Quercetin Attenuates the Combined Effects of Zearalenone and Lipopolysaccharide on IPEC-J2 Cell Injury through Activating the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
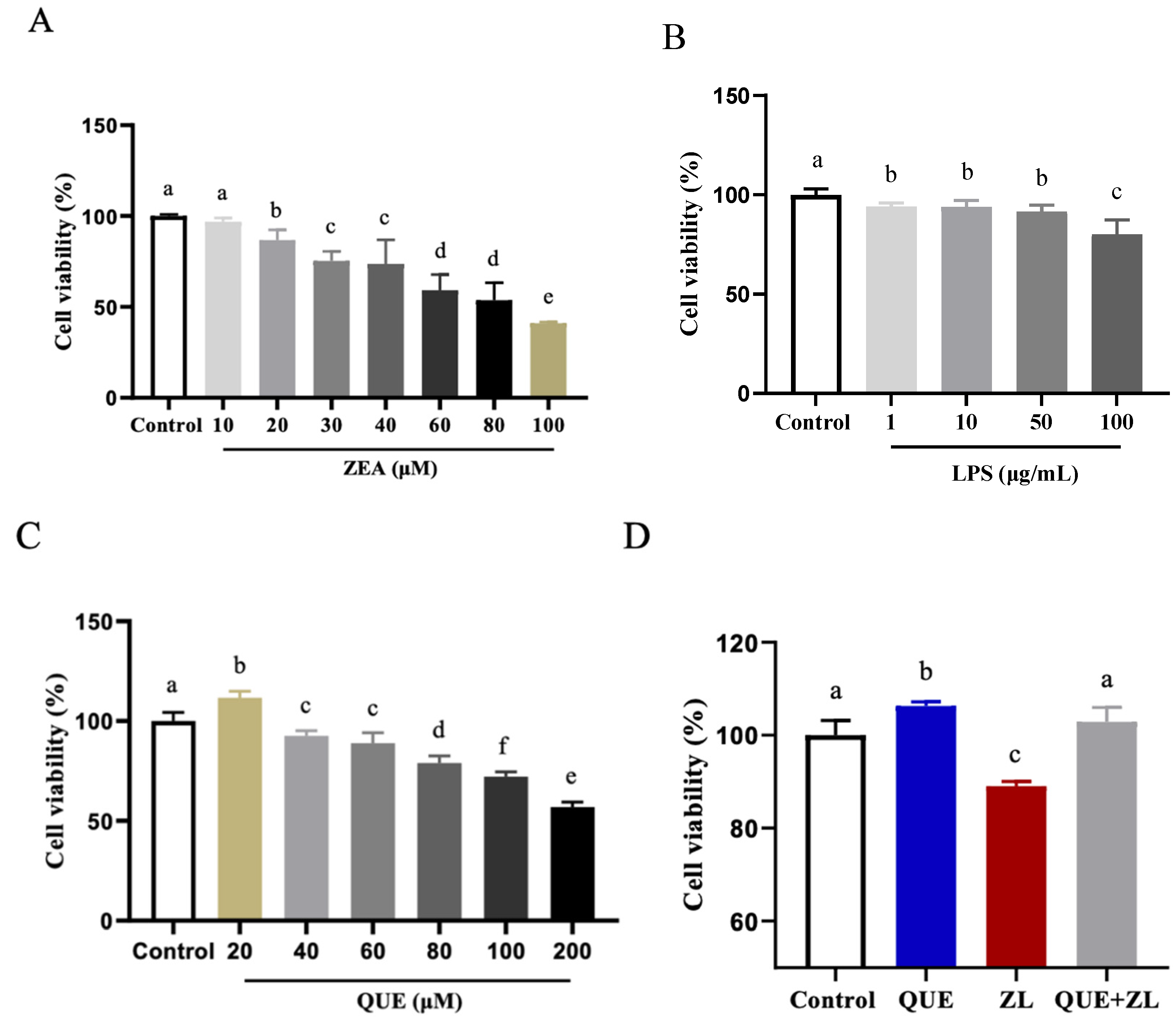
2.1. Effect of Quercetin-Mitigated Zearalenone and LPS on the Cellular Viability
2.2. Quercetin Alleviates the Effect of Zearalenone and LPS on Cellular Lactate Dehydrogenase
2.3. Effect of Quercetin Mitigation of Zearalenone in Combination with LPS on the Cellular Total Antioxidant Capacity
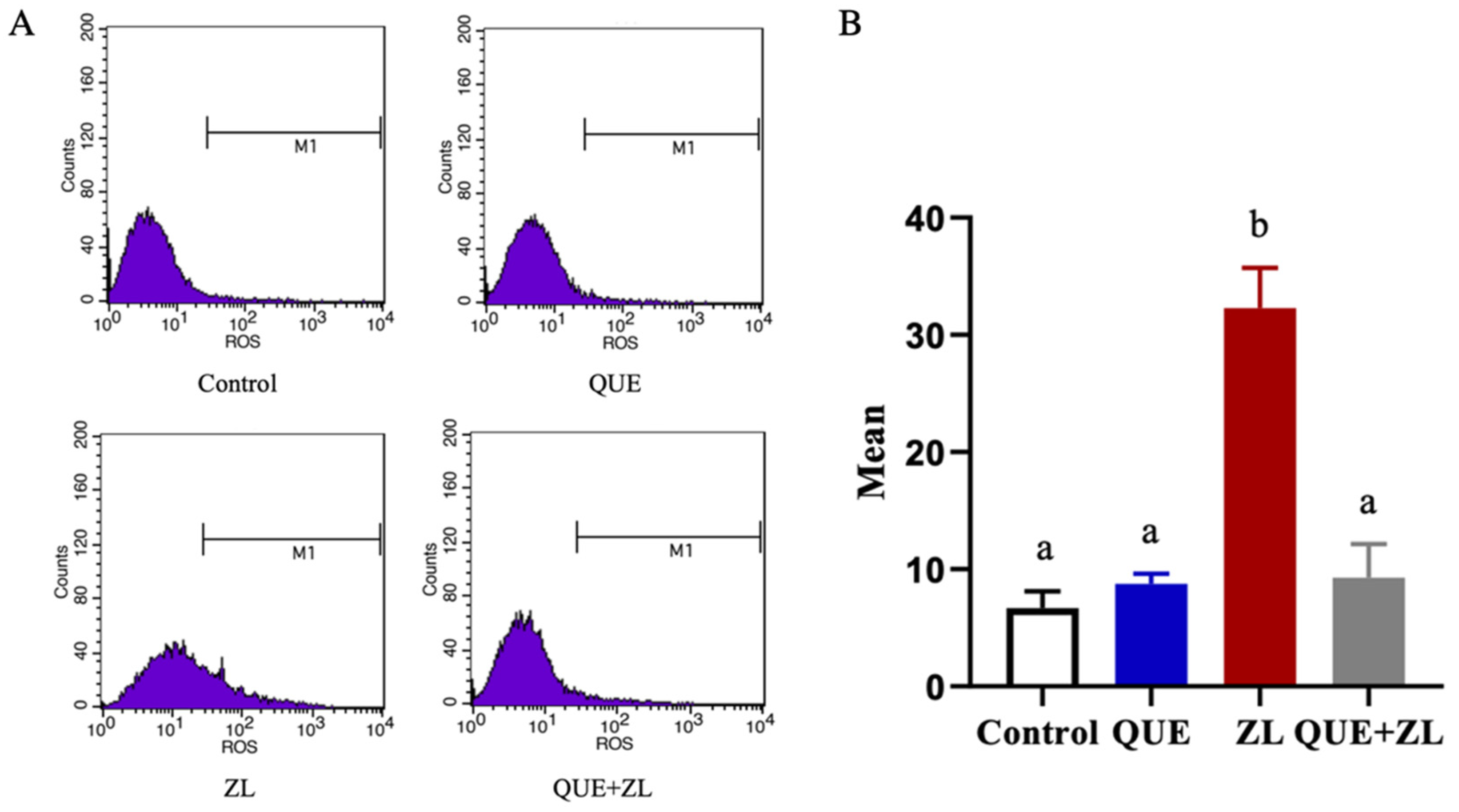
2.4. Quercetin Alleviates the Effect of Zearalenone in Combination with LPS on the Cellular Reactive Oxygen Species
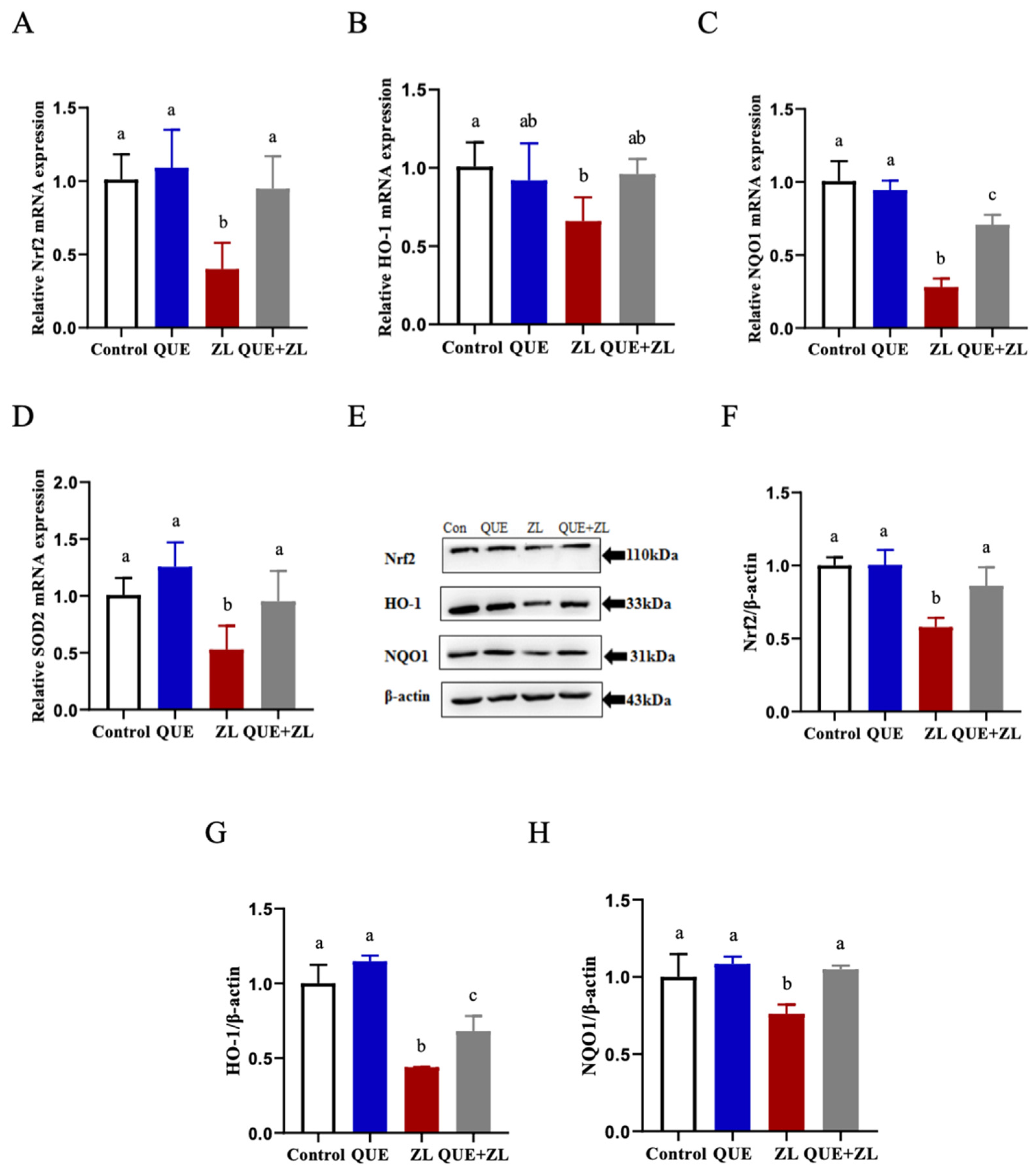
2.5. Quercetin Alleviates the Effect of Zearalenone in Combination with LPS on the Nrf2 Pathway Relative Genes of IPEC-J2 Cells
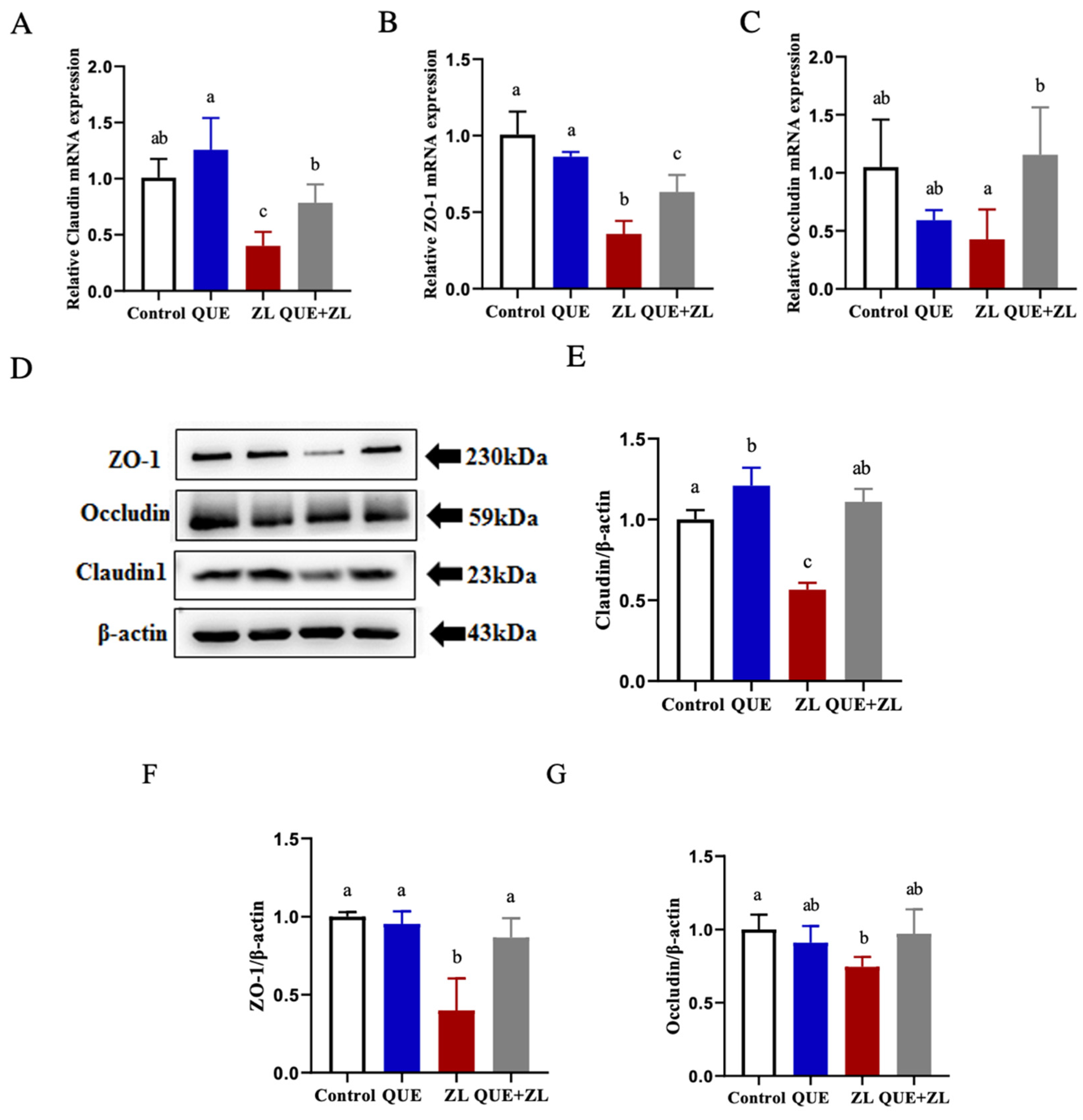
2.6. Quercetin Alleviates the Effect of Zearalenone in Combination with LPS on Cellular Tight Junctions
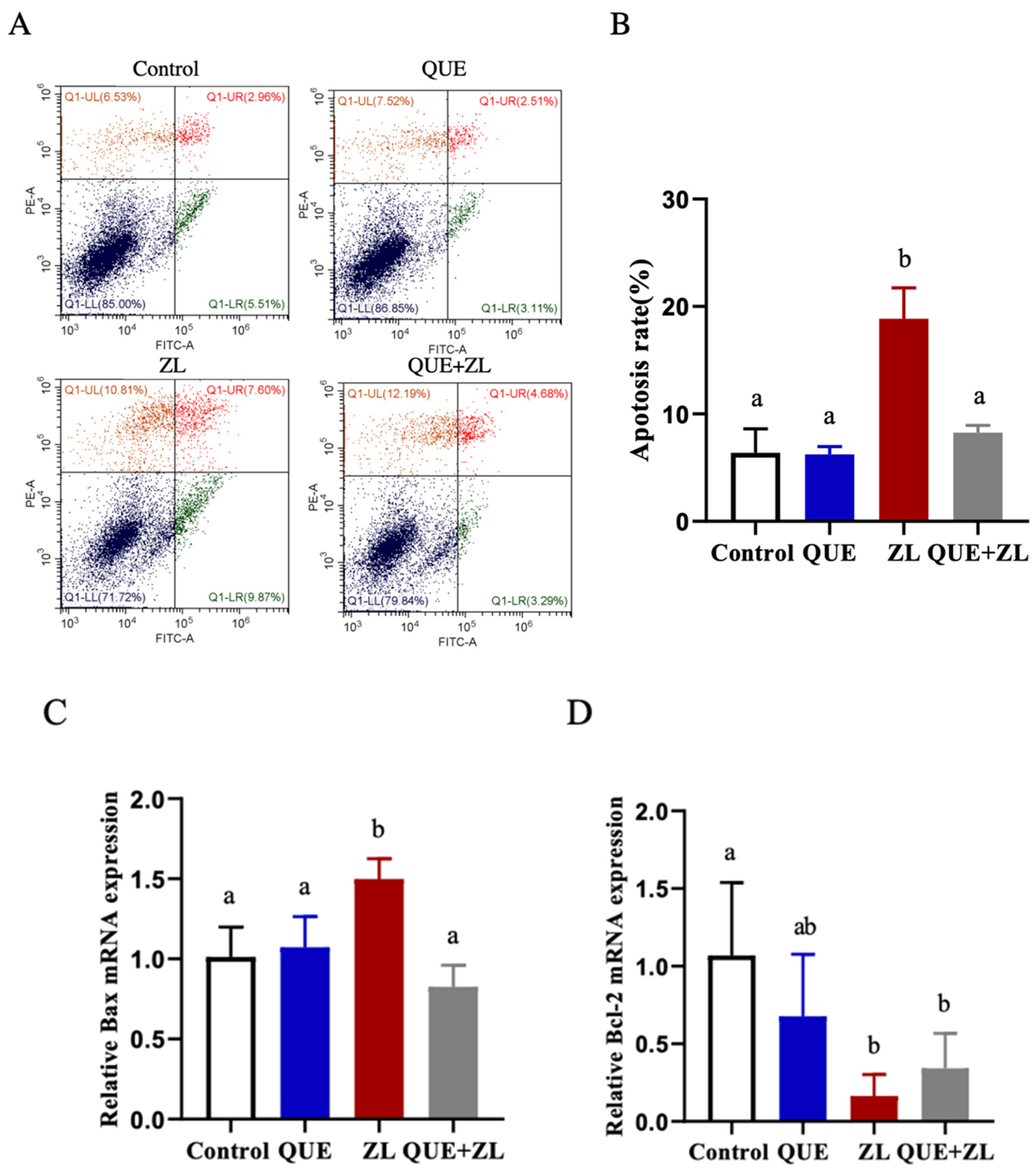
2.7. Quercetin Alleviates the Effect of Zearalenone in Combination with LPS on Apoptosis
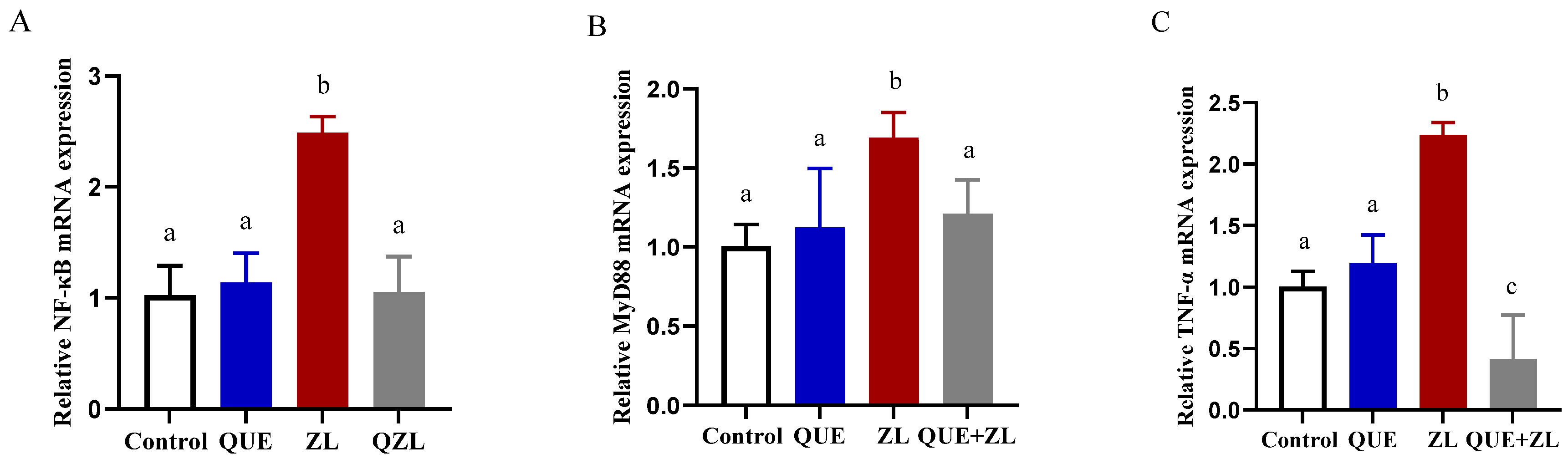
2.8. Quercetin Mitigates the Effect of Zearalenone in Combination with LPS on Inflammation-Related Genes of IPEC-J2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals and Reagents
5.2. Cell Culture
5.3. Cell Viability Assay
5.4. Cell Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay (LDH)
5.5. Total Antioxidant Capacity (T-AOC) Assay
5.6. Reactive Oxygen Assay
5.7. Total RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
5.8. Western Blot
5.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aichinger, G.; Puntscher, H.; Beisl, J.; Kuett, M.-L.; Warth, B.; Marko, D. Delphinidin protects colon carcinoma cells against the genotoxic effects of the mycotoxin altertoxin II. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 284, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abassi, H.; Ayed-Boussema, I.; Shirley, S.; Abid, S.; Bacha, H.; Micheau, O. The mycotoxin zearalenone enhances cell proliferation, colony formation and promotes cell migration in the human colon carcinoma cell line HCT116. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 254, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Puel, O.; Pinton, P.; Cossalter, A.-M.; Chou, T.-C.; Oswald, I.P. Co-exposure to low doses of the food contaminants deoxynivalenol and nivalenol has a synergistic inflammatory effect on intestinal explants. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2677–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Hsiao, F.S.H.; Cheng, Y.H. Effects of deoxynivalenol and mycotoxin adsorbent agents on mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways and inflammation-associated gene expression in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Toxins 2021, 13, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Moon, Y. Mycotoxin detoxifiers detoxifiers attenuate deoxynivalenol-induced pro-inflammatory barrier insult in porcine enterocytes as an in vitro evaluation model of feed mycotoxin reduction. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 38, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.A.; Li, Y.; Ma, Z.F.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhu, W.F.; Jiang, G.J. Protective effects of lycopene against zearalenone-induced reproductive toxicity in early pregnancy through anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-apoptotic effects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 179, 113936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, L.; Stella, A.; Seva, J.; Jose Pallares, F.; Lahjouji, T.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Oswald, I.P. Proteome changes induced by a short, non-cytotoxic exposure to the mycoestrogen zearalenone in the pig intestine. J. Proteom. 2020, 224, 103842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.J.; Fu, W.; Zhao, X.Y.; Chang, X.J.; Liu, H.J.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, R.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; et al. Zearalenone disturbs the reproductive-immune axis in pigs: The role of gut microbial metabolites. Microbiome 2022, 10, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylska-Gornowicz, B.; Lewczuk, B.; Prusik, M.; Hanuszewska, M.; Petrusewicz-Kosinska, M.; Gajecka, M.; Zielonka, L.; Gajecki, M. The effects of deoxynivalenol and zearalenone on the pig large intestine. A light and electron microscopy study. Toxins 2018, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Shen, T.; Ding, Q.; Lv, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, K.; Yan, L.; Song, S. Zearalenone induces ROS-mediated mitochondrial damage in porcine IPEC-J2 cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017, 31, e21944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Fang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Transcriptional profiling of zearalenone-induced inhibition of IPEC-J2 cell proliferation. Toxicon 2019, 172, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Lin, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, T.; Xie, G.; Wu, D.; Xu, Y. Quercetin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via the Sirt1/Nrf2/Gpx4 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 52, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, M.R.; Nabavi, S.M.; Braidy, N.; Setzer, W.N.; Ahmed, T.; Nabavi, S.F. Quercetin and the mitochondria: A mechanistic view. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 532–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekalina, N.; Burmak, Y.; Petrov, Y.; Borisova, Z.; Manusha, Y.; Kazakov, Y.; Kaidashev, I. Quercetin reduces the transcriptional activity of NF-kB in stable coronary artery disease. Indian Heart J. 2018, 70, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sul, O.J.; Ra, S.W. Quercetin Prevents LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Modulating NOX2/ROS/NF-kB in Lung Epithelial Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; He, X. Quercetin inhibits TNF-alpha induced HUVECs apoptosis and inflammation via downregulating NF-kB and AP-1 signaling pathway in vitro. Medicine 2020, 99, e22241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Fu, H.; Zhou, R.; Yang, Z.; Bai, G.; Shi, B. Toxic effects of glyphosate on intestinal morphology, antioxidant capacity and barrier function in weaned piglets. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Effects of mycotoxin-contaminated feed on farm animals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Guo, C.; Yu, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H.; Deng, J. Progress in mycotoxins affecting intestinal mucosal barrier function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Chang, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, C.; Yuan, L.; Yin, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, F. Effect of the combined compound probiotics with glycyrrhinic acid on alleviating cytotoxicity of IPEC-J2 Cells induced by multi-mycotoxins. Toxins 2022, 14, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Lv, Y.; Ren, S.; Shao, M.; Shen, T.; Huang, K.; Zhou, J.; Yan, L.; Song, S. Zearalenone (ZEA)-induced intestinal inflammation is mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Gu, A.; Li, J.; Shan, A. The antagonistic effect of glutamine on zearalenone-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in IPEC-J2 Cells. Toxins 2021, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Ajuwon, K.M. Butyrate modifies intestinal barrier function in IPEC-J2 cells through a selective upregulation of tight junction proteins and activation of the Akt signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e017958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halawa, A.; Daenicke, S.; Kersten, S.; Breves, G. Intestinal transport of deoxynivalenol across porcine small intestines. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2013, 67, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.Y.M.; Turner, P.C.; El-Nezami, H. Individual and combined cytotoxic effects of Fusarium toxins (deoxynivalenol, nivalenol, zearalenone and fumonisins B1) on swine jejunal epithelial cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 57, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, D.E.; Motiu, M.; Taranu, I. Food contaminant zearalenone and its metabolites affect cytokine synthesis and intestinal epithelial integrity of porcine cells. Toxins 2015, 7, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Liu, W.; Zhao, L.; Cao, L.; Shen, Z. Low doses of individual and combined deoxynivalenol and zearalenone in naturally moldy diets impair intestinal functions via inducing inflammation and disrupting epithelial barrier in the intestine of piglets. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 333, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Obremski, K.; Zielonka, L.; Gonkowski, S. The influence of low doses of zearalenone and T-2 toxin on calcitonin gene related peptide-like immunoreactive (CGRP-LI) neurons in the ENS of the porcine descending colon. Toxins 2017, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speijers, G.J.A.; Speijers, M.H.M. Combined toxic effects of mycotoxins. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 153, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creppy, E.E.; Lorkowski, G.; Beck, G.; Roschenthaler, R.; Dirheimer, G. Combined action of citrinin and ochratoxin A on hepatoma tissue culture cells. Toxicol. Lett. 1980, 5, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinkellner, H.; Binaglia, M.; Dall’Asta, C.; Gutleb, A.C.; Metzler, M.; Oswald, I.P.; Parent-Massin, D.; Alexander, J. Combined hazard assessment of mycotoxins and their modified forms applying relative potency factors: Zearalenone and T2/HT2 toxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Jiang, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W. Zearalenone exposure affects the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway and glucose nutrient absorption related genes of porcine jejunal epithelial cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajecka, M.; Zielonka, L.; Gajecki, M. Activity of zearalenone in the porcine intestinal tract. Molecules 2017, 22, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), oxygen radicals and antioxidants: Where are we now, where is the field going and where should we go? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 633, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, X.; Wang, X.; Ge, Q.; Bian, F. The effects of SIRT1/FoxO1 on LPS induced INS-1 cells dysfunction. Stress-Int. J. Biol. Stress 2019, 22, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Diao, P.; Shu, X.; Li, L.; Xiong, L. Quercetin and quercitrin attenuates the inflammatory response and oxidative stress in LPS-induced RAW264.7 Cells: In vitro assessment and a theoretical model. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7039802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nioi, P.; Nguyen, T.; Sherratt, P.J.; Pickett, C.B. The carboxy-terminal Neh3 domain of Nrf2 is required for transcriptional activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 10895–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Shan, A. DL-Selenomethionine alleviates oxidative stress induced by zearalenone via Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway in IPEC-J2 Cells. Toxins 2021, 13, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyong, C.; Vardhanabhuti, N.; Jianmongkol, S. Natural polyphenols prevent indomethacin-induced and diclofenac-induced Caco-2 cell death by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress regardless of their direct reactive oxygen species scavenging capacity. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Jiang, S.Z.; Huang, L.B.; Yang, W.R.; Yang, Z.B. Zearalenone regulates key factors of the Kelch-like erythroid cell-derived protein with CNC homology-associated protein 1-nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling pathway in duodenum of post-weaning gilts. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, W.P.P.; Mohd-Redzwan, S. Mycotoxin: Its impact on gut health and microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.X.; Yang, L.G.; Wang, J.J.; Li, J.P.; Shan, A.S. Protective effect of glutamine and alanyl-glutamine against zearalenone-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in IPEC-J2 cells. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 137, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid-Essefi, S.; Bouaziz, C.; El Golli-Bennour, E.; Ouanes, Z.; Bacha, H. Comparative Study of Toxic Effects of Zearalenone and Its Two Major Metabolites α-Zearalenol and β-Zearalenol on Cultured Human Caco-2 Cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2009, 23, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Gao, R.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, C.; Shan, A. Toxic Effects of Maternal Zearalenone Exposure on Intestinal Oxidative Stress, Barrier Function, Immunological and Morphological Changes in Rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Huang, S.; Pan, S.; Zou, Y.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. Quercetin ameliorates ulcerative colitis by activating aryl hydrocarbon receptor to improve intestinal barrier integrity. Phytother. Res. PTR, 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Quercetin effectively improves LPS-induced intestinal inflammation, pyroptosis, and disruption of the barrier function through the TLR4/NF-kappa B/NLRP3 signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Food Nutr. Res. 2022, 66, 8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, K.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, T.; Qian, L.; Yang, C.; Ji, X.; Wu, D. Recent advances in the role of endogenous hydrogen sulphide in cancer cells. Cell Prolif. 2023, 56, e13449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeel, B.; Orrenius, S. Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in human disease. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 258, 479–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ali, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, M.S.; Alam, S.I.; Ikram, M.; Muhammad, T.; Saeed, K.; Badshah, H.; Kim, M.O. Neuroprotective effect of quercetin against the detrimental effects of LPS in the adult mouse brain. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Salem, I.; Prola, A.; Boussabbeh, M.; Guilbert, A.; Bacha, H.; Abid-Essefi, S.; Lemaire, C. Crocin and Quercetin protect HCT116 and HEK293 cells from Zearalenone-induced apoptosis by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Salem, I.; Prola, A.; Boussabbeh, M.; Guilbert, A.; Bacha, H.; Lemaire, C.; Abid-Essefi, S. Activation of ER stress and apoptosis by alpha- and beta-zearalenol in HCT116 cells, protective role of Quercetin. Neurotoxicology 2016, 53, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Sun, H.; Jiang, X.; Guan, X.; Gao, F.; Shi, B. Maternal Oxidized Soybean Oil Administration in Rats during Pregnancy and Lactation Alters the Intestinal DNA Methylation in Offspring. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6224–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Genes | Forward/Reverse Primer (5′-3′) | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | F: TCTGGCACCACACCTTCT R: TGATCTGGGTCATCTTCTCAC | XM_021086047.1 |
| Nrf2 | F: AACCAAACCGACAGAAATTGACAAC R: TGGAGAGGATGCTGCTGAAGG | XM_013984303.2 |
| HO-1 | F: CCAGGTCCTCAAGAAGATTGCTCAG R: GGGTCATCTCCAGAGTGTTCATTCG | NM_001004027.1 |
| NQO1 | F: GTGGAAGCCGCAGACCTTGTG R: CATGGCAGCGTATGTGTAAGCAAAC | NM_001159613.1 |
| SOD2 | F: TGTATCCGTCGGCGTCCAAGG F: TCCTGGTTAGAACAAGCGGCAATC | NM_214127.2 |
| Claudin-1 | F: TACTTTCCTGCTCCTGTC R: AAGGCGTTAATGTCAATC | NM_001244539.1 |
| ZO-1 | F: ACCCACCAAACCCACCAA R: CCATCTCTTGCTGCCAAACTATC | XM_021098856.1 |
| Occludin | F: GCTGGAGGAAGACTGGAT R: ATCCGCAGATCCCTTAAC | NM_001163647.2 |
| Bax | F: CGCTGGACTTCCTTCGAGAT R: CGATCTTGGTGAAGTACTC | XM_003127290.5 |
| Bcl-2 | F: GGATAACGGAGGCTGGGATG R: TTATGGCCCAGATAGGCACC | XM_021099593.1 |
| NF-κB | F: CCGTGTCTGCTGCTGCTGATG R: GCCCGCCAAGGAGATGTTGTC | NM_001048232.1 |
| MyD88 | F: CTCCATGTCCTCCCTGCCTCTG R: CTCCTCCGCCAGCCCAGTC | NM_001099923.1 |
| TNF-α | F: GCACTGAGAGCATGATCCGAGAC | NM_214022.1 |
| R: CGACCAGGAGGAAGGAGAAGAGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Fu, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J. Quercetin Attenuates the Combined Effects of Zearalenone and Lipopolysaccharide on IPEC-J2 Cell Injury through Activating the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Toxins 2023, 15, 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15120679
Wang C, Fu Y, Wang R, Wang Q, Yu H, Zhang J. Quercetin Attenuates the Combined Effects of Zearalenone and Lipopolysaccharide on IPEC-J2 Cell Injury through Activating the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Toxins. 2023; 15(12):679. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15120679
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chuanqi, Yurong Fu, Ruqi Wang, Qiyuan Wang, Hao Yu, and Jing Zhang. 2023. "Quercetin Attenuates the Combined Effects of Zearalenone and Lipopolysaccharide on IPEC-J2 Cell Injury through Activating the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway" Toxins 15, no. 12: 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15120679
APA StyleWang, C., Fu, Y., Wang, R., Wang, Q., Yu, H., & Zhang, J. (2023). Quercetin Attenuates the Combined Effects of Zearalenone and Lipopolysaccharide on IPEC-J2 Cell Injury through Activating the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Toxins, 15(12), 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15120679





