Latitudinal Variation in the Toxicity and Sexual Compatibility of Alexandrium catenella Strains from Southern Chile
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Molecular and Morphological Identification
2.2. PSP Toxins
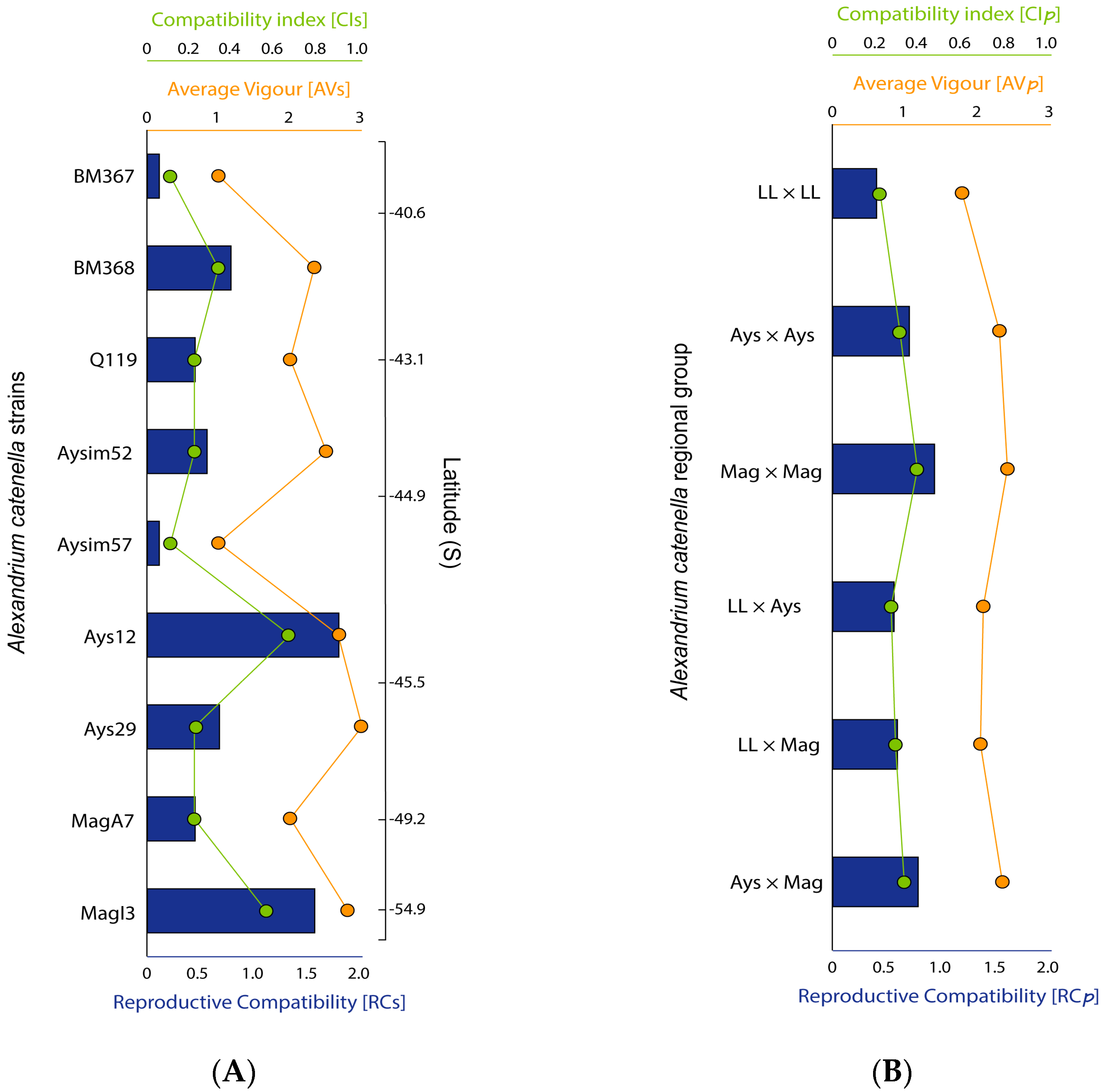
2.3. Strains Sexual Compatibility
3. Discussion
3.1. Sexual Compatibility Rises from North to South
3.2. Latitude, Toxicity, and RC: Relationship and Ecological Implications
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Strains Origin and Culture Conditions
5.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
5.3. Morphological Identification
5.4. Sexual Compatibility Study with Isolated Clonal Strains
5.5. Toxin Extraction
5.6. Analysis of PSP Toxins
5.7. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guzmán, L.; Pacheco, H.; Pizarro, G.; Alárcon, C. Alexandrium catenella y veneno paralizante de los mariscos en Chile. In Floraciones Algales Nocivas en el Cono Sur Americano; Sar, E.A., Ferrario, M.E., Reguera, B., Eds.; Instituto Español de Oceanografía: Madrid, España, 2002; pp. 235–255. [Google Scholar]
- Lagos, N. Microalgal blooms A global issue with negative impact in Chile. Biol. Res. 1998, 31, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Díaz, P.A.; Reguera, B.; Ruiz-Villarreal, M. Pseudo-Nitzschia Australis Blooms Are Not Always Toxic; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Quebec City, QC, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, P.A.; Peréz-Santos, I.; Álvarez, G.; Garreaud, R.; Pinilla, E.; Díaz, M.; Sandoval, A.; Araya, M.; Álvarez, F.; Rengel, J. Multiscale physical background to an exceptional harmful algal bloom of Dinophysis acuta in a fjord system. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrich, Á.M.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Álvarez, G.; Reguera, B.; Fernández-Pena, C.; Rodríguez-Villegas, C.; Araya, M.; Álvarez, F.; Barrera, F.; Karasiewicz, S.; et al. Niche differentiation of Dinophysis acuta and D. acuminata in a stratified fjord. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 102010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-de-Souza, C.; Varela, D.; Contreras, C.; de La Iglesia, P.; Fernandez, P.; Hipp, B.; Hernandez, C.; Riobó, P.; Reguera, B.; Franco, J.M. Seasonal variability of Dinophysis spp. and Protoceratium reticulatum associated to lipophilic shellfish toxins in a strongly stratified Chilean fjord. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 101, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Díaz, P.; Molinet, C.; Seguel, M.; Dıaz, M.; Labra, G.; Figueroa, R.I. Coupling planktonic and benthic shifts during a bloom of Alexandrium catenella in southern Chile: Implications for bloom dynamic and recurrence. Harmful Algae 2014, 40, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, M.; D’agostino, P.M.; Mihali, T.K.; Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. Neurotoxic alkaloids: Saxitoxin and its analogs. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2185–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dolah, F.M. Marine algal toxins: Origins, health effects, and their increased occurrence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etheridge, S.M. Paralytic shellfish poisoning: Seafood safety and human health perspectives. Toxicon 2010, 56, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Díaz, P.A.; Álvarez, A.; Varela, D.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Díaz, M.; Molinet, C.; Seguel, M.; Aguilera-Belmonte, A.; Guzmán, L.; Uribe, E. Impacts of harmful algal blooms on the aquaculture industry: Chile as a case study. Perspect. Phycol. 2019, 6, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, J.I.; Holland, D.S.; Anderson, L.; Le Bihan, V.; Gianella, F.; Clément, A.; Davidson, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Yoshida, T.; Trainer, V.L. 5 Estimating and Mitigating the Economic Costs of Harmful Algal Blooms on Commercial and Recreational Shellfish Harvesters. In GlobalHAB: Evaluating, Reducing and Mitigating the Cost of Harmful Algal Blooms: A Compendium of Case Studies; Report, P.S., Ed.; North Pacific Marine Science Organization: Sidney, BC, Canada, 2020; pp. 66–83. [Google Scholar]
- Molinet, C.; Niklitschek, E.; Seguel, M.; Díaz, P. Trends of natural accumulation and detoxification of paralytic shellfish poison in two bivalves from the Northwest Patagonian inland sea. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2010, 45, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzmán, L.; Campodónico, I.; Antunovic, M. Estudios sobre un florecimiento tóxico causado por Gonyaulax catenella en Magallanes. IV. Distribución y niveles de toxicidad del Veneno Paralítico de los Mariscos (noviembre de 1972-noviembre de 1973). An. Inst. Patagon. 1975, 6, 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, C.; Díaz, P.A.; Molinet, C.; Seguel, M. Exceptional climate anomalies and north wards expansion of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning outbreaks in Southern Chile. Harmful Algae News 2016, 54, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes-Mella, J.; Mardones, J.I.; Norambuena, L.; Fuenzalida, G.; Labra, G.; Espinoza-González, O.; Guzmán, L. Toxic Alexandrium catenella expanding northward along the Chilean coast: New risk of paralytic shellfish poisoning off the Bío-Bío region (36° S). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschmann, A.; Farias, L.; Tapia, F.; Varela, D.; Vasquez, M. Scientific Report on the 2016 Southern Chile Red Tide. Chilean Department of Economy. 2016. Available online: http://www.academiadeciencias.cl/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/InfoFinal_ComisionMareaRoja_21Nov2016.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Álvarez, G.; Díaz, P.A.; Godoy, M.; Araya, M.; Ganuza, I.; Pino, R.; Álvarez, F.; Rengel, J.; Hernández, C.; Uribe, E. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Surf Clams Mesodesma donacium during a Large Bloom of Alexandrium catenella Dinoflagellates Associated to an Intense Shellfish Mass Mortality. Toxins 2019, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzmán, L.; Espinoza–González, O.; Pinilla, E.; Besoaín, V.; Calderón, M.; Cáceres, J.; Iriarte, L.; Muñoz, V.; Martínez, R.; Hernández, C. Atmospheric and oceanographic processes on the distribution and abundance of Alexandrium catenella in the North of Chilean fjords. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio-de-Salud. Decreto 76, Decreta Alerta Sanitaria y Otorga Facultades Extraordinarias que Indica Ministerio de Salud SUBSECRETARÍA-DE-SALUD-PÚBLICA, Ed. Santiago de Chile. 2018. Available online: http://bcn.cl/2f7gq (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Genovesi-Giunti, B.; Laabir, M.; Vaquer, A. The benthic resting cyst: A key actor in harmful dinoflagellate blooms—A review. Vie Milieu 2006, 56, 327–337. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa, R.I.; Rengefors, K.; Bravo, I.; Bensch, S. From homothally to heterothally: Mating preferences and genetic variation within clones of the dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K.; Fukuyo, Y. Technical Guide for Modern Dinoflagellate Cyst Study; WESTPAC-HAB, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science: Tokyo, Japan, 2000; pp. 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka, K.; Fukuyo, Y. Taxonomy of cysts. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2003; pp. 563–592. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, I.; Figueroa, R. Towards an ecological understanding of dinoflagellate cyst functions. Microorganisms 2014, 2, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blackburn, S.; Parker, N. Microalgal life cycles: Encystment and excystment. In Algal Culturing Techniques; Andersen, R.A., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 399. [Google Scholar]
- Mardones, J.I.; Bolch, C.; Guzmán, L.; Paredes, J.; Varela, D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Role of resting cysts in Chilean Alexandrium catenella dinoflagellate blooms revisited. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Villegas, C.; Díaz, P.A.; Pizarro, G.; Salgado, P.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Díaz, M.; Seguel, M.; Baldrich, Á.; Bravo, I.; Iriarte, L.; et al. Alexandrium catenella cyst accumulation by passive and active dispersal agents: Implications for the potential spreading risk in Chilean Patagonian fjords. Harmful Algae 2020, 96, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, D.; Paredes, J.; Alves-de-Souza, C.; Seguel, M.; Sfeir, A.; Frangópulos, M. Intraregional variation among Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae) strains from southern Chile: Morphological, toxicological and genetic diversity. Harmful Algae 2012, 15, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.; Hallegraeff, G. Harmful Algae Introductions: Vectors of Transfer, Mitigation, and Management. Harmful Algal Bloom. A Compend. Desk Ref. 2018, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.L.; Karlson, B.; Wulff, A.; Kudela, R.; Trick, C.; Asnaghi, V.; Berdalet, E.; Cochlan, W.; Davidson, K.; De Rijcke, M. Future HAB science: Directions and challenges in a changing climate. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.K.; Trainer, V.L.; Mantua, N.J.; Parker, M.S.; Laws, E.A.; Backer, L.C.; Fleming, L.E. Impacts of climate variability and future climate change on harmful algal blooms and human health. Environ. Health 2008, 7, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, S.K.; Mantua, N.J.; Hickey, B.M.; Trainer, V.L. Recent trends in paralytic shellfish toxins in Puget Sound, relationships to climate, and capacity for prediction of toxic events. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovesi, B.; Mouillot, D.; Laugier, T.; Fiandrino, A.; Laabir, M.; Vaquer, A.; Grzebyk, D. Influences of sedimentation and hydrodynamics on the spatial distribution of Alexandrium catenella/tamarense resting cysts in a shellfish farming lagoon impacted by toxic blooms. Harmful Algae 2013, 25, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.W.; Montero, P.; Daneri, G. Blooms of Alexandrium catenella in Coastal Waters of Chilean Patagonia: Is Subantarctic Surface Water Involved? Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.A.; Sgrò, C.M. Climate change and evolutionary adaptation. Nature 2011, 470, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Dassow, P.; Montresor, M. Unveiling the mysteries of phytoplankton life cycles: Patterns and opportunities behind complexity. J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellegaard, M.; Ribeiro, S. The long-term persistence of phytoplankton resting stages in aquatic ‘seed banks’. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Figueroa, R.I.; Estrada, M.; Garcés, E. Life histories of microalgal species causing harmful blooms: Haploids, diploids and the relevance of benthic stages. Harmful Algae 2018, 73, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, S.I.; Bolch, C.J.; Haskard, K.A.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Reproductive compatibility among four global populations of the toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum (Dinophyceae). Phycologia 2001, 40, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, N. Sexual Reproduction and Bloom Dynamics of Toxic Dinoflagellates from Australian Estuarine Waters. Ph.D Thesis, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Australia, 2002; p. 289. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa, R.I.; Dapena, C.; Bravo, I.; Cuadrado, A. The hidden sexuality of Alexandrium minutum: An example of overlooked sex in dinoflagellates. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dia, A.; Guillou, L.; Mauger, S.; Bigeard, E.; Marie, D.; Valero, M.; Destombe, C. Spatiotemporal changes in the genetic diversity of harmful algal blooms caused by the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes-Mella, J.; Varela, D. Genetic population structure of the toxigenic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella in the Patagonian Fjords System, southern Chile. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2020, 55, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruzat, F.A.; Muñoz, C.; González-Saldía, R.R.; Inostroza, A.; Andree, K.B. High genetic variability of Alexandrium catenella directly detected in environmental samples from the Southern Austral Ecosystem of Chile. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cembella, A. Ecophysiology and metabolism of paralytic shellfish toxins in marine microalgae. In Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; NATO-Advanced Study Institute Series; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 41, pp. 381–404. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.; Kulis, D.; Doucette, G.; Gallagher, J.; Balech, E. Biogeography of toxic dinoflagellates in the genus Alexandrium from the northeastern United States and Canada. Mar. Biol. 1994, 120, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.; Seguel, C.G.; Cembella, A.D. Toxin profile of Alexandrium catenella from the Chilean coast as determined by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection and liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilera-Belmonte, A.; Inostroza, I.; Franco, J.M.; Riobó, P.; Gómez, P.I. The growth, toxicity and genetic characterization of seven strains of Alexandrium catenella (Whedon and Kofoid) Balech 1985 (Dinophyceae) isolated during the 2009 summer outbreak in southern Chile. Harmful Algae 2011, 12, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Villegas, C.; Lee, M.R.; Salgado, P.; Figueroa, R.I.; Baldrich, Á.M.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Tomasetti, S.J.; Niklitschek, E.; Díaz, M.; Álvarez, G.; et al. Drivers of dinoflagellate benthic cyst assemblages in the NW Patagonian fjords system and its adjacent oceanic shelf, with a focus on harmful species. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Ito, A. Variety of PSP toxin profiles in various culture strains of Alexandrium tamarense and change of toxin profile in natural A. tamarense population. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 273, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stüken, A.; Riobó, P.; Franco, J.; Jakobsen, K.S.; Guillou, L.; Figueroa, R.I. Paralytic shellfish toxin content is related to genomic sxtA4 copy number in Alexandrium minutum strains. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.; Kulis, D.; Sullivan, J.; Hall, S.; Lee, C. Dynamics and physiology of saxitoxin production by the dinoflagellates Alexandrium spp. Mar. Biol. 1990, 104, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.; Flynn, K. Growth dynamics and toxicity of Alexandrium fundyense (Dinophyceae): The effect of changing N [ratio] P supply ratios on internal toxin and nutrient levels. Eur. J. Phycol. 2000, 35, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Barua, A.; Ruvindy, R.; Savela, H.; Ajani, P.A.; Murray, S.A. The genetic basis of toxin biosynthesis in dinoflagellates. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, X.; Adolf, J.E.; Bachvaroff, T.; Place, A.R.; Coats, D.W. The interplay between host toxins and parasitism by Amoebophrya. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.F.; Lu, Y.H. Influence of environmental and nutritional factors on growth, toxicity, and toxin profile of dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. Toxicon 2000, 38, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, S.P.-k.; Lee, F.W.-f.; Mak, D.Y.-l.; Kong, H.-k.; Chan, K.K.-y.; Lo, P.-y.; Lo, S.C.-l. Production of paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs) in toxic Alexandrium catenella is intertwined with photosynthesis and energy production. Toxins 2020, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillard, R.; Hargraves, P. Stichochrysis immobilis is a diatom, not a chrysophyte. Phycologia 1993, 32, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Franco, J.M.; Bravo, I. Differences in the toxin profiles of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) strains isolated from different geographic origins: Evidence of paralytic toxin, spirolide, and gymnodimine. Toxicon 2015, 103, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ki, J.S.; Han, M.S. Informative characteristics of 12 divergent domains in complete large subunit rDNA sequences from the harmful dinoflagellate genus, Alexandrium (Dinophyceae). J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2007, 54, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotob, S.; McLaughlin, S.; Van Berkum, P.; Faisal, M. Discrimination between two Perkinsus spp. isolated from the softshell clam, Mya arenaria, by sequence analysis of two internal transcribed spacer regions and the 5.8S ribosomal RNA gene. Parasitology 1999, 119, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kishino, H.; Yano, T.-A. Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rourke, W.A.; Murphy, C.J.; Pitcher, G.; van de Riet, J.M.; Burns, B.G.; Thomas, K.M.; Quilliam, M.A. Rapid postcolumn methodology for determination of paralytic shellfish toxins in shellfish tissue. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, F.; Garrido, J.L.; Sobrino, C.; Johnsen, G.; Riobó, P.; Franco, J.; Aamot, I.; Ramilo, I.; Sanz, N.; Kremp, A. Divinyl chlorophyll a in the marine eukaryotic protist Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae). Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EFSA. Scientific opinion of the panel on contaminants in the food chainon: A request from the European Commission on marine biotoxins in shellfish: Saxitoxin group (question noEFSA-Q-2006-065E). EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, J.M.; Fernández-Vila, P. Separation of paralytic shellfish toxins by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography, with postcolumn reaction and fluorimetric detection. Chromatographia 1993, 35, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Crawley, M. The R Book; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer Publishing Company, Incorporated: New York, NY, USA, 2010; p. 495. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S-PLUS, 3rd ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 501. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserstein, R.L.; Lazar, N.A. The ASA statement on p-values: Context, process, and purpose. Am. Stat. 2016, 70, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amrhein, V.; Greenland, S.; McShane, B. Scientists rise up against statistical significance. Nature 2019, 567, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Linear Model | Df | Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F Value | Pr (>F) | AIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxins | 1 | 715.5 | 715.50 | 4.016 | 0.083 | 75.822 * |
| Residuals | 7 | 1233.3 | 176.19 | |||
| Null | 575.99 | |||||
| CIs | 1 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 2.219 | 0.179 | 1.660 * |
| Residuals | 7 | 0.224 | 0.032 | |||
| Null | 658.15 | |||||
| AVs | 1 | 1.109 | 1.109 | 2.465 | 0.160 | 22.088 * |
| Residuals | 7 | 3.148 | 0.449 | |||
| Null | 608.24 | |||||
| RCs | 1 | 0.801 | 0.801 | 2.890 | 0.132 | 17.738 * |
| Residuals | 7 | 1.941 | 0.277 | |||
| Null | 620.72 |
| Regional Group | Strain | BM367 | BM368 | Q119 | Aysim52 | Aysim57 | Ays12 | Ays29 | MagA7 | MagI3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Los Lagos | BM367 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (98) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| BM368 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (11) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) | 3 (25) | ||
| Q119 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (39) | |||
| Aysén | Aysim52 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (20) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (10) | |||
| Aysim57 | 0 (0) | 3 (11) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |||||
| Ays12 | 0 (0) | 3 (29) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||||||
| Ays29 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (34) | |||||||
| Magallanes | MagA7 | 0 (0) | 3 (24) | |||||||
| MagI3 | 0 (0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Villegas, C.; Díaz, P.A.; Riobó, P.; Rossignoli, A.E.; Rodríguez, F.; Loures, P.; Baldrich, Á.M.; Varela, D.; Sandoval-Sanhueza, A.; Figueroa, R.I. Latitudinal Variation in the Toxicity and Sexual Compatibility of Alexandrium catenella Strains from Southern Chile. Toxins 2021, 13, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120900
Rodríguez-Villegas C, Díaz PA, Riobó P, Rossignoli AE, Rodríguez F, Loures P, Baldrich ÁM, Varela D, Sandoval-Sanhueza A, Figueroa RI. Latitudinal Variation in the Toxicity and Sexual Compatibility of Alexandrium catenella Strains from Southern Chile. Toxins. 2021; 13(12):900. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120900
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Villegas, Camilo, Patricio A. Díaz, Pilar Riobó, Araceli E. Rossignoli, Francisco Rodríguez, Patricia Loures, Ángela M. Baldrich, Daniel Varela, Alondra Sandoval-Sanhueza, and Rosa I. Figueroa. 2021. "Latitudinal Variation in the Toxicity and Sexual Compatibility of Alexandrium catenella Strains from Southern Chile" Toxins 13, no. 12: 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120900
APA StyleRodríguez-Villegas, C., Díaz, P. A., Riobó, P., Rossignoli, A. E., Rodríguez, F., Loures, P., Baldrich, Á. M., Varela, D., Sandoval-Sanhueza, A., & Figueroa, R. I. (2021). Latitudinal Variation in the Toxicity and Sexual Compatibility of Alexandrium catenella Strains from Southern Chile. Toxins, 13(12), 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120900






