Mechanisms of Cellular Responses of the Natural Alkaloid Caulerpin and Its Similarities with the Lipid-Lowering Agent Fenofibrate in Mytilus galloprovincialis
Abstract
1. Introduction
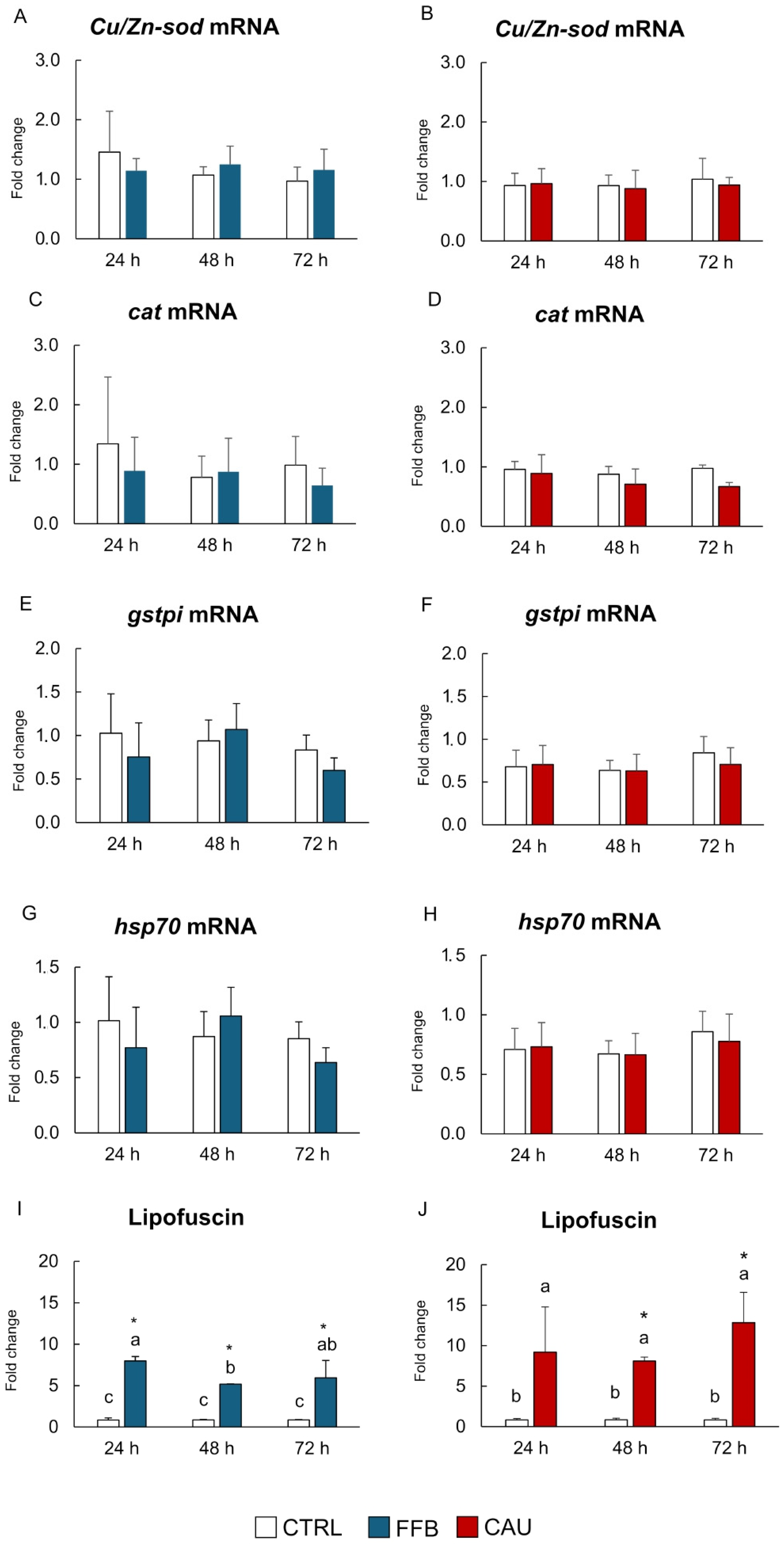
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Solutions and Culture Medium
5.2. Animal Maintenance
5.3. Exposure of Precision-Cut Tissue Slices (PCTSs)
5.4. Histological Analysis of Neutral Lipids and Lipofuscin
5.5. Quantitative Analysis of mRNA Levels
5.6. Activity of Acyl-CoA Oxidase (ACOX)
5.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mezzelani, M.; Regoli, F. The biological effects of pharmaceuticals in the marine environment. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2022, 14, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, R.; Luesch, H. Marine Natural Products: A New Wave of Drugs? Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Hou, M.F.; Huang, H.W.; Chang, F.R.; Yeh, C.C.; Tang, J.Y.; Chang, H.W. Marine algal natural products with anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Nah, J.-W.; Jeon, Y.-J. Potential anti-inflammatory natural products from marine algae. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourikis, P.; Zako, S.; Dannenberg, L.; Nia, A.M.; Heinen, Y.; Busch, L.; Richter, H.; Hohlfeld, T.; Zeus, T.; Kelm, M.; et al. Lipid lowering therapy in cardiovascular disease: From myth to molecular reality. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 213, 107592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-L.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chiang, Y.-M.; Wang, S.-G.; Lee, H.-M. Fenofibrate lowers lipid accumulation in myotubes by modulating the PPARα/AMPK/FoxO1/ATGL pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.A.; Hassan, S.S.U.; Bungau, S.; Si, Y.; Xu, H.; Rahman, H.; Behl, T.; Gitea, D.; Pavel, F.-M.; Aron, R.A.C.; et al. Chemically diverse and biologically active secondary metabolites from marine Phylum chlorophyta. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrheem, D.A.; Ahmed, S.A.; El-Mageed, H.R.A.; Mohamed, H.S.; Rahman, A.A.; Elsayed, K.N.M.; Ahmed, S.A. The inhibitory effect of some natural bioactive compounds against SARS-CoV-2 main protease: Insights from molecular docking analysis and molecular dynamic simulation. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 55 Pt A, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, J.; Tariq, A.; Azam, M.; Ahmed, V.U. Caulerpin from a new source spatoglossum asperum: A brown alga. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2019, 41, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, N.R.P.V.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Villaça, R.C.; Ferreira, W.; Pinto, A.M.; Teixeira, V.L.; Cirne-Santos, C.; Paixão, I.C.N.P.; Giongo, V. Caulerpin as a potential antiviral drug against Herpes simplex virus type 1. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2012, 22, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, P.O.; de Oliveira, M.C.; de Souza Barros, C.; Cirne-Santos, C.C.; Laneuvlille, V.T.; Palmer Paixão, I.C. Antiviral Effect of Caulerpin Against Chikungunya. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Abdelrheem, D.A.; Abd El-Mageed, H.; Mohamed, H.S.; Rahman, A.A.; Elsayed, K.N.; Ahmed, S.A. Destabilizing the structural integrity of COVID-19 by caulerpin and its derivatives along with some antiviral drugs: An in-silico approaches for a combination therapy. Struct. Chem. 2020, 31, 2391–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canché Chay, C.I.; Cansino, R.G.; Espitia Pinzón, C.I.; Torres Ochoa, R.O.; Martínez, R. Synthesis and anti-tuberculosis activity of the marine natural product caulerpin and its analogues. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1757–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante-Silva, L.H.A.; Falcão, M.A.P.; Vieira, A.C.S.; Viana, M.D.M.; De Araújo-Júnior, J.X.; Sousa, J.C.F.; da Silva, T.M.S.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Noël, F.; De Miranda, G.E.C.; et al. Assessment of mechanisms involved in antinociception produced by the alkaloid caulerpine. Molecules 2014, 19, 14699–14709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, É.T.; De Lira, D.P.; De Queiroz, A.C.; Da Silva, D.J.C.; De Aquino, A.B.; Campessato Mella, E.A.; Lorenzo, V.P.; De Miranda, G.E.C.; De Araújo-Júnior, J.X.; De Oliveira Chaves, M.C.; et al. The antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of caulerpin, a bisindole alkaloid isolated from seaweeds of the genus Caulerpa. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, J.S.P.; Silva, D.K.C.; da Silva Oliveira, V.; Junior, S.S.S.; dos Santos Rodrigues, E.; de Souza, C.V.C.; Martinez, S.T.; Santos-Filho, O.A.; Meira, C.S.; Soares, M.B.P. The Alkaloid Caulerpin Exhibits Potent and Selective Anti-Inflammatory Activity Through Interaction with the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaswir, I.; Monsur, H.A. Anti-inflammatory compounds of macro algae origin: A review. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 7146–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liao, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, R.; Long, W.; Li, L.; Gu, L.; Xu, S. An Economical Synthesis of Caulerpin and Evaluation of Its New Anticancer Activities. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 12406–12409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Bhushan, S.; Bast, F.; Singh, S. Marine macroalga Caulerpa: Role of its metabolites in modulating cancer signaling. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 3545–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbi, S.; Giuliani, M.E.; Pittura, L.; D’Errico, G.; Terlizzi, A.; Felline, S.; Grauso, L.; Mollo, E.; Cutignano, A.; Regoli, F. Could molecular effects of Caulerpa racemosa metabolites modulate the impact on fish populations of Diplodus sargus? Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 96, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felline, S.; Mollo, E.; Ferramosca, A.; Zara, V.; Regoli, F.; Gorbi, S.; Terlizzi, A. Can a marine pest reduce the nutritional value of Mediterranean fish flesh? Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coco, L.; Felline, S.; Girelli, C.R.; Angil, F.; Magliozzi, L.; Almada, F.; Aniello, B.D.; Mollo, E.; Terlizzi, A.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H NMR Spectroscopy and MVA to evaluate the effects of caulerpin-based diet on Diplodus sargus lipid profiles. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, R.M.; D’Aniello, E.; Gorbi, S.; Martella, A.; Silvestri, C.; Giuliani, M.E.; Fellous, T.; Gentile, A.; Carbone, M.; Cutignano, A.; et al. Fishing for targets of alien metabolites: A novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonist from a marine pest. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.; Coppola, F.; Leite, C.; Carbone, M.; Paris, D.; Motta, A.; Di Cosmo, A.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Mollo, E.; Freitas, R.; et al. An alien metabolite vs. a synthetic chemical hazard: An ecotoxicological comparison in the Mediterranean blue mussel. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Y.; Demizieux, L.; Degrace, P.; Gresti, J.; Moindrot, B.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L.X.; Cao, J.M.; Clouet, P. Alteration of 20:5n−3 and 22:6n−3 fat contents and liver peroxisomal activities in fenofibrate-treated rainbow trout. Lipids 2004, 39, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.-Y.; Clouet, P.; Degrace, P.; Zheng, W.-H.; Frøyland, L.; Tian, L.-X.; Liu, Y.-J. Hypolipidaemic effects of fenofibrate and fasting in the herbivorous grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) fed a high-fat diet. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, S.A.; Haller, J.F.; Ferrante, T.; Zoeller, R.A.; Corkey, B.E. Reactive Oxygen Species Facilitate Translocation of Hormone Sensitive Lipase to the Lipid Droplet during Lipolysis in Human Differentiated Adipocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.K.; Lee, J.N.; Maharjan, Y.; Park, C.; Choe, S.K.; Ho, Y.S.; Park, R. Catalase deficiency facilitates the shuttling of free fatty acid to brown adipose tissue through lipolysis mediated by ROS during sustained fasting. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivero-Verbel, J.; Harkema, J.R.; Roth, R.A.; Ganey, P. Fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha agonist, blocks steatosis and alters the inflammatory response in a mouse model of inflammation-dioxin interaction. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 345, 109521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveidahl Johansen, O.; Ma, T.; Hansen, J.B. Lipolysis drives expression of the constitutively active receptor GPR3 to induce adipose thermogenesis. Cell 2021, 184, 3502–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, L.; Ordonez, G.P.M.; Pham, K.T.; Kennelly, J.P.; Rodríguez, M.L.; Tran, L.; Tontonoz, P.; Nguyen, A. PPARɑ variant V227A reduces plasma triglycerides through enhanced lipoprotein lipolysis. J. Lipid Res. 2025, 66, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lu, W.; Shi, B.; Klein, S.; Su, X. Peroxisomal regulation of redox homeostasis and adipocyte metabolism. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzelani, M.; Notarstefano, V.; Panni, M.; Giorgini, E.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Exposure to environmental pharmaceuticals affects the macromolecular composition of mussels digestive glands. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajaraville, M.P.; Orbea, A.; Marigómez, I.; Cancio, I. Peroxisome proliferation in the digestive epithelium of mussels exposed to the water accommodated fraction of three oils. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1997, 117, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajaraville, M.P.; Cancio, I.; Ibabe, A.; Orbea, A. Peroxisome proliferation as a biomarker in environmental pollution assessment. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 61, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancio, I.; Cajaraville, M.P. Cell biology of peroxisomes and their characteristics in aquatic organisms. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2000, 199, 201–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancio, I.; Orbea, A.; Völkl, A.; Fahimi, H.D.; Cajaraville, M.P. Induction of peroxisomal oxidases in mussels: Comparison of effects of lubricant oil and benzo[a]pyrene with two typical peroxisome proliferators on peroxisome structure and function in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1998, 149, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbea, A.; Cajaraville, M.P. Peroxisome proliferation and antioxidant enzymes in transplanted mussels of four Basque estuaries with different levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and polychlorinated biphenyl pollution. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Wei, R.; Xu, B.; Cao, H.; Zhi, Y.; Guo, F.; Liu, H.; Li, B.; Wu, J.; Gao, Y.; et al. Qiwei Jinggan Ling regulates oxidative stress and lipid metabolism in alcoholic liver disease by activating AMPK. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, M.E.; Sparaventi, E.; Lanzoni, I.; Pittura, L.; Regoli, F.; Gorbi, S. Precision-Cut Tissue Slices (PCTS) from the digestive gland of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis: An ex vivo approach for molecular and cellular responses in marine invertebrates. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 61, 104603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes 2010. Text with EEA Relevance; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2010.
- D’Aniello, E.; Amodeo, P.; Vitale, R.M. Marine natural and nature-inspired compounds targeting peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPARs). Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Z.; Kong, F.; Liao, K.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Shi, P.; Zhang, M.; Wu, K.; Yan, X. Identification and Expression of PPAR in Sinonovacula constricta and Their Potential Regulatory Effects on Δ6 Fad Transcription. J. Ocean Univ. China 2021, 20, 1557–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Carrera, M.; Wahli, W. PPARs as key mediators in the regulation of metabolism and inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 23, 5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzzocrea, S.; Mazzon, E.; Di Paola, R.; Peli, A.; Bonato, A.; Britti, D.; Genovese, T.; Muià, C.; Crisafulli, C.; Caputi, A.P. The role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPAR-alpha) in the regulation of acute inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougarne, N.; Weyers, B.; Desmet, S.J.; Deckers, J.; Ray, D.W.; Staels, B.; De Bosscher, K. Molecular actions of PPARα in lipid metabolism and inflammation. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 760–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, P.; Tapper, M.; Linnum, A.; Denny, J.; Kolanczyk, R.; Johnson, R. Optimization of a precision-cut trout liver tissue slice assay as a screen for vitellogenin induction: Comparison of slice incubation techniques. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 49, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, I.A.; Groothuis, G.M.M.; Olinga, P. Precision-cut tissue slices as a tool to predict metabolism of novel drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2007, 3, 879–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, B.; Debier, C.; Buc Calderon, P.; Thomé, J.P.; Stegeman, J.; Mork, J.; Rees, J.F. Precision-cut liver slices to investigate responsiveness of deep-sea fish to contaminants at high pressure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10310–10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, J.P.; Baste, J.M.; Gay, A.; Crochemore, C.; Corbière, C.; Monteil, C. Precision cut lung slices as an efficient tool for in vitro lung physio-pharmacotoxicology studies. Xenobiotica 2013, 43, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizarro, C.; Eide, M.; Hitchcock, D.J.; Goksøyr, A.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M. Single and mixture effects of aquatic micropollutants studied in precision-cut liver slices of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 177, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Gilabert, A.; Porte, C. Precision cut tissue slices to investigate the effects of triclosan exposure in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicol. Vitr. 2022, 85, 105477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, R.A.; He, S.; Newton, R.S. Differential regulation of human apolipoprotein AI and high-density lipoprotein by fenofibrate in hapoAI and hapoAI-CIII-AIV transgenic mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1811, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gureev, A.P.; Shmatkova, M.L.; Bashmakov, V.Y.; Starkov, A.A.; Popov, V.N. The effect of fenofibrate on expression of genes involved in fatty acids beta-oxidation and associated free-radical processes. Biochem. Suppl. Ser. B Biomed. Chem. 2016, 10, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, A.N.; Crane, J.S. Histology, Lipofuscin; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537358/ (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Regoli, F.; Giuliani, M.E. Oxidative pathways of chemical toxicity and oxidative stress biomarkers in marine organisms. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 93, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marigómez, I.; Zorita, I.; Izagirre, U.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M.; Navarro, P.; Etxebarria, N.; Cajaraville, M.P. Combined use of native and caged mussels to assess biological effects of pollution through the integrative biomarker approach. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 136, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capolupo, M.; Valbonesi, P.; Kiwan, A.; Buratti, S.; Franzellitti, S.; Fabbri, E. Use of an integrated biomarker-based strategy to evaluate physiological stress responses induced by environmental concentrations of caffeine in the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroux, N.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Katsumiti, A.; Porte, C.; Cajaraville, M.P. Lipidomic analysis of mussel hemocytes exposed to polystyrene nanoplastics. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, M.; Abad, T.N.; Martinez, M.F.; Calcagno, J.A.; Sabatini, S.E.; Genovese, G. Histological alterations as a recommended biomarker in the mussel Mytilus platensis (Bivalvia, Mytilidae) to study anthropic impact on seaports. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2024, 70, 103373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, R.S.; Allen, R.G.; Farmer, K.J.; Procter, J. Effect of physical-activity on superoxide-dismutase, catalase, inorganic peroxides and glutathione in the adult male housefly, musca-domestica. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1984, 26, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laville, N.; Aït-Ässa, S.; Gomez, E.; Casellas, C.; Porcher, J.M. Effects of human pharma-ceuticals on cytotoxicity, EROD activity and ROS production in fish hepatocytes. Toxicology 2004, 196, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mates, J.M. Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology. Toxicology 2000, 153, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abele, D.; Puntarulo, S. Formation of reactive species and induction of antioxidant defence systems in polar and temperate marine invertebrates and fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2004, 138, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.H.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, M.K.; Shin, C.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Chung, J.H. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha improves aged and UV-irradiated skin by catalase induction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.B.; Rømma, S.; Garmo, Ø.A.; Pedersen, S.A.; Olsvik, P.A.; Andersen, R.A. Induction and activity of oxidative stress-related proteins during waterborne Cd/Zn-exposure in brown trout (Salmo trutta). Chemosphere 2007, 67, 2241–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.B.; Spence, J.D. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Fibric Acid Derivatives (Fibrates). Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1998, 34, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, F.D.; Soares, A.R.; Houghton, P.J.; Pereira, R.C.; Kaplan, M.A.C.; Teixeira, V.L. Potential cytotoxic activity of some Brazilian seaweeds on human melanoma cells. Phytother. Res. Int. J. Devoted Pharmacol. Toxicol. Eval. Nat. Product. Deriv. 2007, 21, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzelani, M.; Peruzza, L.; d’Errico, G.; Milan, M.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Mixtures of environmental pharmaceuticals in marine organisms: Mechanistic evidence of carbamazepine and valsartan effects on Mytilus galloprovincialis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Borghi, C.; Ciacci, C.; Fabbri, R.; Vergani, L.; Gallo, G. Bisphenol-A alters gene expression and functional parameters in molluscan hepatopancreas. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 276, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Borghi, C.; Ciacci, C.; Fabbri, R.; Lorusso, L.C.; Vergani, L.; Marcomini, A.; Poiana, G. Short-term effects of environmentally relevant concentrations of EDC mixtures on Mytilus galloprovincialis digestive gland. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 87, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellura, C.; Toubiana, M.; Parrinello, N.; Roch, P. HSP70 gene expression in Mytilus galloprovincialis hemocytes is triggered by moderate heat shock and Vibrio anguillarum, but not by V. splendidus or Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsogiannaki, S.; Franzellitti, S.; Kalogiannis, S.; Fabbri, E.; Dimitriadis, V.V.; Kaloyianni, M. Effects of cadmium and 17β-estradiol on Mytilus galloprovincialis redox status. Prooxidant–antioxidant balance (PAB) as a novel approach in biomonitoring of marine environments. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 103, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittura, L.; Avio, C.G.; Giuliani, M.E.; d’Errico, G.; Keiter, S.H.; Cormier, B.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Microplastics as vehicles of environmental PAHs to marine organisms: Combined chemical and physical hazards to the mediterranean mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzellitti, S.; Fabbri, E. Cyclic-AMP mediated regulation of ABCB mRNA expression in mussel haemocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Leon, E.; Puinean, A.M.; Labadie, P.; Ciocan, C.; Itoh, N.; Kishida, M.; Osada, M.; Minier, C.; Hill, E.M.; Rotchell, M. Two CYP3A-like genes in the marine mussel Mytilus edulis: MRNA expression modulation following short-term exposure to endocrine disruptors. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 74, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panni, M.; Mezzelani, M.; Giuliani, M.E.; Nisi Cerioni, P.; Nardi, A.; Mollo, E.; Regoli, F.; Benedetti, M.; Gorbi, S. Mechanisms of Cellular Responses of the Natural Alkaloid Caulerpin and Its Similarities with the Lipid-Lowering Agent Fenofibrate in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxins 2025, 17, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100512
Panni M, Mezzelani M, Giuliani ME, Nisi Cerioni P, Nardi A, Mollo E, Regoli F, Benedetti M, Gorbi S. Mechanisms of Cellular Responses of the Natural Alkaloid Caulerpin and Its Similarities with the Lipid-Lowering Agent Fenofibrate in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxins. 2025; 17(10):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100512
Chicago/Turabian StylePanni, Michela, Marica Mezzelani, Maria Elisa Giuliani, Paola Nisi Cerioni, Alessandro Nardi, Ernesto Mollo, Francesco Regoli, Maura Benedetti, and Stefania Gorbi. 2025. "Mechanisms of Cellular Responses of the Natural Alkaloid Caulerpin and Its Similarities with the Lipid-Lowering Agent Fenofibrate in Mytilus galloprovincialis" Toxins 17, no. 10: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100512
APA StylePanni, M., Mezzelani, M., Giuliani, M. E., Nisi Cerioni, P., Nardi, A., Mollo, E., Regoli, F., Benedetti, M., & Gorbi, S. (2025). Mechanisms of Cellular Responses of the Natural Alkaloid Caulerpin and Its Similarities with the Lipid-Lowering Agent Fenofibrate in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxins, 17(10), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100512





