Snake Venom Pharmacokinetics and Acute Toxic Outcomes Following Daboia siamensis Envenoming: Experimental and Clinical Correlations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Profile of Russell’s Viper Bite Patients
2.1.1. Demographic Characteristics
2.1.2. Laboratory Investigation Results of Patients with D. siamensis Bites
2.1.3. Hematological and Systemic Effects of Patients Following D. siamensis Bites
2.2. Measuring of Venom Concentration in Experimentally Envenomed Rats
2.2.1. Serum Venom Concentration
2.2.2. Urine Venom Concentration
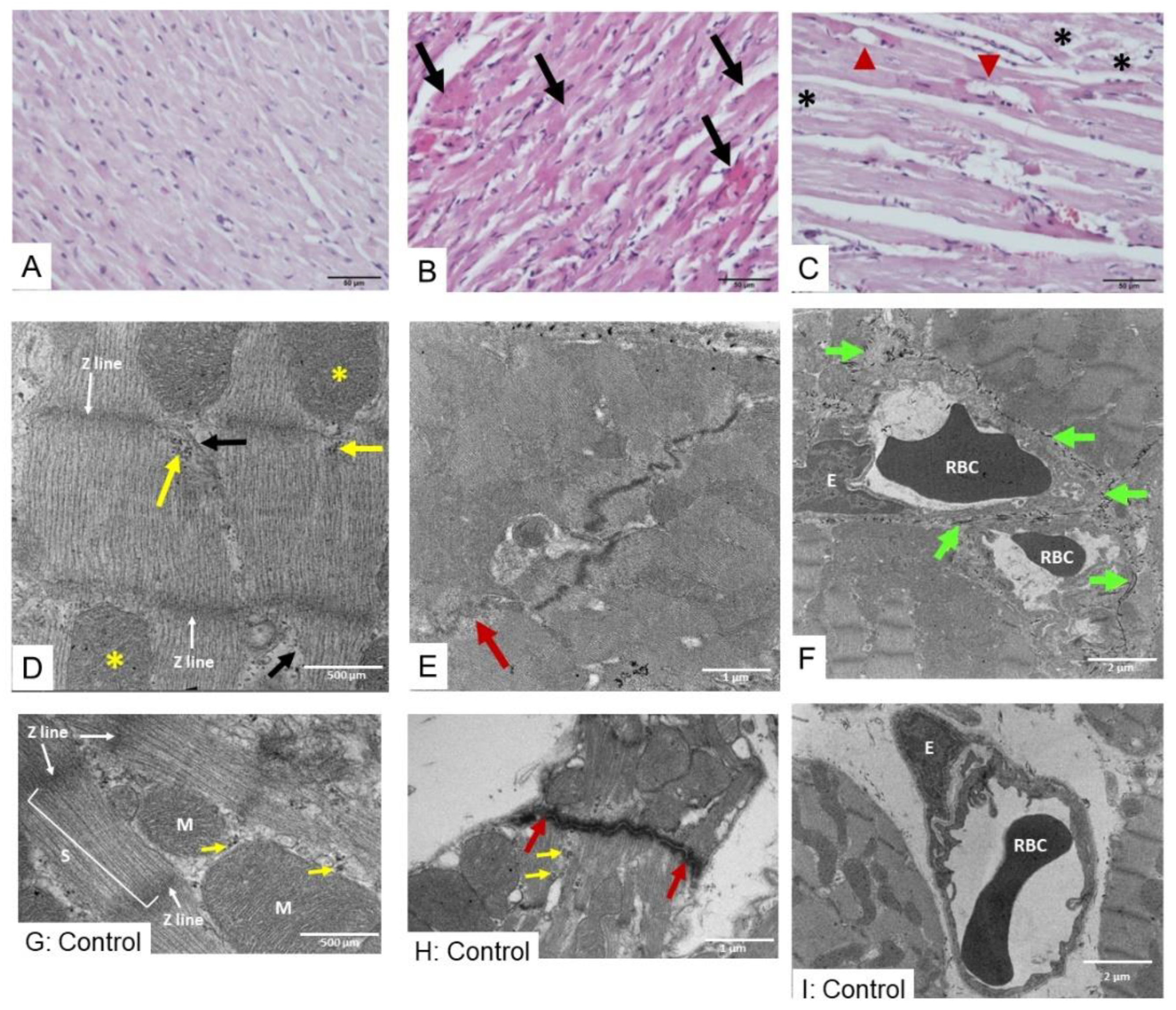
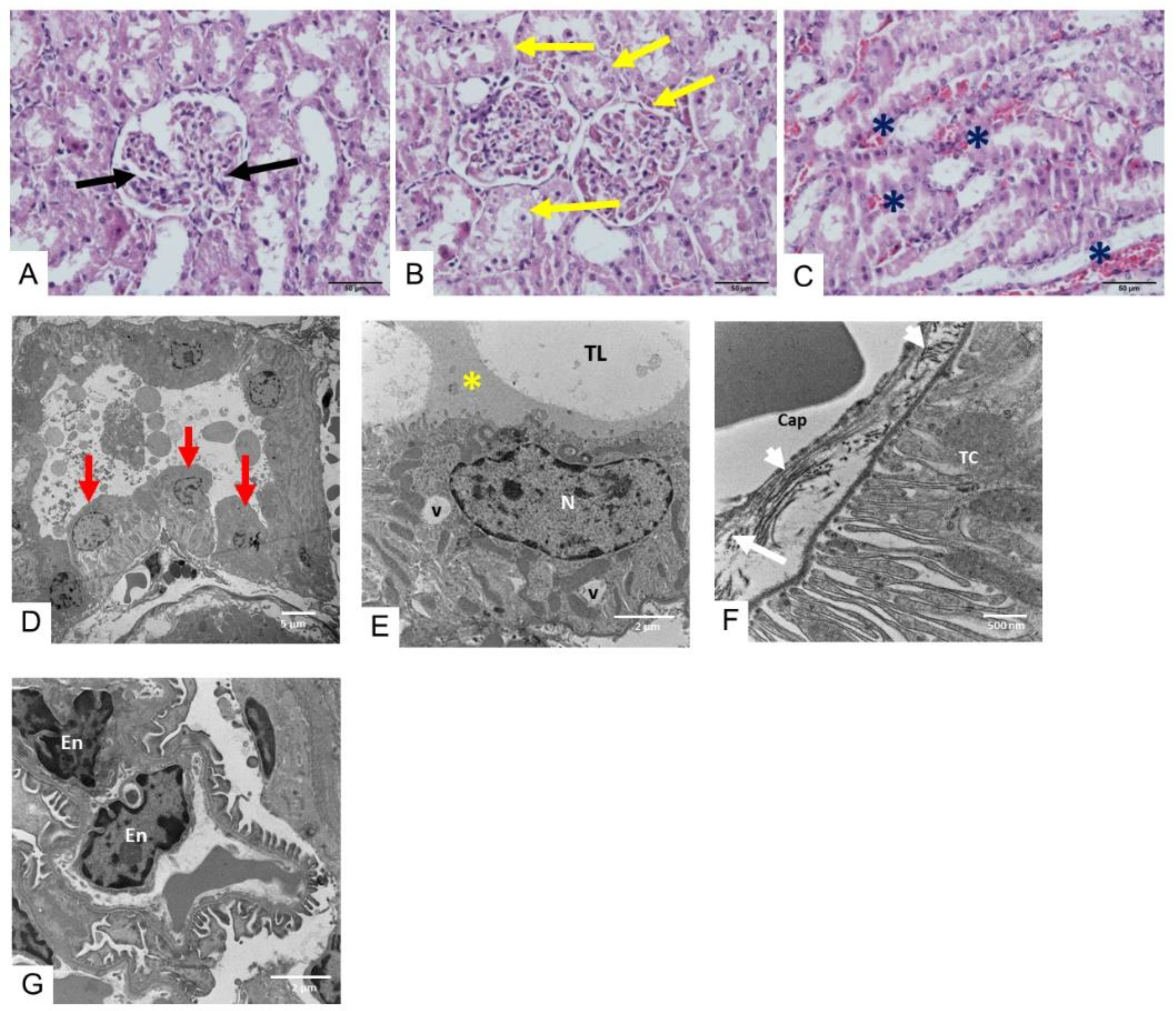
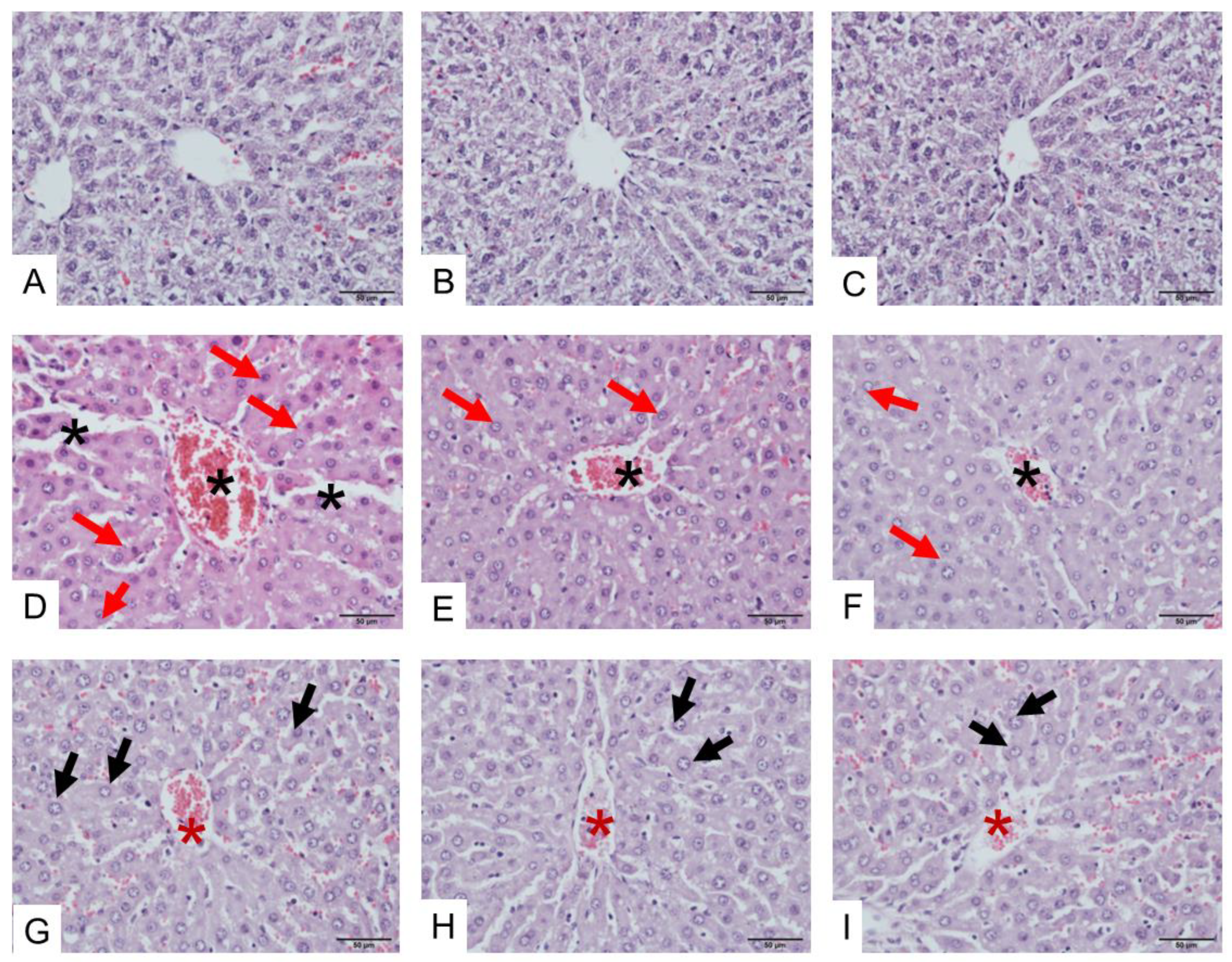
2.3. Histopathological Study of Heart, Kidney, and Liver Tissues Following D. siamensis Envenoming
2.3.1. Morphological Changes in Heart Following Envenoming
2.3.2. Morphological Changes in the Kidney Following Envenoming
2.3.3. Morphological Changes in the Liver Following Envenoming
3. Discussion
3.1. Snake Venom Pharmacokinetic Study in Animal Model
3.2. Toxic Outcomes Following D. siamensis Envenoming in Experimentally Envenomed Animals
3.3. Clinical Observations and Laboratory Examinations of D. siamensis Envenomed Patients
3.4. Association Between Experimental Study Using Animal Model and Clinical Study
3.5. Limitations
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Clinical Profile of Envenomed Patients
5.1.1. Study Design and Subjects
5.1.2. Data Collection
5.1.3. Ethics Considerations
5.2. Experimentally Envenomed Rat Studies
5.2.1. Snake Venoms
5.2.2. Animal Ethics and Care
5.2.3. Anesthetized Rat Preparation
5.2.4. Venom Dose Optimization
5.3. Measurement of Serum D. siamensis Venom Concentration
5.3.1. Preparation of IgG
5.3.2. Preparation of Peroxidase-Conjugated Specific IgG of Russell’s Viper Snake Venom
5.3.3. Detection of Russell’s Viper Snake Venom by ELISA Method
5.4. Histopathological Studies
5.4.1. Histological Preparation for Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
5.4.2. Histological Preparation for Transmission Electron Microscopy Method
5.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The Global Burden of Snakebite: A Literature Analysis and Modelling Based on Regional Estimates of Envenoming and Deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.-P. Snakebite Envenomation Turns Again into a Neglected Tropical Disease! J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Correction: Snakebite Envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO World Health Organization (WHO) Regional Office in South-East Asia. Guidelines for Management of Snakebites, 2nd ed.; WHO Regional Office in South-East Asia: New Delhi, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal, T.; Tan, K.Y.; Sim, S.M.; Quraishi, N.; Tan, N.H.; Tan, C.H. Proteomics, Functional Characterization and Antivenom Neutralization of the Venom of Pakistani Russell’s Viper (Daboia Russelii) from the Wild. J. Proteom. 2018, 183, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, D.-Z.; Yu, Y.-J.; Hsu, C.-L.; Lin, T.-J. Antivenom Treatment and Renal Dysfunction in Russell’s Viper Snakebite in Taiwan: A Case Series. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 100, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint-Lwin; Phillips, R.E.; Tun-Pe; Warrell, D.A.; Tin-Nu-SWE. Maung-Maung-Lay Bites by Russell’s viper (Vipera russelli siamensis) in Burma: Haemostatic, vascular, and renal disturbances and response to treatment. Lancet 1985, 326, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitprija, V. Snakebite Nephropathy (Review Article). Nephrology 2006, 11, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maduwage, K.; Isbister, G.K. Current Treatment for Venom-Induced Consumption Coagulopathy Resulting from Snakebite. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Samarasinghe, R.; Pilapitiya, S.; Dahanayake, N.; Siribaddana, S. Viper Bites Complicate Chronic Agrochemical Nephropathy in Rural Sri Lanka. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, M.; Hodgson, W.C. A Comparison of the Efficacy of Antivenoms and Varespladib against the In Vitro Pre-Synaptic Neurotoxicity of Thai and Javanese Russell’s Viper (Daboia Spp.) Venoms. Toxins 2024, 16, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaisakul, J.; Khow, O.; Wiwatwarayos, K.; Rusmili, M.R.A.; Prasert, W.; Othman, I.; Abidin, S.A.Z.; Charoenpitakchai, M.; Hodgson, W.C.; Chanhome, L.; et al. A Biochemical and Pharmacological Characterization of Phospholipase A2 and Metalloproteinase Fractions from Eastern Russell’s Viper (Daboia Siamensis) Venom: Two Major Components Associated with Acute Kidney Injury. Toxins 2021, 13, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.Y.; Tan, N.H.; Tan, C.H. Venom Proteomics and Antivenom Neutralization for the Chinese Eastern Russell’s Viper, Daboia Siamensis from Guangxi and Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risch, M.; Georgieva, D.; von Bergen, M.; Jehmlich, N.; Genov, N.; Arni, R.K.; Betzel, C. Snake Venomics of the Siamese Russell’s Viper (Daboia Russelli Siamensis)—Relation to Pharmacological Activities. J. Proteom. 2009, 72, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrmoonpitak, C.; Chulasugandha, P.; Khow, O.; Noiprom, J.; Chaiyabutr, N.; Sitprija, V. Effects of Phospholipase A2 and Metalloprotease Fractions of Russell’s Viper Venom on Cytokines and Renal Hemodynamics in Dogs. Toxicon 2013, 61, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitprija, V.; Sitprija, S. Renal Effects and Injury Induced by Animal Toxins. Toxicon 2012, 60, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.M.; Saremi, K.; Tan, N.H.; Fung, S.Y. Pharmacokinetics of Cryptelytrops Purpureomaculatus (Mangrove Pit Viper) Venom Following Intravenous and Intramuscular Injections in Rabbits. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.J.; Hodgson, W.C.; O’Leary, M.; Isbister, G.K. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of the Myotoxic Venom of Pseudechis Australis (Mulga Snake) in the Anesthetised Rat. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, M.K.K.; Tan, N.H.; Sim, S.M.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, C.H. Pharmacokinetics of Naja Sumatrana (Equatorial Spitting Cobra) Venom and Its Major Toxins in Experimentally Envenomed Rabbits. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K. Pharmacokinetic–Pharmacodynamic Modeling in Overdose Patients—Is It Worth the Trouble? Clin. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 896–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanvivatvong, O.; Mahasandana, S.; Karnchanachetanee, C. Kinetic Study of Russell’s Viper Venom in Envenomed Patients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 57, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisakul, J.; Rusmili, M.R.A.; Hodgson, W.C.; Hatthachote, P.; Suwan, K.; Inchan, A.; Chanhome, L.; Othman, I.; Chootip, K. A Pharmacological Examination of the Cardiovascular Effects of Malayan Krait (Bungarus candidus) Venoms. Toxins 2017, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaisakul, J.; Alsolaiss, J.; Charoenpitakchai, M.; Wiwatwarayos, K.; Sookprasert, N.; Harrison, R.A.; Chaiyabutr, N.; Chanhome, L.; Tan, C.H.; Casewell, N.R. Evaluation of the Geographical Utility of Eastern Russell’s Viper (Daboia Siamensis) Antivenom from Thailand and an Assessment of Its Protective Effects against Venom-Induced Nephrotoxicity. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenpitakchai, M.; Wiwatwarayos, K.; Jaisupa, N.; Rusmili, M.R.A.; Mangmool, S.; Hodgson, W.C.; Ruangpratheep, C.; Chanhome, L.; Chaisakul, J. Non-Neurotoxic Activity of Malayan Krait (Bungarus candidus) Venom from Thailand. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 24, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanhajariya, S.; Duffull, S.; Isbister, G. Pharmacokinetics of Snake Venom. Toxins 2018, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanhajariya, S.; Isbister, G.K.; Duffull, S.B. The Influence of the Different Disposition Characteristics of Snake Toxins on the Pharmacokinetics of Snake Venom. Toxins 2020, 12, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.H.; Sim, S.M.; Gnanathasan, C.A.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, N.H. Pharmacokinetics of the Sri Lankan Hump-Nosed Pit Viper (Hypnale hypnale) Venom Following Intravenous and Intramuscular Injections of the Venom into Rabbits. Toxicon 2014, 79, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theakston, R.D.G. The Application of Immunoassay Techniques, Including Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), to Snake Venom Research. Toxicon 1983, 21, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvanayagam, Z.E.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Tests for Detection of Snake Venoms, Toxins and Venom Antibodies: Review on Recent Trends (1987–1997). Toxicon 1999, 37, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choowongkomon, K.; Chaisakul, J.; Seetaha, S.; Vasaruchapong, T.; Hodgson, W.C.; Rasri, N.; Chaeksin, K.; Boonchaleaw, S.; Sookprasert, N. Development of a Biosensor to Detect Venom of Malayan Krait (Bungarus candidus). Toxins 2024, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saul, M.E.; Thomas, P.A.; Dosen, P.J.; Isbister, G.K.; O’Leary, M.A.; Whyte, I.M.; McFadden, S.A.; van Helden, D.F. A Pharmacological Approach to First Aid Treatment for Snakebite. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 809–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivière, G.; Choumet, V.; Audebert, F.; Sabouraud, A.; Debray, M.; Scherrmann, J.M.; Bon, C. Effect of Antivenom on Venom Pharmacokinetics in Experimentally Envenomed Rabbits: Toward an Optimization of Antivenom Therapy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 281, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khunsap, S.; Promruangreang, K.; Suntrarachun, S.; Noiphrom, J.; Khow, O. Local Inflammatory Mediators Alterations Induced by Daboia siamensis Venom. Toxicon X 2021, 12, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiyabutr, N.; Chanhome, L.; Vasaruchapong, T.; Laoungbua, P.; Khow, O.; Rungsipipat, A.; Sitprija, V. The Pathophysiological Effects of Russell’s Viper (Daboia siamensis) Venom and Its Fractions in the Isolated Perfused Rabbit Kidney Model: A Potential Role for Platelet Activating Factor. Toxicon X 2020, 7, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, S.M.; Linardi, A.; Rennó, A.L.; Tarsitano, C.A.B.; Pereira, E.M.; Hyslop, S. Renal Kinetics of Bothrops alternatus (Urutu) Snake Venom in Rats. Toxicon 2010, 55, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, R.; Swindells, K.; Mansfield, C. Prospective Determination of the Specificity of a Commercial Snake Venom Detection Kit in Urine Samples from Dogs and Cats. Aust. Vet. J. 2010, 88, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audebert, F.; Urtizberea, M.; Sabouraud, A.; Scherrmann, J.M.; Bon, C. Pharmacokinetics of Vipera aspis Venom after Experimental Envenomation in Rabbits. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 268, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, R.B.; Gawarammana, I.B.; De Silva, D.D.N.; Dangolla, A.; Mallawa, C.; Premarathna, A.D.; Silva, I.D. Clinico-Epidemiology and Management of Russell’s Viper (Daboia russelii) Envenoming in Dogs in Sri Lanka. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedasingha, S.; Isbister, G.; Silva, A. Bedside Coagulation Tests in Diagnosing Venom-Induced Consumption Coagulopathy in Snakebite. Toxins 2020, 12, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.-S.; Liu, C.-C.; Chuang, P.-C. Personal Experience of Daboia Siamensis Envenomation. Case Rep. Med. 2021, 2021, 3396373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lertsakulbunlue, S.; Suebtuam, R.; Eamchotchawalit, T.; Chantkran, W.; Chaisakul, J. Clinical Profile and Pharmacological Management of Snakebites in Community Care Units: A Retrospective Study Using Two Military Hospital Databases in South Thailand. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesor, M.; Chaisakul, J.; Promsorn, P.; Chantkran, W. Clinical Laboratory Investigations and Antivenom Administration after Malayan Pit Viper (Calloselasma rhodostoma) Envenoming: A Retrospective Study from Southernmost Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2024, 110, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, K.X.; Khac, Q.L.; Trinh, L.X.; Warrell, D.A. Hyponatraemia, Rhabdomyolysis, Alterations in Blood Pressure and Persistent Mydriasis in Patients Envenomed by Malayan Kraits (Bungarus candidus) in Southern Viet Nam. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kularatne, S.A.M. Common Krait (Bungarus caeruleus) Bite in Anuradhapura, Sri Lanka: A Prospective Clinical Study, 1996–98. Postgrad. Med. J. 2002, 78, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, J.P.; Soares, A.M.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Polymorphonuclear Neutrophil Leukocytes in Snakebite Envenoming. Toxicon 2020, 187, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnayake, I.; Mohamed, F.; Buckley, N.A.; Gawarammana, I.B.; Dissanayake, D.M.; Chathuranga, U.; Munasinghe, M.; Maduwage, K.; Jayamanne, S.; Endre, Z.H.; et al. Early Identification of Acute Kidney Injury in Russell’s Viper (Daboia russelii) Envenoming Using Renal Biomarkers. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojnuckarin, P.; Intragumtornchai, T.; Sattapiboon, R.; Muanpasitporn, C.; Pakmanee, N.; Khow, O.; Swasdikul, D. The Effects of Green Pit Viper (Trimeresurus albolabris and Trimeresurus macrops) Venom on the Fibrinolytic System in Human. Toxicon 1999, 37, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khimmaktong, W.; Nuanyaem, N.; Lorthong, N.; Hodgson, W.C.; Chaisakul, J. Histopathological Changes in the Liver, Heart and Kidneys Following Malayan Pit Viper (Calloselasma rhodostoma) Envenoming and the Neutralising Effects of Hemato Polyvalent Snake Antivenom. Toxins 2022, 14, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Total | 23 (100.0) |
| Year | |
| 2014–2017 | 4 (17.4) |
| 2018–2020 | 6 (26.1) |
| 2021–2023 | 13 (56.5) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 19 (82.6) |
| Female | 4 (17.4) |
| Admission | |
| Outpatient | 0 (0.0) |
| Admit | 6 (26.1) |
| Refer | 17 (73.9) |
| Bitten area | |
| Trunk | 0 (0.0) |
| Upper extremities | 6 (26.1) |
| Lower extremities | 17 (73.9) |
| Clinical Manifestation | |
| Local Pain | 15 (65.2) |
| Swelling | 18 (78.3) |
| Erythema | 20 (87.0) |
| Compartment syndrome | 0 (0.0) |
| Dyspnea | 1 (4.4) |
| Ptosis | 0 (0.0) |
| Duration from the bite to arrival at the hospital | |
| ≤15 min | 4 (17.4) |
| 15–60 min | 11 (47.8) |
| 60–90 min | 5 (21.7) |
| Blood Chemistry and White Blood Cell Count (Normal Range) | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Serum sodium (135–145 mmol/L) | |
| No hyponatremia (≥135 mmol/L) | 18 (78.3) |
| Hyponatremia (<135 mmol/L) | 5 (21.7) |
| Serum potassium (3.5–5.0 mmol/L) | |
| No hypokalemia (≥3.5 mmol/L) | 8 (34.8) |
| Hypokalemia (<3.5 mmol/L) | 15 (65.2) |
| Serum bicarbonate (22–31 mmol/L) | |
| No metabolic acidosis (≥22 mmol/L) | 15 (65.2) |
| Metabolic acidosis (<22 mmol/L) | 8 (34.8) |
| ** Creatinine level (0.7–1.2 mg/dL) | |
| 0.7–1.2 mg/dL | 19 (86.4) |
| ≥1.2 mg/dL | 3 (13.6) |
| White blood cell count (4 × 103 – 11 × 103cells/µL) | |
| <4 × 103 cells/µL | - |
| 4–11 × 103 cells/µL | 19 (82.6) |
| >11 × 103 cells/µL | 4 (17.4) |
| ** Chloride (90–105 mmol/L) | |
| <90 mmol/L | - |
| 90–105 mmol/L | 15 (65.22) |
| >105 mmol/L | 4 (17.39) |
| Systemic Effects | n (% of 23 Patients) |
|---|---|
| VCT (min) | |
| ≤20 | 23 (100) |
| >20 | - |
| INR | |
| ≤1.2 | 13 (56.5) |
| >1.2 | 6 (26.1) |
| Platelet (×109/L) | |
| Mean ± SD | 202.0 ± 83.1 |
| <140 × 103 | 5 (21.7) |
| ≥140 × 103 | 18 (78.3) |
| Systemic bleeding | |
| No | 4 (17.4) |
| Yes | 19 (82.6) |
| Local effects (Pain, swelling, redness) | |
| No | 3 (13.0) |
| Yes | 20 (87.0) |
| Antivenom treatment | |
| No | 13 (56.5) |
| Yes | 10 (43.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lertsakulbunlue, S.; Khimmaktong, W.; Khow, O.; Chantkran, W.; Noiphrom, J.; Promruangreang, K.; Chanhome, L.; Chaisakul, J. Snake Venom Pharmacokinetics and Acute Toxic Outcomes Following Daboia siamensis Envenoming: Experimental and Clinical Correlations. Toxins 2025, 17, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010010
Lertsakulbunlue S, Khimmaktong W, Khow O, Chantkran W, Noiphrom J, Promruangreang K, Chanhome L, Chaisakul J. Snake Venom Pharmacokinetics and Acute Toxic Outcomes Following Daboia siamensis Envenoming: Experimental and Clinical Correlations. Toxins. 2025; 17(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLertsakulbunlue, Sethapong, Wipapan Khimmaktong, Orawan Khow, Wittawat Chantkran, Jureeporn Noiphrom, Kanyanat Promruangreang, Lawan Chanhome, and Janeyuth Chaisakul. 2025. "Snake Venom Pharmacokinetics and Acute Toxic Outcomes Following Daboia siamensis Envenoming: Experimental and Clinical Correlations" Toxins 17, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010010
APA StyleLertsakulbunlue, S., Khimmaktong, W., Khow, O., Chantkran, W., Noiphrom, J., Promruangreang, K., Chanhome, L., & Chaisakul, J. (2025). Snake Venom Pharmacokinetics and Acute Toxic Outcomes Following Daboia siamensis Envenoming: Experimental and Clinical Correlations. Toxins, 17(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010010






