Shiga Toxins as Antitumor Tools
Abstract
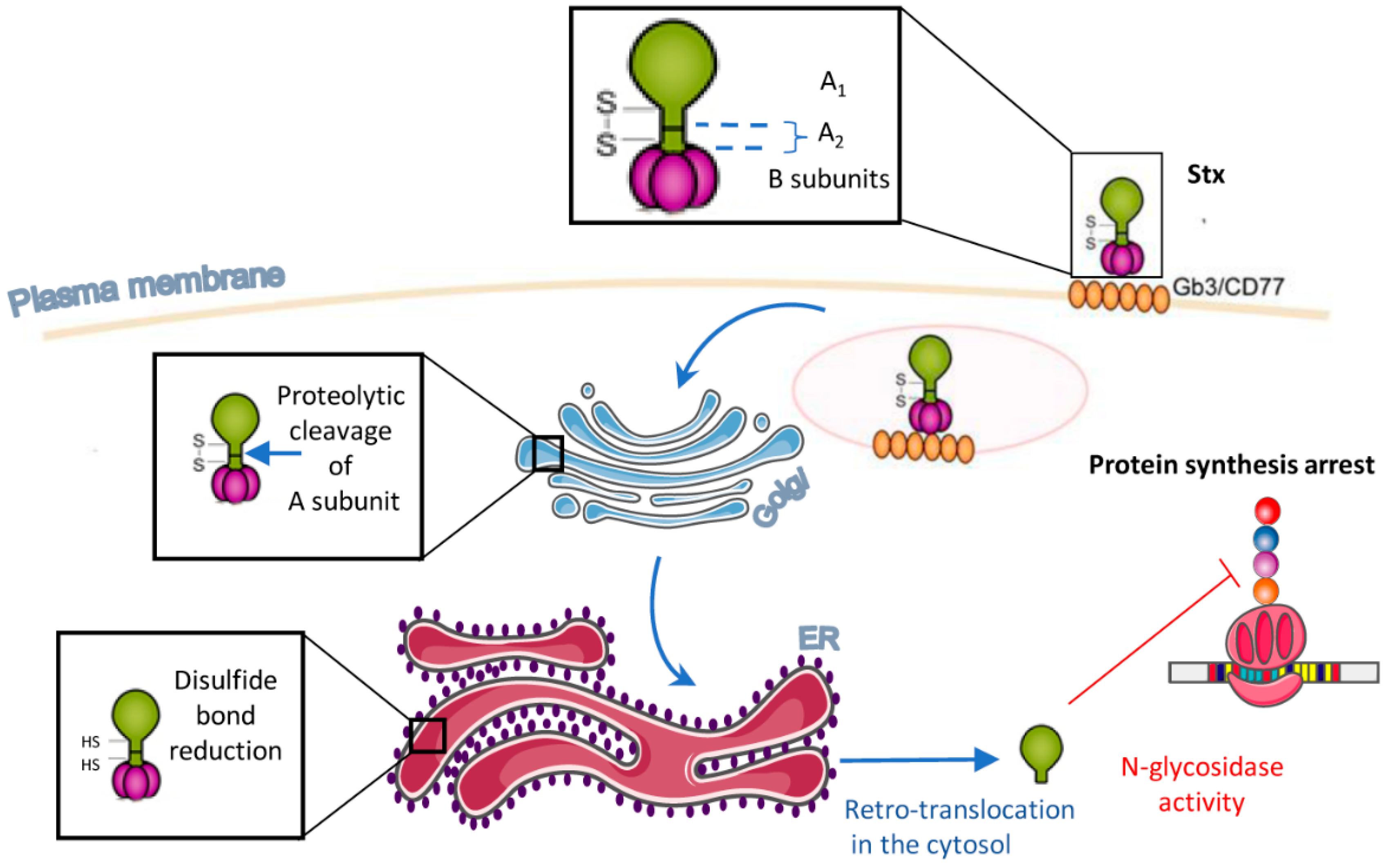
1. Introduction
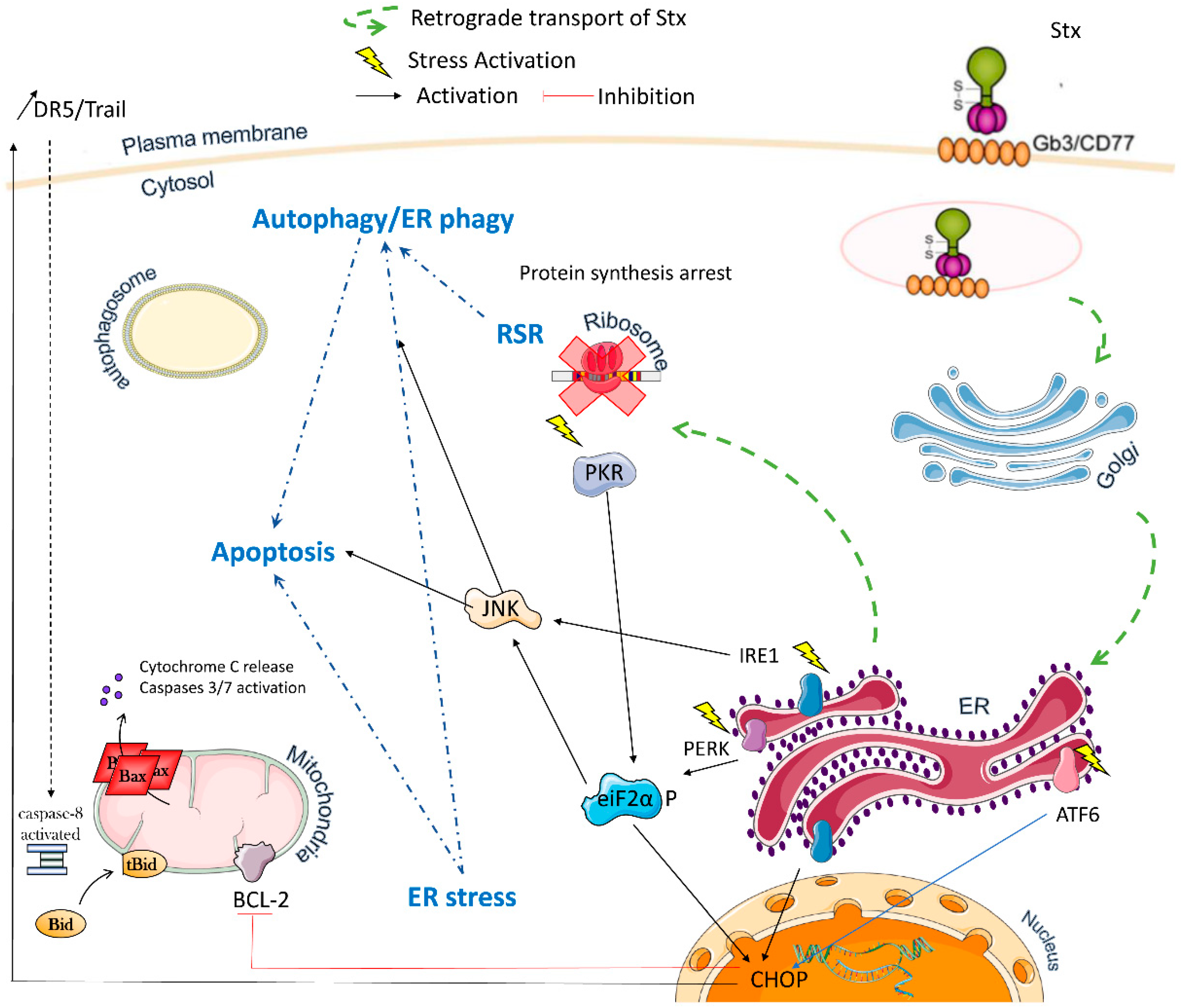
2. Multiple Stxs-Triggered Signaling Pathways
2.1. Ribotoxic Stress
2.2. ER Stress
2.3. Autophagy
2.4. Apoptosis
3. Biomedical Applications of Shiga Toxins
3.1. Holotoxins as Antitumor Tools
3.2. The Antibody-Coupled A Subunit for Cancer Treatment
3.3. The B Subunit as a Delivery Tool
3.3.1. In Vivo Imaging
3.3.2. In-Tumor Targeting
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trofa, A.F.; Ueno-Olsen, H.; Oiwa, R.; Yoshikawa, M. Kiyoshi Shiga: Discoverer of the dysentery bacillus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.C.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, Q.; He, X. Structural and Functional Characterization of Stx2k, a New Subtype of Shiga Toxin 2. Microorganisms 2019, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konowalchuk, J.; Speirs, J.I.; Stavric, S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1977, 18, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karch, H.; Tarr, P.I.; Bielaszewska, M. Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli in human medicine. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 295, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, A.; Hofer, J.; Zimmerhackl, L.B.; Jungraithmayr, T.C.; Riedl, M.; Giner, T.; Strasak, A.; Orth-Holler, D.; Wurzner, R.; Karch, H.; et al. Need for long-term follow-up in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome due to late-emerging sequelae. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyand, M.; Mariani-Kurkdjian, P.; Gouali, M.; de Valk, H.; King, L.A.; Le Hello, S.; Bonacorsi, S.; Loirat, C. Hemolytic uremic syndrome due to Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infection. Med. Mal. Infect. 2018, 48, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangeney, M.; Richard, Y.; Coulaud, D.; Tursz, T.; Wiels, J. CD77: An antigen of germinal center B cells entering apoptosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 1991, 21, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiels, J.; Tursz, T. CD77 workshop panel report. In Leukocyte Typing V; Schlossman, S., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995; pp. 597–599. [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz, M.; Clausen, H.; Nudelman, E.; Donohue-Rolfe, A.; Keusch, G.T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea. XI. Isolation of a shigella toxin-binding glycolipid from rabbit jejunum and HeLa cells and its identification as globotriaosylceramide. J. Exp. Med. 1986, 163, 1391–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzari, A.; Pang, H.; Lingwood, C.A. Binding of verocytotoxin 1 to its receptor is influenced by differences in receptor fatty acid content. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Boodhoo, A.; Hazes, B.; Cummings, M.D.; Armstrong, G.D.; Brunton, J.L.; Read, R.J. Structure of the shiga-like toxin I B-pentamer complexed with an analogue of its receptor Gb3. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGrandis, S.; Law, H.; Brunton, J.; Gyles, C.; Lingwood, C.A. Globotetraosylceramide is recognized by the pig edema disease toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 12520–12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utskarpen, A.; Massol, R.; van Deurs, B.; Lauvrak, S.U.; Kirchhausen, T.; Sandvig, K. Shiga toxin increases formation of clathrin-coated pits through Syk kinase. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzel, I.U.; Pohlentz, G.; Storck, W.; Radamm, L.; Hoffmann, P.; Bielaszewska, M.; Bauwens, A.; Cichon, C.; Schmidt, M.A.; Mormann, M.; et al. Association of Shiga toxin glycosphingolipid receptors with membrane microdomains of toxin-sensitive lymphoid and myeloid cells. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 692–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenouchi, H.; Kiyokawa, N.; Taguchi, T.; Matsui, J.; Katagiri, Y.U.; Okita, H.; Okuda, K.; Fujimoto, J. Shiga toxin binding to globotriaosyl ceramide induces intracellular signals that mediate cytoskeleton remodeling in human renal carcinoma-derived cells. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 3911–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falguières, T.; Mallard, F.; Baron, C.; Hanau, D.; Lingwood, C.; Goud, B.; Salamero, J.; Johannes, L. Targeting of Shiga toxin B-subunit to retrograde transport route in association with detergent-resistant membranes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 2453–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.G.; Bright, N.A.; Howard, G.; Nichols, B.J. SDPR induces membrane curvature and functions in the formation of caveolae. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshkian, W.; Hansen, A.G.; Johannes, L.; Khandelia, H.; Shillcock, J.C.; Kumar, P.B.; Ipsen, J.H. Membrane invagination induced by Shiga toxin B-subunit: From molecular structure to tube formation. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 5164–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römer, W.; Berland, L.; Chambon, V.; Gaus, K.; Windschiegl, B.; Tenza, D.; Aly, M.R.; Fraisier, V.; Florent, J.C.; Perrais, D.; et al. Shiga toxin induces tubular membrane invaginations for its uptake into cells. Nature 2007, 450, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, E.B.; Majewski, J.; Chi, E.Y.; Gao, H.; Florent, J.C.; Johannes, L. Shiga Toxin Induces Lipid Compression: A Mechanism for Generating Membrane Curvature. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 7365–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayan, R.; Wunder, C.; Becken, U.; Howes, M.T.; Benzing, C.; Arumugam, S.; Sales, S.; Ariotti, N.; Chambon, V.; Lamaze, C.; et al. Galectin-3 drives glycosphingolipid-dependent biogenesis of clathrin-independent carriers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkham, M.; Fujita, A.; Chadda, R.; Nixon, S.J.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Sharma, D.K.; Pagano, R.E.; Hancock, J.F.; Mayor, S.; Parton, R.G. Ultrastructural identification of uncoated caveolin-independent early endocytic vehicles. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 168, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, L. Shiga Toxin-A Model for Glycolipid-Dependent and Lectin-Driven Endocytosis. Toxins 2017, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsnes, S.; Pihl, A. Chimeric toxins. Pharmacol. Ther. 1981, 15, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.B.; Chelliah, R.; Kang, J.E.; Rubab, M.; Banan-MwineDaliri, E.; Elahi, F.; Oh, D.H. Role of Recent Therapeutic Applications and the Infection Strategies of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 614963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, S.; Russel, E.; Chapman, W.B.; Rosen, B.; Lingwood, C.A. Expression of the verotoxin receptor glycolipid, globotriaosylceramide, in ovarian hyperplasias. Oncol. Res. 1997, 9, 553–563. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.; Bhinge, K.N.; Hosain, S.B.; Xiong, K.; Gu, X.; Shi, R.; Ho, M.Y.; Khoo, K.H.; Li, S.C.; Li, Y.T.; et al. Ceramide glycosylation by glucosylceramide synthase selectively maintains the properties of breast cancer stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37195–37205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, C.; Fukushi, Y.; Satoh, M.; Saitoh, S.; Orikasa, S.; Nudelman, E.; Straud, M.; Hakomori, S. Changes in glycolipid expression in human testicular tumor. Int. J. Cancer 1990, 45, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsnes, M.S.; Roed, S.S.; Tranulis, M.A.; Espenes, A.; Christophersen, B. Yessotoxin triggers ribotoxic stress. Toxicol. Vitr. 2014, 28, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordanov, M.S.; Pribnow, D.; Magun, J.L.; Dinh, T.H.; Pearson, J.A.; Chen, S.L.; Magun, B.E. Ribotoxic stress response: Activation of the stress-activated protein kinase JNK1 by inhibitors of the peptidyl transferase reaction and by sequence-specific RNA damage to the alpha-sarcin/ricin loop in the 28S rRNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 3373–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrig, T.G.; Moran, T.P.; Brown, J.E. The mode of action of Shiga toxin on peptide elongation of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Biochem. J. 1987, 244, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.R.; Lau, A.S.; Pestka, J.J. Role of double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase R (PKR) in deoxynivalenol-induced ribotoxic stress response. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 74, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, S.K.; Yoon, S.J.; Choi, S.; Jeong, D.G.; Chung, S.W.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, J.H.; Tesh, V.L.; et al. Shiga Toxins Induce Apoptosis and ER Stress in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Toxins 2017, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, P.; Smith, S.J.; Giembycz, M.A.; Rotondo, D.; Plevin, R. Verotoxin activates mitogen-activated protein kinase in human peripheral blood monocytes: Role in apoptosis and proinflammatory cytokine release. Br. J. Pharm. 2003, 140, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherla, R.P.; Lee, S.Y.; Mees, P.L.; Tesh, V.L. Shiga toxin 1-induced cytokine production is mediated by MAP kinase pathways and translation initiation factor eIF4E in the macrophage-like THP-1 cell line. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.E.; Kane, A.V.; Campbell, S.T.; Acheson, D.W.; Cochran, B.H.; Thorpe, C.M. Shiga toxin 1 triggers a ribotoxic stress response leading to p38 and JNK activation and induction of apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandhyala, D.M.; Ahluwalia, A.; Schimmel, J.J.; Rogers, A.B.; Leong, J.M.; Thorpe, C.M. Activation of the Classical Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases Is Part of the Shiga Toxin-Induced Ribotoxic Stress Response and May Contribute to Shiga Toxin-Induced Inflammation. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibal, J.; Hollville, E.; Renouf, B.; Tetaud, C.; Wiels, J. Caspase-8-mediated cleavage of Bid and protein phosphatase 2A-mediated activation of Bax are necessary for Verotoxin-1-induced apoptosis in Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. Cell Signal 2010, 22, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolotti, A.; Zhang, Y.; Hendershot, L.M.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, M.S.; Cherla, R.P.; Tesh, V.L. Shiga toxin 1 induces apoptosis through the endoplasmic reticulum stress response in human monocytic cells. Cell Microbiol. 2008, 10, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Cherla, R.P.; Leyva-Illades, D.; Tesh, V.L. Bcl-2 regulates the onset of shiga toxin 1-induced apoptosis in THP-1 cells. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 5233–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debernardi, J.; Pioche-Durieu, C.; Cam, E.L.; Wiels, J.; Robert, A. Verotoxin-1-Induced ER Stress Triggers Apoptotic or Survival Pathways in Burkitt Lymphoma Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentz, E.K.; Leyva-Illades, D.; Lee, M.S.; Cherla, R.P.; Tesh, V.L. Differential response of the human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell line HK-2 to Shiga toxin types 1 and 2. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3527–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Cherla, R.P.; Lentz, E.K.; Leyva-Illades, D.; Tesh, V.L. Signaling through C/EBP homologous protein and death receptor 5 and calpain activation differentially regulate THP-1 cell maturation-dependent apoptosis induced by Shiga toxin type 1. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3378–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Cherla, R.P.; Jenson, M.H.; Leyva-Illades, D.; Martinez-Moczygemba, M.; Tesh, V.L. Shiga toxins induce autophagy leading to differential signalling pathways in toxin-sensitive and toxin-resistant human cells. Cell Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1479–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parello, C.S.; Mayer, C.L.; Lee, B.C.; Motomochi, A.; Kurosawa, S.; Stearns-Kurosawa, D.J. Shiga toxin 2-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress is minimized by activated protein C but does not correlate with lethal kidney injury. Toxins 2015, 7, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandvig, K.; van Deurs, B. Toxin-induced cell lysis: Protection by 3-methyladenine and cycloheximide. Exp. Cell Res. 1992, 200, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X.H.; Wang, H.G.; Li, N.; Fang, Y.; Wang, K.; Jia, Y.P.; Zhu, P.; Gu, J.; et al. Shiga toxins induce autophagic cell death in intestinal epithelial cells via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Autophagy 2015, 11, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, K.P.; Sharpnack, D.D.; Collins, H.; Formal, S.B.; O’Brien, A.D. Morphologic evaluation of the effects of Shiga toxin and E coli Shiga-like toxin on the rabbit intestine. Am. J. Pathol. 1986, 125, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, C.H.; Kelly, J.K.; Meyers, G.L. Experimental infection of infant rabbits with verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1986, 51, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, S.; Murakami, M.; Dirks, P.; Boyd, B.; Hubbard, S.L.; Lingwood, C.A.; Rutka, J.T. Verotoxins inhibit the growth of and induce apoptosis in human astrocytoma cells. J. Neuro-Oncol. 1998, 40, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inward, C.D.; Williams, J.; Chant, I.; Crocker, J.; Milford, D.V.; Rose, P.E.; Taylor, C.M. Verocytotoxin-1 induces apoptosis in vero cells. J. Infect. 1995, 30, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangeney, M.; Lingwood, C.A.; Taga, S.; Caillou, B.; Tursz, T.; Wiels, J. Apoptosis induced in Burkitt’s lymphoma cells via Gb3/CD77, a glycolipid antigen. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 5314–5319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pijpers, A.; Setten, P.A.V.; Heuvel, L.; Assmann, K.J.M.; Dijkman, H.; Pennings, A.H.M.; Monnens, L.A.H.; Hinsbergh, V. Verocytotoxin-induced apoptosis of human microvascular endothelial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2001, 12, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, Y.U.; Mori, T.; Nakajima, H.; Katagiri, C.; Taguchi, T.; Takeda, T.; Kiyokawa, N.; Fujimoto, J. Activation of Src family kinase yes induced by Shiga toxin binding to globotriaosyl ceramide (Gb3/CD77) in low density, detergent-insoluble microdomains. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 35278–35282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Kiyokawa, N.; Katagiri, Y.U.; Taguchi, T.; Suzuki, T.; Sekino, T.; Sato, N.; Ohmi, K.; Nakajima, H.; Takeda, T.; et al. Globotriaosyl ceramide (CD77/Gb3) in the glycolipid-enriched membrane domain participates in B-cell receptor-mediated apoptosis by regulating lyn kinase activity in human B cells. Exp. Hematol. 2000, 28, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojio, S.; Zhang, H.; Ohmura, M.; Gondaira, F.; Kobayashi, N.; Yamamoto, T. Caspase-3 activation and apoptosis induction coupled with the retrograde transport of shiga toxin: Inhibition by brefeldin A. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 29, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyokawa, N.; Mori, T.; Taguchi, T.; Saito, M.; Mimori, K.; Suzuki, T.; Sekino, T.; Sato, N.; Nakajima, H.; Katagiri, Y.U.; et al. Activation of the caspase cascade during Stx1-induced apoptosis in Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2001, 81, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, J.C.; Jones, N.L.; Ceponis, P.J.; Karmali, M.A.; Sherman, P.M. Escherichia coli shiga-like toxins induce apoptosis and cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase via in vitro activation of caspases. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4669–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, J.; Matsui, T.; Heatherly, D.P.; Schlegel, K.H.; Lobo, P.I.; Yutsudo, T.; Ciraolo, G.M.; Morris, R.E.; Obrig, T. Rapid apoptosis induced by Shiga toxin in HeLa cells. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2724–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetaud, C.; Falguieres, T.; Carlier, K.; Lecluse, Y.; Garibal, J.; Coulaud, D.; Busson, P.; Steffensen, R.; Clausen, H.; Johannes, L.; et al. Two distinct Gb3/CD77 signaling pathways leading to apoptosis are triggered by anti-Gb3/CD77 mAb and verotoxin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45200–45208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.; Challa, A.; Levens, J.M.; Gregory, C.D.; Williams, J.M.; Armitage, R.J.; Cook, J.P.; Roberts, L.M.; Lord, J.M. CD40 ligand, Bcl-2, and Bcl-xL spare group I Burkitt lymphoma cells from CD77-directed killing via Verotoxin-1 B chain but fail to protect against the holotoxin. Cell Death Differ. 2000, 7, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Erwert, R.D.; Eiting, K.T.; Tupper, J.C.; Winn, R.K.; Harlan, J.M.; Bannerman, D.D. Shiga toxin induces decreased expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1 concomitant with the onset of endothelial apoptosis. Microb. Pathog. 2003, 35, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Watanabe-Takahashi, M.; Ohoka, N.; Hamabata, T.; Furukawa, K.; Nishikawa, K.; Naito, M. Proteasome inhibitors prevent cell death and prolong survival of mice challenged by Shiga toxin. FEBS Open Bio 2015, 5, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, I.; Nakata, M.; Kawabata, S.; Hamada, S. Regulated expression of the Shiga toxin B gene induces apoptosis in mammalian fibroblastic cells. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 33, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Cherla, R.P.; Caliskan, I.; Tesh, V.L. Shiga toxin 1 induces apoptosis in the human myelogenous leukemia cell line THP-1 by a caspase-8-dependent, tumor necrosis factor receptor-independent mechanism. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 5115–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.M.; Lea, N.; Lord, J.M.; Roberts, L.M.; Milford, D.V.; Taylor, C.M. Comparison of ribosome-inactivating proteins in the induction of apoptosis. Toxicol. Lett. 1997, 91, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distler, U.; Souady, J.; Hulsewig, M.; Drmic-Hofman, I.; Haier, J.; Friedrich, A.W.; Karch, H.; Senninger, N.; Dreisewerd, K.; Berkenkamp, S.; et al. Shiga toxin receptor Gb3Cer/CD77: Tumor-association and promising therapeutic target in pancreas and colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falguieres, T.; Maak, M.; von Weyhern, C.; Sarr, M.; Sastre, X.; Poupon, M.F.; Robine, S.; Johannes, L.; Janssen, K.P. Human colorectal tumors and metastases express Gb3 and can be targeted by an intestinal pathogen-based delivery tool. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2498–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, D.; Johansson, A.; Grankvist, K.; Andersson, U.; Henriksson, R.; Bergstrom, P.; Brannstrom, T.; Behnam-Motlagh, P. Verotoxin-1 induction of apoptosis in Gb3-expressing human glioma cell lines. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovbasnjuk, O.; Mourtazina, R.; Baibakov, B.; Wang, T.; Elowsky, C.; Choti, M.A.; Kane, A.; Donowitz, M. The glycosphingolipid globotriaosylceramide in the metastatic transformation of colon cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19087–19092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, D.; Kosovac, E.; Moharer, J.; Ljuslinder, I.; Brannstrom, T.; Johansson, A.; Behnam-Motlagh, P. Expression of verotoxin-1 receptor Gb3 in breast cancer tissue and verotoxin-1 signal transduction to apoptosis. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nudelman, E.; Kannagi, R.; Hakomori, S.; Parsons, M.; Lipinski, M.; Wiels, J.; Fellous, M.; Tursz, T. A glycolipid antigen associated with Burkitt lymphoma defined by a monoclonal antibody. Science 1983, 220, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimmer, L.; Dehay, S.; Nemati, F.; Massonnet, G.; Richon, S.; Decaudin, D.; Klijanienko, J.; Johannes, L. Human breast cancer and lymph node metastases express Gb3 and can be targeted by STxB-vectorized chemotherapeutic compounds. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas-Himsley, H.; Hill, R.; Rosen, B.; Arab, S.; Lingwood, C.A. The bacterial colicin active against tumor cells in vitro and in vivo is verotoxin 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 6996–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath-Engel, H.M.; Lingwood, C.A. Verotoxin sensitivity of ECV304 cells in vitro and in vivo in a xenograft tumour model: VT1 as a tumour neovascular marker. Angiogenesis 2003, 6, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, D.; Andersson, C.; Moharer, J.; Johansson, A.; Behnam-Motlagh, P. Cisplatin-induced expression of Gb3 enables verotoxin-1 treatment of cisplatin resistance in malignant pleural mesothelioma cells. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, S.; Rutka, J.; Lingwood, C. Verotoxin induces apoptosis and the complete, rapid, long-term elimination of human astrocytoma xenografts in nude mice. Oncol. Res. 1999, 11, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Salhia, B.; Rutka, J.T.; Lingwood, C.; Nutikka, A.; Van Furth, W.R. The treatment of malignant meningioma with verotoxin. Neoplasia 2002, 4, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitoya, S.; Kurazono, H.; Nishiyama, H.; Nakamura, E.; Kamoto, T.; Habuchi, T.; Terai, A.; Ogawa, O.; Yamamoto, S. Verotoxin induces rapid elimination of human renal tumor xenografts in SCID mice. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engedal, N.; Skotland, T.; Torgersen, M.L.; Sandvig, K. Shiga toxin and its use in targeted cancer therapy and imaging. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bast, D.J.; Sandhu, J.; Hozumi, N.; Barber, B.; Brunton, J. Murine antibody responses to the verotoxin 1 B subunit: Demonstration of major histocompatibility complex dependence and an immunodominant epitope involving phenylalanine 30. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 2978–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.M.; McEwen, J.; Losonsky, G.; Reymann, M.; Harari, I.; Brown, J.E.; Taylor, D.N.; Donohue-Rolfe, A.; Cohen, D.; Bennish, M.; et al. Antibodies to shiga holotoxin and to two synthetic peptides of the B subunit in sera of patients with Shigella dysenteriae 1 dysentery. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1636–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, K.; Sarkim, V.; Bitzan, M.; Karmali, M.A.; Bobrowski, C.; Ruder, H.; Laufs, R.; Sobottka, I.; Petric, M.; Karch, H.; et al. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infection and antibodies against Stx2 and Stx1 in household contacts of children with enteropathic hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallera, D.A.; Kreitman, R.J. Immunotoxins Targeting B cell Malignancy-Progress and Problems With Immunogenicity. Biomedicines 2018, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, F.; Aucoin, M.G.; Jahanian-Najafabadi, A. Targeted Diphtheria Toxin-Based Therapy: A Review Article. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Duque, A.E.; Perekhrestenko, T.; Musteata, V.; Zodelava, M.; Guthrie, T.H.; Strack, T.; Burnett, C.; Wilson, S.; Waltzman, R.J.; Baetz, T.D.; et al. A phase II study of MT-3724, a novel CD20-targeting engineered toxin body, to evaluate safety, pharmacodynamics, and efficacy in subjects with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, TPS8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tache, J.; Katz, D.A.; Burnett, C.; Strack, T.; Lehner, T.; Waltzman, R.; Lee, S. A Phase 2a open-label study of mt-3724, a novel cd20-targeting engineered toxin body, in combination with lenalidomide (len) in subjects with relapsed or refractory b-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma. In Proceedings of the 25th European Hematological Association (EHA) Virtual Annual Meeting, Virtual Meeting, 11–21 June 2020. EP1261. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.K.; Cornell, R.F.; Landgren, O.; Ailawadhi, S.; Higgins, J.P.; Willert, E.K.; Waltzman, R.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lublinsky, A.R.; et al. A Phase 1 First-in-Human Study of the Anti-CD38 Dimeric Fusion Protein TAK-169 for the Treatment of Patients (pts) with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM) Who Are Proteasome Inhibitor (PI)- and Immunomodulatory Drug (IMiD)-Refractory, Including Pts Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) or Naïve to Daratumumab (dara). Blood 2019, 134, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltzman, R.J.; Sarkar, A.; Williams, E.T.; Iberg, A.T.; Higgins, J.T.; Willert, E.K. MT-5111: A novel HER2 targeting engineered toxin body in clinical development. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainberg, Z.A.; Barve, M.A.; Hamilton, E.P.; Brenner, A.J.; Valdes, F.; Mita, M.M.; González, V.; Anand, B.S.; Burnett, C.; Pelham, J.; et al. A phase I study of the novel immunotoxin, MT-5111, in subjects (subj) with HER-2 positive tumors: Interim results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, e15567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainberg, Z.A.; Mita, M.M.; Barve, M.A.; Hamilton, E.P.; Brenner, A.J.; Valdes, F.; Ahn, D.H.; Hubbard, J.M.; Starr, J.S.; Burnett, C.; et al. A phase I open-label study to investigate safety and tolerability, efficacy, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of MT-5111 in patients with HER2-positive tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, TPS258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, H.J.; Brieschke, B.; LeMar, S.; Dekker, J.D.; Cornelison, G.; Sarkar, A.; Williams, E.; Robinson, G.L.; Zhao, J.; Iberg, I.; et al. In vivo efficacy of a PD-L1 targeted, antigen seeding engineered toxin body. In Proceedings of the AACR Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 27–28 April 2020. Abstract Number 3366. [Google Scholar]
- Dekker, J.D.; Khanna, S.; Saputra, E.; Dong, W.; Aschenbach, L.; Rabia, L.A.; Cornelison, G.L.; Sousares, M.; Zhao, J.; Robinson, G.L.; et al. Engineered Toxin Bodies Targeting PD-L1 to Alter Tumor Immunophenotypes and Delivery Broad Antigenic Diversity and Patient Coverage. In Proceedings of the AACR Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 9–14 April 2021. Abstract number 1628. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, K.P.; Vignjevic, D.; Boisgard, R.; Falguieres, T.; Bousquet, G.; Decaudin, D.; Dolle, F.; Louvard, D.; Tavitian, B.; Robine, S.; et al. In vivo tumor targeting using a novel intestinal pathogen-based delivery approach. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7230–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viel, T.; Dransart, E.; Nemati, F.; Henry, E.; Theze, B.; Decaudin, D.; Lewandowski, D.; Boisgard, R.; Johannes, L.; Tavitian, B. In vivo tumor targeting by the B-subunit of shiga toxin. Mol. Imaging 2008, 7, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couture, O.; Dransart, E.; Dehay, S.; Nemati, F.; Decaudin, D.; Johannes, L.; Tanter, M. Tumor delivery of ultrasound contrast agents using Shiga toxin B subunit. Mol. Imaging 2011, 10, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batisse, C.; Dransart, E.; Ait Sarkouh, R.; Brulle, L.; Bai, S.K.; Godefroy, S.; Johannes, L.; Schmidt, F. A new delivery system for auristatin in STxB-drug conjugate therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 95, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Alaoui, A.; Schmidt, F.; Sarr, M.; Decaudin, D.; Florent, J.C.; Johannes, L. Synthesis and properties of a mitochondrial peripheral benzodiazepine receptor conjugate. Chem. Med. Chem. 2008, 3, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostova, V.; Dransart, E.; Azoulay, M.; Brulle, L.; Bai, S.K.; Florent, J.C.; Johannes, L.; Schmidt, F. Targeted Shiga toxin-drug conjugates prepared via Cu-free click chemistry. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 7150–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, P.E.; Maak, M.; Nitsche, U.; Perl, M.; Novotny, A.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Dransart, E.; Holtorf, A.; Johannes, L.; Janssen, K.P. Gastric Adenocarcinomas Express the Glycosphingolipid Gb3/CD77: Targeting of Gastric Cancer Cells with Shiga Toxin B-Subunit. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maak, M.; Nitsche, U.; Keller, L.; Wolf, P.; Sarr, M.; Thiebaud, M.; Rosenberg, R.; Langer, R.; Kleeff, J.; Friess, H.; et al. Tumor-specific targeting of pancreatic cancer with Shiga toxin B-subunit. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrago-Trani, M.T.; Jiang, S.; Harich, K.C.; Storrie, B. Shiga-like toxin subunit B (SLTB)-enhanced delivery of chlorin e6 (Ce6) improves cell killing. Photochem. Photobiol. 2006, 82, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amessou, M.; Carrez, D.; Patin, D.; Sarr, M.; Grierson, D.S.; Croisy, A.; Tedesco, A.C.; Maillard, P.; Johannes, L. Retrograde delivery of photosensitizer (TPPp-O-beta-GluOH)3 selectively potentiates its photodynamic activity. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmit, N.E.; Neopane, K.; Hantschel, O. Targeted Protein Degradation through Cytosolic Delivery of Monobody Binders Using Bacterial Toxins. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni, Z.; Sedighian, H.; Halabian, R.; Amani, J.; Behzadi, E.; Imani Fooladi, A.A. Potent in vitro antitumor activity of B-subunit of Shiga toxin conjugated to the diphtheria toxin against breast cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 899, 174057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryou, J.H.; Sohn, Y.K.; Hwang, D.E.; Park, W.Y.; Kim, N.; Heo, W.D.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, H.S. Engineering of bacterial exotoxins for highly efficient and receptor-specific intracellular delivery of diverse cargos. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vingert, B.; Adotevi, O.; Patin, D.; Jung, S.; Shrikant, P.; Freyburger, L.; Eppolito, C.; Sapoznikov, A.; Amessou, M.; Quintin-Colonna, F.; et al. The Shiga toxin B-subunit targets antigen in vivo to dendritic cells and elicits anti-tumor immunity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robert, A.; Wiels, J. Shiga Toxins as Antitumor Tools. Toxins 2021, 13, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13100690
Robert A, Wiels J. Shiga Toxins as Antitumor Tools. Toxins. 2021; 13(10):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13100690
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobert, Aude, and Joëlle Wiels. 2021. "Shiga Toxins as Antitumor Tools" Toxins 13, no. 10: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13100690
APA StyleRobert, A., & Wiels, J. (2021). Shiga Toxins as Antitumor Tools. Toxins, 13(10), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13100690





