The Role of Indoxyl Sulfate in Exacerbating Colorectal Cancer During Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: Insights into the Akt/β-Catenin/c-Myc and AhR/c-Myc Pathways in HCT-116 Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
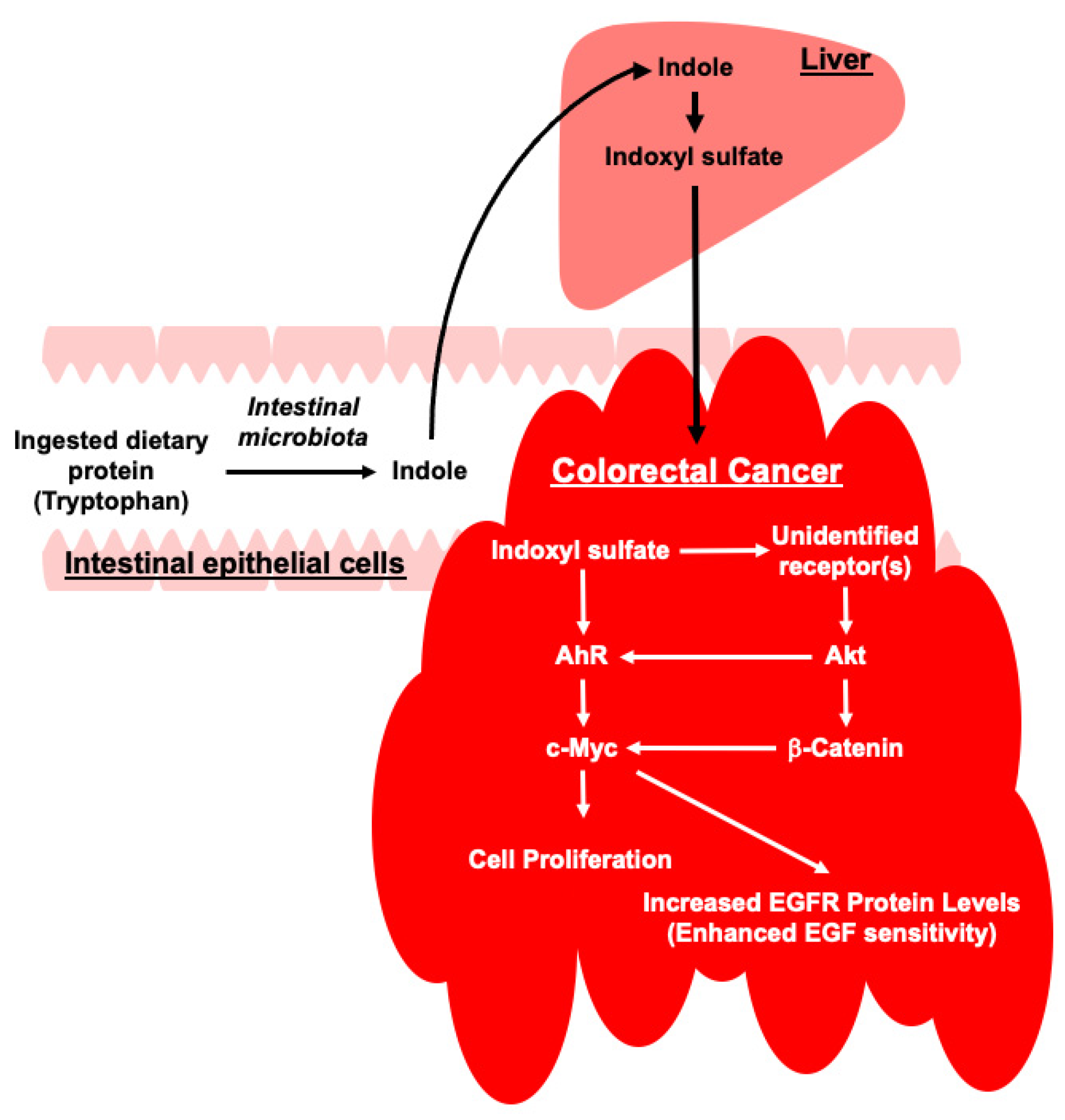
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Indoxyl Sulfate Induces Proliferation of HCT-116 CRC Cells
2.2. Indoxyl Sulfate-Induced Proliferation of HCT-116 CRC Cells Is Mediated by Increased c-Myc Expression
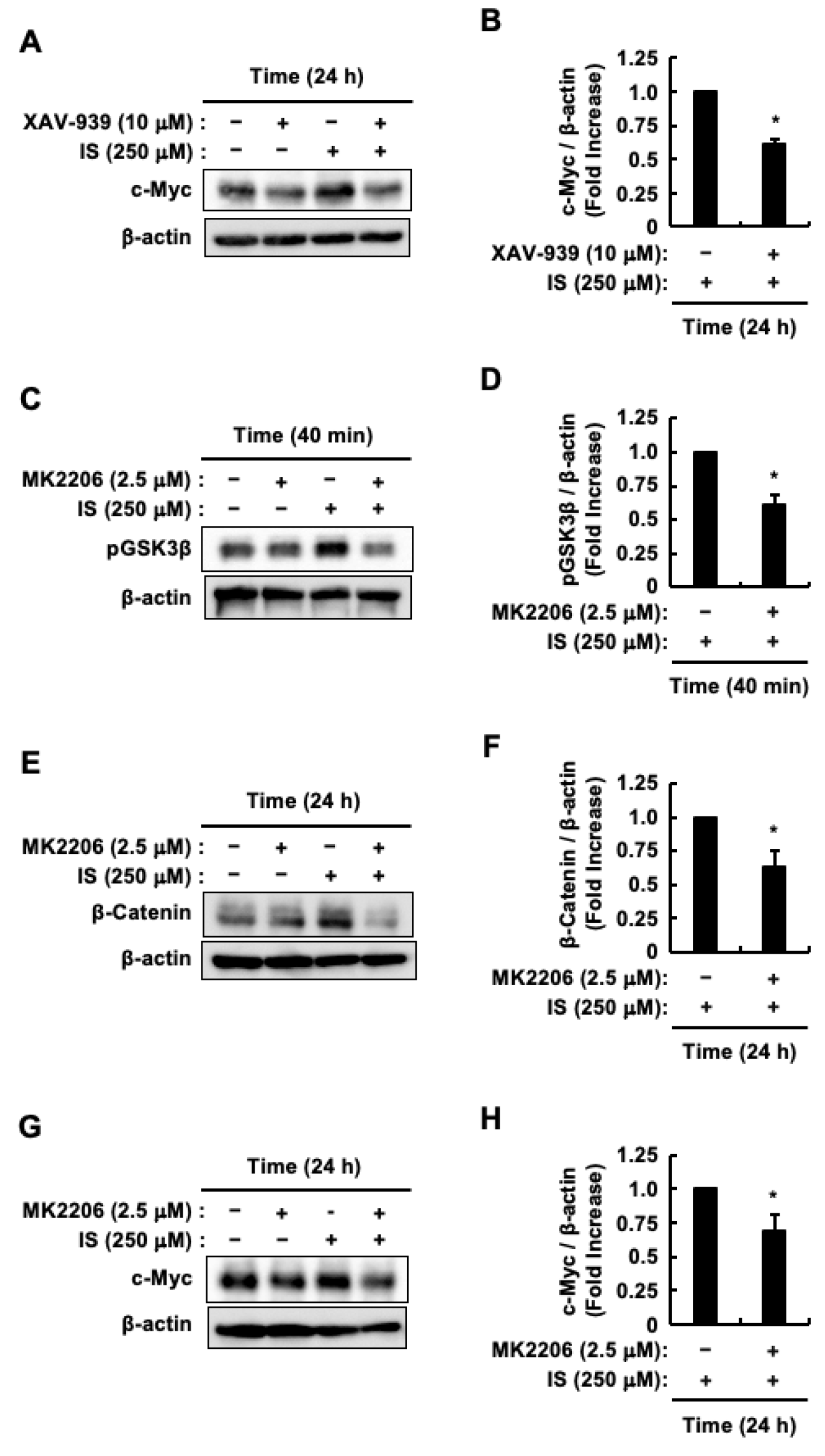
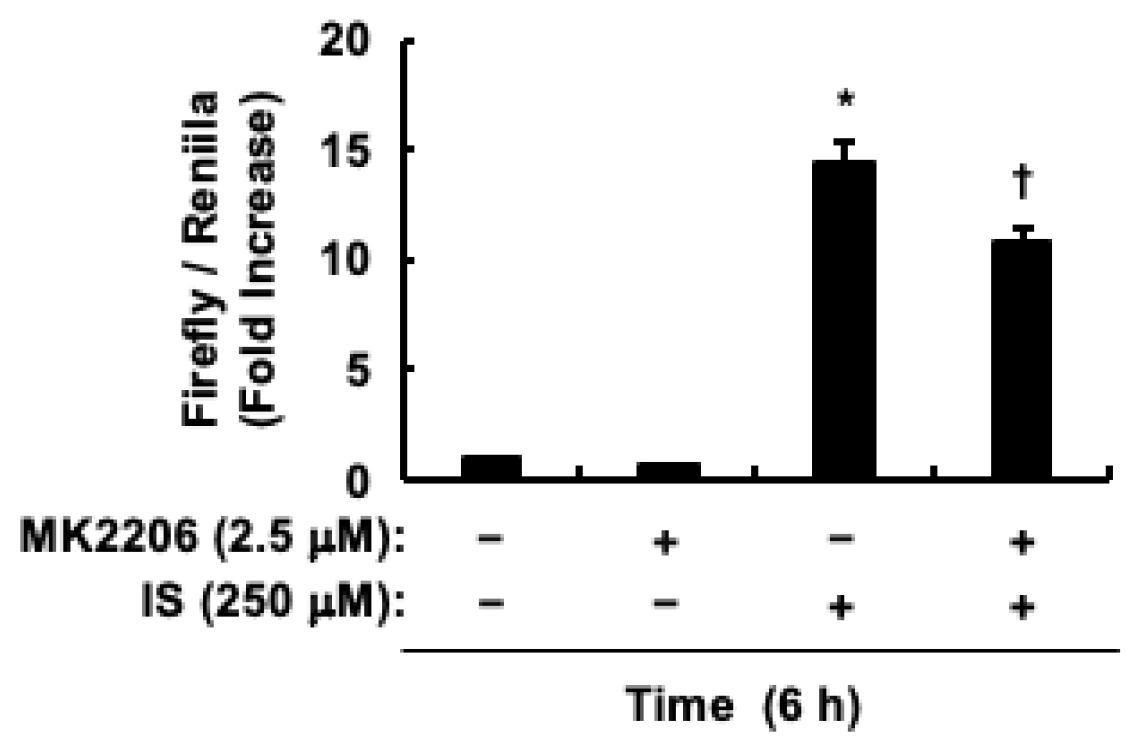
2.3. Indoxyl Sulfate Activates Akt/β-Catenin/c-Myc Signaling Pathway in HCT-116 CRC Cells
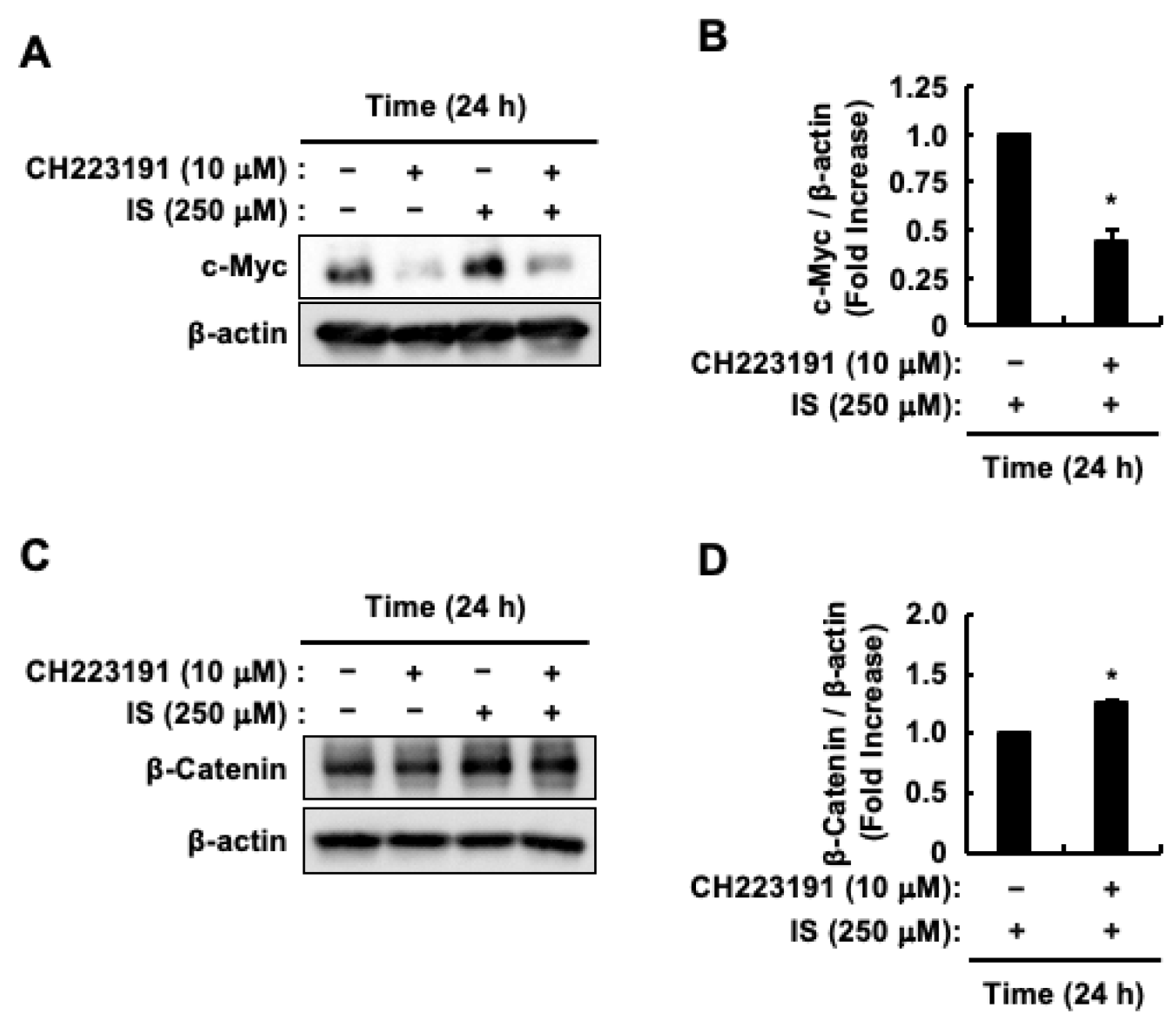
2.4. AhR Activation Induced by Indoxyl Sulfate Increases the Protein Levels of c-Myc But Decreases the Protein Levels of β-Catenin in HCT-116 CRC Cells
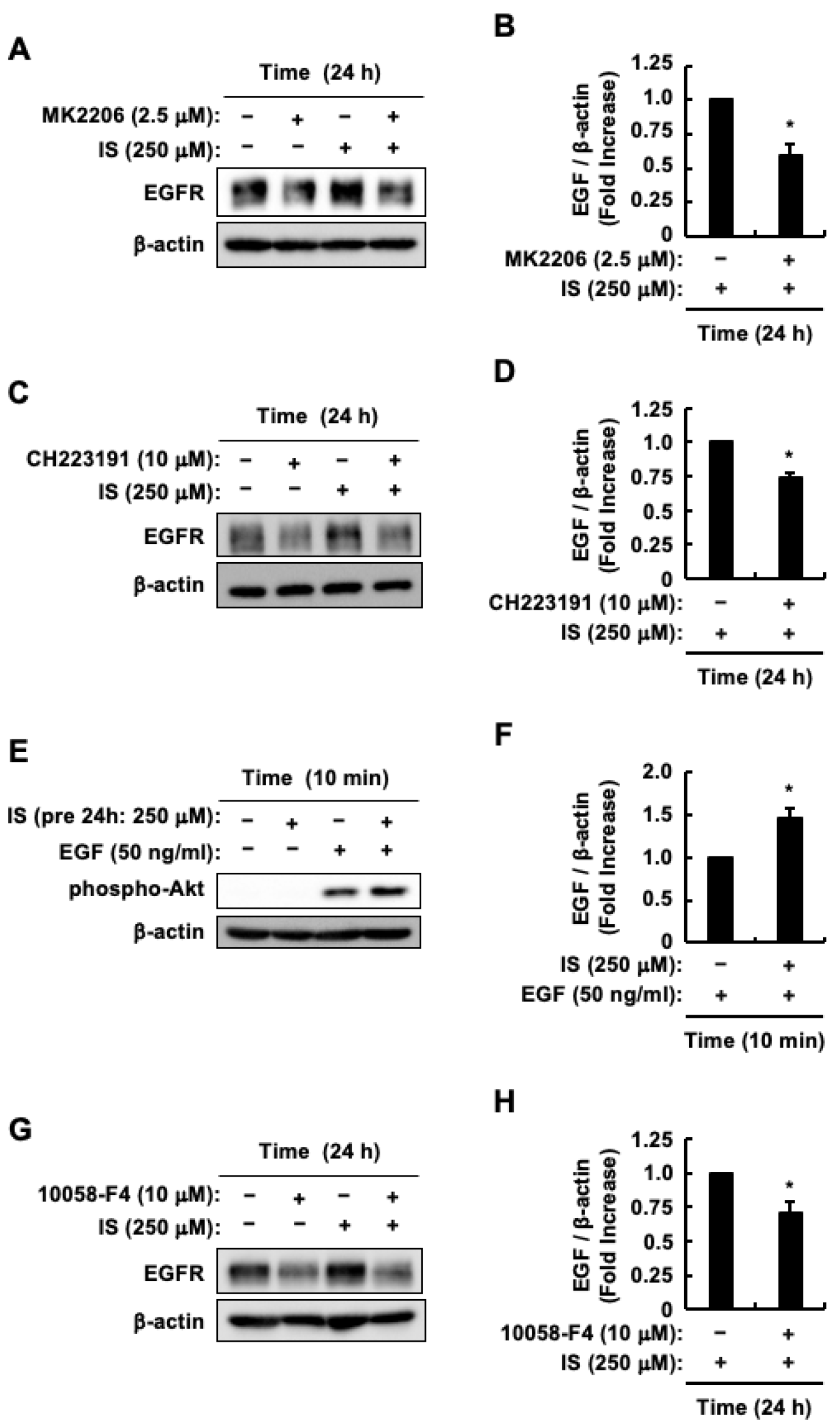
2.5. Enhanced Sensitivity of HCT-116 CRC Cells to EGF Was Caused by an Increase in EGFR Protein Levels Through Indoxyl Sulfate-Induced Activation of the AhR/c-Myc and Akt/β-Catenin/c-Myc Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Cell Culture
5.3. Quantitation of Cell Proliferation
5.4. Immunoblotting
5.5. Transfection and Luciferase Assays
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Osborn, J.W.; Tyshynsky, R.; Vulchanova, L. Function of Renal Nerves in Kidney Physiology and Pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2021, 83, 429–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E.; Bilous, R.W.; Coresh, J.; De Francisco, A.L.M.; De Jong, P.E.; Griffith, K.E.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Iseki, K.; Lamb, E.J.; et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.K.; Knicely, D.H.; Grams, M.E. Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis and Management: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.Y. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, D.E.; Sutherland, R.L.; Town, S.; Chow, K.; Fan, J.; Forbes, N.; Heitman, S.J.; Hilsden, R.J.; Brenner, D.R. Risk Factors for Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1229–1240.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, P.; Xu, X. Risk factors for early-onset colorectal cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1132306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qudimat, A.R.; Al Darwish, M.B.; Altahtamouni, S.B.; Singh, K.; Al-Zoubi, R.M.; Aboumarzouk, O.M.; Al-Ansari, A. Chronic kidney diseases and the risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arab J. Urol. 2023, 21, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abureesh, M.; Alkhayyat, M.; Abou Saleh, M.; Deeb, L. The Epidemiology of Colorectal Cancer in Chronic Kidney Disease in the U.S.: A Population-Based Study (2014–2019). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, S75–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Chang, T.C.; Chao, T.Y.; Huang, M.T.; Lin, H.W. Risk of colorectal cancer in chronic kidney disease: A matched cohort study based on administrative data. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 3885–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Nam, H.; Lee, B.; Park, B.K.; Kim, J.K.; Ryoo, S.B.; Park, K.J.; Han, E.C. Real-world survival after colorectal surgery for malignancy in Korean patients with chronic kidney disease: An analysis of Korean healthcare big data, 2002–2019. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2023, 105, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.; Schmidt, S.; Kastner, C.; Denk, S.; Kettler, J.; Müller, N.; Germer, C.; Wolf, E.; Gallant, P.; Wiegering, A. Targeting bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) inhibits MYC expression in colorectal cancer cells. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Zhou, T.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Dong, X.; Yi, F.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Z.; et al. RNF8 induces β-catenin-mediated c-Myc expression and promotes colon cancer proliferation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandvold, K.A.; Neiman, P.; Ruddell, A. Angiogenesis is an early event in the generation of myc-induced lymphomas. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2780–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casacuberta-Serra, S.; Soucek, L. Myc and Ras, the Bonnie and Clyde of immune evasion. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, S457–S459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Lu, M.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, L. c-Myc maintains the self-renewal and chemoresistance properties of colon cancer stem cells. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4487–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, M.; Greathouse, K.L. Targeting Dietary and Microbial Tryptophan-Indole Metabolism as Therapeutic Approaches to Colon Cancer. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango, D.; Mariadason, J.M.; Wilson, A.J.; Yang, W.; Corner, G.A.; Nicholas, C.; Aranes, M.J.; Augenlicht, L.H. c-Myc overexpression sensitises colon cancer cells to camptothecin-induced apoptosis. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawy, M.; Usui, T.; Yamawaki, H.; Sasaki, K. Emerging Roles of C-Myc in Cancer Stem Cell-Related Signaling and Resistance to Cancer Chemotherapy: A Potential Therapeutic Target Against Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Jung, D.B.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Kang, S.E.; Srivastava, S.K.; Yun, M.; Kim, S.H. Zinc finger protein 746 promotes colorectal cancer progression via c-Myc stability mediated by glycogen synthase kinase 3β and F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3715–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strippoli, A.; Cocomazzi, A.; Basso, M.; Cenci, T.; Ricci, R.; Pierconti, F.; Cassano, A.; Fiorentino, V.; Barone, C.; Bria, E.; et al. c-MYC Expression Is a Possible Keystone in the Colorectal Cancer Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors. Cancers 2020, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.C.; Sparks, A.B.; Rago, C.; Hermeking, H.; Zawel, L.; da Costa, L.T.; Morin, P.J.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science 1998, 281, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Lv, J.; Sun, D.; Huang, Y. Therapeutic strategies targeting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling for colorectal cancer (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, Y.; Li, W.H.; Zhao, G.F.; Li, X.H.; Wei, L.; Liu, G.B.; Huang, H. MicroRNA-124 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and suppresses tumor growth by interacting with PLCB1 and regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Z.; An, N.; Qin, J.; Yang, J.; Sun, H.; Yang, W. Long non-coding RNA Linc00675 suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer via acting on miR-942 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormanns, S.; Neumann, J.; Horst, D.; Kirchner, T.; Jung, A. WNT signaling and distant metastasis in colon cancer through transcriptional activity of nuclear β-Catenin depend on active PI3K signaling. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2999–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Gazourian, L.; Quadri, S.A.; Romieu-Mourez, R.; Sherr, D.H.; Sonenshein, G.E. The RelA NF-kappaB subunit and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) cooperate to transactivate the c-myc promoter in mammary cells. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5498–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, W. Tryptophan metabolism induced by TDO2 promotes prostatic cancer chemotherapy resistance in a AhR/c-Myc dependent manner. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Davidson, L.A.; Hensel, M.; Yoon, G.; Landrock, K.; Allred, C.; Jayaraman, A.; Ivanov, I.; Safe, S.H.; Chapkin, R.S. Loss of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Promotes Colon Tumorigenesis in ApcS580/+; KrasG12D/+ Mice. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, I.A.; Patterson, A.D.; Perdew, G.H. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands in cancer: Friend and foe. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.; Stanford Zulick, E.; Novikov, O.; Parks, A.J.; Schlezinger, J.J.; Wang, Z.; Laroche, F.; Feng, H.; Mulas, F.; Monti, S.; et al. Towards Resolving the Pro- and Anti-Tumor Effects of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Peng, Z.; Raufman, J.P. Src-mediated aryl hydrocarbon and epidermal growth factor receptor cross talk stimulates colon cancer cell proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G1006–G1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, T.; Chung, S.; Sakai, H.; Ohata, H.; Obata, Y.; Shiokawa, D.; Mizoguchi, Y.; Kubo, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Taniguchi, H.; et al. Stemness and immune evasion conferred by the TDO2-AHR pathway are associated with liver metastasis of colon cancer. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanford, E.A.; Wang, Z.; Novikov, O.; Mulas, F.; Landesman-Bollag, E.; Monti, S.; Smith, B.W.; Seldin, D.C.; Murphy, G.J.; Sherr, D.H. The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the development of cells with the molecular and functional characteristics of cancer stem-like cells. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Yu, S.; Tan, Q.; Guo, P.; Liu, H. Role of AhR in regulating cancer stem cell-like characteristics in choriocarcinoma. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Du, Q.; Yang, M.; Ding, Y.; Hu, R. Blockade of IDO-Kynurenine-AhR Axis Ameliorated Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer via Inhibiting Immune Tolerance. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 1179–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachida, S.; Mizutani, S.; Shiroma, H.; Shiba, S.; Nakajima, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Watanabe, H.; Masuda, K.; Nishimoto, Y.; Kubo, M.; et al. Metagenomic and metabolomic analyses reveal distinct stage-specific phenotypes of the gut microbiota in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Zhao, L.; Hao, Y.; Qin, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Bian, W.; Zuo, L.; et al. Aberrant gut microbiota alters host metabolome and impacts renal failure in humans and rodents. Gut 2020, 69, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J. Indole as an intercellular signal in microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, T.; Shimizu, H. Indoxyl sulfate induces nephrovascular senescence. J. Ren. Nutr. 2012, 22, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, T.; Ise, M. Indoxyl sulfate, a circulating uremic toxin, stimulates the progression of glomerular sclerosis. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1994, 124, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, E.; Saigusa, D.; Mishima, E.; Uchida, T.; Miura, D.; Morikawa-Ichinose, T.; Kisu, K.; Sekimoto, A.; Saito, R.; Oe, Y.; et al. Impact of the Oral Adsorbent AST-120 on Organ-Specific Accumulation of Uremic Toxins: LC-MS/MS and MS Imaging Techniques. Toxins 2017, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, K.; Kawahara, H.; Nishimura, K.; Jisaka, M.; Yokota, K.; Shimizu, H. Skatole regulates intestinal epithelial cellular functions through activating aryl hydrocarbon receptors and p38. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 510, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.M.I.; Kurata, K.; Yuasa, K.; Koto, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Shimizu, H. Suppression of TNFα expression induced by indole-3-acetic acid is not mediated by AhR activation in Caco-2 cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2021, 85, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kurata, K.; Ishii, K.; Koto, Y.; Naito, K.; Yuasa, K.; Shimizu, H. Skatole-induced p38 and JNK activation coordinately upregulates, whereas AhR activation partially attenuates TNFα expression in intestinal epithelial cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2023, 87, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomii, A.; Higa, M.; Naito, K.; Kurata, K.; Kobayashi, J.; Takei, C.; Yuasa, K.; Koto, Y.; Shimizu, H. Activation of the TLR4-JNK but not the TLR4-ERK pathway induced by indole-3-acetic acid exerts anti-proliferative effects on Caco-2 cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2023, 87, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.; Naito, K.; Tanaka, D.; Koto, Y.; Kurata, K.; Shimizu, H. Molecular Mechanisms of Skatole-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Intestinal Epithelial Caco-2 Cells: Implications for Colorectal Cancer and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cells 2024, 13, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, R.; De, A.; Izhar, R.; Abate, M.; Zappavigna, S.; Capasso, A.; Perna, A.F.; La Russa, A.; Capasso, G.; Caraglia, M.; et al. Possible Effects of Uremic Toxins p-Cresol, Indoxyl Sulfate, p-Cresyl Sulfate on the Development and Progression of Colon Cancer in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure. Genes 2023, 14, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichisaka, Y.; Yano, S.; Nishimura, K.; Niwa, T.; Shimizu, H. Indoxyl sulfate contributes to colorectal cancer cell proliferation and increased EGFR expression by activating AhR and Akt. Biomed. Res. 2024, 45, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, H.; Kitayama, J.; Sunami, E.; Watanabe, T. Impact of chronic kidney disease on outcomes of surgical resection for primary colorectal cancer: A retrospective cohort review. Dis. Colon Rectum 2012, 55, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, T.W.; Pawlak, K.; Karbowska, M.; Myśliwiec, M.; Pawlak, D. Indoxyl sulfate—the uremic toxin linking hemostatic system disturbances with the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, X.W.; Krausz, K.W.; Nichols, R.G.; Xu, W.; Patterson, A.D.; Gonzalez, F.J. Modulation of colon cancer by nutmeg. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming-de-Moraes, C.D.; Rocha, M.R.; Tessmann, J.W.; de Araujo, W.M.; Morgado-Diaz, J.A. Crosstalk between PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin pathways promote colorectal cancer progression regardless of mutational status. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2022, 23, 12108690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ruan, P.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, S.; Hou, J.; Li, W.; et al. Spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase regulates cell growth and metastasis via AKT/β-catenin signaling pathways in hepatocellular and colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1092–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, K.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Yi, K.; Kang, C. EGFR/c-myc axis regulates TGFβ/Hippo/Notch pathway via epigenetic silencing miR-524 in gliomas. Cancer Lett. 2017, 406, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.H.; Yu, G.Y.; Gong, H.F.; Liu, L.J.; Xu, Y.; Hao, L.Q.; Liu, P.; Liu, Z.H.; Bai, C.G.; Zhang, W. Differences of protein expression profiles, KRAS and BRAF mutation, and prognosis in right-sided colon, left-sided colon and rectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jen, J.; Vogelstein, B.; Hamilton, S.R. Clinical and pathological characteristics of sporadic colorectal carcinomas with DNA replication errors in microsatellite sequences. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 145, 148–156. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, S.; Sattler, H.P.; Hack, M.; Romanakis, K.; Rohde, V.; Seitz, G.; Wullich, B. Microsatellite instability in sporadic carcinomas of the proximal colon: Association with diploid DNA content, negative protein expression of p53, and distinct histomorphologic features. Surgery 1998, 123, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, A.; Isaakidou, A.; Demetriou, E.; Marinis, A.; Ayiomamitis, G.; Karaiskakis, M. Molecular differences in colon cancer according to location: A literature review. Hell. J. Surg. 2023, 93, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Han, P.; Song, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Xie, H.; Zhao, W.; Xu, H.; Cai, Y.; Rong, Z.; et al. Plasma metabolomic profiling distinguishes right-sided from left-sided colon cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 487, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Makharia, G.K.; Dalal, M.; Mohan, A.; Singh, R.; Kumar, A. Gut Metabolite Indoxyl Sulfate Has Selective Deleterious and Anticancer Effect on Colon Cancer Cells. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 17074–17085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawajiri, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohtake, F.; Ikuta, T.; Matsushima, Y.; Mimura, J.; Pettersson, S.; Pollenz, R.S.; Sakaki, T.; Hirokawa, T.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor suppresses intestinal carcinogenesis in ApcMin/+ mice with natural ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13481–13486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, U.H.; Lee, S.O.; Sridharan, G.; Lee, K.; Davidson, L.A.; Jayaraman, A.; Chapkin, R.S.; Alaniz, R.; Safe, S. Microbiome-derived tryptophan metabolites and their aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent agonist and antagonist activities. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiizaki, K.; Kido, K.; Mizuta, Y. Insight into the relationship between aryl-hydrocarbon receptor and β-catenin in human colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Castro, L.; Venkateswaran, N.; Garcia, R.; Hao, Y.H.; Lafita-Navarro, M.C.; Kim, J.; Segal, D.; Saponzik, E.; Chang, B.J.; Fiolka, R.; et al. The AHR target gene scinderin activates the WNT pathway by facilitating the nuclear translocation of β-catenin. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs260028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.B. Epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2003, 2, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldus, S.E.; Mönig, S.P.; Huxel, S.; Landsberg, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Engelmann, K.; Schneider, P.M.; Thiele, J.; Hölscher, A.H.; Dienes, H.P. MUC1 and nuclear β-catenin are coexpressed at the invasion front of colorectal carcinomas and are both correlated with tumor prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 2790–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprangers, B.; Abudayyeh, A.; Latcha, S.; Perazella, M.A.; Jhaveri, K.D. How to determine kidney function in cancer patients? Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 132, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, Y.; Han, M.; Wang, A.; Guo, S.; et al. The Role of Tryptophan Metabolism in the Occurrence and Progression of Acute and Chronic Kidney Diseases. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2300218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyohara, T.; Suzuki, T.; Morimoto, R.; Akiyama, Y.; Souma, T.; Shiwaku, H.O.; Takeuchi, Y.; Mishima, E.; Abe, M.; Tanemoto, M.; et al. SLCO4C1 transporter eliminates uremic toxins and attenuates hypertension and renal inflammation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 2546–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massó-Vallés, D.; Soucek, L. Blocking Myc to Treat Cancer: Reflecting on Two Decades of Omomyc. Cells 2020, 9, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, G.; Vanholder, R.; Niwa, T. AST-120 for the management of progression of chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y.; Ezawa, A.; Kikuchi, K.; Tsuruta, Y.; Niwa, T. Protein-bound uremic toxins in hemodialysis patients measured by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry and their effects on endothelial ROS production. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bammens, B.; Verbeke, K.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Evenepoel, P. Evidence for impaired assimilation of protein in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 2196–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, K.; Aono, K.; Fujimoto, Y.; Kuwamura, M.; Okada, T.; Tokumoto, H.; Izawa, T.; Okano, R.; Nakajima, H.; Takeuchi, T.; et al. Chronic kidney disease after 5/6 nephrectomy disturbs the intestinal microbiota and alters intestinal motility. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 6667–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgane, K.; Yoshioka, H. Quantification of gel bands by an image J macro, band/peak quantification tool. Protoc. IO 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ichisaka, Y.; Takei, C.; Naito, K.; Higa, M.; Yano, S.; Niwa, T.; Shimizu, H. The Role of Indoxyl Sulfate in Exacerbating Colorectal Cancer During Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: Insights into the Akt/β-Catenin/c-Myc and AhR/c-Myc Pathways in HCT-116 Colorectal Cancer Cells. Toxins 2025, 17, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010017
Ichisaka Y, Takei C, Naito K, Higa M, Yano S, Niwa T, Shimizu H. The Role of Indoxyl Sulfate in Exacerbating Colorectal Cancer During Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: Insights into the Akt/β-Catenin/c-Myc and AhR/c-Myc Pathways in HCT-116 Colorectal Cancer Cells. Toxins. 2025; 17(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleIchisaka, Yu, Chihiro Takei, Kazuma Naito, Manami Higa, Shozo Yano, Toshimitsu Niwa, and Hidehisa Shimizu. 2025. "The Role of Indoxyl Sulfate in Exacerbating Colorectal Cancer During Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: Insights into the Akt/β-Catenin/c-Myc and AhR/c-Myc Pathways in HCT-116 Colorectal Cancer Cells" Toxins 17, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010017
APA StyleIchisaka, Y., Takei, C., Naito, K., Higa, M., Yano, S., Niwa, T., & Shimizu, H. (2025). The Role of Indoxyl Sulfate in Exacerbating Colorectal Cancer During Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: Insights into the Akt/β-Catenin/c-Myc and AhR/c-Myc Pathways in HCT-116 Colorectal Cancer Cells. Toxins, 17(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010017




