Assessing the Utility of Broad-Acting Inhibitors as Therapeutics in Diverse Venoms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
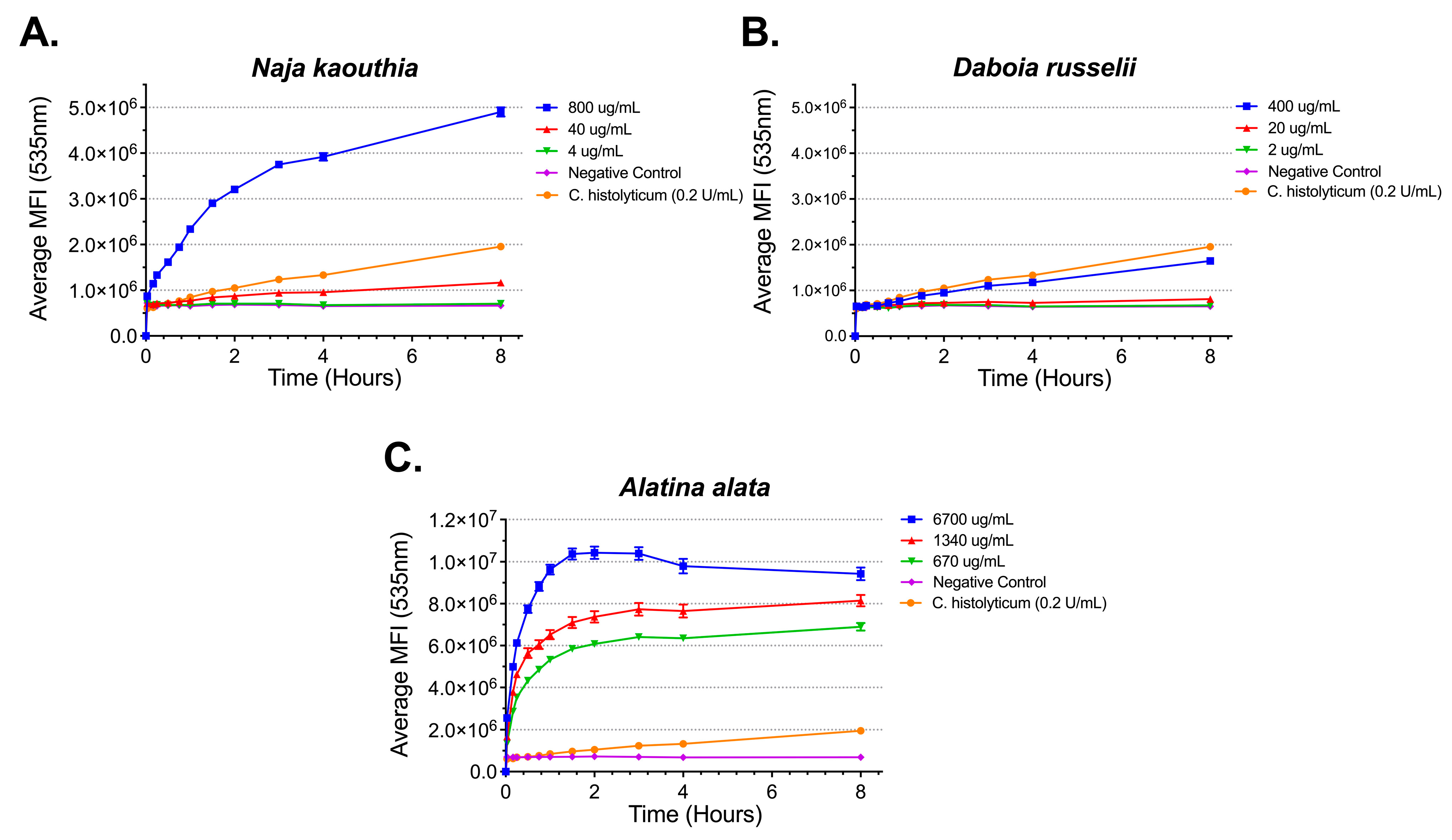
2.1. Phospholipase A2 Activity of Snake, Bee, and Jellyfish Venoms
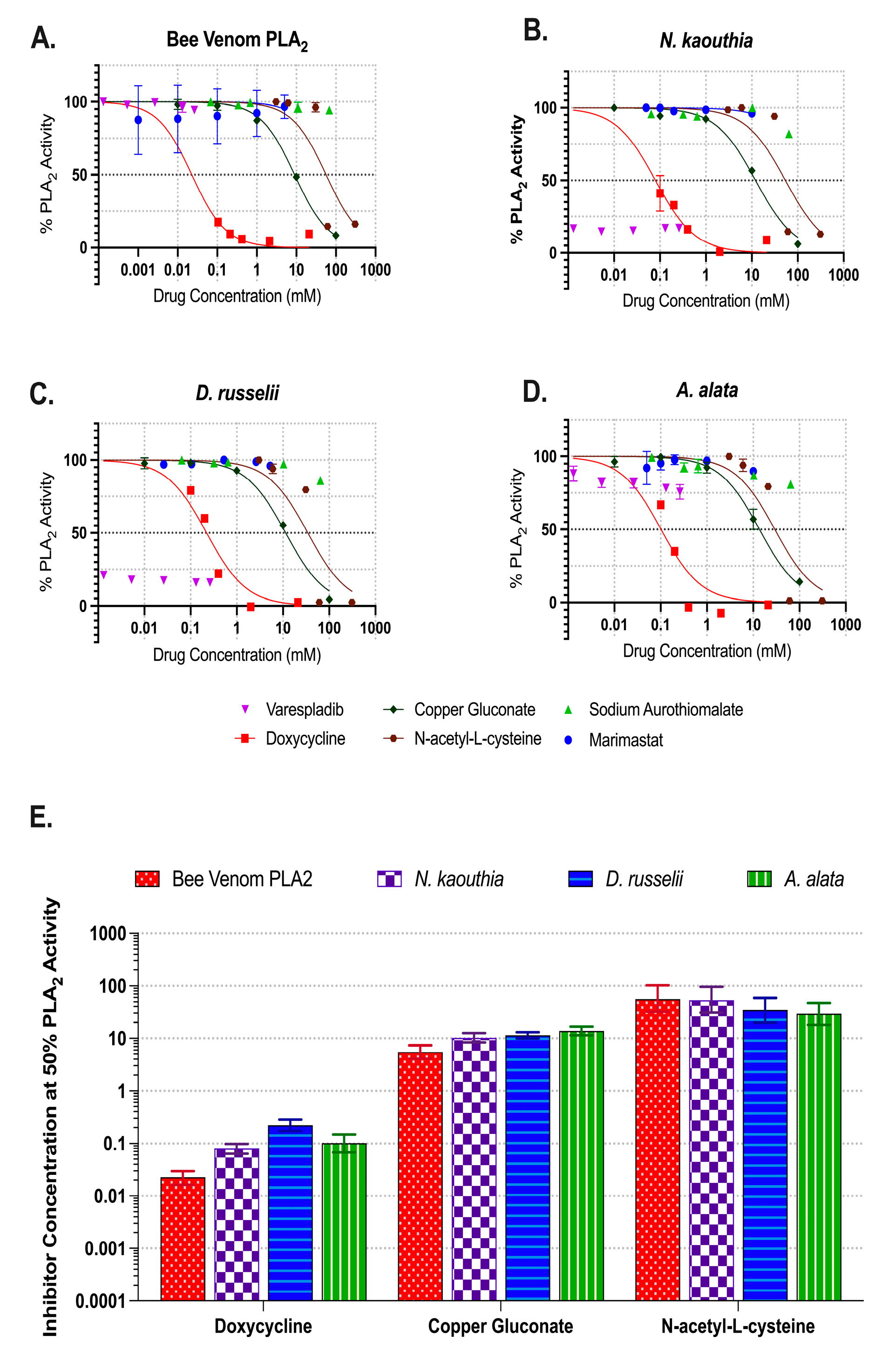
2.2. Inhibition of Phospholipase A2 Activities
2.3. Gelatinase Activity of Snake and Jellyfish Venoms
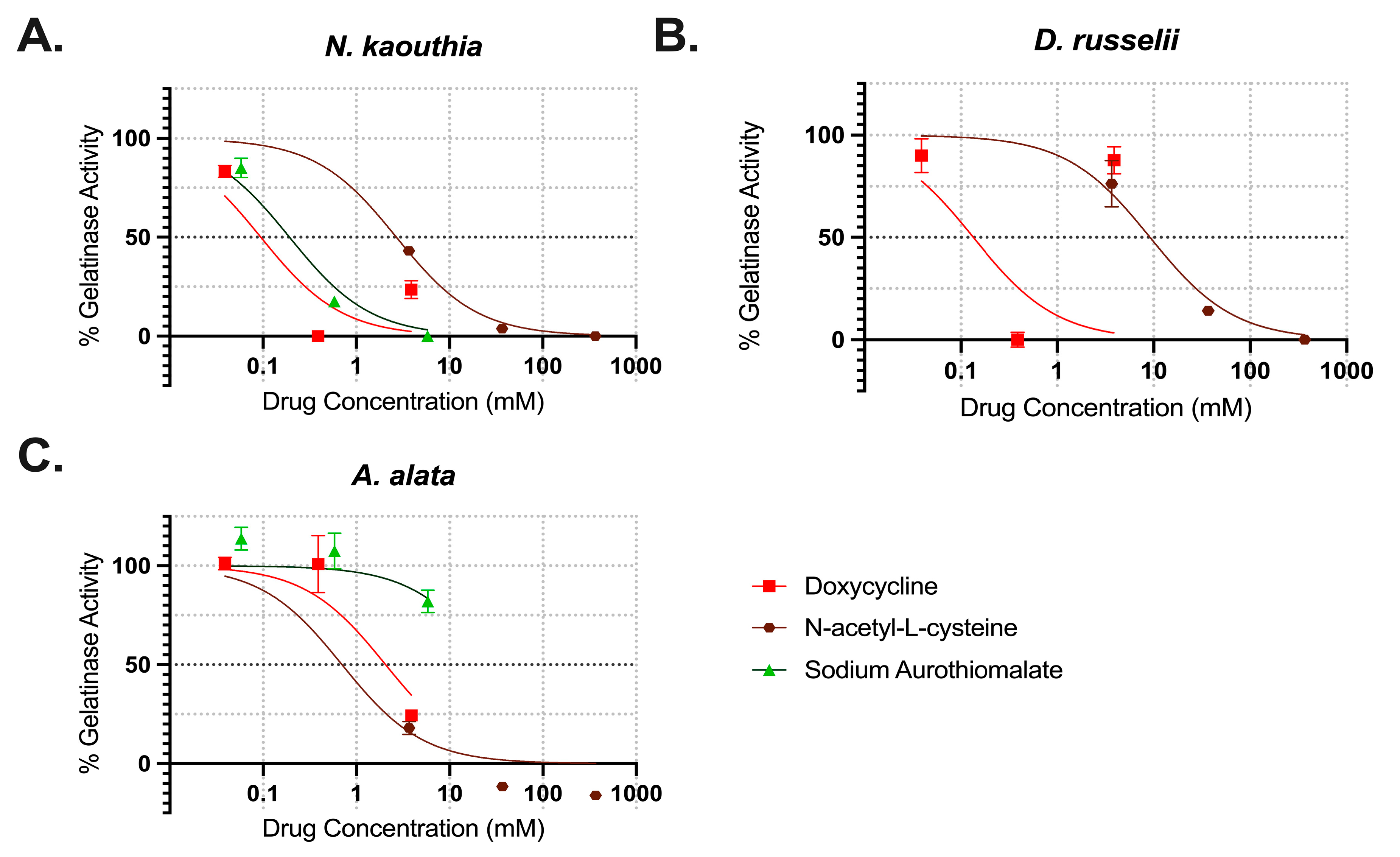
2.4. Inhibition of Gelatinase Activities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Venom Preparation
4.2. In Vitro Experiments
4.3. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| PLA2 | Phospholipase A2 |
| SSS | Snakebite Severity Score |
References
- Chippaux, J.P. Snake-Bites: Appraisal of the Global Situation. Bull. World Health Organ. 1998, 76, 515–524. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Warrell, D.A. Confronting the Neglected Problem of Snake Bite Envenoming: The Need for a Global Partnership. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaikruea, L.; Siriariyaporn, P.; Wutthanarungsan, R.; Smithsuwan, P. Review of Fatal and Severe Cases of Box Jellyfish Envenomation in Thailand. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2015, 27, NP1639–NP1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenner, P.J.; Lippmann, J.; Gershwin, L. Fatal and Nonfatal Severe Jellyfish Stings in Thai Waters. J. Travel. Med. 2010, 17, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippmann, J.M.; Fenner, P.J.; Winkel, K.; Gershwin, L.-A. Fatal and Severe Box Jellyfish Stings, Including Irukandji Stings, in Malaysia, 2000–2010. J. Travel Med. 2011, 18, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaikruea, L.; Siriariyaporn, P. The Magnitude of Severe Box Jellyfish Cases on Koh Samui and Koh Pha-Ngan in the Gulf of Thailand. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, A.I.; Wan Mohd Shukri, W.N.A.; Ismail, A.K. Estimation of Local Incidence of Jellyfish Envenomation in Developed Marine Coastal Areas and Large Populated Island on the Western Coast of Peninsular Malaysia Using Case Surveillance of Government Health Facilities in Manjung, Perak and Langkawi Island. Int. Marit. Health 2021, 72, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chippaux, J.-P.; Goyffon, M. Epidemiology of Scorpionism: A Global Appraisal. Acta Trop. 2008, 107, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsford, M.; Mooney, C. The Ecology of Box Jellyfishes (Cubozoa). In Jellyfish Blooms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 267–302. ISBN 978-94-007-7014-0. [Google Scholar]
- Needleman, R.K.; Neylan, I.P.; Erickson, T.B. Environmental and Ecological Effects of Climate Change on Venomous Marine and Amphibious Species in the Wilderness. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2018, 29, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, D.; Brinkman, D.L.; Luna-Ramírez, K.; Wright, C.E.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J. Comparative Study of the Toxic Effects of Chrysaora quinquecirrha (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) and Chironex fleckeri (Cnidaria: Cubozoa) Venoms Using Cell-Based Assays. Toxicon 2015, 106, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.H.; Koh, P.-O.; Mohan Prakash, R.L.; Chae, J.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. Comparative Study of Toxic Effects and Pathophysiology of Envenomations Induced by Carybdea brevipedalia (Cnidaria: Cubozoa) and Nemopilema nomurai (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) Jellyfish Venoms. Toxins 2022, 14, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, J.A.; Fenner, P.J.; Burnett, J.W.; Rifkin, J. Venomous and Poisonous Marine Animals: A Medical and Biological Handbook; University of New South Wales Press: Sydney, Australia, 1996; ISBN 978-0-86840-279-6. [Google Scholar]
- Fenner, P.J.; Harrison, S.L. Irukandji and Chironex fleckeri Jellyfish Envenomation in Tropical Australia. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2000, 11, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenner, P.J.; Hadok, J.C. Fatal Envenomation by Jellyfish Causing Irukandji Syndrome. Med. J. Aust. 2002, 177, 362–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, B.J.; Jacups, S.P. Prospective Study of Chironex fleckeri and Other Box Jellyfish Stings in the “Top End” of Australia’s Northern Territory. Med. J. Aust. 2005, 183, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Barry, J.; Corkeron, M.; Keir, P.; Little, M.; Seymour, J. Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Death after Envenoming by the Jellyfish Carukia Barnesi. Clin. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girl Dies After Box Jellyfish Sting. Available online: https://www.smh.com.au/national/girl-dies-after-box-jellyfish-sting-20060109-gdmqzc.html (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Teenager Dies After Box Jellyfish Sting at Queensland Beach. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/australia-news/2022/feb/28/teenager-dies-after-box-jellyfish-sting-at-queensland-beach (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Queensland Teenager Dies from Box Jellyfish Sting in First Fatality from the Animal in 15 Years. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/australia-news/2021/mar/04/queensland-teenager-dies-from-box-jellyfish-sting-in-first-fatality-from-the-animal-in-15-years (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Suntrarachun, S.; Roselieb, M.; Wilde, H.; Sitprija, V. A Fatal Jellyfish Encounter in the Gulf of Siam. J. Travel. Med. 2001, 8, 150–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thaikruea, L. The Dermatological Effects of Box Jellyfish Envenomation in Stinging Victims in Thailand: Underestimated Severity. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2023, 34, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedish Tour Operators Hiding the Threat of Deadly Jellyfish? Available online: https://scandasia.com/7758-swedish-tour-operators-hiding-the-threat-of-deadly-jellyfish/ (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- 31 Year Old Thai Woman Died of Box Jelly Fish Stings on Koh Phangan. Available online: https://samui-weather.blogspot.com/2015/08/31-year-old-thai-woman-died-of-box.html (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- The Deadly Sting That Destroyed Our Paradise. Available online: https://www.dailymail.co.uk/home/you/article-4222830/Real-lives-deadly-sting-destroyed-paradise.html (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Israeli Boy, 9, Dies in Thailand After Jellyfish Sting. Available online: https://www.timesofisrael.com/israeli-boy-9-dies-in-thailand-after-jellyfish-sting/ (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Law, Y.-H. Stopping the Sting. Science 2018, 362, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- “Mama, What’s Going to Happen?” Final Words of Seven-Year-Old Girl Who Died on Family Holiday After Stepping on a Jellyfish. Available online: https://www.thesun.co.uk/news/6987148/girl-dead-family-holiday-jellyfish-sting/ (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Child Barely Survives Philippines Box Jellyfish Sting 2021. Available online: https://www.boxjellyfish.online/2021/02/child-barely-survives-philippines-box.html#:~:text=A%205%2Dyear%20old%20girl,Nabulao%20Beach%20when%20disaster%20struck (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- 7 Year-Old Daughter of OFW Dies Due to Box Jellyfish Sting in CamSur. Available online: https://www.philstar.com/nation/2018/08/01/1838498/seven-year-old-girl-italy-dies-jellyfish-sting-camarines-sur (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Box Jellyfish Sting Kills Woman in Sta. Fe Town in Cebu. Available online: https://cebudailynews.inquirer.net/512531/jellyfish-sting-kills-woman-in-sta-fe-town-in-cebu (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Jellyfish Sting Kills 10-Year-Old Girl in Araceli, Palawan. Available online: https://www.gmanetwork.com/news/topstories/regions/901636/jellyfish-sting-kills-10-year-old-girl-in-araceli-palawan/story/ (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Kadler, R.; Pirkle, C.; Yanagihara, A. A Systematic Review of Reports on Aquatic Envenomation: Are There Global Hot Spots and Vulnerable Populations? J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 30, e20240032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C. Phylum Cnidaria; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-0-19-177470-6. [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann, A.; Özbek, S. The Nematocyst: A Molecular Map of the Cnidarian Stinging Organelle. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, A.A.; Kuroiwa, J.M.Y.; Oliver, L.M.; Chung, J.J.; Kunkel, D.D. Ultrastructure of a Novel Eurytele Nematocyst of Carybdea alata Reynaud (Cubozoa, Cnidaria). Cell Tissue Res. 2002, 308, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitatani, R.; Yamada, M.; Kamio, M.; Nagai, H. Length Is Associated with Pain: Jellyfish with Painful Sting Have Longer Nematocyst Tubules than Harmless Jellyfish. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ambra, I.; Lauritano, C. A Review of Toxins from Cnidaria. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-de-Torre, E.; Palacios-Ortega, J.; Gavilanes, J.G.; Martínez-del-Pozo, Á.; García-Linares, S. Pore-Forming Proteins from Cnidarians and Arachnids as Potential Biotechnological Tools. Toxins 2019, 11, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, A.; Wilcox, C.; Smith, J.; Surrett, G. Cubozoan Envenomations: Clinical Features, Pathophysiology, and Management. In The Cnidaria, Past Present and Future; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 637–652. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman, D.L.; Burnell, J.N. Biochemical and Molecular Characterisation of Cubozoan Protein Toxins. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecucco, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Cellular Pathology Induced by Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 Myotoxins and Neurotoxins: Common Aspects of Their Mechanisms of Action. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2897–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevalainen, T.J.; Peuravuori, H.J.; Quinn, R.J.; Llewellyn, L.E.; Benzie, J.A.H.; Fenner, P.J.; Winkel, K.D. Phospholipase A2 in Cnidaria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 139, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittenbinder, M.A.; van Thiel, J.; Cardoso, F.C.; Casewell, N.R.; Gutiérrez, J.-M.; Kool, J.; Vonk, F.J. Tissue Damaging Toxins in Snake Venoms: Mechanisms of Action, Pathophysiology and Treatment Strategies. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slagboom, J.; Kool, J.; Harrison, R.A.; Casewell, N.R. Haemotoxic Snake Venoms: Their Functional Activity, Impact on Snakebite Victims and Pharmaceutical Promise. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 177, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markland, F.S.; Swenson, S. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases: Their Role in the Pathogenesis of Local Tissue Damage. Biochimie 2000, 82, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasanov, S.E.; Dagda, R.K.; Rael, E.D. Snake Venom Cytotoxins, Phospholipase A2s, and Zn2+-Dependent Metalloproteinases: Mechanisms of Action and Pharmacological Relevance. J. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 4, 1000181. [Google Scholar]
- Molière, S.; Jaulin, A.; Tomasetto, C.-L.; Dali-Youcef, N. Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Natural Inhibitors in Metabolism: Insights into Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, E.; Gurrola, G.B.; Schwartz, E.F.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion Venom Components as Potential Candidates for Drug Development. Toxicon 2015, 93, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouiaei, M.; Yanagihara, A.; Madio, B.; Nevalainen, T.; Alewood, P.; Fry, B. Ancient Venom Systems: A Review on Cnidaria Toxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 2251–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, G.M.; Graudins, A. Spiders of Medical Importance in the Asia–Pacific: Atracotoxin, Latrotoxin and Related Spider Neurotoxins. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, D.L.; Jia, X.; Potriquet, J.; Kumar, D.; Dash, D.; Kvaskoff, D.; Mulvenna, J. Transcriptome and Venom Proteome of the Box Jellyfish Chironex fleckeri. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoka, I.A.; Robb, E.L.; Baker, M.B. Brown Recluse Spider Toxicity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G.K. A Review and Database of Snake Venom Proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido-Patiño, J.C.; Plisson, F. Profiling Hymenopteran Venom Toxins: Protein Families, Structural Landscape, Biological Activities, and Pharmacological Benefits. Toxicon X 2022, 14, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Albulescu, L.-O.; Clare, R.H.; Casewell, N.R.; Abd El-Aziz, T.M.; Escalante, T.; Rucavado, A. The Search for Natural and Synthetic Inhibitors That Would Complement Antivenoms as Therapeutics for Snakebite Envenoming. Toxins 2021, 13, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, A.; Shohet, R.V. Cubozoan Venom-Induced Cardiovascular Collapse Is Caused by Hyperkalemia and Prevented by Zinc Gluconate in Mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.; Samuel, S.; Merkel, J.; Bickler, P. Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albulescu, L.-O.; Xie, C.; Ainsworth, S.; Alsolaiss, J.; Crittenden, E.; Dawson, C.A.; Softley, R.; Bartlett, K.E.; Harrison, R.A.; Kool, J.; et al. A Therapeutic Combination of Two Small Molecule Toxin Inhibitors Provides Broad Preclinical Efficacy against Viper Snakebite. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.R.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Crittenden, E.; Dawson, C.A.; Bartlett, K.E.; Westhorpe, A.P.; Albulescu, L.-O.; Kool, J.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Casewell, N.R. Repurposed Drugs and Their Combinations Prevent Morbidity-Inducing Dermonecrosis Caused by Diverse Cytotoxic Snake Venoms. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, A.A. Methods and Compositions for Treating and/or Inhibiting Toxins Using Copper-Containing Compounds 2019. U.S. Patent US10172883B2, 4 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dalhat, M.M.; Potet, J.; Mohammed, A.; Chotun, N.; Tesfahunei, H.A.; Habib, A.G. Availability, Accessibility and Use of Antivenom for Snakebite Envenomation in Africa with Proposed Strategies to Overcome the Limitations. Toxicon X 2023, 18, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias, A.S.; Gomes Filho, M.R.; da Costa Arévalo, M.; Cristino, J.S.; Farias, F.R.; Sachett, A.; Silva-Neto, A.V.; de Carvalho, F.G.; Ambrosio, S.A.; da Silva Carvalho, E.; et al. Snakebite Envenomations and Access to Treatment in Communities of Two Indigenous Areas of the Western Brazilian Amazon: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, W.M.; de Farias, A.S.; Val, F.; Neto, A.V.S.; Sachett, A.; Lacerda, M.; Sampaio, V.; Cardoso, D.; Garnelo, L.; Vissoci, J.R.N.; et al. Providing Antivenom Treatment Access to All Brazilian Amazon Indigenous Areas: ‘Every Life Has Equal Value’. Toxins 2020, 12, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M.; Sidhu, S.S.; Laustsen, A.H. Biosynthetic Oligoclonal Antivenom (BOA) for Snakebite and Next-Generation Treatments for Snakebite Victims. Toxins 2018, 10, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.W.; Gerardo, C.J.; Samuel, S.P.; Kumar, S.; Kotehal, S.D.; Mukherjee, P.P.; Shirazi, F.M.; Akpunonu, P.D.; Bammigatti, C.; Bhalla, A.; et al. The BRAVO Clinical Study Protocol: Oral Varespladib for Inhibition of Secretory Phospholipase A2 in the Treatment of 75. Toxins 2022, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.R.; Carter, R.W.; Matteo, I.A.; Samuel, S.P.; Rao, S.; Fry, B.G.; Bickler, P.E. Varespladib in the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming: Development History and Preclinical Evidence Supporting Advancement to Clinical Trials in Patients Bitten by Venomous Snakes. Toxins 2022, 14, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardo, C.J.; Carter, R.W.; Kumar, S.; Shirazi, F.M.; Kotehal, S.D.; Akpunonu, P.D.; Bhalla, A.; Schwartz, R.B.; Bammigatti, C.; Manikath, N.; et al. Oral Varespladib for the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming in India and the USA (BRAVO): A Phase II Randomised Clinical Trial. BMJ Glob. Health 2024, 9, e015985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, A.; Adams, S.; Mignatti, P. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy: Turning Past Failures Into Future Successes. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, S.K.; Clare, R.H.; Xie, C.; Westhorpe, A.; Hall, S.R.; Edge, R.J.; Alsolaiss, J.; Crittenden, E.; Harrison, R.A.; Kool, J.; et al. In Vitro and in Vivo Venom-Inhibition Assays Identify Metalloproteinase-Inhibiting Drugs as Potential Treatments for Snakebite Envenoming by Dispholidus Typus. bioRxiv 2022, 2022, 475313. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, J.M.; Frezzatti, R.; Silveira, P.F. Effects of N-Acetyl-l-Cysteine on Redox Status and Markers of Renal Function in Mice Inoculated with Bothrops jararaca and Crotalus durissus terrificus Venoms. Toxicon 2014, 79, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunitha, K.; Hemshekhar, M.; Santhosh, M.S.; Kumar, M.S.; Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S. Inhibition of Hemorrhagic Activity of Viper Venoms by N-Acetyl Cysteine: Involvement of N-Acetyl and Thiol Groups. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 2589–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingprasertchai, S.; Bunyasrisawat, S.; Ratanabanangkoon, K. Hyaluronidase Inhibitors (Sodium Cromoglycate and Sodium Auro-Thiomalate) Reduce the Local Tissue Damage and Prolong the Survival Time of Mice Injected with Naja kaouthia and Calloselasma rhodostoma Venoms. Toxicon 2003, 42, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arens, D.K.; Rose, M.A.; Salazar, E.M.; Harvey, M.A.; Huh, E.Y.; Ford, A.A.; Thompson, D.W.; Sanchez, E.E.; Hwang, Y.Y. Doxycycline-Mediated Inhibition of Snake Venom Phospholipase and Metalloproteinase. Mil. Med. 2024, 189, e2430–e2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeiro, P.; Romanelli, M.; Cesar, M.; Noguiera-Souza, P.; Monteiro-Machado, M.; Oliveira, S.; Santos, A.; Melo, P.; Lara, L. Doxycycline Treatment Reestablishes Renal Function of Wistar Rats in Experimental Envenomation with Bothrops jararacussu Venom. Toxicon 2021, 199, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Li, P. Topical Exposure to Nemopilema nomurai Venom Triggers Oedematogenic Effects: Enzymatic Contribution and Identification of Venom Metalloproteinase. Toxins 2021, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, D.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, L. Protective Effects of Batimastat against Hemorrhagic Injuries in Delayed Jellyfish Envenomation Syndrome Models. Toxicon 2015, 108, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Elizárraga, V.H.; Ocharán-Mercado, A.; Olguín-López, N.; Hernández-Matehuala, R.; Caballero-Pérez, J.; Ibarra-Alvarado, C.; Rojas-Molina, A. New Insights into the Toxin Diversity and Antimicrobial Activity of the “Fire Coral” Millepora complanata. Toxins 2022, 14, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.L.; Headlam, J.L.; Doyle, T.K.; Yanagihara, A.A. Assessing the Efficacy of First-Aid Measures in Physalia Sp. Envenomation, Using Solution- and Blood Agarose-Based Models. Toxins 2017, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, A.A.; Wilcox, C.; King, R.; Hurwitz, K.; Castelfranco, A.M. Experimental Assays to Assess the Efficacy of Vinegar and Other Topical First-Aid Approaches on Cubozoan (Alatina alata) Tentacle Firing and Venom Toxicity. Toxins 2016, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.; Roelants, K.; Champagne, D.; Scheib, H.; Tyndall, J.; King, G.; Nevalainen, T.; Norman, J.; Lewis, R.; Norton, R.; et al. The Toxicogenomic Multiverse: Convergent Recruitment of Proteins Into Animal Venoms. Annu. Rev. 2009, 10, 483–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite Envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antivenoms. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/control-of-neglected-tropical-diseases/snakebite-envenoming/antivenoms (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Dalm, D.; Palm, G.J.; Aleksandrov, A.; Simonson, T.; Hinrichs, W. Nonantibiotic Properties of Tetracyclines: Structural Basis for Inhibition of Secretory Phospholipase A2. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 398, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruzanski, W.; Greenwald, R.A.; Street, I.P.; Laliberte, F.; Stefanski, E.; Vadas, P. Inhibition of Enzymatic Activity of Phospholipases A2 by Minocycline and Doxycycline. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992, 44, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucavado, A.; Henríquez, M.; García, J.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Assessment of Metalloproteinase Inhibitors Clodronate and Doxycycline in the Neutralization of Hemorrhage and Coagulopathy Induced by Bothrops asper. Snake Venom. Toxicon 2008, 52, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Gao, D.; Yu, F.; Han, J.; Yuan, H.; Hu, F. Phospholipase A2 Inhibitor Varespladib Prevents Wasp Sting-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Toxicon 2022, 215, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearth, J.; Linne, K.; Harrison, J.; Zolfaghari, H.; Lewin, M.R. Feasibility Study: Varespladib Protects CD-1 Mice from Lethal Doses of Whole Bee (Apis mellifera) Venom. Toxicon X 2025, 25, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, G.H.M.; Gomes, A.A.S.; Bryan-Quirós, W.; Fernández, J.; Lewin, M.R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Fontes, M.R.M. Structural Basis for Phospholipase A2-like Toxin Inhibition by the Synthetic Compound Varespladib (LY315920). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambelli, V.O.; Picolo, G.; Fernandes, C.A.H.; Fontes, M.R.M.; Cury, Y. Secreted Phospholipases A2 from Animal Venoms in Pain and Analgesia. Toxins 2017, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, L.; Jundia, D.; Rima, M.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Fajloun, Z. Bee Venom PLA2 versus Snake Venom PLA2: Evaluation of Structural and Functional Properties. Available online: http://www.eurekaselect.com (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Chung, J.J.; Ratnapala, L.A.; Cooke, I.M.; Yanagihara, A.A. Partial Purification and Characterization of a Hemolysin (CAH1) from Hawaiian Box Jellyfish (Carybdea alata) Venom. Toxicon 2001, 39, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jung, E.; Kang, C.; Yoon, W.D.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, E. Scyphozoan Jellyfish Venom Metalloproteinases and Their Role in the Cytotoxicity. Toxicon 2011, 58, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Li, P. Inhibitory Effect of Metalloproteinase Inhibitors on Skin Cell Inflammation Induced by Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai Nematocyst Venom. Toxins 2019, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, K.; Saunier, F.; Rigaill, J.; Audoux, E.; Botelho-Nevers, E.; Prier, A.; Dickerscheit, Y.; Pillet, S.; Pozzetto, B.; Bourlet, T.; et al. Evaluation of in Vitro Activity of Copper Gluconate against SARS-CoV-2 Using Confocal Microscopy-Based High Content Screening. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. Organ. Soc. Miner. Trace Elem. GMS 2021, 68, 126818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Caprio, R.; Lembo, S.; Di Costanzo, L.; Balato, A.; Monfrecola, G. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Low and High Doxycycline Doses: An in Vitro Study. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 329418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel, K.D.; Tibballs, J.; Molenaar, P.; Lambert, G.; Coles, P.; Ross-Smith, M.; Wiltshire, C.; Fenner, P.J.; Gershwin, L.-A.; Hawdon, G.M.; et al. Cardiovascular Actions of the Venom from the Irukandji (Carukia barnesi) Jellyfish: Effects in Human, Rat and Guinea-Pig Tissues in Vitro and in Pigs in Vitro. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2005, 32, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, A.A.; Barnhill, J.C.; Uyehara, C. Tropical Lethal Box Jellyfish Venom Dose-Dependent Outcome in a Piglet Model. In Proceedings of the Military Health System Research Symposium, Kissimmee, FL, USA,, 27–30 August 2017. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadler, R.; Morrison, B.; Yanagihara, A.A. Assessing the Utility of Broad-Acting Inhibitors as Therapeutics in Diverse Venoms. Toxins 2025, 17, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040188
Kadler R, Morrison B, Yanagihara AA. Assessing the Utility of Broad-Acting Inhibitors as Therapeutics in Diverse Venoms. Toxins. 2025; 17(4):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040188
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadler, Raechel, Breanna Morrison, and Angel Anne Yanagihara. 2025. "Assessing the Utility of Broad-Acting Inhibitors as Therapeutics in Diverse Venoms" Toxins 17, no. 4: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040188
APA StyleKadler, R., Morrison, B., & Yanagihara, A. A. (2025). Assessing the Utility of Broad-Acting Inhibitors as Therapeutics in Diverse Venoms. Toxins, 17(4), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040188




