Insights from Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses into Sulforaphane’s Protective Mechanism Against Deoxynivalenol Toxicity via Spermine Regulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
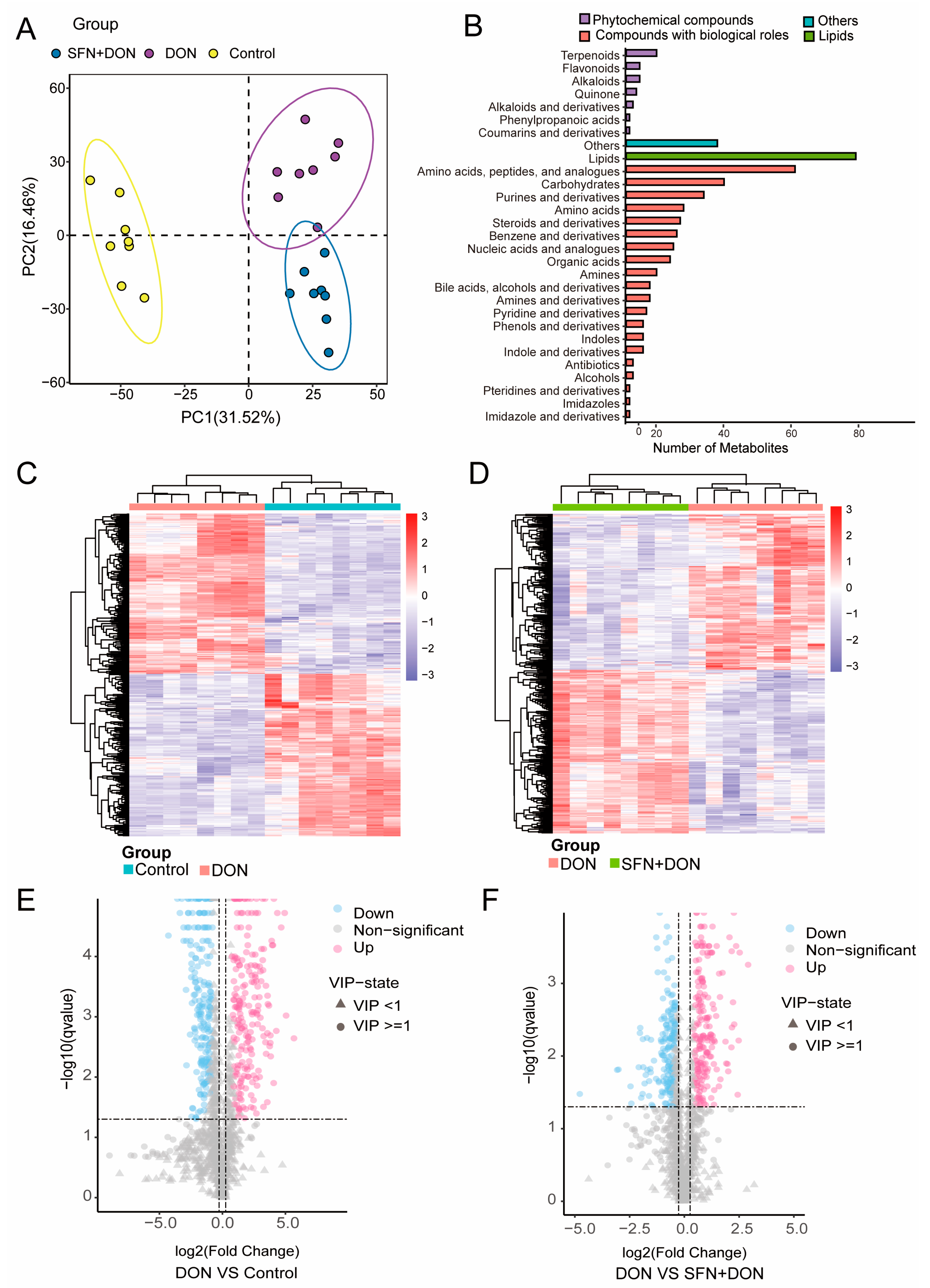
2.1. Alterations in Cellular Metabolites Induced by SFN Treatment and DON Exposure
2.2. Analysis of Differential Metabolites Caused by SFN Treatment and DON Exposure
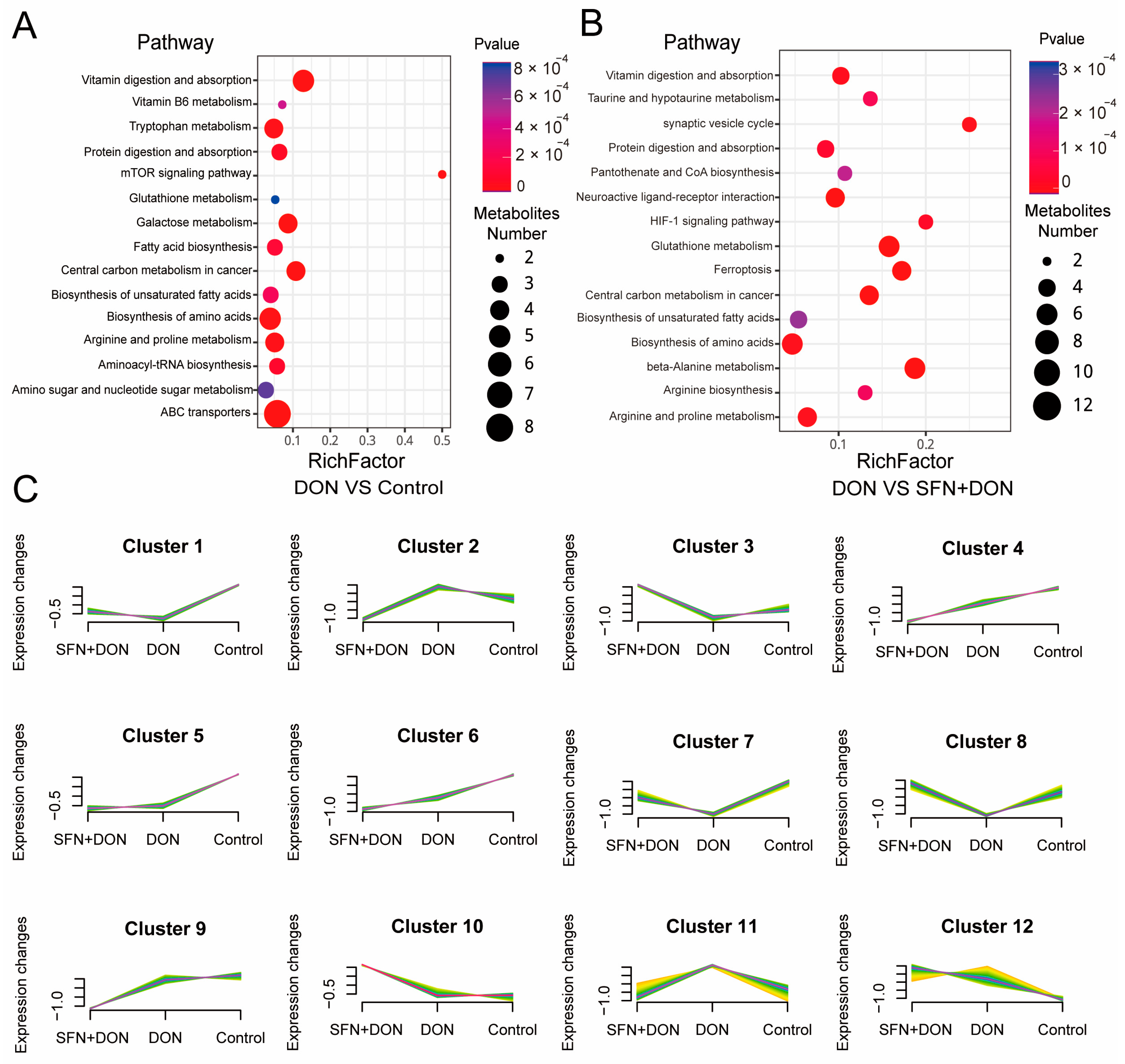
2.3. Integrated Analysis of Transcriptome and Metabolome
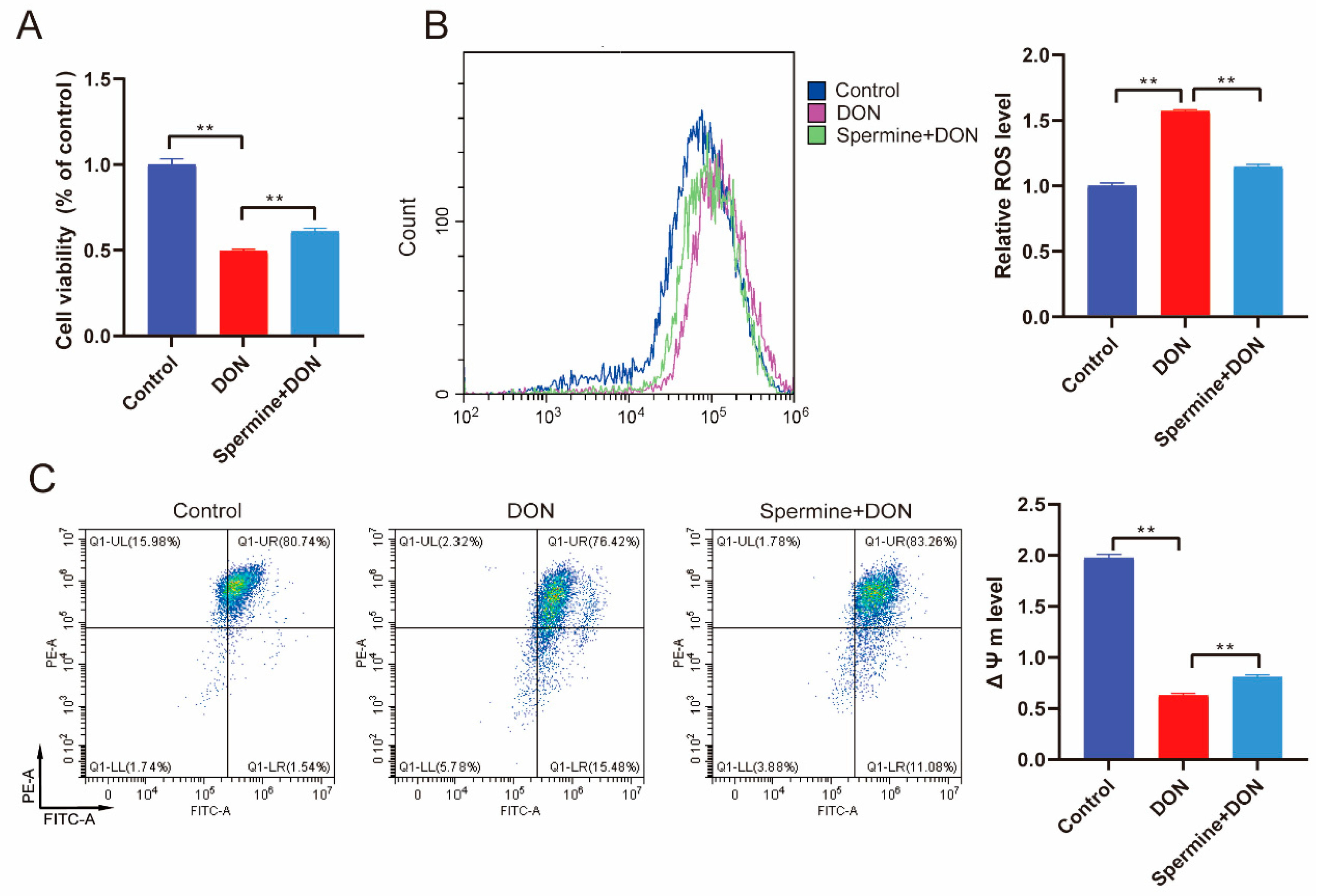
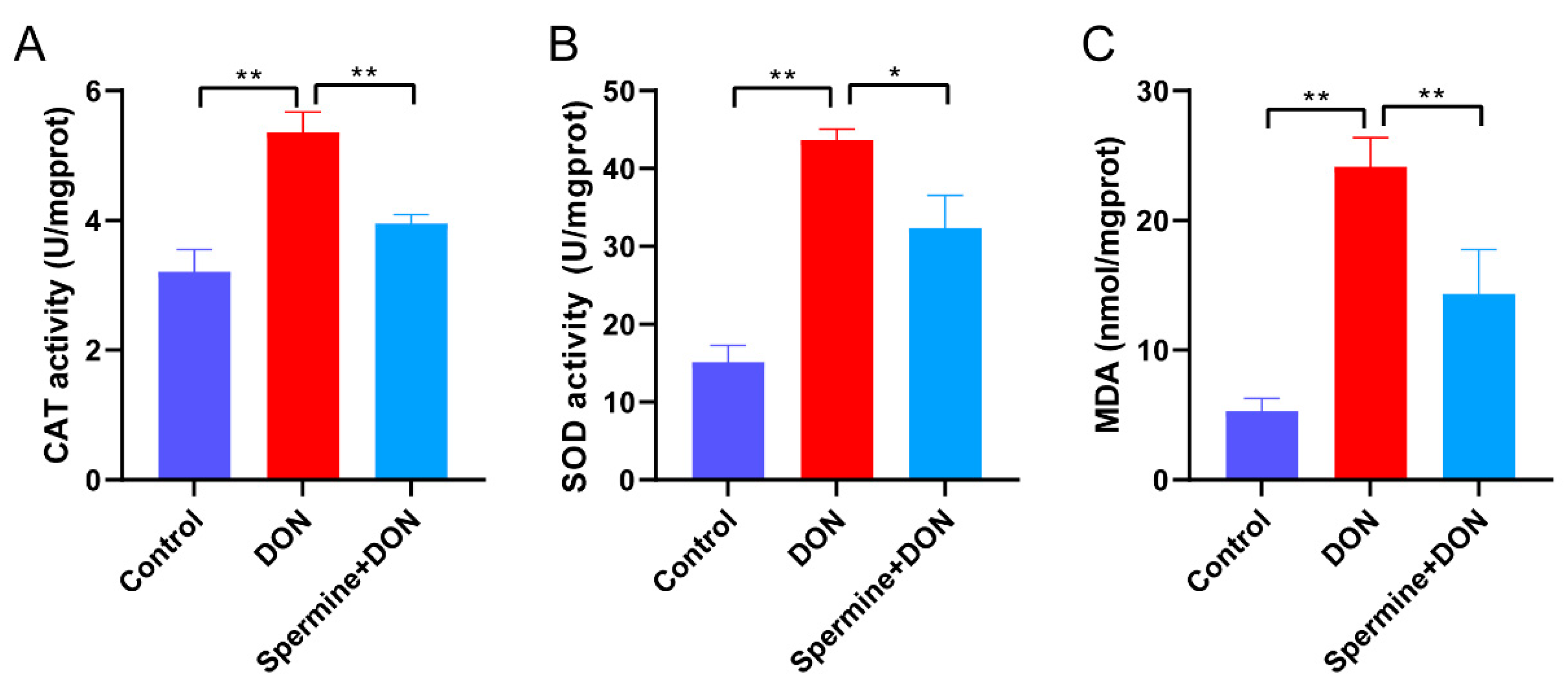
2.4. Spermine Alleviates Oxidative Stress Induced by DON
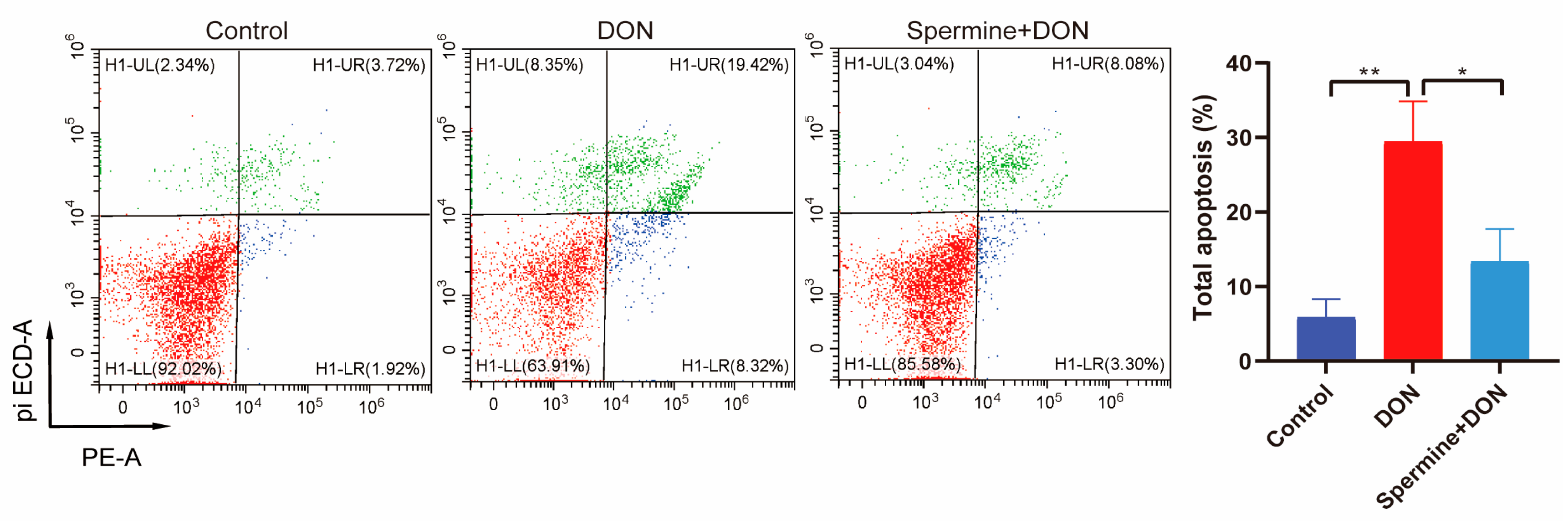
2.5. Spermine Alleviates Cell Apoptosis Induced by DON
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals
5.2. Cell Treatment
5.3. Transcriptome Analysis
5.4. Metabolomic Analysis
5.5. Comprehensive Analysis of Transcriptomics and Metabolomics
5.6. Analysis of Flow Cytometry
5.7. Analysis of Cell Viability
5.8. Measurement of Antioxidant Parameters
5.9. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thapa, A.; Horgan, K.A.; White, B.; Walls, D. Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone-Synergistic or Antagonistic Agri-Food Chain Co-Contaminants? Toxins 2021, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeinvand-Lorestani, H.; Sabzevari, O.; Setayesh, N.; Amini, M.; Nili-Ahmadabadi, A.; Faramarzi, M. Comparative study of in vitro prooxidative properties and genotoxicity induced by aflatoxin B1 and its laccase-mediated detoxification products. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, J.; Vandenbroucke, V.; Pasmans, F.; De Baere, S.; Devreese, M.; Osselaere, A.; Verbrugghe, E.; Haesebrouck, F.; De Saeger, S.; Eeckhout, M.; et al. Influence of mycotoxins and a mycotoxin adsorbing agent on the oral bioavailability of commonly used antibiotics in pigs. Toxins 2012, 4, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dersjant-Li, Y.; Verstegen, M.W.; Gerrits, W.J. The impact of low concentrations of aflatoxin, deoxynivalenol or fumonisin in diets on growing pigs and poultry. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2003, 16, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, S.; Huo, L.; Ding, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Lv, C.; Wu, H.; et al. Deoxynivalenol exposure inhibits biosynthesis of milk fat and protein by impairing tight junction in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113504. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, X.; Zhou, C.; Wu, W.; Zhang, H. Deoxynivalenol Induces Inflammation in IPEC-J2 Cells by Activating P38 Mapk and Erk1/2. Toxins 2020, 12, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Kang, W.; Mao, X.; Du, H.; Ge, L.; Hou, L.; Yuan, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Low dose of arsenic exacerbates toxicity to mice and IPEC-J2 cells exposed with deoxynivalenol: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and autophagy might be novel therapeutic targets. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Shi, D.; Hui, P.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Wu, S.; Bao, W.; Fan, H. DNA ligase III mediates deoxynivalenol exposure-induced DNA damage in intestinal epithelial cells by regulating oxidative stress and interaction with PCNA. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137137. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Shen, J.; Lin, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, M.; Ma, X. PXR Activation Relieves Deoxynivalenol-Induced Liver Oxidative Stress Via Malat1 LncRNA m6A Demethylation. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2308742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, K.; Xue, D.; Zhang, C.; Rajput, S.A.; Qi, D. Mechanism of deoxynivalenol mediated gastrointestinal toxicity: Insights from mitochondrial dysfunction. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 153, 112214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Budihardjo, I.; Oliver, H.; Lutter, M.; Luo, X.; Wang, X. Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999, 15, 269–290. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lu, F.; Gu, S.; Cao, C.; Xiao, Y.; Bao, W.; Wang, H. Lycopene alleviates Deoxynivalenol-induced toxicity in Porcine intestinal epithelial cells by mediating mitochondrial function. Toxicology 2024, 506, 153880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; He, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, X.; Jia, L.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J. Resveratrol Alleviated T-2 Toxin-Induced Liver Injury via Preservation of Nrf2 Pathway and GSH Synthesis. Environ. Toxicol. 2025, 40, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Vázquez, S.; Codina Moreno, R.; Della Badia, A.; Castro, O.; Riahi, I. Promising Phytogenic Feed Additives Used as Anti-Mycotoxin Solutions in Animal Nutrition. Toxins 2024, 16, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konermann, S.; Brigham, M.D.; Trevino, A.E.; Joung, J.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Barcena, C.; Hsu, P.D.; Habib, N.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Nishimasu, H.; et al. Genome-scale transcriptional activation by an engineered CRISPR-Cas9 complex. Nature 2015, 517, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, J.K.; Chen, J.; Pommier, G.C.; Cogan, J.Z.; Replogle, J.M.; Adriaens, C.; Ramadoss, G.N.; Shi, Q.; Hung, K.L.; Samelson, A.J.; et al. Genome-wide programmable transcriptional memory by CRISPR-based epigenome editing. Cell 2021, 184, 2503–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, M.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Q.; Pan, M.; Ma, B. Sulforaphane Suppresses H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via the Activation of AMPK/NFE2L2 Signaling Pathway in Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, T.; Xu, F.; Yan, X.; Li, S.; Li, H. Sulforaphane exerts anti-inflammatory effects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice through the Nrf2/ARE pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.R. The Alleviation Effect and Mechanism Analysis of Sulforaphane on Deoxynivalenol-Induced Porcine Intestinal Injury. Master’s Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chamoto, K.; Zhang, B.; Tajima, M.; Honjo, T.; Fagarasan, S. Spermidine-an old molecule with a new age-defying immune function. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, 34, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cao, W.; Jia, G.; Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Wu, C.; Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, G. New insights into the role of spermine in enhancing the antioxidant capacity of rat spleen and liver under oxidative stress. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 3, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Gao, K.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, Z. Dietary resveratrol attenuation of intestinal inflammation and oxidative damage is linked to the alteration of gut microbiota and butyrate in piglets challenged with deoxynivalenol. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Xin, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhai, Z.; Ni, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, K.; Liao, P.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Z.; et al. The cytoprotective effects of dihydromyricetin and associated metabolic pathway changes on deoxynivalenol treated IPEC-J2 cells. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Mo, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Karrow, N.A.; Wu, H.; Sun, L. Ferroptosis is involved in deoxynivalenol-induced intestinal damage in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta Ojeda, Á.; Tapia Cerda, C.; Poblete Salvatierra, M.F.; Barahona-Fuentes, G.; Jorquera Aguilera, C. Effects of Beta-Alanine Supplementation on Physical Performance in Aerobic-Anaerobic Transition Zones: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barritt, S.A.; DuBois-Coyne, S.E.; Dibble, C.C. Coenzyme A biosynthesis: Mechanisms of regulation, function and disease. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 1008–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, B.; Elliott-Sale, K.; Artioli, G.G.; Swinton, P.A.; Dolan, E.; Roschel, H.; Sale, C.; Gualano, B. β-alanine supplementation to improve exercise capacity and performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.E.; Stout, J.R.; Kendall, K.L.; Fukuda, D.H.; Cramer, J.T. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: The effects of β-alanine supplementation in women. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pegg, A.E. Mammalian polyamine metabolism and function. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Hu, J.; Shao, X.; Song, N.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Exogenous spermine attenuates rat diabetic cardiomyopathy via suppressing ROS-p53 mediated downregulation of calcium-sensitive receptor. Redox Biol. 2020, 32, 101514. [Google Scholar]
- Sava, I.G.; Battaglia, V.; Rossi, C.A.; Salvi, M.; Toninello, A. Free radical scavenging action of the natural polyamine spermine in rat liver mitochondria. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.Q.; Chen, Y.; Jia, W.; Hsie, R.; Chen, Y.; Luh, F.; Zheng, S.; et al. Ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2B deficiency leads to mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening and is associated with aggressive clinicopathologic manifestations of breast cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 3635–3649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agostinelli, E.; Przybytkowski, E.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Glucose, glutathione, and cellular response to spermine oxidation products. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.H.; Gunyuzlu, P.L.; Toyn, J.H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is capable of de Novo pantothenic acid biosynthesis involving a novel pathway of beta-alanine production from spermine. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10794–10800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackowski, S.; Rock, C.O. Regulation of coenzyme A biosynthesis. J. Bacteriol. 1981, 148, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Meng, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y. Polyamines and related signaling pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, G.; Jia, G.; Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, J. Effects of spermine on the proliferation and migration of porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, P.; Zheng, X.; Dong, J.; Lu, F.; Xu, C.; Qu, H.; Zhu, X.; Uemoto, Y.; Lv, X.; Yin, Z.; et al. Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Analyses of Curcumin Alleviation of Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Wu, J.; Feng, M.; Wang, J.; Qi, L.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Bao, W. Insights from Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses into Sulforaphane’s Protective Mechanism Against Deoxynivalenol Toxicity via Spermine Regulation. Toxins 2025, 17, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040178
Xiao Y, Wu J, Feng M, Wang J, Qi L, Xu C, Wang H, Bao W. Insights from Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses into Sulforaphane’s Protective Mechanism Against Deoxynivalenol Toxicity via Spermine Regulation. Toxins. 2025; 17(4):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040178
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yeyi, Jianliang Wu, Menke Feng, Jie Wang, Lele Qi, Chao Xu, Haifei Wang, and Wenbin Bao. 2025. "Insights from Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses into Sulforaphane’s Protective Mechanism Against Deoxynivalenol Toxicity via Spermine Regulation" Toxins 17, no. 4: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040178
APA StyleXiao, Y., Wu, J., Feng, M., Wang, J., Qi, L., Xu, C., Wang, H., & Bao, W. (2025). Insights from Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses into Sulforaphane’s Protective Mechanism Against Deoxynivalenol Toxicity via Spermine Regulation. Toxins, 17(4), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040178






