ProToxin, a Predictor of Protein Toxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Choice of Algorithm
2.2. Features and Feature Selection
2.3. Method Development
2.4. Comparison to Other Methods
2.5. ProToxin Server
3. Conclusions
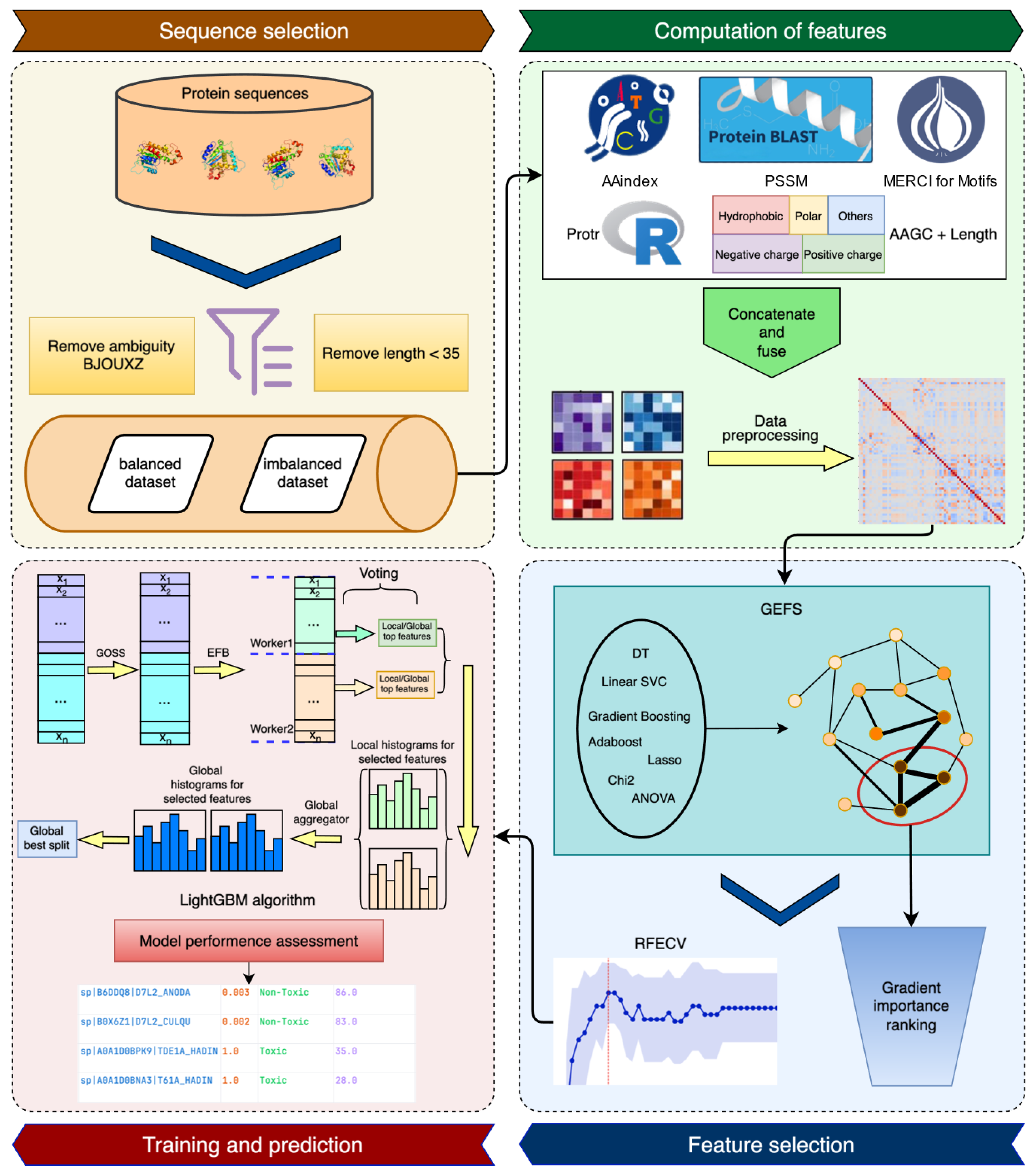
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection and Cleaning
4.2. Features
4.3. Feature Selection
4.4. Model Architecture
4.5. Performance Assessment
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Utkin, Y. Animal Venoms and Their Components: Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Toxins 2021, 13, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schendel, V.; Rash, L.D.; Jenner, R.A.; Undheim, E.A.B. The Diversity of Venom: The Importance of Behavior and Venom System Morphology in Understanding Its Ecology and Evolution. Toxins 2019, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J. Venomous animals: Clinical toxinology. EXS 2010, 100, 233–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M. The venom menace. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, R1209–R1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, H.; Moin, S.F.; Choudhary, M.I. Snake Venom: From Deadly Toxins to Life-saving Therapeutics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1874–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, T.B.; Clark, R.J. Advances in venom peptide drug discovery: Where are we at and where are we heading? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Hwang, D.H.; Mohan Prakash, R.L.; Asirvatham, R.D.; Lee, H.; Heo, Y.; Munawir, A.; Seyedian, R.; Kang, C. Animal Venom in Modern Medicine: A Review of Therapeutic Applications. Toxins 2025, 17, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, E. AI-designed proteins tackle century-old problem—Making snake antivenoms. Nature 2025, 637, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, L.; Naderi, M.; Liu, T.; Wu, H.C.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Brylinski, M. eToxPred: A machine learning-based approach to estimate the toxicity of drug candidates. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setiya, A.; Jani, V.; Sonavane, U.; Joshi, R. MolToxPred: Small molecule toxicity prediction using machine learning approach. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 4201–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Eckert, A.O.; Schrey, A.K.; Preissner, R. ProTox-II: A webserver for the prediction of toxicity of chemicals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W257–W263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sá, A.G.C.; Long, Y.; Portelli, S.; Pires, D.E.V.; Ascher, D.B. toxCSM: Comprehensive prediction of small molecule toxicity profiles. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ning, C.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Shu, Y.; Liang, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. ToxMPNN: A deep learning model for small molecule toxicity prediction. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 44, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, M.; Amawate, A.; Singh, A.; Bagler, G. ToxinPredictor: Computational models to predict the toxicity of molecules. Chemosphere 2025, 370, 143900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P. BTXpred: Prediction of bacterial toxins. In Silico Biol. 2007, 7, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, H.; Guo, Z.; Ahmad, R.M.; Ahmed, Z.; Cai, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Shi, Z. Deep-STP: A deep learning-based approach to predict snake toxin proteins by using word embeddings. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1291352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringeval, A.; Farhat, S.; Fedosov, A.; Gerdol, M.; Greco, S.; Mary, L.; Modica, M.V.; Puillandre, N. DeTox: A pipeline for the detection of toxins in venomous organisms. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P. Prediction of neurotoxins based on their function and source. In Silico Biol. 2007, 7, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, E.S.; Hardy, M.C.; Wood, D.; Bailey, T.; King, G.F. SVM-based prediction of propeptide cleavage sites in spider toxins identifies toxin innovation in an Australian tarantula. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khabbaz, H.; Karimi-Jafari, M.H.; Saboury, A.A.; BabaAli, B. Prediction of antimicrobial peptides toxicity based on their physico-chemical properties using machine learning techniques. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ye, X.; Xue, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Wei, L. ATSE: A peptide toxicity predictor by exploiting structural and evolutionary information based on graph neural network and attention mechanism. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naamati, G.; Askenazi, M.; Linial, M. ClanTox: A classifier of short animal toxins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W363–W368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimikondori, H.; Sutherland, D.; Yanai, A.; Richter, A.; Salehi, A.; Li, C.; Coombe, L.; Kotkoff, M.; Warren, R.L.; Birol, I. Structure-aware deep learning model for peptide toxicity prediction. Protein Sci. 2024, 33, e5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, W.; Tang, Y. ToxGIN: An In silico prediction model for peptide toxicity via graph isomorphism networks integrating peptide sequence and structure information. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Ye, X.; Sakurai, T.; Mu, Z.; Wei, L. ToxIBTL: Prediction of peptide toxicity based on information bottleneck and transfer learning. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1514–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathore, A.S.; Choudhury, S.; Arora, A.; Tijare, P.; Raghava, G.P.S. ToxinPred 3.0: An improved method for predicting the toxicity of peptides. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 179, 108926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morozov, V.; Rodrigues, C.H.M.; Ascher, D.B. CSM-Toxin: A Web-Server for Predicting Protein Toxicity. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Kihara, D. NNTox: Gene Ontology-Based Protein Toxicity Prediction Using Neural Network. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gacesa, R.; Barlow, D.J.; Long, P.F. Machine learning can differentiate venom toxins from other proteins having non-toxic physiological functions. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2016, 2, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zuallaert, J.; Wang, X.; Shen, H.B.; Campos, E.P.; Marushchak, D.O.; De Neve, W. ToxDL: Deep learning using primary structure and domain embeddings for assessing protein toxicity. Bioinformatics 2021, 36, 5159–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.J.; Brewer, M.S. TOXIFY: A deep learning approach to classify animal venom proteins. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Naorem, L.D.; Jain, S.; Raghava, G.P.S. ToxinPred2: An improved method for predicting toxicity of proteins. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mall, R.; Singh, A.; Patel, C.N.; Guirimand, G.; Castiglione, F. VISH-Pred: An ensemble of fine-tuned ESM models for protein toxicity prediction. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Cao, D.S.; Zhu, M.F.; Xu, Q.S. protr/ProtrWeb: R package and web server for generating various numerical representation schemes of protein sequences. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1857–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Vihinen, M. Conservation and covariance in PH domain sequences: Physicochemical profile and information theoretical analysis of XLA-causing mutations in the Btk PH domain. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2004, 17, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, S.; Kanehisa, M. AAindex: Amino acid index database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vens, C.; Rosso, M.N.; Danchin, E.G. Identifying discriminative classification-based motifs in biological sequences. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistella, E.; Ghiassian, D.; Barabási, A.L. Improving the performance and interpretability on medical datasets using graphical ensemble feature selection. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, btae341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darst, B.F.; Malecki, K.C.; Engelman, C.D. Using recursive feature elimination in random forest to account for correlated variables in high dimensional data. BMC Genet. 2018, 19, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the KDD ‘16: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree; Neural Information Processing Systems: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]

| LightGBM | RF | SVM | XGBoost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | 360.05 | 354.35 | 368.4 | 366.55 |
| TN | 389.95 | 397.20 | 329.55 | 389.75 |
| FP | 30.65 | 23.40 | 91.05 | 30.85 |
| FN | 60.55 | 66.25 | 152.20 | 54.05 |
| NPV | 0.866 | 0.857 | 0.684 | 0.879 |
| PPV | 0.922 | 0.938 | 0.747 | 0.923 |
| Specificity | 0.927 | 0.944 | 0.738 | 0.927 |
| Sensitivity | 0.856 | 0.842 | 0.638 | 0.871 |
| Accuracy | 0.892 | 0.894 | 0.711 | 0.899 |
| MCC | 0.786 | 0.791 | 0.426 | 0.800 |
| OPM | 0.711 | 0.717 | 0.363 | 0.728 |
| F1 | 0.888 | 0.888 | 0.688 | 0.896 |
| AUC | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.711 | 0.899 |
| Features | Selected Features | Protr-Based Features | PSSM | AAindex | Amino Acid Groups + Length | Motifs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimension | 88 | 1920 | 20 | 617 | 7 | 50 |
| TP | 371.45 | 357.45 | 369.10 | 357.90 | 300.65 | 31.10 |
| TN | 396.10 | 401.60 | 393.10 | 392.55 | 320.95 | 420.55 |
| FP | 24.50 | 19.00 | 27.50 | 28.05 | 99.65 | 0.05 |
| FN | 49.15 | 63.15 | 51.50 | 62.70 | 119.95 | 389.50 |
| NPV | 0.890 | 0.864 | 0.884 | 0.863 | 0.728 | 0.519 |
| PPV | 0.938 | 0.950 | 0.931 | 0.928 | 0.751 | 0.999 |
| Specificity | 0.942 | 0.955 | 0.935 | 0.933 | 0.763 | 1.000 |
| Sensitivity | 0.883 | 0.850 | 0.877 | 0.851 | 0.715 | 0.074 |
| Accuracy | 0.912 | 0.902 | 0.906 | 0.892 | 0.739 | 0.537 |
| MCC | 0.827 | 0.809 | 0.814 | 0.787 | 0.479 | 0.195 |
| OPM | 0.761 | 0.739 | 0.746 | 0.713 | 0.404 | 0.231 |
| F1 | 0.910 | 0.897 | 0.903 | 0.887 | 0.732 | 0.137 |
| AUC | 0.912 | 0.902 | 0.906 | 0.892 | 0.739 | 0.537 |
| Feature Group | Feature Name | Feature Group | Feature Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| protr_ctd a | prop2.G2.residue25 | protr_ctriad | VS362 |
| prop1.G3.residue0 | VS261 | ||
| prop7.G3.residue0 | VS131 | ||
| prop7.G1.residue25 | VS314 | ||
| prop5.G2.residue0 | VS552 | ||
| prop1.G3.residue25 | VS236 | ||
| prop5.G2.residue25 | VS215 | ||
| prop6.G1.residue75 | VS136 | ||
| prop5.G3.residue0 | VS722 | ||
| prop6.G1.residue50 | VS652 | ||
| prop5.G1.residue0 | VS216 | ||
| prop2.G2.residue50 | VS327 | ||
| prop2.G3.residue0 | protr_dpc | SL | |
| prop1.G2.residue0 | CS | ||
| prop6.G1.residue0 | QL | ||
| prop2.G2.residue75 | CC | ||
| prop2.G1.residue25 | VE | ||
| secondarystruct.Group2 | HC | ||
| prop6.G3.residue25 | CY | ||
| prop7.G1.residue50 | VC | ||
| prop7.G3.residue100 | RV | ||
| prop7.G1.residue0 | GY | ||
| prop5.G3.residue100 | EI | ||
| prop1.G1.residue25 | GA | ||
| prop6.G3.residue0 | LA | ||
| prop5.G3.residue75 | ID | ||
| prop1.G3.residue50 | VR | ||
| secondarystruct.Group1 | DI | ||
| prop2.G2.residue0 | AL | ||
| protr_mb | CHAM820102.lag3 | QA | |
| CHAM820102.lag30 | CF | ||
| protr_qso | Schneider.Xd.28 | SC | |
| Schneider.Xd.27 | CE | ||
| protr_apaac | Pc1.N | protr_geary | CIDH920105.lag1 |
| Pc1.A | protr_aac | C | |
| Pc1.C | Q | ||
| AAindex | FASG760104 | PSSM | PSSM_W |
| QIAN880117 | PSSM_C | ||
| GEOR030101 | PSSM_Q | ||
| RISJ880101 | PSSM_S | ||
| BEGF750102 | PSSM_N | ||
| BURA740102 | PSSM_G | ||
| BEGF750101 | PSSM_F | ||
| SUYM030101 | PSSM_A |
| Model | TP | TN | FP | FN | NPV | PPV | Specificity | Sensitivity | Accuracy | MCC | OPM | F1 | AUC | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ProToxin | 225 | 457 | 17 | 54 | 0.894 | 0.930 | 0.964 | 0.806 | 0.906 | 0.797 | 0.728 | 0.864 | 0.885 | 1.000 |
| XGBoost-88 | 229 | 453 | 21 | 50 | 0.901 | 0.916 | 0.956 | 0.821 | 0.906 | 0.796 | 0.728 | 0.866 | 0.888 | 1.000 |
| ToxinPred2 | 194 | 451 | 23 | 85 | 0.841 | 0.894 | 0.951 | 0.695 | 0.857 | 0.690 | 0.608 | 0.782 | 0.823 | 1.000 |
| ToxinPred2-hybrid | 225 | 430 | 44 | 54 | 0.888 | 0.836 | 0.907 | 0.806 | 0.870 | 0.719 | 0.639 | 0.821 | 0.857 | 1.000 |
| ToxIBTL | 161 | 459 | 15 | 118 | 0.795 | 0.915 | 0.968 | 0.577 | 0.823 | 0.622 | 0.540 | 0.708 | 0.773 | 1.000 |
| VISH-Pred | 210 | 451 | 7 | 67 | 0.871 | 0.968 | 0.985 | 0.758 | 0.899 | 0.789 | 0.718 | 0.850 | 0.871 | 0.976 |
| CSM-Toxin | 203 | 469 | 5 | 76 | 0.861 | 0.976 | 0.989 | 0.728 | 0.892 | 0.774 | 0.701 | 0.834 | 0.859 | 1.000 |
| MultiToxPred | 172 | 278 | 196 | 107 | 0.722 | 0.467 | 0.586 | 0.616 | 0.598 | 0.196 | 0.214 | 0.532 | 0.601 | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Vihinen, M. ProToxin, a Predictor of Protein Toxicity. Toxins 2025, 17, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100489
Yang Y, Zhang H, Vihinen M. ProToxin, a Predictor of Protein Toxicity. Toxins. 2025; 17(10):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100489
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yang, Haohan Zhang, and Mauno Vihinen. 2025. "ProToxin, a Predictor of Protein Toxicity" Toxins 17, no. 10: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100489
APA StyleYang, Y., Zhang, H., & Vihinen, M. (2025). ProToxin, a Predictor of Protein Toxicity. Toxins, 17(10), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100489





