Livest. Prod. 2024, 12, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, J.W. Shell Formation and Growth of the California Xanthid Crabs. Ecology 1959, 40, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredrick, W.S.; Ravichandran, S.; Balasubramanian, T. Toxicity of Brachuryan crabs in India. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2011, 93, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Saruwatari, T.; Minami, T. Redescription of the first zoea of Zosimus aeneus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Decapoda, Xanthidae). Crustac. Res. 2009, 38, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghory, F.a.J.A. Morpho-taxonomic study of first zoeas of Atergatis integerrimus (Lamarck, 1801) and A. floridus (Linnaeus, 1767)(Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura: Xanthidae) reared in the laboratory. Arthropods 2022, 11, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H.; Konishi, K. Atergatis floridus (Linnaeus, 1767) (Decapoda: Xanthidae): Re-examination and correction of zoeal characters. Crustac. Res. 2009, 38, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, K.; Noguchi, T.; Uzu, A.; Hashimoto, K. Individual, local, and size-dependent variations in toxicity of the xanthid crab Zosimus aeneus. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1983, 49, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, U.; Haq, H.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. The occurrence of paralytic shellfish toxins in two species of xanthid crab from Suva barrier reef, Fiji Islands. Toxicon 1983, 21, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumura, D.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T.; Alcala, A.C.; Alcala, L.C. Tetrodotoxin and Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Philippine Crabs. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.-H.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Hwang, C.-C.; Hwang, P.-A.; Hwang, J.-H.; Hwang, D.-F. Paralytic toxins in four species of coral reef crabs from Kenting National Park in southern Taiwan. Food Control 2006, 17, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagara, T.; Taniyama, S.; Takatani, T.; Nishibori, N.; Nishio, S.; Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O. Toxicity and toxin profiles of xanthid crabs collected around Nakanoshima in the Tokara Islands, Japan. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 50, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Daigo, K.; Hashimoto, K. Local differences in toxin composition of a xanthid crab Atergatis floridus inhabiting Ishigaki Island, Okinawa. Toxicon 1986, 24, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Hwang, D.-F.; Chai, T.-J.; Jeng, S.-S. Toxicity and toxic components of two xanthid crabs, Atergatis floridus and Demania reynaudi, in taiwan. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Kohama, T.; Ui, K.; Watabe, S. Distribution of tetrodotoxin in the xanthid crab (Atergatis floridus) collected in the coastal waters of Kanagawa and Wakayama Prefectures. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2006, 1, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, M.; Tsuruda, S.; Ishimoto, Y.; Shimomura, M.; Kishimoto, K.; Shida, Y.; Barte-Quilantang, M.; Gomez-Delan, G. Paralytic toxin profiles of xanthid crab Atergatis floridus collected on reefs of Ishigaki Island, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan and Camotes Island, Cebu Province, Philippines. Sci. J. Clin. Med. 2014, 3, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yamate, Y.; Takegaki, T.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T. Tetrodotoxin Profiles in Xanthid Crab Atergatis floridus and Blue-Lined Octopus Hapalochlaena cf. fasciata from the Same Site in Nagasaki, Japan. Toxins 2023, 15, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Yasumura, D.; Ohizumi, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Alcala, A.C.; Alcala, L.C. Palytoxin in Two Species of Xanthid Crab from the Philippines. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.O.; Khoo, H.E.; Yuen, R.; Wan, M.; Tan, C.H. Isolation of a novel fluorescent toxin from the coral reef crab, Lophozozymus pictor. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, D.G.B.; Lau, C.O.; Ng, P.K.L.; Tan, C.H. Localization of toxins in the poisonous mosaic crab, Lophozozymus pictor (Fabricius, 1798) (Brachyura, Xanthidae). Toxicon 1993, 31, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Hwang, D.-F.; Chai, T.-J.; Jeng, S.-S. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin and paralytic shellfish poison in the Taiwanese crab Lophozozymus pictor. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Hwang, D.-F.; Chai, T.-J.; Jeng, S.-S. Occurrence of paralytic toxin in Taiwanese crab Atergatopsis germaini. Toxicon 1996, 34, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, L.E.; Endean, R. Toxins extracted from Australian specimens of the crab, Eriphia sebana (Xanthidae). Toxicon 1989, 27, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcala, A.C.; Alcala, L.C.; Garth, J.S.; Yasumura, D.; Yasumoto, T. Human fatality due to ingestion of the crab Demania reynaudii that contained a palytoxin-like toxin. Toxicon 1988, 26, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, M.; Gomez-Delan, G.; Tsuruda, S.; Shimomura, M.; Shida, Y.; Taniyama, S.; Barte-Quilantang, M.; Shindo, J. Toxicity assessment of the xanthid crab Demania cultripes from Cebu Island, Philippines. J. Toxicol. 2010, 2010, 172367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, L.E.; Endean, R. Toxic coral reef crabs from Australian waters. Toxicon 1988, 26, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleibs, S.; Mebs, D.; Werding, B. Studies on the origin and distribution of palytoxin in a Caribbean coral reef. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleibs, S.; Mebs, D. Distribution and sequestration of palytoxin in coral reef animals. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Ho, P.-H.; Jeng, S.-S.; Hwang, D.-F. Paralytic toxins in Taiwanese crab Xanthias lividus. Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, C.H. Xanthidae of Hawaii. Citeseer: University Park, PA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, P.K.L.; Guinot, D.; Davie, P. Systema Brachyurorum: Part I. An annotated checklist of extant Brachyuran crabs of the world. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2008, 17, 1–296. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, D.F.; Tsai, Y.H. Toxins in toxic Taiwanese crabs. Food Rev. Int. 1999, 15, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.; Chia, D. Lophozozymus erinnyes, a new species of poisonous crab from Australia, with notes on L. pictor (Fabricius, 1798), L. incisus (H. Milne Edwards, 1834) and L. edwardsi (Odhner, 1925) (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura: Xanthidae). Raffles Bull. Zool. 1997, 45, 419–443. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, P.K.; Yang, C.M. On some species of Demania Laurie, 1906 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura: Xanthidae) from Malaysia, Singapore and the Philippines, with a key for the genus. Raffles Bull. Zool. 1989, 37, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T.; Onoue, Y. Paralytic shellfish toxin profiles of xanthid crabs Zosimus aeneus and Atergatis floridus collected on reefs of Ishigaki Island. Fish. Sci. 1995, 61, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T.; Shida, Y.; Onoue, Y. Occurrence of 11-Oxotetrodotoxin and 11-Nortetrodotoxin-6 (R)-ol in a xanthid crab Atergatis floridus collected at Kojima, Ishigaki Island. Fish. Sci. 1994, 60, 769–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aligizaki, K.; Katikou, P.; Milandri, A.; Diogène, J. Occurrence of palytoxin-group toxins in seafood and future strategies to complement the present state of the art. Toxicon 2011, 57, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, V.; Vasconcelos, V. Palytoxin and Analogs: Biological and Ecological Effects. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, H. Effects of harmful algal blooms on the physiological, immunity and resistance to environmental stress of bivalves: Special focus on paralytic shellfish poisoning and diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. Aquaculture 2023, 563, 739000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schantz, E.J.; Ghazarossian, V.E.; Schnoes, H.K.; Strong, F.M.; Springer, J.P.; Pezzanite, J.O.; Clardy, J. Structure of saxitoxin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 1238–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Occurrence of saxitoxin in puffer fish. Toxicon 1984, 22, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, J.C.; Ogata, T.; Veit, C.H.; Kodama, M. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin and paralytic shellfish toxins in Phallusia nigra (Tunicata, Ascidiacea) from the Brazilian coast. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins 1996, 2, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.F.; Cristiano, M.L.S. Marine paralytic shellfish toxins: Chemical properties, mode of action, newer analogues, and structure–toxicity relationship†. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T.; Shida, Y.; Onoue, Y. Occurrence of carbamoyl-N-hydroxy derivatives of saxitoxin and neosaxitoxin in a xanthid crab Zosimus aeneus. Toxicon 1994, 32, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, O.; Nishio, S.; Noguchi, T.; Shida, Y.; Onoue, Y. A new saxitoxin analogue from a xanthid crab Atergatis floridus. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusick, K.D.; Sayler, G.S. An Overview on the Marine Neurotoxin, Saxitoxin: Genetics, Molecular Targets, Methods of Detection and Ecological Functions. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 991–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaki, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Bacterial transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins in coral reef crabs and a marine snail. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1985, 51, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T.; Onoue, Y. Transformation of gonyautoxins in the xanthid crab Atergatis floridus. Fish. Sci. 1998, 64, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, M.I.C.; Gomes, M.T.S.R.; Botelho, M.J.; Rudnitskaya, A. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins (PST)-Transforming Enzymes: A Review. Toxins 2020, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katikou, P.; Gokbulut, C.; Kosker, A.R.; Campàs, M.; Ozogul, F. An Updated Review of Tetrodotoxin and Its Peculiarities. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnikova, D.I.; Magarlamov, T.Y. An Overview of the Anatomical Distribution of Tetrodotoxin in Animals. Toxins 2022, 14, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T.; Taniyama, S.; Tatsuno, R. Toxins of Pufferfish—Distribution, Accumulation Mechanism, and Physiologic Functions. Aqua-Biosci. Monogr. ABSM 2017, 10, 41–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheumack, D.; Howden, M.; Spence, I.; Quinn, R.J.S. Maculotoxin: A neurotoxin from the venom glands of the octopus Hapalochlaena maculosa identified as tetrodotoxin. Science 1978, 199, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosher, H.; Fuhrman, F.; Buchwald, H.; Fischer, H.J.S. Tarichatoxin—Tetrodotoxin: A Potent Neurotoxin: A nonprotein substance isolated from the California newt is the same as the toxin from the puffer fish. Science 1964, 144, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Brown, G.B.; Mosher, F.A. Tetrodotoxin: Occurrence in atelopid frogs of Costa Rica. Science 1975, 189, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bane, V.; Lehane, M.; Dikshit, M.; O’Riordan, A.; Furey, A. Tetrodotoxin: Chemistry, Toxicity, Source, Distribution and Detection. Toxins 2014, 6, 693–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Takai, A.; Yasumoto, T. Effects of Specific Modifications of Several Hydroxyls of Tetrodotoxin on Its Affinity to Rat Brain Membrane. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, N.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. Selective Blocking Effects of 4,9-Anhydrotetrodotoxin, Purified from a Crude Mixture of Tetrodotoxin Analogues, on NaV1.6 Channels and Its Chemical Aspects. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.E.; Scheuer, P.J. Palytoxin: A New Marine Toxin from a Coelenterate. Science 1971, 172, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usami, M.; Satake, M.; Ishida, S.; Inoue, A.; Kan, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Palytoxin analogs from the dinoflagellate Ostreopsis siamensis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 5389–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aligizaki, K.; Katikou, P.; Nikolaidis, G.; Panou, A. First episode of shellfish contamination by palytoxin-like compounds from Ostreopsis species (Aegean Sea, Greece). Toxicon 2008, 51, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniyama, S.; Arakawa, O.; Terada, M.; Nishio, S.; Takatani, T.; Mahmud, Y.; Noguchi, T. Ostreopsis sp., a possible origin of palytoxin (PTX) in parrotfish Scarus ovifrons. Toxicon 2003, 42, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Dello Iacovo, E.; Forino, M.; Tartaglione, L.; Pelin, M.; Sosa, S.; Tubaro, A.; Chaloin, O.; Poli, M.; et al. Stereoisomers of 42-Hydroxy Palytoxin from Hawaiian Palythoa toxica and P. tuberculosa: Stereostructure Elucidation, Detection, and Biological Activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Sogamoso, E.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Mancera-Pineda, J.E.; Franco-Angulo, J. First record of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum borbonicum in the continental coast of Colombian Caribbean: A new 42 hydroxi-palytoxin producer. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 973250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeds, J.R.; Schwartz, M.D. Human risk associated with palytoxin exposure. Toxicon 2010, 56, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Miyazawa, K.; Daigo, K.; Arakawa, O. Paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxin- and/or tetrodotoxin-contaminated crabs and food poisoning by them. Toxin Rev. 2011, 30, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garth, J.; Emeritus, C.; Foundation, A.; Alcala, A. Poisonous crabs of Indo-west Pacific coral reefs, with special reference to the genus Demania Laurie. In Proceedings of the Third International Coral Reef Symposium, Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, Miami, FL, USA, May 1977; pp. 645–651. [Google Scholar]
- Dao Viet, H.; Hy, L.H.K.; Trinh, T.S.H.; Tung, N.N.; Ky, P.X. Toxin Responsible for Xanthid Crab Poisoning in Tinh Gia District, Thanh Hoa Province, Viet Nam. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2023, 49, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcala, A.; Halstead, B. Human Fatality Due to Ingestion of the Crab Demania sp. in the Philippines. Clin. Toxicol. 1971, 3, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, R.B.; Alcala, A.C. Fatalities from crab poisoning on Negros Island, Phillippines. Toxicon 1977, 15, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, L.E. Human fatalities in Vanuatu after eating a crab (Daira perlata). Med. J. Aust. 2001, 175, 343–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, L.E.; Dodd, M.J.; Robertson, A.; Ericson, G.; de Koning, C.; Negri, A.P. Post-mortem analysis of samples from a human victim of a fatal poisoning caused by the xanthid crab, Zosimus aeneus. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebs, D. Occurrence and sequestration of toxins in food chains. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1519–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jal, S.; Khora, S.S. An overview on the origin and production of tetrodotoxin, a potent neurotoxin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, M.; D’Agostino, P.M.; Mihali, T.K.; Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. Neurotoxic Alkaloids: Saxitoxin and Its Analogs. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2185–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O. Tetrodotoxin--distribution and accumulation in aquatic organisms, and cases of human intoxication. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 220–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, P.; Gernert, C.; Schmitt, S.; Mebs, D.; Hentschel, U. Detection of hemolytic bacteria from Palythoa caribaeorum (Cnidaria, Zoantharia) using a novel palytoxin-screening assay. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2009, 96, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbrat, A.S.; Amzil, Z.; Pawlowiez, R.; Golubic, S.; Sibat, M.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Laurent, D. First Evidence of Palytoxin and 42-Hydroxy-palytoxin in the Marine Cyanobacterium Trichodesmium. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, K.J.; Hatfield, R.G.; Lee, V.; Alexander, R.P.; Lewis, A.M.; Maskrey, B.H.; Teixeira Alves, M.; Hatton, B.; Coates, L.N.; Capuzzo, E.; et al. Multiple New Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Vectors in Offshore North Sea Benthos, a Deep Secret Exposed. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Saruwatari, T.; Minami, T. Larval development of two Atergatis species (Decapoda, Xanthidae) described from laboratory-reared material. Crustac. Res. 2010, 39, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monniot, C.; Monniot, F.; Laboute, P. Coral Reef Ascidians of New Caledonia; ORSTOM: Paris, France, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, O.; Houghton, S.D. A review and classification of fossil didemnid ascidian spicules. J. Micropalaeontol. 1996, 15, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, M.; Tochikubo, T.; Hirose, E. Taxonomic significance of tunic spicules in photosymbiotic ascidians: A quantitative and molecular evaluation. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2010, 90, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roje-Busatto, R.; Ujević, I. PSP toxins profile in ascidian Microcosmus vulgaris (Heller, 1877) after human poisoning in Croatia (Adriatic Sea). Toxicon 2014, 79, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaki, Y.; Tajiri, M.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Identification of a calcareous red alga as the primary source of paralytic shellfish toxins in coral reef crabs and gastropods. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1983, 49, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aratake, S.; Taira, Y.; Fujii, T.; Roy, M.C.; Reimer, J.D.; Yamazaki, T.; Jenke-Kodama, H. Distribution of palytoxin in coral reef organisms living in close proximity to an aggregation of Palythoa tuberculosa. Toxicon 2016, 111, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarlamov, T.Y.; Melnikova, D.I.; Chernyshev, A.V. Tetrodotoxin-Producing Bacteria: Detection, Distribution and Migration of the Toxin in Aquatic Systems. Toxins 2017, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Persson, K.M. Quick detection method for paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs) monitoring in freshwater—A review. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 128591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hua, Y. Contamination status of paralytic shellfish toxins in shellfish from Southeastern China in 2017–2021. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 34728–34740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Jeon, J.-k.; Arakawa, O.; Sugita, H.; Deguchi, Y.; Shida, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin and anhydrotetrodotoxin in Vibrio sp. isolated from the intestines of a xanthid crab, Atergatis floridus. J. Biochem. 1986, 99, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumoto, T.; Yasumura, D.; Yotsu, M.; Michishita, T.; Endo, A.; Kotaki, Y. Bacterial production of tetrodotoxin and anhydrotetrodotoxin. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kungsuwan, A.; Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Simidu, U.; Tsukamoto, K.; Shida, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Tetrodotoxin-Producing Bacteria from the Horseshoe Crab Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1988, 54, 1799–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.; Kogure, K.; Simidu, U.J.A. Identification of deep-sea-sediment bacteria which produce tetrodotoxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1162–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T. TTX accumulation in pufferfish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2006, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Kanahara, Y.; Yamada, M.; Tatsuno, R.; Yoshikawa, H.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O. Contrasting toxin selectivity between the marine pufferfish Takifugu pardalis and the freshwater pufferfish Pao suvattii. Toxins 2019, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Sonoyama, T.; Yamada, M.; Gao, W.; Tatsuno, R.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O. Co-Occurrence of Tetrodotoxin and Saxitoxins and Their Intra-Body Distribution in the Pufferfish Canthigaster valentini. Toxins 2020, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarlamov, T.Y.; Beleneva, I.A.; Chernyshev, A.V.; Kuhlevsky, A.D. Tetrodotoxin-producing Bacillus sp. from the ribbon worm (Nemertea) Cephalothrix simula (Iwata, 1952). Toxicon 2014, 85, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, J.; Lai, Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Cai, Z.; Yu, C.-F. Puffer Fish Gut Microbiota Studies Revealed Unique Bacterial Co-Occurrence Patterns and New Insights on Tetrodotoxin Producers. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amzil, Z.; Sibat, M.; Chomerat, N.; Grossel, H.; Marco-Miralles, F.; Lemee, R.; Nezan, E.; Sechet, V. Ovatoxin-a and Palytoxin Accumulation in Seafood in Relation to Ostreopsis cf. ovata Blooms on the French Mediterranean Coast. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, E.; Nozawa, Y. Photosymbiotic Ascidians from Kenting and Lyudao in Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 2010, 49, 681–687. [Google Scholar]
- Hirose, E.; Nozawa, Y. Latitudinal Difference in the Species Richness of Photosymbiotic Ascidians Along the East Coast of Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 2020, 59, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Noguchi, T.; Harada, T.; Murata, O.; Abe, T.; Hashimoto, K. Resistibility of Toxic and Nontoxic Pufferfish against Tetrodotoxin. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1985, 51, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Hashimoto, Y. Isolation of tetrodotoxin from a goby Gobius criniger. Toxicon 1973, 11, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Connell, L.; Konoki, K.; MacQuarrie, S.P.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A.; Trainer, V.L. Sodium channel mutation leading to saxitoxin resistance in clams increases risk of PSP. Nature 2005, 434, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Matsumoto, G.; Hanyu, Y. TTX resistivity of Na+ channel in newt retinal neuron. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 240, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Noguchi, T.; Uzu, A.; Hashimoto, K. Resistibility of Toxic and Nontoxic Crabs against Paralytic Shellfish Poison and Tetrodotoxin. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1983, 49, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigo, K.; Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T.; Uzu, A.; Hashimoto, K. Resistibility of Two Xanthid Crabs Zosimus aeneus and Daira perlata against Paralytic Shellfish Poison and Tetrodotoxin. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1987, 53, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigo, K.; Noguchi, T.; Miwa, A.; Kawai, N.; Hashimoto, K. Resistance of nerves from certain toxic crabs to paralytic shellfish poison and tetrodotoxin. Toxicon 1988, 26, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zheng, J.; Xu, Q.; Chen, K.; Zhang, C. Adaptive evolution of the vertebrate skeletal muscle sodium channel. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2011, 34, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Terakawa, T.; Shoji, Y.; Miyazawa, T.; Yasumoto, T. Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning of a novel soluble saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin binding protein from plasma of the puffer fish, Fugu pardalis. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 5937–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Guo, H.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Xie, W. Identification of novel paralytic shellfish toxin binding protein via homology modeling and molecular docking. Toxicon 2022, 211, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takati, N.; Mountassif, D.; Taleb, H.; Lee, K.; Blaghen, M. Purification and partial characterization of paralytic shellfish poison-binding protein from Acanthocardia tuberculatum. Toxicon 2007, 50, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Shimakura, K.; Shiomi, K. A tetrodotoxin-binding protein in the hemolymph of shore crab Hemigrapsus sanguineus: Purification and properties. Toxicon 2002, 40, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, L.E. Haemolymph protein in xanthid crabs: Its selective binding of saxitoxin and possible role in toxin bioaccumulation. Mar. Biol. 1997, 128, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Okai, M.; Kitani, Y.; Yoshinaga-Kiriake, A.; Ishizaki, S. Primary Structure and Conformation of a Tetrodotoxin-Binding Protein in the Hemolymph of Non-Toxic Shore Crab Hemigrapsus sanguineus. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Daigo, K.; Arakawa, O.; Hashimoto, Y. Release of paralytic shellfish poison from the exoskeleton of a xanthid crab Zosimus aeneus. In Toxic Dinoflagellates; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 495–500. [Google Scholar]
- Yamate, Y.; Takatani, T.; Takegaki, T. Levels and distribution of tetrodotoxin in the blue-lined octopus Hapalochlaena fasciata in Japan, with special reference to within-body allocation. J. Molluscan Stud. 2021, 87, eyaa042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacups, S.P.; Currie, B.J. Blue-ringed Octopuses: A Brief Review of Their Toxicology. North. Territ. Nat. 2008, 20, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, R.F. Food preferences, prey availability, and the diet of Octopus Bimaculatus Verrill. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1984, 77, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.L.; Lovenburg, V.; Huffard, C.L.; Caldwell, R.L. Chemical defense in pelagic octopus paralarvae: Tetrodotoxin alone does not protect individual paralarvae of the greater blue-ringed octopus (Hapalochlaena lunulata) from common reef predators. Chemoecology 2011, 21, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pech-Puch, D.; Cruz-López, H.; Canche-Ek, C.; Campos-Espinosa, G.; García, E.; Mascaro, M.; Rosas, C.; Chávez-Velasco, D.; Rodríguez-Morales, S. Chemical Tools of Octopus maya during Crab Predation Are Also Active on Conspecifics. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roggatz, C.C.; Fletcher, N.; Benoit, D.M.; Algar, A.C.; Doroff, A.; Wright, B.; Wollenberg Valero, K.C.; Hardege, J.D. Saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin bioavailability increases in future oceans. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, F.O.; Lopes, V.M.; Amorim, A.; Santos, C.F.; Costa, P.R.; Rosa, R. Projecting Future Climate Change-Mediated Impacts in Three Paralytic Shellfish Toxins-Producing Dinoflagellate Species. Biology 2022, 11, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamate, Y.; Toyomasu, N.; Takegaki, T. Distribution, body size and maturation pattern of the blue-lined octopus Hapalochlaena cf. fasciata in Japan. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 2022, 88, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajino, N.; Shin, J.-S.; Hong, H.-K.; Subramaniam, T.; Chae, J.H.; Noh, T.H.; Chun, H.S.; Choi, K.-S. Detection of Tetrodotoxin in the Xanthid Crab Atergatis floridus (Linnaeus, 1767) Collected from Jeju Island off the South Coast of Korea, Using Competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (cELISA). Ocean Sci. J. 2024, 59, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y. Post-column devivatization HPLC method for analysis of PSP. J. AOAC Int. 1995, 78, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, P.; Alfonso, A.; Otero, P.; Katikou, P.; Georgantelis, D.; Botana, L.M. Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method to detect Tetrodotoxin and Its analogues in the puffer fish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) from European waters. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Fong, S.Y.T.; Hungerford, J.; McNabb, P.S.; Boundy, M.J.; Harwood, D.T.; Collaborators. Ultrahigh-Performance Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Tetrodotoxin in Mussels, Oysters, Clams, Cockles, and Scallops: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 533–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, H.; Fujita, T.; Saito, K.; Watabe, S.; Satomi, M.; Yano, Y. Comparison of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin between carnivorous crabs (Telmessus acutidens and Charybdis japonica) and their prey mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) in an inshore food chain. Toxicon 2004, 43, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoi, S.; Sato, T.; Takei, M.; Yamada, R.; Ogata, R.; Oyama, H.; Teranishi, S.; Kishiki, A.; Wada, T.; Noguchi, K.; et al. The planocerid flatworm is a main supplier of toxin to tetrodotoxin-bearing fish juveniles. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassel, M.A.; Makabe-Kobayashi, Y.; Iqbal, M.M.; Takatani, T.; Sakakura, Y.; Hamasaki, K. The impact of tetrodotoxin (TTX) on the gut microbiome in juvenile tiger pufferfish, Takifugu rubripes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, D.I.; Nijland, R.; Magarlamov, T.Y. The First Data on the Complete Genome of a Tetrodotoxin-Producing Bacterium. Toxins 2021, 13, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O. Toxin Accumulation, Distribution, and Sources of Toxic Xanthid Crabs. Toxins 2025, 17, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050228
Zhang Y, Zhu H, Takatani T, Arakawa O. Toxin Accumulation, Distribution, and Sources of Toxic Xanthid Crabs. Toxins. 2025; 17(5):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050228
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuchengmin, Hongchen Zhu, Tomohiro Takatani, and Osamu Arakawa. 2025. "Toxin Accumulation, Distribution, and Sources of Toxic Xanthid Crabs" Toxins 17, no. 5: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050228
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhu, H., Takatani, T., & Arakawa, O. (2025). Toxin Accumulation, Distribution, and Sources of Toxic Xanthid Crabs. Toxins, 17(5), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050228





