Effects of Peptidoglycan, Lipoteichoic Acid and Lipopolysaccharide on Inflammation, Proliferation and Milk Fat Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
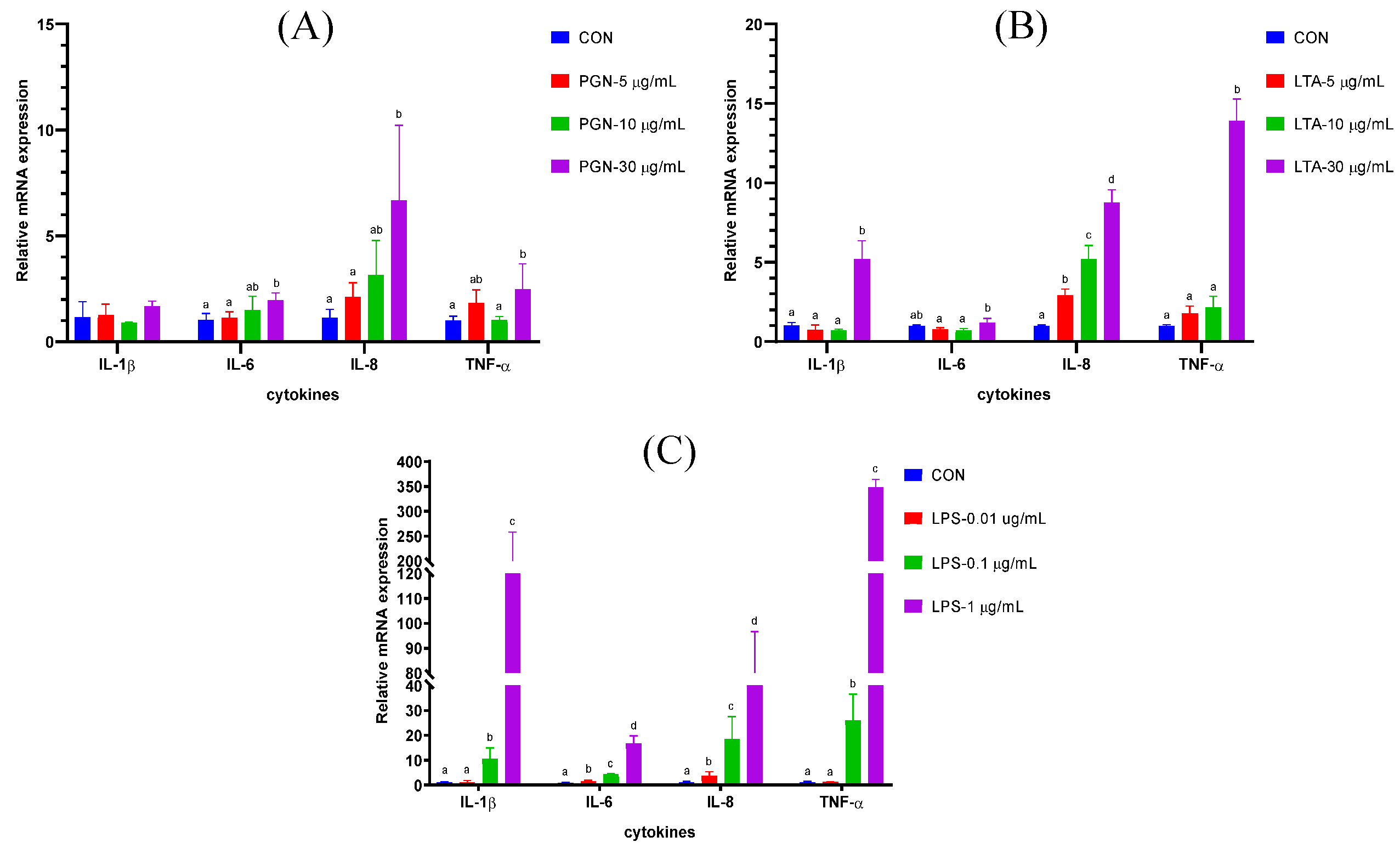
2.1. The Effects of Various Concentrations of PGN, LTA and LPS on Gene Expression of Cytokines in BMECs
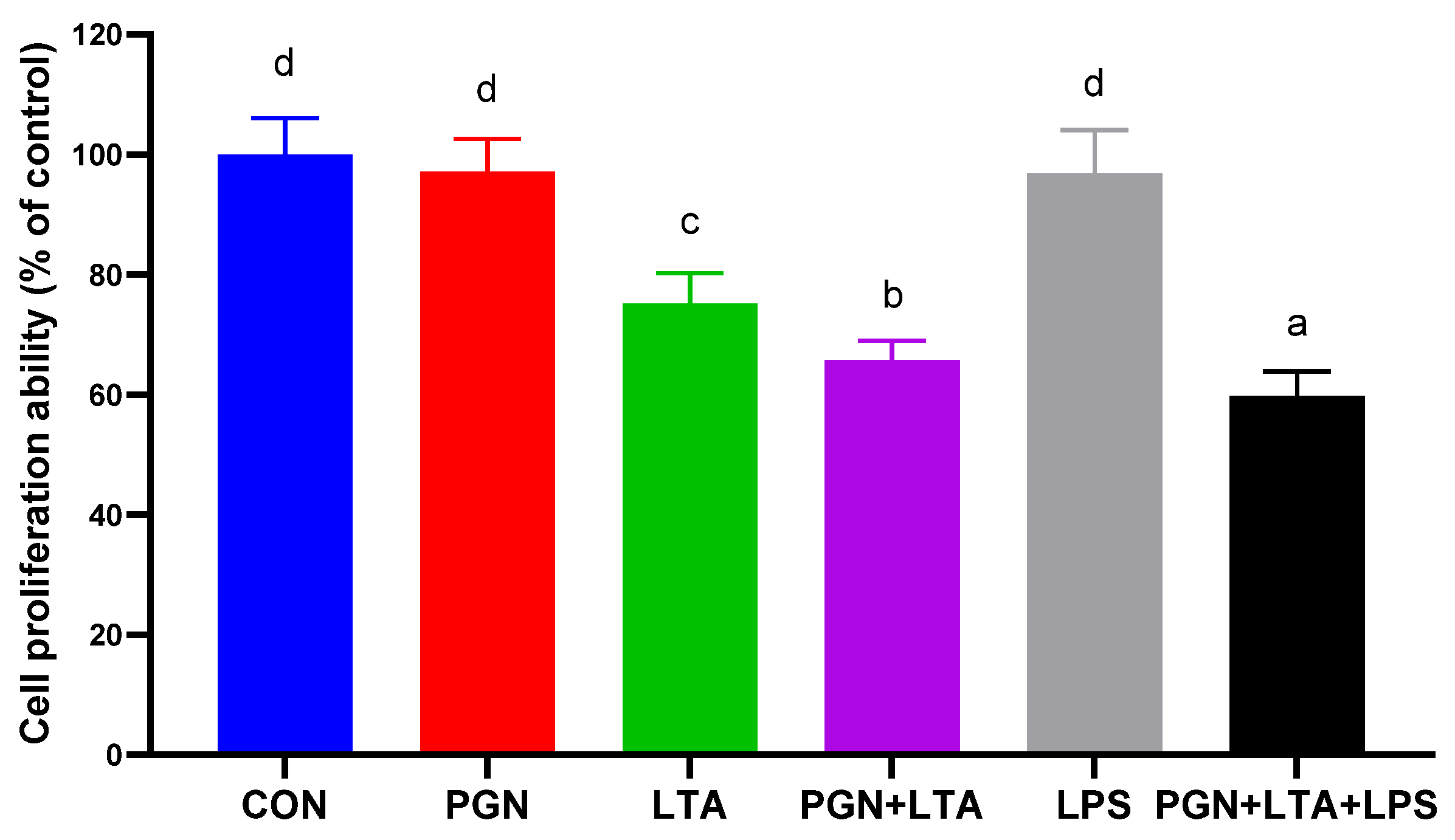
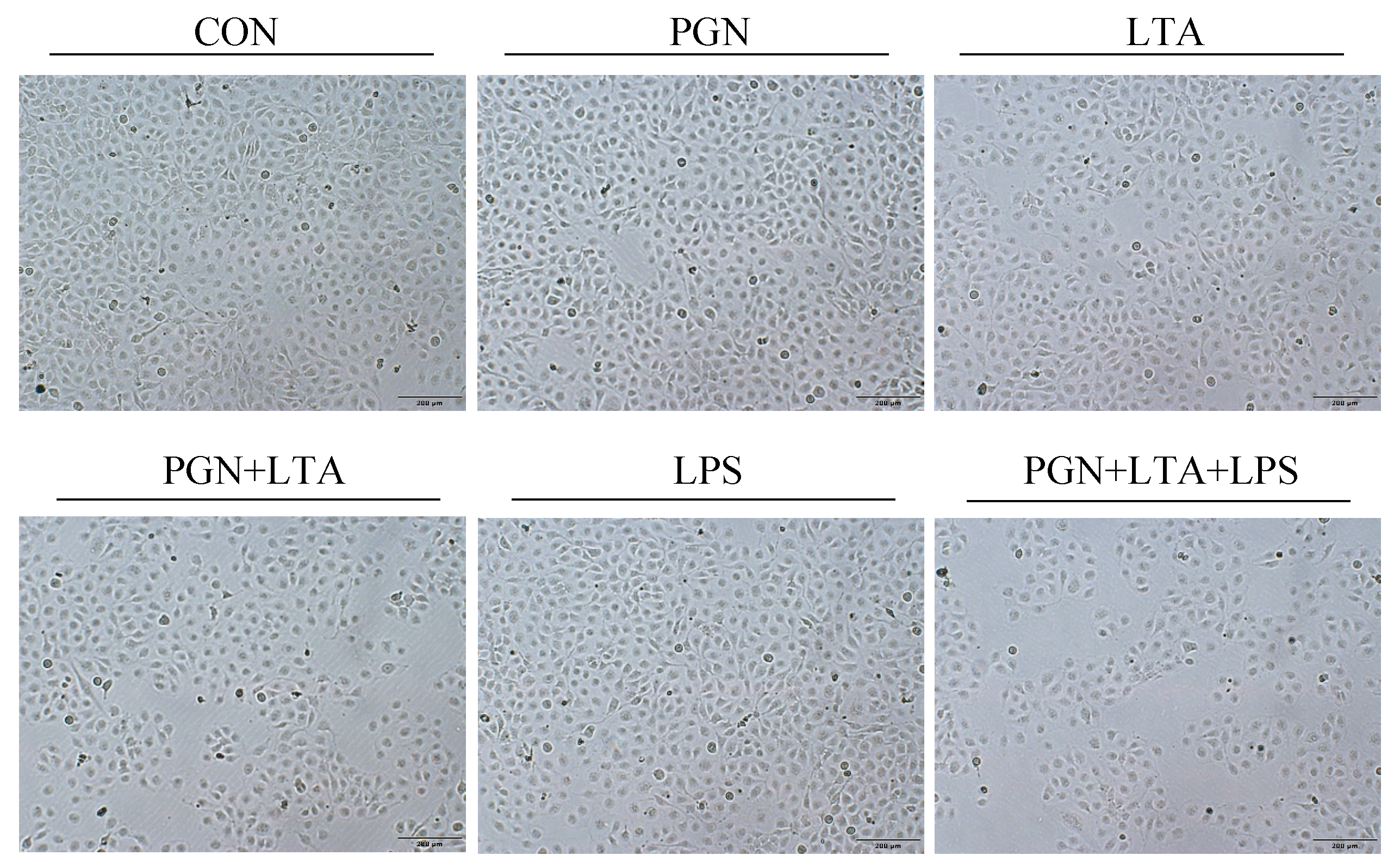
2.2. The Effects of PGN, LTA and LPS on Proliferation of BMECs
2.3. The Effects of PGN, LTA and LPS on Milk Fat Synthesis
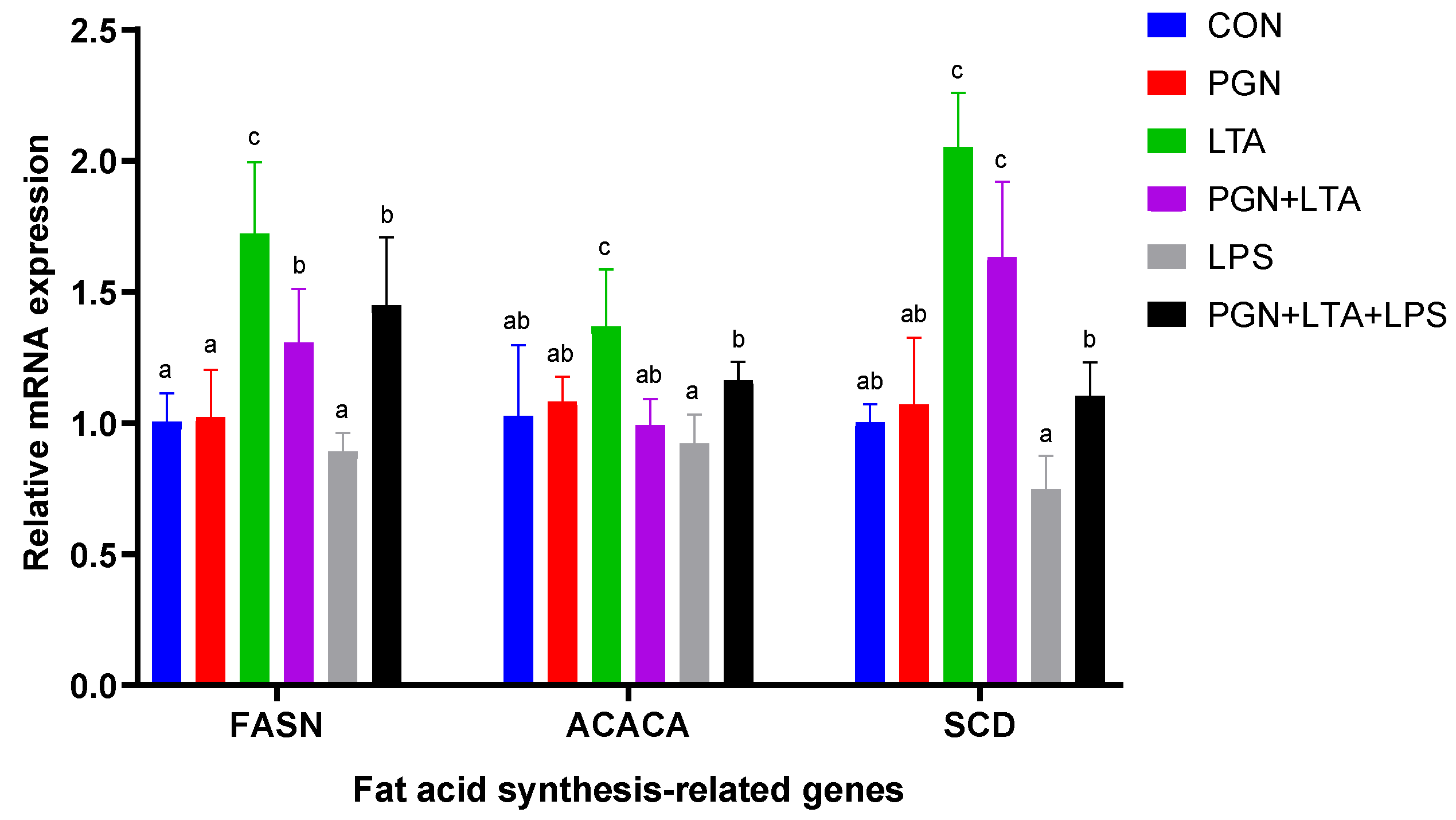
2.3.1. The Effects of PGN, LTA and LPS on the Expression of Fat Acid Synthesis-Related Genes
2.3.2. The Effects of PGN, LTA and LPS on the Content of Intracellular NEFAs and TG
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
5.2. Total RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription, and RT-qPCR
5.3. Cell Proliferation Assay and Morphology Observation
5.4. Intracellular NEFAs and TG Detection
5.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Viguier, C.; Arora, S.; Gilmartin, N.; Welbeck, K.; O’Kennedy, R. Mastitis detection: Current trends and future perspectives. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szyda, J.; Mielczarek, M.; Fraszczak, M.; Minozzi, G.; Williams, J.L.; Maksymiec, K.W. The genetic background of clinical mastitis in holstein-friesian cattle. Animal 2019, 13, 2156–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasawa, Y.; Kiku, Y.; Sugawara, K.; Tanabe, F.; Hayashi, T. Exfoliation rate of mammary epithelial cells in milk on bovine mastitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus is associated with bacterial load. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.J.; Lian, S.; Zhang, X.; Hao, D.D.; Shan, X.F.; Wang, D.; Sun, D.B.; Wu, R.; Wang, J.F. Contribution of PPAR gamma in modulation of LPS-induced reduction of milk lipid synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2019, 22, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Yan, S.; Sheng, R.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X. Effects of saturated long-chain fatty acid on mRNA expression of genes associated with milk fat and protein biosynthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, B.M.; Reigan, P.; Combs, K.D.M.; Orlicky, D.J.; McManaman, J.L. Determinants of adipophilin function in milk lipid formation and secretion. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zowalaty, A.E.E.; Li, R.; Chen, W.; Ye, X. Seipin deficiency leads to increased endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in mammary gland alveolar epithelial cells during lactation. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 98, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Wang, Y.Z.; Loor, J.J.; Bucktrout, R.; Shu, X.; Jia, H.D.; Dong, J.H.; Zuo, R.K.; Liu, G.W.; Li, X.B.; et al. High expression of cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector a (CIDEA) promotes milk fat content in dairy cows with clinical ketosis. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1682–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, B. Integrated analysis of the gene expression profile and DNA methylation profile of obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7636–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, R.; Yan, S.M.; Qi, L.Z.; Zhao, Y.L. Effect of the ratios of unsaturated fatty acids on the expressions of genes related to fat and protein in the bovine mammary epithelial cells. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2015, 51, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, R.; Yan, S.M.; Qi, L.Z.; Zhao, Y.L.; Jin, L.; Guo, X.Y. Effect of the ratios of acetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate on the expression of milk fat and protein-related genes in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 60, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Tang, S.; Zhou, C.; Han, X.; Tan, Z. Effects of free fatty acids with different chain lengths and degrees of saturability on the milk fat synthesis in primary cultured bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8485–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, R.K.; Hundal, J.S.; Wadhwa, M.; Choudhary, S.; Neetika. Expression of lipogenic and milk protein genes in milk fat layer of goat after dietary supplementation of omega-3 rich linseed and chia oils. Small Rumin. Res. 2020, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanos, R.; Murray, I.A.; Smith, P.B.; Patterson, A.; Perdew, G.H. Role of the AH receptor in homeostatic control of fatty acid synthesis in the liver. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 129, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Deng, Z.S.; Shi, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.Y.; Zhong, S.Y.; Xiao, Y.L.; Wong, N.K.; Zhou, Y.Q. Molecular imaging and in situ quantitative profiling of fatty acid synthase with a chemical probe. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4419–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kozaki, A. Design of a seed-specific chimeric promoter with a modified expression profile to improve seed oil content. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, A.; Khan, M.I.; Syed, D.N.; Abram, B.; Lewis, S.; Neill, L.O.; Mukhtar, H.; Ntambi, J.M. Hepatic stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 deficiency-mediated activation of mTORC1-PGC-1 alpha axis regulates ER stress during high-carbohydrate feeding. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagielski, T.; Krukowski, H.; Bochniarz, M.; Piech, T.; Roeske, K.; Bakula, Z.; Wlazlo, L.; Woch, P. Prevalence of Prototheca spp. on dairy farms in Poland-a cross-country study. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertl, J.A.; Groehn, Y.T.; Leach, J.D.G.; Bar, D.; Bennett, G.J.; Gonzalez, R.N.; Rauch, B.J.; Welcome, F.L.; Tauer, L.W.; Schukken, Y.H. Effects of clinical mastitis caused by gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and other organisms on the probability of conception in New York State holstein dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertl, J.A.; Schukken, Y.H.; Bar, D.; Bennett, G.J.; Gonzalez, R.N.; Rauch, B.J.; Welcome, F.L.; Tauer, L.W.; Groehn, Y.T. The effect of recurrent episodes of clinical mastitis caused by gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and other organisms on mortality and culling in holstein dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 4863–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.; Guenther, J.; Talbot, R.; Petzl, W.; Zerbe, H.; Schuberth, H.-J.; Seyfert, H.-M.; Glass, E.J. Escherichia coli-and Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis differentially modulate transcriptional responses in neighbouring uninfected bovine mammary gland quarters. BMC Genom. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schukken, Y.H.; Gunther, J.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Fontaine, M.C.; Goetze, L.; Holst, O.; Leigh, J.; Petzl, W.; Schuberth, H.J.; Sipka, A.; et al. Host-response patterns of intramammary infections in dairy cows. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 144, 270–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Lim, W.; Bae, H.; Bazer, F.W.; Song, G. C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 induces proliferation and prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4527–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, Y.; Yan, S.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, B. The protective effect of selenium on the lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress and depressed gene expression related to milk protein synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.Y.; Guo, X.Y.; Yan, S.M.; Guo, Y.M.; Shi, B.L.; Zhao, Y.L. VA inhibits LPS-induced oxidative stress via modulating Nrf2/NF-kappa B-signalling pathways in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Sun, S.-P.; Zhu, H.-S.; Jiao, X.-Q.; Zhong, K.; Guo, Y.-J.; Zha, G.-M.; Han, L.-Q.; Yang, G.-Y.; Li, H.-P. GABA regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of MAC-T cells through the LPS-induced TLR4 signaling pathway. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 118, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, H.; Shan, X.; Li, C.; Sun, D.; Wu, R. LPS-induced reduction of triglyceride synthesis and secretion in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells via decreased SREBP1 expression and activity. J. Dairy Res. 2018, 85, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Y.; Bian, Y.; Gao, X.; Qu, B.; Li, Q. 14-3-3 gamma regulates cell viability and milk fat synthesis in lipopolysaccharide-induced dairy cow mammary epithelial cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, J.A.; Karrow, N.A.; Caswell, J.L.; Boermans, H.J.; Leslie, K.E. Assessment of bovine mammary chemokine gene expression in response to lipopolysaccharide, lipotechoic acid plus peptidoglycan, and CpG oligodeoxynucleotide 2135. Can. J. Vet. Res. Rev. Can. Rech. Vet. 2009, 73, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Dong, G. PGN and LTA from Staphylococcus aureus induced inflammation and decreased lactation through regulating DNA methylation and histone H3 acetylation in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Shi, Z.R.; Chu, C.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Zhao, X.; Lee, J.W. Expression of bovine granulocyte chemotactic protein-2 (GCP-2) in neutrophils and a mammary epithelial cell line (MAC-T) in response to various bacterial cell wall components. Vet. J. 2010, 186, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, J.; Lee, T.; Jeon, J.H.; Baik, J.E.; Kim, K.W.; Kang, S.-S.; Yun, C.-H.; Kim, H.; Han, S.H. Gene expression profiling of bovine mammary gland epithelial cells stimulated with lipoteichoic acid plus peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus Aureus. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 21, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.A.; Takagi, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Komatsu, R.; Albarracin, L.; Nochi, T.; Suda, Y.; Ohtsubo, W.I.; Rutten, V.; Eden, W.V.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of the inflammatory responses of bovine mammary epithelial cells: Exploring immunomodulatory target genes for bovine mastitis. Pathogens 2020, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Coleman, D.N.; Hu, L.; Cortes, I.M.; Wang, M.; Parys, C.; Shen, X.; Loor, J.J. Methionine and arginine supplementation alter inflammatory and oxidative stress responses during lipopolysaccharide challenge in bovine mammary epithelial cells in vitro. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Liu, Q.P.; Zhang, T.; Guo, W.Y.; Qiao, W.Q.; Deng, M. Protective effects of lixisenatide against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation response in MAC-T bovine mammary epithelial cells: A therapeutic implication in mastitis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M.; Li, L.; Chen, K.L.; Wang, Y.R.; Yang, F.X.; Wang, G.L. UFL1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced cell damage and inflammation via regulation of the TLR4/NF-kappa B pathway in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, C.; Wei, Z.; He, X.; Kou, J.; Zhou, E.; Yang, Z.; Fu, Y. Morin suppresses inflammatory cytokine expression by downregulation of nuclear factor-kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated primary bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3016–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, J.; Petzl, W.; Zerbe, H.; Schuberth, H.-J.; Koczan, D.; Goetze, L.; Seyfert, H.-M. Lipopolysaccharide priming enhances expression of effectors of immune defence while decreasing expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in mammary epithelia cells from cows. BMC Genomics 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweh, M.F.; Merriman, K.E.; Nelson, C.D. Short communication: Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase increases beta-defensin expression but not the effects of lipopolysaccharide or 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-3 in bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 5706–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, M.O.; Bruckmaier, R.M.; Wellnitz, O. Meloxicam affects the inflammatory responses of bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 10277–10290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Kuang, M.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, G. UFL1 modulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and protects against pyroptosis in LPS-stimulated bovine mammary epithelial cells. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, L.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Q.; Luo, Z.; Luo, Q.; Yu, S.; Yao, X.; Ren, Z.; Hu, Y.; et al. Metabolomic profiles of bovine mammary epithelial cells stimulated by lipopolysaccharide. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Dong, G. The synergism of PGN, LTA and LPS in inducing transcriptome changes, inflammatory responses and a decrease in lactation as well as the associated epigenetic mechanisms in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Dong, G. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induced alterations of genome-wide DNA methylation and promoter methylation of lactation-related genes in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Toxins 2019, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijver, I.A.; Melief, M.J.; Markusse, H.M.; Van Aelst, I.; Opdenakker, G.; Hazenberg, M.P.; Laman, J.D. Peptidoglycan from sterile human spleen induces T-cell proliferation and inflammatory mediators in rheumatoid arthritis patients and healthy subjects. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Su, Y.-N.; Bai, H.; Wang, C.-B.; Ma, X.-H.; Ou, J.-F.; Zhao, Q.; He, X.-X.; Song, W.-W. Effects of peptidoglycan on proliferation and cell cycle of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Exp. Hematol. 2010, 18, 986–990. [Google Scholar]
- Echigo, R.; Sugimoto, N.; Yachie, A.; Ohno-Shosaku, T. Cannabinoids inhibit peptidoglycan-induced phosphorylation of NF-kappa B and cell growth in U87MG human malignant glioma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcullen, J.K.; Ly, Q.P.; Chang, T.H.; Levenson, S.M.; Steinberg, J.J. Nonviable staphylococcus aureus and its peptidoglycan stimulate macrophage recruitment, angiogenesis, fibroplasia, and collagen accumulation in wounded rats. Wound Repair Regen. 1998, 6, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chang, T.H.; Rojkind, M.; Levenson, S.M. Wound fluids from saline solution- and Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan-inoculated sponges induce expression of matrix metalloproteinase 13 messenger ribonucleic acid by cultured rat fibroblasts. Wound Repair Regen. 1997, 5, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvinho, L.F.; Almeida, R.A.; Oliver, S.P. Influence of bacterial factors on proliferation of bovine mammary epithelial cells. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2001, 33, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, S.; Wang, L.; Chang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, M.-Q. MCPIP1 mediates inflammatory responses induced by lipopolysaccharide and lipoteichoic acid in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Xu, T.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, M.-Q. Inflammatory responses of stromal fibroblasts to inflammatory epithelial cells are involved in the pathogenesis of bovine mastitis. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 349, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.X.; Li, X.R.; Qi, S.P.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, M.Q. TGF-beta 1 Induces EMT in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells Through the TGF beta 1/Smad Signaling Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.L.; Lai, Y.H.; Zhao, P.L.; Shen, Q.; Su, W.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, W.Z. Effects of peptidoglycan on the development of steatohepatitis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids. 2020, 1865, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachithanandan, N.; Graham, K.L.; Galic, S.; Honeyman, J.E.; Fynch, S.L.; Hewitt, K.A.; Steinberg, G.R.; Kay, T.W. Macrophage deletion of SOCS1 increases sensitivity to LPS and palmitic acid and results in systemic inflammation and hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bi, C.; Pang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y. Plasma metabolic profiling analysis of gout party on acute gout arthritis rats based on UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebeli, Q.; Ametaj, B.N. Relationships between rumen lipopolysaccharide and mediators of inflammatory response with milk fat production and efficiency in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3800–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Dong, G. Bacterial endotoxin decreased histone H3 acetylation of bovine mammary epithelial cells and the adverse effect was suppressed by sodium butyrate. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, H.T.; Robitaille, G.; Turner, J.D. Establishment of bovine mammary epithelial-cells (MAC-T): An invitro model for bovine lactation. Exp. Cell Res. 1991, 197, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Dong, G. Effects of Peptidoglycan, Lipoteichoic Acid and Lipopolysaccharide on Inflammation, Proliferation and Milk Fat Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080497
Wu Y, Sun Y, Zhang Z, Chen J, Dong G. Effects of Peptidoglycan, Lipoteichoic Acid and Lipopolysaccharide on Inflammation, Proliferation and Milk Fat Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Toxins. 2020; 12(8):497. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080497
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yongjiang, Yawang Sun, Zhu Zhang, Juncai Chen, and Guozhong Dong. 2020. "Effects of Peptidoglycan, Lipoteichoic Acid and Lipopolysaccharide on Inflammation, Proliferation and Milk Fat Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells" Toxins 12, no. 8: 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080497
APA StyleWu, Y., Sun, Y., Zhang, Z., Chen, J., & Dong, G. (2020). Effects of Peptidoglycan, Lipoteichoic Acid and Lipopolysaccharide on Inflammation, Proliferation and Milk Fat Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Toxins, 12(8), 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080497




