A Highly Sensitive Fluorescence and Screen-Printed Electrodes—Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor for Ricin Detection Based on CdSe/ZnS QDs with Dual Signal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
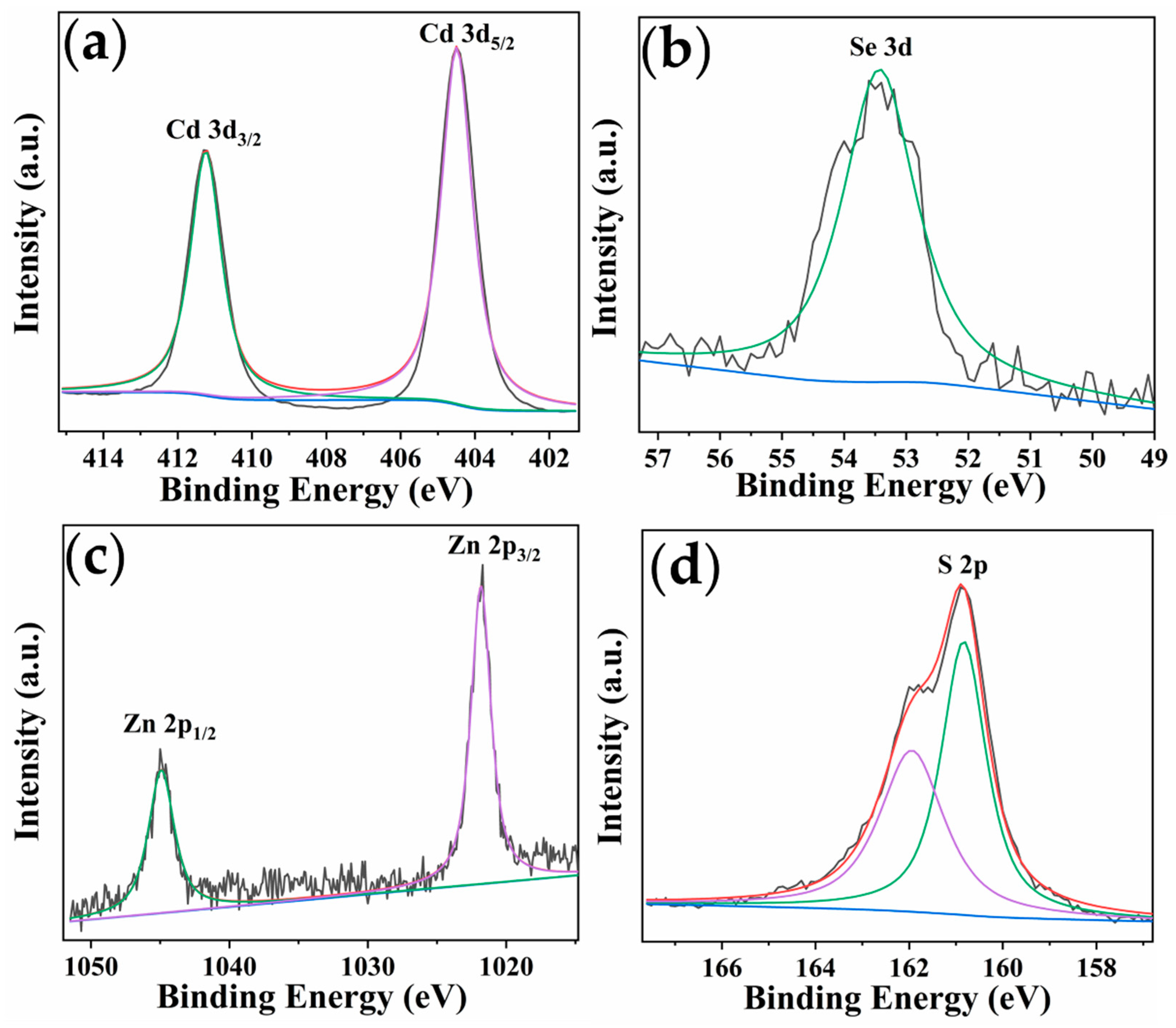
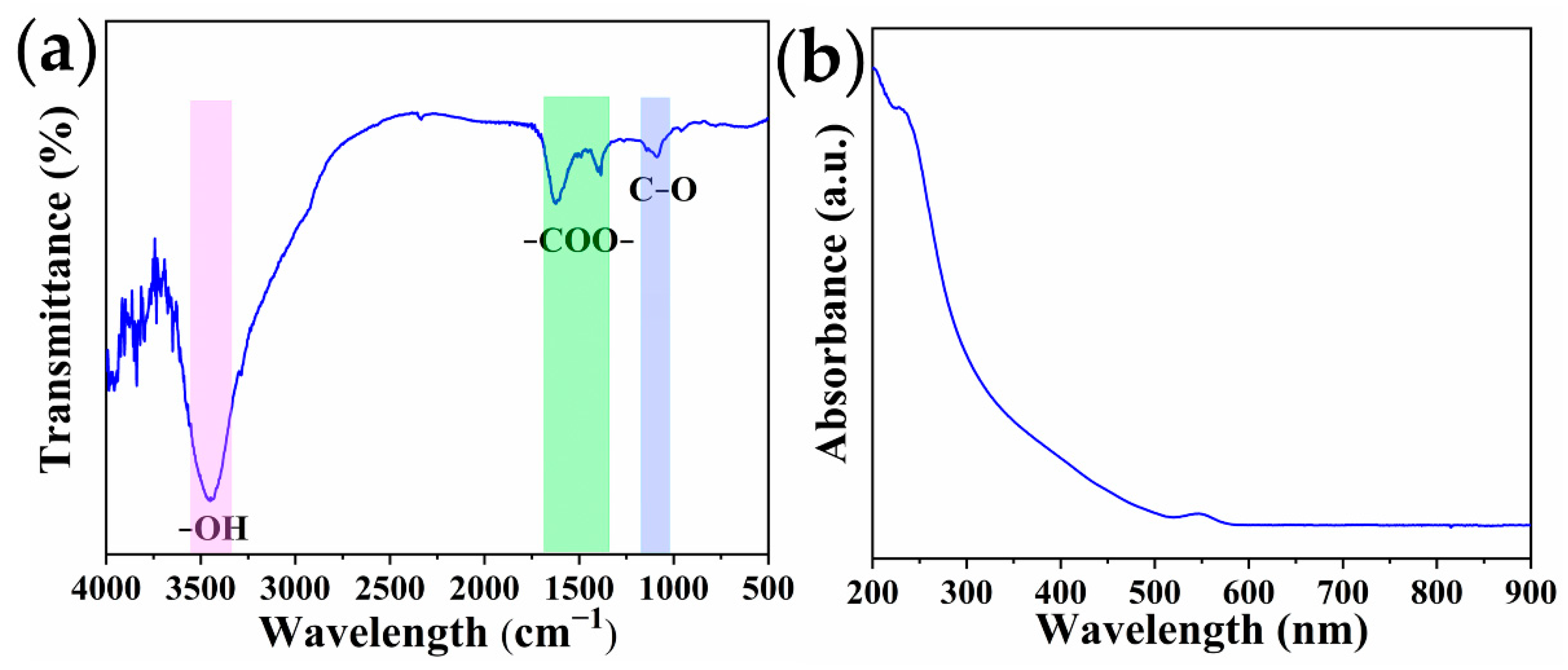
2.1. Characterization of QDs
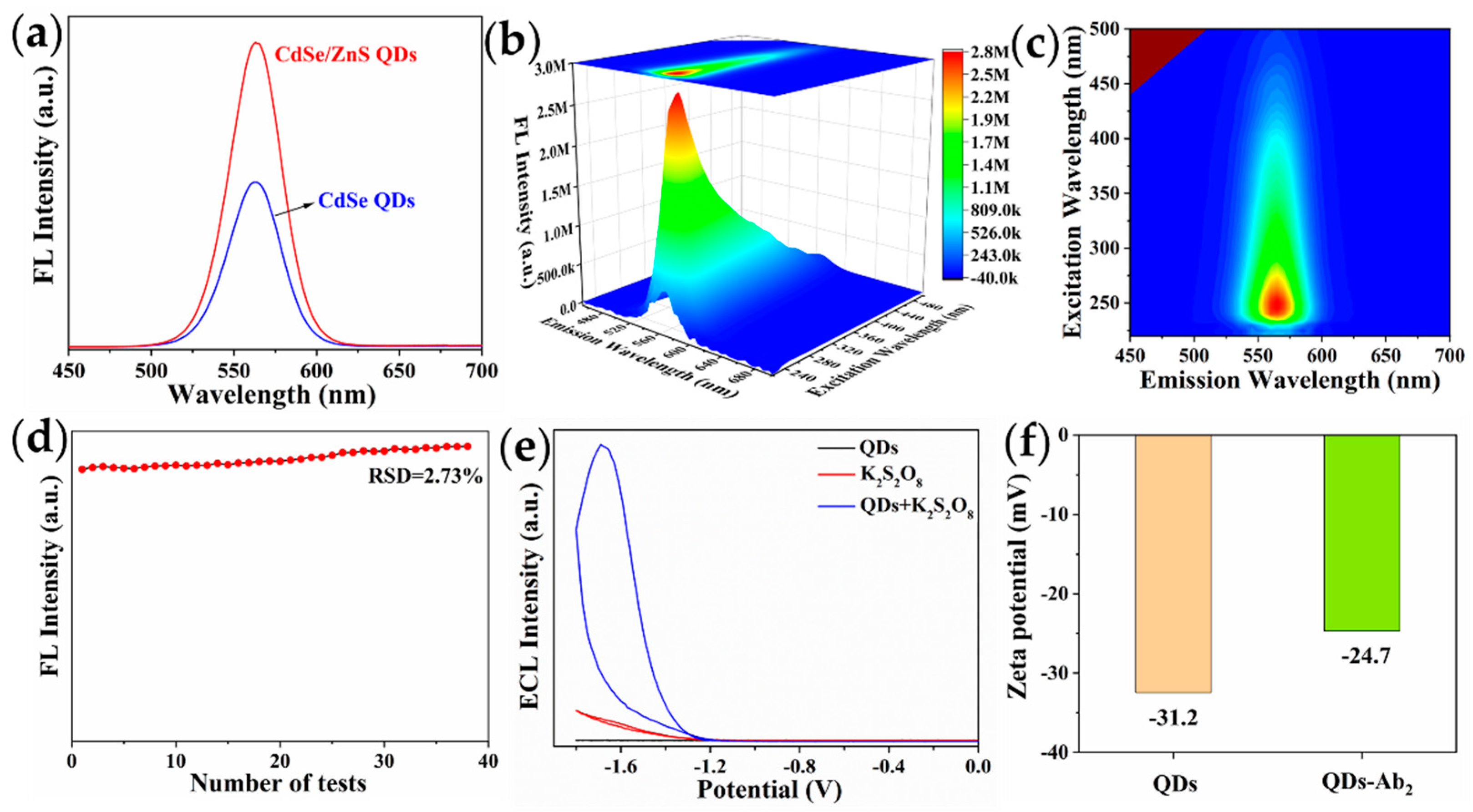
2.2. Optical Properties of CdSe/ZnS QDs
2.3. Zeta Potential
2.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
2.4.1. Optimization of Reaction Time of ZnS
2.4.2. Optimization of Added Amount of bio-Ab1
2.4.3. Optimization of Incubation Time between QDs-Ab2 Conjugates and Ricin
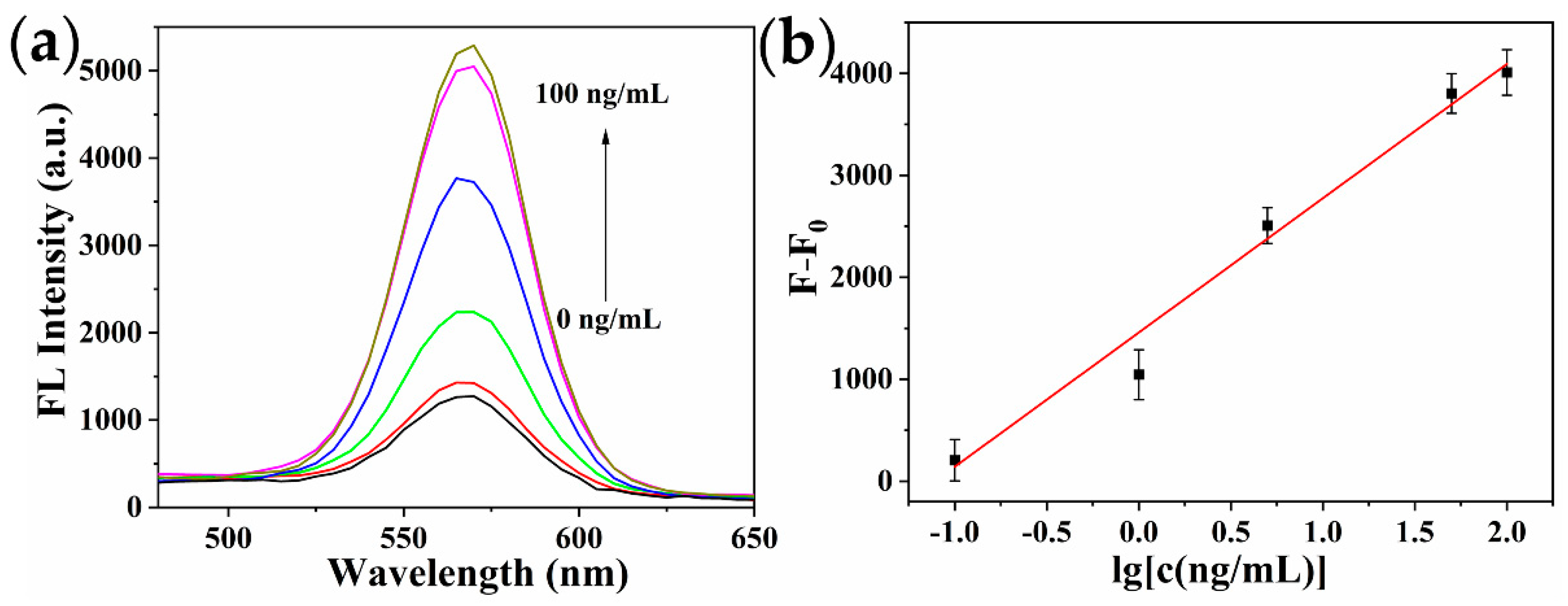
2.5. Analytical Performance of the Immunosensor
2.6. Selectivity, Stability, and Reproducibility of the Immunosensor
2.7. Detection of Ricin in Simulated Samples
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Apparatus
4.2. Preparation of the Soil Sample
4.3. Synthesis of CdSe/ZnS QDs
4.4. Preparation of SA-MBs/bio-Ab1
4.5. Preparation of QDs-Ab2 Bioconjugates
4.6. Detection of Ricin
4.7. Fluorescence and ECL Measurements
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simon, S.; Worbs, S.; Avondet, M.A.; Tracz, D.M.; Dano, J.; Schmidt, L.; Volland, H.; Dorner, B.G.; Corbett, C.R. Recommended immunological assays to screen for ricin-containing samples. Toxins 2015, 7, 4967–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roxas-Duncan, V.I.; Smith, L.A. Of beans and beads: Ricin and abrin in bioterrorism and biocrime. J. Bioterr. Biodef. 2012, S7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, E.; Ceremuga, M.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M. Biological toxins as the potential tools for bioterrorism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Battelli, M.G.; Calafato, G.; Bolognesi, A. Ricin: An ancient story for a timeless plant toxin. Toxins 2019, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Rao, V.K.; Kumar, O.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Amperometric immunosensor for ricin by using on graphite and carbon nanotube paste electrodes. Talanta 2010, 81, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Xie, J.; Shao, B.; Xue, D.; Tang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. Ultrasensitive on-site detection of biological active ricin in complex food matrices based on immunomagnetic enrichment and fluorescence switch-on nanoprobe. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6454–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.H.; Tong, Z.Y.; Huang, Q.B.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.W.; Hao, L.Q.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J.P.; Gao, C. An electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on gold-magnetic nanoparticles and phage displayed antibodies. Sensors 2016, 16, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubelli, C.; Chatgilialoglu, A.; Bolognesi, A.; Strocchi, P.; Colombatti, M.; Stirpe, F. Detection of ricin and other ribosome-inactivating proteins by an immuno-polymerase chain reaction assay. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 355, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Tran, H.; Foo, L.Y.; Sew, T.W.; Loke, W.K. Development and validation of an ELISA kit for the detection of ricin toxins from biological specimens and environmental samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5157–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Guo, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; et al. Label-free differentiation and quantification of ricin, abrin from their agglutinin biotoxins by surface plasmon resonance. Talanta 2022, 238, 122860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Meng, S.Y.; Shen, X.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Yan, X.H.; You, T.Y. Dual-ratiometric aptasensor for streptomycin detection based on the in-situ coupling of photoelectrochemical and electrochemical assay with a bifunctional probe of methylene blue. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 332, 129529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.H.; Chen, Y.Q.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, D.H. Dual-signal based immunoassay for colorimetric and photothermal detection of furazolidone. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 331, 129431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.X.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.L.; Qiu, H.D. Recent progress and prospects of alkaline phosphatase biosensor based on fluorescence strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.L.; Gu, C.Y.; Wang, M.H.; Dong, Y.F.; Nie, X.; Li, M.X.; Zhu, Z.W.; Yang, D.; Shao, Y.H. Triethanolamine-modified gold nanoparticles synthesized by a one-pot method and their application in electrochemiluminescent immunoassy. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2826–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.M.; Wang, A.J.; Yuan, P.X.; Feng, J.J. Flower-like metal-organic framework microsphere as a novel enhanced ECL luminophore to construct the coreactant-free biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of breast cancer 1 gene. Sens. Actuators B 2020, 320, 128395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Su, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhuang, Q.; Wei, C.; Deng, H.; Chen, W.; Peng, H. Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay platform with immunoglobulin g-encapsulated gold nanoclusters as a "two-in-one" probe. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13022–13028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tong, Z.Y.; Mu, X.H.; Liu, B.; Du, B.; Liu, Z.W.; Gao, C. Detection of abrin by electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on screen printed electrode. Sensors 2018, 18, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.L.; Zhang, M.; Guo, L.A.; Xie, Y.Z.; Luo, R.F.; Chen, W.X.; Cheng, F.L.; Wang, L.S. A dual-signal self-checking photoelectrochemical immunosensor based on the sole composite of MIL-101(Cr) and CdSe quantum dots for the detection of alpha-fetoprotein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 189, 113389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.N.; Song, X.X.; Deng, T.; Zhang, J.; Deng, D.W. Water transfer of oil-soluble ZnAgInSe/ZnS quantum dots by DHLA-PEG-Suc-cRGD ligands for tumor targeted bio-imaging. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 1934–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.F.; Liu, J.L.; Chai, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, R. Three-dimensional cadmium telluride quantum dots-DNA nanoreticulation as a highly efficient electrochemiluminescent emitter for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA from cancer cells. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7765–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.F.; Quinn, B.M.; Haram, S.K.; Pell, L.E.; Korgel, B.A.; Bard, A.J. Electrochemistry and electrogenerated chemiluminescence from silicon nanocrystal quantum dots. Science 2002, 296, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medintz, I.L.; Uyeda, H.T.; Goldman, E.R.; Mattoussi, H. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, G.M.; Plata, M.R.; Zougagh, M.; Contento, A.M.; Rios, A. Microwave-assisted synthesis of water soluble thiol capped CdSe/ZnS quantum dots and its interaction with sulfonylurea herbicides. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 428, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, M.A.; Guyot-Sionnest, P. Synthesis and characterization of strongly luminescing ZnS-capped CdSe nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbousi, B.O.; Rodriguez-Viejo, J.; Mikulec, F.V.; Heine, J.R.; Mattoussi, H.; Ober, R.; Jensen, K.F.; Bawendi, M.G. (CdSe)ZnS core-shell quantum dots: Synthesis and characterization of a size series of highly luminescent nanocrystallites. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 9463–9475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, M.; Sarhani, F.; Bardsiri, F.S.; Karmipour, M. CdSe/ZnS core–shell QDs: Synthesis and investigating optical properties. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 30, 1650093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ma, Y.; Ye, J.; Jin, J. A closed bipolar electrochemiluminescence sensing platform based on quantum dots: A practical solution for biochemical analysis and detection. Sens. Actuators B 2020, 311, 127930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranmanesh, M.; Hulliger, J. Magnetic separation: Its application in mining, waste purification, medicine, biochemistry and chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5925–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, D.; Mei, S. Recent applications of magnetic composites as extraction adsorbents for determination of environmental pollutants. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yektaniroumand Digehsaraei, S.; Salouti, M.; Amini, B.; Mahmazi, S.; Kalantari, M.; Kazemizadeh, A.; Mehrvand, J. Developing a fluorescence immunosensor for detection of HER2-positive breast cancer based on graphene and magnetic nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 106300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallinayagam, S.; Rajendran, K.; Lakkaboyana, S.K.; Soontarapa, K.; Remya, R.R.; Sharma, V.K.; Kumar, V.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Koduru, J.R. Recent developments in magnetic nanoparticles and nano-composites for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, R.; Cheng, H.; Ma, J.; Komarneni, S. Manganese doped magnetic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for dye degradation via a novel heterogeneous chemical catalysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avan, A.A.; Filik, H.; Demirata, B. Solid-phase extraction of Cr(VI) with magnetic melamine-formaldehyde resins, followed by its colorimetric sensing using gold nanoparticles modified with p-amino hippuric acid. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 105962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, M.; Sun, J.; Xie, M.; Jiang, X. Streptavidin-biotin-peroxidase nanocomplex-amplified microfluidics immunoassays for simultaneous detection of inflammatory biomarkers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 982, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Xu, L.; Dias, A.C.P.; Zhang, X. A sensitive sandwich ELISA using a modified biotin-streptavidin amplified system for histamine detection in fish, prawn and crab. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wiencek, J.R. Mitigating biotin interference in two Roche immunoassays by premixing biotinylated capturing molecules with streptavidin coated beads. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 505, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekis, I.; Talapin, D.V.; Kornowski, A.; Haase, M.; Weller, H. One-pot synthesis of highly luminescent CdSe/CdS core-shell nanocrystals via organometallic and “greener” chemical approaches. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 7454–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbe, H.; Rades, S.; Unger, W.E.S. Determining shell thicknesses in stabilised CdSe@ZnS core-shell nanoparticles by quantitative XPS analysis using an Infinitesimal Columns model. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2016, 212, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Oluwafemi, O.S.; Songca, S.P.; George, S.C.; Miska, P.; Rouxel, D.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Green synthesis of yellow emitting PMMA–CdSe/ZnS quantum dots nanophosphors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 39, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, N.; Ding, Z.; Bard, A.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of CdSe nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, R.; Wang, G.; Wu, M.; Shen, H.; Li, L.S. Silica-encapsulated quantum dots for highly efficient and stable fluorescence immunoassay of C-reactive protein. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 137, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.H.; Liu, H.F.; Tong, Z.Y.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Dong, H. A new rapid detection method for ricin based on tunneling magnetoresistance biosensor. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 284, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Fei, R.; Zhang, L.; Huo, B.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ning, B.; He, J.; Gao, Z.; Hu, Y. Bio-barcode triggered isothermal amplification in a fluorometric competitive immunoassay for the phytotoxin abrin. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zou, G. Bandgap engineered and high monochromatic electrochemiluminescence from dual-stabilizers-capped CdSe nanocrystals with practical application potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sample | Original (ng/mL) | Added (ng/mL) | Found (ng/mL) | Recovery % | RSD % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| River water | 0 | 1 | 0.916 | 91.6 | 3.58 |
| Soil | 0 | 1 | 1.096 | 109.6 | 4.37 |
| Tap water | 0 | 1 | 1.042 | 104.2 | 3.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, S.; Hu, W.; Pei, F.; Liu, Z.; Du, B.; Mu, X.; Liu, B.; Hao, Q.; Lei, W.; Tong, Z. A Highly Sensitive Fluorescence and Screen-Printed Electrodes—Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor for Ricin Detection Based on CdSe/ZnS QDs with Dual Signal. Toxins 2022, 14, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100710
Feng S, Hu W, Pei F, Liu Z, Du B, Mu X, Liu B, Hao Q, Lei W, Tong Z. A Highly Sensitive Fluorescence and Screen-Printed Electrodes—Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor for Ricin Detection Based on CdSe/ZnS QDs with Dual Signal. Toxins. 2022; 14(10):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100710
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Shasha, Wei Hu, Fubin Pei, Zhiwei Liu, Bin Du, Xihui Mu, Bing Liu, Qingli Hao, Wu Lei, and Zhaoyang Tong. 2022. "A Highly Sensitive Fluorescence and Screen-Printed Electrodes—Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor for Ricin Detection Based on CdSe/ZnS QDs with Dual Signal" Toxins 14, no. 10: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100710
APA StyleFeng, S., Hu, W., Pei, F., Liu, Z., Du, B., Mu, X., Liu, B., Hao, Q., Lei, W., & Tong, Z. (2022). A Highly Sensitive Fluorescence and Screen-Printed Electrodes—Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor for Ricin Detection Based on CdSe/ZnS QDs with Dual Signal. Toxins, 14(10), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100710





