A Comparison of the Efficacy of Antivenoms and Varespladib against the In Vitro Pre-Synaptic Neurotoxicity of Thai and Javanese Russell’s Viper (Daboia spp.) Venoms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
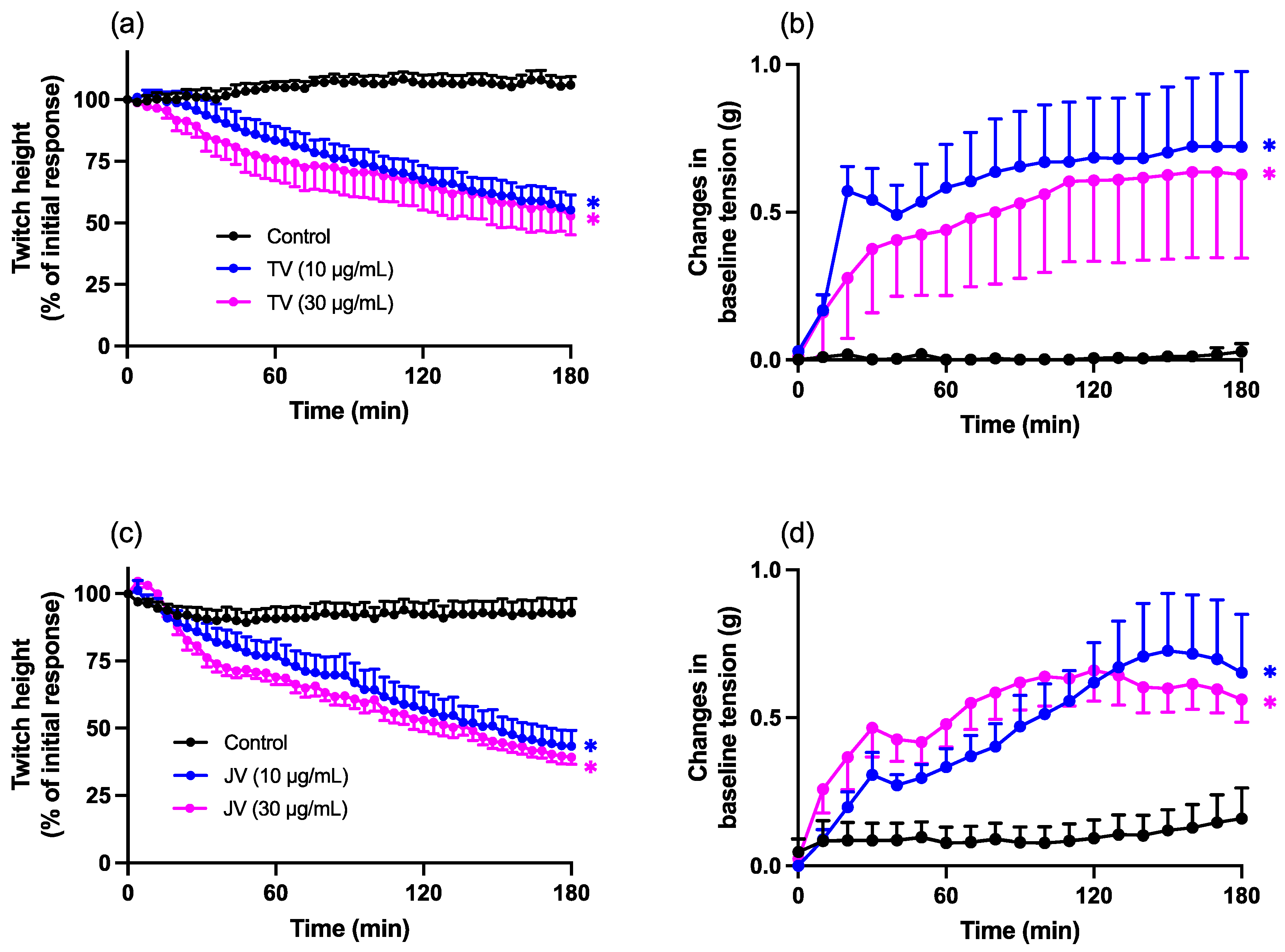
2.1. Neurotoxic Effects of Thai and Javanese D. siamensis Venoms
2.2. Myotoxic Effects of Thai and Javanese D. siamensis Venoms
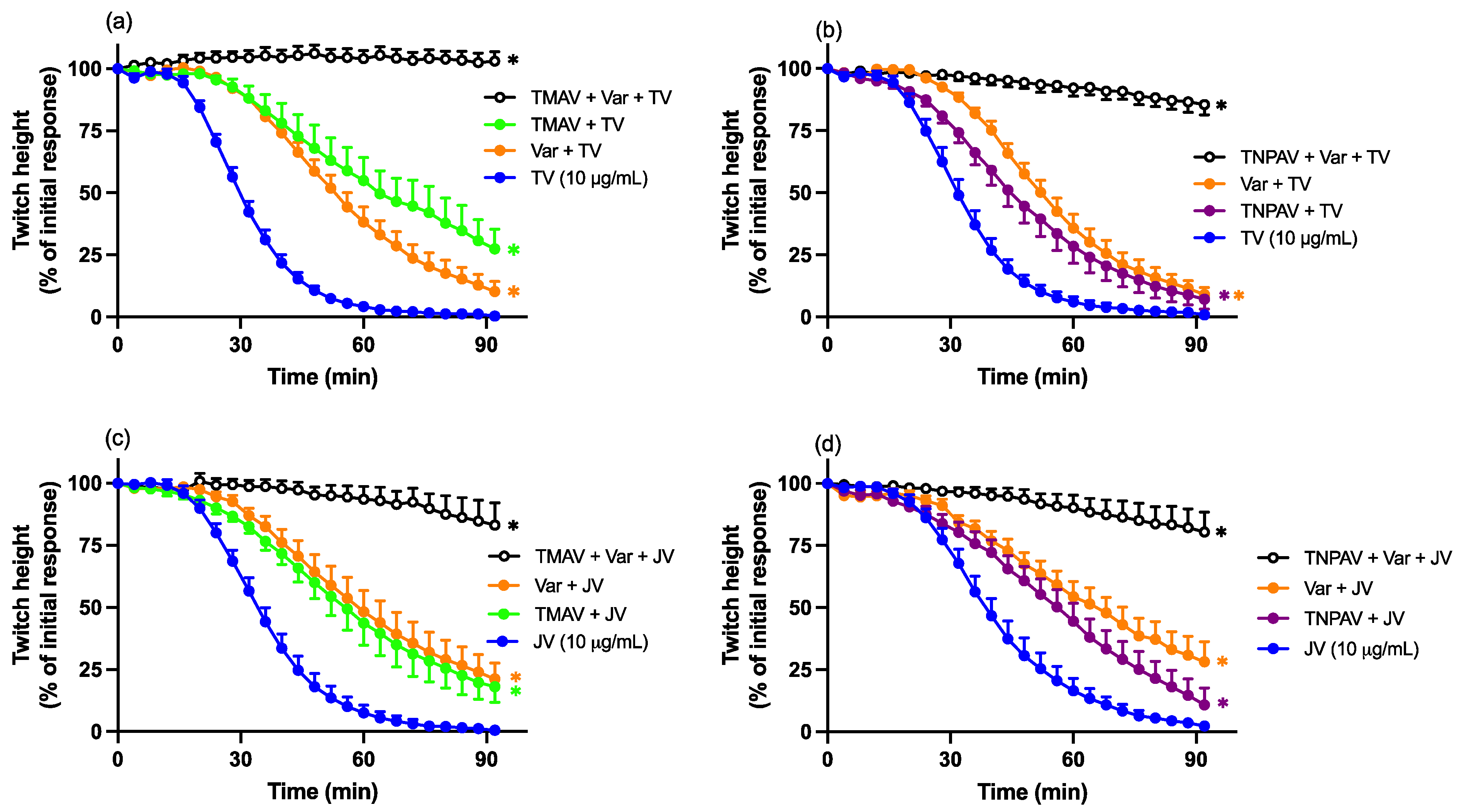
2.3. Neurotoxicity: Antivenom Protection Studies
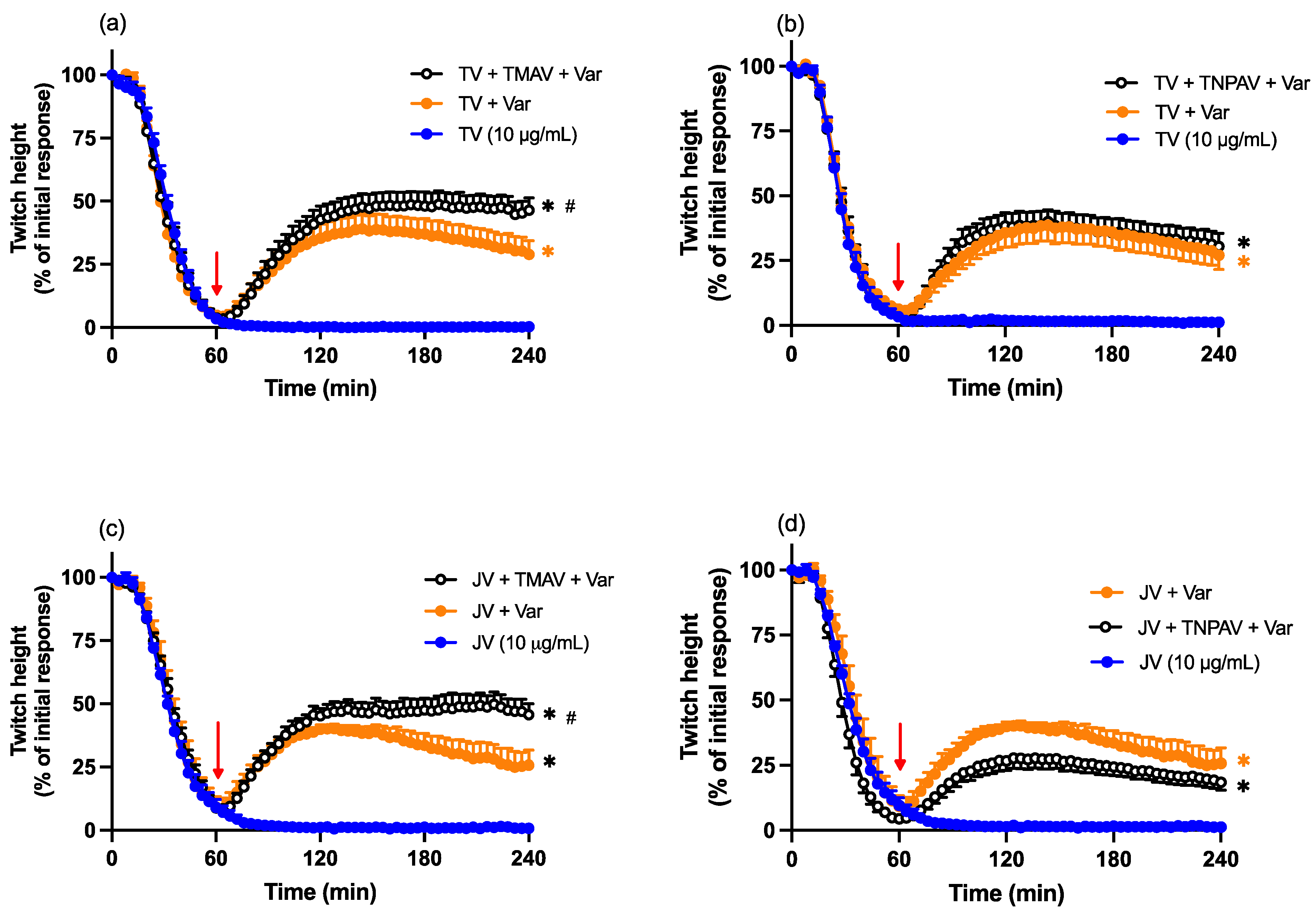
2.4. Neurotoxicity: Antivenom Reversal Studies
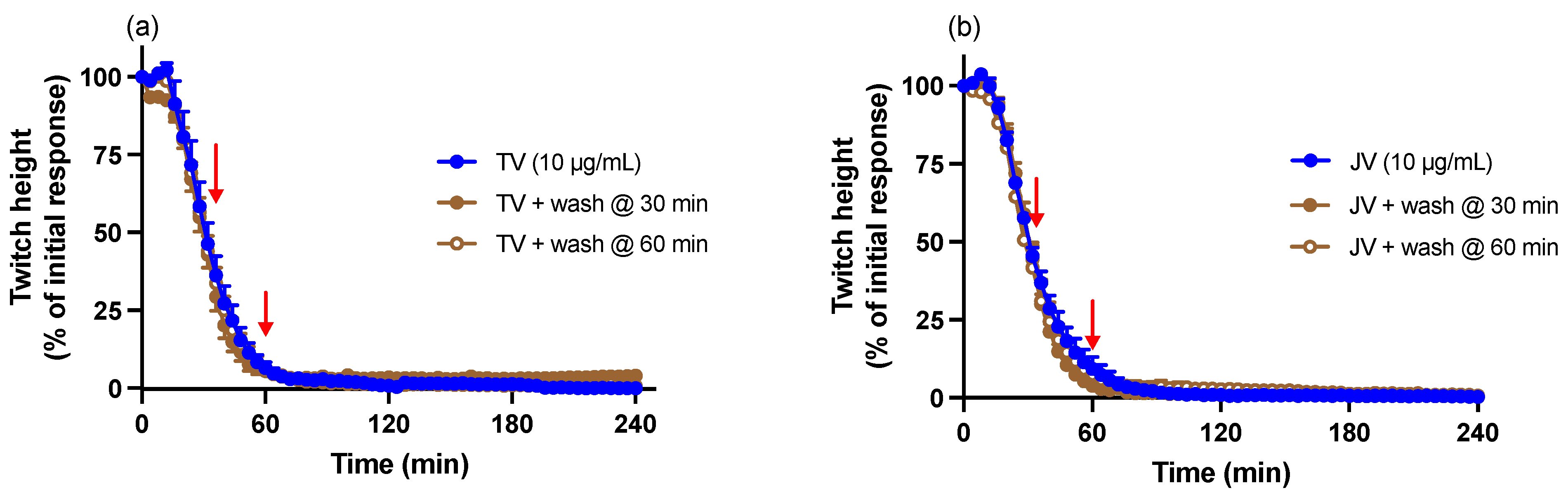
2.5. Washing Reversal Studies
2.6. Varespladib Protection Studies
2.7. Varespladib Reversal Studies
2.8. Antivenom and Varespladib Combination Prevention Studies
2.9. Antivenom and Varespladib Combination Reversal Studies
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animals
5.2. Chemicals and Drugs
5.3. Venoms and Antivenoms
5.4. Chick Biventer Cervicis Nerve–Muscle Preparation
5.5. Data Analysis and Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belt, P.J.; Malhotra, A.; Thorpe, R.S.; Warrell, D.A.; Wüster, W. Russell’s viper in Indonesia: Snakebite and systematics. Symp. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1997, 70, 219–234. [Google Scholar]
- Wüster, W. The genus Daboia (Serpentes: Viperidae): Russell’s Viper. Hamadryad 1998, 23, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Casewell, N.R.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Laustsen, A.H.; Sunagar, K. Causes and Consequences of Snake Venom Variation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumaran, S.; Almeida, J.R.; Williams, J.; Williams, H.F.; Thirumalaikolundusubramanian, P.; Patel, K.; Vaiyapuri, S. Rapid identification of bilateral adrenal and pituitary haemorrhages induced by Russell’s viper envenomation results in positive patient outcome. Toxicon 2023, 225, 107068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfred, S.; Bates, D.; White, J.; Mahmood, M.A.; Warrell, D.A.; Thwin, K.T.; Thein, M.M.; Sint San, S.S.; Myint, T.L.; Swe, H.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury Following Eastern Russell’s Viper (Daboia siamensis) Snakebite in Myanmar. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, B.; Mackessy, S.P.; Mukherjee, A.K. Proteomic analysis reveals geographic variation in venom composition of Russell’s Viper in the Indian subcontinent: Implications for clinical manifestations post-envenomation and antivenom treatment. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2018, 15, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senji Laxme, R.R.; Khochare, S.; Attarde, S.; Suranse, V.; Iyer, A.; Casewell, N.R.; Whitaker, R.; Martin, G.; Sunagar, K. Biogeographic venom variation in Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) and the preclinical inefficacy of antivenom therapy in snakebite hotspots. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Kuruppu, S.; Othman, I.; Goode, R.J.; Hodgson, W.C.; Isbister, G.K. Neurotoxicity in Sri Lankan Russell’s Viper (Daboia russelii) Envenoming is Primarily due to U1-viperitoxin-Dr1a, a Pre-Synaptic Neurotoxin. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 31, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, R.S.; Pook, C.E.; Malhotra, A. Phylogeography of the Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) complex in relation to variation in the colour pattern and symptoms of envenoming. Herpetol. J. 2007, 17, 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Warrell, D.A. Snake venoms in science and clinical medicine. 1. Russell’s viper: Biology, venom and treatment of bites. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1989, 83, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chuanzhu, L.V.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Lai, D.R. Experts Group of Snake-bites Rescue and Treatment Consensus in China. Expert Consensus on China Snake-bites rescue and Treatment. Chin. J. Emer. Med. 2018, 27, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, D.Z.; Wu, M.L.; Deng, J.F.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y. Russell’s viper snakebite in Taiwan: Differences from other Asian countries. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanhome, L.; Cox, M.J.; Wilde, H.; Jintakoon, P.; Chaiyabutr, N.; Sitprija, V. Venomous snakebite in Thailand. I: Medically important snakes. Mil. Med. 1998, 163, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüster, W.; Otsuka, S.; Malhotra, A.; Thorpe, R.S. Population systematics of Russell’s viper: A multivariate study. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 47, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingam, T.M.C.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, C.H. Thai Russell’s viper monospecific antivenom is immunoreactive and effective in neutralizing the venom of Daboia siamensis from Java, Indonesia. Toxicon 2019, 168, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingam, T.M.C.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, C.H. Proteomics and antivenom immunoprofiling of Russell’s viper (Daboia siamensis) venoms from Thailand and Indonesia. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 26, e20190048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingam, T.M.C.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, C.H. Capillary leak syndrome induced by the venoms of Russell’s Vipers (Daboia russelii and Daboia siamensis) from eight locales and neutralization of the differential toxicity by three snake antivenoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 250, 109186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisukal, J.; Khow, O.; Wiwatwarayos, K.; Rusmili, M.R.A.; Prasert, W.; Othman, I.; Abidin, S.A.Z.; Charoenpitakchai, M.; Hodgson, W.C.; Chanhome, L.; et al. A Biochemical and Pharmacological Characterization of Phospholipase A2 and Metalloproteinase Fractions from Eastern Russell’s Viper (Daboia siamensis) Venom: Two Major Components Associated with Acute Kidney Injury. Toxins 2021, 13, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, T.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, N.H.; Sim, S.M.; Gnanathasan, C.A.; Tan, C.H. Proteomics, toxicity and antivenom neutralization of Sri Lankan and Indian Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) venoms. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 27, e20200177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.H.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, K.Y.; Yap, M.K.K.; Gnathasan, C.A.; Tan, C.H. Functional Venomics of the Sri Lankan Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) and its toxinological correlations. J. Proteom. 2016, 128, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lay, M.; Liang, Q.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. In Vitro Toxicity of Chinese Russell’s Viper (Daboia siamensis) Venom and Neutralisation by Antivenoms. Toxins 2022, 14, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, M.; Liang, Q.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. In Vitro Efficacy of Antivenom and Varespladib in Neutralising Chinese Russell’s Viper (Daboia siamensis) Venom Toxicity. Toxins 2023, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisakul, J.; Alsolaiss, J.; Charoenpitakchai, M.; Wiwatwarayos, K.; Sookprasert, N.; Harrison, R.A.; Chaiyabutr, N.; Chanhome, L.; Tan, C.H.; Casewell, N.R. Evaluation of the geographical utility of Eastern Russell’s viper (Daboia siamensis) antivenom from Thailand and an assessment of its protective effects against venom-induced nephrotoxicity. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risch, M.; Georgieva, D.; von Bergen, M.; Jehmlich, N.; Genov, N.; Arni, R.K.; Betzel, C. Snake venomics of the Siamese Russell’s viper (Daboia russelli siamensis)—Relation to pharmacological activities. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 72, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Maduwage, K.; Sedgwick, M.; Pilapitiya, S.; Weerawansa, P.; Dahanayaka, N.J.; Buckley, N.A.; Siribaddana, S.; Isbister, G.K. Neurotoxicity in Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) envenoming in Sri Lanka: A clinical and neurophysiological study. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, I.H.; Lu, P.J.; Su, J.C. Two types of Russell’s viper revealed by variation in Phospholipases A2 from venom of the subspecies. Toxicon 1996, 34, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Liew, J.L.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, N.H. Assessing SABU (Serum Anti Bisa Ular), the sole Indonesian antivenom: A proteomic analysis and neutralization efficacy study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, P.K.; Sim, S.M.; Fung, S.Y.; Sumana, K.; Sitprija, V.; Tan, N.H. Cross neutralization of Afro-Asian cobra and Asian krait venoms by a Thai polyvalent snake antivenom (Neuro Polyvalent Snake Antivenom). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, P.K.; Tan, C.H.; Sim, S.M.; Fung, S.Y.; Sumana, K.; Sitprija, V.; Tan, N.H. Cross neutralization of common Southeast Asian viperid venoms by a Thai polyvalent snake antivenom (Hemato Polyvalent Snake Antivenom). Acta Trop. 2014, 132, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K. Antivenom availability, delays and use in Australia. Toxicon X 2023, 17, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, M.; Samuel, S.; Merkel, J.; Bickler, P. Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lewin, M.R.; Williams, D.J.; Lomonte, B. Varespladib (LY315920) and Methyl Varespladib (LY333013) Abrogate or Delay Lethality Induced by Presynaptically Acting Neurotoxic Snake Venoms. Toxins 2020, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Carvalho, R.; Gaspar, M.Z.; Quadros, L.H.B.; Lobo, L.G.G.; Rogério, L.M.; Santos, N.T.S.; Zerbinatti, M.C.; Santarém, C.L.; Silva, E.O.; Gerez, J.R.; et al. In Vivo Treatment with Varespladib, a Phospholipase A2 Inhibitor, Prevents the Peripheral Neurotoxicity and Systemic Disorders Induced by Micrurus corallinus (Coral Snake) in Rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2022, 356, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.H.; Lingam, T.M.C.; Tan, K.Y. Varespladib (LY315920) rescued mice from fatal neurotoxicity caused by venoms of five major Asiatic kraits (Bungarus spp.) in an experimental envenoming and rescue model. Acta Trop. 2022, 227, 106289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.; Huang, C. Inactivation of Venom PLA2 Alleviates Myonecrosis and Facilitates Muscle Regeneration in Envenomed Mice: A Time Course Observation. Molecules 2018, 23, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Samuel, S.P.; Herrera, M.; Bryan-Quirós, W.; Lomonte, B.; Bickler, P.E.; Bulfone, T.C.; Williams, D.J. Delayed Oral LY333013 Rescues Mice from Highly Neurotoxic, Lethal Doses of Papuan Taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) Venom. Toxins 2018, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.C.F.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lewin, M.R.; Oshima-Franko, Y. Varespladib (LY315920) inhibits neuromuscular blockade induced by Oxyuranus scutellatus venom in nerve-muscle preparation. Toxicon 2020, 187, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.R.; Gilliam, L.L.; Gilliam, J.; Samuel, S.P.; Bulfone, T.C.; Bickler, P.E.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Delayed LY333013 (Oral) and LY315920 (Intravenous) Reverse Severe Neurotoxicity and Rescue Juvenile Pigs from Lethal Doses of Micrurus fulvius (Eastern Coral Snake) Venom. Toxins 2018, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Johnston, C.; Kuruppu, S.; Kneisz, D.; Maduwage, K.; Kleifeld, O.; Smith, A.I.; Siribaddana, S.; Buckley, N.A.; Hodgson, W.C.; et al. Clinical and Pharmacological Investigation of Myotoxicity in Sri Lankan Russell’s Viper (Daboia russelii) Envenoming. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, L.; Quesada-bernat, S.; Chen, P.Y.; Lee, C.D.; Chiang, J.R.; Calvete, J.J. Translational Venomics: Third-Generation Antivenomics of Anti-Siamese Russell’s Viper, Daboia siamensis, Antivenom Manufactured in Taiwan CDC’s Vaccine Center. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damico, D.C.; Bueno, L.G.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Marangoni, S.; da Cruz-Höfling, M.A.; Novello, J.C. Neurotoxic and myotoxic actions from Lachesis muta muta (surucucu) whole venom on the mouse and chick nerve-muscle preparations. Toxicon 2005, 46, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Zamunér, S.R.; Cogo, J.C.; Borja-Oliveira, C.R.; Prado-Franceschi, J.; da Cruz-Höfling, M.A.; Corrado, A.P. Pharmacological evidence for a presynaptic action of venoms from Bothrops insularis (jararaca ilhoa) and Bothrops neuwiedi (jararaca pintada). Toxicon 2004, 43, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamunér, S.R.; da Cruz-Höfling, M.A.; Corrado, A.P.; Hyslop, S.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L. Comparison of the neurotoxic and myotoxic effects of Brazilian Bothrops venoms and their neutralization by commercial antivenom. Toxicon 2004, 44, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, C.M.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. Solving the ‘Brown snake paradox’: In vitro characterisation of Australasian snake presynaptic neurotoxin activity. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 210, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soopairin, S.; Patikorn, C.; Taychakhoonavudh, S. Antivenom preclinical efficacy testing against Asian snakes and their availability in Asia: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.; Hodgson, W.C.; Isbister, G.K. Cross-Neutralisation of In Vitro Neurotoxicity of Asian and Australian Snake Neurotoxins and Venoms by Different Antivenoms. Toxins 2016, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhushani, U.; Isbister, G.K.; Tasoulis, T.; Hodgson, W.C.; Silva, A. In-Vitro Neutralization of the Neurotoxicity of Coastal Taipan Venom by Australian Polyvalent Antivenom: The Window of Opportunity. Toxins 2020, 12, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, J.; Oliveira, I.C.F.; Yoshida, E.H.; Cantuaria, N.M.; Cogo, J.C.; Torres-Bonilla, K.A.; Hyslop, S.; Silva Junior, N.J.; Floriano, R.S.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. Effect of the phospholipase A2 inhibitor Varespladib, and its synergism with crotalic antivenom, on the neuromuscular blockade induced by Crotalus durissus terrificus venom (with and without crotamine) in mouse neuromuscular preparations. Toxicon 2022, 214, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, F.V.; Ramos Pinto, Ê.K.; Valério Souza, N.M.; Gonçalves de Abreu, T.A.; Ortolani, P.L.; Fortes-Dias, C.L.; Garrido Cavalcante, W.L. Varespladib (LY315920) prevents neuromuscular blockage and myotoxicity induced by crotoxin on mouse neuromuscular preparations. Toxicon 2021, 202, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilliam, L.L.; Gilliam, J.; Samuel, S.P.; Carter, R.W.; Ritchey, J.; Bulfone, T.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Williams, D.J.; Durkin, D.M.; Stephens, S.I.; et al. Oral and IV Varespladib Rescue Experiments in Juvenile Pigs with Weakness Induced by Australian and Papuan Oxyuranus scutellatus Venoms. Toxins 2023, 15, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, G.H.M.; Borges, R.J.; Lomonte, B.; Lewin, M.R.; Fontes, M.R.M. The synthetic varespladib molecule is a multi-functional inhibitor for PLA2 and PLA2-like ophidic toxins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2021, 1865, 129913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, G.H.M.; Gomes, A.A.S.; Bryan-Quirós, W.; Fernández, J.; Lewin, M.R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Fontes, M.R.M. Structural basis for phospholipase A2-like toxin inhibition by the synthetic compound Varespladib (LY315920). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, M.R.; Carter, R.W.; Matteo, I.A.; Samuel, S.P.; Rao, S.; Fry, B.G.; Bickler, P.E. Varespladib in the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming: Development History and Preclinical Evidence Supporting Advancement to Clinical Trials in Patients Bitten by Venomous Snakes. Toxins 2022, 14, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Solano, G.; Pla, D.; Herrera, M.; Segura, Á.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Sánchez, A.; Sanz, L.; Lomonte, B.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of the Efficacy of Antivenoms for Snakebite Envenoming: State-of-the-Art and Challenges Ahead. Toxins 2017, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulfone, T.C.; Samuel, S.P.; Bickler, P.E.; Lewin, M.R. Developing Small Molecule Therapeutics for the Initial and Adjunctive Treatment of Snakebite. J. Trop. Med. 2018, 2018, 4320175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lay, M.; Hodgson, W.C. A Comparison of the Efficacy of Antivenoms and Varespladib against the In Vitro Pre-Synaptic Neurotoxicity of Thai and Javanese Russell’s Viper (Daboia spp.) Venoms. Toxins 2024, 16, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030124
Lay M, Hodgson WC. A Comparison of the Efficacy of Antivenoms and Varespladib against the In Vitro Pre-Synaptic Neurotoxicity of Thai and Javanese Russell’s Viper (Daboia spp.) Venoms. Toxins. 2024; 16(3):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030124
Chicago/Turabian StyleLay, Mimi, and Wayne C. Hodgson. 2024. "A Comparison of the Efficacy of Antivenoms and Varespladib against the In Vitro Pre-Synaptic Neurotoxicity of Thai and Javanese Russell’s Viper (Daboia spp.) Venoms" Toxins 16, no. 3: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030124
APA StyleLay, M., & Hodgson, W. C. (2024). A Comparison of the Efficacy of Antivenoms and Varespladib against the In Vitro Pre-Synaptic Neurotoxicity of Thai and Javanese Russell’s Viper (Daboia spp.) Venoms. Toxins, 16(3), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030124




