Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity Induced by Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
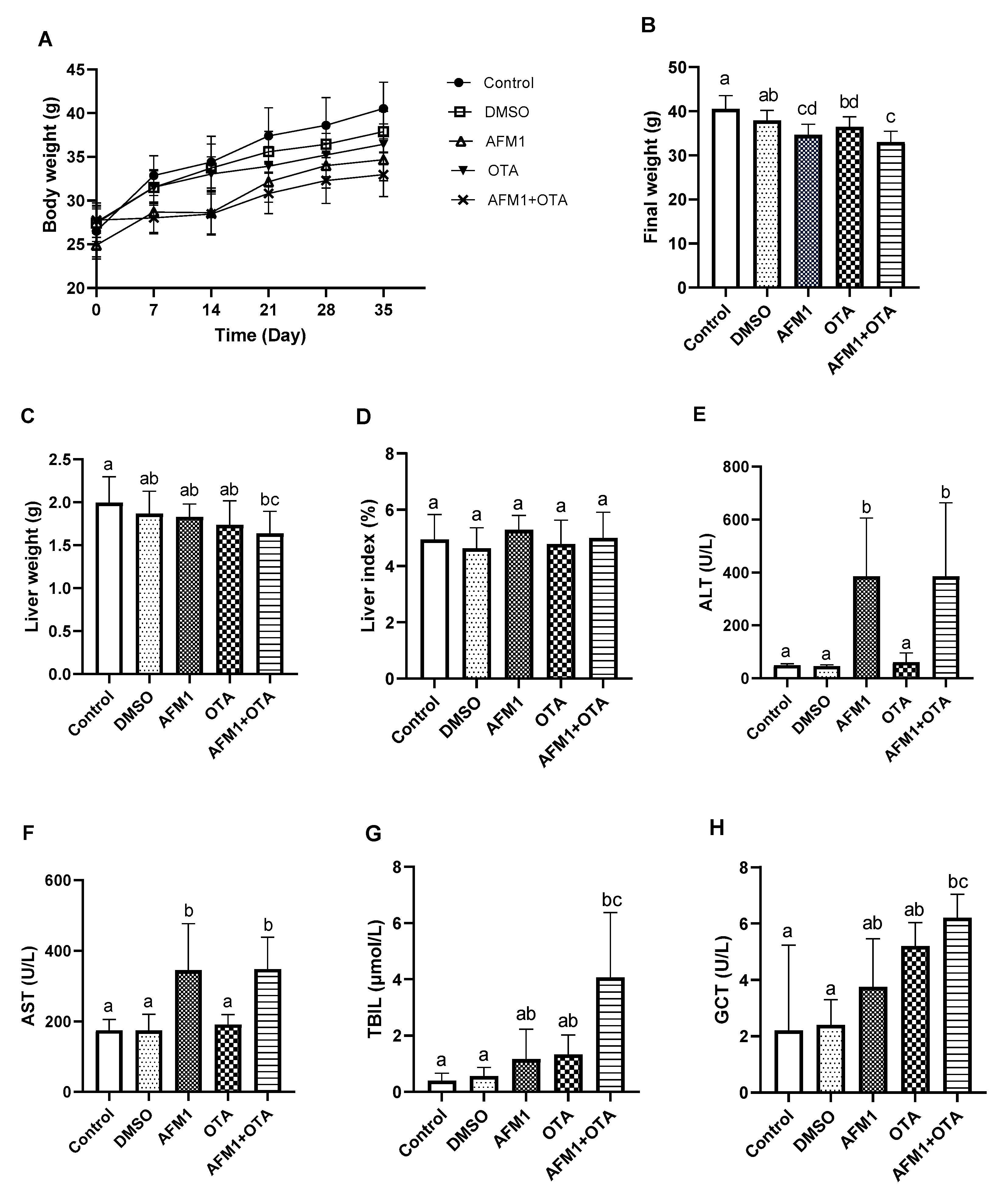
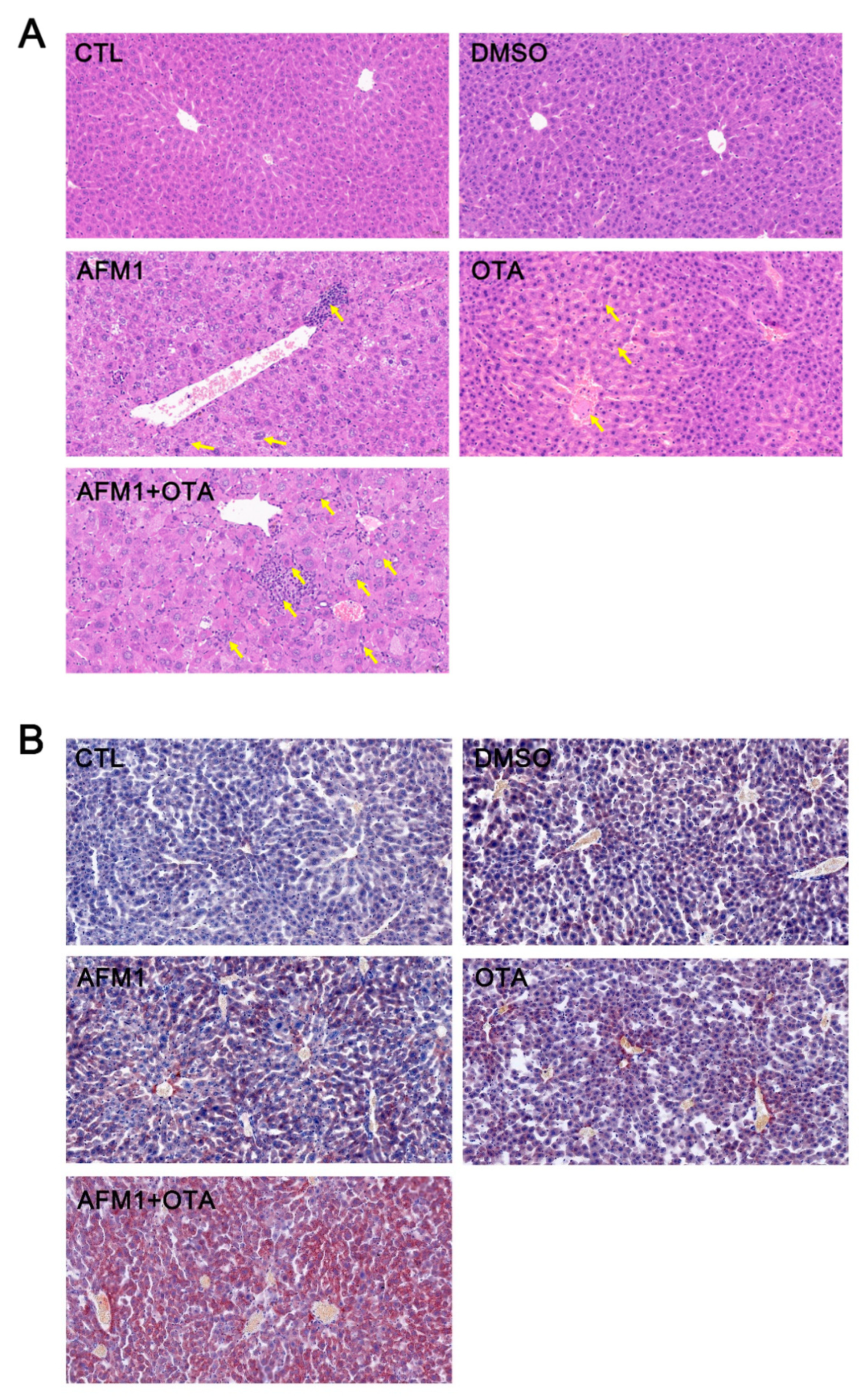
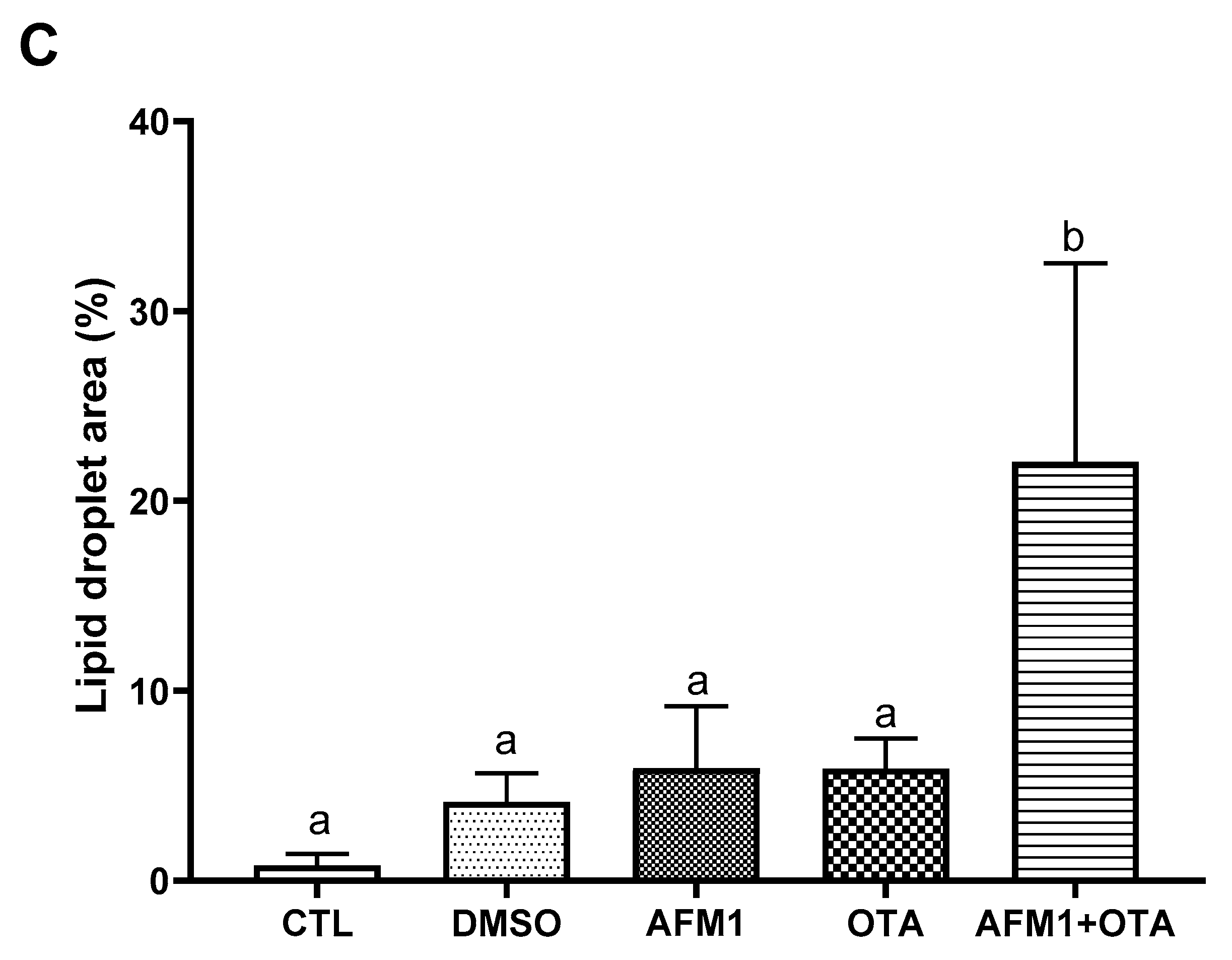
2.1. AFM1 and OTA-Induced Liver Injury in Mice
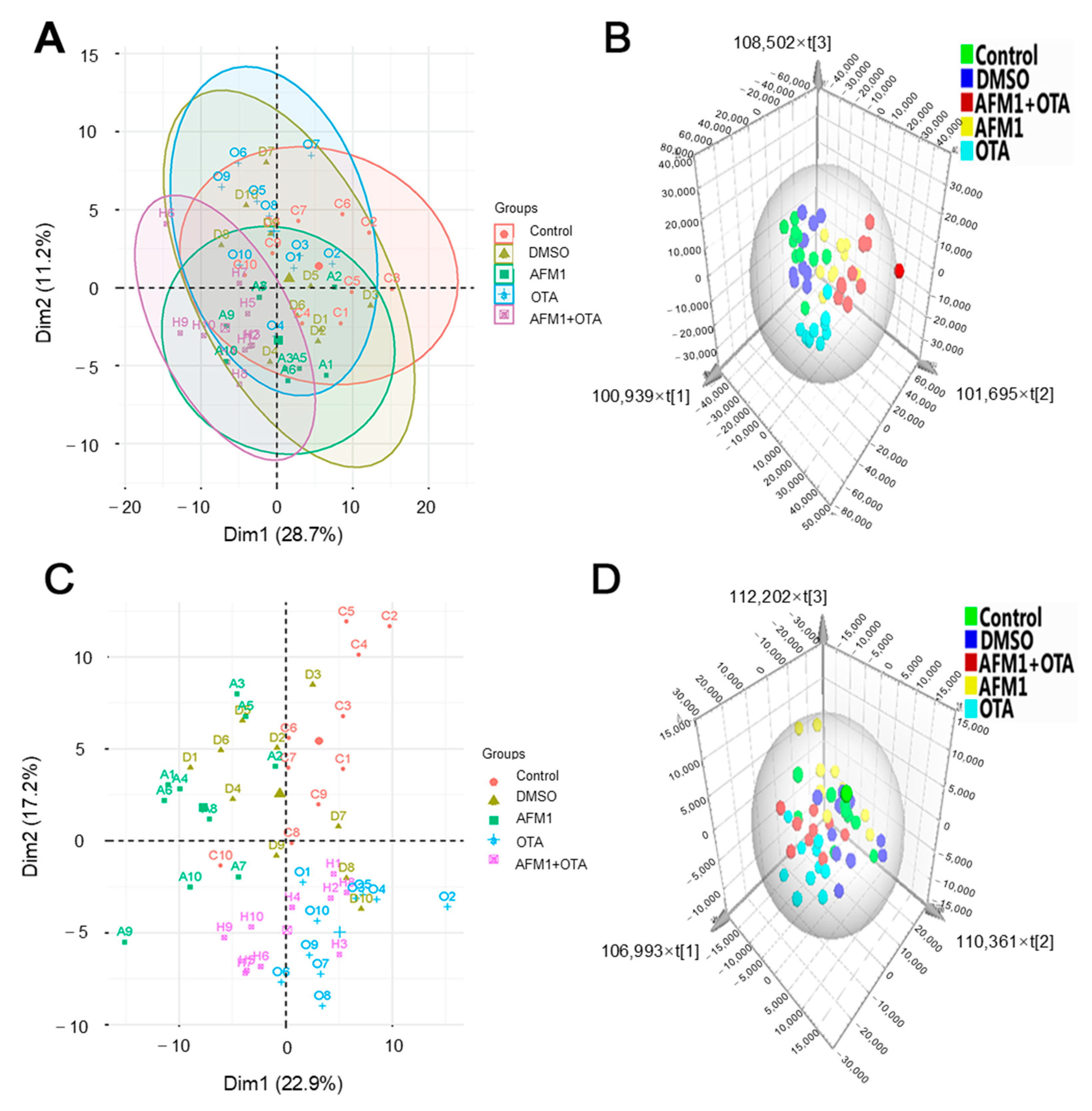
2.2. Multivariate Analysis of the Metabolic Profiles
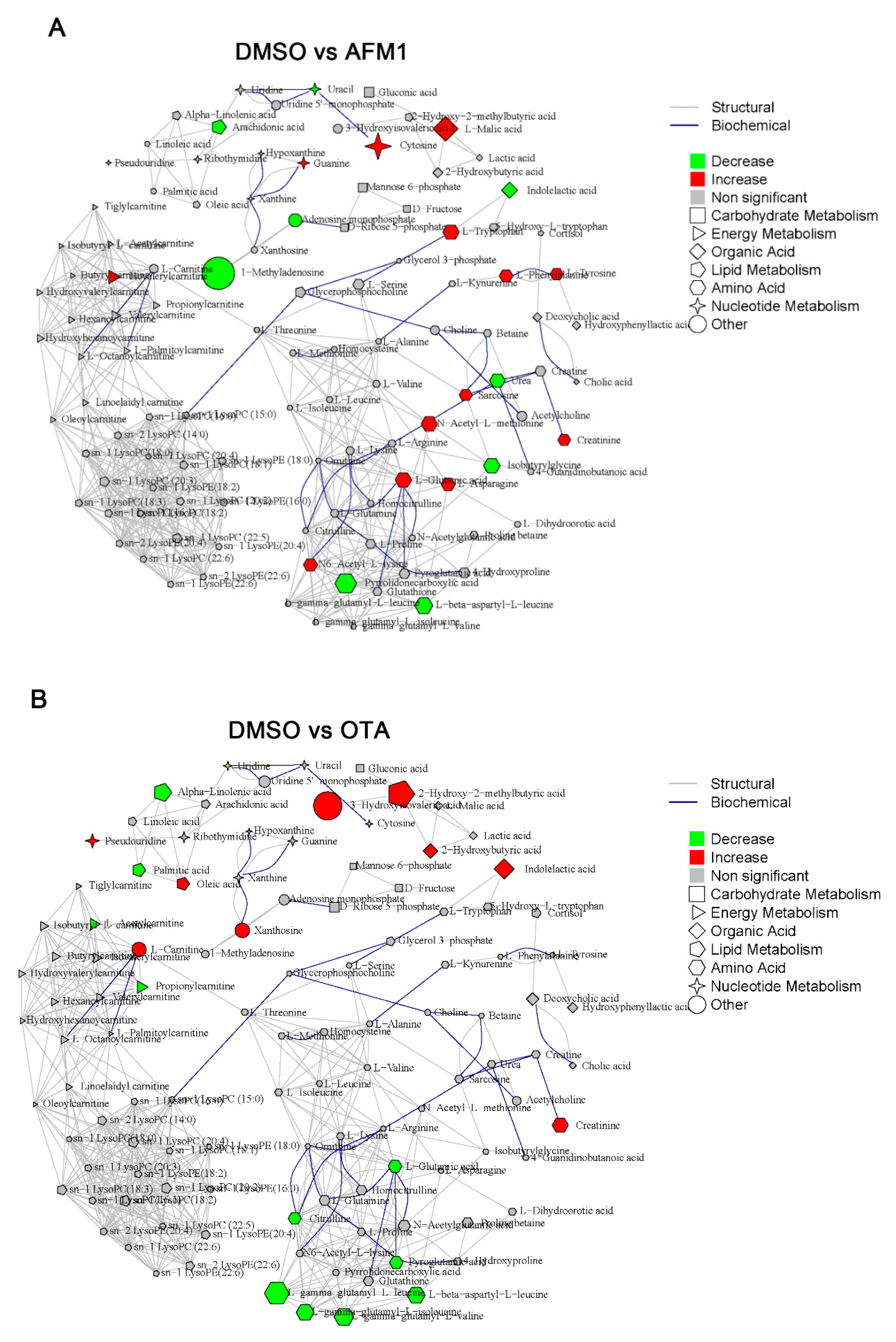
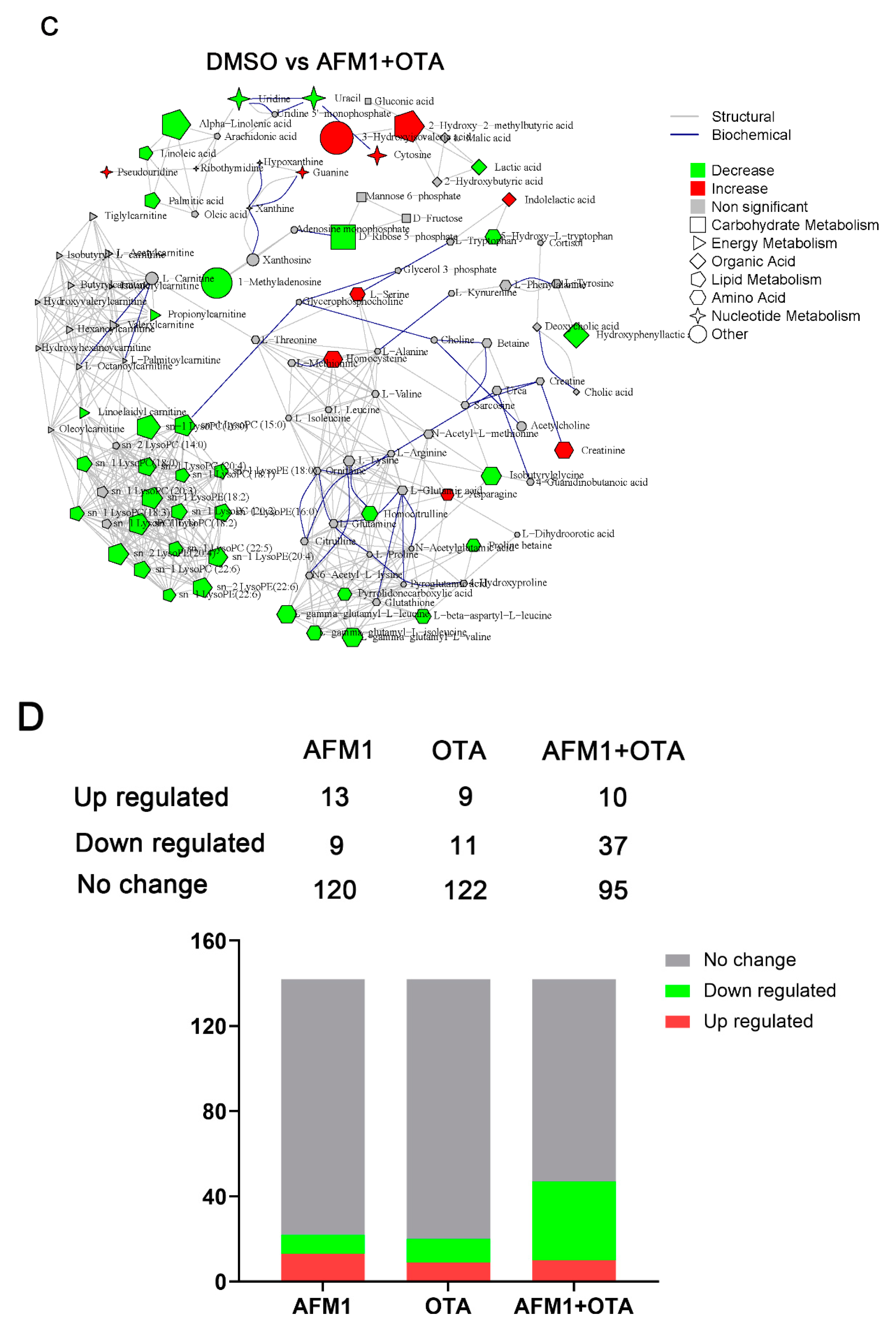
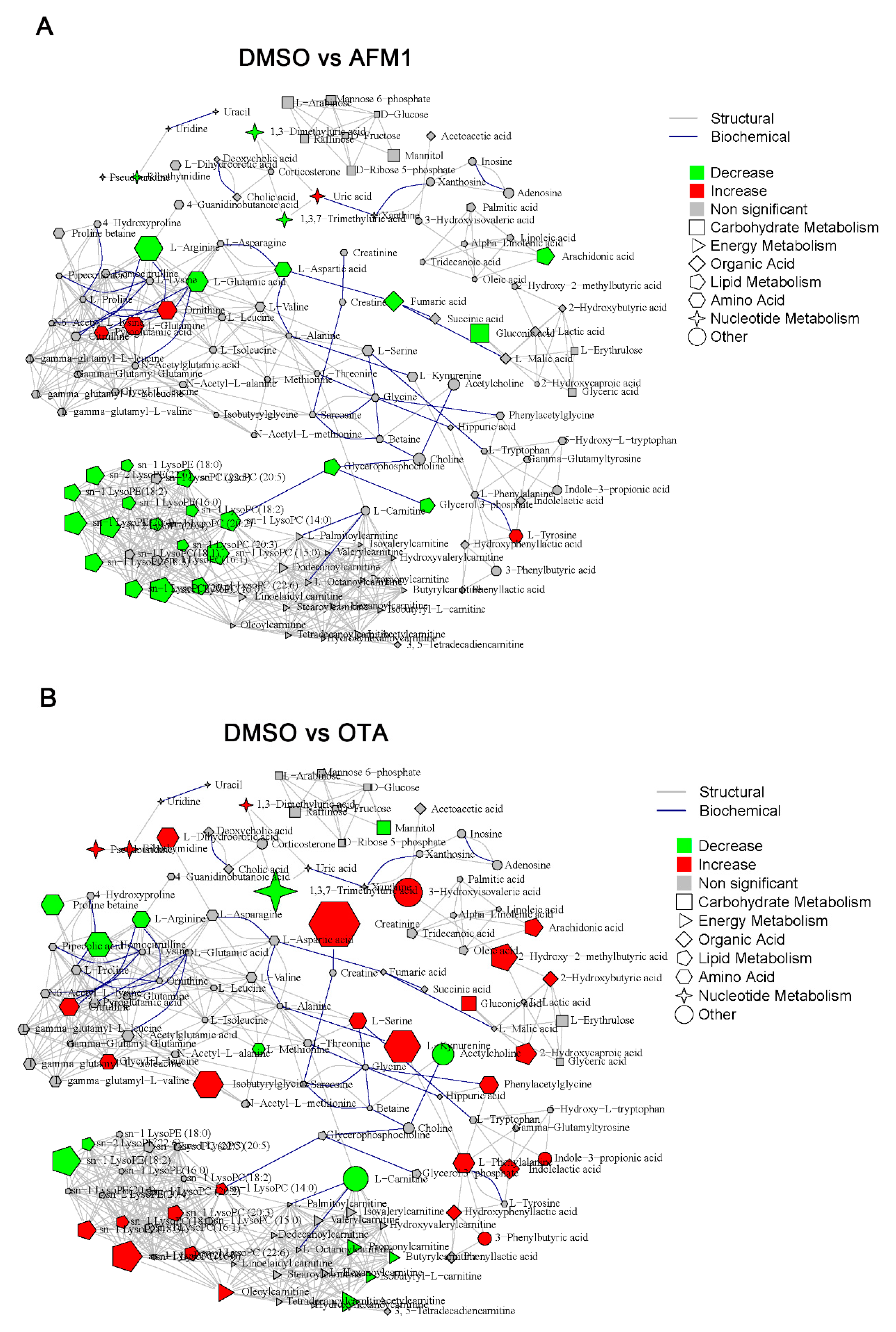
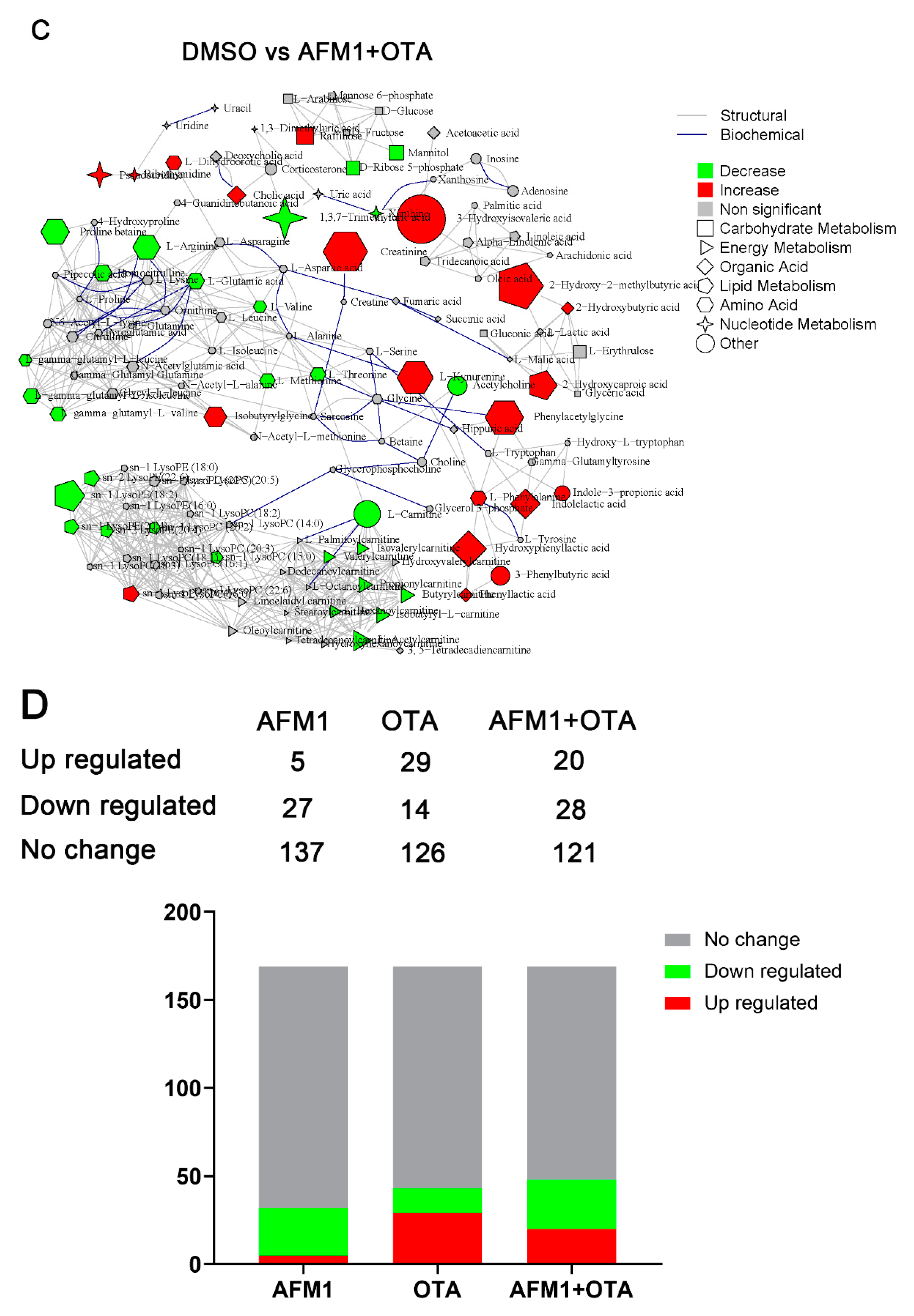
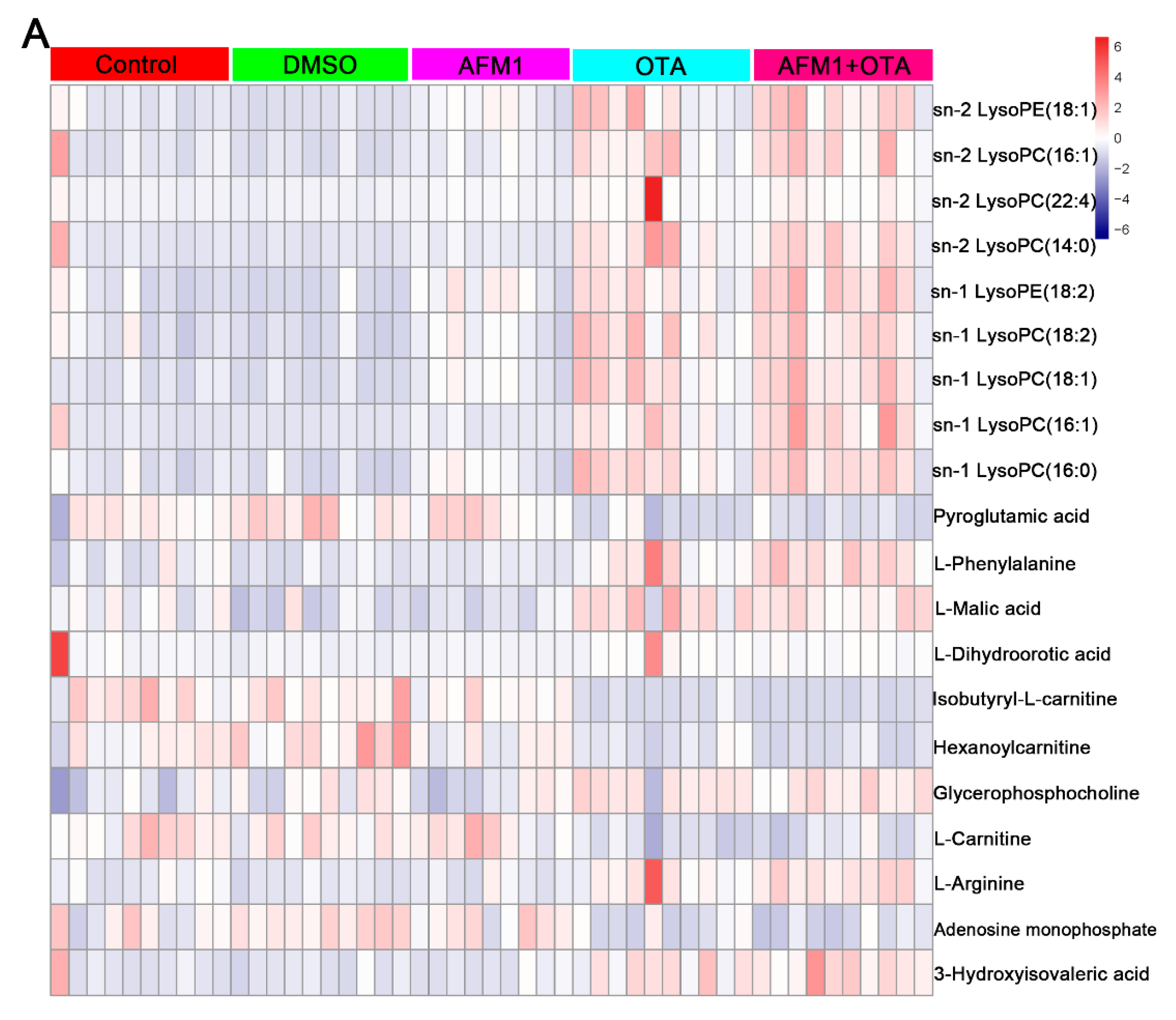
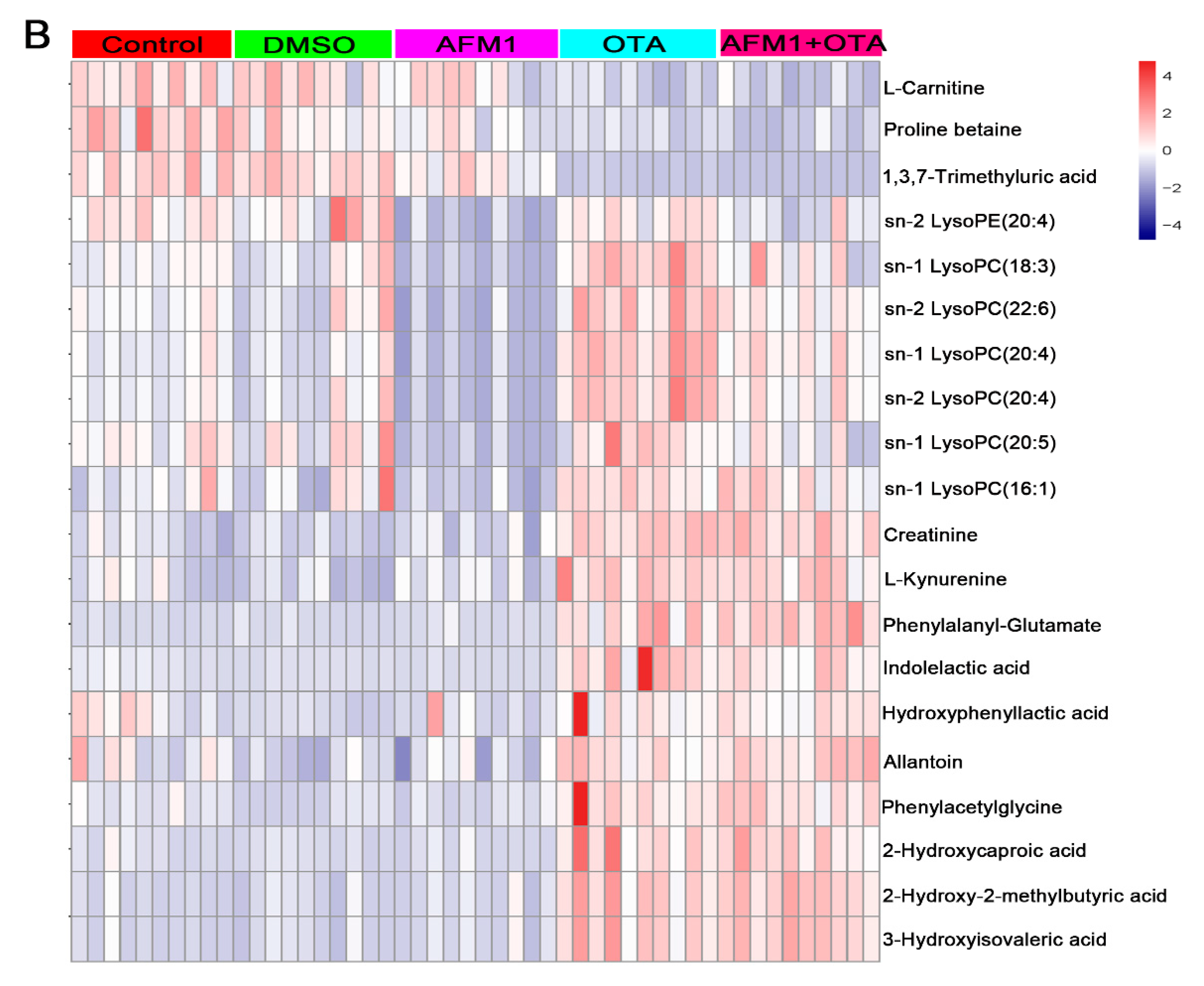
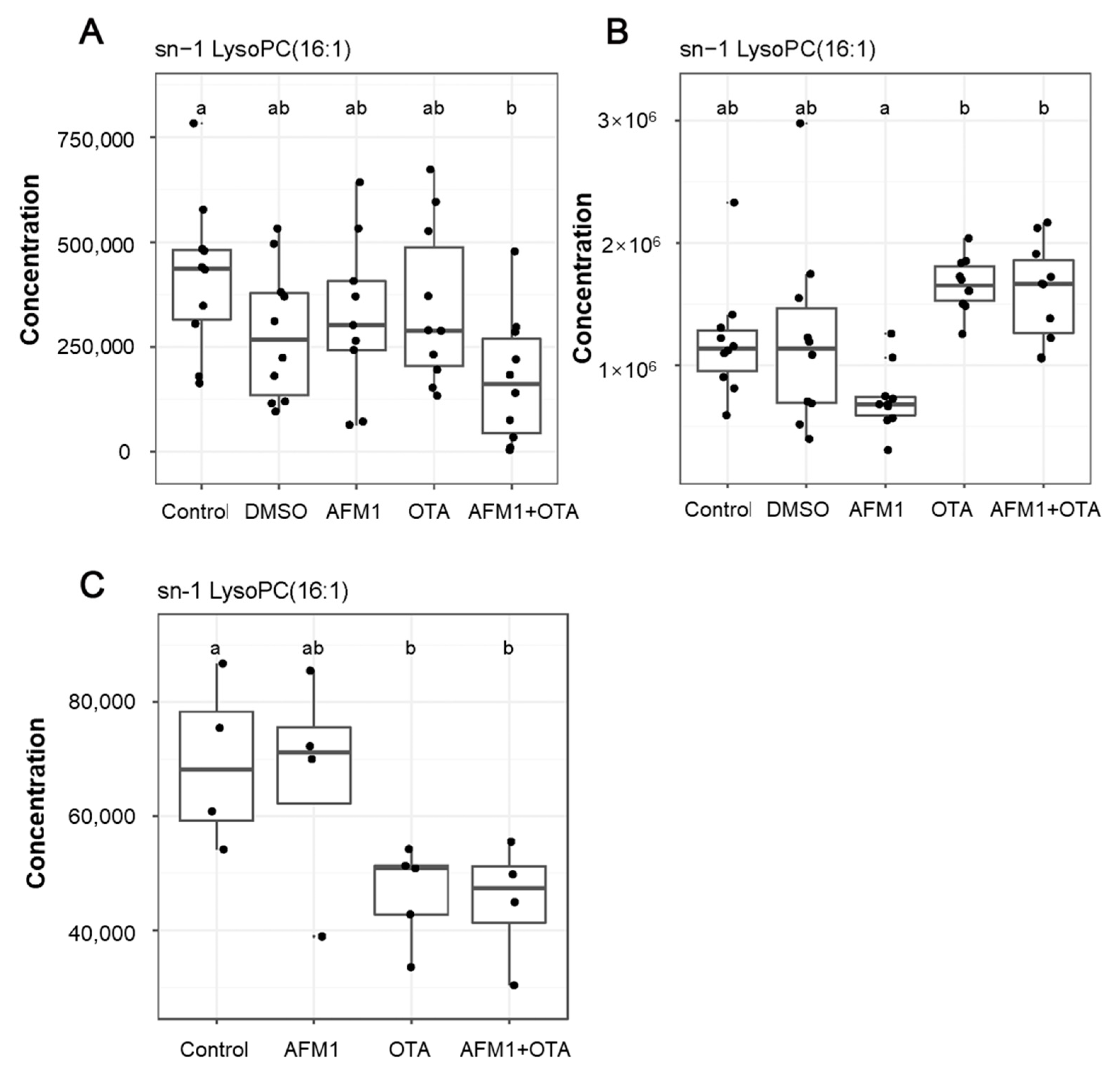
2.3. Identification of Differential Metabolites of Mice
2.4. The Main Type of Metabolites Affected by AFM1 and OTA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Animals and Treatment
4.3. Determination of Liver Index and Serum Biochemical Indicators
4.4. Histopathological Assessment of Liver
4.5. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.6. Metabolomics Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Hajslova, J.; Mayar, S.; Krska, R. Worldwide contamination of food-crops with mycotoxins: Validity of the widely cited ‘FAO estimate’ of 25. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2773–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromme, H.; Gareis, M.; Volkel, W.; Gottschalk, C. Overall internal exposure to mycotoxins and their occurrence in occupational and residential settings—An overview. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2016, 219, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer). IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 82. Aflatoxins: B1, B2, G1, G2, M1. In Some Traditional Herbal Medicines, Some Mycotoxins, Naphthalene, and Styrene; World Health Organization: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 82, pp. 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Jinap, S.; Pirouz, A.A.; Ahmad Faizal, A.R. Aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products, occurrence and recent challenges: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Min, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J. Aflatoxin M1 contamination in raw milk from major milk-producing areas of China during four seasons of 2016. Food Control 2017, 82, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Min, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J. Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in pasteurized and UHT milks in China in 2014–2015. Food Control 2017, 78, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Sun, P.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhen, Y.P.; Han, R.W.; Xu, X.M. Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in UHT milk and pasteurized milk in China market. Food Control 2013, 29, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Ryu, D. Worldwide Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Cereals and Cereal-Derived Food Products: Public Health Perspectives of Their Co-occurrence. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7034–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Fakhri, Y.; Raeisi, S.; Armoon, B.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Prevalence and concentration of ochratoxin A, zearalenone, deoxynivalenol and total aflatoxin in cereal-based products: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 118, 830–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, D.E.; Braicu, C.; Dumitrescu, G.; Pistol, G.C.; Cojocneanu, R.; Neagoe, I.B.; Taranu, I. MicroRNA profiling in kidney in pigs fed ochratoxin A contaminated diet. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostry, V.; Malir, F.; Toman, J.; Grosse, Y. Mycotoxins as human carcinogens-the IARC Monographs classification. Mycotoxin Res. 2017, 33, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brera, C.; Debegnach, F.; De Santis, B.; Pannunzi, E.; Berdini, C.; Prantera, E.; Gregori, E.; Miraglia, M. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in baby foods and paprika by HPLC with fluorescence detection: A single-laboratory validation study. Talanta 2011, 83, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elaridi, J.; Dimassi, H.; Hassan, H. Aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A in baby formulae marketed in Lebanon: Occurrence and safety evaluation. Food Control 2019, 106, 106680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkoglu, C.; Keyvan, E. Determination of Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A in Raw, Pasteurized and UHT Milk in Turkey. Acta Sci. Vet. 2019, 47, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad-Hussein, A.; Elserougy, S.; Beshir, S.; Ibrahim, M.I.M.; Awad, A.H.A.; Abdel-Wahhab, M.A. Work-related airborne fungi and the biological levels of mycotoxin in Textile workers. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 8, 719–726. [Google Scholar]
- Mekuria, A.N.; Routledge, M.N.; Gong, Y.Y.; Sisay, M. Aflatoxins as a risk factor for liver cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pharm. Toxicol. 2020, 21, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.J.; Zhao, J.F.; Huang, F.; Sun, G.L.; Gao, W.; Lu, L.; Xiao, Q. Protective Effect of Procyanidin B2 on Acute Liver Injury Induced by Aflatoxin B1 in Rats. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lv, Z.; Chen, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Long, M.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B10 can alleviate liver apoptosis and oxidative stress induced by aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 151, 112124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Shi, W.; Lv, P.; Meng, W.; Mao, G.; Gong, C.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, J.; et al. Critical role of caveolin-1 in aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity via the regulation of oxidation and autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, D.E.; Pistol, G.C.; Gras, M.; Palade, M.; Taranu, I. A comparison between the effects of ochratoxin A and aristolochic acid on the inflammation and oxidative stress in the liver and kidney of weanling piglets. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharm. 2018, 391, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhai, S.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Ruan, D.; Zhou, T.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Ye, H.; et al. Ochratoxin A induces liver inflammation: Involvement of intestinal microbiota. Microbiome 2019, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.S.; Ruan, D.; Zhu, Y.W.; Li, M.C.; Ye, H.; Wang, W.C.; Yang, L. Protective effect of curcumin on ochratoxin A-induced liver oxidative injury in duck is mediated by modulating lipid metabolism and the intestinal microbiota. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, A.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, M.; Loor, J.J.; Wang, H. Melatonin ameliorates ochratoxin A induced liver inflammation, oxidative stress and mitophagy in mice involving in intestinal microbiota and restoring the intestinal barrier function. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Sun, J.; Zhong, G.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Biodistribution and toxicity of intravenously administered silica nanoparticles in mice. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, R.; Wei, G.; Guo, G.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ishfaq, M.; Fazilani, S.A.; Zhang, X. Curcumin protects against Aflatoxin B1-induced liver injury in broilers via the modulation of long non-coding RNA expression. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eraslan, G.; Essiz, D.; Akdogan, M.; Karaoz, E.; Oncü, M.; Özyildiz, Z. Efficacy of dietary sodium bentonite against subchronic exposure to dietary aflatoxin in broilers. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2006, 50, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Hu, B.; Shao, L.; Tian, Y.; Jin, T.; Jin, Y.; Ji, S.; Fan, X. Integrated analysis of transcriptomics and metabonomics profiles in aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.L.; Henke, S.E.; Fedynich, A.M.; Laurenz, J.C.; Morgan, R. Acute effects of aflatoxin on northern bobwhites (Colinus virginianus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Li, W.; Muhammad, I.; Sun, X.; Cui, X.; Cheng, P.; Qayum, A.; Zhang, X. Biochemical basis for the age-related sensitivity of broilers to aflatoxin B1. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2018, 28, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, L.; Dhivya, R.; Dhanasekaran, D.; Periasamy, V.S.; Alshatwi, A.A.; Akbarsha, M.A. Hepatotoxic effect of ochratoxin A and citrinin, alone and in combination, and protective effect of vitamin E: in vitro study in HepG2 cell. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 83, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Liu, S.; Zhao, C.; Fan, L.; Hu, H.; Yin, S. The combination of T-2 toxin and acrylamide synergistically induces hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity via the activation of oxidative stress and the mitochondrial pathway. Toxicon 2021, 189, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, M.C.; Shin, H.S.; Jeon, G.Y.; Lee, K.W. Synergistic interaction of ochratoxin A and acrylamide toxins in human kidney and liver cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.H.; Lei, M.Y.; Zhang, N.Y.; Zhao, L.; Krumm, C.S.; Qi, D.S. Hepatotoxic effects of mycotoxin combinations in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 74, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Zhu, P.; Cui, F.; Pi, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, X. The Antagonistic Effect of Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone on Metabolic Profiling in Serum and Liver of Mice. Toxins 2017, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Yin, S.; Zhao, C.; Fan, L.; Hu, H. Combining Patulin with Cadmium Induces Enhanced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Toxins 2021, 13, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Qiu, P.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, P.; Huang, X.; Li, C.; Chai, K.; Shou, D. Metabolomics study of the hepatoprotective effect of Phellinus igniarius in chronic ethanol-induced liver injury mice using UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with ingenuity pathway analysis. Phytomedicine 2020, 74, 152697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Du, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Duan, J. Metabolomic characteristics of hepatotoxicity in rats induced by silica nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Tang, X.; Hao, F.; Gao, Y. Hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity assessment on ethanol extract of Fructus Psoraleae in Sprague Dawley rats using a UPLC-Q-TOF-MS analysis of serum metabolomics. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2021, 35, e5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, W.; Wang, E.; Du, J.; Wei, B.; Xu, X. Protective effect of metformin on BPA-induced liver toxicity in rats through upregulation of cystathionine beta synthase and cystathionine gamma lyase expression. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.X.; Bi, Y.N.; Yuan, X.M.; Song, L.; Jiang, M.M.; Sun, L.K.; Zhou, K. A Study of NMR-Based Hepatic and Serum Metabolomics in a Liver Injury Sprague-Dawley Rat Model Induced by Psoralen. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhu, P.; Blazenovic, I.; Cui, F.; Gholami, M.; Sun, J.; Habimana, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Explaining combinatorial effects of mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone in mice with urinary metabolomic profiling. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Yin, P.; Tang, L.; Xing, W.; Huang, Q.; Cao, D.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Lu, X.; Xu, Z.; et al. Metabolomics study of stepwise hepatocarcinogenesis from the model rats to patients: Potential biomarkers effective for small hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, M111010694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.A.; Lee, H.; Park, S.Y.; Lim, Y.; Kwon, O.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, D.; Jung, B.H. Analysis of plasma metabolic profiling and evaluation of the effect of the intake of Angelica keiskei using metabolomics and lipidomics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 243, 112058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zheng, K.; Xin, Y.; Jia, S.; Zhao, X. Metabonomics analysis of liver in rats administered with chronic low-dose acrylamide. Xenobiotica 2020, 50, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.J.; Jung, K.J.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.; Kang, M.; Jee, S.H.; Choi, Y.; Lee, J.H. Liver Cirrhosis Patients Who Had Normal Liver Function Before Liver Cirrhosis Development Have the Altered Metabolic Profiles Before the Disease Occurrence Compared to Healthy Controls. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsvik, P.A.; Skjaerven, K.H.; Softeland, L. Metabolic signatures of bisphenol A and genistein in Atlantic salmon liver cells. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuykx, M.; Rodrigues, R.M.; Laukens, K.; Vanhaecke, T.; Covaci, A. in vitro assessment of hepatotoxicity by metabolomics: A review. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 3007–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.; Gao, J.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, G. Metabolomics revealed the toxicity of cationic liposomes in HepG2 cells using UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS and multivariate data analysis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, e4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.A.; Choi, S.; Suh, S.H. Superoxide is a potential culprit of caspase-3 dependent endothelial cell death induced by lysophosphatidylcholine. J. Physiol. Pharm. 2010, 61, 375–381. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, C.; Li, S.; He, L.; Han, X.; Tang, F.; Huang, R.; Lin, Z.; Deng, S.; Xu, J.; Huang, H.; et al. Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 contributes to the lysophosphatidylcholine-induced oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in OLN-93 oligodendrocyte. Cell Stress Chaperones 2020, 25, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Lei, P.; Chen, D.Q.; Feng, Y.L.; Bai, X. Renal metabolic profiling of early renal injury and renoprotective effects of Poria cocos epidermis using UPLC Q-TOF/HSMS/MSE. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 81, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhou, J.; Ma, H.; Guo, H.; Ni, Z.; Duan, J.; Tao, W.; Qian, D. An in vitro metabolomics approach to identify hepatotoxicity biomarkers in human L02 liver cells treated with pekinenal, a natural compound. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesano, A.; Senesi, P.; Vacante, F.; Mollica, G.; Benedini, S.; Mariotti, M.; Luzi, L.; Terruzzi, I. L-Carnitine counteracts in vitro fructose-induced hepatic steatosis through targeting oxidative stress markers. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 43, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosavi, M.; Rezaei, M.; Kalantari, H.; Behfar, A.; Varnaseri, G. L-carnitine protects rat hepatocytes from oxidative stress induced by T-2 toxin. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 39, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, N. Aflatoxin M1 cytotoxicity against human intestinal Caco-2 cells is enhanced in the presence of other mycotoxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Metabolomics analysis underlay mechanisms in the renal impairment of mice caused by combination of aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A. Toxicology 2021, 458, 152835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Bao, X.; Luo, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, N. Transcriptional and proteomic analysis revealed a synergistic effect of aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A mycotoxins on the intestinal epithelial integrity of differentiated human Caco-2 cells. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3128–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Luo, C.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, N. Modulation of intestinal epithelial permeability in differentiated Caco-2 cells exposed to aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A individually or collectively. Toxins 2018, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ye, Q.; Bao, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Transcriptomic and proteomic profiling reveals the intestinal immunotoxicity induced by aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A. Toxicon 2020, 180, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Modulation of mucin (MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC5B) mRNA expression and protein production and secretion in Caco-2/HT29-MTX co-cultures following exposure to individual and combined aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A. Toxins 2019, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bao, X.; Meng, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Aflatoxin B1 and Aflatoxin M1 Induce Compromised Intestinal Integrity through Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis. Toxins 2021, 13, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.W.; Lam, S.M.; Fan, X.; Cao, W.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Tian, H.; Chua, G.H.; Zhang, C.; Meng, F.P.; Xu, Z.; et al. Omics-Driven Systems Interrogation of Metabolic Dysregulation in COVID-19 Pathogenesis. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 188–202.e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.-N.; Wu, C.-Q.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zheng, N. Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity Induced by Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A. Toxins 2022, 14, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020141
Gao Y-N, Wu C-Q, Wang J-Q, Zheng N. Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity Induced by Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A. Toxins. 2022; 14(2):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020141
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ya-Nan, Chen-Qing Wu, Jia-Qi Wang, and Nan Zheng. 2022. "Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity Induced by Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A" Toxins 14, no. 2: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020141
APA StyleGao, Y.-N., Wu, C.-Q., Wang, J.-Q., & Zheng, N. (2022). Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity Induced by Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A. Toxins, 14(2), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020141





