Correlation between Saliva Levels and Serum Levels of Free Uremic Toxins in Healthy Volunteers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
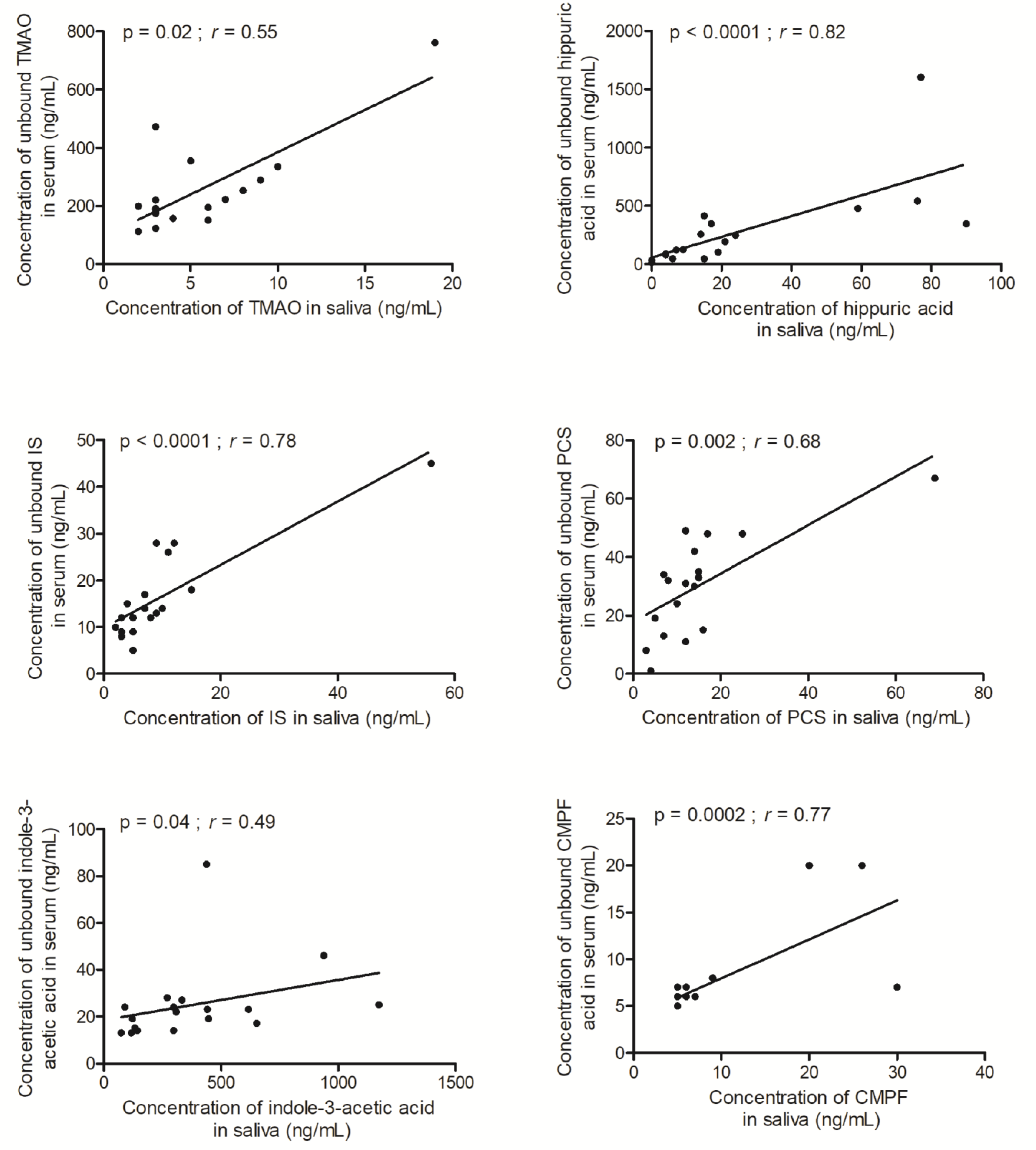
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Method
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Stock Solution Preparation
4.3. Method
4.3.1. Sample Collection
4.3.2. Sample Preparation
- Saliva
- Serum
4.3.3. The LC-MS/MS Apparatus
4.3.4. Method Validation
- The matrix effect
- Stability
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaidya, S.R.; Aeddula, N.R. Chronic Renal Failure. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vanholder, R.; De Smet, R.; Glorieux, G.; Argilés, A.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Clark, W.; Cohen, G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Deppisch, R.; et al. Review on uremic toxins: Classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liabeuf, S.; Barreto, D.V.; Barreto, F.C.; Meert, N.; Glorieux, G.; Schepers, E.; Temmar, M.; Choukroun, G.; Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.A.; et al. Free p-cresylsulphate is a predictor of mortality in patients at different stages of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 25, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atherton, J.G.; Hains, D.S.; Bissler, J.; Pendley, B.D.; Lindner, E. Generation, clearance, toxicity, and monitoring possibilities of unaccounted uremic toxins for improved dialysis prescriptions. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018, 315, F890–F902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Y. -Martin, R.M.; Orlander, P.R. Salivary Cortisol Can Replace Free Serum Cortisol Measurements in Patients with Septic Shock. Chest 2011, 140, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, K.; Forney, R.B.; Voeller, K. Monitoring Phenytoin in Salivary and Plasma Ultrafiltrates of Pediatric Patients. Ther. Drug Monit. 1983, 5, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatapathy, R.; Govindarajan, V.; Oza, N.; Parameswaran, S.; Pennagaram Dhanasekaran, B.; Prashad, K.V. Salivary Creatinine Estimation as an Alternative to Serum Creatinine in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Int. J. Nephrol. 2014, 2014, 742724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobitch, R.K.; Svensson, C.K. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Saliva. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1992, 23, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korytowska, N.; Sankowski, B.; Wyczałkowska-Tomasik, A.; Pączek, L.; Wroczyński, P.; Giebułtowicz, J. The utility of saliva testing in the estimation of uremic toxin levels in serum. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 57, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabresse, N.; Uteem, I.; Lamy, E.; Massy, Z.; Larabi, I.A.; Alvarez, J.-C. Quantification of free and protein bound uremic toxins in human serum by LC-MS/MS: Comparison of rapid equilibrium dialysis and ultrafiltration. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 507, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giebułtowicz, J.; Korytowska, N.; Sankowski, B.; Wroczyński, P. Development and validation of a LC-MS/MS method for quantitative analysis of uraemic toxins p-cresol sulphate and indoxyl sulphate in saliva. Talanta 2016, 150, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoudi Rad, H.; Rabiei, M.; Sobhani, A.; Sadegh Khanjani, M.; Rahbar Taramsar, M.; Kazemnazhad Leili, E. Free amino acids in stimulated and unstimulated whole saliva: Advantages or disadvantages. J. Oral Rehabil. 2014, 41, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuc, D.; Rahnama, M.; Tomaszewski, T.; Rzeski, W.; Wejksza, K.; Urbanik-Sypniewska, T.; Parada-Turska, J.; Wielosz, M.; Turski, W.A. Kynurenic Acid in Human Saliva–Does It Influence Oral Microflora? Pharmacol. Rep. 2006, 58, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Bush, K.T.; Nigam, S.K. Key Role for the Organic Anion Transporters, OAT1 and OAT3, in the in vivo Handling of Uremic Toxins and Solutes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masereeuw, R.; Mutsaers, H.A.M.; Toyohara, T.; Abe, T.; Jhawar, S.; Sweet, D.H.; Lowenstein, J. The Kidney and Uremic Toxin Removal: Glomerulus or Tubule? Semin. Nephrol. 2014, 34, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakamatsu, A.; Ochiai, S.; Suzuki, E.; Yokota, Y.; Ochiai, M.; Kotani, Y.; Sasahara, S.; Nakanaga, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ueno, S.; et al. Proposed selection strategy of surrogate matrix to quantify endogenous substances by Japan Bioanalysis Forum DG2015-15. Bioanalysis 2018, 10, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, Y.; Ezawa, A.; Kikuchi, K.; Tsuruta, Y.; Niwa, T. Protein-bound uremic toxins in hemodialysis patients measured by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry and their effects on endothelial ROS production. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Uremic Toxins (UT) | LOD (ng/mL) | Linearity (ng/mL) | Matrix Effect (CV%) 100 ng/mL n = 6 | Matrix Effect (CV%) 1000 ng/mL n = 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMPF | 0.3 | 1–50,000 | +21% (10%) | +8% (9%) |
| Hippuric acid | 2 | 5–50,000 | −11% (12%) | −10% (12%) |
| Indole-3-acetic acid | 2 | 5–50,000 | +16% (15%) | +3% (15%) |
| Indoxyl sulfate | 0.3 | 1–50,000 | +4% (11%) | −7% (13%) |
| Kynurenine | 20 | 50–50,000 | −11% (12%) | −6% (14%) |
| Kynurenic acid | 20 | 10–50,000 | −7% (14%) | −4% (13%) |
| P-cresyl glucuronide | 20 | 10–10,000 | −4% (13%) | −5% (13%) |
| PCS | 0.3 | 1–50,000 | +4% (13%) | −2% (11%) |
| Phenylacetylglutamine | 3 | 10–50,000 | +1% (12%) | 0% (15%) |
| Phenylalanine | 20 | 50–50,000 | −3% (12%) | −9% (7%) |
| TMAO | 3 | 1–50,000 | −34% (3%) | −38% (5%) |
| Tryptophan | 20 | 50–50,000 | +6% (13%) | −4% (13%) |
| Tyrosine | 20 | 50–50,000 | −5% (11%) | −20% (13%) |
| Molecules | Median (Range) UT Concentration in Saliva (ng/mL) | Median (Range) Concentration of Free UT in Serum (ng/mL) | Serum/Saliva Ratio | Spearman Correlation Coefficient (r) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMAO | 4 (2–19) | 197 (112–761) | 51 (24–143) | 0.55 | 0.02 |
| Tyrosine | 2536 (976–11,404) | 7632 (5022–13,530) | 3.1 (0.5–12) | −0.43 | 0.08 |
| Phenylalanine | 2047 (1000–16,624) | 8159 (5457–13,933) | 4.6 (0.5–11.8) | −0.11 | 0.66 |
| Kynurenine | <50 | < 50 (<50–54) | 12.7 (2.6–267) | NF4 | NF4 |
| Tryptophan | 143 (<50–1863) | 1335 (662–2292) | 12 (0.5–108) | −0.30 | 0.22 |
| Hippuric acid | 15 (<5–90) | 159 (16–1604) | 15 (3.0–78.5) | 0.82 | <0.0001 |
| Phenylacetylglutamine | 11 (<10–20) | 203 (22–340) | 10 (4.8–17) | 0.21 | 0.41 |
| Indoxyl sulfate | 7 (2–56) | 14 (5–45) | 2.4 (0.8–4.6) | 0.78 | <0.0001 |
| Kynurenic acid | <10 | <10 | NF4 | NF4 | NF4 |
| P-cresyl glucuronide | <10 (<10–12) | 10 (<10–57) | 4.0 (0.1–48) | NF4 | NF4 |
| PCS | 12 (3–69) | 31 (1–67) | 2.4 (0.4–5.3) | 0.68 | 0.002 |
| Indole-3-acetic acid | 302 (74–1174) | 22 (13–85) | 0.08 (0.02–0.28) | 0.49 | 0.04 |
| CMPF | 5 (5–30) | 6 (5–20) | 0.1 (0.2–1.4) | 0.77 | 0.0002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fabresse, N.; Larabi, I.A.; Abe, E.; Lamy, E.; Rigothier, C.; Massy, Z.A.; Alvarez, J.-C. Correlation between Saliva Levels and Serum Levels of Free Uremic Toxins in Healthy Volunteers. Toxins 2023, 15, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020150
Fabresse N, Larabi IA, Abe E, Lamy E, Rigothier C, Massy ZA, Alvarez J-C. Correlation between Saliva Levels and Serum Levels of Free Uremic Toxins in Healthy Volunteers. Toxins. 2023; 15(2):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020150
Chicago/Turabian StyleFabresse, Nicolas, Islam Amine Larabi, Emuri Abe, Elodie Lamy, Claire Rigothier, Ziad A. Massy, and Jean-Claude Alvarez. 2023. "Correlation between Saliva Levels and Serum Levels of Free Uremic Toxins in Healthy Volunteers" Toxins 15, no. 2: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020150
APA StyleFabresse, N., Larabi, I. A., Abe, E., Lamy, E., Rigothier, C., Massy, Z. A., & Alvarez, J.-C. (2023). Correlation between Saliva Levels and Serum Levels of Free Uremic Toxins in Healthy Volunteers. Toxins, 15(2), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020150






