Dihydrodinophysistoxin-1 Produced by Dinophysis norvegica in the Gulf of Maine, USA and Its Accumulation in Shellfish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
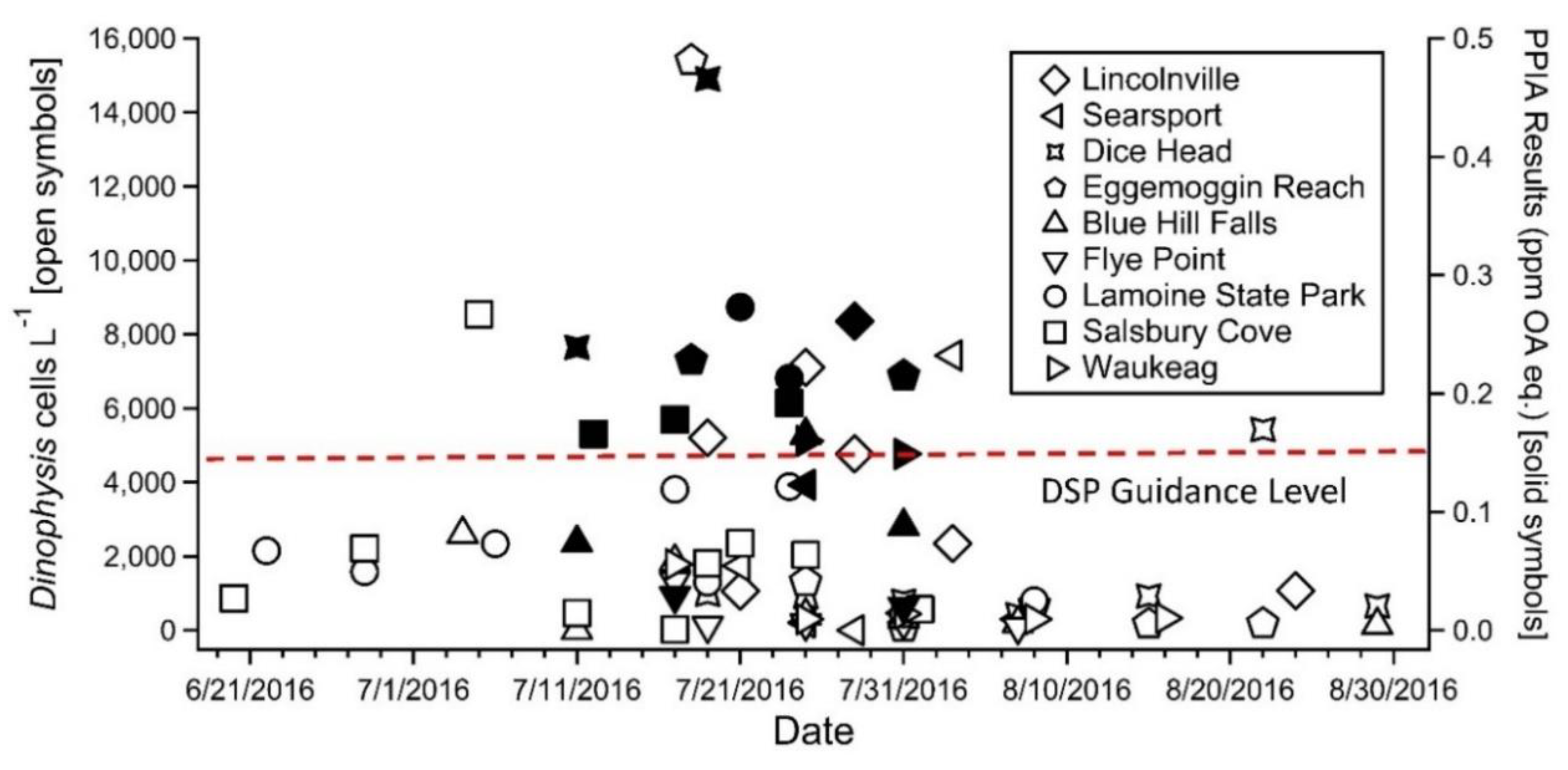
2.1. Initial Testing of Shellfish Collected during the 2016 D. norvegica Bloom in the Gulf of Maine
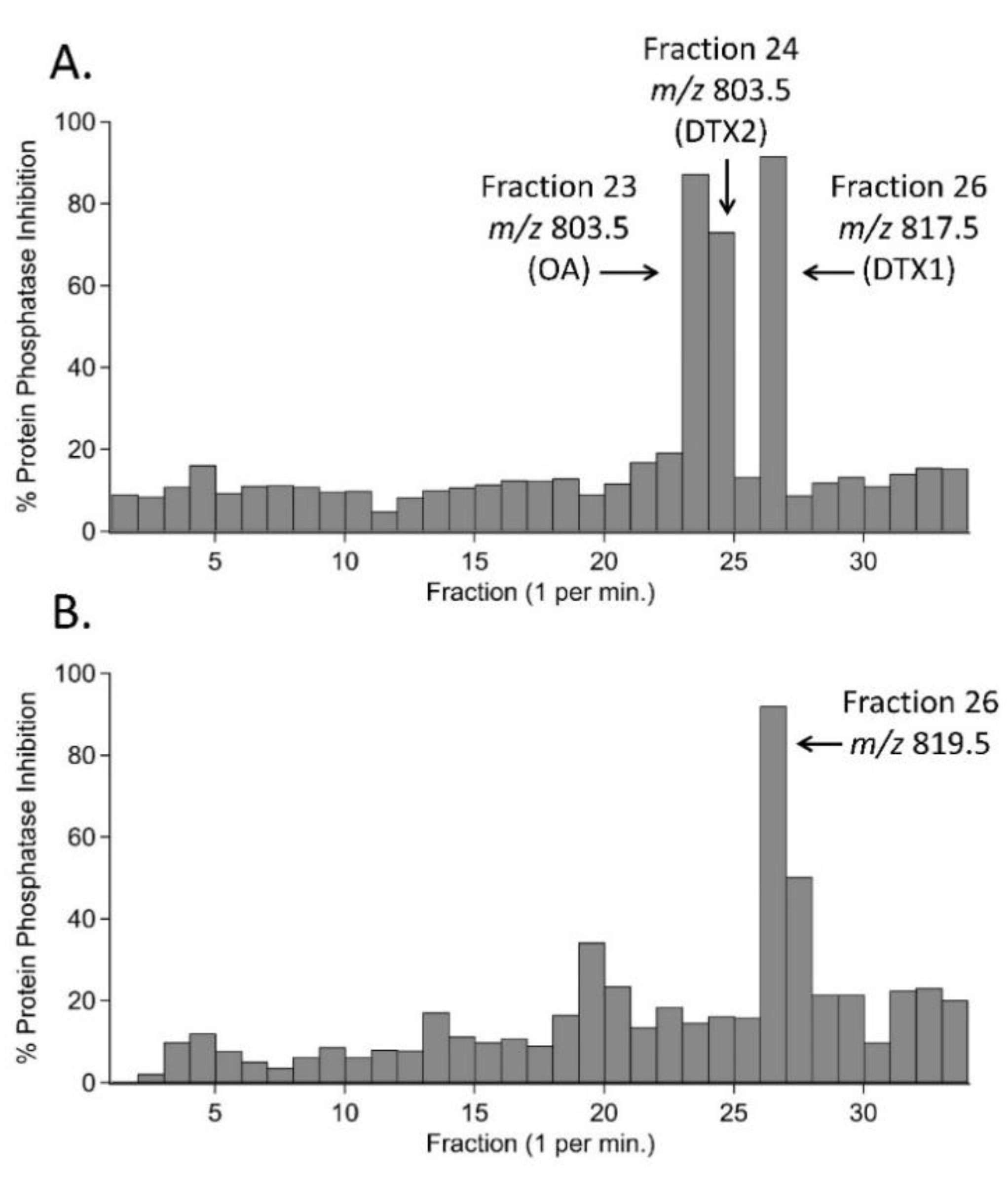
2.2. Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation
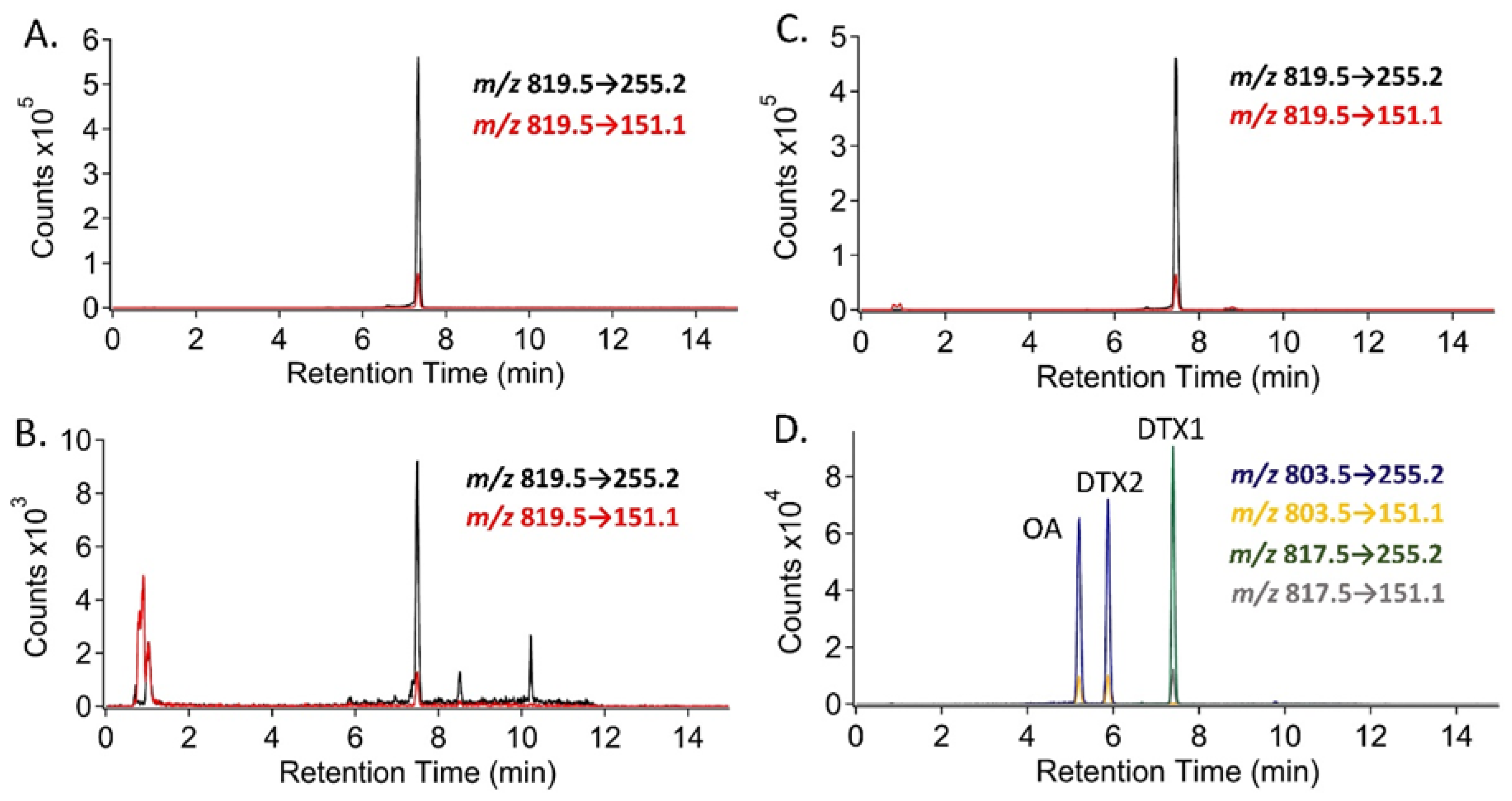
2.3. Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS) Measurements of the PPIA Active Fraction
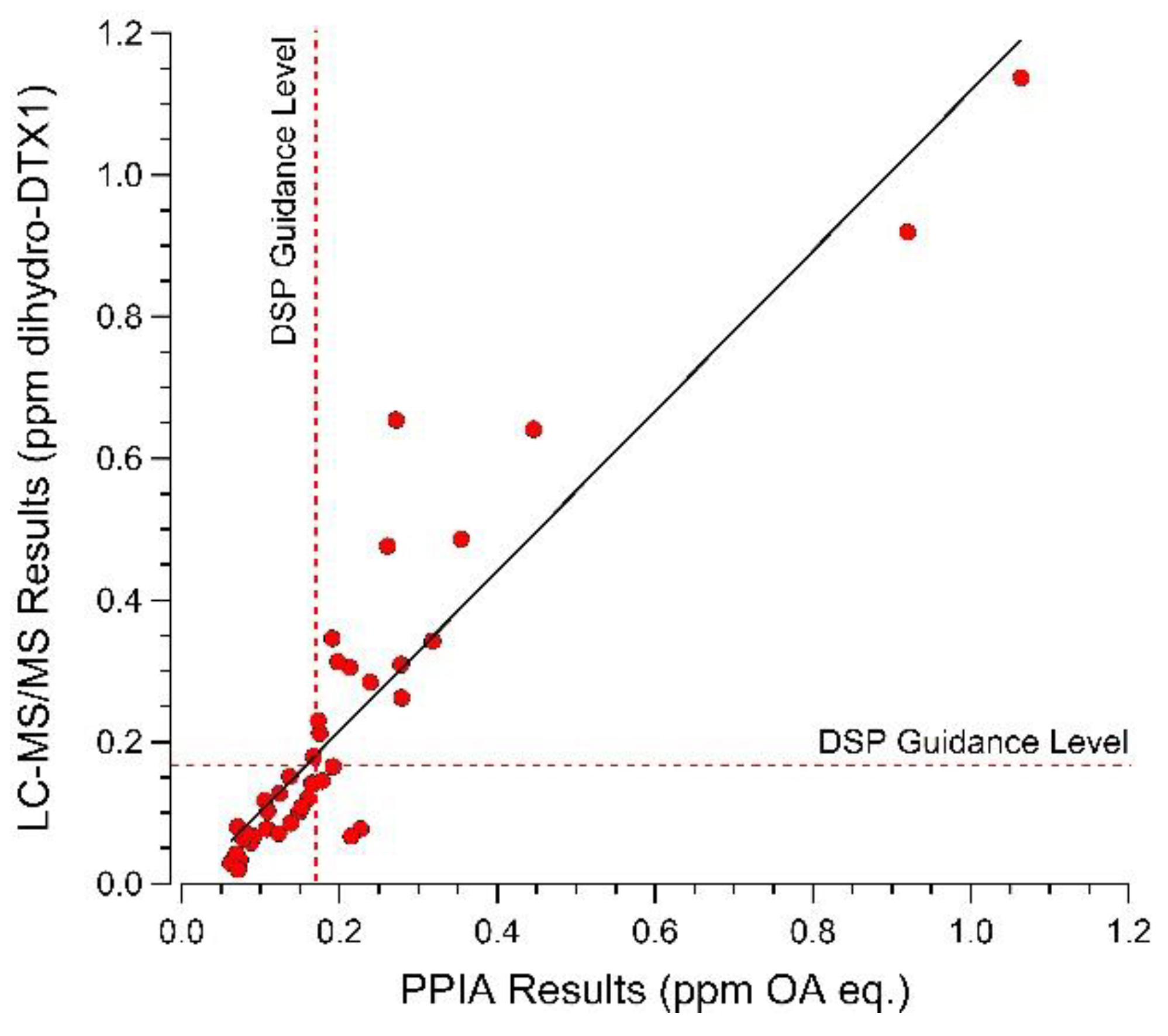
2.4. Selected Reaction Monitoring (SRM) Analysis for DSP Toxins and Dihydro-DTX1 in Water and Shellfish Samples and Comparison with PPIA
2.5. Production of Dihydro-DTX1 in a Culture of Gulf of Maine D. norvegica
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Phytoplankton and Shellfish Sampling
4.2. Standards and Reagents
4.3. Commercial Test Kits
4.4. Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation
4.5. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
4.5.1. Lipophilic Toxin Screening by Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS) Analysis
4.5.2. Q1 Scanning and MS/MS Analysis of the Unknown DST-Like Compound
4.5.3. LC-HRMS Analysis of Dihydrodinophysistoxin-1
4.5.4. LC-MS/MS Selected Reaction Monitoring (SRM) Analysis for OA, DTX1, DTX2, and Dihydro-DTX1
4.6. Analysis of Gulf of Maine Shellfish for Dihydro-DTX1 by LC-MS/MS SRM and Comparison with PPIA
4.7. Testing of a Gulf of Maine Dinophysis norvegica Culture for DST Production
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campbell, L.; Olson, R.J.; Sosik, H.M.; Abraham, A.; Henrichs, D.W.; Hyatt, C.J.; Buskey, E.J. First harmful Dinophysis (Dinophyceae, Dinophysiales) bloom in the U.S. revealed by automated imaging flow cytometry. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeds, J.R.; Wiles, K.; Heideman, G.B., VI; White, K.D.; Abraham, A. First US report of shellfish harvesting closures due to confirmed okadaic acid in Texas Gulf coast oysters. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.K.; Duchin, J.S.; Borchert, J.; Flores Quintana, H.; Robertson, A. Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning, Washington, USA, 2011. Emerg. Infec. Dis. 2013, 19, 1314–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, V.L.; Moore, L.; Bill, B.D.; Adams, N.G.; Harrington, N.; Borchert, J.; da Silva, D.A.M.; Eberhart, B.L. Diarrhetic shellfish toxins and other lipophilic toxins of human health concern in Washington State. Mar. Drugs. 2013, 11, 1815–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tango, P.; Butler, W.; Lacouture, R.; Goshorn, D.; Magnien, R.; Michael, B.; Hall, S.; Browhawn, K.; Wittman, R.; Beatty, W. An unprecedented bloom of Dinophysis acuminata in Chesapeake Bay. In Harmful Algae 2002; Steidinger, K.A., Landsberg, J.H., Tomas, C.R., Vargo, G.A., Eds.; Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, Florida Institute of Oceanography, and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 358–360. [Google Scholar]
- Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Marcoval, M.A.; Berry, D.L.; Fire, S.; Wang, Z.; Morton, S.L.; Gobler, C.J. The emergence of Dinophysis acuminata blooms and DSP toxins in shellfish in New York waters. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolny, J.L.; Egerton, T.A.; Handy, S.M.; Stutts, W.L.; Smith, J.L.; Whereat, E.B.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Henrichs, D.W.; Campbell, L.; Deeds, J.D. Characterization of Dinophysis spp. (Dinophyceae, Dinophysiales) from the mid-Atlantic region of the US. J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 404–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendong, Z.; Sibat, M.; Herrenknecht, C.; Hess, P.; McCarron, P. Relative molar response of lipophilic marine algal toxins in liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid. Comm. Mass Spec. 2017, 31, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yamaguchi, H. Occurrence of a new type of shellfish poisoning in the Tohoku district. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1978, 44, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Sugawara, W.; Fukuyo, Y.; Oguri, H.; Igarashi, T.; Fujita, N. Identification of Dinophysis firtii as the causative organism of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish 1980, 46, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, F.J.; Prasad, R.S.; Gopichand, Y.; Hossain, M.B.; van der Helm, D. Acanthifolicin, a new episulfide-containing polyether carboxylic acid from extracts of the marine sponge Pandaros acanthifolium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 2467–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibami, K.; Scheuer, P.J.; Tsukitani, Y.; Kikuchi, H.; Van Engen, D.; Clardy, J.; Gopichand, Y.; Schmitz, F.J. Okadaic acid, a cytotoxic polyether from two marine sponges of the genus Halichondria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 2469–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Shimatani, M.; Sugitani, H.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and structural elucidation of the causative toxin of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1982, 48, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Identification of Okadaic acid as a toxic component of a marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish 1982, 48, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Murata, M.; Oshima, Y.; Sano, M. Diarrhetic shellfish toxins. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagi, M.; Yanagi, T.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Kat, M.; Lassus, P.; Rodriguez-Vasquez, J.A. Okadaic acid as the causative toxin of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in Europe. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 2853–2857. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Doyle, J.; Jackson, D.; Marr, J.; Nixon, E.; Pleasance, S.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Isolation of a new diarrhetic shellfish poison from Irish mussels. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 1, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, F.J.; Yasumoto, T. The 1990 United States—Japan seminar on bioorganic marine chemistry, meeting report. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 1469–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lee, F.C.; Khoo, H.W.; Ming Teo, S.L. Production of 7-deoxy-okadaic acid by a New Caledonian strain of Prorocentrum lima (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2001, 37, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, P.G.; Hernández Daranas, A.; Fernández, J.J.; Norte, M. 19-epi-okadaic acid, A novel protein phosphatase inhibitor with enhanced selectivity. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 3045–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, D.G.; Crain, S.; Lewis, N.; LaBlanc, P.; Hardstaff, W.R.; Perez, R.A.; Giddings, S.D.; Martinez-Farina, C.E.; Stefanova, R.; Burtan, I.W.; et al. Development of certified reference materials for diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins. Part 1: Calibration solutions. J. AOAC Int. 2016, 99, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, A.; Murata, M.; Torigoe, K.; Isobe, M.; Mieskes, G.; Yasumoto, T. Inhibitory effect of okadaic acid derivatives on protein phosphatases. Biochem. J. 1992, 284, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, R.; Rinehart, K.L. A new polyether acid from a cold water marine sponge, a Phykellia species. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, D.V.S.; Pan, Y.; Zitko, V.; Bugden, G.; Mackeigan, K. Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) associated with a subsurface bloom of Dinophysis norvegica in Bedford Basin, eastern Canada. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 97, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Marr, J.C.; Jackson, A.E.; McLachlan, J.L. Occurrence of Prorocentrum lima, a DSP toxin-producing species from the Atlantic coast of Canada. J. Appl. Phycol. 1992, 4, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilliam, M.A.; Gilgan, M.W.; Pleasance, S.; de Freitas, A.S.W.; Douglas, D.; Fritz, L.; Hu, T.; Marr, J.C.; Smyth, C.; Wright, J.L.C. Confirmation of an incident of diarrhatic shellfish poisoning in eastern Canada. In Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea; Smayda, T.J., Shimizu, Y., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 547–552. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, S.A.; Leighfield, T.A.; Haynes, B.L.; Petitpain, D.L.; Busman, M.A.; Moeller, P.D.R.; Bean, L.; McGowan, J.; Hurst, J.W., Jr.; Van Dolah, F.M. Evidence of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning along the coast of Maine. J. Shellfish Res. 1999, 18, 681–686. [Google Scholar]
- Maranda, L.; Corwin, S.; Hargraves, P.E. Prorocentrum lima (Dinophyceae) in northeastern USA coastal waters: I. Abundance and distribution. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranda, L.; Corwin, S.; Dover, S.; Morton, S.L. Prorocentrum lima (Dinophyceae) in northeastern USA coastal waters: II. Toxin loads in the epibiota and in shellfish. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSSP (National Shellfish Sanitation Program). Guide for the Control of Molluscan Shellfish: 2017 Revision. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/Food/GuidanceRegulation/FederalStateFoodPrograms/ucm2006754.htm (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- Botana, L.M.; Hess, P.; Munday, R.; Nathalie, A.; Degrasse, S.L.; Feeley, M.; Suzuki, T.; van der Berg, M.; Fattori, V.; Gamarro, E.G.; et al. Derivation of toxicity equivalency factors for marine biotoxins associated with bivalve molluscs. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2017, 59, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, D.; Campbell, L.; Kudela, R.M. Trends in Dinophysis adundance and diarrhetic shellfish toxin levels in California mussels (Mytilus californianus) from Monterey Bay, California. Harmful Algae 2019, 88, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séchet, V.; Safran, P.; Hovgaard, P.; Yasumoto, T. Causative species of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) in Norway. Mar. Biol. 1990, 105, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Janson, S.; Boje, R.; Pollehne, P.; Chang, J. The dinoflagellate Dinophysis norvegica: Biological and ecological observations in the Baltic Sea. Eur. J. Phycol. 1995, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, B.; Velo-Suárez, L.; Raine, R.; Park, M.G. Harmful Dinophysis species: A review. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, B.; Riobó, P.; Rodriguez, F.; Díaz, P.A.; Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M.; Blanco, J. Dinophysis toxins: Causative organisms, distribution, and fate in shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 394–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Samdall, I.A.; Sandvik, M.; Petersen, D.; Quilliam, M.A.; Naustvoll, L.J.; Rundberget, T.; Torgersen, T.; Hovgaard, P.; et al. A novel pectenotoxin, PTX-12, in Dinophysis Spp. and shellfish in Norway. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Miyazono, A.; Baba, K.; Sugawara, R.; Kamiyama, T. LC-MS/MS analysis of okadaic acid analogs and other lipophilic toxins in single-cell isolates of several Dinophysis species collected in Hokkaido, Japan. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, C.F.B. Liquid chromatography-linked protein phosphatase bioassay; a highly sensitive marine bioscreen for okadaic acid and related diarrhetic shellfish toxins. Toxicon 1991, 29, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, P.; Wright, E.; Quilliam, M.A. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry of domoic acid and lipophilic shellfish toxins with selected reaction monitoring and optional confirmation by library searching of product ion spectra. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blay, P.; Hui, J.P.M.; Chang, J.M.; Melanson, J.E. Screening for multiple classes of marine biotoxins by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Method for the Determination of Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning (DSP) Toxins in Shellfish. Available online: http://www.issc.org/Data/Sites/1/media/00-2017biennialmeeting/--taskforcei2017/17-103-supporting-documentation.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- Tong, M.; Kulis, D.M.; Fux, E.; Smith, J.L.; Hess, P.; Zhou, Q.; Anderson, D.M. The effects of growth phase and light intensity on toxin production by Dinophysis acuminata from the northeastern United States. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitani, G.O.H.; Nagai, S.; Sakiyama, S.; Kamiyama, T. Successful cultivation of the toxic dinoflagellate Dinophysis caudata (Dinophyceae). Plankton Benthos Res. 2008, 3, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.G.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.S.; Myung, G.; Kang, Y.G.; Yih, W. First successful culture of the marine dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuminata. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 45, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, J.D.; Tong, M.; Kulis, D.M.; Fux, E.; Hess, P.; Bire, R.; Anderson, D.M. DSP toxin production de novo in cultures of Dinophysis acuminata (Dinophyceae) from North America. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Kulis, D.M.; Doucette, G.J.; Gallagher, J.C.; Balech, E. Biogeography of toxic dinoflagellates in the genus Alexandrium from the northeastern United States and Canada. Mar. Biol. 1994, 120, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Lusty, M.W.; Wallace, R.B.; Haynes, B.; Wang, Z.; Broadwater, M.; Deeds, J.R.; Morton, S.L.; Hastback, W.; Porter, L.; et al. Evaluation of Rapid, Early Warning Approaches to Track Shellfish Toxins Associated with Dinophysis and Alexandrium Blooms. Marine Drugs 2018, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onofrio, M.D.; Mallet, C.R.; Place, A.R.; Smith, J.L. A screening tool for the direct analysis of marine and freshwater phycotoxins in organic SPATT extracts from the Chesapeake Bay. Toxins 2020, 12, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ] Dice Head, [⬠] Eggemoggin Reach, [△] Blue Hill Falls, [▽] Flye Point, [◯] Lamoine State Park, [☐] Salsbury Cove, [▷] Waukeag. Numbers indicate shellfish sampling only and correspond to data in Table 1: (1) Stinson Neck Causeway, (2) Oak Point, (3) Pretty Marsh Harbor, (4) Trenton Sea Plane Ramp, (5) Googins Ledge, (6,7) Bar Harbor, (8) Raccoon Cove, (9,10) Lumbo’s Hole (control site outside of bloom area). Abbreviations: ME—Maine, NH—New Hampshire, MA—Massachusetts. Sampling site coordinates provided in Table S1.
] Dice Head, [⬠] Eggemoggin Reach, [△] Blue Hill Falls, [▽] Flye Point, [◯] Lamoine State Park, [☐] Salsbury Cove, [▷] Waukeag. Numbers indicate shellfish sampling only and correspond to data in Table 1: (1) Stinson Neck Causeway, (2) Oak Point, (3) Pretty Marsh Harbor, (4) Trenton Sea Plane Ramp, (5) Googins Ledge, (6,7) Bar Harbor, (8) Raccoon Cove, (9,10) Lumbo’s Hole (control site outside of bloom area). Abbreviations: ME—Maine, NH—New Hampshire, MA—Massachusetts. Sampling site coordinates provided in Table S1.
 ] Dice Head, [⬠] Eggemoggin Reach, [△] Blue Hill Falls, [▽] Flye Point, [◯] Lamoine State Park, [☐] Salsbury Cove, [▷] Waukeag. Numbers indicate shellfish sampling only and correspond to data in Table 1: (1) Stinson Neck Causeway, (2) Oak Point, (3) Pretty Marsh Harbor, (4) Trenton Sea Plane Ramp, (5) Googins Ledge, (6,7) Bar Harbor, (8) Raccoon Cove, (9,10) Lumbo’s Hole (control site outside of bloom area). Abbreviations: ME—Maine, NH—New Hampshire, MA—Massachusetts. Sampling site coordinates provided in Table S1.
] Dice Head, [⬠] Eggemoggin Reach, [△] Blue Hill Falls, [▽] Flye Point, [◯] Lamoine State Park, [☐] Salsbury Cove, [▷] Waukeag. Numbers indicate shellfish sampling only and correspond to data in Table 1: (1) Stinson Neck Causeway, (2) Oak Point, (3) Pretty Marsh Harbor, (4) Trenton Sea Plane Ramp, (5) Googins Ledge, (6,7) Bar Harbor, (8) Raccoon Cove, (9,10) Lumbo’s Hole (control site outside of bloom area). Abbreviations: ME—Maine, NH—New Hampshire, MA—Massachusetts. Sampling site coordinates provided in Table S1.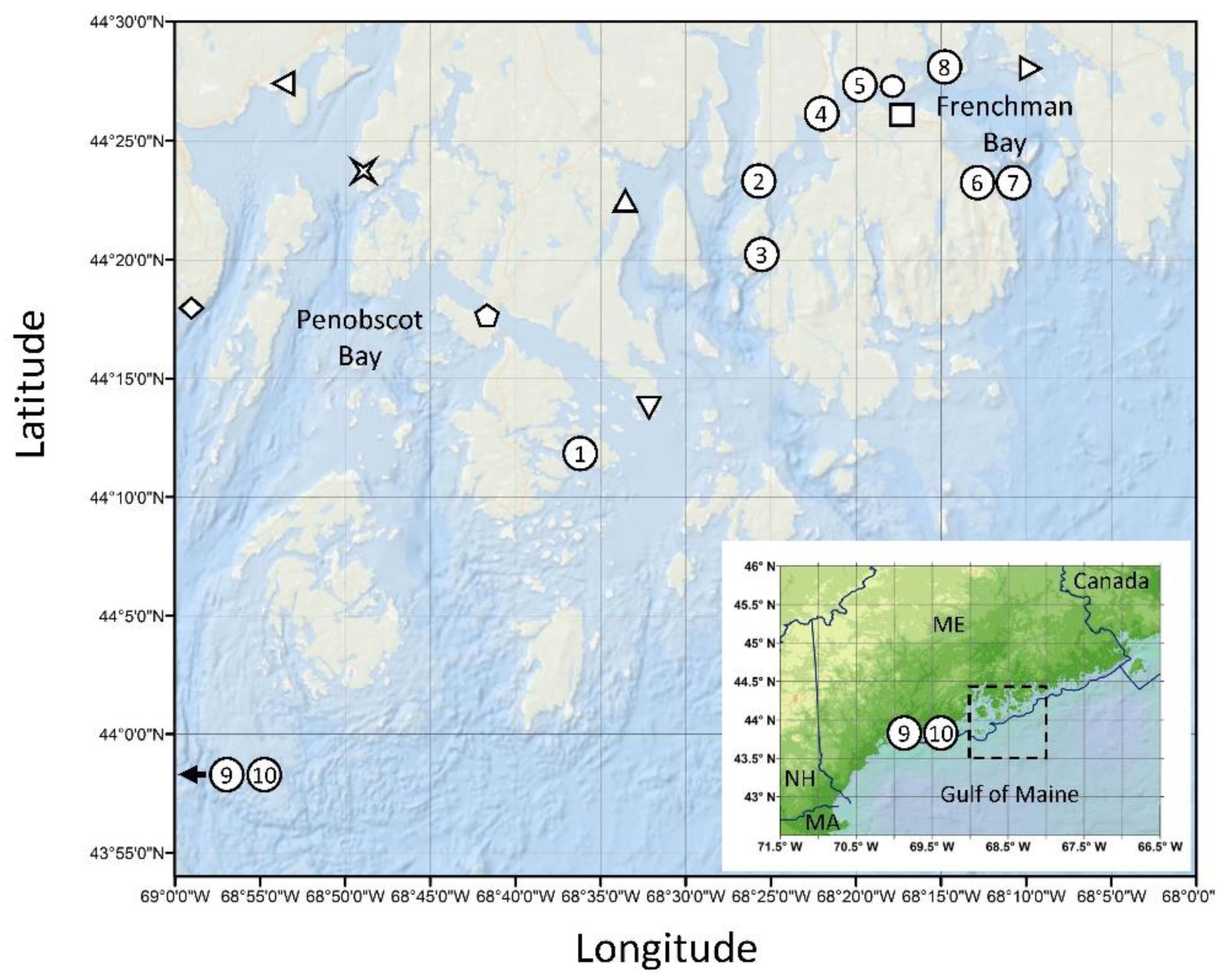


| Sample a | PPIA | ELISA | LC-MS/MS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative | Quantitative | OA, DTX1, DTX2 | Dihydro-DTX1 b | ||
| 1 | 0.20 | Positive | 0.24 | ND | 0.24 |
| 2 | >0.35 | Positive | 0.67 | ND | 1.08 |
| 3 | 0.08 | Negative | 0.08 | ND | 0.06 |
| 4 | 0.10 | Negative | 0.07 | ND | 0.07 |
| 5 | 0.28 | Positive | 0.34 | ND | 0.79 |
| 6 | 0.17 | Positive | 0.16 | ND | 0.20 |
| 7 | 0.19 | Negative | 0.14 | ND | 0.21 |
| 8 | 0.14 | Negative | 0.15 | ND | 0.16 |
| 9 | <0.06 | Negative | <LOD | ND | ND |
| 10 | <0.06 | Negative | 0.06 | 0.04 DTX1 | Trace |
| Isolate | dihydro-DTX1 (ppb) | PTX2 (ppb) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intracellular | Extracellular | Intracellular | Extracellular | |||||
| Free | Esterified | Total | Free | Esterified | Total | |||
| DNBH-FB4 | 1 | 60.6 | 61.5 | 1.3 | 5.3 | 6.5 | 36.3 | 3.9 |
| DNBH-B3F | 0.5 | 43.1 | 43.6 | 1.4 | 7.1 | 8.5 | 26.5 | 2.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deeds, J.R.; Stutts, W.L.; Celiz, M.D.; MacLeod, J.; Hamilton, A.E.; Lewis, B.J.; Miller, D.W.; Kanwit, K.; Smith, J.L.; Kulis, D.M.; et al. Dihydrodinophysistoxin-1 Produced by Dinophysis norvegica in the Gulf of Maine, USA and Its Accumulation in Shellfish. Toxins 2020, 12, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12090533
Deeds JR, Stutts WL, Celiz MD, MacLeod J, Hamilton AE, Lewis BJ, Miller DW, Kanwit K, Smith JL, Kulis DM, et al. Dihydrodinophysistoxin-1 Produced by Dinophysis norvegica in the Gulf of Maine, USA and Its Accumulation in Shellfish. Toxins. 2020; 12(9):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12090533
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeeds, Jonathan R., Whitney L. Stutts, Mary Dawn Celiz, Jill MacLeod, Amy E. Hamilton, Bryant J. Lewis, David W. Miller, Kohl Kanwit, Juliette L. Smith, David M. Kulis, and et al. 2020. "Dihydrodinophysistoxin-1 Produced by Dinophysis norvegica in the Gulf of Maine, USA and Its Accumulation in Shellfish" Toxins 12, no. 9: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12090533
APA StyleDeeds, J. R., Stutts, W. L., Celiz, M. D., MacLeod, J., Hamilton, A. E., Lewis, B. J., Miller, D. W., Kanwit, K., Smith, J. L., Kulis, D. M., McCarron, P., Rauschenberg, C. D., Burnell, C. A., Archer, S. D., Borchert, J., & Lankford, S. K. (2020). Dihydrodinophysistoxin-1 Produced by Dinophysis norvegica in the Gulf of Maine, USA and Its Accumulation in Shellfish. Toxins, 12(9), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12090533





