LC-MS/MS Analysis of Fumonisin B1, B2, B3, and Their Hydrolyzed Metabolites in Broiler Chicken Feed and Excreta
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sample Preparation
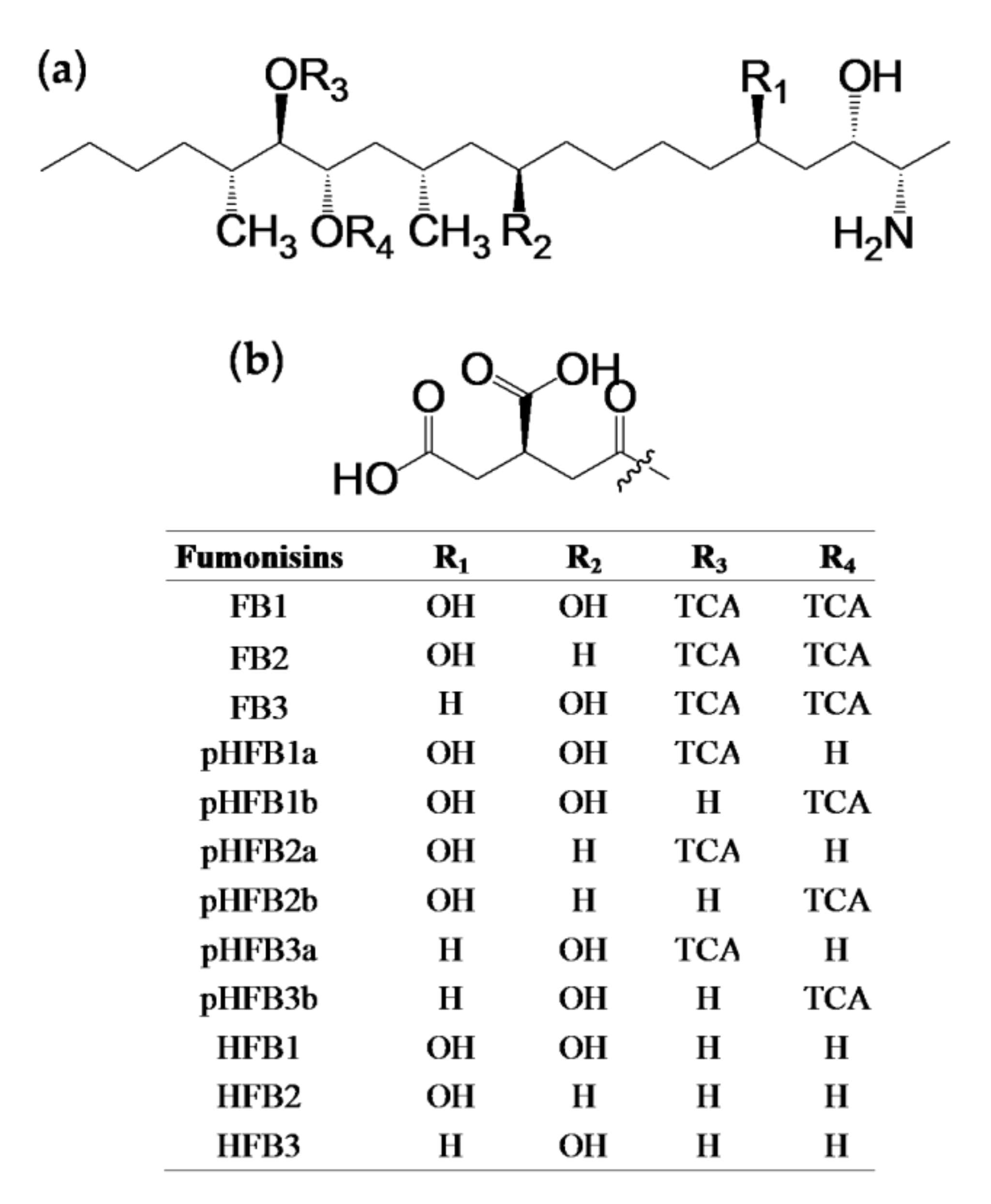
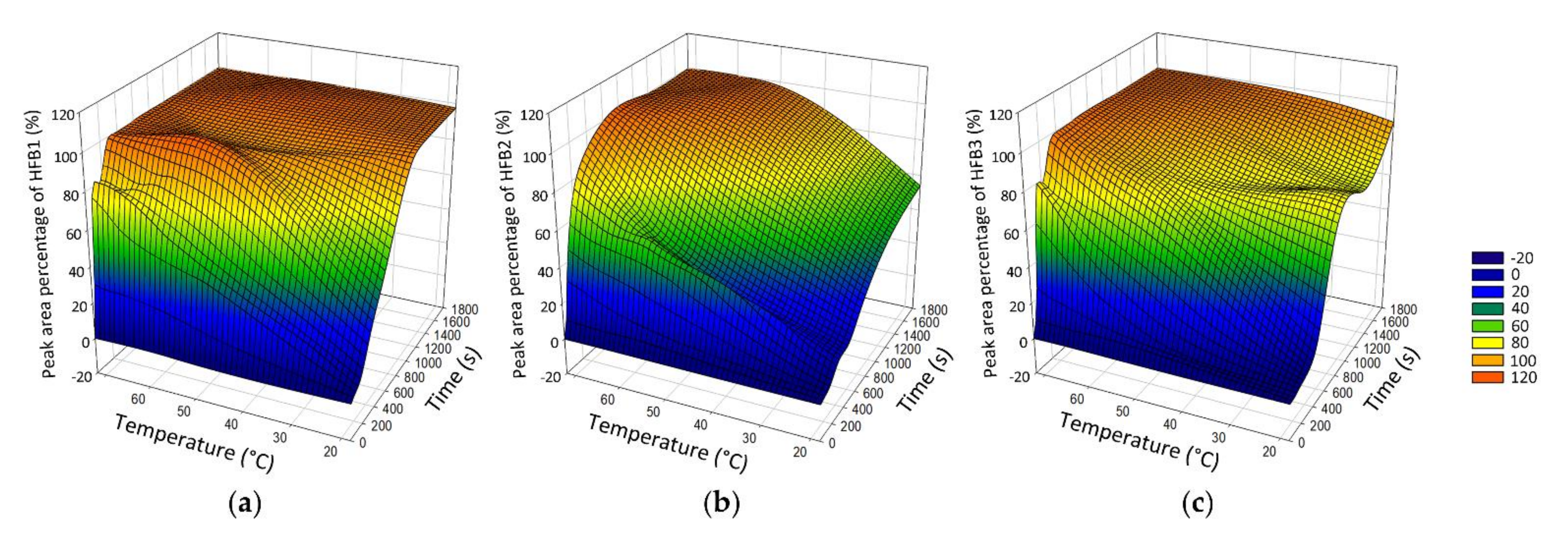
2.1.1. Alkaline Hydrolysis
2.1.2. MAX Procedure
2.2. Preparation of Standard Solutions
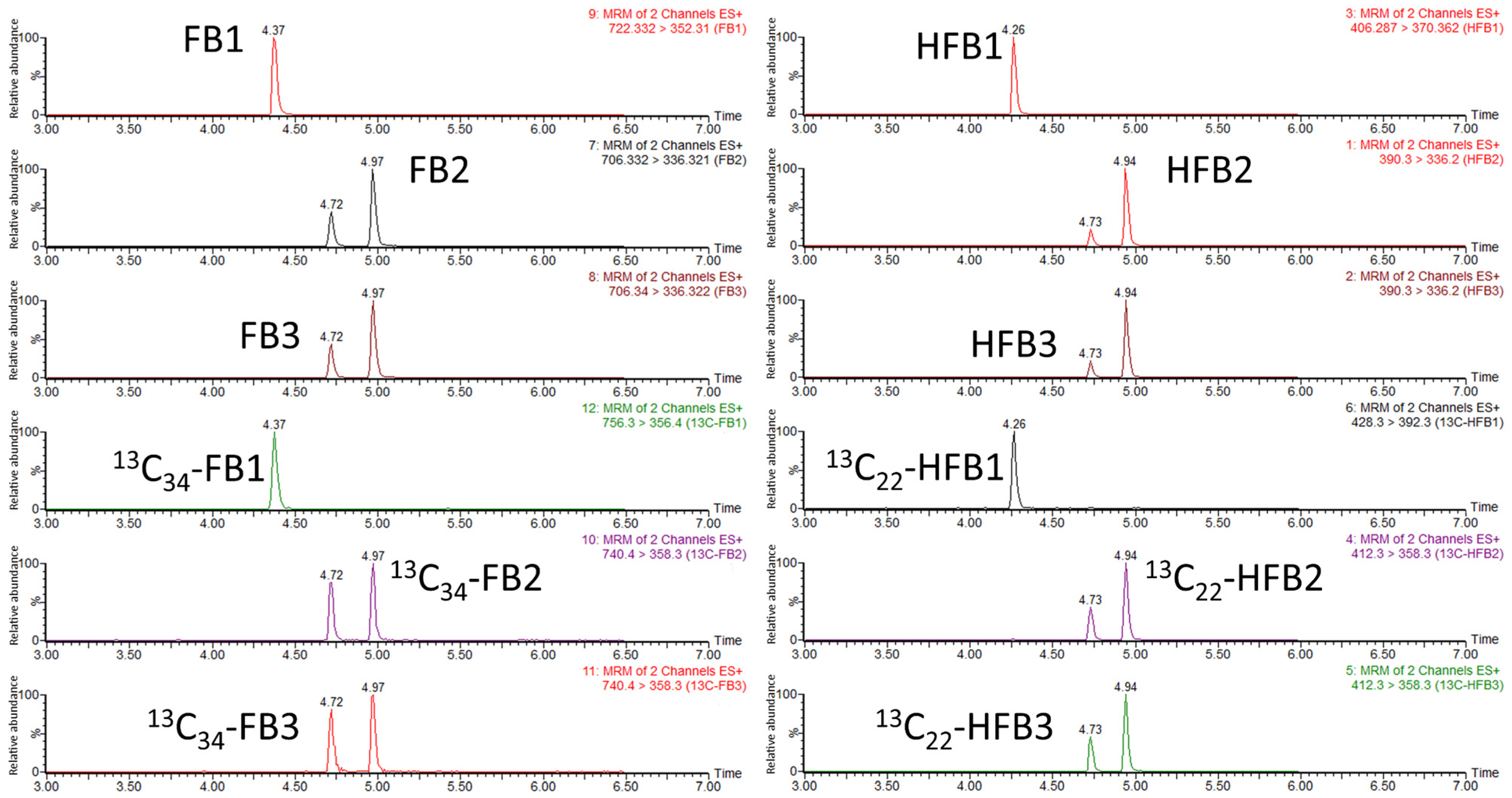
2.3. Optimization of LC-MS/MS
2.4. Method Validation
2.4.1. Linearity and Sensitivity
2.4.2. Matrix Effects
2.4.3. Accuracy and Precision
2.5. Analysis of Real Samples
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Sample Collection
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. LC-MS/MS
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Risks for animal healthrelated to the presence of fumonisins, their modified forms and hidden forms in feed. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05242. [Google Scholar]
- Degen, G.H. Highlight report: Metabolism and toxicity by fumonisins. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 2477–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riley, R.T.; Torres, O.; Matute, J.; Gregory, S.G.; Ashley-Koch, A.E.; Showker, J.L.; Mitchell, T.; Voss, K.A.; Maddox, J.R.; Gelineau-van Waes, J.B. Evidence for fumonisin inhibition of ceramide synthase in humans consuming maize-based foods and living in high exposure communities in Guatemala. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2209–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Some Traditional Herbal Medicines, Some Mycotoxins, Naphthalene and Styrene; IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 82, pp. 301–366. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). Evaluation of Certain Mycotoxins in Food, Fifty-Sixth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Technical Report Series No 906; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42448 (accessed on 4 February 2022).
- European Commission. Commission regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission recommendation (2006/576/EC) of 17 August 2006 on the presence of deoxynivalenol, zearalenone, ochratoxin A, T-2 and HT-2 and fumonisins in products intended for animal feeding. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 229, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- United States Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Fumonisin Levels in Human Foods and Animal Feeds. 2001. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/guidance-industry-fumonisin-levels-human-foods-and-animal-feeds/ (accessed on 2 December 2021).
- Hartinger, D.; Schwartz, H.; Hametner, C.; Schatzmayr, G.; Haltrich, D.; Moll, W.D. Enzyme characteristics of aminotransferase FumI of Sphingopyxis sp. MTA144 for deamination of hydrolyzed fumonisin B1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escriva, L.; Font, G.; Manyes, L. In vivo toxicity studies of fusarium mycotoxins in the last decade: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodor, J.; Balogh, K.; Weber, M.; Miklós, M.; Kametler, L.; Pósa, R.; Mamet, R.; Bauer, J.; Horn, P.; Kovács, F.; et al. Absorption, distribution and elimination of fumonisin B(1) metabolites in weaned piglets. Food Addit. Contam. A Chem. Anal. Control Expos. Risk Assess. 2008, 25, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hahn, I.; Nagl, V.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Varga, E.; Schwarz, C.; Slavik, V.; Reisinger, N.; Malachová, A.; Cirlini, M.; Generotti, S.; et al. Effects of orally administered fumonisin B1 (FB1), partially hydrolysed FB1, hydrolysed FB1 and N-(1-deoxy-D-fructos-1-yl) FB1 on the sphingolipid metabolism in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 76, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier, B.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Gruber-Dorninger, C.; Dohnal, I.; Aleschko, M.; Schatzmayr, G.; Moll, W.D.; Applegate, T.J. Enzymatic hydrolysis of fumonisins in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 4342–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Baere, S.; Croubels, S.; Novak, B.; Bichl, G.; Antonissen, G. Development and Validation of a UPLC-MS/MS and UPLC-HR-MS Method for the Determination of Fumonisin B1 and Its Hydrolysed Metabolites and Fumonisin B2 in Broiler Chicken Plasma. Toxins 2018, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dall’Asta, C.; Galaverna, G.; Aureli, G.; Dossena, A.; Marchelli, R. A LC/MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of free and masked fumonisins in maize and maize-based products. World Mycotoxin J. 2008, 1, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.S.; Diel, A.C.L.; Rauber, R.H.; Fontoura, F.P.; Mallmann, A.; Dilkin, P.; Mallmann, C.A. Free and hidden fumonisins in Brazilian raw maize samples. Food Control 2015, 53, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrade, P.D.; Dantas, R.R.; Moura-Alves, T.L.D.S.; Caldas, E.D. Determination of multi-mycotoxins in cereals and of total fumonisins in maize products using isotope labeled internal standard and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry with positive ionization. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1490, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X. Free and hidden fumonisins in raw maize and maize-based products from China. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveill. 2019, 12, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC). General standard for contaminants and toxins in food and feed. CXS 193-1995. 2019. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/en/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCXS%2B193-1995%252FCXS_193e.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2022).
- Guerre, P. Fusariotoxins in Avian Species: Toxicokinetics, Metabolism and Persistence in Tissues. Toxins 2015, 7, 2289–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Analytes | Linear Range (ng/mL) | Correlation Coefficients r | Chicken Feed | Chicken Excreta | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOD (µg/kg) | LOQ (µg/kg) | ME % | LOD (µg/kg) | LOQ (µg/kg) | ME % | |||
| FB1 | 0.5–1000 | 0.9995 | 50.0 | 160 | 112.3 | 50.0 | 160 | 137.6 |
| FB2 | 0.5–1000 | 0.9975 | 50.0 | 160 | 86.5 | 50.0 | 160 | 120.2 |
| FB3 | 0.5–1000 | 0.9947 | 50.0 | 160 | 76.5 | 50.0 | 160 | 102.5 |
| HFB1 | 0.5–1000 | 0.9991 | 50.0 | 160 | 95.6 | 50.0 | 160 | 115.4 |
| HFB2 | 0.5–1000 | 0.9979 | 50.0 | 160 | 105.6 | 50.0 | 160 | 89.5 |
| HFB3 | 0.5–1000 | 0.9968 | 50.0 | 160 | 84.6 | 50.0 | 160 | 92.7 |
| Analytes | Spiked Levels (µg/kg) | Chicken Feed | Chicken Excreta | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery% | RSD% | Recovery% | RSD% | ||
| FB1 | 200 | 89.6 | 7.5 | 90.9 | 3.9 |
| 4000 | 95.6 | 4.5 | 102.5 | 10.6 | |
| 20,000 | 90.7 | 6.6 | 105.6 | 8.4 | |
| FB2 | 200 | 91.3 | 8.9 | 94.2 | 4.6 |
| 4000 | 102.3 | 12.5 | 103.3 | 7.8 | |
| 20,000 | 87.4 | 18.9 | 110.8 | 15.3 | |
| FB3 | 200 | 98.2 | 8.6 | 89.7 | 7.9 |
| 4000 | 96.4 | 9.7 | 98.4 | 12.3 | |
| 20,000 | 92.3 | 5.6 | 107.6 | 9.7 | |
| HFB1 | 200 | 90.6 | 10.2 | 90.4 | 6.3 |
| 4000 | 91.7 | 8.1 | 97.3 | 5.7 | |
| 20,000 | 94.6 | 15.9 | 112.6 | 10.7 | |
| HFB2 | 200 | 106.4 | 17.2 | 87.6 | 12.8 |
| 4000 | 94.6 | 10.1 | 90.7 | 6.3 | |
| 20,000 | 82.6 | 15.9 | 106.5 | 7.7 | |
| HFB3 | 200 | 115.8 | 14.0 | 88.4 | 10.5 |
| 4000 | 107.9 | 11.5 | 100.2 | 4.8 | |
| 20,000 | 96.6 | 8.9 | 95.5 | 14.5 | |
| Analytes | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Cone Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB1 | 722.3 | 352.3 *, 334.3 | 80 | 40.34 |
| FB2 | 706.3 | 336.3 *, 318.4 | 80 | 34.38 |
| FB3 | 706.3 | 336.3 *, 318.4 | 20 | 32.36 |
| 13C34-FB1 | 756.3 | 356.4 *, 738.5 | 50 | 43.56 |
| 13C34-FB2 | 740.4 | 358.3 *, 722.4 | 50 | 53.42 |
| 13C34-FB3 | 740.4 | 358.3 *, 376.4 | 70 | 53.47 |
| HFB1 | 406.3 | 352.3 *, 370.4 | 10 | 22.18 |
| HFB2 | 390.3 | 336.2 *, 354.3 | 10 | 28.22 |
| HFB3 | 390.3 | 336.2 *, 354.3 | 10 | 28.22 |
| 13C22-HFB1 | 428.3 | 374.3 *, 392.3 | 10 | 20.20 |
| 13C22-HFB2 | 412.3 | 356.3 *, 376.3 | 10 | 28.22 |
| 13C22-HFB3 | 412.3 | 358.3 *, 376.3 | 10 | 28.22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zhou, S.; Yu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, A. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Fumonisin B1, B2, B3, and Their Hydrolyzed Metabolites in Broiler Chicken Feed and Excreta. Toxins 2022, 14, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020131
Zhang S, Zhou S, Yu S, Zhao Y, Wu Y, Wu A. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Fumonisin B1, B2, B3, and Their Hydrolyzed Metabolites in Broiler Chicken Feed and Excreta. Toxins. 2022; 14(2):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020131
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuo, Shuang Zhou, Song Yu, Yunfeng Zhao, Yongning Wu, and Aibo Wu. 2022. "LC-MS/MS Analysis of Fumonisin B1, B2, B3, and Their Hydrolyzed Metabolites in Broiler Chicken Feed and Excreta" Toxins 14, no. 2: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020131
APA StyleZhang, S., Zhou, S., Yu, S., Zhao, Y., Wu, Y., & Wu, A. (2022). LC-MS/MS Analysis of Fumonisin B1, B2, B3, and Their Hydrolyzed Metabolites in Broiler Chicken Feed and Excreta. Toxins, 14(2), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020131






