Bioremediation of Contaminated Water: The Potential of Aquatic Plants Ceratophyllum demersum and Pistia stratiotes Against Toxic Bloom
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Environmental Parameters on Pistia stratiotes and Ceratophyllum demersum
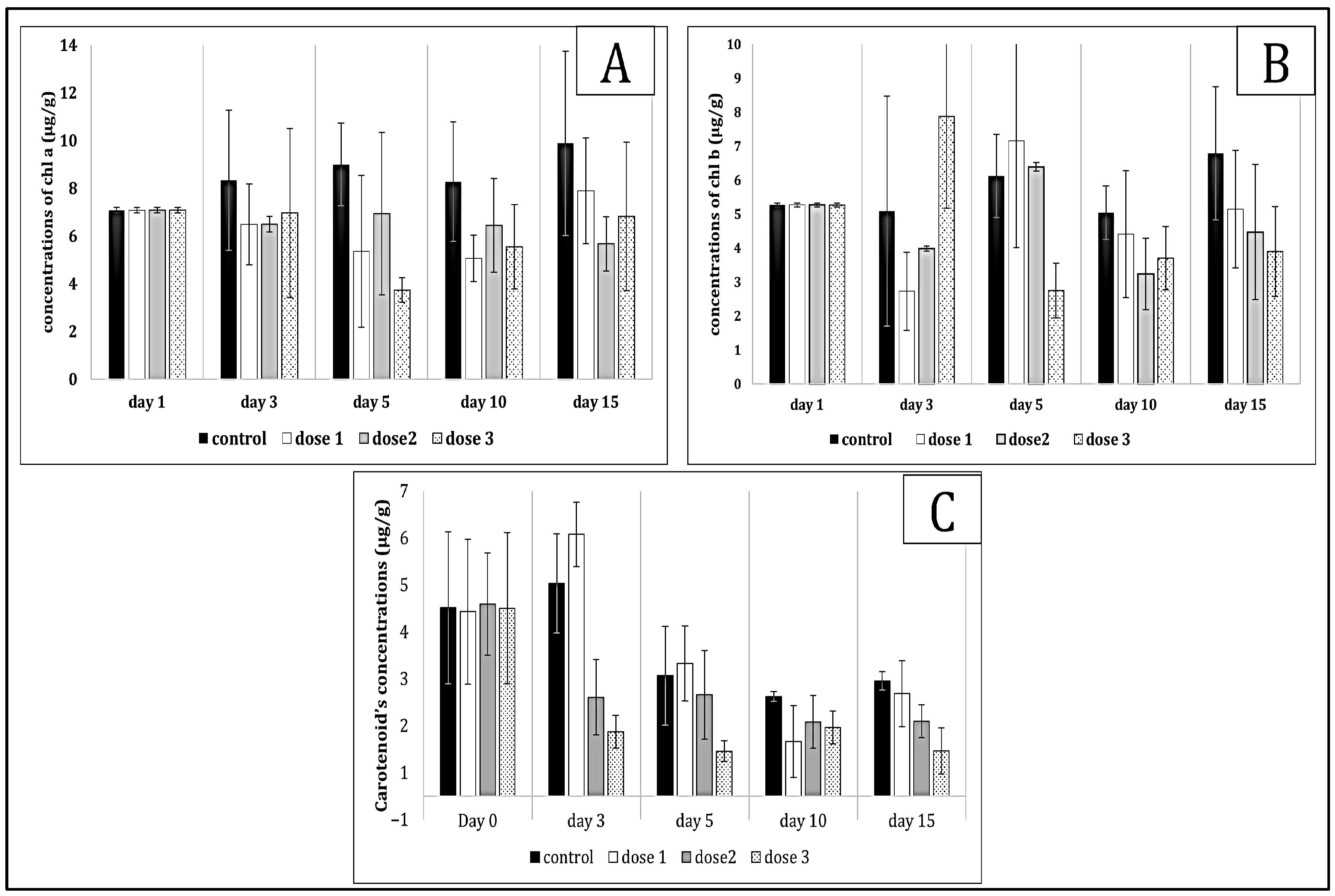
2.2. Effects on Chlorophyll a, b, and Carotenoids
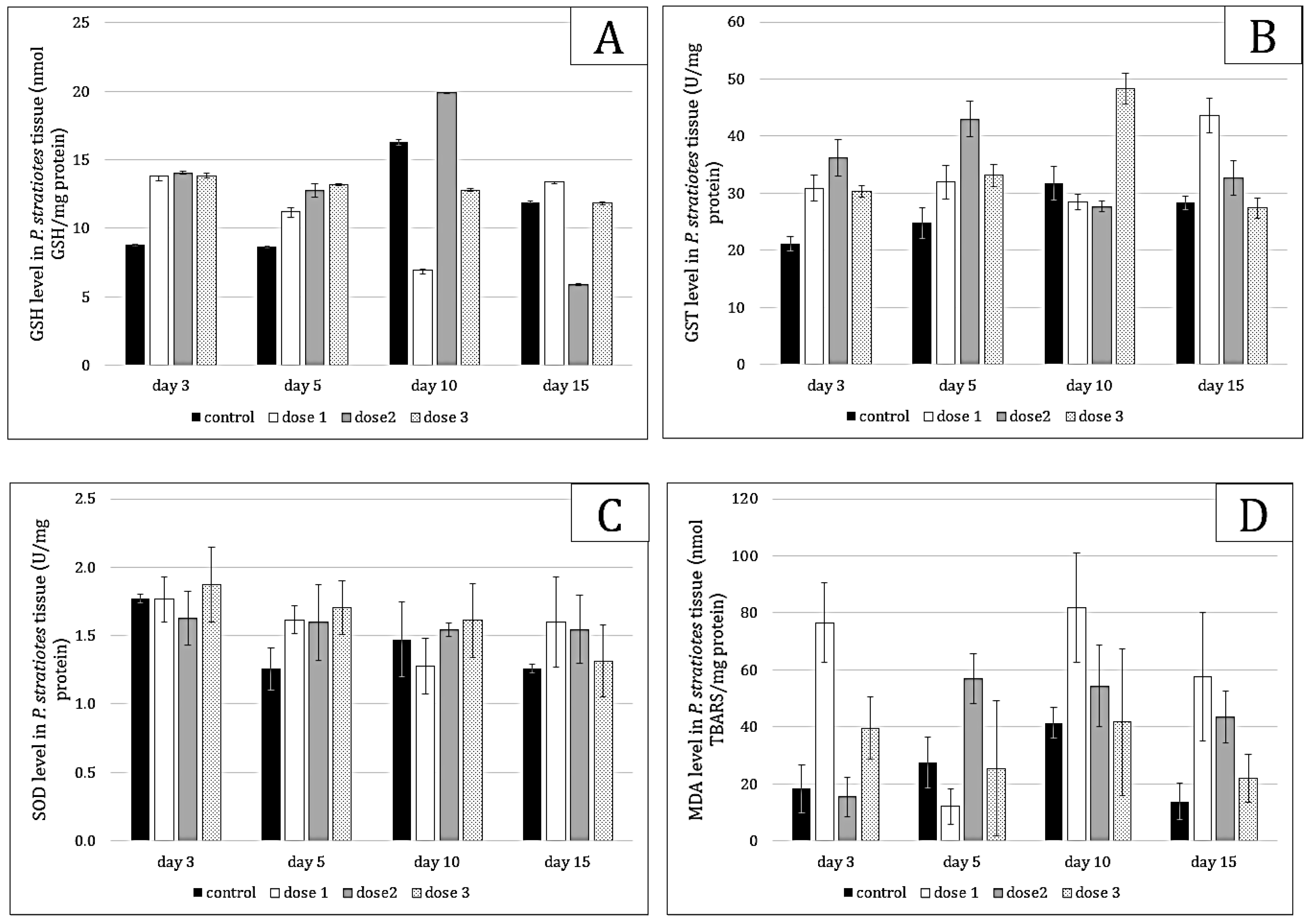
2.3. Stress Effect and Dose–Response Relationship
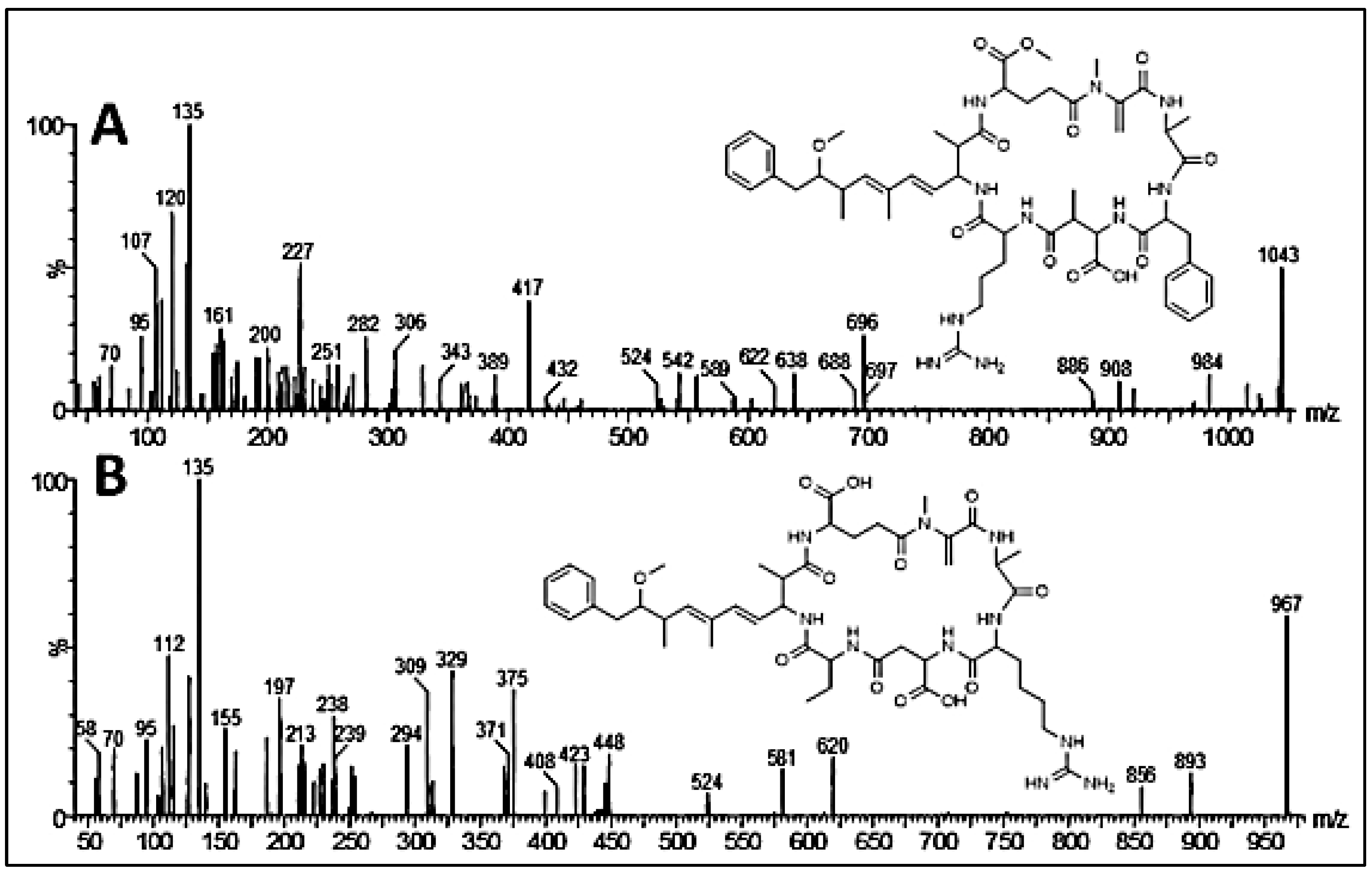
2.4. Bioaccumulation Results
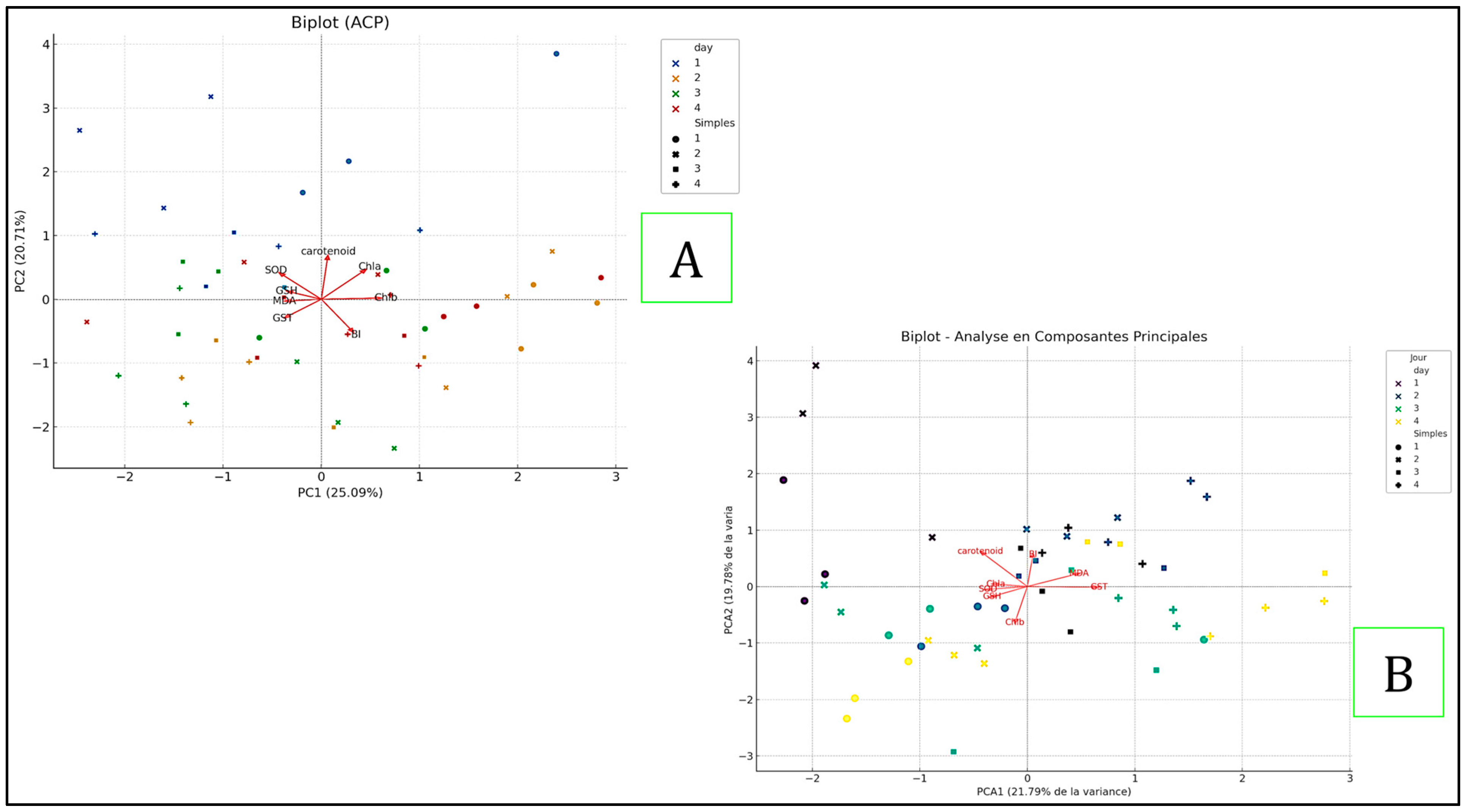
2.5. Comparison of the Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Material and Methods
5.1. Cyanobacteria Bloom Samples
5.2. Experiment Design
5.3. Environmental Parameters
5.4. Measurements of Biological Parameters
5.5. Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
5.6. Extraction, Determination, and Analysis of Microcystin Concentration
5.6.1. Detection and Quantification of Microcystins in Plant Cells
5.6.2. Calculation of Bioaccumulation Rate
5.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Cyanobacterial toxins: Microcystin-LR in drinking water. In Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C.; Oberemm, A.; Beattie, K.A.; Krause, E.; Codd, G.A.; Steinberg, C.E. Cyanobacterial toxins and the growth of aquatic plants: A review. Aquat. Toxicol. 1999, 46, 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sheekh, M.; Nabawy, S.; Osman, M.E. Bioaccumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in aquatic plants and their effects on plant biochemistry. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2010, 45, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Chorus, I.; Bartram, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Strategies for managing cyanobacterial blooms and protecting water quality in eutrophic lakes. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1749–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Water 2010, 2, 530–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Oliva, C.S.; Munoz, R.; De la Rosa, F. Antioxidant responses in macrophytes exposed to microcystins. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 204, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.H.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Increased production of antioxidant enzymes in plants exposed to microcystins. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barko, J.W.; Smart, R.M. Sediment-related mechanisms of growth limitation in submersed macrophytes. Ecology 1986, 67, 1328–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, G.; Jones, R. Photosynthesis and regulation of Rubisco in marine algae. Biochem. J. 2000, 349, 887–895. [Google Scholar]
- Blindow, I.; Hargeby, A.; Hilt, S. Facilitation of clear-water conditions in shallow lakes by macrophytes: Differences between charophyte and angiosperm dominance. Hydrobiologia 2014, 737, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodier, J. L’analyse de l’eau: Eaux Naturelles, eaux Résiduaires, eau de mer, 8th ed.; Dunod: Paris, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fogem, J.P. Conductivity and water quality: Parameters and considerations. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar]
- Mainstone, C.P.; Parr, W. Phytoremediation of cyanobacterial toxins. Water Res. 2002, 36, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Pflugmacher, S. Increased toxicity of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-RR in the presence of glutathione conjugation. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P. Effects of microcystins on chlorophyll fluorescence of aquatic plant species. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, V.M.; Pereira, E.; Antunes, J. Toxic cyanobacteria blooms in Portugal: Occurrence, types and toxins. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 1996, 31, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, M.H.; Pflugmacher, S. Increased production of carotenoids in response to microcystins. Phytochemistry 2013, 94, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, S.M.; Pinheiro, M.; Figueira, R. The role of antioxidant enzymes in cyanobacteria-plants interactions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Pflugmacher, S. Antioxidant responses in Ceratophyllum demersum exposed to microcystins. J. Plant Physiol. 2004, 161, 134–146. [Google Scholar]
- Pflugmacher, S. Promotion of oxidative stress in the aquatic macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum during biotransformation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-LR. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 70, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, B. Responses of Vallisneria natans to microcystin exposure. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Intensified oxidative stress in Ceratophyllum demersum during biotransformation of microcystin-LR. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18245–18254. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, P.; Srivastava, A. Glutathione-mediated detoxification in plants: A review. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2008, 63, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, L.L.; Monserrat, J.M. Biochemical responses to microcystins in aquatic organisms: A review. Toxicon 2010, 55, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, C. Effects of microcystin-LR on the tissue growth and physiological responses of the aquatic plant Iris pseudacorus L. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 200, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qin, B.; Zeng, Q. Enzymatic responses to microcystins in aquatic plants. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2004, 42, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Nimptsch, J.; Wiegand, C.; Pflugmacher, S. Uptake of microcystin-LR and -RR by aquatic macrophytes and the detoxification mechanism. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, N.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Accumulation and effects of microcystin-LR on the macrophyte Eichhornia crassipes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 91, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C.; Oberemm, A.; Beattie, K.A.; Krause, E.; Codd, G.A.; Steinberg, C.E.W. Identification of an enzymatically formed glutathione conjugate of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR: The first step of detoxication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gen. Subj. 1998, 1425, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Rahman, M.; Ali, S. Rapid bioaccumulation of microcystins in aquatic macrophytes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7486–7495. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.; Abid, M.; Zahid, A.; Malik, R.N. Metabolic limitations in aquatic plants exposed to microcystins. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 113586. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, R.; Baig, M.A.; Khan, S. Long-term bioaccumulation capacity of Ceratophyllum demersum in contaminated water. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhaddada, R.; Nélieu, S.; Nasri, H.; Delarue, G.; Bouaïcha, N. High diversity of microcystins in a Microcystis bloom from an Algerian lake. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikoshi, M.; Rinehart, K.L.; Sakai, R.; Stotts, R.R.; Dahlem, A.M.; Beasley, V.R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Evans, W.R. Identifica-tion of 12 hepatotoxins from a Homer Lake bloom of the cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis viridis, and Microcystis wesenbergii: Nine new microcystins. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Namikoshi, M.; Otsuki, A.; Rinehart, K.L.; Sivonen, K.; Watanabe, M.F. Low-energy collisionally activated decomposition and structural characterization of cyclic heptapeptide microcystins by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 34, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweigenbaum, J.A.; Henion, J.D.; Beattie, K.A.; Codd, G.A.; Poon, G.K. Direct analysis of microcystins by microbore liquid chromatography electrospray ionization ion-trap tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 23, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okello, W.; Portmann, C.; Erhard, M.; Gademann, K.; Kurmayer, R. Occurrence of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria in Ugandan freshwater habitats. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Sandvik, M.; Nonga, H.E.; Rundberget, T.; Wilkins, A.L.; Rise, F.; Ballot, A. Identification of microcystins in a Lake Victoria cyanobacterial bloom using LCeMS with thiol derivatization. Toxicon 2013, 70, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puddick, J.; Prinsep, M.R.; Wood, S.A.; Kaufononga, S.A.F.; Cary, S.C.; Hamilton, D.P. High levels of structural diversity observed in microcystins from Microcystis CAWBG11 and characterization of six new microcystin congeners. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5372–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geider, R.J.; Osborne, B.A. Algal Photosynthesis; Chapman Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol. 1987, 148, 350–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantization of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckberker, G.G.; Cory, J.G. Ribonucleotide reductase activity and growth of glutathione-depleted mouse leukemia L1210 cells in vitro. Cancer Lett. 1988, 40, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione-S-transferases: The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund, S.; Marklund, G. Involvement of the Superoxide Anion Radical in the Autoxidation of Pyrogallol and a Convenient Assay for Superoxide Dismutase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1974, 47, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, M.; Ahmad, I.; Sayeed, I.; Athar, M.; Raisuddin, S. Pollutant-induced overactivation of phagocytes is concomitantly associated with peroxidative damage in fish tissues. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 49, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xie, P.; Zhang, X. Oxidative stress response after prolonged exposure of domestic rabbit to a lower dosage of extracted microcystins. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 27, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamer, F.Z.; Zaidi, H.; Nasri, H.; Lvova, L.; Nouri, N.; Sedrati, F.; Amrani, A.; Beldjoudi, N.; Li, X. Bioremediation of Contaminated Water: The Potential of Aquatic Plants Ceratophyllum demersum and Pistia stratiotes Against Toxic Bloom. Toxins 2025, 17, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100490
Tamer FZ, Zaidi H, Nasri H, Lvova L, Nouri N, Sedrati F, Amrani A, Beldjoudi N, Li X. Bioremediation of Contaminated Water: The Potential of Aquatic Plants Ceratophyllum demersum and Pistia stratiotes Against Toxic Bloom. Toxins. 2025; 17(10):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100490
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamer, Fatma Zohra, Hadjer Zaidi, Hichem Nasri, Larisa Lvova, Nada Nouri, Fateh Sedrati, Amina Amrani, Nassima Beldjoudi, and Xi Li. 2025. "Bioremediation of Contaminated Water: The Potential of Aquatic Plants Ceratophyllum demersum and Pistia stratiotes Against Toxic Bloom" Toxins 17, no. 10: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100490
APA StyleTamer, F. Z., Zaidi, H., Nasri, H., Lvova, L., Nouri, N., Sedrati, F., Amrani, A., Beldjoudi, N., & Li, X. (2025). Bioremediation of Contaminated Water: The Potential of Aquatic Plants Ceratophyllum demersum and Pistia stratiotes Against Toxic Bloom. Toxins, 17(10), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100490






