Transcriptomic Analysis of the Venom Gland and Enzymatic Characterization of the Venom of Phoneutria depilata (Ctenidae) from Colombia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Transcriptomic Analysis
2.1.1. Venom Gland, RNA Extraction, Transcriptome Sequencing, and Assembly
2.1.2. Functional Transcripts Nomenclature
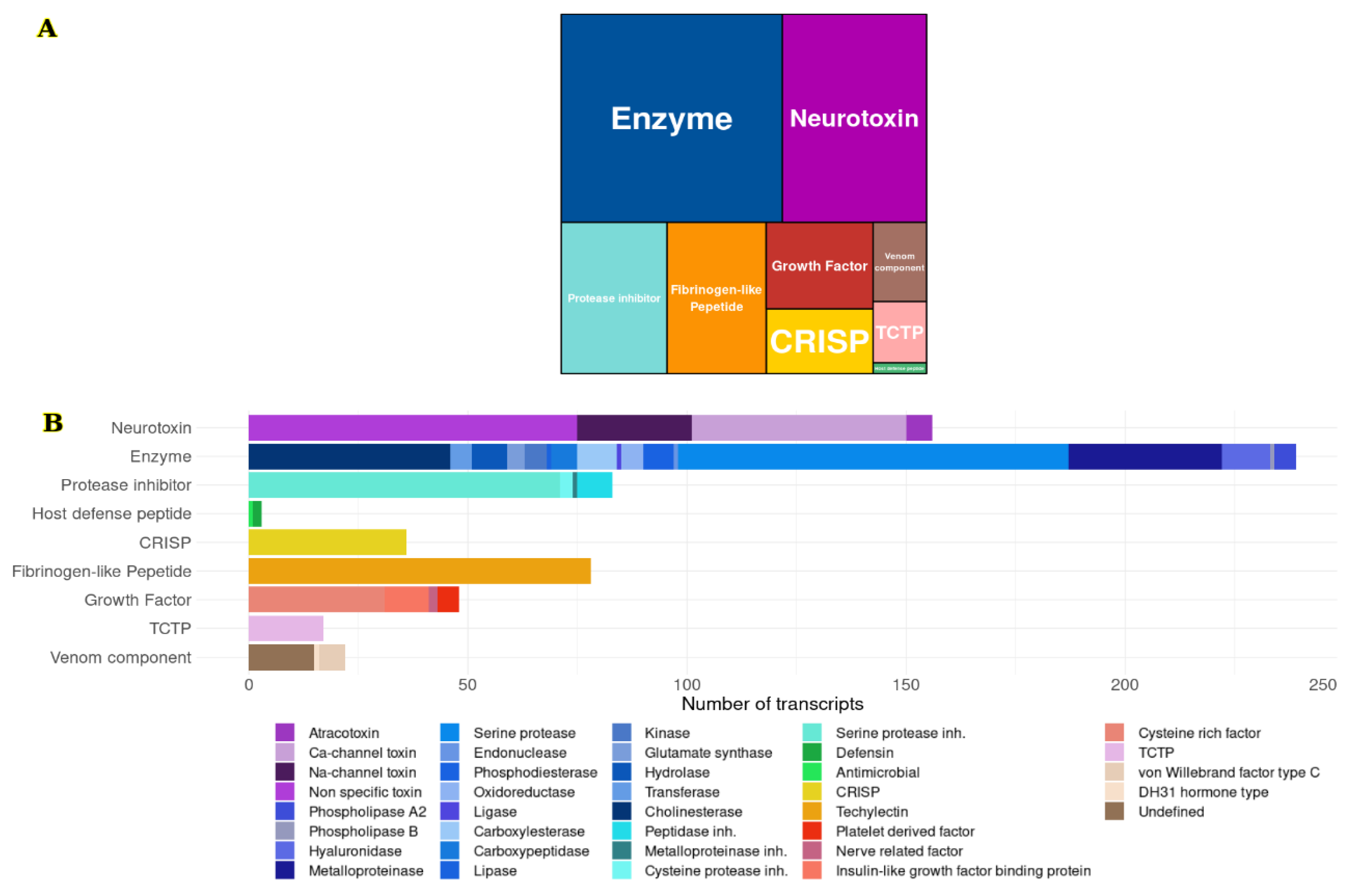
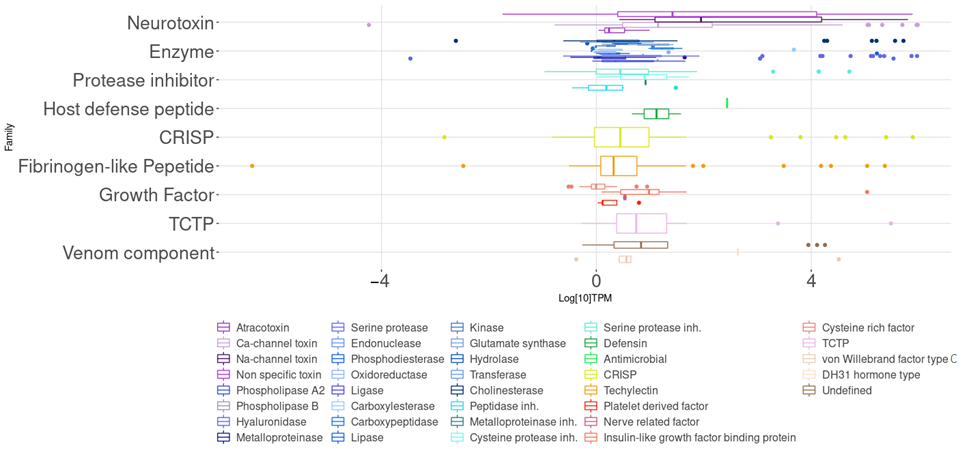
2.1.3. Putative Venom Gland Components
Neurotoxins
Fibrinogen-like Peptides
Proteases Inhibitors
Growth Factors
CRISP
TCTP
Host Defense Peptides
Other Venom Components
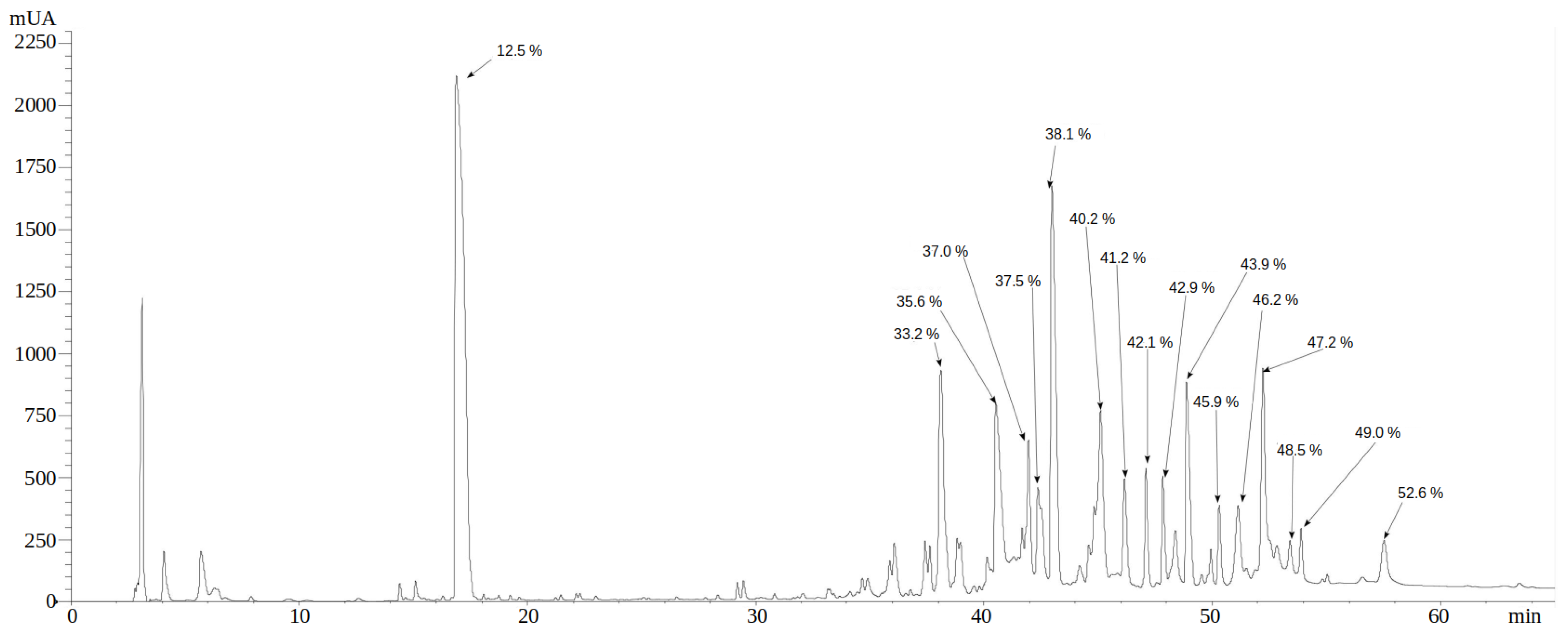
2.2. Reverse Phase HPLC Separation of P. depilate Venom
2.3. Enzymatic Characterization of P. depilata Venom and Venom Fractions
2.3.1. Phospholipase Activity
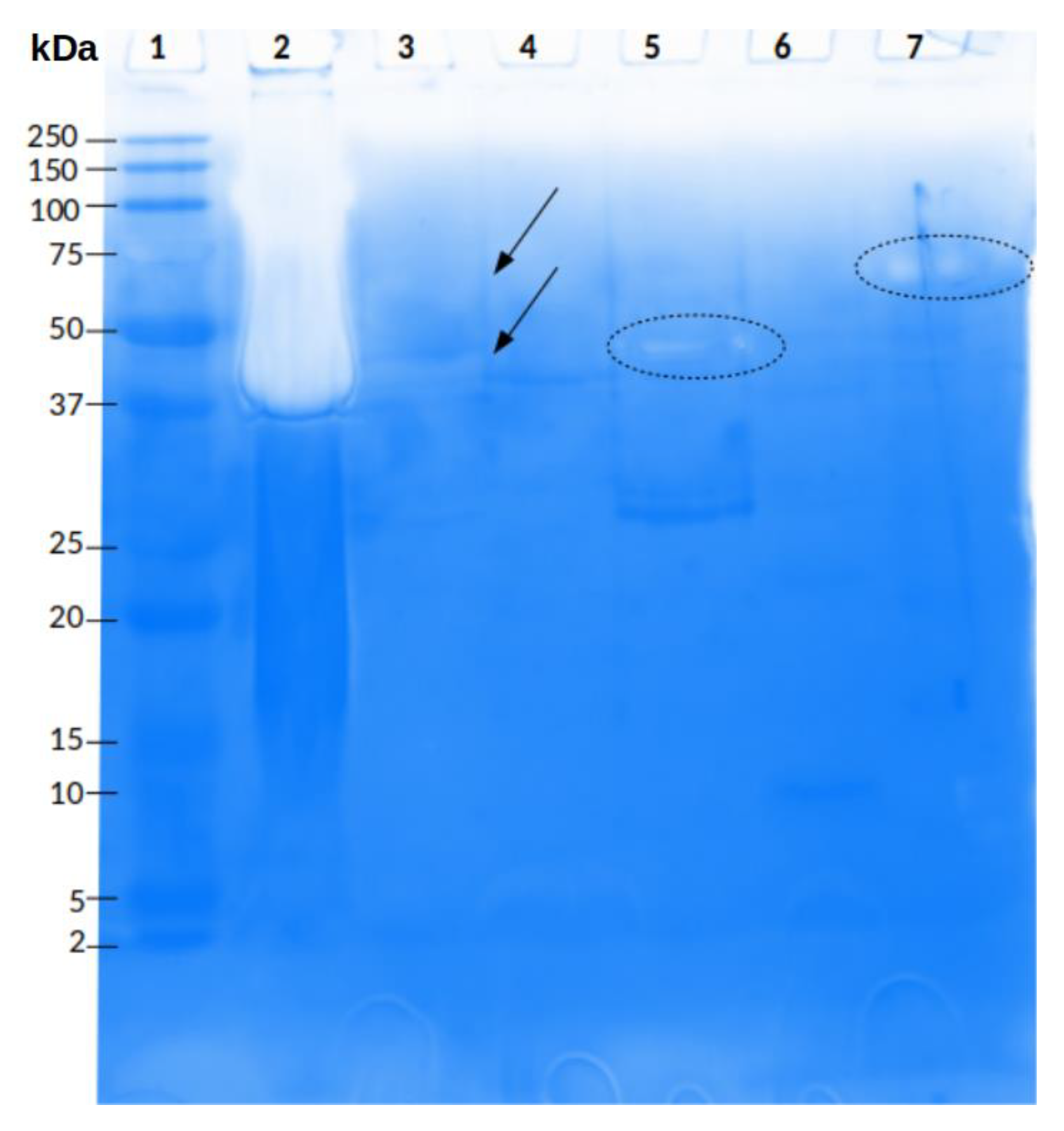
2.3.2. Protease Activity
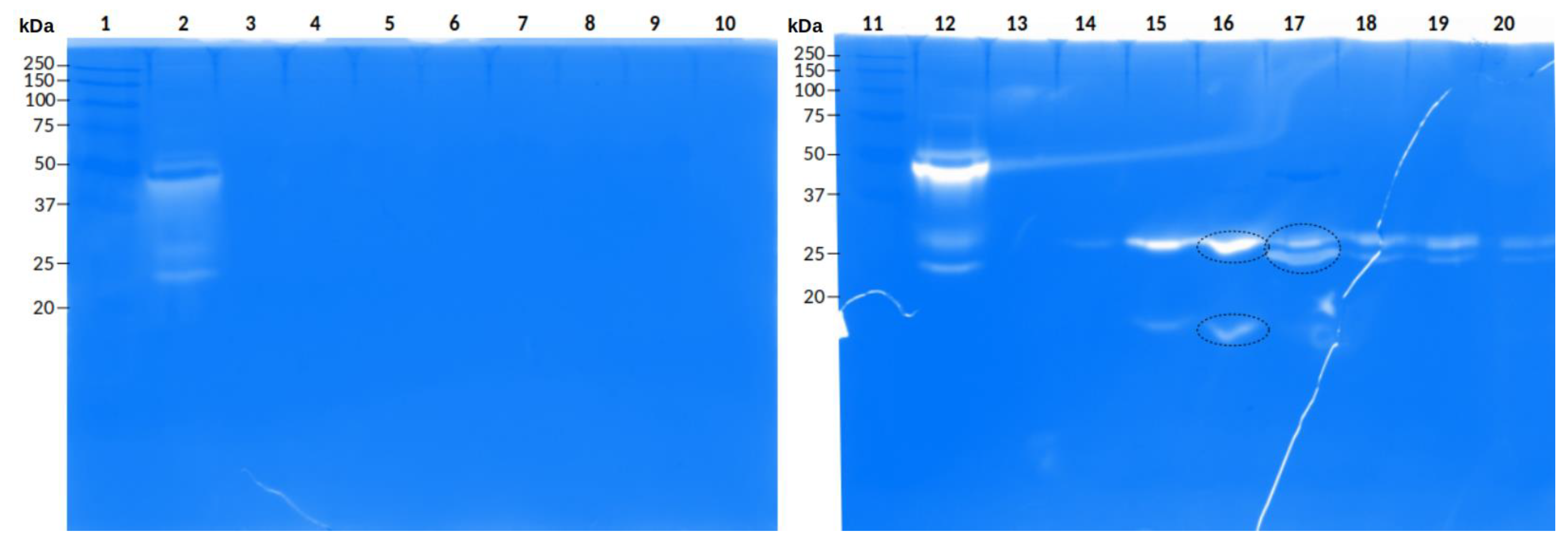
2.3.3. Hyaluronidase Activity
2.4. Proteomic Correlation between Transcripts and Enzymatic Activity
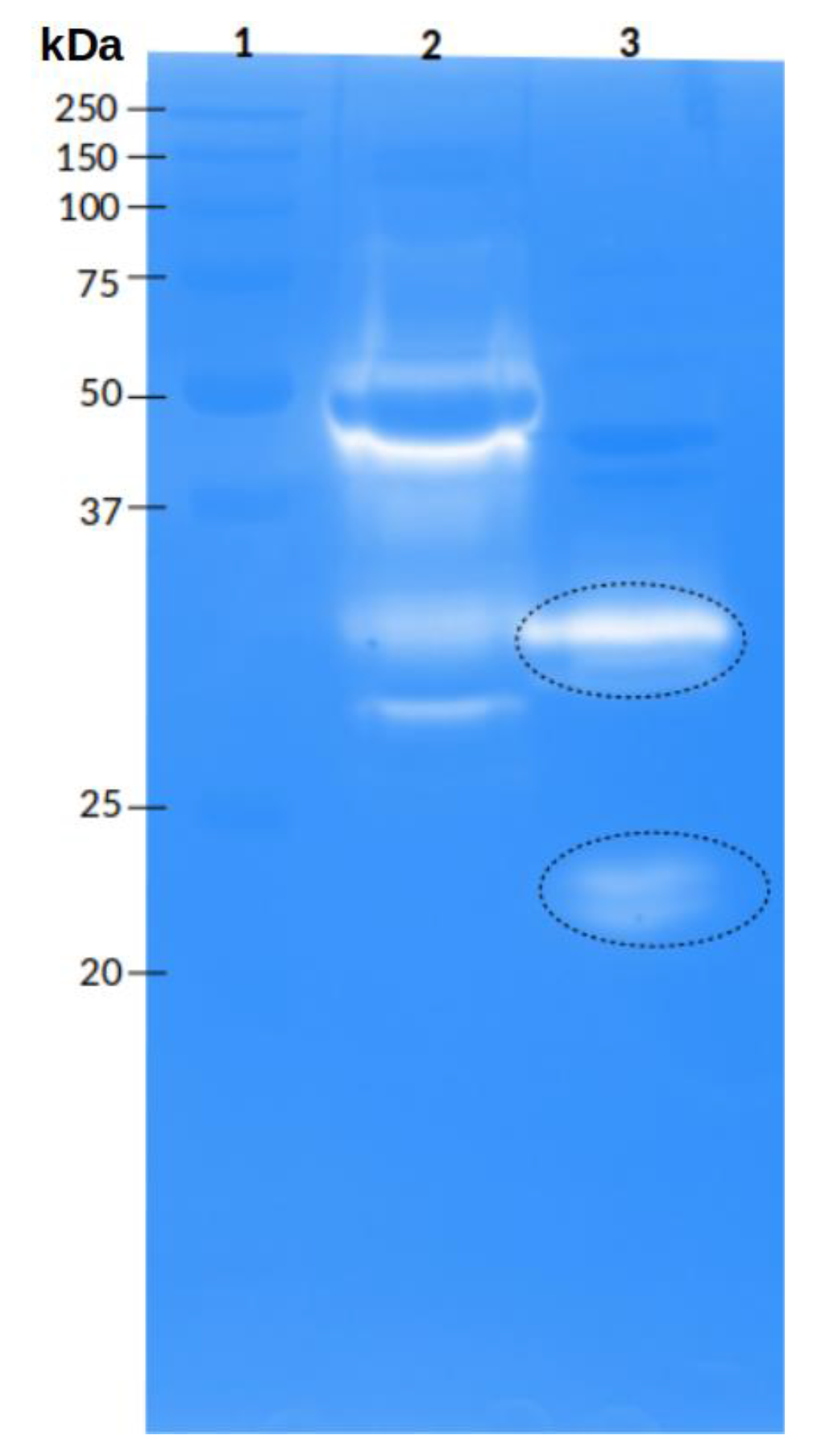
2.4.1. Peptide Sequences Obtained from the Gelatin Zymogram
2.4.2. Peptide Sequences Obtained from the Hyaluronic Acid Zymogram
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Spiders’ Collection
5.2. Transcriptomic Analysis
5.2.1. Venom Gland and RNA Extraction
5.2.2. Sequencing, Transcriptome Assembly and Annotation
5.2.3. RNA-Seq Quantification
5.3. Venom Extraction
5.4. RP-HPLC Profile
5.5. Enzymatic Characterization
5.5.1. Phospholipase Activity
5.5.2. Protease Activity
5.5.3. Hyaluronidase Activity
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klint, J.K.; Senff, S.; Rupasinghe, D.B.; Er, S.Y.; Herzig, V.; Nicholson, G.M.; King, G.F. Spider-venom peptides that target voltage-gated sodium channels: Pharmacological tools and potential therapeutic leads. Toxicon 2012, 60, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saez, N.J.; Senff, S.; Jensen, J.E.; Er, S.Y.; Herzig, V.; Rash, L.D.; King, G.F. Spider-venom peptides as therapeutics. Toxins 2010, 2, 2851–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rash, L.D.; Hodgson, W.C. Pharmacology and biochemistry of spider venoms. Toxicon 2002, 40, 225–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Spider Catalog. Available online: https://wsc.nmbe.ch/ (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Vassilevski, A.; Kozlov, S.; Grishin, E.V. Molecular Diversity of Spider Venom. Biochemistry 2009, 74, 1505–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Gomez, S.; Muñoz, L.J.V.; Lanchero, P.; Latorre, C.S. Partial characterization of venom from the Colombian spider Phoneutria boliviensis (Aranae: Ctenidae). Toxins 2015, 7, 2872–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hazzi, N.A. Natural history of Phoneutria boliviensis (Araneae: Ctenidae): Habitats, reproductive behavior, postembryonic development and prey-wrapping. J. Arachnol. 2014, 42, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazzi, N.A.; Valderrama-Ardila, C.; Brescovit, A.D.; Polotow, D.; Simó, M. New records and geographical distribution of ctenid spiders (Araneae: Ctenidae) in Colombia. Zootaxa 2013, 3709, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazzi, N.A.; Hormiga, G. Morphological and molecular evidence support the taxonomic separation of the medically important Neotropical spiders Phoneutria depilata (Strand, 1909) and P. boliviensis (F.O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1897) (Araneae, Ctenidae). ZooKeys 2021, 1022, 13–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnebeck, E.C.; Millar, C.D.; Warman, G.R. Why Does Insect RNA Look Degraded? J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Gutierrez, T.; Peguero-Sanchez, E.; Cevallos, M.A.; Batista, C.V.F.; Ortiz, E.; Possani, L.D. A Deeper Examination of Thorellius atrox Scorpion Venom Components with Omic Technologies. Toxins 2017, 9, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OmPraba, G.; Chapeaurouge, A.; Doley, R.; Devi, K.D.; Padmanaban, P.; Venkatraman, C.; Velmurugan, D.; Lin, Q.; Kini, R.M. Identification of a Novel Family of Snake Venom Proteins Veficolins from Cerberus rynchops Using a Venom Gland Transcriptomics and Proteomics Approach. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkin, Y.N. Modern trends in animal venom research-omics and nanomaterials. World J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 8, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, E.F.; Camargos, T.S.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Silva, L.P.; Bloch, C.; Caixeta, F.; Schwartz, C.A.; Possani, L.D. Mass spectrometry analysis, amino acid sequence and biological activity of venom components from the Brazilian scorpion Opisthacanthus cayaporum. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmanov, P.V.; Nuritova, F.A. The anticoagulant action of a phospholipase A from Eresus niger spider venom. Toxicon 1994, 32, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vines, C.M.; Bill, C.A. Phospholipases. In eLS; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sannaningaiah, D.; Subbaiah, G.K.; Kempaiah, K. Pharmacology of spider venom toxins. Toxin Rev. 2014, 33, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, R.B.; Pigozzo, R.B.; Chaim, O.M.; Appel, M.H.; Dreyfuss, J.L.; Toma, L.; Mangili, O.C.; Gremski, W.; Dietrich, C.P.; Nader, H.B.; et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of two isoforms of dermonecrotic toxin from Loxosceles intermedia (brown spider) venom gland. Biochimie 2006, 88, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn-Nentwig, L.; Langenegger, N.; Heller, M.; Koua, D.; Nentwig, W. The Dual Prey-Inactivation Strategy of Spiders—In-Depth Venomic Analysis of Cupiennius salei. Toxins 2019, 11, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diniz, M.R.V.; Paiva, A.L.B.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; Nishiyama, M.Y., Jr.; Mudadu, M.A.; de oliveira, U.; Borges, M.H.; Yates, J.R.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.de.L. An overview of Phoneutria nigriventer spider venom using combined transcriptomic and proteomic approaches. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.L.B.; Mudadu, M.A.; Pereira, E.H.T.; Marri, C.A.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; Diniz, M.R.V. Transcriptome analysis of the spider Phoneutria pertyi venom glands reveals novel venom components for the genus Phoneutria. Toxicon 2019, 163, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, J.C.; Patiño, R.O. Envenenamiento aracnídico en las Américas. MedUnab 2002, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kini, R.M. Serine proteases affecting blood coagulation and fibrinolysis from snake venoms. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005, 33, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feitosa, L.; Gremski, W.; Veiga, S.S.; Elias, M.C.; Graner, E.; Mangili, O.C.; Brentani, R.R. Detection and characterization of metalloproteinases with gelatinolytic, fibronectinolytic and fibrinogenolytic activities in brown spider (Loxosceles intermedia) venom. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, S.S.; da Silveira, R.B.; Dreyfuss, J.L.; Haoach, J.; Pereira, A.M.; Mangili, O.C.; Gremski, W. Identification of high molecular weight serine-proteases in Loxosceles intermedia (brown spider) venom. Toxicon 2000, 38, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, S.; Devaraja, S.; Kemparaju, K. Purification and properties of hyaluronidase from Hippasa partita (funnel web spider) venom gland extract. Toxicon 2007, 50, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, S.; Girish, K.S.; Fox, J.W.; Kemparaju, K. ‘Partitagin’ a hemorrhagic metalloprotease from Hippasa partita spider venom: Role in tissue necrosis. Biochimie 2007, 89, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanetti, V.C.; da Silveria, R.B.; Dreyfuss, J.L.; Haoach, J.; Mangili, O.C.; Veiga, S.S.; Gremski, W. Morphological and biochemical evidence of blood vessel damage and fibrinogenolysis triggered by brown spider venom. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2002, 13, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraja, S.; Nagaraju, S.; Mahadeshwara-Swamy, Y.H.; Girish, K.S.; Kemparaju, K. A low molecular weight serine protease: Purification and characterization from Hippasa agelenoides (Funnel web) spider venom gland extract. Toxicon 2008, 52, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraja, S.; Girish, K.S.; Devaraj, V.R.; Kemparaju, K. Factor Xa-like and fibrin(ogen)olytic activities of a serine protease from Hippasa agelenoides spider venom gland extract. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2010, 29, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraja, S.; Girish, K.S.; Gowtham, Y.N.; Kemparaju, K. The Hag-protease-II is a fibrin(ogen)ase from Hippasa agelenoides spider venom gland extract: Purification, characterization and its role in hemostasis. Toxicon 2011, 57, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenberg, S.; Pereira-Lima, F.A. Phoneutria nigriventer venom—Pharmacology and biochemestry of its components. In Venomous Animals and Their Venoms, 1st ed.; Wolfgang, B., Buckley, E.E., Deulofeu, V., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 279–297. [Google Scholar]
- Peigneur, S.; de Lima, M.E.; Tytgat, J. Phoneutria nigriventer venom: A pharmacological treasure. Toxicon 2018, 151, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Tan, K.Y.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, N.H. Venom-gland transcriptome and venom proteome of the Malaysian king cobra (Ophiophagus hannah). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffiths, A.J.F.; Gelbart, W.M.; Miller, J.H.; Lewontin, R. The Molecular Basis of Mutation. In Modern Genetic Analysis, 6th ed.; Freeman W.H.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, E.R.J.; Northfield, T.D.; Daly, N.L.; Wilson, D.T. Venom Costs and Optimization in Scorpions. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carcamo-Noriega, E.N.; Possani, L.D.; Ortiz, E. Venom content and toxicity regeneration after venom gland depletion by electrostimulation in the scorpion Centruroides limpidus. Toxicon 2019, 157, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzel, E.J.; Farr, C. Hyaluronidases and its substrate: Biochemistry, biological activities and therapeutic uses. Cancer Lett. 1988, 131, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, R.B.; Chaim, O.M.; Mangili, O.C.; Gremski, W.; Dietrich, C.P.; Nader, H.B.; Veiga, S.S. Hyaluronidases in Loxosceles intermedia (Brown spider) venom are endo-b-N-acetyl-D-hexosaminidases hydrolases. Toxicon 2007, 49, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silveira, R.B.; Pigozzo, R.B.; Chaim, O.M.; Appel, M.H.; Silva, D.T.; Dreyfuss, J.L.; Toma, L.; Dietrich, C.P.; Nader, H.B.; Veiga, S.S.; et al. Two novel dermonecrotic toxins LiRecDT4 and LiRecDT5 from brown spider (Loxosceles intermedia) venom: From cloning to functional characterization. Biochimie 2007, 89, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silveira, R.B.; Wille, A.C.; Chaim, O.M.; Appel, M.H.; Silva, D.T.; Franco, C.R.; Toma, L.; Mangili, O.C.; Gremski, W.; Dietrich, C.P.; et al. Identification, cloning, expression and functional characterization of an astacin-like metalloprotease toxin from Loxosceles intermedia (brown spider) venom. J. Biochem. 2007, 406, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaiser, E. Enzymatic activity of spider venoms. In Venoms; Buckley, E.E., Porges, N., Eds.; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 1956; pp. 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn-Nentwig, L.; Schaller, J.; Nentwig, W. Purification of toxic peptides and the aminoacid sequence of CSTX-1 from the multi-component venom of Cupiennius salei (Araneae: Ctenidae). Toxicon 1994, 32, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, K.C.; Knysak, I.; Martins, R.; Hogan, C.; Winkel, K. Enzymatic characterizations, antigenic cross reactivity and neutralization of dermonecrotic activity of five Loxosceles spider venoms of medical importance in the Americas. Toxicon 2005, 45, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, S.; Mahadeshwara-swamy, Y.H.; Girish, K.S.; Kemparaju, K. Venom from spiders of the genus Hippasa: Biochemical and pharmacological studies. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2006, 144, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.P.; Elgert, K.D.; Campell, B.J.; Barrett, J.T. Hyaluronidase and esterase activities of the venom of poisonous brown recluse spider. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1973, 159, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.R.; Pincus, S.J. Comparison of enzymatic activity from three species of necrotizing arachnids in Australia: Loxosceles rufescens, Badumma insignis and Lampona cylindrata. Toxicon 2001, 39, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanbacher, F.L.; Lee, C.K.; Wilson, I.B.; Howell, D.E.; Odell, G.V. Purification and characterization of tarantula Dugesiella hentzi (Girard) venom hyaluronidase. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1973, 44B, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.; Pimienta, A.M.C.; Bemquerer, M.P.; Santoro, M.M.; Beirao, P.S.L.; Lima, M.E.; Figueiredo, S.G.; Bloch, C., Jr.; Vasconcelos, E.A.R.; Campos, F.A.P.; et al. Comparison of the partial proteomes of the venom of Brazilian spiders of the genus Phoneutria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 142, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colović, M.B.; Krstić, D.Z.; Lazarević-Pašti, T.D.; Bondžić, A.M.; Vasić, V.M. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Pharmacology and toxicology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moura, J.R.; Prado, M.A.; Gomez, M.V.; Kalapothakis, E.; Diniz, C.R.; Cordeiro, M.N.; Romano-Silva, M.A. Investigation of the effect of PhTx2, from the venom of the spider Phoneutria nigriventer, on the release of [3H]-acetylcholine from rat cerebrocortical synaptosomes. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.F.; Huang, C.; Chong, C.M.; Leung, S.W.; Prieto-da-Silva, A.R.; Havt, A.; Quinet, Y.P.; Martins, A.M.; Lee, S.M.; Rádis-Baptista, G. Transcriptome analysis in venom gland of the predatory giant ant Dinoponera quadriceps: Insights into the polypeptide toxin arsenal of hymenopterans. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blank, S.; Seismann, H.; Bockisch, B.; Braren, I.; Bredehorst, R.; Grunwald, T.; Ollert, M.; Spillner, E. Identification and Recombinant Expression of a Novel IgE-Reactive 70 kDa Carboxylesterase from Apis mellifera Venom. Available online: http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/B2D0J5 (accessed on 21 August 2021).
- Xin, B.; Liu, P.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y. Identification of Venom Proteins of the Indigenous Endoparasitoid Chouioia cunea (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 2022–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciscotto, P.; Machado de Avila, R.A.; Coelho, E.A.F.; Oliveira, J.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C.; Diniz, C.G.; Farías, L.M.; de Carvalho, M.A.R.; Maria, W.S.; Sanchez, E.F.; et al. Antigenic, microbicidal and antiparasitic properties of an l-amino acid oxidase isolated from Bothrops jararaca snake venom. Toxicon 2008, 53, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.L.; Vaquero, T.S.; Paes-Leme, A.F.; Serrano, S.M.T. NPP-BJ, a nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase from Bothrops jararaca snake venom, inhibits platelet aggregation. Toxicon 2009, 54, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, X. Recent Advances in Research on Widow Spider Venoms and Toxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 5055–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corrêa-Netto, C.; de LM Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.; Silva, D.A.; Ho, P.L.; Leitão-de-Araújo, M.; Alves, M.L.M.; Sanz, L.; Foguel, D.; Zingali, R.B.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics and venom gland transcriptomic analysis of Brazilian coral snakes, Micrurus altirostris and M. corallinus. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanggaard, K.; Bechsgaard, J.; Fang, X.; Duan, J.; Dyrlund, T.F.; Gupta, V.; Jiang, X.; Cheng, L.; Fan, D.; Feng, Y.; et al. Spider genomes provide insight into composition and evolution of venom and silk. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatrath, S.T.; Chapeaurouge, A.; Lin, Q.; Lim, T.K.; Dunstan, N.; Mirtschin, P.; Kumar, P.P.; Kini, R.M. Identification of novel proteins from the venom of a cryptic snake Drysdalia coronoides by a combined transcriptomics and proteomics approach. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 739e750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, L.; Meng, E.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Liang, S. Transcriptome analysis revealed novel possible venom components and cellular processes of the tarantula Chilobrachys jingzhao venom gland. Toxicon 2008, 52, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, G. Near fatal envenomation from the funnel-web spider in an infant. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 1997, 13, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Brutto, O.H. Neurological effects of venomous bites and stings: Snakes, spiders, and scorpions. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; García, H.H., Tanowitz, H.B., del Brutto, O.H., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 114, pp. 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, W.C. Pharmacological action of australian animal venoms. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1997, 24, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Gomez, H.F.; Snider, R.J.; Stephens, E.L.; Czop, R.M.; Warren, J.S. Detection of Loxosceles venom in lesional hair shafts and skin: Application of a specific immunoassay to identify dermonecrotic arachnidism. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2000, 18, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoubas, P.; de Weille, J.R.; Lecoq, A.; Diochot, S.; Waldmann, R.; Champigny, G.; Moinier, D.; Ménez, A.; Lazdunski, M. Isolation of a Tarantula Toxin Specific for a Class of Proton-gated Na+ Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25116–25121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escoubas, P.; Diochot, S.; Corzo, G. Structure and pharmacology of spider venom neurotoxins. Biochimie 2000, 82, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Wilson, D.T.R.; Kuruppu, S.; Korsinczky, M.L.J.; Hedrick, J.; Pang, L.; Szeto, T.; Hodgson, W.C.; Alewood, P.F.; Nicholson, G.M. Discovery of an MIT-like atracotoxin family: Spider venom peptides that share sequence homology but not pharmacological properties with AVIT family proteins. Peptides 2005, 26, 2412–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, P.B. The contribution of proteinase inhibitors to immune defense. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De F Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.; de LM Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.; Gonçalves-de-Andrade, R.M.; Kobashi, L.S.; Almeida, D.D.; Ho, O.L.; Tambourgi, D.V. Transcriptome analysis of Loxosceles laeta (Araneae, Sicariidae) spider venomous gland using expressed sequence tags. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gremski, L.H.; da Silveira, R.B.; Chaim, O.M.; Probst, C.M.; Ferrer, V.P.; Nowatzki, J.; Weinschutz, H.C.; Madeira, H.M.; Gremski, W.; Nader, H.B.; et al. A novel expression profile of the Loxosceles intermedia spider venomous gland revealed by transcriptome analysis. Mol. BioSys. 2010, 6, 2403–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gremski, L.H.; Trevisan-Silva, D.; Ferrer, V.P.; Matsubara, F.H.; Meissner, G.O.; Wille, A.C.; Vuitika, L.; Dias-Lopes, C.; Ullah, A.; de Moraes, F.R.; et al. Recent advances in the understanding of brown spider venoms: From the biology of spiders to the molecular mechanisms of toxins. Toxicon 2014, 83, 91–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.H.; He, Q.Y.; Peng, K.; Diao, J.-B.; Jiang, L.-P.; Tang, X.; Liang, S.-P. Discovery of a distinct superfamily of Kunitz-type toxin (KTT) from tarantulas. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqueira de Azevedo, I.D.L.M.; Poliselli Farsky, S.H.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; Ho, P.L. Molecular Cloning and Expression of a Functional Snake Venom Vascular Endothelium Growth Factor (VEGF) from the Bothrops insularis Pit Viper: A new member of the VEGF family of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 39836–39842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suto, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Morita, T.; Mizuno, H. Crystal structures of novel vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) from snake venoms: Insight into selective VEGF binding to kinase insert domain-containing receptor but not to fms-like tyrosine kinase-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 2126–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golde, D.W.; Herschman, H.R.; Lusis, A.J.; Groopman, J.E. Growth factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 1980, 92, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Morita, T. Snake Venom Components Affecting Blood Coagulation and the Vascular System: Structural Similarities and Marked Diversity. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 2872–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, L.D.; Dias, N.B.; Pinto, J.R.A.S.; Palma, M.S. Brown recluse spider venom: Proteomic analysis and proposal of a putative mechanism of action. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.D.; Safavi-Hemami, H. Insulin as a weapon. Toxicon 2016, 123, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonk, F.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Henkel, C.V.; Heimberg, A.M.; Jansen, H.J.; McCleary, R.J.R.; Kerkkamp, H.M.E.; Vos, R.A.; Guerreiro, I.; Calvete, J.J.; et al. The king cobra genome reveals dynamic gene evolution and adaptation in the snake venom system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20651–20656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kostiza, T.; Meier, J. Nerve growth factors from snake venoms: Chemical properties, mode of action and biological significance. Toxicon 1996, 34, 787–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, L.C. Pathogenesis-related proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 1985, 4, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Ono, S.; Kubo, T. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding toxin-like peptides from the venom glands of tarantula Grammostola rosea. Int. J. Pept. 2012, 2012, 731293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bheekha-Escura, R.; MacGlashan, D.W.; Langdon, J.M.; MacDonald, S.M. Human recombinant histamine-releasing factor activates human eosinophils and the eosinophilic cell line, AML14-3D10. Blood 2000, 96, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, F.; Liu, X.; Li, Q. Novel translationally controlled tumor protein homologue in the buccal gland secretion of Lampetra japonica. Biochimie 2008, 90, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaim, O.M.; Trevisan-Silva, D.; Chaves-Moreira, D.; Wille, A.C.M.; Ferrer, V.P.; Matsubara, F.H.; Mangili, O.C.; Silveira, R.B.D.; Gremski, L.H.; Gremski, W.; et al. Brown spider (Loxosceles genus) venom toxins: Tools for biological purposes. Toxins 2011, 3, 309–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weisel-Eichler, A.; Libersat, F. Venom effects on monoaminergic systems. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural. Behav. Physiol. 2004, 190, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.W.; Haney, E.F.; Gill, E.E. The immunology of host defence peptides: Beyond antimicrobial activity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuperus, T.; Coorens, M.; van Dijk, A.; Haagsman, H.P. Avian host defense peptides. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 352–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinstraesser, L.; Kraneburg, U.; Jacobsen, F.; Al-Benna, S. Host defense peptides and their antimicrobial-immunomodulatory duality. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Jia, X.-T.; Zhao, L.; Li, C.-Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.-G.; Weng, S.-P.; He, J.-G. Identification and functional characterization of Dicer2 and five single VWC domain proteins of Litopenaeus vannamei. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.; Oliphant, A.; Wilcockson, D.C.; Webster, S.G. Functional Identification and Characterization of the Diuretic Hormone 31 (DH31) Signaling System in the Green Shore Crab, Carcinus maenas. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero-Gutierrez, T. Caracterización del Transcriptoma de la Glándula Venenosa y el Proteoma del Veneno del Alacrán Thorellius atrox. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Cuernavaca, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Haberman, E.; Hardt, K.L. A sensitive and specific plater test for the quantitation of Phospholipases. Anal. Biochem. 1972, 50, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heussen, C.; Dowdle, E.B. Electrophoretic analysis of plasminogen activators in polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulfate and copolimerized substrates. Anal. Biochem. 1980, 102, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevallos, M.A.; Navarro-Duque, C.; Varela-Julia, M.; Alagón, A.C. Molecular mass determination and assay of venom hyaluronidases by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Toxicon 1992, 30, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo, J.C. Caracterización Bioquímica, Biológica, Molecular y Funcional de la Enzima Hialuronidasa del Yeneno de la Serpiente Peruana Bothrops atrox “Jergon de la Selva”. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos, Lima, Peru, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Gao, R.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Isolation and characterization of a hyaluronidase from the venom of Chinese red scorpion Buthus martensi. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 148, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutti, R.; Tamascia, M.L.; Hyslop, S.; Rocha-e-Silva, T.A. Purification and characterization of a hyaluronidase from venom of the spider Vitalius dubius (Araneae, Theraphosidae). J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop Dis. 2014, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Species Code | Meaning | Family Code | Meaning | Subtype Code | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phd | Phoneutria depilata | Enz | Enzyme | SeP | Serine protease | PhdEnzSeP01 |
| Cho | Cholinesterase | PhdEnzCho01 | ||||
| MtP | Matelloprotease | PhdEnzMtP01 | ||||
| Hya | Hyaluronidase | PhdEnzHya01 | ||||
| Ces | Carboxylesterase | PhdEnzCes01 | ||||
| Hyd | Hydrolase | PhdEnzHyd01 | ||||
| Cxp | Carboxypeptidase | PhdEnzCxp01 | ||||
| Kin | Kinase | PhdEnzKin01 | ||||
| Pho | Phosphatase | PhdEnzPho01 | ||||
| PA2 | Phospholipase 2 | PhdEnzPA201 | ||||
| OxR | Oxidoreductase | PhdEnzOxR01 | ||||
| Tra | Transferase | PhdEnzTra01 | ||||
| GlS | Glutamate synthase | PhdEnzGlS01 | ||||
| Phd | Phosphodiesterase | PhdEnzPhd01 | ||||
| Lig | Ligase | PhdEnzLig01 | ||||
| PLB | Phospholipase B | PhdEnzPLB01 | ||||
| End | Endonuclease | PhdEnzEnd01 | ||||
| Lip | Lipase | PhdEnzLip01 | ||||
| Ntx | Neurotoxin | Nav | Na-channel toxin | PhdNtxNav01 | ||
| Cav | Ca-channel toxin | PhdNtxCav01 | ||||
| Atx | Atracotoxin | PhdNtxAtx01 | ||||
| NSp | Nonspecific toxin | PhdNtxNSp01 | ||||
| PIn | Protease inhibitor | SeP | Serine protease inh. | PhdPInSeP01 | ||
| Pep | Peptidase inh. | PhdPInPeP01 | ||||
| CyP | Cysteine protease inh. | PhdPInCyP01 | ||||
| MtP | Metalloprotease inh. | PhdPInMtP01 | ||||
| GrF | Growth factor | Cys | Cysteine rich factor | PhdGrFCyS01 | ||
| PDG | Platelet derived factor | PhdGrFPDG01 | ||||
| Ins | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein | PhdGrFIns01 | ||||
| NeR | Nerve related factor | PhdGrFNeR01 | ||||
| Fib | Fibrinogen like | Tec | Techylectin | PhdFibTec01 | ||
| TCT | Translationally controlled tumor protein | PhdTCT01 | ||||
| CRI | CRISP | PhdCRI01 | ||||
| HDP | Host Defense Peptides | Def | Defensin | PhdHDPDef01 | ||
| AMB | Antimicrobial | PhdHDPAMB01 | ||||
| Oth | Other venom components | vWC | von Willebrand factor type C | PhdOthvWC01 | ||
| HDH | DH31 hormone type | PhdOthHDH01 | ||||
| Und | Undefined | PhdOthUnd01 | ||||
| Family | Subtype | Number of Coding Sequences (NCS) | Abundance within the Family (%) | Abundance within the Transcriptome (%) | Median Transcripts per Million (TPM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme | Serine proteases | 89 | 37.2 | 13.1 | 3.2 |
| Fibrinogen like | Techylectin | 78 | - | 11.4 | 2.0 |
| Neurotoxin | Nonspecific toxin | 75 | 48.1 | 11.0 | 26.1 |
| Protease inhibitor | Serine Proteases Inh. | 71 | 85.5 | 10.4 | 2.6 |
| Neurotoxin | Ca-channel toxin | 49 | 31.4 | 7.2 | 13.5 |
| Enzyme | Cholinesterases | 46 | 19.3 | 6.7 | 1.2 |
| CRISP | 36 | - | 5.3 | 2.3 | |
| Enzyme | Metalloproteinases | 35 | 14.6 | 5.1 | 1.7 |
| Growth factor | Cysteine rich growth factor | 31 | 64.6 | 4.5 | 3.4 |
| Neurotoxin | Na-channel toxin | 26 | 16.7 | 3.8 | 89.1 |
| TCTP | 17 | - | 2.5 | 4.6 | |
| Venom component | Undefined | 15 | 68.2 | 2.2 | 6.5 |
| Enzyme | Hyaluronidases | 11 | 4.6 | 1.6 | 2.8 |
| Growth factor | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein | 10 | 20.8 | 1.5 | 9.6 |
| Enzyme | Carboxylesterases | 9 | 3.8 | 1.3 | 16.5 |
| Enzyme | Hydrolases | 8 | 3.4 | 1.2 | 2.5 |
| Protease inhibitor | Peptidase inh. | 8 | 9.6 | 1.2 | 4.9 |
| Enzyme | Carboxypeptidases | 6 | 2.5 | 0.9 | 2.7 |
| Neurotoxin | Atracotoxin | 6 | 3.8 | 0.9 | 1.6 |
| Venom component | von Willebrand factor type C | 6 | 27.3 | 0.9 | 3.7 |
| Enzyme | Phospholipases A2 | 5 | 2.1 | 0.7 | 2.3 |
| Enzyme | Kinases | 5 | 2.1 | 0.7 | 1.7 |
| Enzyme | Phosphatases | 5 | 2.1 | 0.7 | 3.4 |
| Enzyme | Oxidoreductases | 5 | 2.1 | 0.7 | 1.1 |
| Enzyme | Transferases | 5 | 2.1 | 0.7 | 1.5 |
| Growth factor | Platelet derived growth factor | 5 | 10.4 | 0.7 | 1.3 |
| Enzyme | Glutamate synthase | 4 | 1.7 | 0.6 | 15.5 |
| Protease inhibitor | Cysteine protease inh. | 3 | 3.6 | 0.4 | 20.6 |
| Enzyme | Phosphodiesterases | 2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 83,230 |
| Growth factor | Nerve related growth factor | 2 | 4.2 | 0.3 | 3.4 |
| Host Defense Peptide | Defensin | 2 | 66.7 | 0.3 | 21.1 |
| Enzyme | Phospholipase B | 1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 13.8 |
| Enzyme | Endonuclease | 1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 7.3 |
| Enzyme | Ligases | 1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.8 |
| Enzyme | Lipases | 1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 1 |
| Protease inhibitor | Metalloproteinases Inh. | 1 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 8.2 |
| Host Defense Peptide | Antimicrobial | 1 | 33.3 | 0.1 | 271 |
| Venom component | DH31 hormone type | 1 | 4.5 | 0.1 | 429 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vásquez-Escobar, J.; Romero-Gutiérrez, T.; Morales, J.A.; Clement, H.C.; Corzo, G.A.; Benjumea, D.M.; Corrales-García, L.L. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Venom Gland and Enzymatic Characterization of the Venom of Phoneutria depilata (Ctenidae) from Colombia. Toxins 2022, 14, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14050295
Vásquez-Escobar J, Romero-Gutiérrez T, Morales JA, Clement HC, Corzo GA, Benjumea DM, Corrales-García LL. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Venom Gland and Enzymatic Characterization of the Venom of Phoneutria depilata (Ctenidae) from Colombia. Toxins. 2022; 14(5):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14050295
Chicago/Turabian StyleVásquez-Escobar, Julieta, Teresa Romero-Gutiérrez, José Alejandro Morales, Herlinda C. Clement, Gerardo A. Corzo, Dora M. Benjumea, and Ligia Luz Corrales-García. 2022. "Transcriptomic Analysis of the Venom Gland and Enzymatic Characterization of the Venom of Phoneutria depilata (Ctenidae) from Colombia" Toxins 14, no. 5: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14050295
APA StyleVásquez-Escobar, J., Romero-Gutiérrez, T., Morales, J. A., Clement, H. C., Corzo, G. A., Benjumea, D. M., & Corrales-García, L. L. (2022). Transcriptomic Analysis of the Venom Gland and Enzymatic Characterization of the Venom of Phoneutria depilata (Ctenidae) from Colombia. Toxins, 14(5), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14050295







