Acute Toxicity of Carbon Nanotubes, Carbon Nanodots, and Cell-Penetrating Peptides to Freshwater Cyanobacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Experimental Setup and Control Treatments
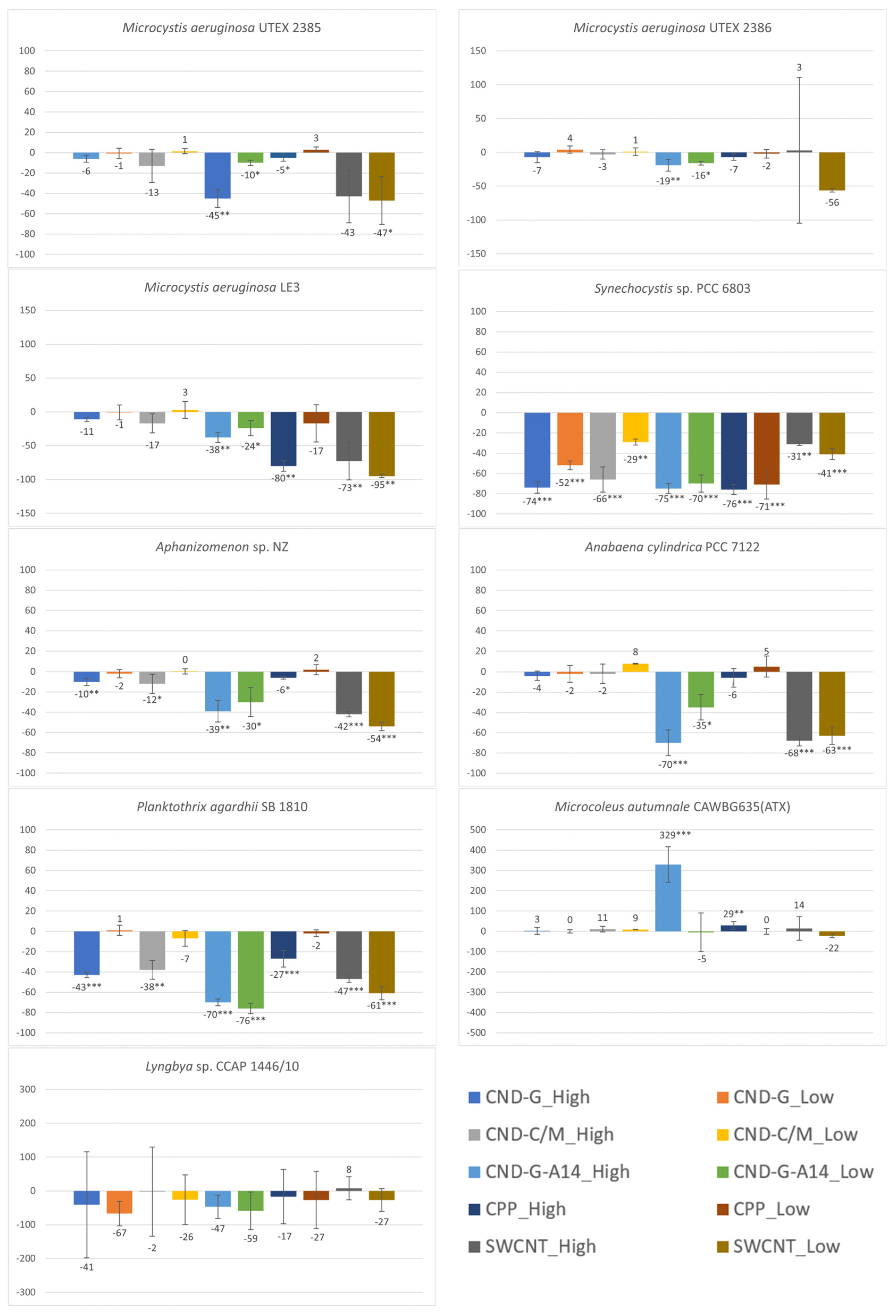
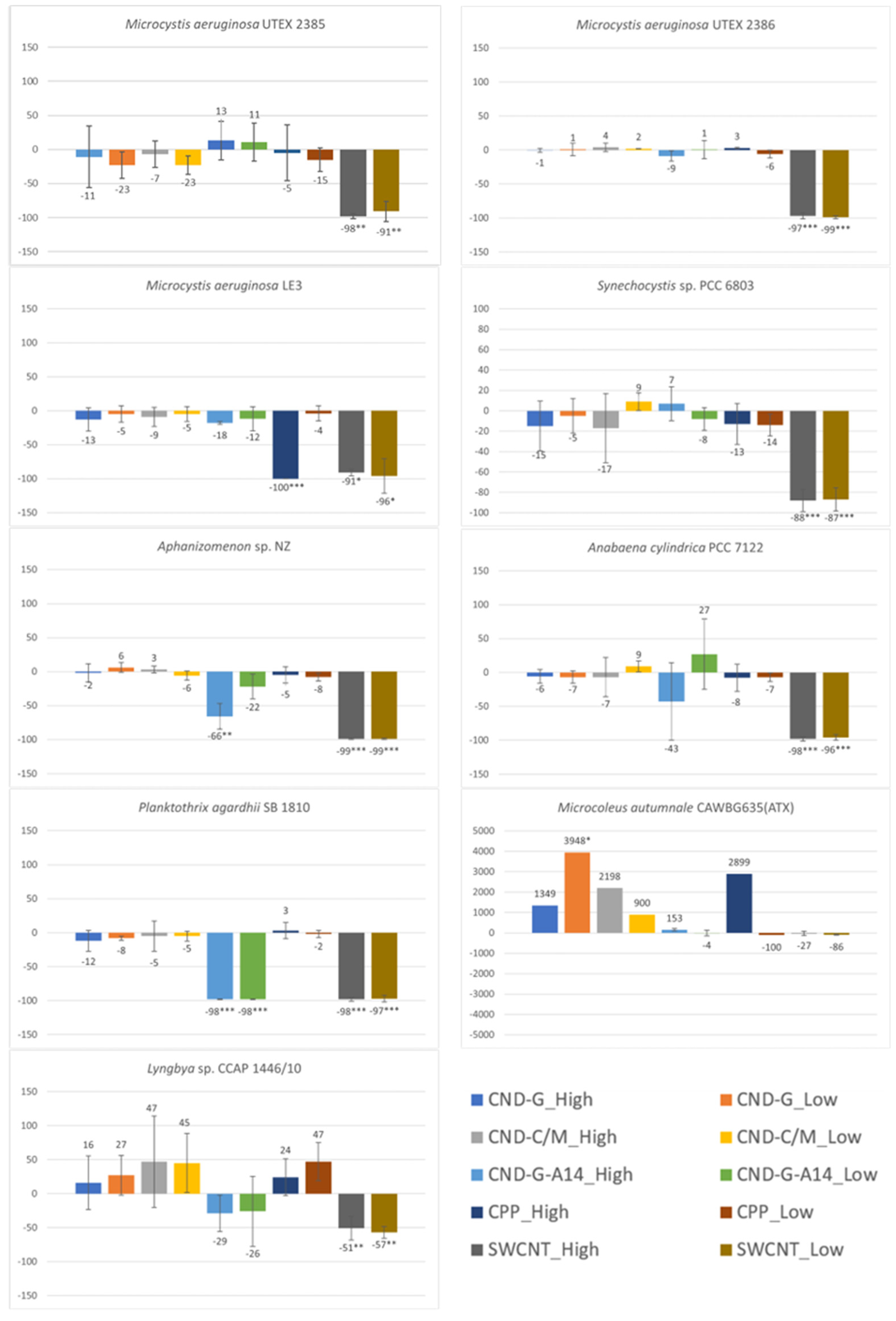
2.2. Effects on Cell Density or Biomass Measured as OD750
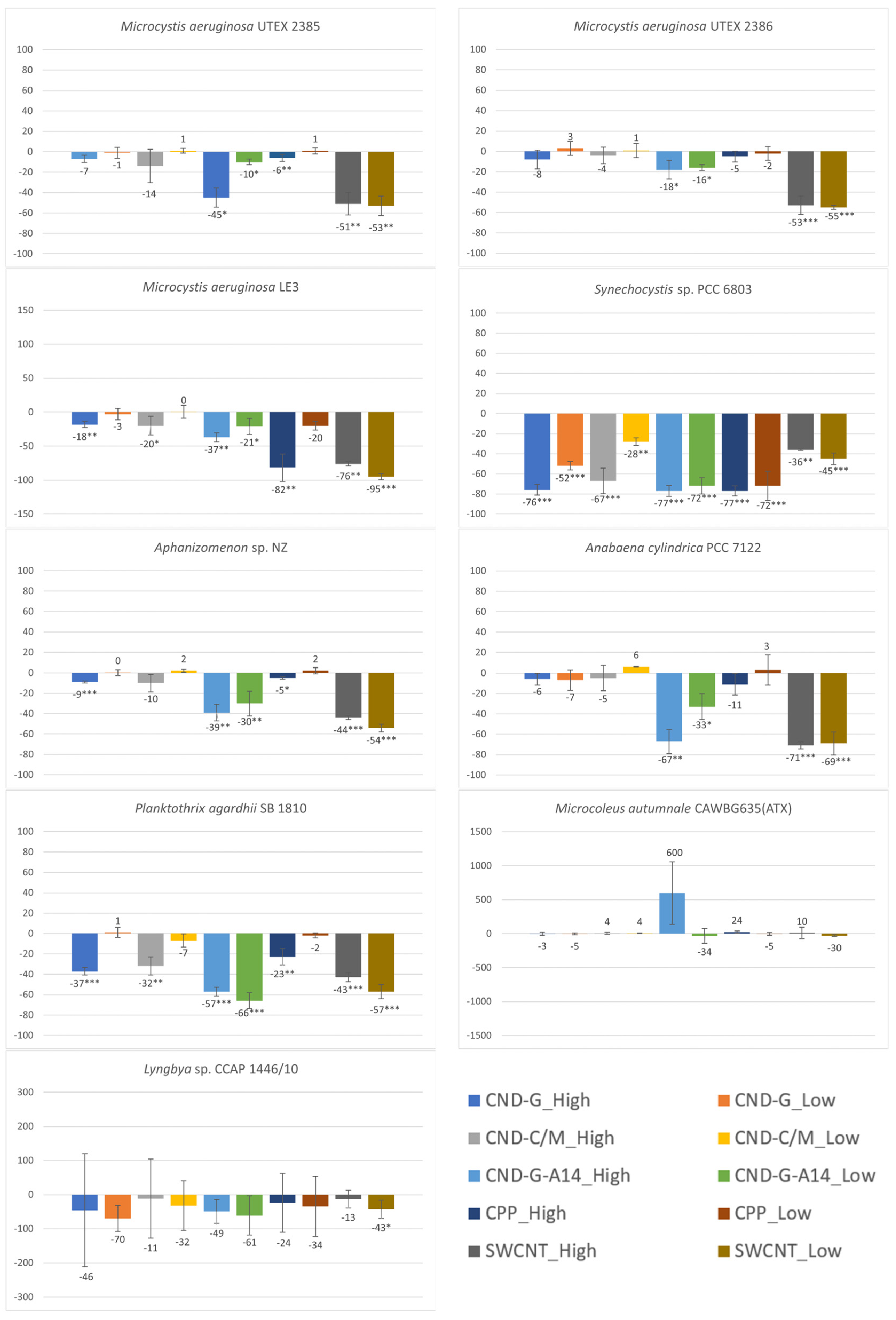
2.3. Effects on chl-a Content Measured as OD680 and FE450
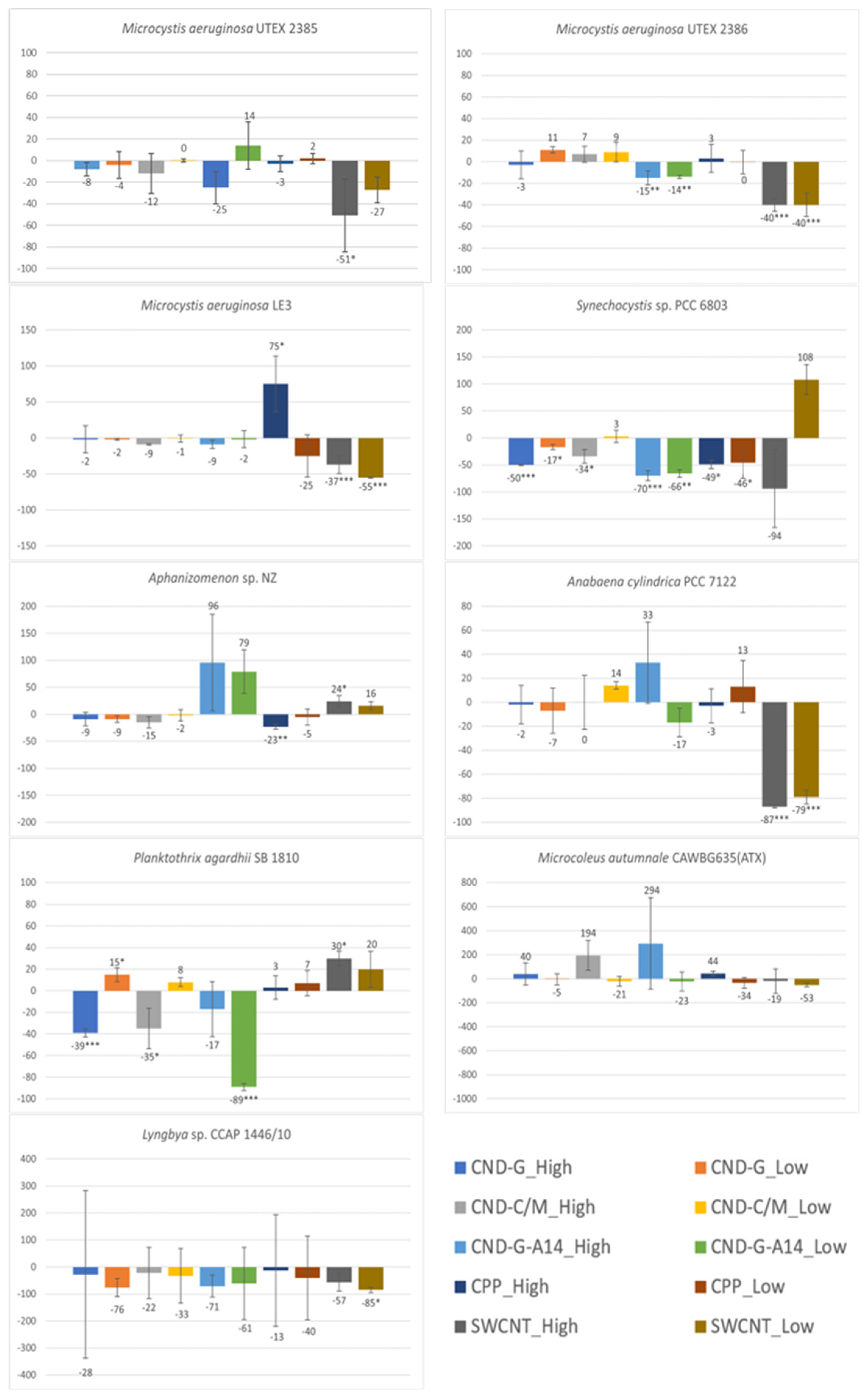
2.4. Effects on Phycocyanin Measured as FE620
2.5. Effects on Photosynthetic Efficiency Measured as QY
3. Discussion
3.1. Differential Sensitivity of Strains to NMNPs
3.2. Differential Sensitivity of Measurement Endpoints
3.3. Toxicological Mode of Action
3.4. Future Research Directions
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
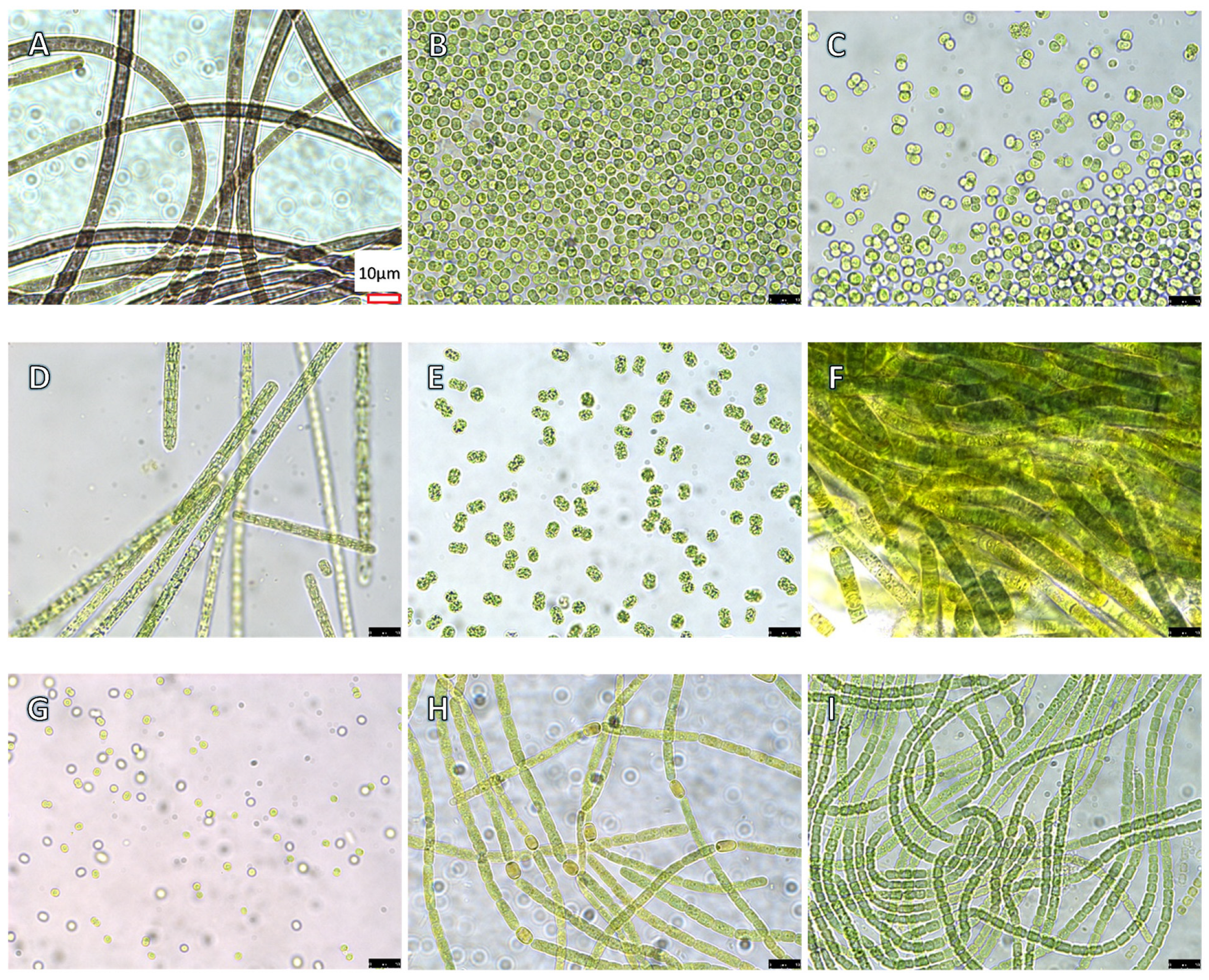
5.1. Cyanobacteria Cultures
5.2. Cell-Penetrating Peptide (CPP)
5.3. Carbon Nanodot (CNDs)
5.3.1. CND-G Synthesis Using 10-kDa bPEI and Glucose
5.3.2. CND-C/M Synthesis Using 10-kDa bPEI and CHCl3/CH3OH
5.4. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs)
5.5. Cyanobacterial Toxicity Testing Protocol
5.6. Data Collection of Endpoint Measurements
5.7. Data Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gobler, C. Climate change and harmful algal blooms: Insights and perspective. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101731. [Google Scholar]
- Sukenik, A.; Kaplan, A. Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in aquatic ecosystems: A comprehensive outlook on current and emerging mitigation and control approaches. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibuye, F.A.; Zamyadi, A.; Wert, E.C. A critical review on operation and performance of source water control strategies for cyanobacterial blooms: Part I-chemical control methods. Harmful Algae 2021, 109, 102099. [Google Scholar]
- Kibuye, F.A.; Zamyadi, A.; Wert, E.C. A critical review on operation and performance of source water control strategies for cyanobacterial blooms: Part II-mechanical and biological control methods. Harmful Algae 2021, 109, 102119. [Google Scholar]
- Balaji-Prasath, B.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.P.; Hamilton, D.P.; Lin, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y. Methods to control harmful algal blooms: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 3133–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Joudeh, N.; Linke, D. Nanoparticle classification, physicochemical properties, characterization, and applications: A comprehensive review for biologists. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 262. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, S.; Hendrix, B.; Hoffer, P.; Sanders, R.; Zheng, W. Carbon dots for efficient small interfering RNA delivery and gene silencing in plants. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bennett, S.W.; Adeleye, A.; Ji, Z.; Keller, A.A. Stability, metal leaching, photoactivity and toxicity in freshwater systems of commercial single wall carbon nanotubes. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4074–4085. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Madani, F.; Lindberg, S.; Langel, U.; Futaki, S.; Graslund, A. Mechanisms of cellular uptake of cell-penetrating peptides. J. Biophys. 2011, 2011, 414729. [Google Scholar]
- Tseytlin, I.N.; Antrim, A.K.; Gong, P. Nanoparticles for mitigation of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Toxins 2024, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J. Nanoparticles, an emerging control method for harmful algal blooms: Current technologies, challenges, and perspectives. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Dong, M.; Huang, C. Low-cost synthesis of carbon nanodots from natural products used as a fluorescent probe for the detection of ferrum(iii) ions in lake water. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2086–2090. [Google Scholar]
- Victoria, F.; Manioudakis, J.; Zaroubi, L.; Findlay, B.; Naccache, R. Tuning residual chirality in carbon dots with anti-microbial properties. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 32202–32210. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Rabe, D.I.; Al Awak, M.M.; Yang, F.; Okonjo, P.A.; Dong, X.; Teisl, L.R.; Wang, P.; Tang, Y.; Pan, N.; Sun, Y.; et al. The dominant role of surface functionalization in carbon dots’ photo-activated antibacterial activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2655–2665. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Rabe, D.I.; Mohammed, O.O.; Dong, X.; Patel, A.K.; Overton, C.M.; Tang, Y.; Kathariou, S.; Sun, Y. Carbon dots for highly effective photodynamic inactivation of multidrug-resistant bacteria. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 321–325. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, K.; Aitken, R.; Tran, L.; Stone, V.; Duffin, R.; Forrest, G.; Alexander, A. Carbon nanotubes: A review of their properties in relation to pulmonary toxicology and workplace safety. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, J.; Waiser, M.; Swerhone, G.; Roy, J.; Tumber, V.; Paule, A.; Hitchcock, A.; Dynes, J.; Korber, D. Effects of fullerene (C60), multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT), single wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) and hydroxyl and carboxyl modified single wall carbon nanotubes on riverine microbial communities. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10090–10102. [Google Scholar]
- Kavosi, A.; Hosseini Ghale Noei, S.; Madani, S.; Khalighfard, S.; Khodayari, S.; Khodayari, H.; Mirzaei, M.; Kalhori, M.R.; Yavarian, M.; Alizadeh, A.M. The toxicity and therapeutic effects of single-and multi-wall carbon nanotubes on mice breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8375. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, N.; Izumi, H.; Morimoto, Y. Review of toxicity studies of carbon nanotubes. J. Occup. Health 2017, 59, 394–407. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Lee, H.; Tolliver, L.M.; Aronstam, R.S. Delivery of nucleic acids and nanomaterials by cell-penetrating peptides: Opportunities and challenges. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 834079. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, E.K.; Chung, S.Y.; Johari, S.A.; Kim, T.G.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kang, S.W.; Yu, I.J. Acute toxicity comparison of single-walled carbon nanotubes in various freshwater organisms. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 323090. [Google Scholar]
- Pikula, K.; Johari, S.A.; Santos-Oliveira, R.; Golokhvast, K. The comparative toxic impact assessment of carbon nanotubes, fullerene, graphene, and graphene oxide on marine microalgae Porphyridium purpureum. Toxics 2023, 11, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, M.; You, X.; Hu, J.; Yang, X.; Sun, W. Carbon nanotubes influence the toxic effects of chloramphenicol and tetracycline on cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. in different ways. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2021, 8, 634–646. [Google Scholar]
- Young, E.B.; Reed, L.; Berges, J.A. Growth parameters and responses of green algae across a gradient of phototrophic, mixotrophic and heterotrophic conditions. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13776. [Google Scholar]
- Chioccioli, M.; Hankamer, B.; Ross, I.L. Flow cytometry pulse width data enables rapid and sensitive estimation of biomass dry weight in the microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Chlorella vulgaris. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97269. [Google Scholar]
- Held, P. Monitoring of algal growth using their intrinsic properties—Use of a multi-mode monochromator-based microplate reader for biofuel research. Biofuel Res. Appl. Note 2011, 5994-3290EN. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/cs/library/applications/monitoring-of-algal-growth-5994-3290EN-agilent.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Schuurmans, R.M.; van Alphen, P.; Schuurmans, J.M.; Matthijs, H.C.P.; Hellingwerf, K.J. Comparison of the photosynthetic yield of cyanobacteria and green algae: Different methods give Different answers. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139061. [Google Scholar]
- Keliri, E.; Paraskeva, C.; Sofokleous, A.; Sukenik, A.; Dziga, D.; Chernova, E.; Brient, L.; Antoniou, M.G. Occurrence of a single-species cyanobacterial bloom in a lake in Cyprus: Monitoring and treatment with hydrogen peroxide-releasing granules. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Bertone, E.; Chuang, A.; Burford, M.A.; Hamilton, D.P. In-situ fluorescence monitoring of cyanobacteria: Laboratory-based quantification of species-specific measurement accuracy. Harmful Algae 2019, 87, 101625. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, J.A.; Curtis, B.S.; Curtis, W.R. Improving accuracy of cell and chromophore concentration measurements using optical density. BMC Biophys. 2013, 6, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, N.L.; Billard, B.D.; Gennaro, T.L. Limits of optical transmission measurements with application to particle sizing techniques. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 5887–5893. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Moradinejad, S.; Guerra Maldonado, J.F.; Zamyadi, A.; Dorner, S.; Prévost, M. Factors affecting the interpretation of online phycocyanin fluorescence to manage cyanobacteria in drinking water sources. Water 2022, 14, 3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippka, R.; Deruelles, J.; Waterbury, J.B.; Herdman, M.; Stanier, R.Y. Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. Microbiology 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Catherine, Q.; Susanna, W.; Isidora, E.S.; Mark, H.; Aurélie, V.; Jean-François, H. A review of current knowledge on toxic benthic freshwater cyanobacteria–Ecology, toxin production and risk management. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5464–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z. A NOVEL RNA Extraction Method for Cyanobacteria. Master’s Thesis, LSU, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2012. Available online: https://repository.lsu.edu/gradschool_theses/3899 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Sato, M.; Amano, Y.; Machida, M.; Imazeki, F. Colony formation of highly dispersed Microcystis aeruginosa by controlling extracellular polysaccharides and calcium ion concentrations in aquatic solution. Limnology 2017, 18, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarek, J.; Kaštovský, J.; Mares, J.; Johansen, J. Taxonomic classification of cyanoprokaryotes (cyanobacterial genera) 2014, using a polyphasic approach. Preslia 2014, 86, 295–335. [Google Scholar]
- De Philippis, R.; Vincenzini, M. Exocellular polysaccharides from cyanobacteria and their possible applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 22, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamizo, S.; Adessi, A.; Torzillo, G.; De Philippis, R. Exopolysaccharide features influence growth success in biocrust-forming cyanobacteria, moving from liquid culture to sand microcosms. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 568224. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Tian, L.L.; Ren, C.Y.; Xu, C.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, L. Extracellular polysaccharide synthesis in a bloom-forming strain of Microcystis aeruginosa: Implications for colonization and buoyancy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V.M.; Pakrasi, H.B. Advances in the understanding of the lifecycle of photosystem II. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sabu, S.; Sangela, V.; Meena, M.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Vinayak, V.; Harish. The mechanism of nanoparticle toxicity to cyanobacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, B.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Toxic effects of different types of zinc oxide nanoparticles on algae, plants, invertebrates, vertebrates and microorganisms. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Lv, X.; Zheng, G.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Z. Effects of carbon quantum dots on aquatic environments: Comparison of toxicity to organisms at different trophic levels. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2018, 52, 14445–14451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.R.; Huang, Y.W.; Lee, H.J. Mechanistic studies of intracellular delivery of proteins by cell-penetrating peptides in cyanobacteria. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Kilk, K.; Mahlapuu, R.; Soomets, U.; Langel, U. Analysis of in vitro toxicity of five cell-penetrating peptides by metabolic profiling. Toxicology 2009, 265, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, F.; Bucheli, T.; Lukhele, L.; Magrez, A.; Nowack, B.; Sigg, L.; Knauer, K. Are carbon nanotube effects on green algae caused by shading and agglomeration? Environ. Sci. Tech. 2011, 45, 6136–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, A.; Ferrante, F.; Gonç, G.; Tobias, G.; Popescu, R.; Gerthsen, D.; Mauro, N.; Giammona, G.; Buscarino, G.; Gelardi, F.; et al. Ultrafast interface charge separation in carbon nanodot− nanotube hybrids. ASC Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 49232–49241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA 712-C-005; Ecological Effects Test Guidelines OCSPP 850.4550: Cyanobacteria (Anabaena flos-aquae) Toxicity. United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- E1218-21; Standard Guide for Conducting Static Toxicity Tests with Microalgae. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Test No. 201: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escher, S.E.; Mangelsdorf, I.; Hoffmann-Doerr, S.; Partosch, F.; Karwath, A.; Schroeder, K.; Zapf, A.; Batke, M. Time extrapolation in regulatory risk assessment: The impact of study differences on the extrapolation factors. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 112, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, G.H.M.; Talling, J.F.; Heaney, S.I. The influence of carbon dioxide-depletion on growth and sinking rate of two planktonic diatoms in culture. Br. Phycol. J. 1981, 16, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, C.; Blackburn, S. Isolation and purification of Australian isolates of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa Kfitz. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 8, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Lu, X.M.; Zhang, M.R.; Hu, K.; Li, Z. Peptide-based nanomaterials: Self-assembly, properties and applications. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 11, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demirer, G.; Zhang, H.; Goh, N.; Gonzales-Grandio, E.; Landry, M. Carbon nanotube-mediated DNA delivery without transgene integration in intact plants. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2954–2971. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Signorell, A. DescTools: Tools for Descriptive Statistics. R Package Version 0.99.54. Available online: https://github.com/AndriSignorell/DescTools/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).


| Treatment | Control | CND-G_High | CND-G_Low | CND-C/M_High | CND-C/M_Low | CND-G-A14_High | CND-G-A14_Low | CPP_High | CPP_ Low | SWCNT_High | SWCNT_Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyanobacteria (mL) | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| CND (µL) | 0.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| CPP (µL) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| SWCNT (µL) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 56.0 | 28.0 |
| Total (mL) | 5.0 | 5.004 | 5.002 | 5.002 | 5.001 | 5.01 | 5.005 | 5.01 | 5.005 | 5.056 | 5.028 |
| NP Conc. (ng/µL) | 0.0 | 2149 | 2149 | 3943 | 3943 | 2030 | 2030 | 5000 | 5000 | 138 | 138 |
| Treatment Conc. (ng/mL) | 0.0 | 1718 | 859 | 1577 | 788 | 4052 | 2028 | 9980 | 4995 | 1528 | 768 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antrim, A.K.; Tseytlin, I.N.; Cooley, E.G.; Fernando, P.U.A.I.; Barker, N.D.; Alberts, E.M.; Jernberg, J.; Kosgei, G.K.; Gong, P. Acute Toxicity of Carbon Nanotubes, Carbon Nanodots, and Cell-Penetrating Peptides to Freshwater Cyanobacteria. Toxins 2025, 17, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040172
Antrim AK, Tseytlin IN, Cooley EG, Fernando PUAI, Barker ND, Alberts EM, Jernberg J, Kosgei GK, Gong P. Acute Toxicity of Carbon Nanotubes, Carbon Nanodots, and Cell-Penetrating Peptides to Freshwater Cyanobacteria. Toxins. 2025; 17(4):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040172
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntrim, Anna K., Ilana N. Tseytlin, Emily G. Cooley, P. U. Ashvin Iresh Fernando, Natalie D. Barker, Erik M. Alberts, Johanna Jernberg, Gilbert K. Kosgei, and Ping Gong. 2025. "Acute Toxicity of Carbon Nanotubes, Carbon Nanodots, and Cell-Penetrating Peptides to Freshwater Cyanobacteria" Toxins 17, no. 4: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040172
APA StyleAntrim, A. K., Tseytlin, I. N., Cooley, E. G., Fernando, P. U. A. I., Barker, N. D., Alberts, E. M., Jernberg, J., Kosgei, G. K., & Gong, P. (2025). Acute Toxicity of Carbon Nanotubes, Carbon Nanodots, and Cell-Penetrating Peptides to Freshwater Cyanobacteria. Toxins, 17(4), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040172





