Anti-Neurotoxins from Micrurus mipartitus in the Development of Coral Snake Antivenoms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
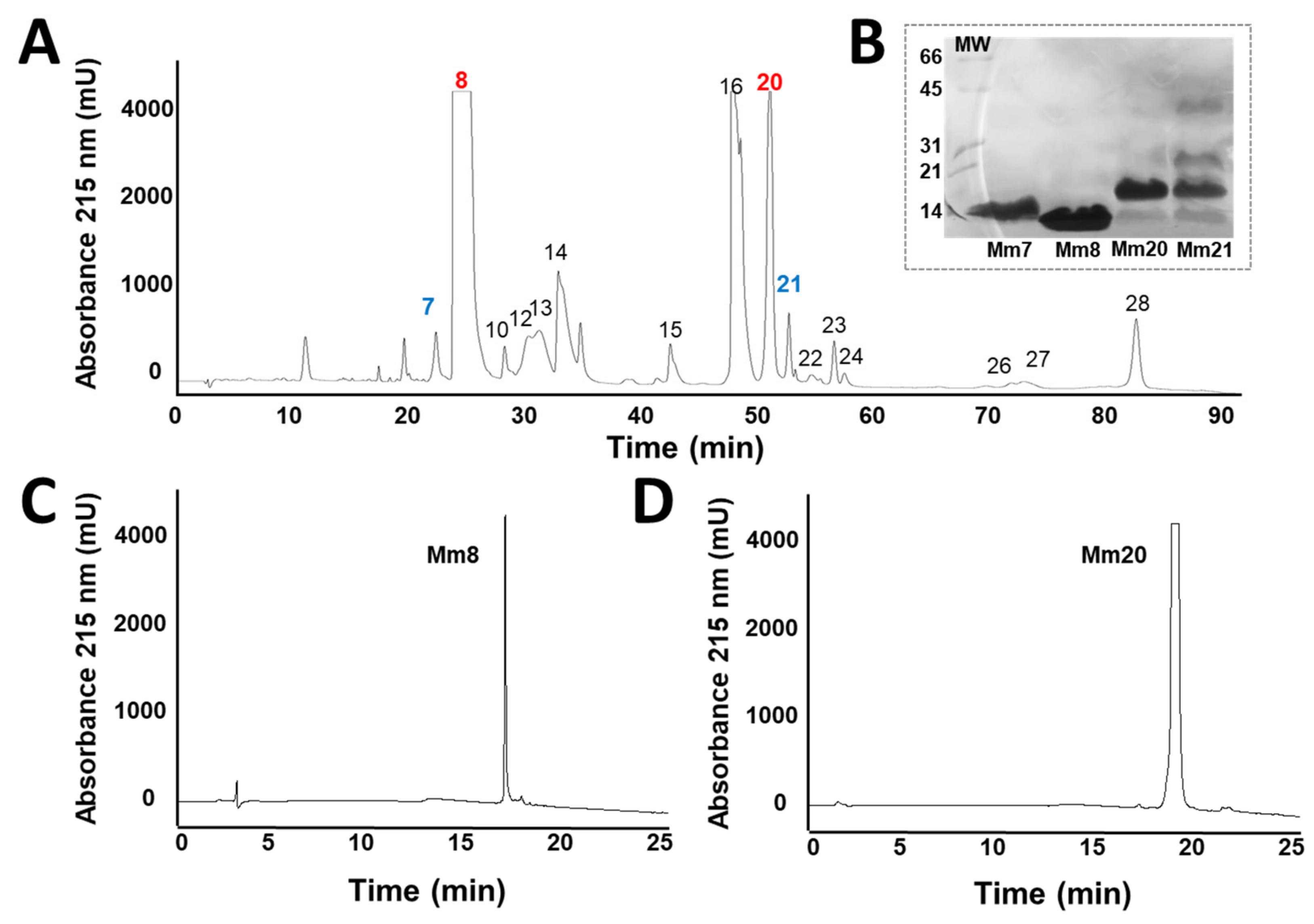
2. Results
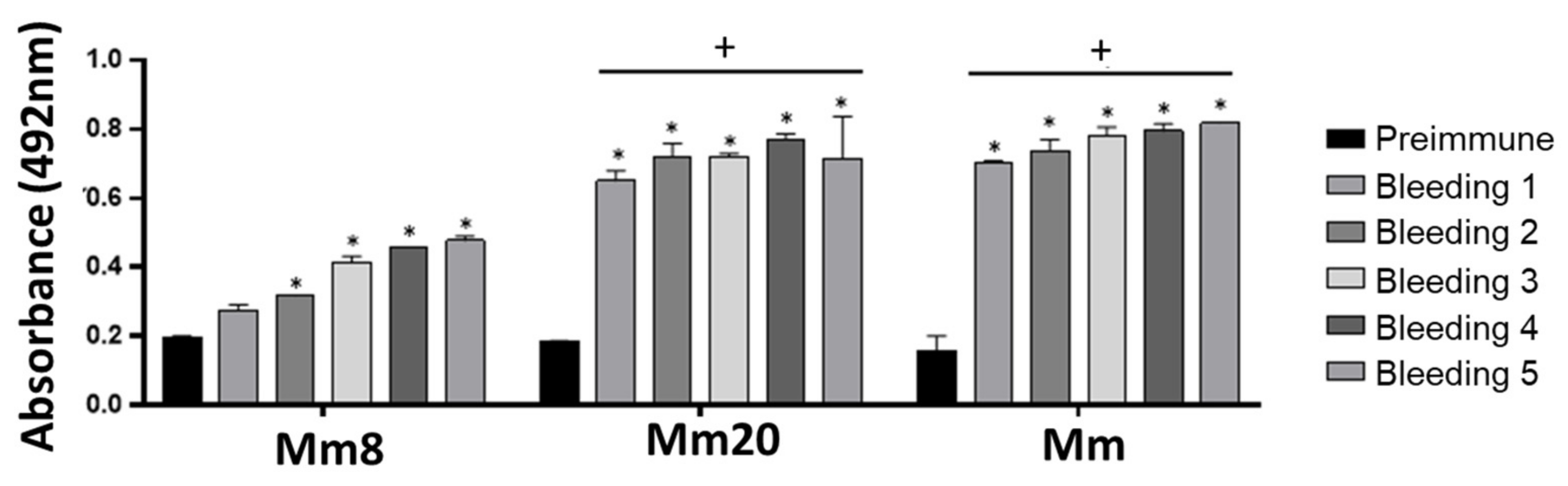
2.1. Production and Evaluation of Hyper Immune Sera
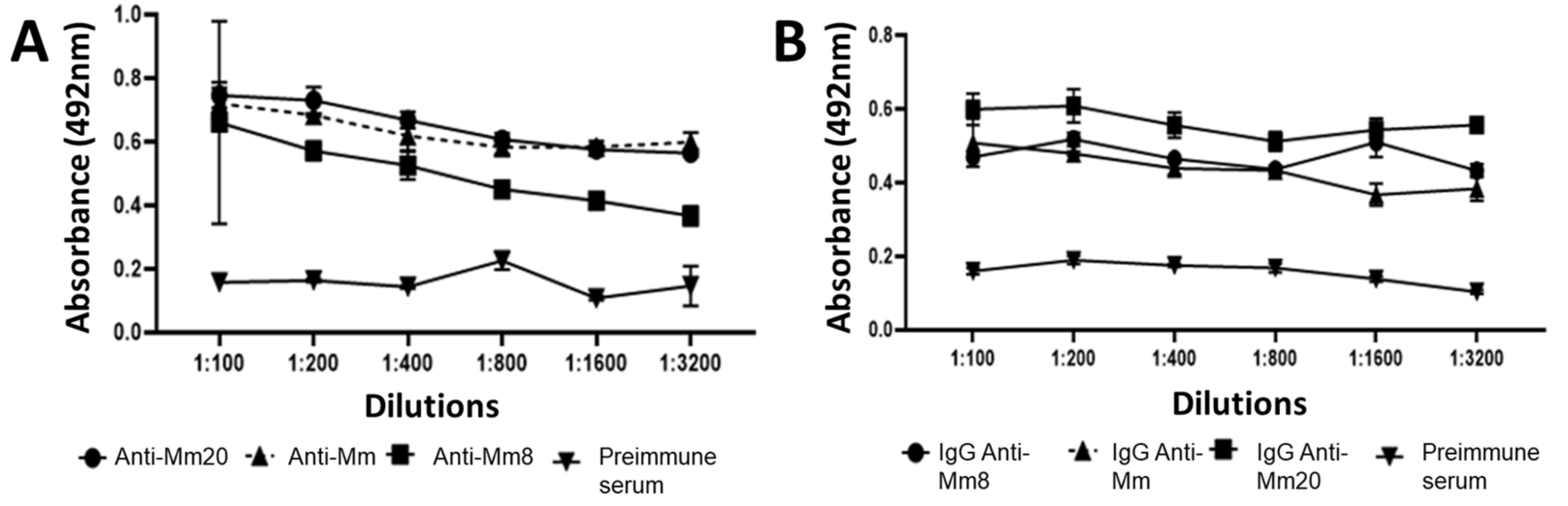
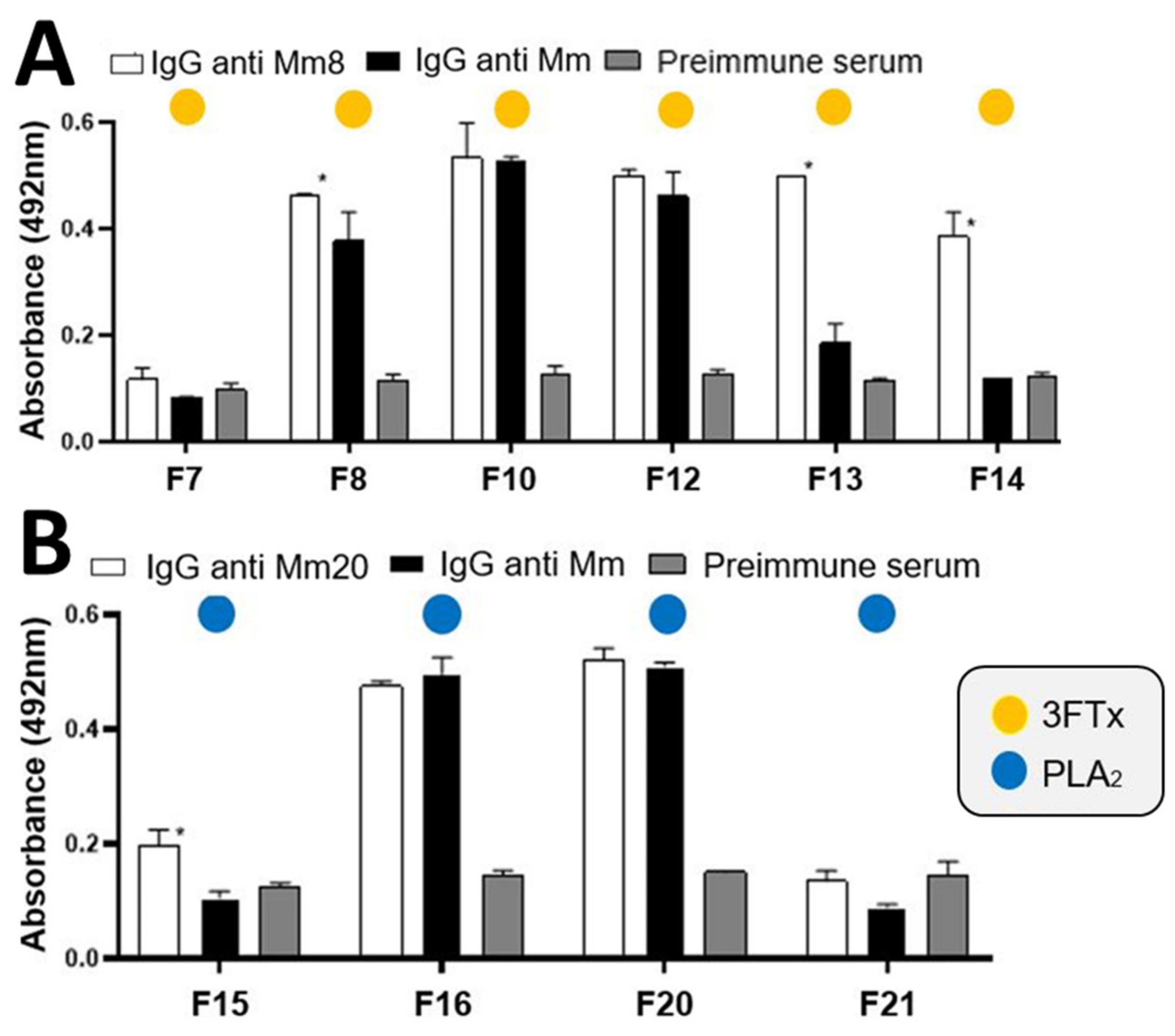
2.2. Fractionation of Hyperimmune Serum and Titration IgGs
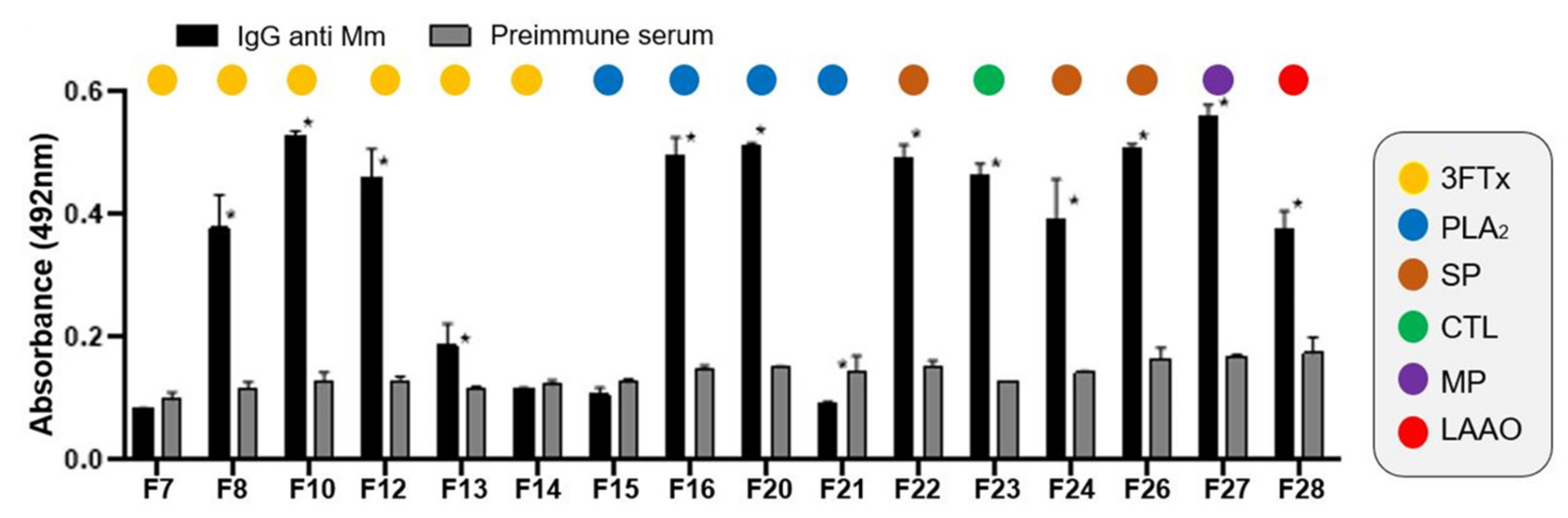
2.3. IgGs Neutralizing Ability against the Lethal Effect of M. Mipartitus
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Venoms and Animals
5.2. Isolation of Toxins from M. mipartitus Venom
5.3. Immunization Protocol
5.4. IgG Purification
5.5. Antibody Titers
5.6. Neutralization of the Lethal Effect of Venom and Toxins with IgGs
5.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uetz, P.; Hallerman, J. The Reptile Database. 2014. Available online: https://reptile-database.reptarium.cz/ (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Instituto Nacional de Salud; Equipo de Enfermedades Transmitidas por Vectores y Zoonosis; Grupo de Enfermedades Transmisibles. Informe de Accidente Ofídico—2019; SIVIGILA: Bogotá, Colombia, 2019; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Montecucco, C.; Rossetto, O. How do presynaptic PLA2 neurotoxins block nerve terminals? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renjifo, C.; Smith, E.N.; Hodgson, W.; Renjifo, J.M.; Sánchez-Godoy, J.A.; Acosta, R.; Maldonado, J.H.; Riveros, A. Neuromuscular activity of the venoms of the Colombian coral snakes Micrurus dissoleucus and Micrurus mipartitus: An evolutionary perspective. Toxicon 2012, 59, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucaretchi, F.; De Capitani, E.M.; Vieira, R.J.; Rodrigues, C.K.; Zannin, M.; Da Silva, N.J.; Casais-E-Silva, L.L.; Hyslop, S. Coral snake bites (Micrurus spp.) in Brazil: A review of literature reports. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Rey-Suárez, P.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Sasa, M.; Núñez, V.; Gutiérrez, J.; Calvete, J.; Lomonte, B. Proteomic studies on Micrurus (coral snakes) venom reveal a dichotomy of phenotypes. Toxicon 2018, 150, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roze, J. Coral Snake of the Americas: Biology, Identification, and Venoms; Universidad Veracruzana: Poza Rica, Mexico, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.A.; Lamar, W.W. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere; Comstock Publishing Associates: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, R.; Osorio, R.G.; Valderrama, R.; Giraldo, C.A. Efectos farmacologicos y enzimaticos de los venenos de serpientes de Antioquia y Choco (Colombia). Toxicon 1992, 30, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Suárez, P.; Núñez, V.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Proteomic and biological characterization of the venom of the redtail coral snake, Micrurus mipartitus (Elapidae), from Colombia and Costa Rica. J. Proteom. 2011, 75, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Suárez, P.; Floriano, R.S.; Rostelato-Ferreira, S.; Saldarriaga-Córdoba, M.; Núñez, V.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Lomonte, B. Mipartoxin-I, a novel three-finger toxin, is the major neurotoxic component in the venom of the redtail coral snake Micrurus mipartitus (Elapidae). Toxicon 2012, 60, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rey-Suárez, P.; Núñez, V.; Saldarriaga-Córdoba, M.; Lomonte, B. Primary structures and partial toxicological characterization of two phospholipases A2 from Micrurus mipartitus and Micrurus dumerilii coral snake venoms. Biochimie 2017, 137, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Assembly. Addressing the Burden of Snakebite Envenoming. 2018, Volume 17. Available online: Apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/EB142/B142_R4-en.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2018).
- Rawat, S.; Laing, G.; Smith, D.C.; Theakston, D.; Landon, J. A new antivenom to treat eastern coral snake (Micrurus fulvius fulvius) envenoming. Toxicon 1994, 32, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, H.; Bourguignon, S.C.; Boller, M.; Dias, A.; Lucas, E.; Santos, I.; Delgado, I. Potency evaluation of antivenoms in Brazil: The national control laboratory experience between 2000 and 2006. Toxicon 2008, 51, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M. Envenenamientos por mordeduras de serpientes en América Latina y el Caribe: Una visión integral de carácter regional. Boletín Malariol. Salud Ambient. 2011, LI, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento, K.; Rodríguez, A.; Quevedo-Buitrago, W.; Torres, I.; Ríos, C.; Ruíz, L.; Salazar, J.; Hidalgo-Martínez, P.; Diez, H. Comparación de la eficacia, la seguridad y la farmacocinética de los antivenenos antiofídicos: Revisión de literatura. Univ. Med. 2019, 61, 30–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao, A.M.; Núñez, V. Maintenance of red-tail coral snake (Micrurus mipartitus) in captivity and evaluation of individual venom variability. Acta Biol. Colomb. 2016, 21, 539–600. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Beltrán, M.C.; Hurtado-Gómez, J.P.; Corredor, V.; Ruiz-Gómez, F.J. A polyvalent coral snake antivenom with broad neutralization capacity. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Engmark, M.; Clouser, C.; Timberlake, S.; Vigneault, F.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Exploration of immunoglobulin transcriptomes from mice immunized with three-finger toxins and phospholipases A2 from the Central American coral snake, Micrurus nigrocinctus. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvete, J.J.; Rodríguez, Y.; Quesada-Bernat, S.; Pla, D. Toxin-resolved antivenomics-guided assessment of the immunorecognition landscape of antivenoms. Toxicon 2018, 148, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Isbister, G.K. Current research into snake antivenoms, their mechanisms of action and applications. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bermúdez-Méndez, E.; Fuglsang-Madsen, A.; Føns, S.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Laustsen, A.H. Innovative Immunization Strategies for Antivenom Development. Toxins 2018, 10, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krifi, M.N.; Marrakchi, N.; El Ayeb, M.; Dellagi, K. Effect of Some Variables on the In Vivo Determination of Scorpion and Viper Venom Toxicities. Biologicals 1998, 26, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández, J.; Alape-Girón, A.; Angulo, Y.; Sanz, L.; Gutièrrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Lomonte, B. Venomic and Antivenomic Analyses of the Central American Coral Snake, Micrurus nigrocinctus (Elapidae). J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotwiwatthanakun, C.; Pratanaphon, R.; Akesowan, S.; Sriprapat, S.; Ratanabanangkoon, K. Production of potent polyvalent antivenom against three elapid venoms using a low dose, low volume, multi-site immunization protocol. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghini, D.G.; Damico, D.C.; Da Cruz-Höfling, M.A.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Delatorre, M.C.; Hyslop, S.; Marangoni, S. Ability of rabbit antiserum against crotapotin to neutralize the neurotoxic, myotoxic and phospholipase A2 activities of crotoxin from Crotalus durissus cascavella snake venom. Toxicol. In Vitro 2008, 22, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, L.S.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Teibler, P.; Maruñak, S.; Acosta, O.; Leiva, L. New immunization protocol to produce crotalic antivenom combining Crotalus durissus terrificus venom and its PLA2. Biologicals 2015, 43, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro, K.L.P.; Lopes-De-Souza, L.; De Oliveira, D.; de Ávila, R.A.M.; Paiva, A.L.B.; De Freitas, C.F.; Ho, P.L.; Olórtegui, C.D.C.; Guerra-Duarte, C. A Combined Strategy to Improve the Development of a Coral Antivenom Against Micrurus spp. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Progress in the Characterization of Venoms and Standardization of Antivenoms; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Solano, G.; Pla, D.; Herrera, M.; Segura, Á.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Sánchez, A.; Sanz, L.; Lomonte, B.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of the Efficacy of Antivenoms for Snakebite Envenoming: State-of-the-Art and Challenges Ahead. Toxins 2017, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laemmly, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbuch, M.; Audran, R. The isolation of IgG from mammalian sera with the aid of caprylic acid. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1969, 134, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B. Manual de Métodos Inmunológicos; Universidad de Costa Rica: San José, Costa Rica, 2007; p. 138. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardona-Ruda, A.; Rey-Suárez, P.; Núñez, V. Anti-Neurotoxins from Micrurus mipartitus in the Development of Coral Snake Antivenoms. Toxins 2022, 14, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040265
Cardona-Ruda A, Rey-Suárez P, Núñez V. Anti-Neurotoxins from Micrurus mipartitus in the Development of Coral Snake Antivenoms. Toxins. 2022; 14(4):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040265
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardona-Ruda, Ana, Paola Rey-Suárez, and Vitelbina Núñez. 2022. "Anti-Neurotoxins from Micrurus mipartitus in the Development of Coral Snake Antivenoms" Toxins 14, no. 4: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040265
APA StyleCardona-Ruda, A., Rey-Suárez, P., & Núñez, V. (2022). Anti-Neurotoxins from Micrurus mipartitus in the Development of Coral Snake Antivenoms. Toxins, 14(4), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14040265




