Multistage Detection of Tetrodotoxin Traces in Diodon hystrix Collected in El Salvador
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. HPLC-MS/MS-SRM
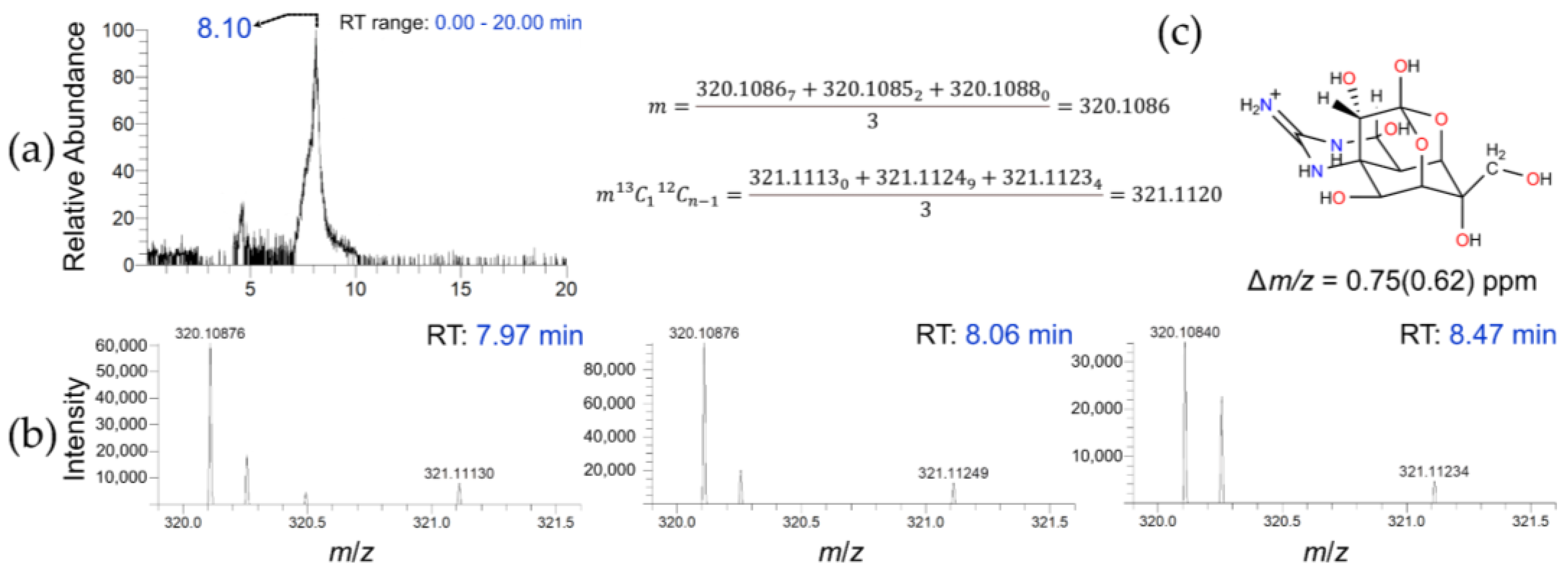
2.2. HPLC-HRFTMS
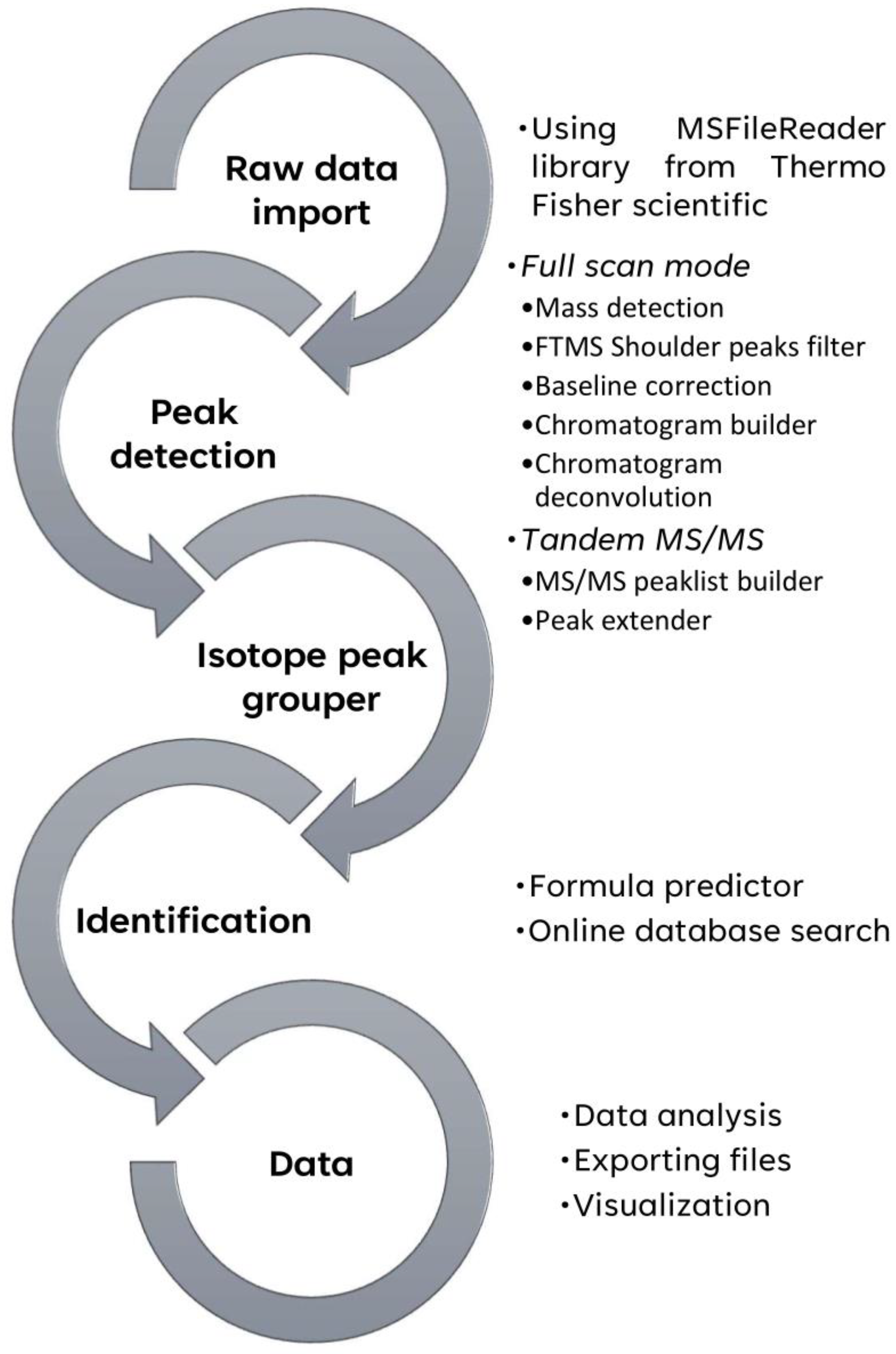
2.3. Post-Acquisition Data Analysis by MZmine
2.4. HPLC-HRFTMS2
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
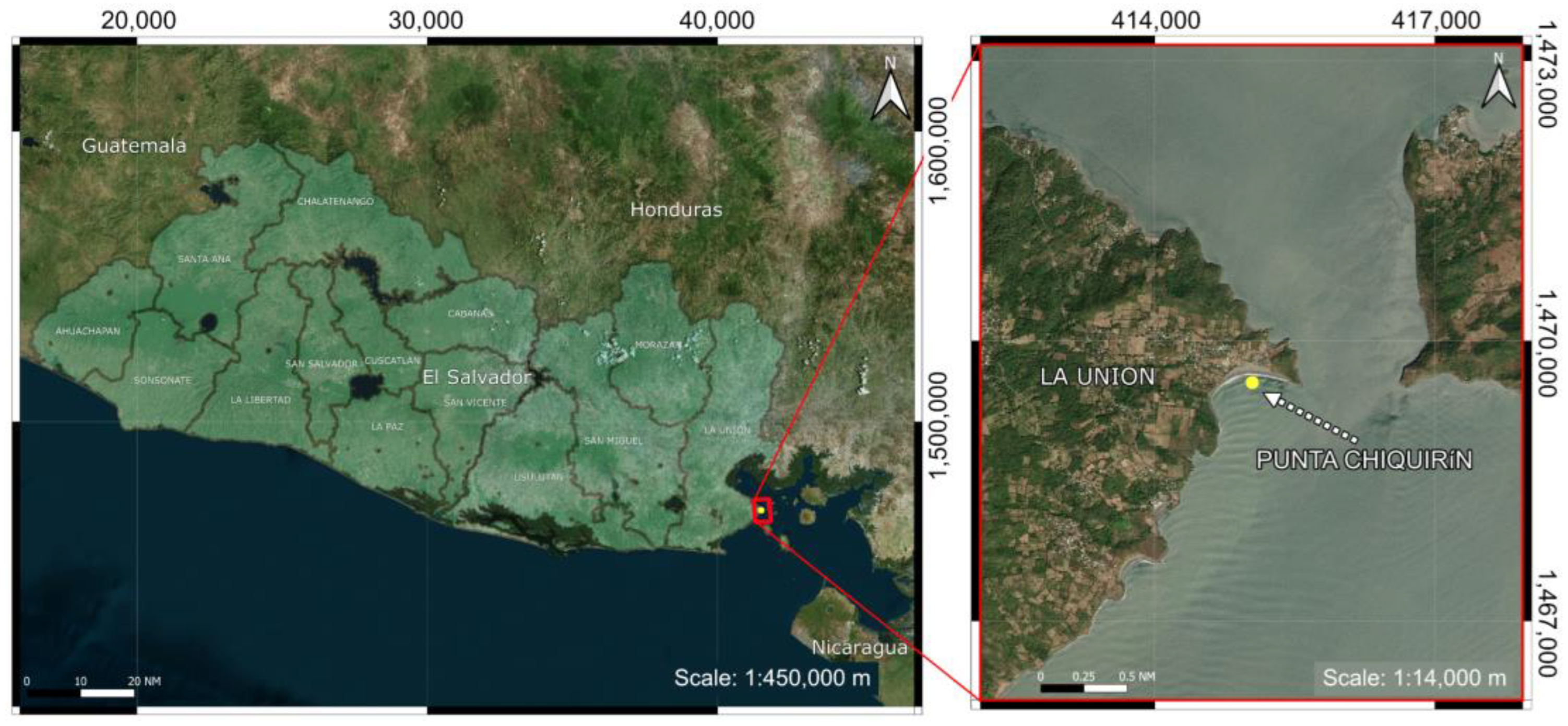
4.2. Specimen Collection
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. Methodology
4.5. Analytic Methodologies Used in Tetrodotoxin Detection
4.5.1. HPLC-MS/MS-SRM
4.5.2. HPLC-HRFTMS
4.5.3. HPLC-HRFTMS2
4.6. Post-Acquisition Data Processing
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katikou, P.; Gokbulut, C.; Kosker, A.R.; Campàs, M.; Ozogul, F. An Updated Review of Tetrodotoxin and Its Peculiarities. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Toennes, S.W.; Mebs, D. Tetrodotoxin in Asian newts (Salamandridae). Toxicon 2017, 134, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanifin, C.T. The chemical and evolutionary ecology of tetrodotoxin (TTX) toxicity in terrestrial vertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, A.N.; Ducey, P.K.; Neuman-Lee, L.; Hanifin, C.T.; French, S.S.; Pfrender, M.E.; Brodie Iii, E.D.; Brodie Jr, E.D. Confirmation and Distribution of Tetrodotoxin for the First Time in Terrestrial Invertebrates: Two Terrestrial Flatworm Species (Bipalium adventitium and Bipalium kewense). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvitti, L.R.; Wood, S.A.; Winsor, L.; Cary, S.C. Intracellular immunohistochemical detection of tetrodotoxin in Pleurobranchaea maculata (Gastropoda) and Stylochoplana sp. (Turbellaria). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hort, V.; Arnich, N.; Guérin, T.; Lavison-Bompard, G.; Nicolas, M. First Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Bivalves and Gastropods from the French Mainland Coasts. Toxins 2020, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-J.; Yu, R.-C.; Luo, X.; Zhou, M.-J.; Lin, X.-T. Toxin-screening and identification of bacteria isolated from highly toxic marine gastropod Nassarius semiplicatus. Toxicon 2008, 52, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, D.I.; Vlasenko, A.E.; Magarlamov, T.Y. Stable Tetrodotoxin Production by Bacillus sp. Strain 1839. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarlamov, T.Y.; Melnikova, D.I.; Chernyshev, A.V. Tetrodotoxin-Producing Bacteria: Detection, Distribution and Migration of the Toxin in Aquatic Systems. Toxins 2017, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheepa, V.; Vasconcelos, V. Microbial diversity associated with tetrodotoxin production in marine organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azman, A.M.N.; Samsur, M.; Othman, M. Distribution of Tetrodotoxin among Tissues of Pufferfish from Sabah and Sarawak Waters. Sains Malays. 2014, 43, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, L.; Manu, A.; Chocalingum, R.; Menta, V.; Kumar, V.; Khanna, G. Genotoxicity of Tetrodotoxin Extracted from Different Organs of Diodon hystrix Puffer Fish from South East Indian Coast. Res. J. Toxins 2016, 8, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamele, I.J.; Timba, I.; Costa, P.R.; Vasconcelos, V. Tetrodotoxin and analogues in two local pufferfish species from Inhaca Island—South of Mozambique: First report in the Mozambican coast. Toxicon 2022, 216, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jal, S.; Khora, S.S. An overview on the origin and production of tetrodotoxin, a potent neurotoxin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, D.I.; Magarlamov, T.Y. An Overview of the Anatomical Distribution of Tetrodotoxin in Animals. Toxins 2022, 14, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Jeong, D.Y.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, H.D.; Kim, C.H.; Park, W.W.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, D.S. A tetrodotoxin-producing Vibrio strain, LM-1, from the puffer fish Fugu vermicularis radiatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, V.C.H.; Yu, P.H.F.; Ho, K.C.; Lee, F.W.F. Isolation and identification of a new tetrodotoxin-producing bacterial species, Raoultella terrigena, from Hong Kong marine puffer fish Takifugu niphobles. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2384–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, M.; Rännar, S.; Madsen, R.; Donten, M.A.; Marsden-Edwards, E.; Moritz, T.; Shockcor, J.P.; Johansson, E.; Trygg, J. Strategy for Optimizing LC-MS Data Processing in Metabolomics: A Design of Experiments Approach. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6869–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguch, T.; Arakawa, O. Tetrodotoxin—Distribution and Accumulation in Aquatic Organisms, and Cases of Human Intoxication. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 220–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xiang, Y.-J.-Y.; Liu, Z.-F.; Wang, Z.-H.; Feng, X.-S. Tetrodotoxin and Its Analogues in Food: Recent Updates on Sample Preparation and Analytical Methods Since 2012. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 12249–12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeij, G.J.; Zipser, E. The Diet of Diodon hystrix (Teleostei: Tetraodontiformes): Shell-crushing on Guam’s Reefs. Bish. Mus. Bull. Zool. 2015, 9, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, J.R. Occurence of exotic fished in east Anglian waters: Porcupinefish Diodon hystrix and Piranha Pygocentrus sp. Trans. Suffolk Nat. Soc. 2006, 42, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Leis, J.M. Nomenclature and distribution of the species of the porcupinefish family Diodontidae (Pisces, Teleostei). Mem. Mus. Vic. 2006, 63, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.K.; Ostman, D.C. Pufferfish Poisoning: Emergency Diagnosis and Management of Mild. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1986, 15, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevett, A.J.; Mavo, B.; Warrell, D.A. Tetrodotoxic Poisoning from Ingestion of a Porcupine Fish (Diodon hystrix) in Papua New Guinea: Nerve Conduction Studies. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 56, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gorcum, T.F.; Janse, M.; Leenders, M.E.C.; de Vries, I.; Meulenbelt, J. Intoxication Following Minor Stabs from the Spines of a Porcupine Fish. Clin. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpezzi, E.L.A.; De Freitas, J.C.; Rantin, F.T. Occurrence of toxins, other than paralysing type, in the skin of tetraodontiformes fish. Toxicon 1997, 35, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.; Harada, R.M.; DeFelice, S.V.; Bienfang, P.K.; Li, Q.X. Bacterial production of tetrodotoxin in the pufferfish Arothron hispidus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khora, S.S.; Isa, J.; Yasumoto, T. Toxicity of Puffers from Okinawa, Japan. Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 1991, 57, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, Y.; Ohta, A.; Yin, X.; Ishizaki, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Doi, H.; Ishibashi, T. Difference in Uptake of Tetrodotoxin and Saxitoxins into Liver Tissue Slices among Pufferfish, Boxfish and Porcupinefish. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anta, C.; González, N.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C. A New Secosterol from the Indonesian Octocoral Pachyclavularia violacea. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1357–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdova, O.A.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Stonik, V.A.; Riguera, R.; Jiménez, C. Cytotoxic Triterpene Glycosides from Far-Eastern Sea Cucumbers Belonging to the Genus Cucumaria. Liebigs Ann. 1997, 1997, 2351–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pech-Puch, D.; Rodríguez, J.; Cautain, B.; Sandoval-Castro, C.A.; Jiménez, C. Cytotoxic Furanoditerpenes from the Sponge Spongia tubulifera Collected in the Mexican Caribbean. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, Y.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Miyazawa, T.; Yasumoto, T. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of tetrodotoxin and its analogs: Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry, tandem mass spectrometry, and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 290, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glish, G.L.; McLuckey, S.A.; Asano, K.G. Determination of daughter ion formulas by multiple stages of mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1990, 1, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loziuk, P.L.; Sederoff, R.R.; Chiang, V.L.; Muddiman, D.C. Establishing ion ratio thresholds based on absolute peak area for absolute protein quantification using protein cleavage isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Analyst 2014, 139, 5439–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C.; Miller, R.D. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 7th ed.; Pearson Education Limited: Harlow, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Makarov, A.; Denisov, E.; Lange, O. Dynamic Range of Mass Accuracy in LTQ Orbitrap Hybrid Mass Spectrometer. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 17, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarov, A.; Denisov, E.; Kholomeev, A.; Balschun, W.; Lange, O.; Strupat, K.; Horning, S. Performance evaluation of a hybrid linear ion trap/orbitrap mass spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, T.; Fiehn, O. Seven Golden Rules for heuristic filtering of molecular formulas obtained by accurate mass spectrometry. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, A.; Walker, S. Accuracy of relative isotopic abundance and mass measurements in a single-stage orbitrap mass spectrometer. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. RCM 2012, 26, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M. Chemistry of puffer fish toxin. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2001, 20, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. Chemical and Etiological Studies on Tetrodotoxin and Its Analogs. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 1996, 15, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas-Paula, D.A.; Oliveira, T.B.; Zhang, T.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Da Costa, F.B. Prediction of anti-inflammatory plants and discovery of their biomarkers by machine learning algorithms and metabolomic studies. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, R.M.K.; Igoli, J.; Gray, A.I.; Ebiloma, G.U.; Clements, C.; Fearnley, J.; Edrada Ebel, R.A.; Zhang, T.; De Koning, H.P.; Watson, D.G. Chemical characterisation of Nigerian red propolis and its biological activity against Trypanosoma Brucei. Phytochem. Anal. 2016, 27, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najdekr, L.; Friedecký, D.; Tautenhahn, R.; Pluskal, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Adam, T. Influence of mass resolving power in orbital ion-trap mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11429–11435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Krauss, M.; Brack, W.; Schulze, T. Optimization of LC-Orbitrap-HRMS acquisition and MZmine 2 data processing for nontarget screening of environmental samples using design of experiments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7905–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürdeniz, G.; Kristensen, M.; Skov, T.; Dragsted, L.O. The Effect of LC-MS Data Preprocessing Methods on the Selection of Plasma Biomarkers in Fed vs. Fasted Rats. Metabolites 2012, 2, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Orešič, M. MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Chou, H.-N. Detection of Tetrodotoxin by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Lined-Moon Shell and Puffer Fish. Acta Zool. Taiwanica 1998, 9, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.R.; Carlson, E.E. Collision-Induced Dissociation Mass Spectrometry: A Powerful Tool for Natural Product Structure Elucidation. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 10668–10678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleno, L.; Volmer, D.A. SPECIAL FEATURE: Ion activation methods for tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 39, 1091–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.W.; Liu, H.X.; Jin, Y.B.; Li, S.F.; Bi, X.; Chung, S.; Zhang, S.S.; Jiang, Y.Y. Separation, identification and quantification of tetrodotoxin and its analogs by LC-MS without calibration of individual analogs. Toxicon 2011, 57, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, D.R.; McShane, A.J.; Wang, S. Investigation of transition ion ratio variation for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: A case study approach. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 486, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, P.G.; Abate-Pella, D.; Hewitt, J.T. Calculation of retention time tolerance windows with absolute confidence from shared liquid chromatographic retention data. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1412, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, R.J.M.; Southam, A.D.; Sommer, U.; Viant, M.R. Characterization of Isotopic Abundance Measurements in High Resolution FT-ICR and Orbitrap Mass Spectra for Improved. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3737–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenton, A.G.; Godfrey, A.R. Accurate mass measurement: Terminology and treatment of data. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 21, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Heilier, J.F.; Madalinski, G.; Genin, E.; Ezan, E.; Tabet, J.C.; Junot, C. Evaluation of accurate mass and relative isotopic abundance measurements in the LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer for further metabolomics database building. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5490–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.T.; David, S.O. An Introduction to Mass Spectrometry: Instrumentation, Applications and Strategies for Data Interpretation; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; p. 834. [Google Scholar]
- Katajamaa, M.; Miettinen, J.; Orešič, M. MZmine: Toolbox for processing and visualization of mass spectrometry based molecular profile data. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.; Krug, D.; Hüttel, S.; Müller, R. Improving Natural Products Identification through Targeted LC-MS/MS in an Untargeted Secondary Metabolomics Workflow. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10780–10788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macintyre, L.; Zhang, T.; Viegelmann, C.; Martinez, I.J.; Cheng, C.; Dowdells, C.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Gernert, C.; Hentschel, U.; Edrada-ebel, R. Metabolomic Tools for Secondary Metabolite Discovery from Marine Microbial Symbionts. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3416–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gender | Weight (g) a | L. (mm) b | Weight c | Liver | Gonads d | Kidney | Skin | Muscle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 913.9 | 199.3 ± 4.5 | Organs (g) | 82.9 | 17.7 | 8.5 | 87.2 | 95.4 |
| Raw Extr. (g) | 10.0 | 7.6 | 3.4 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |||
| Ultrafiltr. (mg) | 65.4 | 156.3 | 400.8 | 45.3 | 227.6 | |||
| Male | 1177.3 | 406.0 | Organs (g) | 33.5 | 6.5 | 10.1 | 22.5 | 75.3 |
| Raw Extr. (g) | 10.0 | 4.0 | 4.8 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |||
| Ultrafiltr. (mg) | 160.4 | 29.9 | 52.2 | 39.9 | 91.4 | |||
| Undef. | 411.9 | 184.0 ± 3.7 | Organs (g) | 39.8 | 3.5 | 3.2 | 52.6 | 48.6 |
| Raw Extr. (g) | 10.0 | 1.6 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |||
| Ultrafiltr. (mg) | 75.3 | 9.7 | 17.2 | 143.2 | 125.2 |
| Gnd. Spec. | Organs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | Gonads | Kidney | Skin | Muscle | |
| Female | - | HPLC-MS/MS-SRM * | - | HPLC-HRFTMS | - |
| Male | HPLC-HRFTMS | - | - | - | - |
| Undef. | HPLC-HRFTMS2 | - | - | - | HPLC-MS/MS-SRM * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuentes-Monteverde, J.C.; Núñez, M.J.; Amaya-Monterosa, O.; Martínez, M.L.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C. Multistage Detection of Tetrodotoxin Traces in Diodon hystrix Collected in El Salvador. Toxins 2023, 15, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070409
Fuentes-Monteverde JC, Núñez MJ, Amaya-Monterosa O, Martínez ML, Rodríguez J, Jiménez C. Multistage Detection of Tetrodotoxin Traces in Diodon hystrix Collected in El Salvador. Toxins. 2023; 15(7):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070409
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuentes-Monteverde, Juan Carlos, Marvin J. Núñez, Oscar Amaya-Monterosa, Morena L. Martínez, Jaime Rodríguez, and Carlos Jiménez. 2023. "Multistage Detection of Tetrodotoxin Traces in Diodon hystrix Collected in El Salvador" Toxins 15, no. 7: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070409
APA StyleFuentes-Monteverde, J. C., Núñez, M. J., Amaya-Monterosa, O., Martínez, M. L., Rodríguez, J., & Jiménez, C. (2023). Multistage Detection of Tetrodotoxin Traces in Diodon hystrix Collected in El Salvador. Toxins, 15(7), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070409








