Optimization of Aflatoxin B1-Lysine Analysis for Public Health Exposure Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
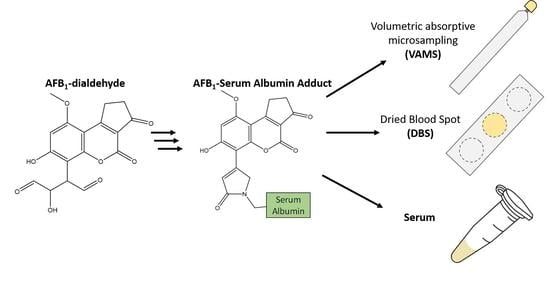
2.1. Coupling of AFB1-Dialdehyde to Serum Albumin
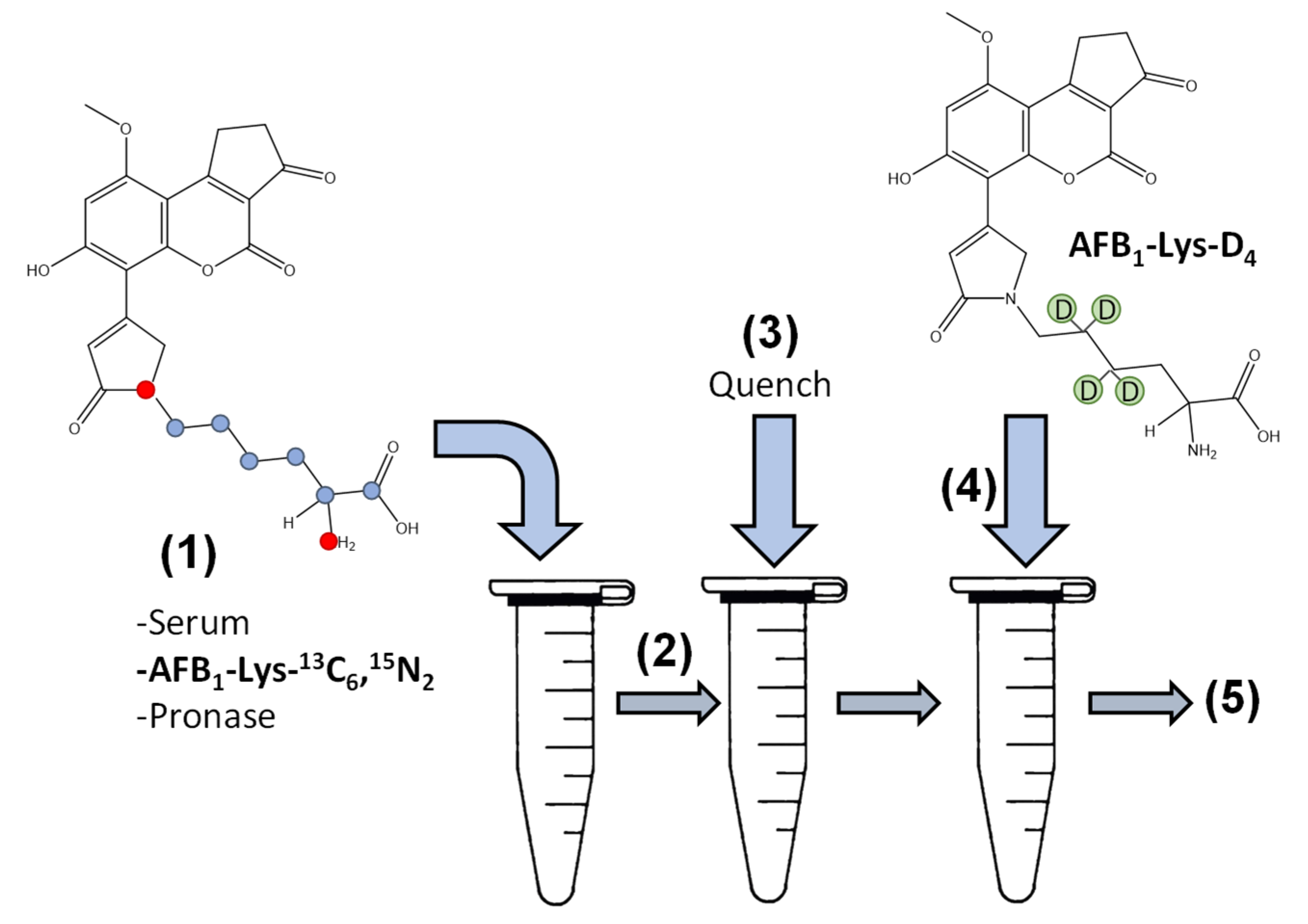
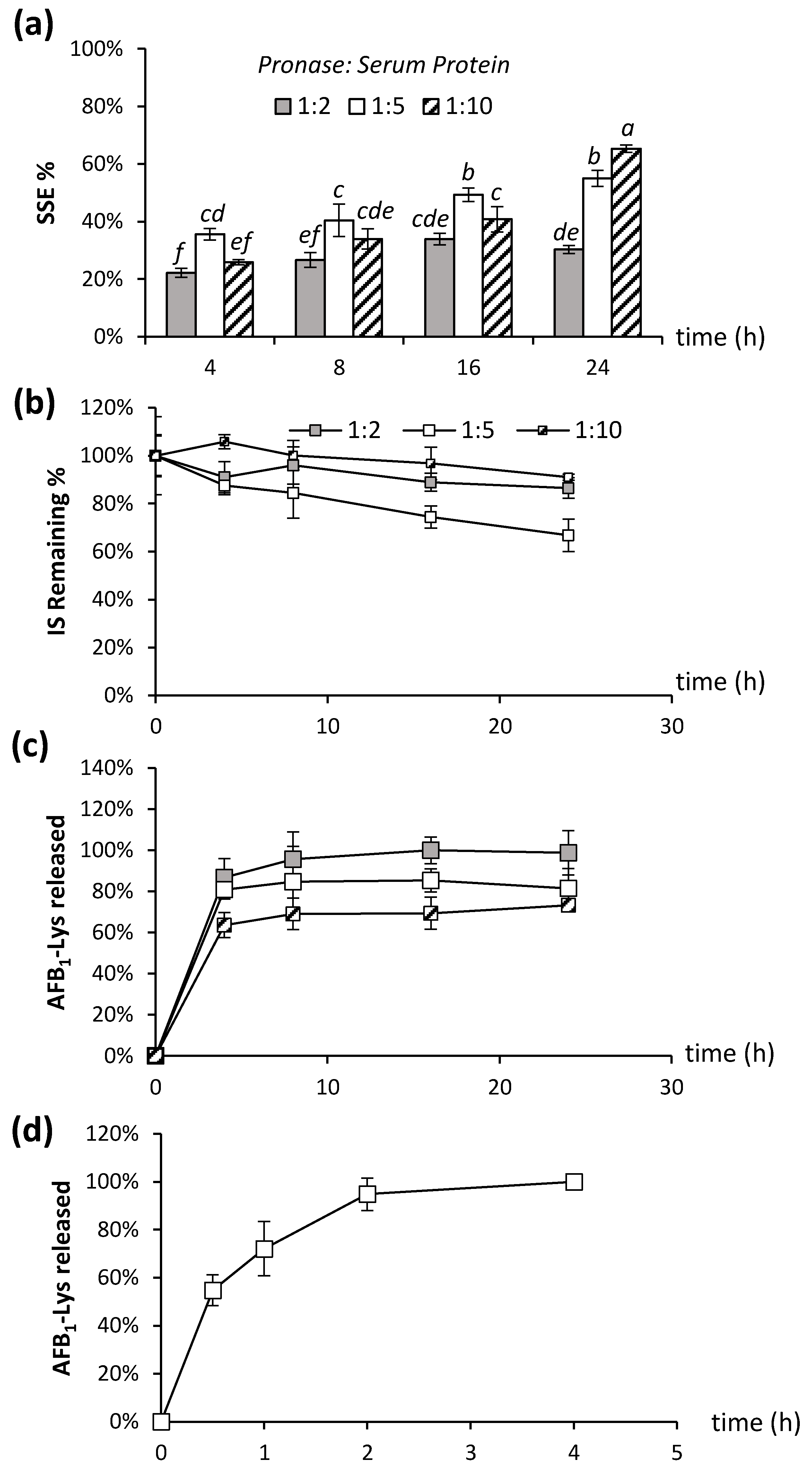
2.2. Factors Affecting Pronase Digestion
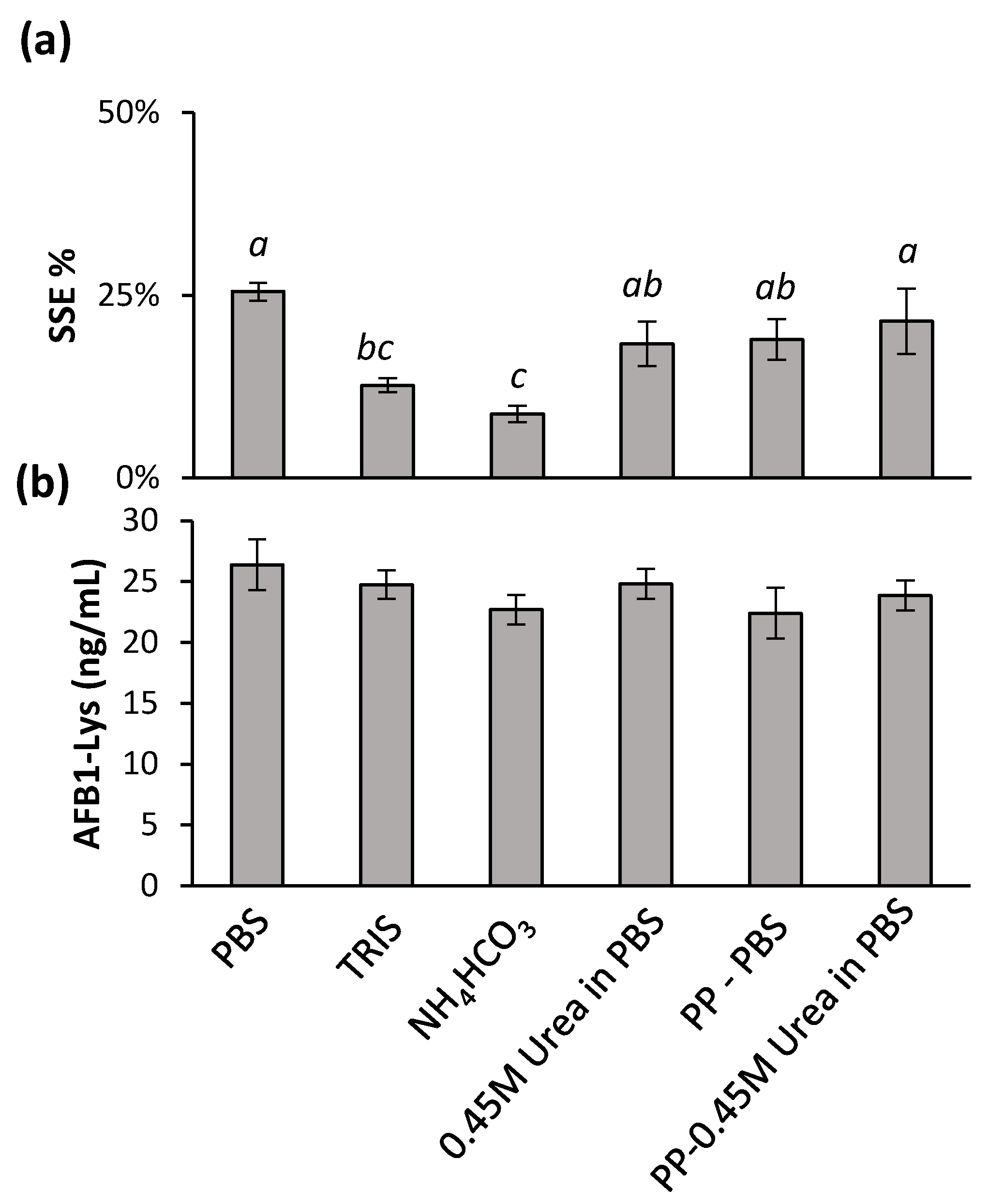
2.3. Effects of Buffers and Denaturants on Digestion
2.4. Effects of Digestion Temperature
2.5. Combined Effects of Temperature and Pronase Concentration on Method Performance
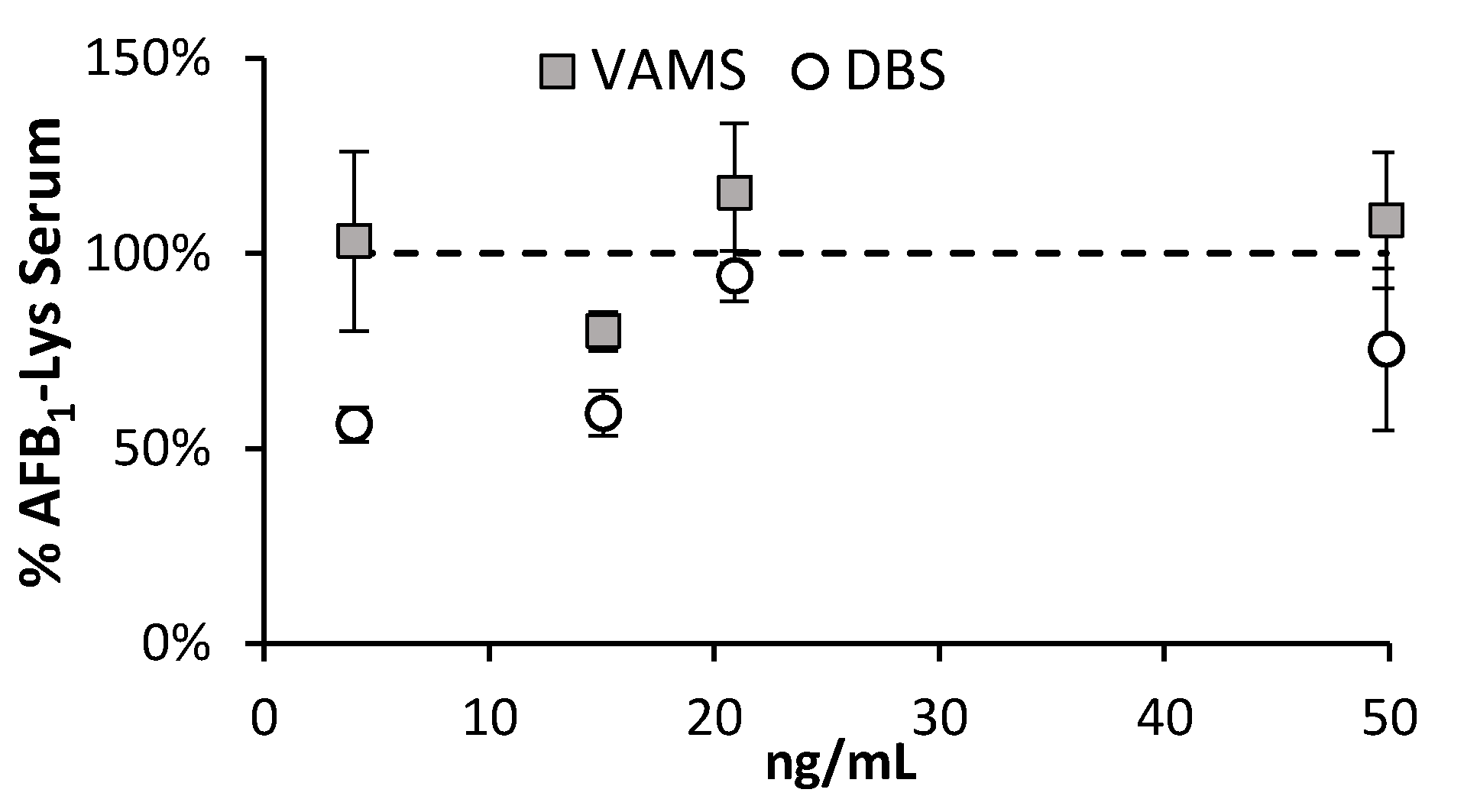
2.6. Comparison of Sample Collection Techniques
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of Fortified AFB1-HSA in Human Serum
4.3. Digestion Assay Conditions
4.4. Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling and Dried Blood Spots
4.5. Online SPE—LC-MS/MS
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization & Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food: Eighty-Third Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; World Health Organization, Joint FAO WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, J.I.; Wild, C.P.; Baan, R.A.; Gelderblom, W.C.; Miller, J.; Riley, R.; Wu, F. Improving Public Health through Mycotoxin Control; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wild, C.P.; Miller, J.D.; Groopman, J.D. Mycotoxin control in low-and middle-income countries. In IARC Working Group Reports, No. 9. Lyon (FR): International Agency for Research on Cancer; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L.; Liu, S.; Ye, Y.; Qiu, X.; Huang, D.; Pan, D.; Chen, J.; Qian, Z.; McMillin, S.E.; Vaughn, M.G. Associations between Serum Aflatoxin-B1 and Anemia in Pregnant Women: Evidence from Guangxi Zhuang Birth Cohort in China. Toxins 2021, 13, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, A.; Renaud, J.B.; Burgess, K.M.; Orimadegun, A.E.; Akinyinka, O.O.; Allen, S.J.; Miller, J.D.; Reid, G.; Sumarah, M.W. Aflatoxin exposure in Nigerian children with severe acute malnutrition. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.L.; Walsh, J.P.; Renaud, J.B.; McMillan, A.; Rulisa, S.; Miller, J.D.; Reid, G.; Sumarah, M.W. Improved methods for biomarker analysis of the big five mycotoxins enables reliable exposure characterization in a population of childbearing age women in Rwanda. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 147, 111854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojnowski, L.; Turner, P.C.; Pedersen, B.; Hustert, E.; Brockmöller, J.; Mendy, M.; Whittle, H.C.; Kirk, G.; Wild, C.P. Increased levels of aflatoxin-albumin adducts are associated with CYP3A5 polymorphisms in The Gambia, West Africa. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2004, 14, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groopman, J.D.; Wild, C.P.; Hasler, J.; Junshi, C.; Wogan, G.N.; Kensler, T.W. Molecular epidemiology of aflatoxin exposures: Validation of aflatoxin-N7-guanine levels in urine as a biomarker in experimental rat models and humans. Environ. Health Perspect. 1993, 99, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Yang, H.; Jiao, Y.; Pang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Dietary curcumin alleviated acute ileum damage of ducks (Anas platyrhynchos) induced by AFB1 through regulating Nrf2-ARE and NF-κB signaling pathways. Foods 2021, 10, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guengerich, F.P.; Voehler, M.; Williams, K.M.; Deng, Z.; Harris, T.M. Structure of the aflatoxin B1 dialdehyde adduct formed from reaction with methylamine. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2002, 15, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guengerich, F.P.; Arneson, K.O.; Williams, K.M.; Deng, Z.; Harris, T.M. Reaction of aflatoxin B1 oxidation products with lysine. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2002, 15, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.W.; Harris, T.M.; Guengerich, F.P. Kinetics and mechanism of hydrolysis of aflatoxin B1 exo-8, 9-epoxide and rearrangement of the dihydrodiol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8213–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbioni, G.; Skipper, P.L.; Büchi, G.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Isolation and characterization of the major serum albumin adduct formed by aflatoxin B 1 in vivo in rats. Carcinogenesis 1987, 8, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.; Megalla, S.; Abd El-Fattah, H.; Hafez, A.; El-Deap, T. Binding of aflatoxin B 1, G 1 and M to plasma albumin. Mycopathologia 1982, 79, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.-S.; Skipper, P.L.; Peng, X.; Groopman, J.D.; Chen, J.-s.; Wogan, G.N.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Serum albumin adducts in the molecular epidemiology of aflatoxin carcinogenesis: Correlation with aflatoxin B 1 intake and urinary excretion of aflatoxin M 1. Carcinogenesis 1988, 9, 1323–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, P.F.; Turner, P.C.; Sutcliffe, A.E.; Sylla, A.; Diallo, M.S.; Friesen, M.D.; Groopman, J.D.; Wild, C.P. Quantitative comparison of aflatoxin B1 serum albumin adducts in humans by isotope dilution mass spectrometry and ELISA. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization & Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Safety Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food: Prepared by the Eighty-Third Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); WHO Food Additives Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 9789241660747. ISSN 0300-0923. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.W.; Ng, D.K.; Alvarez, C.S.; Egner, P.A.; Burke, S.M.; Chen, J.-G.; Kensler, T.W.; Koshiol, J.; Rivera-Andrade, A.; Kroker-Lobos, M.F. Assessing the Validity of Normalizing Aflatoxin B1-Lysine Albumin Adduct Biomarker Measurements to Total Serum Albumin Concentration across Multiple Human Population Studies. Toxins 2022, 14, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, J.B.; Walsh, J.P.; Sumarah, M.W. Simplified Synthesis and Stability Assessment of Aflatoxin B1-Lysine and Aflatoxin G1-Lysine. Toxins 2022, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.S.; Cai, W.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.-S. Aflatoxin B1-lysine adduct in dried blood spot samples of animals and humans. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 98, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueng, Y.-F.; Shimada, T.; Yamazaki, H.; Guengerich, F.P. Oxidation of aflatoxin B1 by bacterial recombinant human cytochrome P450 enzymes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1995, 8, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baertschi, S.W.; Raney, K.D.; Stone, M.P.; Harris, T.M. Preparation of the 8, 9-epoxide of the mycotoxin aflatoxin B1: The ultimate carcinogenic species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 7929–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, K.D.; Coles, B.; Guengerich, F.P.; Harris, T.M. The endo-8, 9-epoxide of aflatoxin B1: A new metabolite. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1992, 5, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, R.S.; Harris, T.M. Preparation of aflatoxin B1 8, 9-epoxide using m-chloroperbenzoic acid. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1993, 6, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, L.F.; Scholl, P.F.; Schleicher, R.L.; Groopman, J.D.; Powers, C.D.; Pfeiffer, C.M. Analysis of aflatoxin B1-lysine adduct in serum using isotope-dilution liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groopman, J.D.; Wogan, G.N.; Roebuck, B.D.; Kensler, T.W. Molecular biomarkers for aflatoxins and their application to human cancer prevention. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 1907s–1911s. [Google Scholar]
- McMillan, A.; Orimadegun, A.E.; Sumarah, M.W.; Renaud, J.; Da Encarnacao, M.M.; Gloor, G.B.; Akinyinka, O.O.; Reid, G.; Allen, S.J. Metabolic derangements identified through untargeted metabolomics in a cross-sectional study of Nigerian children with severe acute malnutrition. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocedi, A.; Cattani, G.; Stella, L.; Massoud, R.; Ricci, G. Thiol disulfide exchange reactions in human serum albumin: The apparent paradox of the redox transitions of Cys34. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 3225–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denniff, P.; Spooner, N. Volumetric absorptive microsampling: A dried sample collection technique for quantitative bioanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8489–8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbioni, G. Chemical and physical properties of the major serum albumin adduct of aflatoxin B1 and their implications for the quantification in biological samples. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 1990, 75, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, W.; Curci, R.; Edwards, J.O. Dioxiranes: A new class of powerful oxidants. Acc. Chem. Res. 1989, 22, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Analyte | Ion Type | RT (min) | Precursor m/z | Quantifier m/z (CE) | Qualifier m/z (CE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1-Lys | [M + H]+ | 2.41 | 457.2 | 394 (25) | 411 (19) |
| AFB1-Lys (13C6,15N2) | [M + H]+ | 2.41 | 465.2 | 400 (25) | 418 (19) |
| AFB1-Lys (D4) | [M + H]+ | 2.41 | 461.2 | 398 (25) | 415 (19) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renaud, J.B.; Walsh, J.P.; Sumarah, M.W. Optimization of Aflatoxin B1-Lysine Analysis for Public Health Exposure Studies. Toxins 2022, 14, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100672
Renaud JB, Walsh JP, Sumarah MW. Optimization of Aflatoxin B1-Lysine Analysis for Public Health Exposure Studies. Toxins. 2022; 14(10):672. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100672
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenaud, Justin B, Jacob P Walsh, and Mark W Sumarah. 2022. "Optimization of Aflatoxin B1-Lysine Analysis for Public Health Exposure Studies" Toxins 14, no. 10: 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100672
APA StyleRenaud, J. B., Walsh, J. P., & Sumarah, M. W. (2022). Optimization of Aflatoxin B1-Lysine Analysis for Public Health Exposure Studies. Toxins, 14(10), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100672