Combined Effect of Deoxynivalenol (DON) and Porcine Circovirus Type 2 (Pcv2) on Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
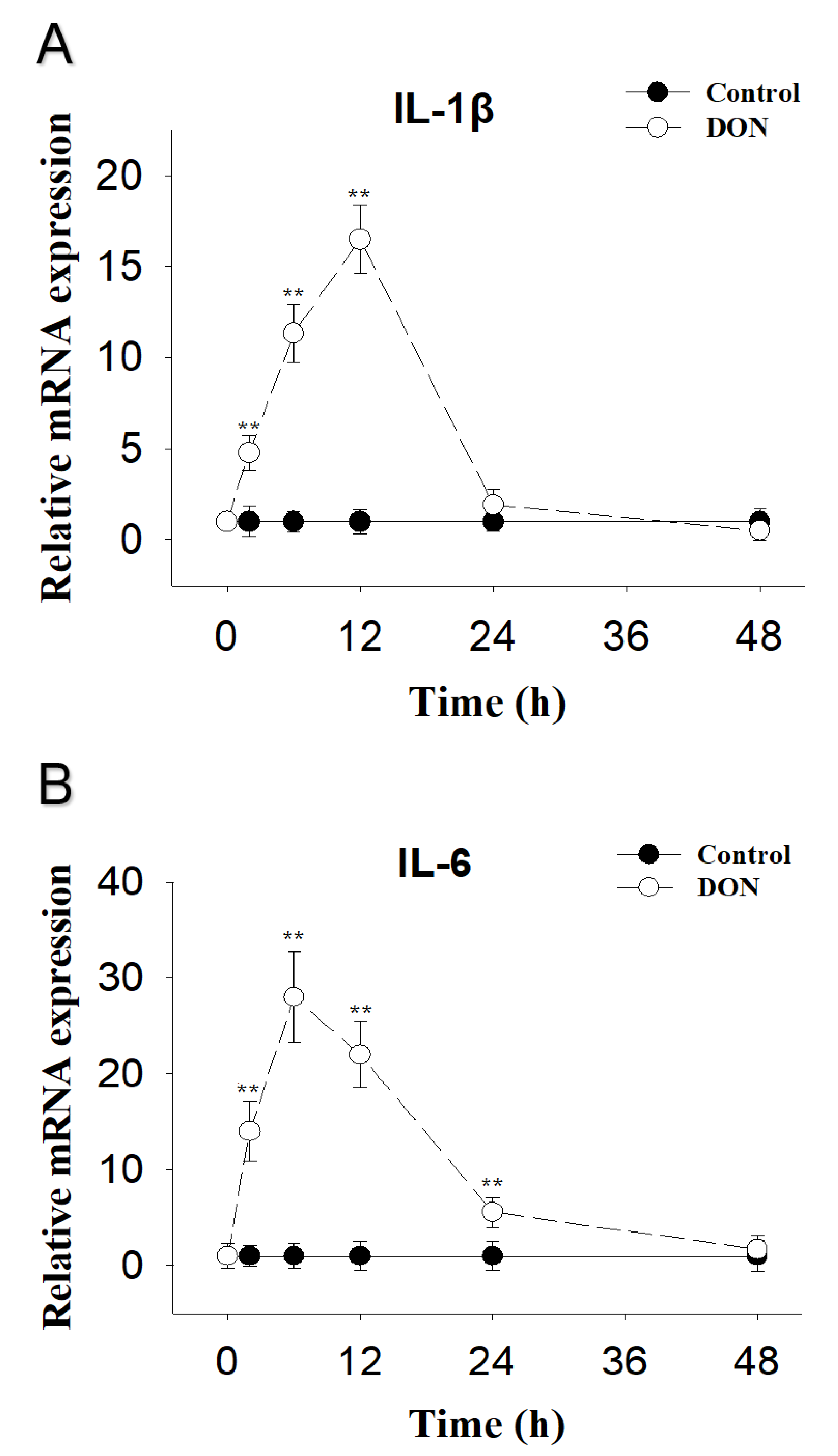
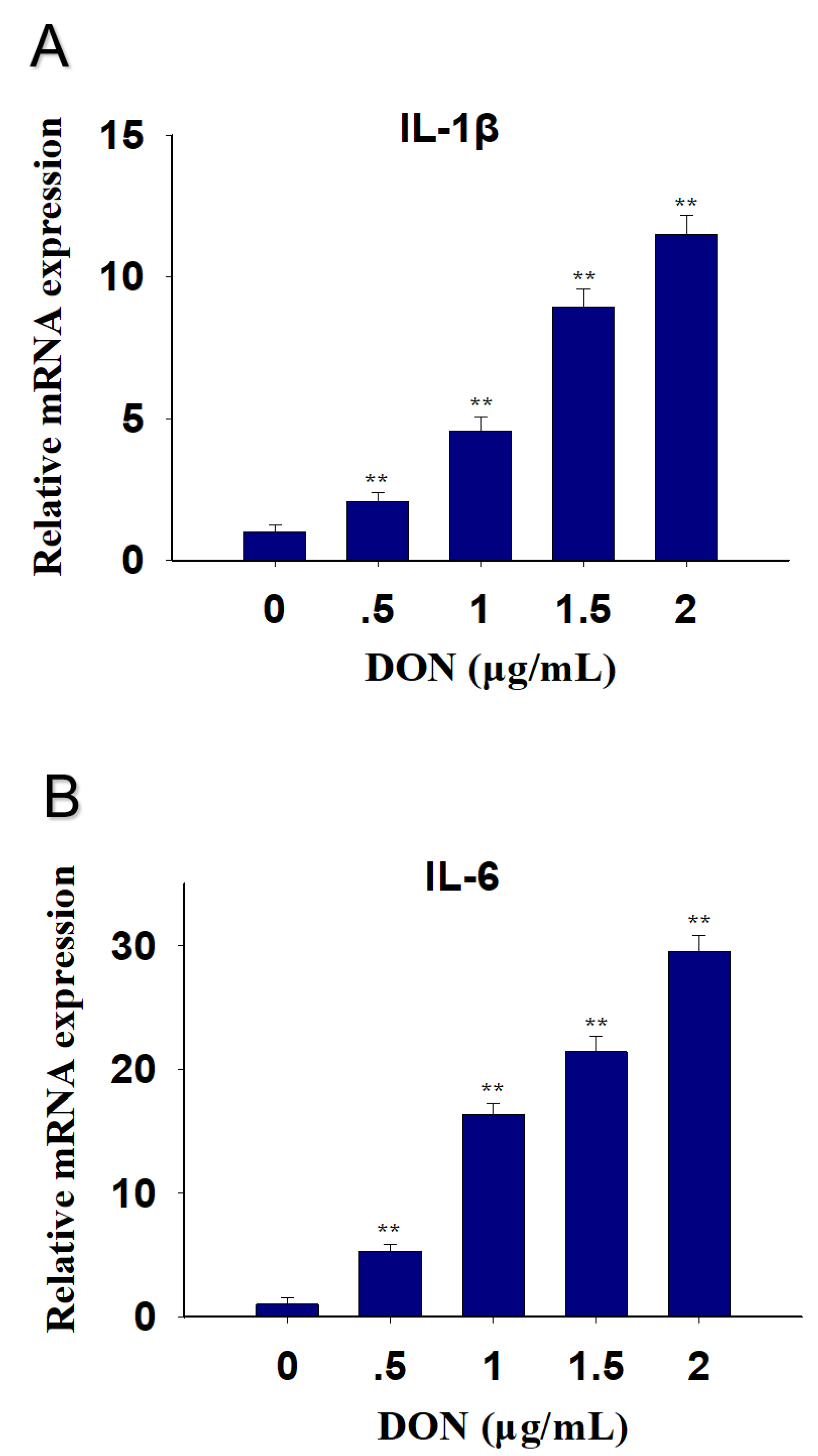
2.1. DON Exposure Induces Elevations in IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA
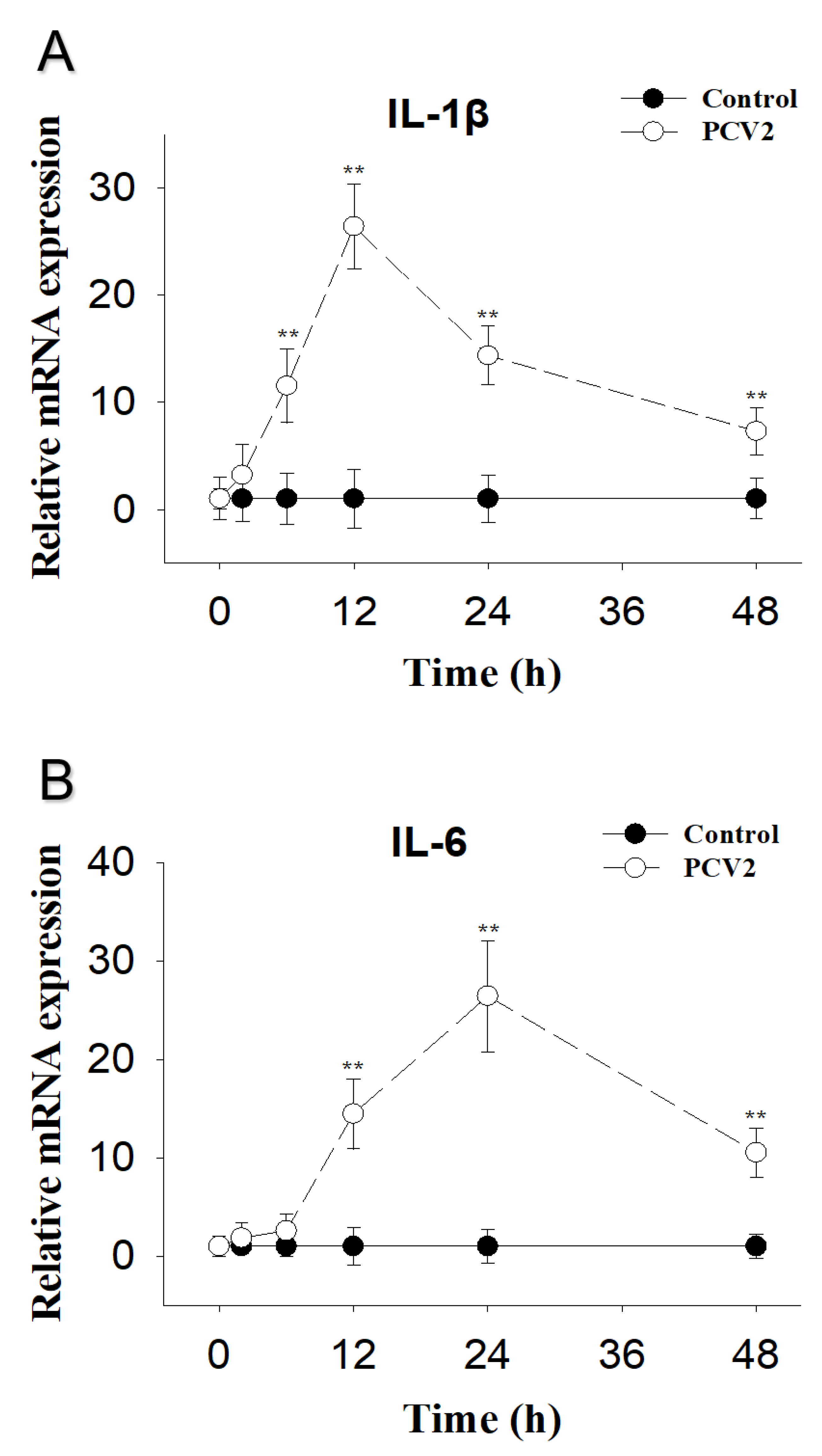
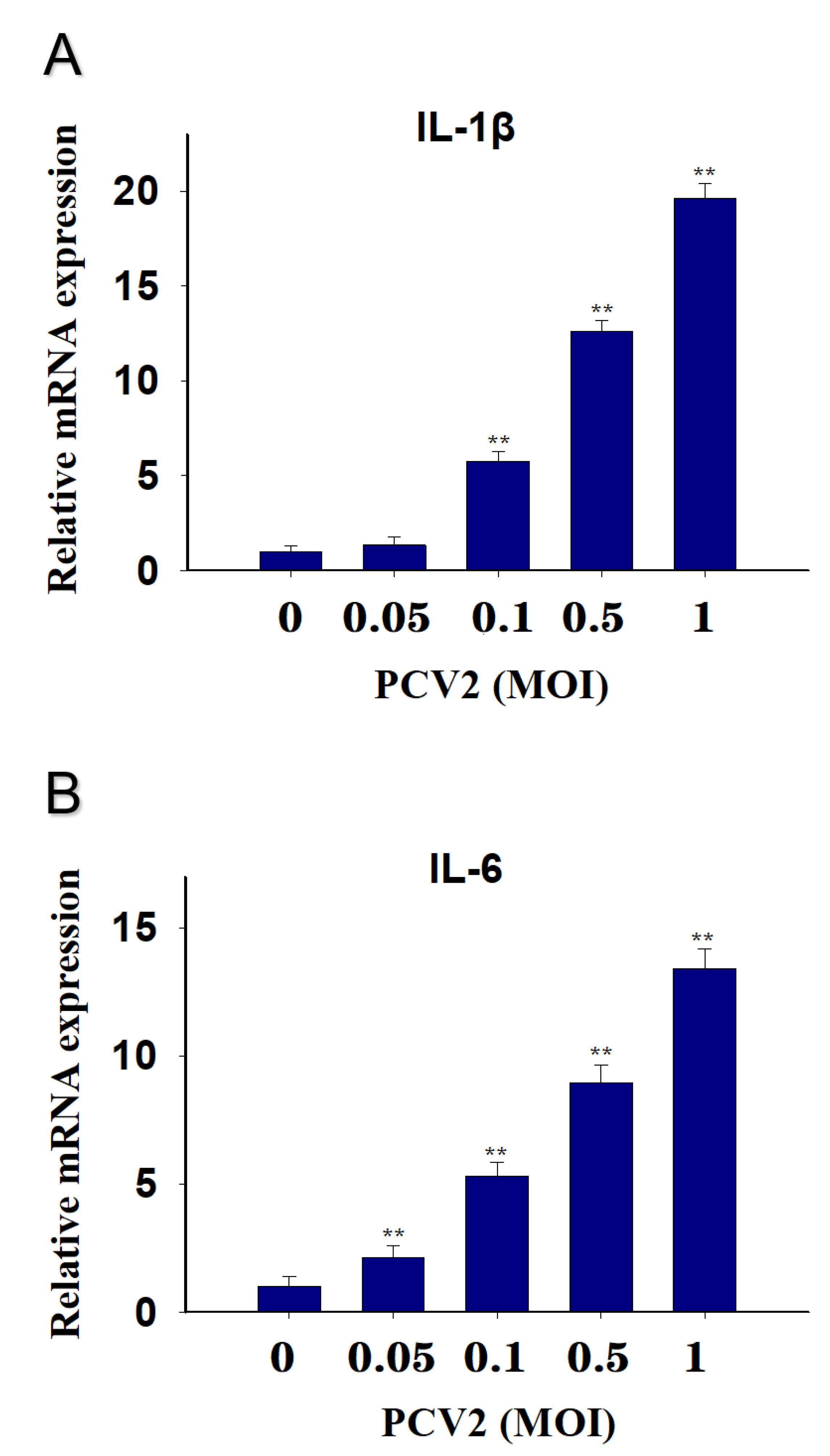
2.2. PCV2 Infection Induces Elevations in IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA
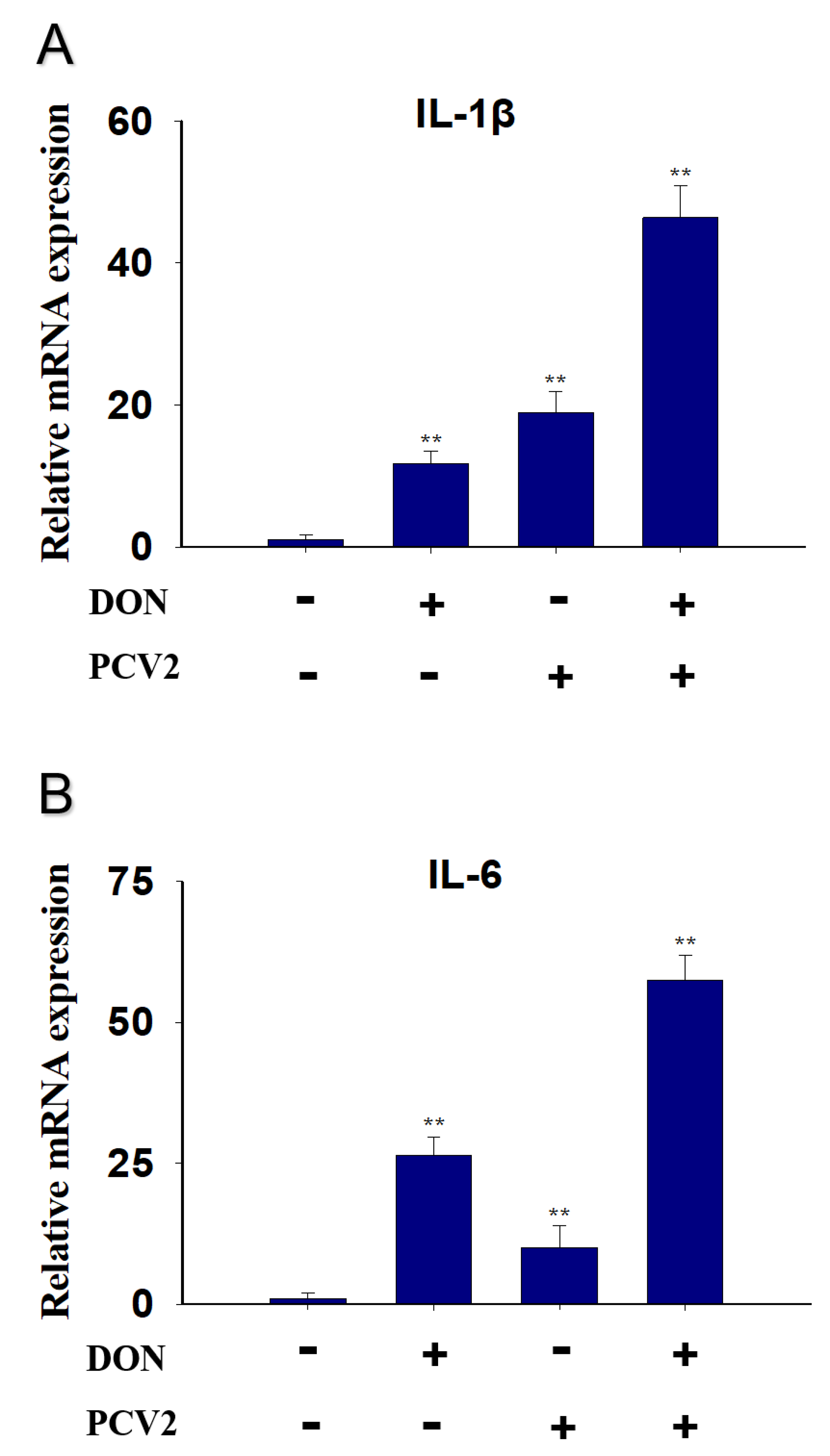
2.3. Combined Effect of DON and PCV2 Induces the Expression of IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA
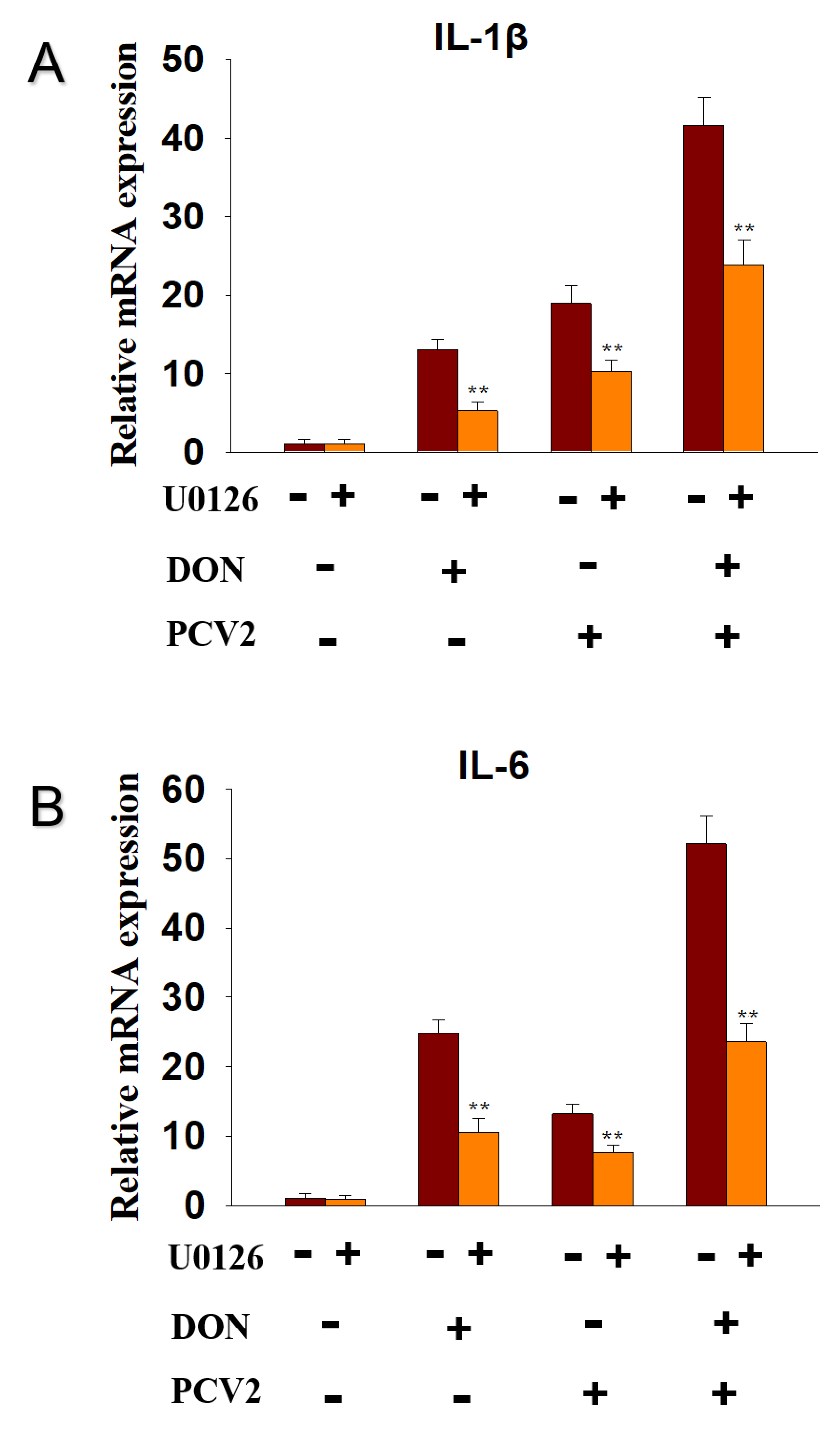
2.4. DON and PCV2 Induce the Expression of IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA via ERK Signaling Pathway
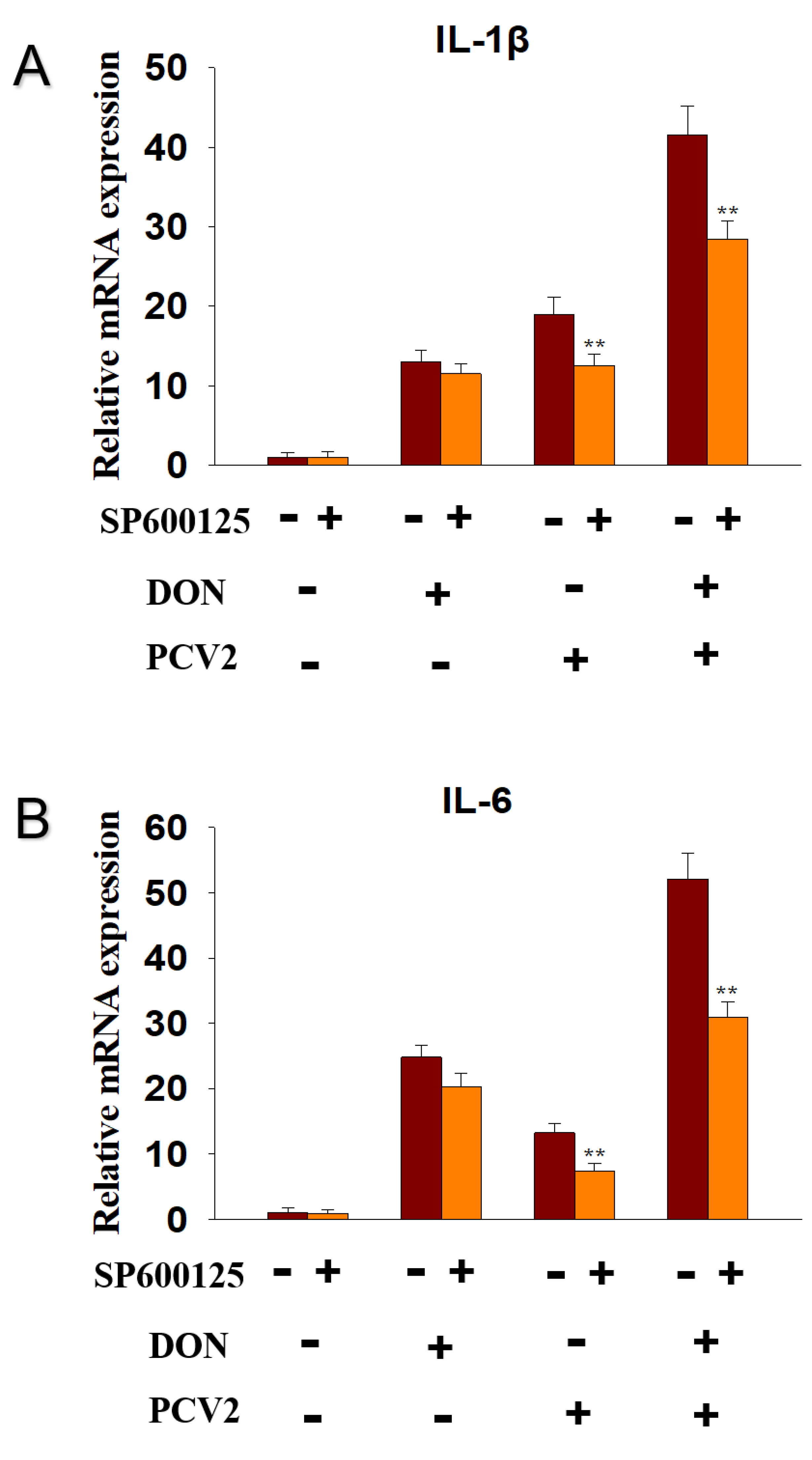
2.5. PCV2 Induces the Expression of IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA via JNK Signaling Pathway
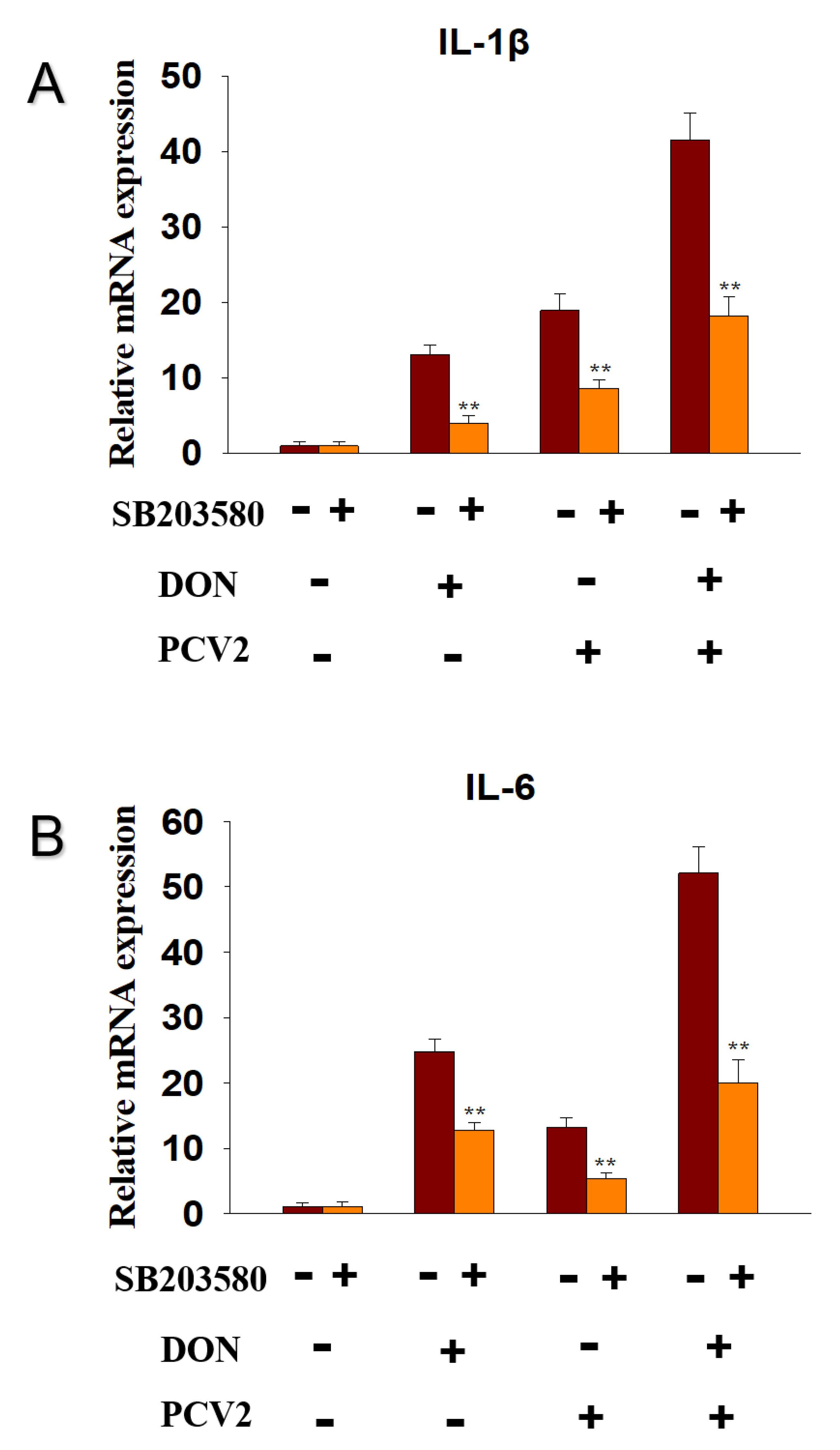
2.6. DON and PCV2 Induce the Expression of IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA via p38 Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Toxin and Virus
5.2. Cell Cultures and Virus Cultures
5.3. Experimental Design
5.4. Quantative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
5.5. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polak-Śliwińska, M.; Paszczyk, B. Trichothecenes in Food and Feed, Relevance to Human and Animal Health and Methods of Detection: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Effects of mycotoxin-contaminated feed on farm animals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Long, M. The biological detoxification of deoxynivalenol: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Chen, L.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, X.; Nüssler, A.K.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, W. Review of mechanisms of deoxynivalenol-induced anorexia: The role of gut microbiota. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, H. Role of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β in anorexia induction following oral exposure to the trichothecene deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin) in the mouse. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 39, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yue, J.; Zhang, H.; Kuca, K.; Wu, W. Anorexic responses to trichothecene deoxynivalenol and its congeners correspond to secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 77, 103371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carty, M.; Guy, C.; Bowie, A.G. Detection of Viral Infections by Innate Immunity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 183, 114316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, I.; Marquis, V.; Pérez-Vendrell, A.M.; Brufau, J.; Esteve-Garcia, E.; Ramos, A.J. Effects of Deoxynivalenol-Contaminated Diets on Metabolic and Immunological Parameters in Broiler Chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plata-Salaman, C.R. Immunomodulators and feeding regulation: A humoral link between the immune and nervous systems. Brain Behav. Immun. 1989, 3, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R.; Kelley, K.W. Twenty years of research on cytokine-induced sickness behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, R.H.; Kelley, K.W. Immune-neural connections: How the immune system’s response to infectious agents influences behavior. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.J.; Yang, G.H.; Islam, Z.; Pestka, J.J. Up-regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein-2 and complement 3A receptor by the trichothecenes deoxynivalenol and satratoxin G. Toxicology 2003, 186, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Pan, X.; Zhou, H.R.; Pestka, J.J. Modulation of inflammatory gene expression by the ribotoxin deoxynivalenol involves coordinate regulation of the transcriptome and translatome. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 131, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.S.; Zhou, H.R.; Marin-Martinez, M.L.; Brooks, K.; Pestka, J.J. Modulation of IL-1beta, IL-6 and TNF-alpha secretion and mRNA expression by the trichothecene vomitoxin in the RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cell line. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.J. Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2): Pathogenesis and interaction with the immune system. Annu Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2013, 1, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.L.; Lu, S.S.; Wei, W.K.; Lv, D.H.; Wen, X.H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, Q.L.; Sun, Y.W.; Xi, Y. Reservoirs of Porcine Circoviruses: A Mini Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segalés, J. Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) infections: Clinical signs, pathology and laboratory diagnosis. Virus Res. 2012, 164, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, B.; Yin, S.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Khan, M.U.Z.; Liu, X.; Cai, J. Porcine Circovirus Type 2 Induces Single Immunoglobulin Interleukin-1 Related Receptor (SIGIRR) Downregulation to Promote Interleukin-1β Upregulation in Porcine Alveolar Macrophage. Viruses 2019, 11, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Lv, Y. Porcine circovirus type 2 increases interleukin-1beta and interleukin-10 production via the MyD88-NF-kappa B signaling pathway in porcine alveolar macrophages in vitro. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 18, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, W.; Duvigneau, J.C.; Willheim, M.; Schilcher, F.; Hartl, R.T.; Hofbauer, G.; Exel, B.; Pietschmann, P.; Schmoll, F. Systemic cytokine profile in feeder pigs suffering from natural postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS) as determined by semiquantitative RT-PCR and flow cytometric intracellular cytokine detection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 99, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Kong, N.; Ye, L.; Han, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, C.; Pan, H. p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Lett. 2014, 344, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; She, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Cheng, L.; Yepes, M.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, Z. p38 MAPK inhibits autophagy and promotes microglial inflammatory responses by phosphorylating ULK1. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; He, K.; Zhou, H.R.; Berthiller, F.; Adam, G.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Krantis, A.; Durst, T.; Zhang, H.; et al. Effects of oral exposure to naturally-occurring and synthetic deoxynivalenol congeners on proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine mRNA expression in the mouse. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 278, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. JNK and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways contribute to porcine circovirus type 2 infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6039–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Memiş, E.Y.; Yalçın, S.S. Human milk mycotoxin contamination: Smoking exposure and breastfeeding problems. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021, 34, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.; Sun, K.; Xia, S.; Feng, Z.; Zou, H.; Gu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Bian, J. Decrease in immune function and the role of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) overactivation in apoptosis during T lymphocytes activation induced by zearalenone, deoxynivalenol, and their combinations. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierron, A.; Mimoun, S.; Murate, L.S.; Loiseau, N.; Lippi, Y.; Bracarense, A.P.; Schatzmayr, G.; He, J.W.; Zhou, T.; Moll, W.D.; et al. Microbial biotransformation of DON: Molecular basis for reduced toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.; Ghareeb, K.; Böhm, J.; Zentek, J. The toxicological impacts of the Fusarium mycotoxin, deoxynivalenol, in poultry flocks with special reference to immunotoxicity. Toxins 2013, 5, 912–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestka, J. Toxicological mechanisms and potential health effects of deoxynivalenol and nivalenol. World Mycotoxin J. 2010, 3, 323–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai-Lan, C.; Hong-Lian, T.; Jian, Y.; Manling, S.; Heyu, F.; Na, K.; Wenyue, H.; Si-Yu, C.; Ying-Yi, W.; Ting-Jun, H. Inhibitory effect of polysaccharide of Sargassum weizhouense on PCV2 induced inflammation in mice by suppressing histone acetylation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Pestka, J. Differential upregulation of TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-8 production by deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin) and other 8-ketotrichothecenes in a human macrophage model. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2001, 64, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, Z.; Gray, J.S.; Pestka, J.J. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates IL-8 induction by the ribotoxin deoxynivalenol in human monocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 213, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amuzie, C.J.; Harkema, J.R.; Pestka, J. Tissue distribution and proinflammatory cytokine induction by the trichothecene deoxynivalenol in the mouse: Comparison of nasal vs. oral exposure. Toxicology 2008, 248, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuzie, C.J.; Shinozuka, J.; Pestka, J. Induction of suppressors of cytokine signaling by the trichothecene deoxynivalenol in the mouse. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 111, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.J.; Zhou, H.R.; Pestka, J. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional roles for p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in upregulation of TNF-alpha expression by deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 193, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.S.; Pestka, J. Transcriptional regulation of deoxynivalenol-induced IL-8 expression in human monocytes. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 99, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Bai, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Jiang, P. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 plays an important role in porcine circovirus type 2 subclinical infection by downregulating proinflammatory responses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Tan, H.L.; Yang, J.; Wei, Y.Y.; Hu, T.J. Sargassum polysaccharide inhibits inflammatory response in PCV2 infected-RAW264.7 cells by regulating histone acetylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tan, H.L.; Gu, L.Y.; Song, M.L.; Wu, Y.Y.; Peng, J.B.; Lan, Z.B.; Wei, Y.Y.; Hu, T.J. Sophora subprosrate polysaccharide inhibited cytokine/chemokine secretion via suppression of histone acetylation modification and NF-κb activation in PCV2 infected swine alveolar macrophage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104 Pt A, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Liu, D.; Hu, J.; Gan, F.; Hou, L.; Chen, X.; Huang, K. Ochratoxin A-induced autophagy in vitro and in vivo promotes porcine circovirus type 2 replication. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Liu, D.; Hou, L.; Hamid, M.; Chen, X.; Gan, F.; Song, S.; Huang, K. Ochratoxin A induces cytoprotective autophagy via blocking AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in PK-15 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Ge, L.; Wang, Q.; Su, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, K. Low-level contamination of deoxynivalenol: A threat from environmental toxins to porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.K.; Pestka, J. Deoxynivalenol induces p38 interaction with the ribosome in monocytes and macrophages. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 105, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.K.; Gray, J.S.; Li, M.; Vines, L.; Kim, J.; Pestka, J. Hematopoietic cell kinase associates with the 40S ribosomal subunit and mediates the ribotoxic stress response to deoxynivalenol in mononuclear phagocytes. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 115, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, C.; Gao, X.; Guo, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Nepovimova, E.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Combined Effect of Deoxynivalenol (DON) and Porcine Circovirus Type 2 (Pcv2) on Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression. Toxins 2021, 13, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13060422
Gu C, Gao X, Guo D, Wang J, Wu Q, Nepovimova E, Wu W, Kuca K. Combined Effect of Deoxynivalenol (DON) and Porcine Circovirus Type 2 (Pcv2) on Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression. Toxins. 2021; 13(6):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13060422
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Chao, Xiuge Gao, Dawei Guo, Jiacai Wang, Qinghua Wu, Eugenie Nepovimova, Wenda Wu, and Kamil Kuca. 2021. "Combined Effect of Deoxynivalenol (DON) and Porcine Circovirus Type 2 (Pcv2) on Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression" Toxins 13, no. 6: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13060422
APA StyleGu, C., Gao, X., Guo, D., Wang, J., Wu, Q., Nepovimova, E., Wu, W., & Kuca, K. (2021). Combined Effect of Deoxynivalenol (DON) and Porcine Circovirus Type 2 (Pcv2) on Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression. Toxins, 13(6), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13060422










