Bongkrekic Acid and Its Novel Isomers: Separation, Identification, and Determination in Food Matrices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
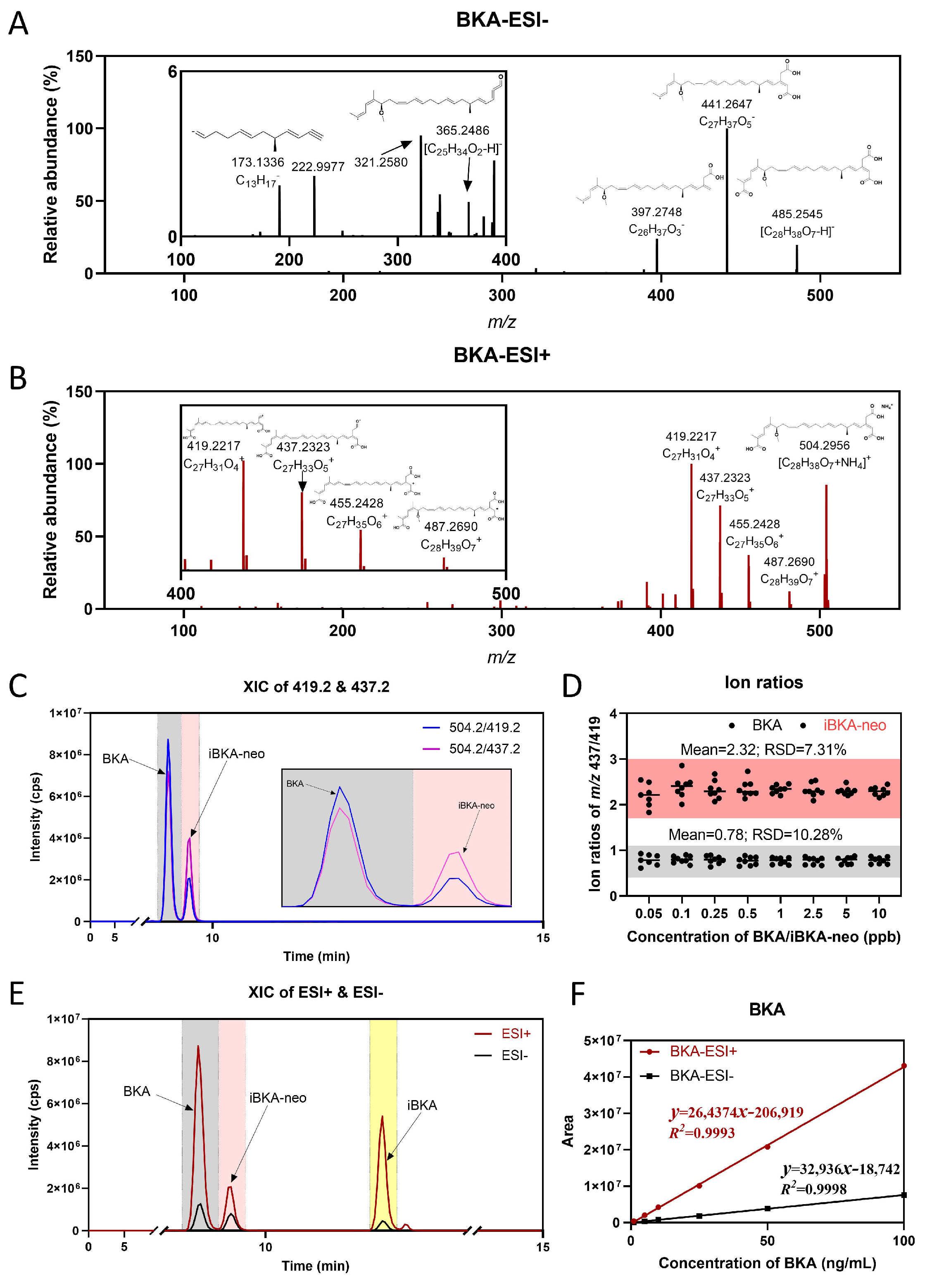
2.1. Structural Identification of iBKA-Neo
2.2. Characteristics of Mass Spectrometry for BKA Isomers
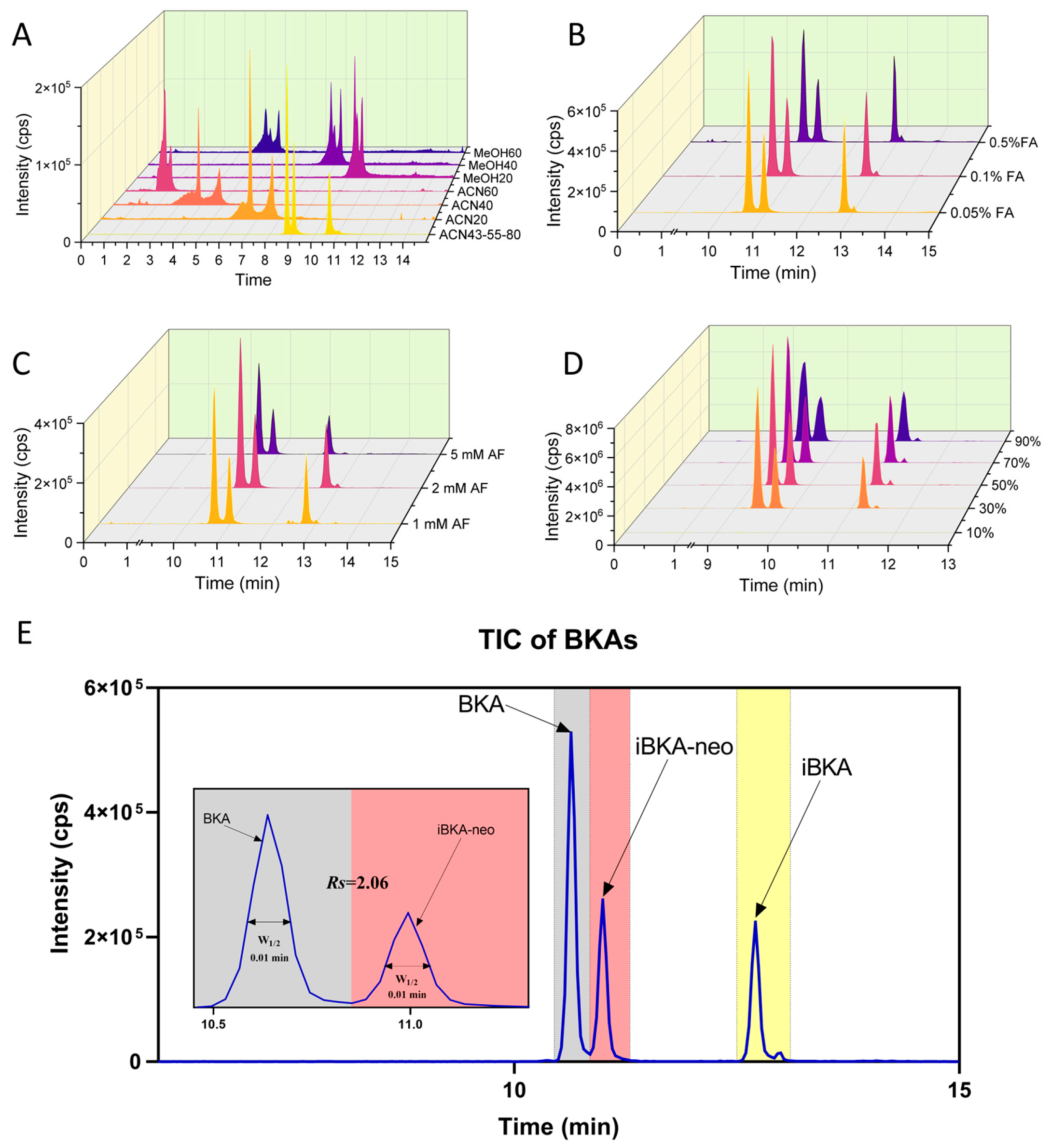
2.3. Optimized Chromatography for Distinguishing BKA Isomers
2.3.1. ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 Column Optimization
2.3.2. Exploring Alternative Columns
2.4. Optimized Extraction and Enrichment of BKA Isomers in Food Matrices
2.5. Methodological Validation of BKA Detection in Food Matrices
2.6. Application of the UHPLC‒MS/MS Method for BKA Isomers
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Equipment
4.3. Bacterial Fermentation and Purification of BKA Isomers
4.4. Collection of Food Matrices
4.5. Food Matrices’ Preparation
4.5.1. Direct Extraction Method
4.5.2. Solid-Phase Extraction Method
4.6. NMR Measurements
4.7. UHPLC‒MS/MS Analysis
4.8. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometry Conditions for HRMS
4.9. Method Validation
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, Y.J. The first time devastating food poisoning happened in Taiwan—Bongkrekic acid poisoning. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2024, 63, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Fu, T.; Xia, S.; Fei, S.; Yin, Z. Unexplained Rhabdomyolysis and Hepatic Renal Dysfunction: A Case of Bongkrekic Acid Poisoning. Cureus 2024, 16, e70625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y. Bongkrekic Acid and Burkholderia gladioli pathovar cocovenenans: Formidable Foe and Ascending Threat to Food Safety. Foods 2023, 12, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, L.U.; Long, C.; Fang, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z.; et al. An Investigation of Bongkrekic Acid Poisoning Caused by Consumption of a Nonfermented Rice Noodle Product without Noticeable Signs of Spoilage. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.; Webster, G.; Mullins, A.J.; Jenner, M.; Bull, M.J.; Dashti, Y.; Spilker, T.; Parkhill, J.; Connor, T.R.; LiPuma, J.J.; et al. Kill and cure: Genomic phylogeny and bioactivity of Burkholderia gladioli bacteria capable of pathogenic and beneficial lifestyles. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, C.; Cao, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xi, J.; Ma, K.; Feng, Q.; Sun, B.; Yan, H.; Wang, L. Bioinspired Core-shell nanospheres integrated in multi-signal immunochromatographic sensor for high throughput sensitive detection of Bongkrekic acid in food. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Chen, R.; Xian, Y.; Hu, J.; Hou, X.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L. Determination of bongkrekic acid and isobongkrekic acid in rice noodles by HPLC-Orbitrap HRMS technology using magnetic halloysite nanotubes. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Kasper, A.; Steck, A.R.; Schier, J.G. Bongkrekic Acid—A Review of a Lesser-Known Mitochondrial Toxin. J. Med. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruprecht, J.J.; Kunji, E.R. Structural changes in the transport cycle of the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 57, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belosludtseva, N.V.; Ilzorkina, A.I.; Serov, D.A.; Dubinin, M.V.; Talanov, E.Y.; Karagyaur, M.N.; Primak, A.L.; Liu, J.; Belosludtsev, K.N. ANT-Mediated Inhibition of the Permeability Transition Pore Alleviates Palmitate-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Lipotoxicity. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiter, J.; Beitz, E.; Pohl, E.E. A Fluorescence-Based Method to Measure ADP/ATP Exchange of Recombinant Adenine Nucleotide Translocase in Liposomes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takegawa, K.; Ito, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Yamazaki, N.; Shindo, M.; Shinohara, Y. KH-17, a simplified derivative of bongkrekic acid, weakly inhibits the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier from both sides of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2023, 101, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, H.; Takeda, S.; Ishii, H.; Takemoto, Y.; Fujita, S.; Suyama, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Shindo, M.; Aramaki, H. A Novel Bongkrekic Acid Analog-Mediated Modulation of the Size of Lipid Droplets: Evidence for the Appearance of Smaller Adipocytes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, T.M.; Kern, S.E.; Brzezinski, J.L.; Turner, J.A.; Boyd, B.L.; Litzau, J.J. Identification of the potent toxin bongkrekic acid in a traditional African beverage linked to a fatal outbreak. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 270, e5–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Français, A.; Leyva-Pérez, A.; Etxebarria-Jardi, G.; Peña, J.; Ley, S.V. Total synthesis of iso- and bongkrekic acids: Natural antibiotics displaying potent antiapoptotic properties. Chemistry 2011, 17, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, H.L.; Ma, J.; Dong, F.; Yu, Y. [Fast determination of bongkrekic acid in plasma by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry]. Chin. J. Ind. Hyg. Occup. Dis. 2022, 40, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y. [Rapid determination of bongkrekic acid in Liushenqu by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry]. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2019, 37, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Jin, M. [Adulteration identification of wheat flour in chestnut flour based on differences in mycotoxin contamination by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry]. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2022, 40, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhao, T.; Wang, X.; Ma, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Quantitative analysis of metabolites in the aflatoxin biosynthesis pathway for early warning of aflatoxin contamination by UHPLC-HRMS combined with QAMS. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debegnach, F.; Brera, C.; Mazzilli, G.; Sonego, E.; Buiarelli, F.; Ferri, F.; Rossi, P.G.; Collini, G.; De Santis, B. Optimization and validation of a LC-HRMS method for aflatoxins determination in urine samples. Mycotoxin Res. 2020, 36, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liang, M.; Xian, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Hou, X.; Wu, Y. Development and validation of a multianalyte method for quantification of aflatoxins and bongkrekic acid in rice and noodle products using PRiME-UHPLC-MS/MS method. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moebius, N.; Ross, C.; Scherlach, K.; Rohm, B.; Roth, M.; Hertweck, C. Biosynthesis of the respiratory toxin bongkrekic acid in the pathogenic bacterium Burkholderia gladioli. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Long, C.; Dai, Y.; Huang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Ma, Q.; Quan, L.; et al. Bongkrekic acid poisoning: Severe liver function damage combined with multiple organ failure caused by eating spoiled food. Leg. Med. 2019, 41, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Vijayakumar, E.K.S.; Roy, K.; Rupp, R.H.; Ganguli, B.N. Structure of isobongkrekic acid, a novel.DELTA.2-E isomer of the antibiotic bongkrekic acid. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 4883–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lv, R.; Song, J.; Chen, X.; Lei, L.; Zeng, W.; She, M.; Li, D.; Yu, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. Establishment and evaluation of a UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of bongkrekic acid and dehydroacetic acid in rice noodles. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1386635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, R. Determination of Bongkrekic Acid and Isobongkrekic Acid in Plasma and Urine by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. J. Chin. Mass Spectrom. Soc. 2020, 41, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Trębacz, H.; Pizoń, M.; Kowalska, A.; Szczęsna, A.; Plech, T. High-performance liquid chromatography thermodynamic study of new potential antiepileptic compounds on a cholesterol column using isocratic elution with methanol/water and acetonitrile/water eluent systems. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4176–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, K.; Shibata, T.; Shinkura, S.; Ohnishi, A. Poly(butylene terephthalate) based novel achiral stationary phase investigated under supercritical fluid chromatography conditions. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1549, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, N.; Deng, J.; Yang, Y.; Luan, T. Rapid and sensitive determination of bongkrekic acid with molecularly imprinted polymer-coated wooden-tip electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Adv. Sample Prep. 2024, 12, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhong, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Xie, C.; Yu, C.; et al. Exploring the characteristics of Burkholderia gladioli pathovar cocovenenans: Growth, bongkrekic acid production, and potential risks of food contamination in wet rice noodles and vermicelli. Food Microbiol. 2024, 120, 104449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gegenschatz, S.A.; Chiappini, F.A.; Teglia, C.M.; Muñoz de la Peña, A.; Goicoechea, H.C. Binding the gap between experiments, statistics, and method comparison: A tutorial for computing limits of detection and quantification in univariate calibration for complex samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1209, 339342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.C.; Wang, J.L.; Hsueh, P.R. Burkholderia gladioli and bongkrekic acid: An under-recognized foodborne poisoning outbreak. J. Infect. 2024, 89, 106182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


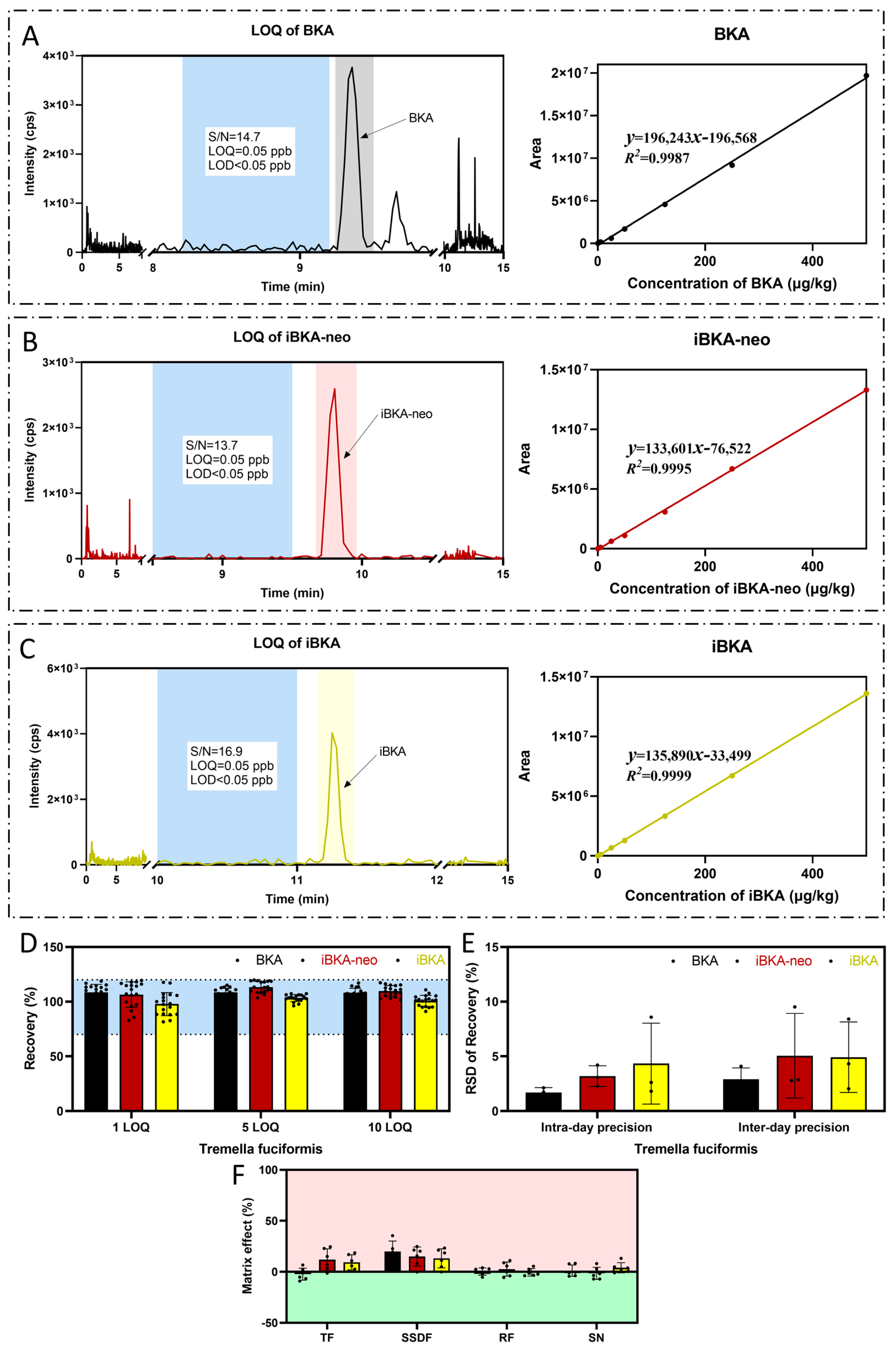

| Food Matrix | Compounds | LOD (μg/kg) | LOQ (μg/kg) | Linear Range (μg/kg) | R2 | Recovery (n = 6) | Intraday RSD (n = 6) | Interday RSD (n = 18) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOQ | 5 LOQ | 10 LOQ | LOQ | 5 LOQ | 10 LOQ | LOQ | 5 LOQ | 10 LOQ | ||||||
| Tremella fuciformis (TF) | Bongkrekic Acid | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9958 | 114.35% | 108.41% | 106.13% | 2.13% | 1.74% | 1.24% | 4.09% | 2.44% | 2.18% |
| Isobongkrekic Acid-neo | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9956 | 112.56% | 108.82% | 105.27% | 4.20% | 3.08% | 2.30% | 9.52% | 2.85% | 2.80% | |
| Isobongkrekic Acid | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9968 | 105.18% | 101.78% | 94.64% | 8.58% | 2.62% | 1.82% | 8.40% | 2.05% | 4.32% | |
| Sweet soup dumpling flour (SSDF) | Bongkrekic Acid | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9949 | 104.78% | 97.49% | 101.76% | 5.10% | 1.68% | 2.67% | 3.92% | 4.92% | 6.05% |
| Isobongkrekic Acid-neo | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9925 | 110.69% | 102.32% | 104.85% | 4.30% | 1.34% | 1.71% | 5.34% | 3.03% | 3.44% | |
| Isobongkrekic Acid | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9976 | 100.72% | 86.47% | 90.89% | 5.31% | 3.34% | 1.24% | 3.23% | 6.72% | 8.55% | |
| Rice flour (RF) | Bongkrekic Acid | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9996 | 111.78% | 102.96% | 91.62% | 3.40% | 1.15% | 1.89% | 0.72% | 8.00% | 12.67% |
| Isobongkrekic Acid-neo | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9990 | 114.84% | 104.35% | 98.90% | 2.10% | 4.31% | 6.27% | 3.97% | 6.25% | 9.37% | |
| Isobongkrekic Acid | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9986 | 95.68% | 100.87% | 93.14% | 4.19% | 2.40% | 1.56% | 6.77% | 7.37% | 9.31% | |
| Sour noodles (SN) | Bongkrekic Acid | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9991 | 92.47% | 87.96% | 84.41% | 2.48% | 1.72% | 2.15% | 9.60% | 10.46% | 11.66% |
| Isobongkrekic Acid-neo | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9990 | 91.91% | 90.08% | 86.99% | 3.47% | 2.32% | 3.50% | 5.22% | 6.69% | 6.08% | |
| Isobongkrekic Acid | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.25–500 | 0.9985 | 97.81% | 85.49% | 82.32% | 2.96% | 3.45% | 2.24% | 6.35% | 7.34% | 8.84% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, S.; Liu, D.; Lin, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, P.; Jiang, X.; Mao, J.; Cao, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhao, T.; et al. Bongkrekic Acid and Its Novel Isomers: Separation, Identification, and Determination in Food Matrices. Toxins 2025, 17, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050223
Dong S, Liu D, Lin R, Zhu Y, Zhu P, Jiang X, Mao J, Cao Y, Peng J, Zhao T, et al. Bongkrekic Acid and Its Novel Isomers: Separation, Identification, and Determination in Food Matrices. Toxins. 2025; 17(5):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050223
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Suhe, Danli Liu, Runfeng Lin, Yingjie Zhu, Peihong Zhu, Xin Jiang, Jie Mao, Yanqing Cao, Jing Peng, Tianyue Zhao, and et al. 2025. "Bongkrekic Acid and Its Novel Isomers: Separation, Identification, and Determination in Food Matrices" Toxins 17, no. 5: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050223
APA StyleDong, S., Liu, D., Lin, R., Zhu, Y., Zhu, P., Jiang, X., Mao, J., Cao, Y., Peng, J., Zhao, T., Shen, D., Li, T., He, K., & Wang, N. (2025). Bongkrekic Acid and Its Novel Isomers: Separation, Identification, and Determination in Food Matrices. Toxins, 17(5), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050223






