Initial Phylotranscriptomic Confirmation of Homoplastic Evolution of the Conspicuous Coloration and Bufoniform Morphology of Pumpkin-Toadlets in the Genus Brachycephalus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
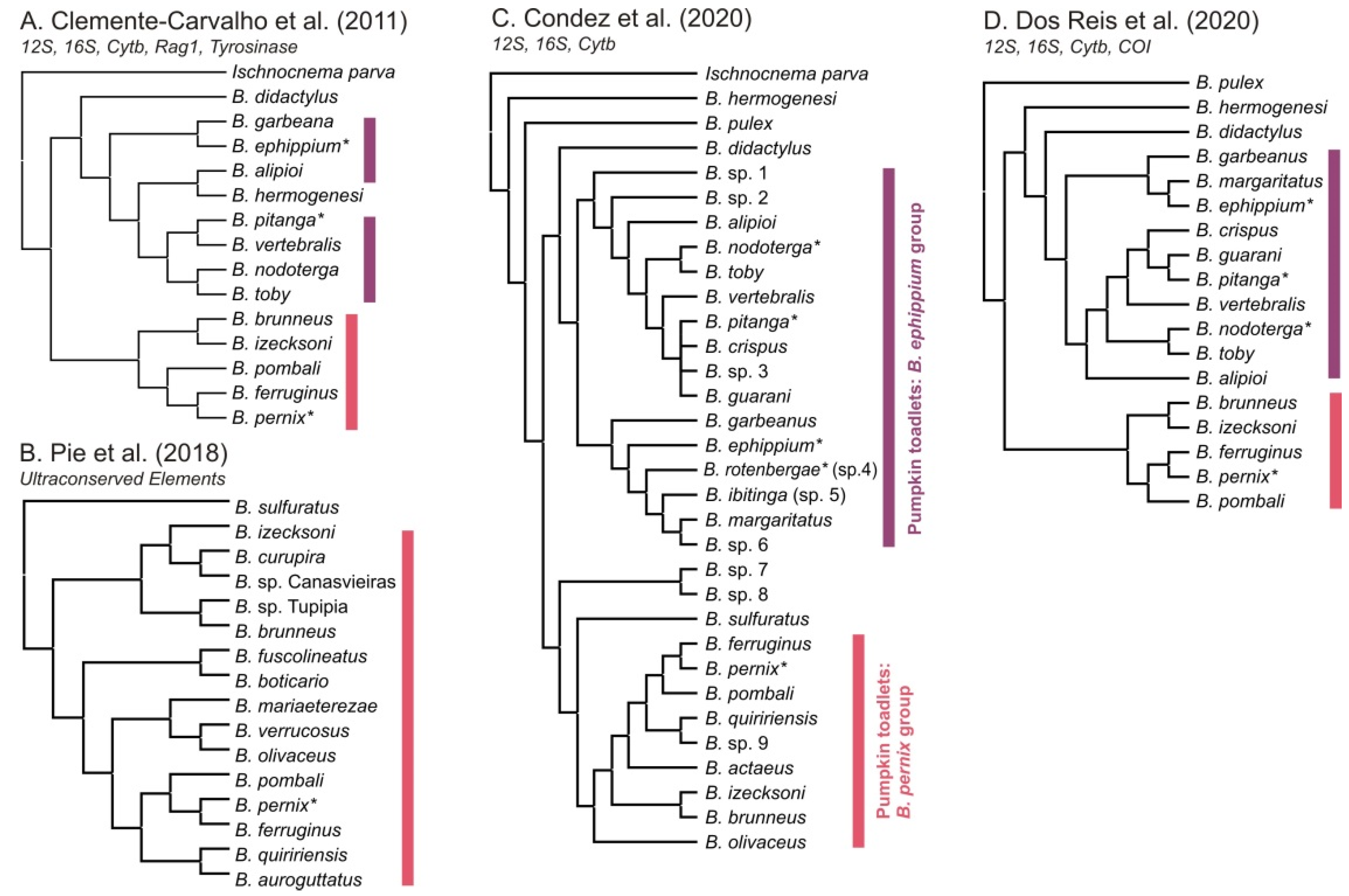
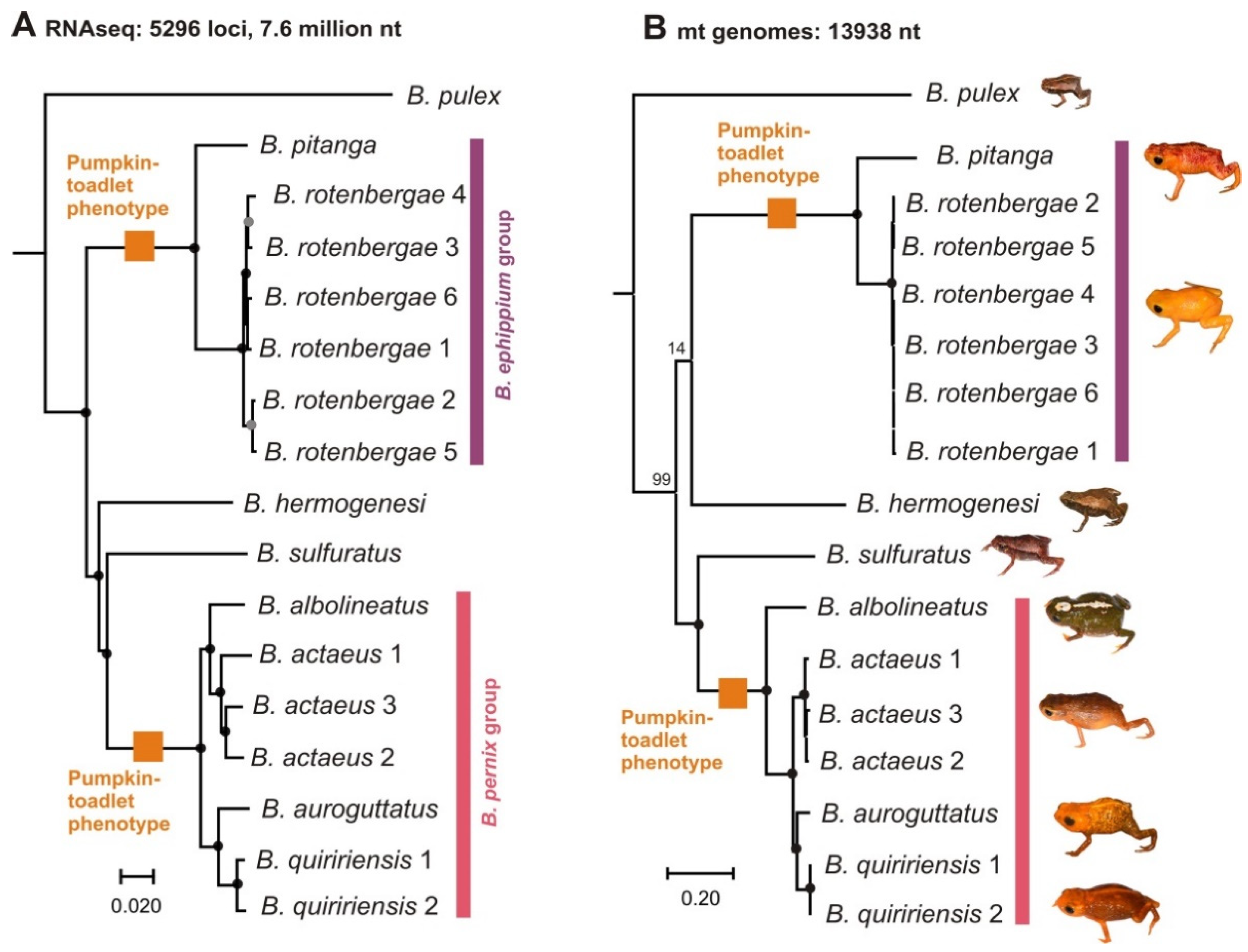
2.1. Phylogenetic Relationships
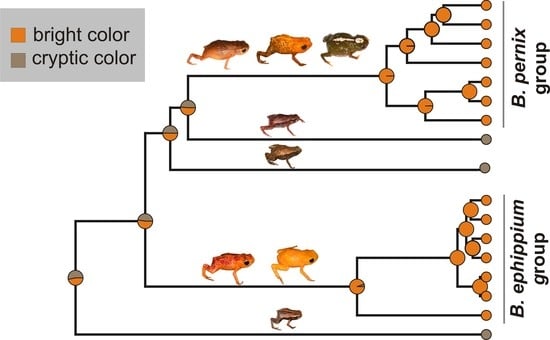
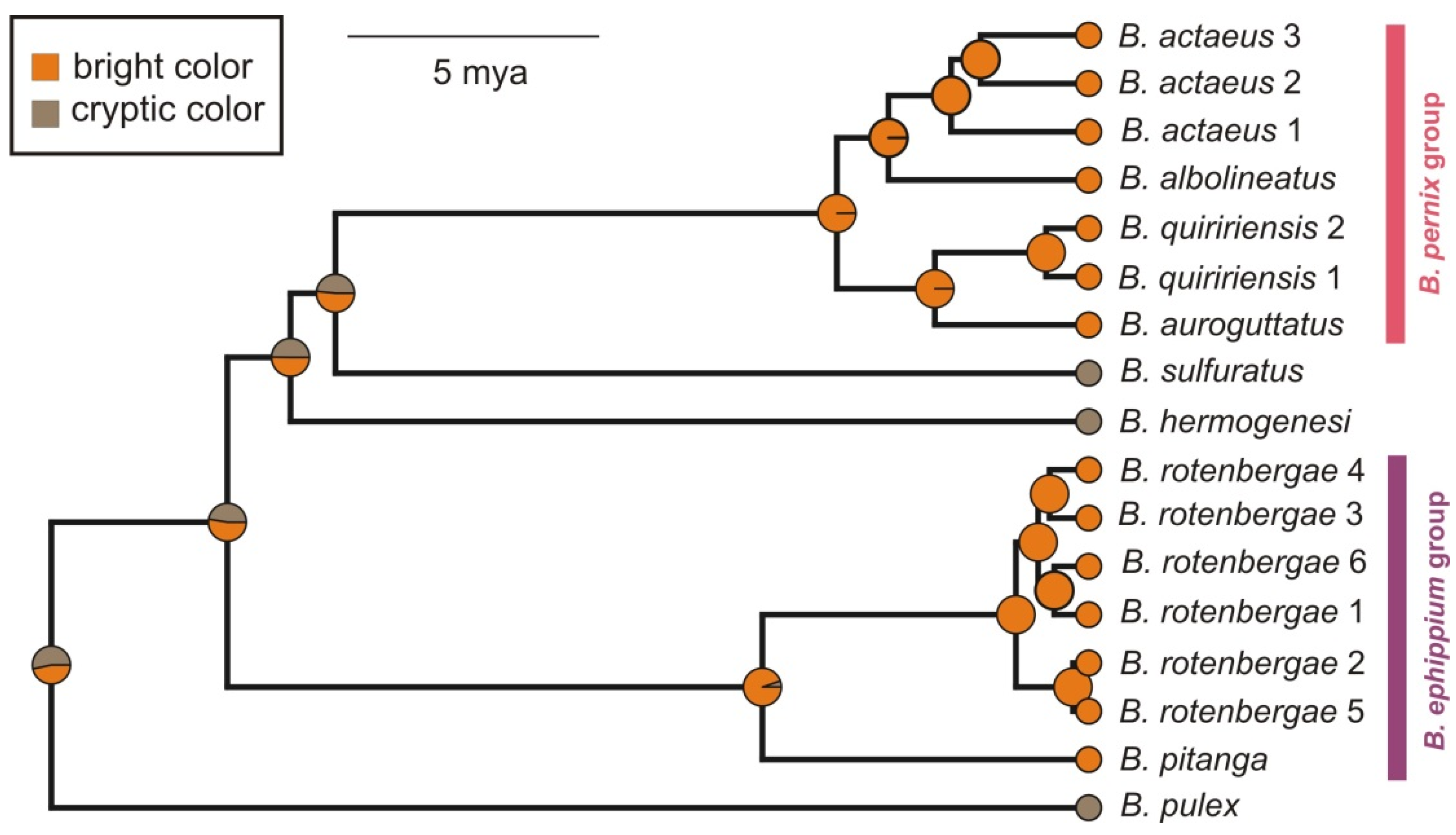
2.2. Reconstruction of Phenotype Evolution
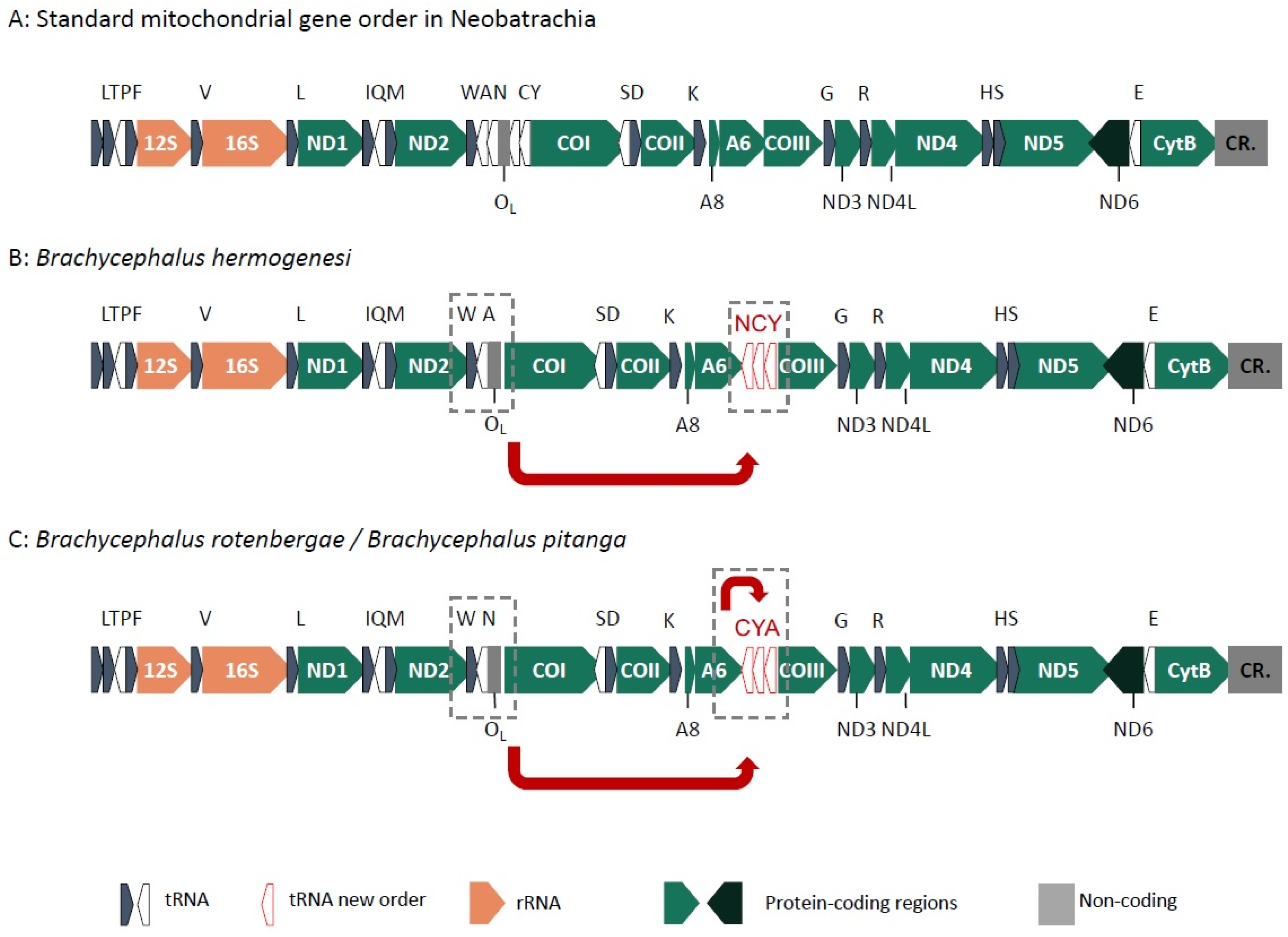
2.3. Mitogenome Gene Order
3. Discussion
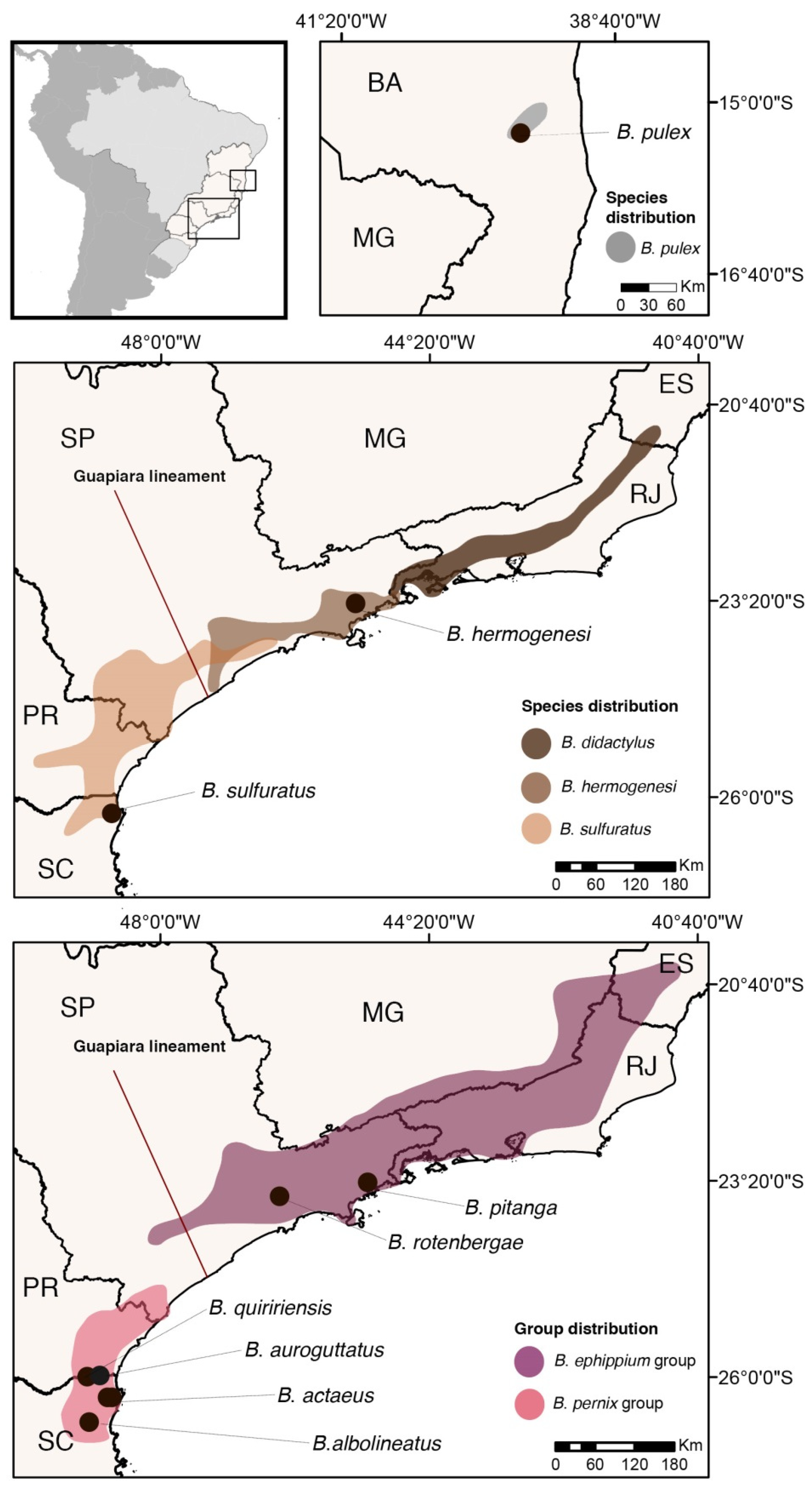
3.1. Evolution and Biogeography of Brachycephalus
3.2. Mitogenome Evolution and Cyto-Nuclear Discordance
3.3. Challenges and Perspectives for Future Taxonomic and Evolutionary Studies
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genetic Sampling
4.2. Phylotranscriptomic Analyses
4.3. Mitochondrial Genome Analyses
4.4. Reconstruction of Phenotype Evolution
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guilford, T.; Dawkins, M. Are warning colors handicaps? Evolution 1993, 47, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruxton, G.D.; Sherratt, T.N.; Speed, M.P. Avoiding Attack: The Evolutionary Ecology of Crypsis, Warning Signals and Mimicry; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mappes, J.; Marples, N.; Endler, J.A. The complex business of survival by aposematism. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, L.F.; Haddad, C.F.B. Colors and some morphological traits as defensive mechanisms in anurans. Int. J. Zool. 2009, 910892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, B.; Valkonen, J.; Nokelainen, O. Aposematism. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R350–R351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, K.; Speed, M.P.; Blount, J.D.; Stuckert, A.M.M. Are aposematic signals honest? A review. J. Evol. Biol. 2015, 28, 1583–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, B.; Burdfield-Steel, E.; De Pasqual, C.; Gordon, S.; Hernández, L.; Mappes, J.; Nokelainen, O.; Rönkä, K.; Lindstedt, C. Multimodal aposematic signals and their emerging role in mate attraction. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.; Cannatella, D.C. Phenotypic integration emerges from aposematism and scale in poison frogs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6175–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saporito, R.A.; Zuercher, R.; Roberts, M.; Kenneth, G.; Donnelly, M. A Poison Frog Oophaga pumilio. Society 2007, 2007, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Bordignon, D.W.; Caorsi, V.Z.; Colombo, P.; Abadie, M.; Brack, I.V.; Dasoler, B.T.; Borges-Martins, M. Are the unken reflex and the aposematic colouration of red-bellied toads efficient against bird predation? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebouças, R.; Carollo, A.B.; Freitas, M.O.; Lambertini, C.; Dos Santos, R.M.N.; Toledo, L.F. Is the conspicuous dorsal coloration of the atlantic forest pumpkin toadlets aposematic? Salamandra 2019, 55, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hagemann, S.; Pröhl, H. Mitochondrial paraphyly in a polymorphic poison frog species (Dendrobatidae; D. pumilio). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 45, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Mundy, N.I.; Ibáñez, R.; Pröhl, H. Being red, blue and green: The genetic basis of coloration differences in the strawberry poison frog (Oophaga pumilio). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudh, A.; Qvarnström, A. Adaptive colouration in amphibians. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 24, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanifin, C.T. The chemical and evolutionary ecology of tetrodotoxin (TTX) toxicity in terrestrial vertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AmphibiaWeb. University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA. Available online: https://amphibiaweb.org (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Bornschein, M.R.; Pie, M.R.; Teixeira, L. Conservation status of Brachycephalus toadlets (Anura: Brachycephalidae) from the Brazilian Atlantic rainforest. Diversity 2019, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Carvalho, R.B.G.; Klaczko, J.; Ivan Perez, S.; Alves, A.C.R.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Dos Reis, S.F. Molecular phylogenetic relationships and phenotypic diversity in miniaturized toadlets, genus Brachycephalus (Amphibia: Anura: Brachycephalidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2011, 61, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condez, T.H.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Zamudio, K.R. Historical biogeography and multi-trait evolution in miniature toadlets of the genus Brachycephalus (Anura: Brachycephalidae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 129, 664–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, S.F.; Clemente-Carvalho, R.B.G.; dos Santos, C.M.S.F.F.; Lopes, R.T.; Von Zuben, F.J.; Laborda, P.R.; Perez, S.I. Skull diversity and evolution in miniaturized amphibians, genus Brachycephalus (Anura: Brachycephalidae). Anat. Rec. 2020, 304, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, O.R.; Sebben, A.; Schwartz, E.F.; Morales, R.A.V.; Bloch, C.; Schwartz, C.A. Further report of the occurrence of tetrodotoxin and new analogues in the Anuran family Brachycephalidae. Toxicon 2005, 45, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimetto Tonon, L.A.; Rua, C.; Crnkovic, C.M.; Bernardi, D.I.; Pires Junior, O.R.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Pedrosa, C.S.G.; Souza, L.R.Q.; Rehen, S.K.; de Azevedo, G.P.R.; et al. Microbiome associated with the tetrodotoxin-bearing anuran Brachycephalus pitanga. Toxicon 2021, 203, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcanjo, D.D.R.; Vasconcelos, A.G.; Comerma-Steffensen, S.G.; Jesus, J.R.; Silva, L.P.; Pires, O.R.; Costa-Neto, C.M.; Oliveira, E.B.; Migliolo, L.; Franco, O.L.; et al. A novel vasoactive proline-rich oligopeptide from the skin secretion of the frog Brachycephalus ephippium. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanken, J. Adaptation of bone growth to miniaturization of body size. Bone 1993, 7, 79–104. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente-Carvalho, R.B.G.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Jared, C.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Alves, A.C.R.; Rocha, H.S.; Pereira, G.R.; Oliveira, D.F.; Lopes, R.T.; dos Reis, S.F. Hyperossification in miniaturized toadlets of the genus Brachycephalus (Amphibia: Anura: Brachycephalidae): Microscopic structure and macroscopic patterns of variation. J. Morphol. 2009, 270, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condez, T.H.; Monteiro, J.P.C.; Malagoli, L.R.; Trevine, V.C.; Schunck, F.; Garcia, P.C.A.; Haddad, C.F.B. Notes on the hyperossified pumpkin toadlets of the genus Brachycephalus (Anura: Brachycephalidae) with the Description of a New Species. Herpetologica 2021, 77, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folly, M.; de Luna-Dias, C.; Miguel, I.R.; Ferreira, J.C.; Machado, A.; Tadeu Lopes, R.; Pombal, J.P. Tiny steps towards greater knowledge: An osteological review with novel data on the Atlantic Forest toadlets of the Brachycephalus ephippium species group. Acta Zool. 2021, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pie, M.R.; Faircloth, B.C.; Ribeiro, L.F.; Bornschein, M.R.; Mccormack, J.E. Phylogenomics of montane frogs of the Brazilian Atlantic Forest is consistent with isolation in sky islands followed by climatic stability. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goloboff, P.A.; Catalano, S.A. TNT version 1.5, including a full implementation of phylogenetic morphometrics. Cladistics 2016, 32, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irisarri, I.; Mauro, D.S.; Abascal, F.; Ohler, A.; Vences, M.; Zardoya, R. The origin of modern frogs (Neobatrachia) was accompanied by acceleration in mitochondrial and nuclear substitution rates. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Liang, D.; Mao, R.L.; Hillis, D.M.; Wake, D.B.; Cannatella, D.C. Efficient sequencing of anuran mtDNAs and a mitogenomic exploration of the phylogeny and evolution of frogs. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1899–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurabayashi, A.; Sumida, M. Afrobatrachian mitochondrial genomes: Genome reorganization, gene rearrangement mechanisms, and evolutionary trends of duplicated and rearranged genes. BMC Genom. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.L.; Boore, J.L. Molecular mechanisms of extensive mitochondrial gene rearrangement in plethodontid salamanders. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 2104–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Mauro, D.; Gower, D.J.; Zardoya, R.; Wilkinson, M. A hotspot of gene order rearrangement by tandem duplication and random loss in the vertebrate mitochondrial genome. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Miura, I.; Wong, P.B.Y.; Murphy, R.W.; Zeng, X. The evolution of mitochondrial genomes in modern frogs (Neobatrachia): Nonadaptive evolution of mitochondrial genome reorganization. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Monteiro, J.P.C.; Condez, T.H.; Garcia, P.C.A.; Comitti, E.J.; Amaral, I.B.; Haddad, C.F.B. A new species of Brachycephalus (Anura, Brachycephalidae) from the coast of Santa Catarina State, Southern Atlantic Forest, Brazil. Zootaxa 2018, 4407, 483–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pie, M.R.; Ribeiro, L.F.; Confetti, A.E.; Nadaline, M.J.; Bornschein, M.R. A new species of Brachycephalus (Anura: Brachycephalidae) from southern Brazil. PeerJ 2018, 2018, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vences, M.; Sanchez, E.; Hauswaldt, J.S.; Eikelmann, D.; Rodríguez, A.; Carranza, S.; Donaire, D.; Gehara, M.; Helfer, V.; Lötters, S.; et al. Nuclear and mitochondrial multilocus phylogeny and survey of alkaloid content in true salamanders of the genus Salamandra (Salamandridae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 73, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgon, J.D.; Vences, M.; Steinfartz, S.; Bogaerts, S.; Bonato, L.; Donaire-Barroso, D.; Martínez-Solano, I.; Velo-Antón, G.; Vieites, D.R.; Mable, B.K.; et al. Phylogenomic inference of species and subspecies diversity in the Palearctic salamander genus Salamandra. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancilhac, L.; Irisarri, I.; Angelini, C.; Arntzen, J.W.; Babik, W.; Bossuyt, F.; Künzel, S.; Lüddecke, T.; Pasmans, F.; Sanchez, E.; et al. Phylotranscriptomic evidence for pervasive ancient hybridization among Old World salamanders. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonoski, K.; Bi, K.; Rosenblum, E.B. Phenotypic and genetic diversity in aposematic Malagasy poison frogs (genus Mantella). Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 2725–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crottini, A.; Orozco-Terwengel, P.; Rabemananjara, F.C.E.; Susanne Hauswaldt, J.; Vences, M. Mitochondrial introgression, color pattern variation, and severe demographic bottlenecks in three species of malagasy poison frogs, genus Mantella. Genes 2019, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutte, S.; Mason, M.J.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, J.; Montealegre-Z, F.; Chivers, B.D.; Sarria-S, F.A.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Jared, C.; Almeida Sato, L.; Felipe Toledo, L. Evidence of auditory insensitivity to vocalization frequencies in two frogs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padial, J.M.; Grant, T.; Frost, D.R. Molecular systematics of terraranas (Anura: Brachycephaloidea) with an assessment of the effects of alignment and optimality criteria. Zootaxa 2014, 3825, 1–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q. Trinity: Reconstructing a full-length transcriptome without a genome from RNA-Seq data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irisarri, I.; Baurain, D.; Brinkmann, H.; Delsuc, F.; Sire, J.Y.; Kupfer, A.; Petersen, J.; Jarek, M.; Meyer, A.; Vences, M.; et al. Phylotranscriptomic consolidation of the jawed vertebrate timetree. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Smith, S.A. Orthology inference in nonmodel organisms using transcriptomes and low-coverage genomes: Improving accuracy and matrix occupancy for phylogenomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 3081–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roure, B.; Rodriguez-Ezpeleta, N.; Philippe, H. SCaFoS: A tool for selection, concatenation and fusion of sequences for phylogenomics. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernomor, O.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. Terrace aware data structure for phylogenomic inference from supermatrices. Syst. Biol. 2016, 65, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirarab, S.; Warnow, T. ASTRAL-II: Coalescent-based species tree estimation with many hundreds of taxa and thousands of genes. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, i44–i52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.P.A.; Van Dongen, S.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Bartonicek, N.; Enright, A.J. Kraken: A set of tools for quality control and analysis of high-throughput sequence data. Methods 2013, 63, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, C.; Bachmann, L.; Chevreux, B. Reconstructing mitochondrial genomes directly from genomic next-generation sequencing reads—A baiting and iterative mapping approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevreux, B.; Wetter, T.; Suhai, S. Genome sequence assembly using trace signals and additional sequence information. In Proceedings of the German Conference on Bioinformatics (GCB99), Hannover, Germany, 4–6 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pie, M.R.; Ströher, P.R.; Bornschein, M.R.; Ribeiro, L.F.; Faircloth, B.C.; McCormack, J.E. The mitochondrial genome of Brachycephalus brunneus (Anura: Brachycephalidae), with comments on the phylogenetic position of Brachycephalidae. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2017, 71, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meng, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, S. MitoZ: A toolkit for animal mitochondrial genome assembly, annotation and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, G.; Lohman, D.J.; Meier, R. SequenceMatrix: Concatenation software for the fast assembly of multigene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics 2011, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. Partitionfinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Nielsen, R.; Bollback, J.P. Stochastic mapping of morphological characters. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 131–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vences, M.; Miralles, A.; Brouillet, S.; Ducasse, J.; Fedosov, A.; Kharchev, V.; Kostadinov, I.; Kumari, S.; Patmanidis, S.; Scherz, M.D.; et al. iTaxoTools 0.1: Kickstarting a specimen-based software toolkit for taxonomists. Megataxa 2021, 6, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.J.; Blackburn, D.C.; Liang, D.; Hillis, D.M.; Wake, D.B.; Cannatella, D.C.; Zhang, P. Phylogenomics reveals rapid, simultaneous diversification of three major clades of Gondwanan frogs at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5864–E5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revell, L.J. phytools: An R package for phylogenetic comparative biology (and other things). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, W.M. Toward defining the course of evolution: Minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst. Zool. 1971, 20, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyra, M.L.; Monteiro, J.P.C.; Rancilhac, L.; Irisarri, I.; Künzel, S.; Sanchez, E.; Condez, T.H.; Rojas-Padilla, O.; Solé, M.; Toledo, L.F.; et al. Initial Phylotranscriptomic Confirmation of Homoplastic Evolution of the Conspicuous Coloration and Bufoniform Morphology of Pumpkin-Toadlets in the Genus Brachycephalus. Toxins 2021, 13, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13110816
Lyra ML, Monteiro JPC, Rancilhac L, Irisarri I, Künzel S, Sanchez E, Condez TH, Rojas-Padilla O, Solé M, Toledo LF, et al. Initial Phylotranscriptomic Confirmation of Homoplastic Evolution of the Conspicuous Coloration and Bufoniform Morphology of Pumpkin-Toadlets in the Genus Brachycephalus. Toxins. 2021; 13(11):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13110816
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyra, Mariana L., Juliane P. C. Monteiro, Loïs Rancilhac, Iker Irisarri, Sven Künzel, Eugenia Sanchez, Thais H. Condez, Omar Rojas-Padilla, Mirco Solé, Luís Felipe Toledo, and et al. 2021. "Initial Phylotranscriptomic Confirmation of Homoplastic Evolution of the Conspicuous Coloration and Bufoniform Morphology of Pumpkin-Toadlets in the Genus Brachycephalus" Toxins 13, no. 11: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13110816
APA StyleLyra, M. L., Monteiro, J. P. C., Rancilhac, L., Irisarri, I., Künzel, S., Sanchez, E., Condez, T. H., Rojas-Padilla, O., Solé, M., Toledo, L. F., Haddad, C. F. B., & Vences, M. (2021). Initial Phylotranscriptomic Confirmation of Homoplastic Evolution of the Conspicuous Coloration and Bufoniform Morphology of Pumpkin-Toadlets in the Genus Brachycephalus. Toxins, 13(11), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13110816