Shiga Toxin 2a Binds to Complement Components C3b and C5 and Upregulates Their Gene Expression in Human Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
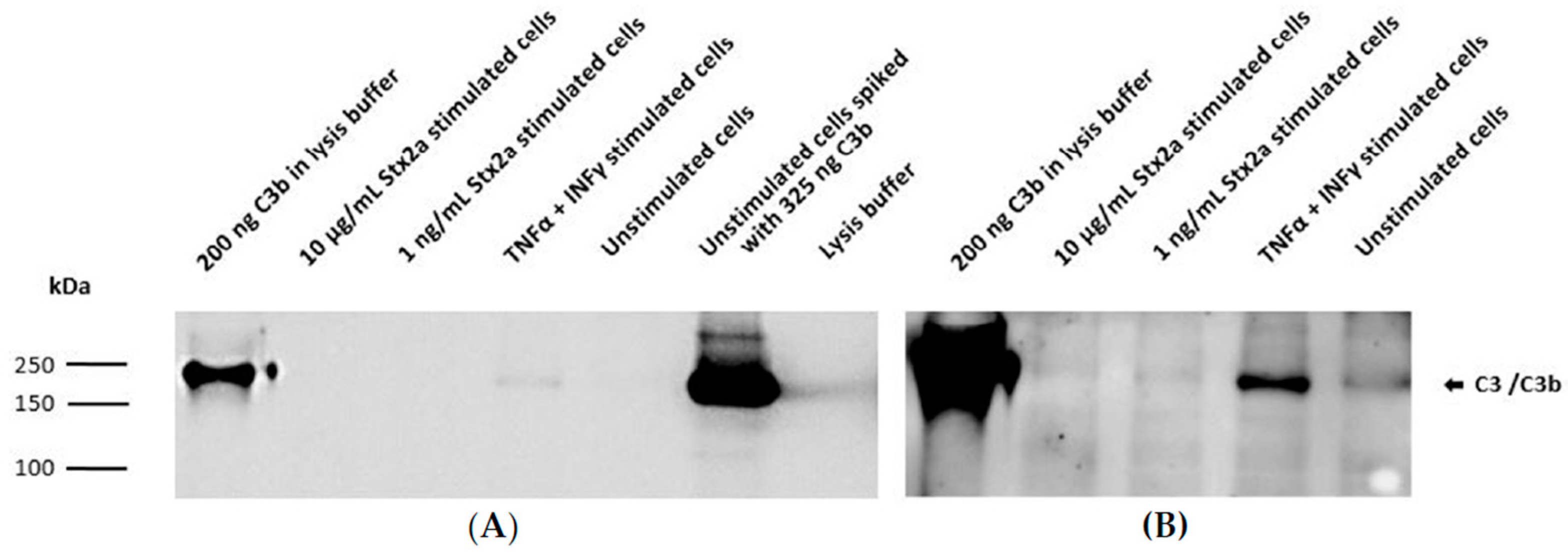
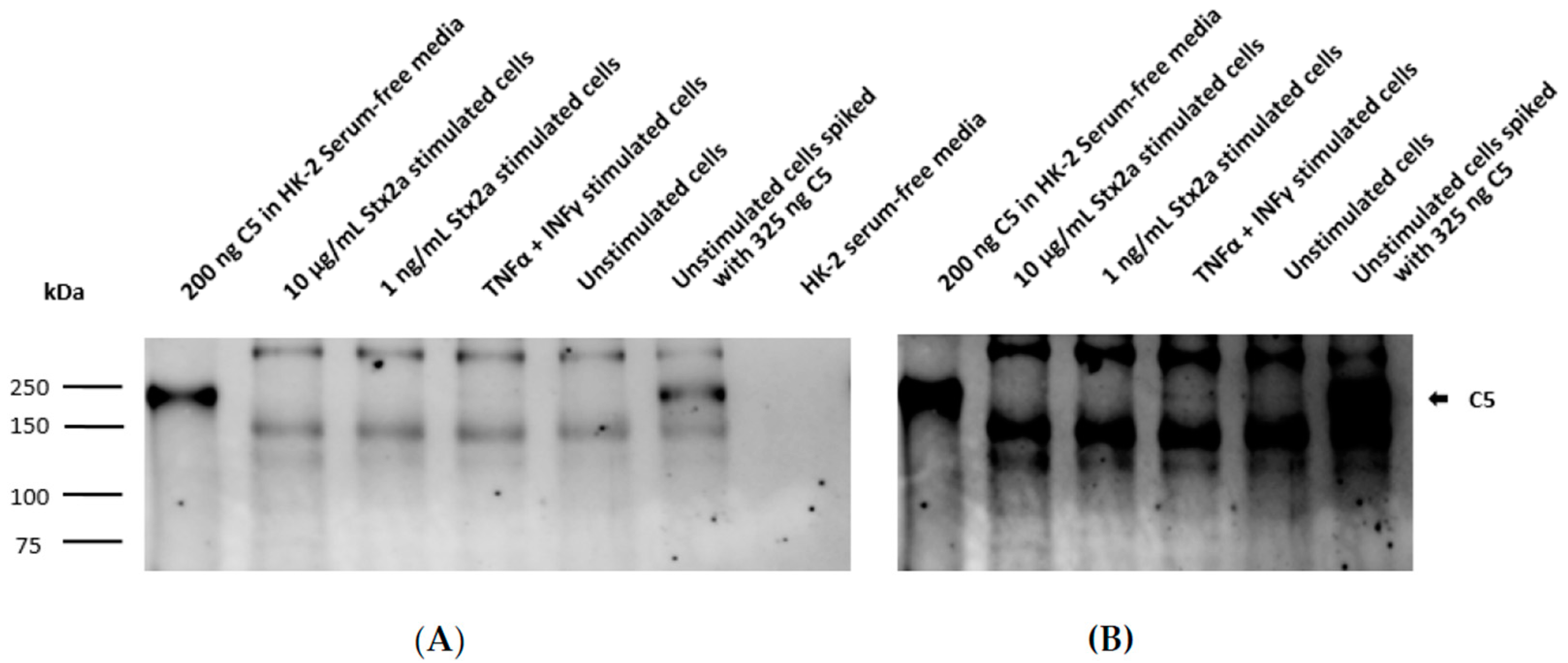
2.1. Stx2a Binds to Complement C3b and C5
2.2. Stx2a Upregulates C3 and C5 mRNA Expression in HK-2 and HCT-8 Cells
2.3. Complement Protein C3 and C5 Synthesis in HK-2 Cells
2.4. Stx2a Impact on the Viability of HK-2 Cells In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Analysis of Binding of Stx2a to Complement C3b and C5
4.4. Alternative Pathway Intracellular Complement Profile Analysis of HK-2 Cells
4.5. Intracellular C3 and C5 mRNA Expression in HCT-8 Cells
4.6. Determination of C3 and C5 in HK-2 Cell Supernatants and Lysates Treated with Stx2a
4.7. Cytotoxicity Assay in HK-2 Cells
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karmali, M.A. Host and pathogen determinants of verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, S4–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigotti, M. The Interactions of Human Neutrophils with Shiga Toxins and Related Plant Toxins: Danger or Safety? Toxins 2012, 4, 157–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, P.I.; Gordon, C.A.; Chandler, W.L. Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli and haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, L.M.; Melton-Celsa, A.R.; Smith, M.J.; O’Brien, A.D. Comparisons of Native Shiga Toxins (Stxs) Type 1 and 2 with Chimeric Toxins Indicate that the Source of the Binding Subunit Dictates Degree of Toxicity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karch, H.; Tarr, P.I.; Bielaszewska, M. Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli in human medicine. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 295, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, B.P.; Jacewicz, M.; Thorpe, C.M.; Lincicome, L.L.; King, A.J.; Keusch, G.T.; Acheson, D.W.K. Shiga Toxins 1 and 2 Translocate Differently across Polarized Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müthing, J.; Meisen, I.; Zhang, W.; Bielaszewska, M.; Mormann, M.; Bauerfeind, R.; Schmidt, M.A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Karch, H. Promiscuous Shiga toxin 2e and its intimate relationship to Forssman. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, E.K.; Leyva-Illades, D.; Lee, M.-S.; Cherla, R.P.; Tesh, V.L. Differential Response of the Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cell Line HK-2 to Shiga Toxin Types 1 and 2. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, N.K.; Henry, A.C.; Johnson-Henry, K.; Sherman, P.M. Pathogenicity, host responses and implications for management of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 138673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, D.; Grif, K.; Khan, A.B.; Naim, A.; Dierich, M.P.; Würzner, R. The Shiga toxin genotype rather than the amount of Shiga toxin or the cytotoxicity of Shiga toxin in vitro correlates with the appearance of the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 59, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noris, M.; Galbusera, M.; Gastoldi, S.; Macor, P.; Banterla, F.; Bresin, E.; Tripodo, C.; Bettoni, S.; Donadelli, R.; Valoti, E. Dynamics of complement activation in aHUS and how to monitor eculizumab therapy. Blood 2014, 124, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraris, J.; Ferraris, V.; Acquier, A.B.; Sorroche, P.; Saez, M.; Ginaca, A.; Mendez, C.F. Activation of the alternative pathway of complement during the acute phase of typical haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 181, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlenbach, S.; Rosales, A.; Posch, W.; Wilflingseder, D.; Hermann, M.; Brockmeyer, J.; Karch, H.; Satchell, S.C.; Würzner, R.; Orth-Höller, D. Shiga Toxin 2 Reduces Complement Inhibitor CD59 Expression on Human Renal Tubular Epithelial and Glomerular Endothelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poolpol, K.; Orth-Höller, D.; Speth, C.; Zipfel, P.F.; Skerka, C.; de Córdoba, S.R.; Brockmeyer, J.; Bielaszewska, M.; Würzner, R. Interaction of Shiga toxin 2 with complement regulators of the factor H protein family. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 58, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, B.P.; Harris, C.L. Complement, a target for therapy in inflammatory and degenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 857–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapeyraque, A.-L.; Malina, M.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Boppel, T.; Kirschfink, M.; Oualha, M.; Proulx, F.; Clermont, M.-J.; Le Deist, F.; Niaudet, P. Eculizumab in severe Shiga-toxin–associated HUS. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2561–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, D.; Khan, A.B.; Naim, A.; Grif, K.; Brockmeyer, J.; Karch, H.; Joannidis, M.; Clark, S.J.; Day, A.J.; Fidanzi, S.; et al. Shiga Toxin Activates Complement and Binds Factor H: Evidence for an Active Role of Complement in Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, M.; Friec, G.L.; Kemper, C. Complement—Tapping into new sites and effector systems. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, M.; Kemper, C. Keeping It All Going—Complement Meets Metabolism. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, N.S.; Church, S.E.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement System Part I—Molecular Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, A.; Fujiyama, Y.; Sumiyoshi, K.; Hodohara, K.; Hidetoshi, O.; Ochi, Y.; Bamba, T.; Brown, W.R. Modulation of complement C3, C4, and factor B production in human intestinal epithelial cells: Differential effects of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-4. Pathophysiology 1995, 2, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, A.; Fujiyama, Y.; Bamba, T.; Hosoda, S. Differential cytokine regulation of complement C3, C4, and factor B synthesis in human intestinal epithelial cell line, Caco-2. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 4239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lubbers, R.; Van Essen, M.; Van Kooten, C.; Trouw, L. Production of complement components by cells of the immune system. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 188, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauchel, H.; Julen, N.; Lemercier, C.; Daveau, M.; Ozanne, D.; Fontaine, M.; Ripoche, J. Expression of complement alternative pathway proteins by endothelial cells. Differential regulation by interleukin 1 and glucocorticoids. Eur. J. Immunol. 1990, 20, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langeggen, H.; Pausa, M.; Johnson, E.; Casarsa, C.; Tedesco, F. The endothelium is an extrahepatic site of synthesis of the seventh component of the complement system. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 121, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufer, J.; Oren, R.; Goldberg, I.; Horwitz, A.; Kopolovic, J.; Chowers, Y.; Passwell, J.H. Cellular localization of complement C3 and C4 transcripts in intestinal specimens from patients with Crohn’s disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 120, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sünderhauf, A.; Skibbe, K.; Preisker, S.; Ebbert, K.; Verschoor, A.; Karsten, C.M.; Kemper, C.; Huber-Lang, M.; Basic, M.; Bleich, A.; et al. Regulation of epithelial cell expressed C3 in the intestine—Relevance for the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease? Mol. Immunol. 2017, 90, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, P.W.; O’Grady, S.; Pussell, B.A.; Charlesworth, J.A. C3a is made by proximal tubular HK-2 cells and activates them via the C3a receptor. Kidney Int. 1999, 56, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsma, J.S.; Gerritsen, A.F.; De Ley, M.; van Es, L.A.; Daha, M.R. Interferon-γ induces biosynthesis of complement components C2, C4 and factor H by human proximal tubular epithelial cells. Cytokine 1997, 9, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.G.; Feuerstein, B.; Strasser, E.; Hirsch, U.; Schreiner, D.; Schuler, G.; Schuler-Thurner, B. Large-scale generation of mature monocyte-derived dendritic cells for clinical application in cell factories™. J. Immunol. Methods 2002, 268, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.; Parikh, A.A.; Szabo, C.; Fischer, J.E.; Salzman, A.L.; Hasseigren, P.-O. Complement C3 production in human intestinal epithelial cells is regulated by interleukin 1β and tumor necrosis factor α. Arch. Surg. 1997, 132, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lardeux, F.; Torrico, G.; Aliaga, C. Calculation of the ELISA’s cut-off based on the change-point analysis method for detection of Trypanosoma cruzi infection in Bolivian dogs in the absence of controls. Memórias Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2016, 111, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurman, J.M.; Marians, R.; Emlen, W.; Wood, S.; Smith, C.; Akana, H.; Holers, V.M.; Lesser, M.; Kline, M.; Hoffman, C.; et al. Alternative Pathway of Complement in Children with Diarrhea-Associated Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morigi, M.; Galbusera, M.; Gastoldi, S.; Locatelli, M.; Buelli, S.; Pezzotta, A.; Pagani, C.; Noris, M.; Gobbi, M.; Stravalaci, M.; et al. Alternative Pathway Activation of Complement by Shiga Toxin Promotes Exuberant C3a Formation That Triggers Microvascular Thrombosis. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ståhl, A.-l.; Sartz, L.; Karpman, D. Complement activation on platelet-leukocyte complexes and microparticles in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli–induced hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 2011, 117, 5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, B.L.; Ramyar, K.X.; Tzekou, A.; Ricklin, D.; McWhorter, W.J.; Lambris, J.D.; Geisbrecht, B.V. Molecular basis for complement recognition and inhibition determined by crystallographic studies of the staphylococcal complement inhibitor (SCIN) bound to C3c and C3b. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 402, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, O.A.; Nilsson, P.H.; Wouters, D.; Lambris, J.D.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Nilsson, B. Complement component C3 binds to activated normal platelets without preceding proteolytic activation and promotes binding to complement receptor 1. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2686–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xing, G.-Q.; Yu, F.; Liu, G.; Zhao, M.-H. Complement deposition in renal histopathology of patients with ANCA-associated pauci-immune glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, S.H.; Zhou, W.; Andrews, P.A.; Hartley, B. Endogenous complement C3 synthesis in immune complex nephritis. Lancet 1993, 342, 1273–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regele, H.; Böhmig, G.A.; Habicht, A.; Gollowitzer, D.; Schillinger, M.; Rockenschaub, S.; Watschinger, B.; Kerjaschki, D.; Exner, M. Capillary deposition of complement split product C4d in renal allografts is associated with basement membrane injury in peritubular and glomerular capillaries: A contribution of humoral immunity to chronic allograft rejection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, J.R.; Basheer, S.A.; Sacks, S.H. Local synthesis of complement component C3 regulates acute renal transplant rejection. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passwell, J.; Schreiner, G.F.; Nonaka, M.; Beuscher, H.U.; Colten, H.R. Local extrahepatic expression of complement genes C3, factor B, C2, and C4 is increased in murine lupus nephritis. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 82, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, B.; Köhl, J.; Leclercq, W.K.; Wolfs, T.G.; van Bijnen, A.A.; Heeringa, P.; Buurman, W.A. Complement factor C5a mediates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury independent from neutrophils. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3883–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feucht, H.E.; Zwirner, J.; Bevec, D.; Lang, M.; Felber, E.; Riethmüller, G.; Weiss, E.H. Biosynthesis of Complement C4 Messenger RNA in Normal Human Kidney. Nephron 1989, 53, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, P.A.; Finn, J.E.; Lloyd, C.M.; Zhou, W.; Mathieson, P.W.; Sacks, S.H. Expression and tissue localization of donor-specific complement C3 synthesized in human renal allografts. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyam, A.; Kannan, L.; Matsumoto, N.; Geha, M.; Lapchak, P.H.; Bosse, R.; Shi, G.-P.; Dalle Lucca, J.J.; Tsokos, M.G.; Tsokos, G.C. Intracellular Activation of Complement 3 Is Responsible for Intestinal Tissue Damage during Mesenteric Ischemia. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigotti, M.; Orth-Höller, D.; Carnicelli, D.; Porcellini, E.; Galassi, E.; Tazzari, P.L.; Ricci, F.; Manoli, F.; Manet, I.; Talasz, H. The structure of the Shiga toxin 2a A-subunit dictates the interactions of the toxin with blood components. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matussek, A.; Lauber, J.; Bergau, A.; Hansen, W.; Rohde, M.; Dittmar, K.E.; Gunzer, M.; Mengel, M.; Gatzlaff, P.; Hartmann, M. Molecular and functional analysis of Shiga toxin–induced response patterns in human vascular endothelial cells. Blood 2003, 102, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, K.A.; Lagerlund, I.; Chamow, S.M. A simple, two-component buffer enhances use of chromatofocusing for processing of therapeutic proteins. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1999, 62, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, W.; Watrach, A.; Schmale, J.; Schultz, R.; Harris, J. Cultural and antigenic properties of newly established cell strains derived from adenocarcinomas of the human colon and rectum. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1974, 52, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, P.; Koppelstaetter, C.; Aydin, S.; Abberger, T.; Wolf, A.M.; Mayer, G.; Pfaller, W. Cyclosporine A induces senescence in renal tubular epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2007, 293, F831–F838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Gene Name | Gene Symbol | Assay ID |
|---|---|---|
| Topoisomerase (DNA) II beta | TOP2B | Hs00172259_m1 |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | GAPDH | Hs02786624_g1 |
| Complement component 3 | C3 | Hs00163811_m1 |
| Complement component 5 | C5 | Hs01004342_m1 |
| Complement factor H | CFH | Hs00962373_m1 |
| Complement factor I | CFI | Hs 00989715_m1 |
| Complement factor B | CFB | Hs00156060_m1 |
| Complement factor P | CFP | Hs01106971_g1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kellnerová, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Bayarri-Olmos, R.; Justesen, L.; Talasz, H.; Posch, W.; Kenno, S.; Garred, P.; Orth-Höller, D.; Grasse, M.; et al. Shiga Toxin 2a Binds to Complement Components C3b and C5 and Upregulates Their Gene Expression in Human Cell Lines. Toxins 2021, 13, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010008
Kellnerová S, Chatterjee S, Bayarri-Olmos R, Justesen L, Talasz H, Posch W, Kenno S, Garred P, Orth-Höller D, Grasse M, et al. Shiga Toxin 2a Binds to Complement Components C3b and C5 and Upregulates Their Gene Expression in Human Cell Lines. Toxins. 2021; 13(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleKellnerová, Sára, Sneha Chatterjee, Rafael Bayarri-Olmos, Louise Justesen, Heribert Talasz, Wilfried Posch, Samyr Kenno, Peter Garred, Dorothea Orth-Höller, Marco Grasse, and et al. 2021. "Shiga Toxin 2a Binds to Complement Components C3b and C5 and Upregulates Their Gene Expression in Human Cell Lines" Toxins 13, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010008
APA StyleKellnerová, S., Chatterjee, S., Bayarri-Olmos, R., Justesen, L., Talasz, H., Posch, W., Kenno, S., Garred, P., Orth-Höller, D., Grasse, M., & Würzner, R. (2021). Shiga Toxin 2a Binds to Complement Components C3b and C5 and Upregulates Their Gene Expression in Human Cell Lines. Toxins, 13(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010008





