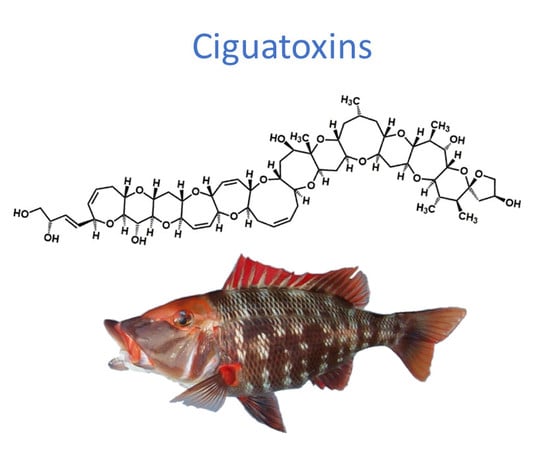
Advances in Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Ciguatoxins
3. Extraction of Ciguatoxins from Fish Tissue
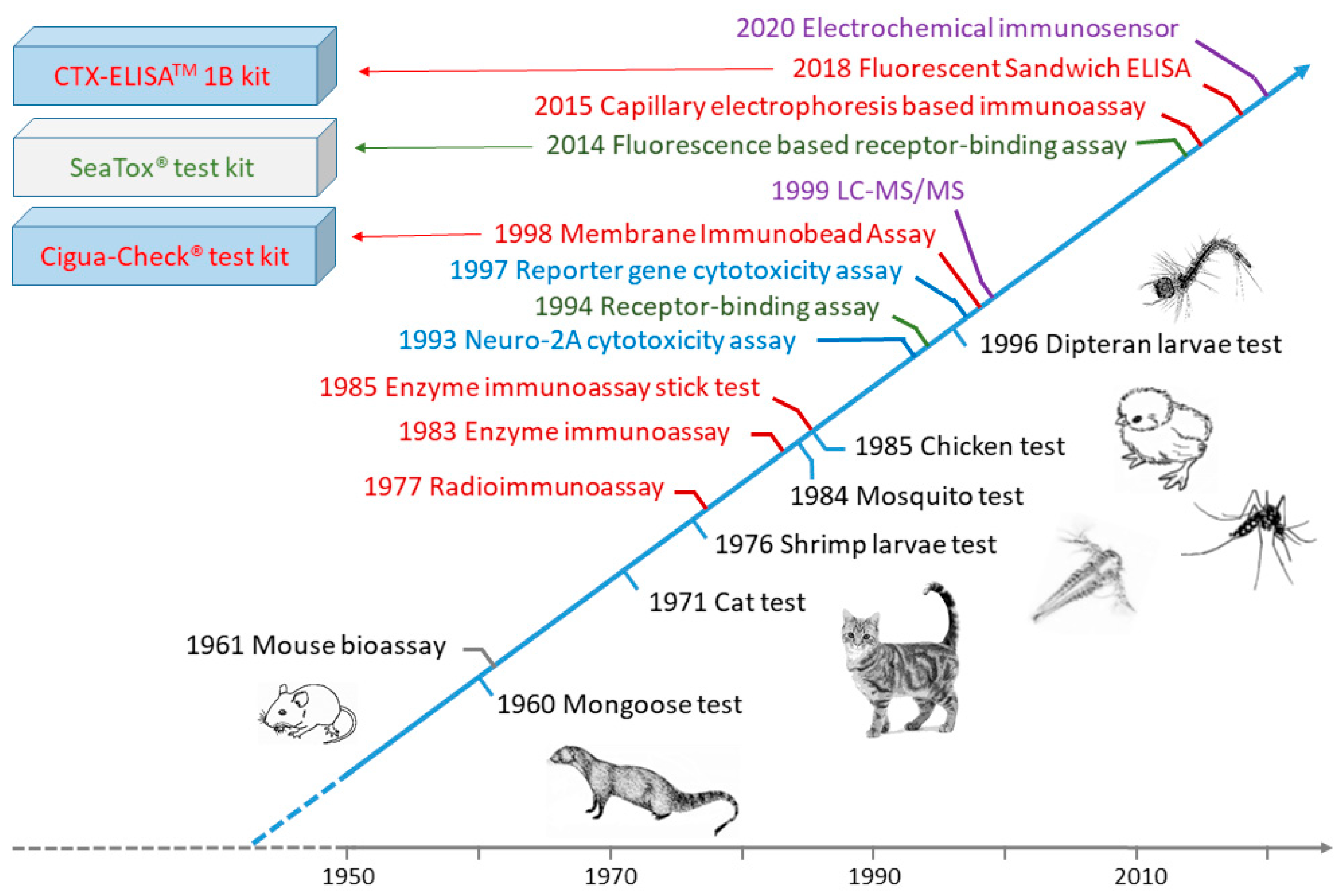
4. Detection and Quantification of Ciguatoxins
4.1. Indigenous Tests
4.2. Animal-Feeding Bioassay Tests
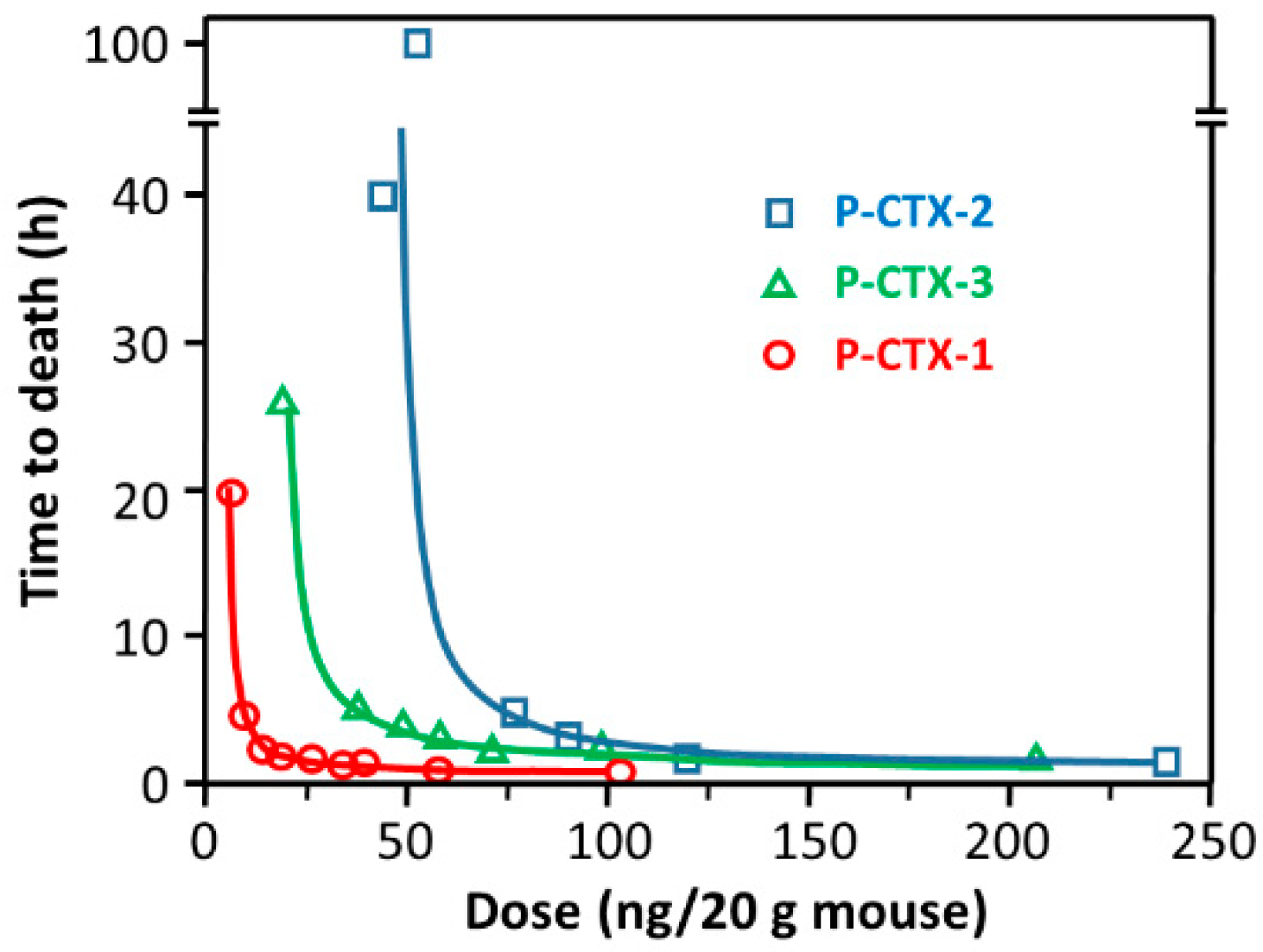
4.3. Mouse Bioassay (MBA)
4.4. Cell-Based Assay (Cytotoxicity Assay)
| Assay 1 | Fish Species (Family) | Equiv. 2 | Mass 3 (g) | Conc. 2 (ng g−1) | LOQ 4,5 (ng g−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBA-N2a | Carcharhinus leucas (Carcharhinidae) | P-CTX-1 | 10 6 | 92.78 | 0.13 | [19] |
| CBA-N2a | Lutjanus sp. (Lutjanidae) | P-CTX-1 | 5 | 0.4708 | 0.032 | [21] |
| CBA-N2a | Gymnothorax spp. (Muraenidae) | P-CTX-1 | 20 7 | 539 | 0.0016 | [23] |
| CBA-N2a | Seriola fasciata (Carangidae) | C-CTX-1 | 15 | 1.4 | n.a. | [51] |
| CBA-N2a | Chlorurus microrhinos (Parrotfish) | P-CTX-3C | 10 | 6.66 | 0.064 | [77] |
| CBA-N2a | Epinephelus merra (Serranidae) | P-CTX-3C | 10 | 3.31 | 0.064 | [77] |
| CBA-N2a | Seriola fasciata (Carangidae) | P-CTX-1 | 10 | 6.231 | 0.0096 | [78] |
| CBA-N2a | Balistes vetula (Balistidae) | C-CTX-1 | n.a. | 0–0.11 | 0.006 | [85] |
| CBA-N2a | Sphyraena barracuda (Sphyraenidae) | C-CTX-1 | 10 7 | 2.1 | 0.039 | [86] |
| CBA-N2a | Balistapus undulatus (Balistidae) | P-CTX-1 | 5 | 4.64 | 0.00195 | [87] |
| CBA-N2a | Epinephelus multinotatus (Serranidae) | P-CTX-1 | 5 | 6.49 | 0.00195 | [87] |
| CBA-N2a | Sphyraena barracuda (Sphyraenidae) | C-CTX-1 | n.a. | 0.099 | 0.001 | [88] |
| R-RBA | Scarus altipinnis (Scaridae) | P-CTX-3C | 5 | 0.36–4.52 | 0.155 | [89] |
| R-RBA | Kyphosus cinerascens (Kyphosidae) | P-CTX-3C | 5 | 0.46–4.25 | 0.155 | [89] |
| R-RBA | Plectropomus leopardus (Serranidae) | P-CTX-3C | 5 | 0.36–3.29 | 0.155 | [89] |
| R-RBA | Liza vaigiensis (Mugilidae) | P-CTX-3C | 5 | 16.23 | 0.155 | [89] |
| F-RBA | Pterois volitans (Scorpaenidae) | C-CTX-1 | 5 | 0.1–0.2 | 0.23 | [90] |
4.5. Receptor-Binding Assays (RBA)
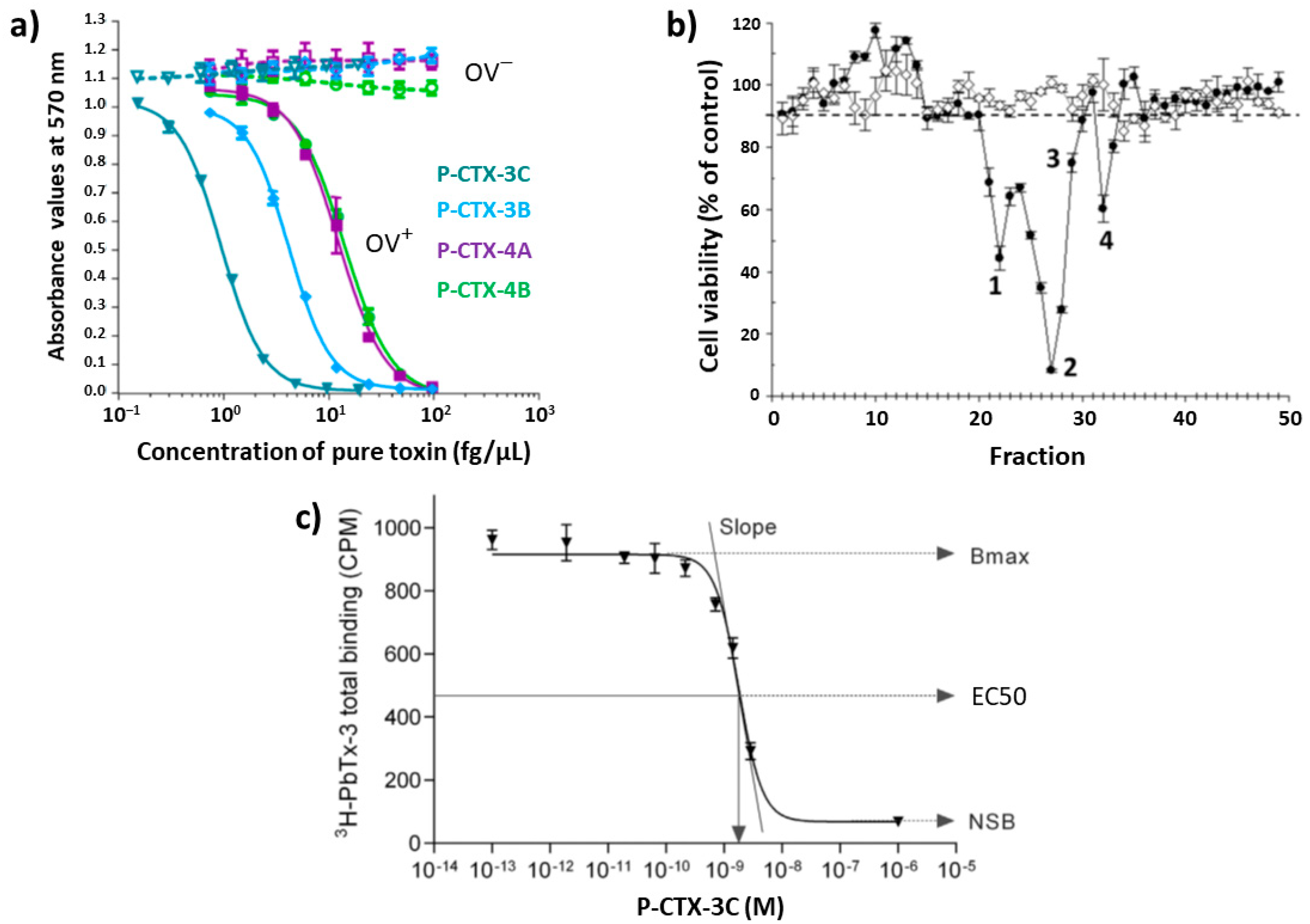
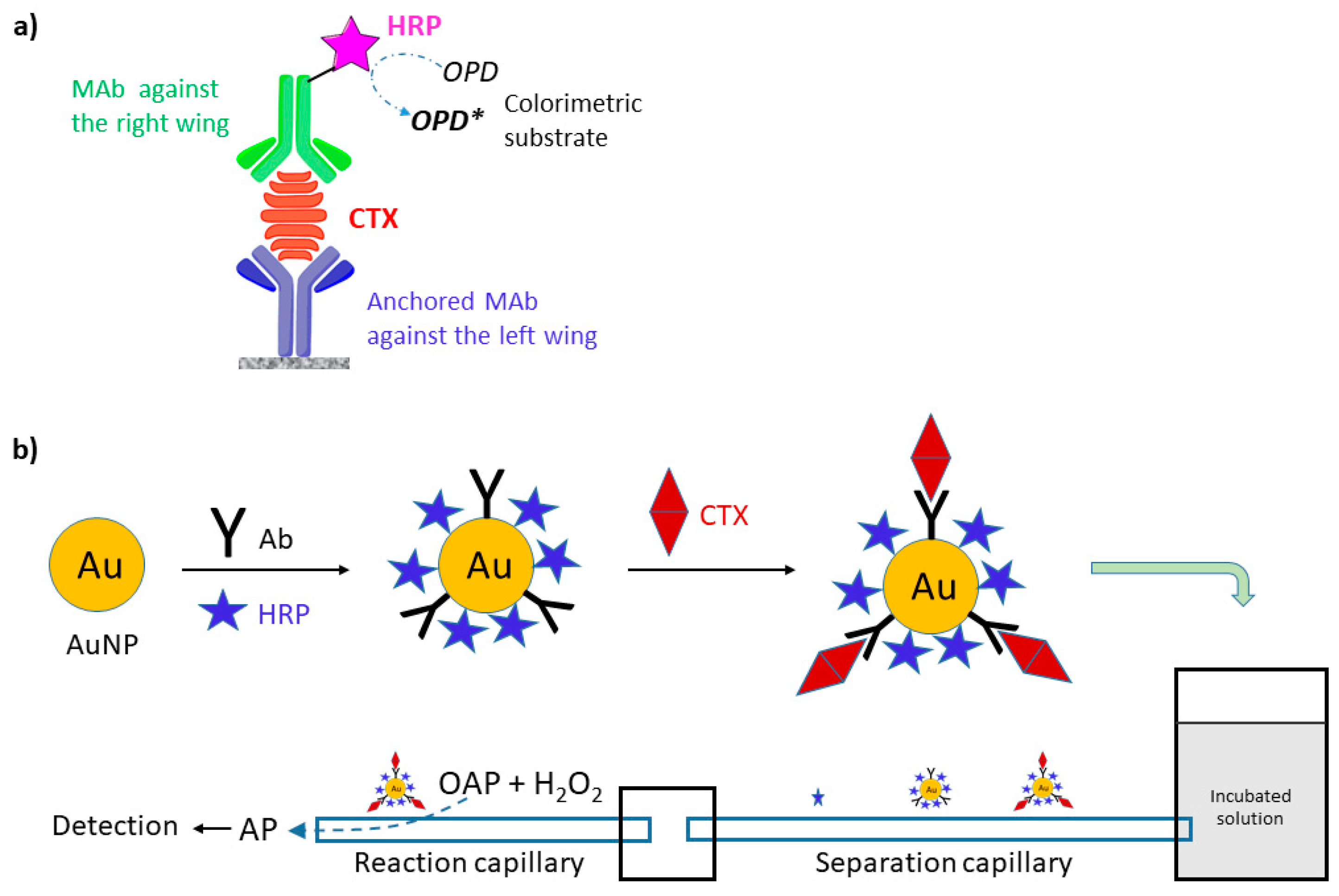
4.6. Immunoassays
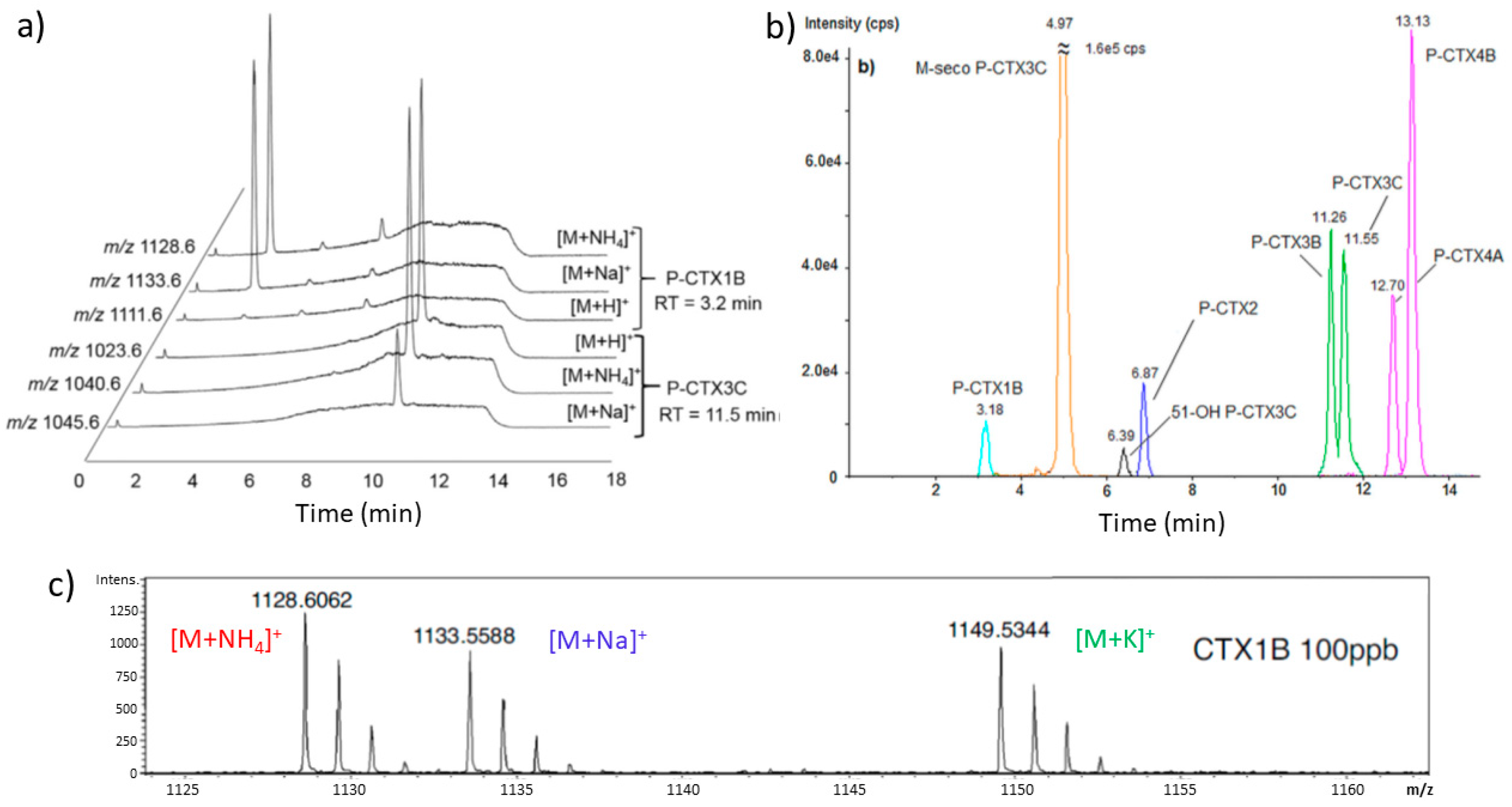
4.7. HPLC, LC-MS/MS and LC-HRMS
5. Outlook and Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific Opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish—Emerging toxins: Ciguatoxin group. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Vetter, I. Ciguatoxin and Ciguatera. In Marine and Freshwater Toxins, Toxinology; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Haddad, V., Jr., Tubaro, A., Kim, E., Kem, W.R., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media: Dordrecht, The Natherlands, 2016; pp. 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inserra, M.; Lavrukhina, Y.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J.; Vetter, I. Ciguatoxin Detection Methods and High-Throughput Assays. In Analysis of Food Toxins and Toxicants, 1st ed.; Wong, Y.-C., Lewis, R.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: New Jersey, USA, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 469–487. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, M.A.; Fleming, L.E.; Fernandez, M.; Bienfang, P.; Schrank, K.; Dickey, R.; Bottein, M.-Y.; Backer, L.; Ayyar, R.; Weisman, R.; et al. Ciguatera Fish Poisoning: Treatment, Prevention and Management. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 456–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J. The changing face of ciguatera. Toxicon 2001, 39, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.A.; Fernandez, M.; Backer, L.C.; Dickey, R.W.; Bernstein, J.; Schrank, K.; Bernstein, J.; Stephan, W.; Weisman, R.; Kibler, S.; et al. An Updated Review of Ciguatera Fish Poisoning: Clinical, Epidemiological, Environmental, and Public Health Management. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, G.M.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatoxins: Cyclic Polyether Modulators of Voltage-gated Ion Channel Function. Mar. Drugs 2006, 4, 82–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehane, L.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera: Recent advances but the risk remains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 61, 91–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, R.W.; Plakas, S.M. Ciguatera: A public health perspective. Toxicon 2010, 56, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juranovic, L.R.; Park, D.L. Foodborne Toxins of Marine Origin: Ciguatera. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Ware, G.W., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 117, pp. 51–94. [Google Scholar]
- Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Fouc, M.T.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Pauillac, S.; Laurent, D. Ciguatera risk management in French Polynesia: The case study of Raivavae Island (Australes Archipelago). Toxicon 2010, 56, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillaud, A.; de la Iglesia, P.; Darius, H.T.; Pauillac, S.; Aligizaki, K.; Fraga, S.; Chinain, M.; Diogene, J. Update on Methodologies Available for Ciguatoxin Determination: Perspectives to Confront the Onset of Ciguatera Fish Poisoning in Europe. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1838–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausing, R.J.; Losen, B.; Oberhaensli, F.R.; Darius, H.T.; Sibat, M.; Hess, P.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Chinain, M.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y. Experimental evidence of dietary ciguatoxin accumulation in an herbivorous coral reef fish. Aqua. Toxicol. 2018, 200, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition: Fish and Fishery Products Hazards and Controls Guidance, Fourth Edition—March 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/80637/download (accessed on 25 June 2020).
- Hamilton, B.; Hurbungs, M.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Multiple ciguatoxins present in Indian Ocean reef fish. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.L.; Smith, K.F.; Murray, J.S.; Nishimura, T.; Finch, S.C. Ciguatera Fish Poisoning: The Risk from an Aotearoa/New Zealand Perspective. Toxins 2020, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.; Suarez, F.C.; Ramirez, A.S.; Acosta, F. Ciguatera, an Emerging Human Poisoning in Europe. J. Aquac. Mar. Biol. 2015, 3, 00053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearn, J. Neurology of ciguatera. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 70, 4–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diogène, J.; Reverté, L.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; del Río, V.; de la Iglesia, P.; Camps, M.; Palacios, O.; Flores, C.; Caixach, J.; Ralijaona, C.; et al. Identification of ciguatoxins in a shark involved in a fatal food poisoning in the Indian Ocean. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, B.; Whittle, N.; Shaw, G.; Eaglesham, G.; Moore, M.R.; Lewis, R.J. Human fatality associated with Pacific ciguatoxin contaminated fish. Toxicon 2010, 56, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, V.; Solino, L.; Leroy, P.; David, E.; Velge, P.; Dragacci, S.; Krys, S.; Flores Quintana, H.; Diogene, J. Contribution to the risk characterization of ciguatoxins: LOAEL estimated from eight ciguatera fish poisoning events in Guadeloupe (French West Indies). Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumoto, Y.; Scheuer, P.J. Marine Toxins of the Pacific-VIII Ciguatoxin from Moray Eel Livers. Toxicon 1969, 7, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.H.; Mak, Y.l.; Wu, J.J.; Jin, L.; Sit, W.H.; Lam, J.C.W.; Sadovy de Mitcheson, Y.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S.; Murphy, M.B. Spatial distribution of ciguateric fish in the Republic of Kiribati. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campora, C.E.; Hokama, Y. Marine Toxins. In Handbook of Seafood and Seafood Products Analysis; Nollet, L.M.L., Toldra, F., Eds.; Taylor and Francis Group, LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 649–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Nakajima, I.; Bagnis, R.; Adachi, R. Finding of a dinoflagellate as a likely culprit of ciguatera. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fisheries 1977, 43, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, S.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Darius, H.T.; Hess, P.; Chinain, M. Intraspecific Variability in the Toxin Production and Toxin Profiles of In Vitro Cultures of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) from French Polynesia. Toxins 2019, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppenrath, M.; Kretzschmar, A.L.; Kaufmann, M.J.; Murray, S.A. Morphological and molecular phylogenetic identification and record verification of Gambierdiscus excentricus (Dinophyceae) from Madeira Island (NE Atlantic Ocean). Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2019, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.; Lewis, R.J. Purification and Characterisation of Large and Small Maitotoxins From Cultured Gambierdiscus toxicus. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisapia, F.; Sibat, M.; Herrenknecht, C.; Lhaute, K.; Gaiani, G.; Ferron, P.-J.; Fessard, V.; Fraga, S.; Nascimento, S.M.; Litaker, R.W.; et al. Maitotoxin-4, a Novel MTX Analog Produced by Gambierdiscus excentricus. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boente-Juncal, A.; Alvarez, M.; Antelo, A.; Rodriguez, I.; Calabro, K.; Vale, C.; Thomas, O.P.; Botana, L.M. Structure elucidation and biological evaluation of maitotoxin-3, a homologue of gambierone, from Gambierdiscus belizeanus. Toxins 2019, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, I.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Alfonso, C.; Calabro, K.; Alonso, E.; Sánchez, J.A.; Alfonso, A.; Thomas, O.P.; Botana, L.M. Gambierone, a Ladder-Shaped Polyether from the Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus belizeanus. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2392–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, A.M.; Litaudon, M.; Genthon, J.N.; Bagnis, R.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and some properties of ciguatoxin. J. Appl. Phycol. 1989, 1, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M.; Poli, M.A.; Norton, R.S.; MacLeod, J.K.; Sheil, M.M. Purification and characterization of ciguatoxins from moray eel (Lycodontis javanicus, Muraenidae). Toxicon 1991, 29, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, I.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Characterization of multiple Caribbean ciguatoxins and congeners in individual specimens of horse-eye jack (Caranx latus) by high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2002, 40, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Brereton, I.M. Structure of Caribbean Ciguatoxin Isolated from Caranx latus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 5914–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, P.; Castro, D.; Manuel Leao, J.; Yasumoto, T.; Dickey, R.; Gago-Martinez, A. Implementation of liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of ciguatera fish poisoning in contaminated fish samples from Atlantic coasts. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, M.; Legrand, A.M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Fukui, M.; Yasumoto, T. Structures and Configurations of Ciguatoxin from the Moray Eel Gymnothorax javanicus and Its Likely Precursor from the Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 4380–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Igarashi, T.; Legrand, A.-M.; Cruchet, P.; Chinain, M.; Fujita, T.; Naoki, H. Structural Elucidation of Ciguatoxin Congeners by Fast-Atom Bombardment Tandem Mass Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4988–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. The Structure of CTX3C, a Ciguatoxin Congener Isolated from Cultured Gambierdiscus Toxicus. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Fukui, M.; Legrand, A.-M.; Cruchet, P.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and Structures of New Ciguatoxin Analogs, 2,3-DihydroxyCTX3C and 51-HydroxyCTX3C, Accumulated in Tropical Reef Fish. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 1197–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Inafuku, Y.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T. Detailed LC-MS/MS Analysis of Ciguatoxins Revealing Distinct Regional and Species Characteristics in Fish and Causative Alga from the Pacific. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8886–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Legrand, A.-M.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and Structure of ciguatoxin-4A, a New Ciguatoxin Precursor, from Cultures of Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus and Parrotfish Scarus Gibbus. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 1997, 60, 2103–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, B.; Hurbungs, M.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Isolation and characterization of Indian Ocean ciguatoxin. Toxicon 2002, 40, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Endean, R. Purification of ciguatoxin-like material from Scomberomorus commersoni, and its effect on the rat phrenic nerve-diaphragm. Toxicon 1983, 3, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darius, H.T.; Roué, M.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; iti Gatti, C.M.; Vandersea, M.W.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; Amzil, Z.; Hess, P.; et al. Tectus niloticus (Tegulidae, Gastropod) as a Novel Vector of Ciguatera Poisoning: Detection of Pacific Ciguatoxins in Toxic Samples from Nuku Hiva Island (French Polynesia). Toxins 2018, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.S.; Boundy, M.J.; Selwood, A.I.; Harwood, D.T. Development of an LC–MS/MS method to simultaneously monitor maitotoxins and selected ciguatoxins in algal cultures and P-CTX-1B in fish. Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottier, I.; Hamilton, B.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J.; Vernoux, J.P. Identification of slow and fast-acting toxins in a highly ciguatoxic barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda) by HPLC/MS and radiolabelled ligand binding. Toxicon 2003, 42, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.J.; Mak, Y.L.; Murphy, M.B.; Lam, J.C.W.; Chan, W.H.; Wang, M.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S. Validation of an accelerated solvent extraction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for Pacific ciguatoxin-1 in fish flesh and comparison with the mouse neuroblastoma assay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 3165–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, D.T.; Murray, S.; Boundy, M.J. Sample Preparation Prior to Marine Toxin Analysis. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2017, 78, 89–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Sato, T.; Hirama, M.; Fujii, I. Highly Sensitive and Practical Fluorescent Sandwich ELISA for Ciguatoxins. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7318–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, P.; Castro, D.; Pequeño-Valtierra, A.; Leao, J.M.; Vilariño, O.; Diogène, J.; Gago-Martínez, A. An Attempt to Characterize the Ciguatoxin Profile in Seriola fasciata Causing Ciguatera Fish Poisoning in Macaronesia. Toxins 2019, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Yang, A.; Jones, A. Rapid extraction combined with LC-tandem mass spectrometry (CREM-LC/MS/MS) for the determination of ciguatoxins in ciguateric fish flesh. Toxicon 2009, 54, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I.; Eaglesham, G.K.; Poole, S.; Graham, G.; Paulo, C.; Wickramasinghe, W.; Sadler, R.; Shaw, G.R. Establishing a public health analytical service based on chemical methods for detecting and quantifying Pacific ciguatoxin in fish samples. Toxicon 2010, 56, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.; Carter, S.; Capper, A. An updated ciguatoxin extraction method and silica cleanup for use with HPLC-MS/MS for the analysis of PCTX-1, PCTX-2 and P-CTX-3. Toxicon 2015, 108, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.D. Disease and Development: Ciguatera Fish Poisoning. Soc. Sci. Med. 1986, 23, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darius, H.T.; Drescher, O.; Ponton, D.; Pawlowiez, R.; Laurent, D.; Dewailly, E.; Chinain, M. Use of folk tests to detect ciguateric fish: A scientific evaluation of their effectiveness in Raivavae Island (Australes, French Polynesia). Food Additiv. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 550–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, N.C.; Lewis, R.J.; Pearn, J.; Burke, A.T.C.; Holmes, M.J.; Bourke, J.B.; Shields, W.J. Ciguatera in Australia: Occurrence, clinical features, pathophysiology and management. Med. J. Aust. 1986, 145, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnis, R.; Fevai, G. La ciguatera feline experimentale a Tahiti. Rev. Med. Vet. 1971, 122, 629–638. [Google Scholar]
- Banner, A.H.; Scheuer, P.J.; Sasaki, S.; Helfrich, P.; Alendert, C.B. Observations on Ciguatera-type Toxin in Fish. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1960, 90, 770–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernoux, J.P.; Lahlou, N.; Magras, L.P.; Greaux, J.B. Chick feeding test: A simple system to detect ciguatoxin. Acta Trop. 1985, 42, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrousse, H.; Matile, L. Toxicological biotest on Diptera larvae to detect ciguatoxins and various other toxic substances. Toxicon 1996, 34, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chungue, E.; Bagnis, R.; Parc, F. The use of mosquitoes (Aedes aegypti) to detect ciguatoxin in surgeon fishes (Ctenochaetus striatus). Toxicon 1984, 22, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granade, H.R.; Cheng, P.C.; Doorenbos, N.J. Ciguatera I: Brine Shrimp (Artemia salina L.) Larval Assay for Ciguatera Toxins. J. Pharm. Sci. 1976, 65, 1414–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnis, R.; Barsinas, M.; Prieur, C.; Pompon, A.; Chungue, E.; Legrand, A.M. The use of the mosquito bioassay for determining the toxicity to man of ciguateric fish. Biol. Bull. 1987, 172, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banner, A.; Sasaki, S.; Helfrich, P.; Alender, C.B.; Scheuer, P.J. Bioassay of Ciguatera Toxin. Nature 1961, 189, 229–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, P.A.; Granade, H.R.; McMillan, J.P. The mouse ciguatoxin bioassay: A dose-response curve and symptomatology analysis. Toxicon 1983, 21, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, S.; Gaiani, G.; Tsumuraya, T.; Hirama, M.; Turquet, J.; Sagristà, N.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Flores, C.; Caixach, J.; Diogène, J.; et al. Addressing the Analytical Challenges for the Detection of Ciguatoxins Using an Electrochemical Biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4858–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endean, R.; Griffith, J.K.; Robins, J.J.; Monks, S.A. Multiple toxins in a specimen of the narrow-barred spanish mackerel, Scomberomorus commersoni. Toxicon 1993, 31, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokama, Y.; Asahina, A.Y.; Titus, E.; Ichinotsubo, D.; Chun, S.; Hong, T.L.W.P.; Shirai, J.L.; Asuncion, D.A.; Miyahara, J.T. Assessment of ciguateric fish in Hawaii by immunological mouse toxicity and guinea pig atrial assay. Mem. Qld. Mus. 1994, 34, 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara, J.; Akau, C.; Yasumoto, T. Effects of ciguatoxin and maitotoxin on the isolated guinea pig atria. Res. Comm. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1979, 25, 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, E.; Legrand, A.M.; Dubois, J.M. Effects of ciguatoxin on current and voltage clamped frog myelinated nerve fibre. Toxicon 1986, 24, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.M.; Tindall, D.R.; Tibbs, B. Ciguatera-type toxins: Bioassay using crayfish nerve cord (Abstract 1103). Fed. Proc. Abstr. 1986, 45, 344. [Google Scholar]
- Shimojo, R.Y.; Iwaoka, W.T. A rapid hemolysis assay for the detection of sodium channel-specific marine toxins. Toxicology 2000, 154, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manger, R.L.; Leja, L.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Hungerford, J.M.; Wekell, M.M. Tetrazolium-based cell bioassay for neurotoxins active on voltage-sensitive sodium channels: Semiautomated assay for saxitoxins, brevetoxins, and ciguatoxins. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 214, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manger, R.L.; Leja, L.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Hungerford, J.M.; Hokama, Y.; Dickey, R.W.; Granade, H.R.; Lewis, R.; Yasumoto, T.; Wekell, M.M. Detection of sodium channel toxins: Directed cytotoxicity assays of purified ciguatoxins, brevetoxins, saxitoxins, and seafood extracts. J. AOAC Intern. 1995, 78, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manger, R.L.; Leja, L.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Hungerford, J.M.; Wekell, M.M. Cell bioassay for the detection of ciguatoxins, brevetoxins. and saxitoxins. Mem. Qld. Mus. 1994, 34, 571–575. [Google Scholar]
- Viallon, J.; Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T. Revisiting the Neuroblastoma Cell-Based Assay (CBA-N2a) for the Improved Detection of Marine Toxins Active on Voltage Gated Sodium Channels (VGSCs). Toxins 2020, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillaud, A.; Eixarch, H.; de la Iglesia, P.; Rodriguez, M.; Dominguez, L.; Andree, K.B.; Diogene, J. Towards the standardisation of the neuroblastoma (neuro-2a) cell-based assay for ciguatoxin-like toxicity detection in fish: Application to fish caught in the Canary Islands. Food Add. Contam. Part A 2012, 29, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, D.; Manger, R.; Vilariño, O.; Gago-Martínez, A. Evaluation of Matrix Issues in the Applicability of the Neuro-2a Cell Based Assay on the Detection of CTX in Fish Samples. Toxins 2020, 12, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Asencio, L.; Clausing, R.J.; Ranada, M.L.; Alonso-Hernandez, C.M.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y. A radioligand receptor binding assay for ciguatoxin monitoring in environmental samples: Method development and determination of quality control criteria. J. Environ. Rad. 2018, 192, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairey, E.R.; Edmunds, J.S.G.; Ramsdell, J.S. A Cell-Based Assay for Brevetoxins, Saxitoxins, and Ciguatoxins Using a Stably Expressed c-fos–Luciferase Reporter Gene. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 251, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairey, E.R.; Ramsdell, J.S. Reporter Gene Assays for Algal-derived Toxins. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, K.; Deuis, J.R.; Inserra, M.C.; Collins, L.S.; Namer, B.; Cabot, P.J.; Reeh, P.W.; Lewis, R.J.; Vetter, I. Analgesic treatment of ciguatoxin-induced cold allodynia. Pain 2013, 154, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Inserra, M.; Vetter, I.; Holland, W.C.; Hardison, R.D.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W. Rapid Extraction and Identification of Maitotoxin and Ciguatoxin-Like Toxins from Caribbean and Pacific Gambierdiscus Using a New Functional Bioassay. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Robertson, A.; Flores Quintana, H.A.; Silander, M.C.; Smith, T.B.; Olsen, D. Ciguatoxin prevalence in 4 commercial fish species along an oceanic exposure gradient in the US Virgin Islands. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 1852–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottein Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Tiedeken, J.A.; Persad, R.; Wang, Z.; Granade, H.R.; Dickey, R.W.; Ramsdell, J.S. Use of two detection methods to discriminate ciguatoxins from brevetoxins: Application to great barracuda from Florida Keys. Toxicon 2005, 46, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, Y.L.; Wai, T.-C.; Murphy, M.B.; Chan, W.H.; Wu, J.J.; Lam, J.C.W.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S. Pacific Ciguatoxins in Food Web Components of Coral Reef Systems in the Republic of Kiribati. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 14070–14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, A.C.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y.; Danylchuk, A.J.; Ramsdell, J.S.; Cooke, S.J. Linking ciguatera poisoning to spatial ecology of fish: A novel approach to examining the distribution of biotoxin levels in the great barracuda by combining non-lethal blood sampling and biotelemetry. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darius, H.T.; Ponton, D.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Ung, A.; Tchou Fouc, M.; Chinain, M. Ciguatera risk assessment in two toxic sites of French Polynesia using the receptor-binding assay. Toxicon 2007, 50, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litaker, R.W.; Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; Bourdelais, A.J.; McCall, J.R.; Baden, D.G.; Morris, J.A., Jr.; Bogdanoff, A.K.; Tester, P.A. Ciguatoxin concentrations in invasive lionfish estimated using a fluorescent receptor binding assay. In Marine and Freshwater Harmful Algae 2014, Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Cawthorn Institute, Nelson, New Zealand, 27–31 October 2014; MacKenzie, A.L., Ed.; The International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae (ISSHA): Helsinki, Finland, 2014; pp. 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Bottein Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Turquet, J.; Chinain, M.; Darius, T.; Cruchet, P.; Radwan, F.F.Y.; Dickey, R.W.; Ramsdell, J.S. Biomonitoring of ciguatoxin exposure in mice using blood collection cards. Toxicon 2005, 46, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottein Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Ramsdell, J.S. Optimization of ciguatoxin extraction method from blood for Pacific ciguatoxin (P-CTX-1). Toxicon 2007, 49, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombet, A.; Bidard, J.-N.; Lazdunski, M. Ciguatoxin and brevetoxins share a common receptor site on the neuronal voltage-dependent Na+ channel. FEBS Lett. 1987, 219, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, S.; Vale, C.; Alonso, E.; Alfonso, C.; Rodríguez, P.; Otero, P.; Alfonso, A.; Vale, P.; Hirama, M.; Vieytes, M.R.; et al. A Comparative Study of the Effect of Ciguatoxins on Voltage-Dependent Na+ and K+ Channels in Cerebellar Neurons. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechraoui, M.Y.; Naar, J.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.-M. Ciguatoxins and brevetoxins, neurotoxic polyether compounds active on sodium channels. Toxicon 1999, 37, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dolah, F.M.; Finley, E.L.; Haynes, B.L.; Doucette, G.J.; Moeller, P.D.; Ramsdell, J.S. Development of rapid and sensitive high throughput pharmacologic assays for marine phycotoxins. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; McCall, J.R.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Baden, D.G.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Tester, P.A.; Shea, D.; Quintana, H.A.F.; et al. Fluorescent Receptor Binding Assay for Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, J.R.; Jacocks, H.M.; Niven, S.C.; Poli, M.A.; Baden, D.G.; Bourdelais, A.J. Development and utilization of a fluorescence-based receptor-binding assay for the site 5 voltage-sensitive sodium channel ligands brevetoxin and ciguatoxin. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokama, Y.; Banner, A.H.; Boylan, D.B. A radioimmunoassay for the detection of ciguatoxin. Toxicon 1977, 15, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, L.H.; Abad, M.A.; Hokama, Y. Evaluation of the radioimmunoassay (RIA) for detection of ciguatoxin (CTX) in fish tissues. J. Fish Biol. 1982, 21, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokama, Y.; Abad, M.A.; Kimura, L.H. A rapid enzyme-immunoassay for the detection of ciguatoxin in contaminated fish tissues. Toxicon 1983, 21, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokama, Y. A rapid, simplified enzyme immunoassay stick test for the detection of ciguatoxin and related polyethers from fish tissues. Toxicon 1985, 23, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokama, Y. Immunological studies using monoclonal antibodies for detection of low dalton marine toxins. Food Add. Contam. 1993, 10, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokama, Y.; Shirai, L.K.; Iwamoto, L.M.; Kobayashi, M.N.; Goto, C.S.; Nakagawa, L.K. Assessment of a rapid enzyme immunoassay stick test for the detection of ciguatoxin and related polyether toxins in fish tissues. Biol. Bull. 1987, 172, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokama, Y.; Honda, S.A.A.; Asahina, A.Y.; Fong, J.M.L.; Matsumoto, C.M.; Gallacher, T.S. Cross-reactivity of ciguatoxin, okadaic acid, and polyethers with monoclonal antibodies. Food Agricult. Immunol. 1989, 1, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaoka, W.; Horita, J.; Shimojo, R.; Tran, T. Analysis of Acanthurus triostegus for marine toxins by the stick enzyme immunoassay and mouse bioassay. Toxicon 1992, 30, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokama, Y. Simplified solid-phase immunobead assay for detection of ciguatoxin and related polyethers. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 1990, 4, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokama, Y. Recent methods for detection of seafood toxins: Recent immunological methods for ciguatoxin and related polyethers. Food Add. Contam. 1993, 10, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.L. Evolution of methods for assessing ciguatera toxins in fish. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; de Voogt, P., Ed.; Springer-Verlag, New York, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 136, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.L.; Gamboa, P.M.; Goldsmith, C.H. Rapid facile solid-phase immunobead assay for screening ciguatoxic fish in the market place. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1992, 85, 504–507. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.J. Immunological, biochemical and chemical features of ciguatoxins: Implications for the detection of ciguateric fish. Mem. Qld. Mus. 1994, 34, 541–548. [Google Scholar]
- Hokama, Y.; Takenaka, W.E.; Nishimura, K.L.; Ebesu, J.S.; Bourke, R.; Sullivan, P.K. A Simple Membrane Immunobead Assay for Detecting Ciguatoxin and Related Polyethers from Human Ciguatera Intoxication and Natural Reef Fishes. J. AOAC Int. 1998, 81, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienfang, P.; DeFelice, S.; Dowling, A. Quantitative Evaluation of Commercially Available Test Kit for Ciguatera in Fish. Food Nutr. Sci. 2011, 2, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campora, C.E.; Hokama, Y.; Yabusaki, K.; Isobe, M. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of Ciguatoxin in fish tissue using chicken immunoglobulin. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2008, 22, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campora, C.E.; Dierking, J.; Tamaru, C.S.; Hokama, Y.; Vincent, D. Detection of ciguatoxin in fish tissue using sandwich ELISA and neuroblastoma cell bioassay. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2008, 22, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Fujii, I.; Hirama, M. Preparation of anti-ciguatoxin monoclonal antibodies using synthetic haptens: Sandwich ELISA detection of ciguatoxins. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Yamashita, S.; Fujii, I.; Hirama, M. Development of a monoclonal antibody against the left wing of ciguatoxin CTX1B: Thiol strategy and detection using a sandwich ELISA. Toxicon 2012, 60, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Fujii, I.; Hirama, M. Production of monoclonal antibodies for sandwich immunoassay detection of Pacific ciguatoxins. Toxicon 2010, 56, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Fujii, I.; Inoue, M.; Tatami, A.; Miyazaki, K.; Hirama, M. Production of monoclonal antibodies for sandwich immunoassay detection of ciguatoxin 51-hydroxyCTX3C. Toxicon 2006, 48, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Hirama, M. Rationally Designed Synthetic Haptens to Generate Anti-Ciguatoxin Monoclonal Antibodies, and Development of a Practical Sandwich ELISA to Detect Ciguatoxins. Toxins 2019, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Luan, W. Horseradish peroxidase and antibody labeled gold nanoparticle probe for amplified immunoassay of ciguatoxin in fish samples based on capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. Toxicon 2015, 96, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Luan, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X. Ultrasensitive and accelerated detection of ciguatoxin by capillary electrophoresis via on-line sandwich immunoassay with rotating magnetic field and nanoparticles signal enhancement. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 888, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernoux, J.-P.; Lewis, R.J. Isolation and characterization of Caribbean ciguatoxins from the horse-eye jack (Caranx latus). Toxicon 1997, 35, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M. Multiple ciguatoxins in the flesh of fish. Toxicon 1992, 30, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Satake, M. Chemistry, Etiology and Determination Methods of Ciguatera Toxins. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 1996, 15, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Fukui, M.; Sasaki, K.; Sugiyama, K. Determinations of marine toxins in foods. J. AOAC Int. 1995, 78, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, A.-M.; Fukui, M.; Cruchet, P.; Yasumoto, T. Progress on Chemical Knowledge of Ciguatoxins. Bull. Soc. Path. Ex. 1992, 85, 467–469. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.J.; Jones, A. Characterization of ciguatoxins and ciguatoxin congeners present in ciguateric fish by gradient reversephase high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Toxicon 1997, 35, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Jones, A.; Vernoux, J.-P. HPLC/Tandem Electrospray Mass Spectrometry for the Determination of Sub-ppb Levels of Pacific and Caribbean Ciguatoxins in Crude Extracts of Fish. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibat, M.; Herrenknecht, C.; Darius, H.T.; Roué, M.; Chinain, M.; Hess, P. Detection of pacific ciguatoxins using liquid chromatography coupled to either low or high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J. Chromat. A 2018, 1571, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreiras, G.; Leao, J.M.; Gago-Martinez, A. Design of experiments for the optimization of electrospray ionization in the LC-MS/MS analysis of ciguatoxins. J. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 53, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshiyuki, S.; Ha, D.V.; Uesugi, A.; Uchida, H. Analytical challenges to ciguatoxins. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 18, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, Y.L.; Wu, J.J.; Chan, W.H.; Murphy, M.B.; Lam, J.C.W.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S. Simultaneous quantification of Pacific ciguatoxins in fish blood using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3331–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.V.; Uesugi, A.; Uchida, H.; Ky, P.X.; Minh, D.Q.; Watanabe, R.; Matsushima, R.; Oikawa, H.; Nagai, S.; Iwataki, M.; et al. Identification of Causative Ciguatoxins in Red Snappers Lutjanus bohar Implicated in Ciguatera Fish Poisonings in Vietnam. Toxins 2018, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, G.S.; Haslauer, K.; Sarowar, C.; Kretzschmar, A.L.; Boulter, M.; Harwood, D.T.; Laczka, O.; Murray, S.A. Qualitative and quantitative assessment of the presence of ciguatoxin, P-CTX-1B, in Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorus commerson) from waters in New South Wales (Australia). Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 4, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.R.; Estevez, P.; Castro, D.; Solino, L.; Gouveia, N.; Santos, C.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Leao, J.M.; Gago-Martinez, A. New insights into the occurrence and toxin profile of ciguatoxins in Selvagens Islands (Madeira, Portugal). Toxins 2018, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, I.; Vernoux, J.P.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Analysis of toxin profiles in three different fish species causing ciguatera fish poisoning in Guadeloupe, French West Indies. Food Add. Contam. 2002, 19, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, P.; Sibat, M.; Leão-Martins, J.M.; Costa, P.R.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Hess, P. Liquid Chromatography Coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry for the Confirmation of Caribbean Ciguatoxin-1 as the Main Toxin Responsible for Ciguatera Poisoning Caused by Fish from European Atlantic Coasts. Toxins 2020, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasinszki, T.; Krebsz, M.; Tung, T.T.; Losic, D. Carbon Nanomaterial Based Biosensors for Non-Invasive Detection of Cancer and Disease Biomarkers for Clinical Diagnosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasinszki, T.; Krebsz, M. Biosensors for Non-Invasive Detection of Celiac Disease Biomarkers in Body Fluids. Biosensors 2018, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasinszki, T.; Krebsz, M. Advances in Celiac Disease Testing. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2019, 91, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
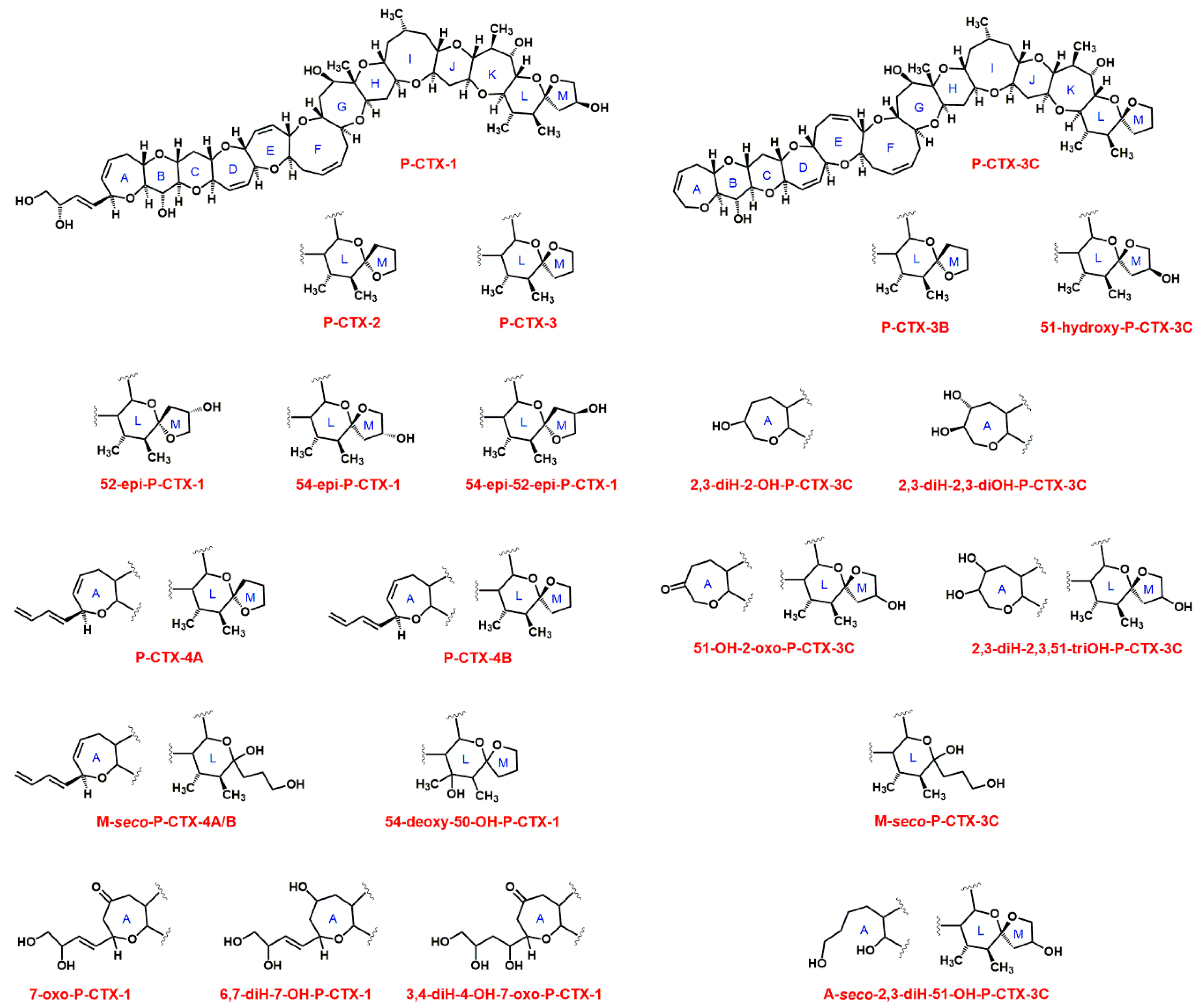
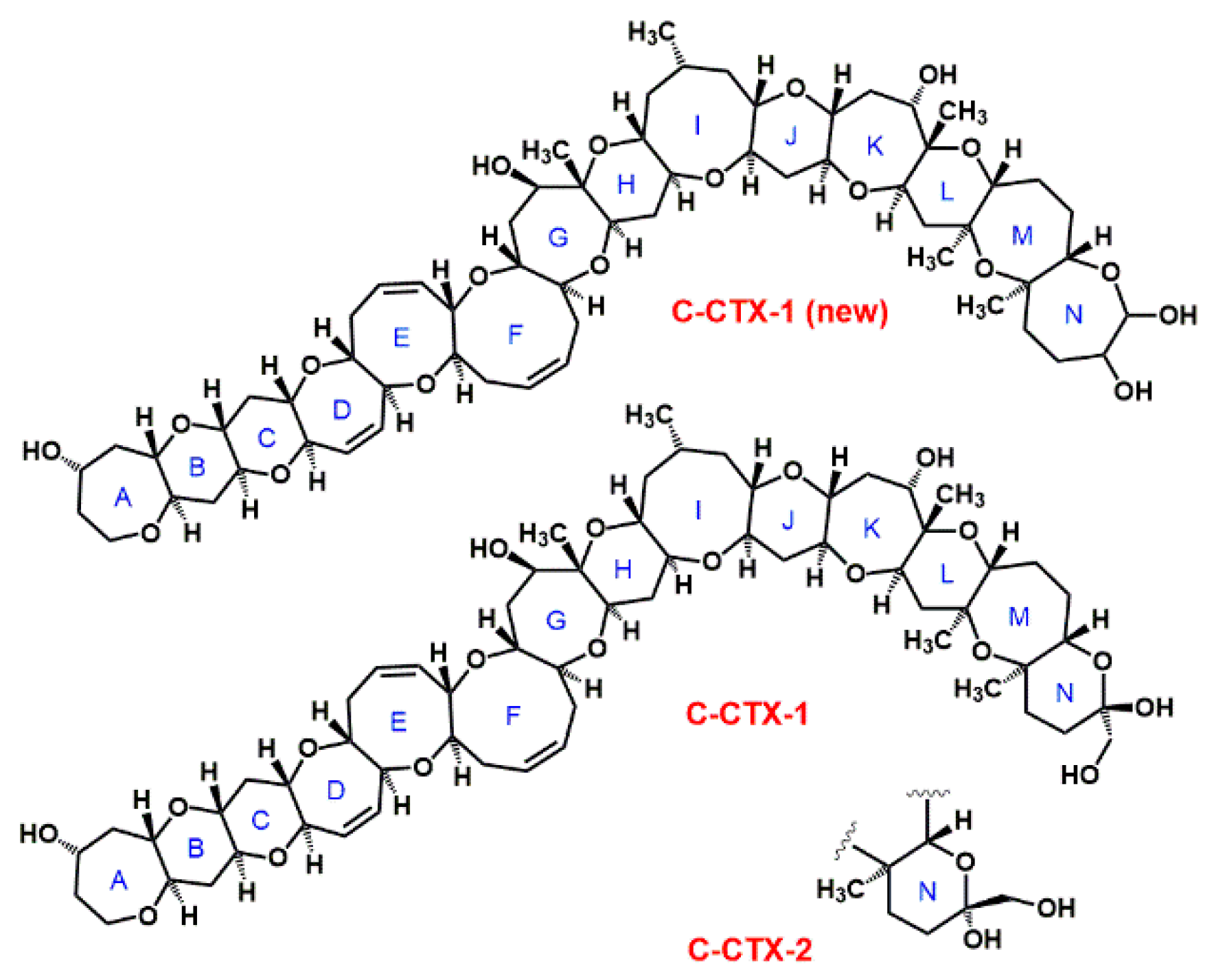

| Pacific CTXs | Caribbean CTXs | ||||
| P-CTX-1 | C60H86O19 | 1110.6 [37] | C-CTX-1 5 | C62H92O19 | 1140.6 [35] |
| 52-epi-P-CTX-1 | C60H86O19 | 1110.6 [38] | C-CTX-2 5 | C62H92O19 | 1140.6 [35] |
| 54-epi-P-CTX-1 | C60H86O19 | 1110.6 [38] | C-CTX-1141a | n.a. | 1140.6 [34] |
| 54-epi-52-epi-P-CTX-1 | C60H86O19 | 1110.6 [38] | C-CTX-1141b | n.a. | 1140.6 [34] |
| P-CTX-2 2 | C60H86O18 | 1094.6 [33] | C-CTX-1141c | n.a. | 1140.6 [34] |
| P-CTX-3 2 | C60H86O18 | 1094.6 [33] | C-CTX-1127 | n.a. | 1126.6 [34] |
| 7-oxo-P-CTX-1 | C60H86O20 | 1126.6 [38] | C-CTX-1143 | n.a. | 1142.6 [34] |
| 6,7-diH-7-OH-P-CTX-1 | C60H88O20 | 1128.6 [38] | C-CTX-1143a | n.a. | 1142.6 [34] |
| 3,4-diH-4-OH-7-oxo-P-CTX-1 | C60H88O21 | 1144.6 [38] | C-CTX-1157 | n.a. | 1156.6 [34] |
| 54-deoxy-50-OH-P-CTX-1 | C60H86O19 | 1110.6 [38] | C-CTX-1157a | n.a. | 1156.6 [34] |
| P-CTX-3C 3 | C57H82O16 | 1022.6 [39] | C-CTX-1157b | n.a. | 1156.6 [34] |
| P-CTX-3B 3 | C57H82O16 | 1022.6 [38] | C-CTX-1159 | n.a. | 1158.6 [34] |
| 51-OH-P-CTX-3C | C57H82O17 | 1038.6 [40] | |||
| 2,3-diH-2-OH-P-CTX-3C | C57H84O17 | 1040.6 [38] | Indian CTXs | ||
| 2,3-diH-2,3-diOH-P-CTX-3C | C57H84O18 | 1056.6 [40] | I-CTX-1 | C62H92O19 | 1140.6 [15] |
| M-seco-P-CTX-3C | C57H84O17 | 1040.6 [41] | I-CTX-2 | C62H92O19 | 1140.6 [15] |
| P-CTX-4A 4 | C60H84O16 | 1060.6 [42] | I-CTX-3 | C62H92O20 | 1156.6 [15] |
| P-CTX-4B 4 | C60H84O16 | 1060.6 [37] | I-CTX-4 | C62H92O20 | 1156.6 [15] |
| M-seco-P-CTX-4A/B | C60H86O17 | 1078.6 [41] | I-CTX-5 | C62H90O19 | 1138.6 [19] |
| 51-OH-2-oxo-CTX-3C | C57H82O18 | 1054.6 [38] | I-CTX-6 | C62H90O20 | 1154.6 [19] |
| 2,3-diH-2,3,51-triOH-P-CTX3C | C57H84O19 | 1072.6 [38] | |||
| A-seco-2,3-diH-51-OH-P-CTX-3C | C57H86O18 | 1058.6 [38] | |||
| Method | Fish Species (Family) | Toxin Detected | Mass 1 (g) | Conc. 2 (ng g−1) | LOQ 3 (ng g−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC-MS/MS | Lutjanus bohar (Lutjanidae) | P-CTX-1 P-CTX-2 P-CTX-3 | 5 | 3.7 0.74 0.36 | 0.32 | [134] |
| LC-MS/MS | Sphyraena putnamae (Sphyraenidae) | P-CTX-1 | 2 | 11.4 | 0.07 | [53] |
| LC-MS/MS | Sphyraena putnamae (Sphyraenidae) | P-CTX-1 P-CTX-2 P-CTX-3 | 2 | 5.6 7.9 1.4 | n.a. | [20] |
| LC-MS/MS | Epinephelus spilotoceps (Serranidae) | P-CTX-1 | 5 | 2.73 | 0.01 | [48] |
| LC-MS/MS | Variola louti (Serranidae) | P-CTX-1 P-CTX-2 P-CTX-3 | 5 | 2.0 4 | <0.01 | [41] |
| LC-MS/MS | Cephalopholis argus (Serranidae) | P-CTX-1 P-CTX-2 P-CTX-3 | 5 | 1.710 0.555 0.711 | 0.0005 0.0050 0.0050 | [87] |
| LC-MS/MS | Gymnothorax flavimarginatus (Muraenidae) | P-CTX-1 P-CTX-2 P-CTX-3 | 5 | 39.20 24.40 5.940 | 0.0005 0.0050 0.0050 | [87] |
| LC-MS/MS | Scomberomorus commerson (Scombridae) | P-CTX-1 | 5 | 0.13 | n.a. | [135] |
| LC-HRMS | Variola louti (Serranidae) | P-CTX-1 | 10 | 1.609 | ~0.4 | [67] |
| LC-MS/MS | Pagrus Pagrus (Sparidae) | C-CTX-1 | 15 | 0.76 | 0.0045 | [36] |
| LC-MS/MS | Lutjanus cyanopterus (Lutjanidae) | C-CTX-1 | 15 | 0.49 | 0.0045 | [36] |
| LC-MS/MS | Seriola fasciata (Carangidae) | C-CTX-1 | 15 | 0.84 | n.a. | [51] |
| LC-MS/MS | Mycteroperca fusca (Serranidae) | C-CTX-1 | 15 | 0.25 | 0.0150 | [136] |
| LC-MS/MS | Caranx lugubris (Carangidae) | C-CTX-1 | 100 | 13.79 | n.a. | [137] |
| LC-HRMS | Bodianus scrofa (Wrasse) | C-CTX-1 | 15 | n.a. | n.a. | [138] |
| LC-HRMS | Carcharhinus leucas (Carcharhinidae) | I-CTX-1,2 I-CTX-3,4 | 10 5 | 6.54 9.74 | 1.67 6 | [19] |
| Method | Extract Preparation 1 | Assay Duration | Parallel Samples 2 | Sensitivity 3 (ng g‒1) | Specificity | Toxin Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBA | 5–6 h | 24 h | 1–10 | 0.56 | No | No |
| R-RBA | 5–6 h | 3–4 h | 96 | 0.03–0.15 | No | No |
| F-RBA | 5–6 h | 2–3 h | 96 | 0.02–0.023 | No | No |
| CBA | 5–6 h 4 | 53 h 4 | 96 | 0.001–0.13 | No | No |
| ELISA | 7–8 h | 2–4 h | 96 | <0.01 5 | Yes | No |
| CE | 5–6 h | 1 h | 1 | <0.01 5 | Yes | No |
| ECS | 5–6 h | 2 h | 1 | 0.01 | Yes | No |
| LC-MS/MS | 5–8 h | 5–15 min 6 | 1 | 0.0005–0.32 | Yes | Yes |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pasinszki, T.; Lako, J.; Dennis, T.E. Advances in Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish. Toxins 2020, 12, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080494
Pasinszki T, Lako J, Dennis TE. Advances in Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish. Toxins. 2020; 12(8):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080494
Chicago/Turabian StylePasinszki, Tibor, Jimaima Lako, and Todd E. Dennis. 2020. "Advances in Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish" Toxins 12, no. 8: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080494
APA StylePasinszki, T., Lako, J., & Dennis, T. E. (2020). Advances in Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish. Toxins, 12(8), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080494