Structural and Functional Insights into the C-terminal Fragment of Insecticidal Vip3A Toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
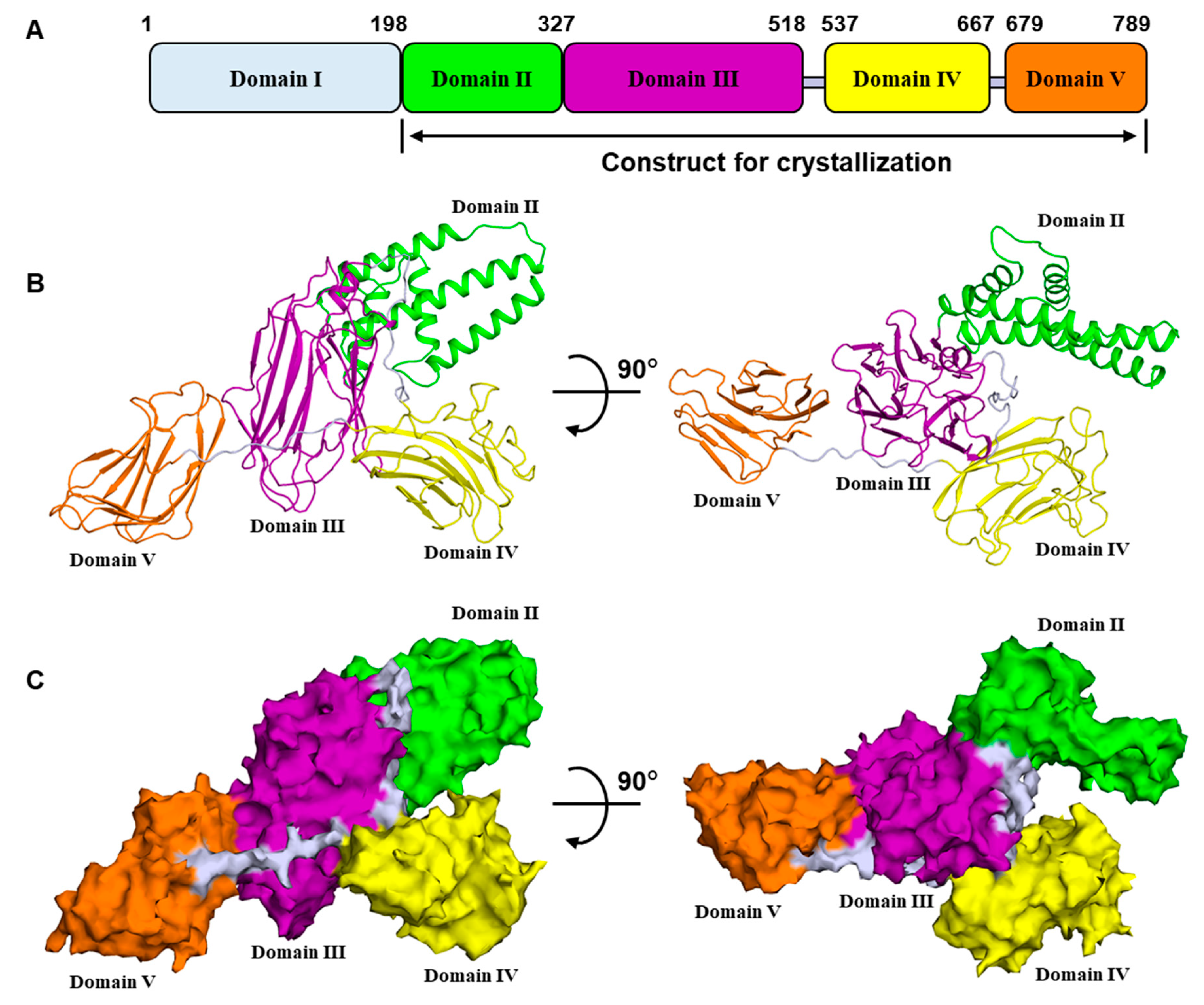
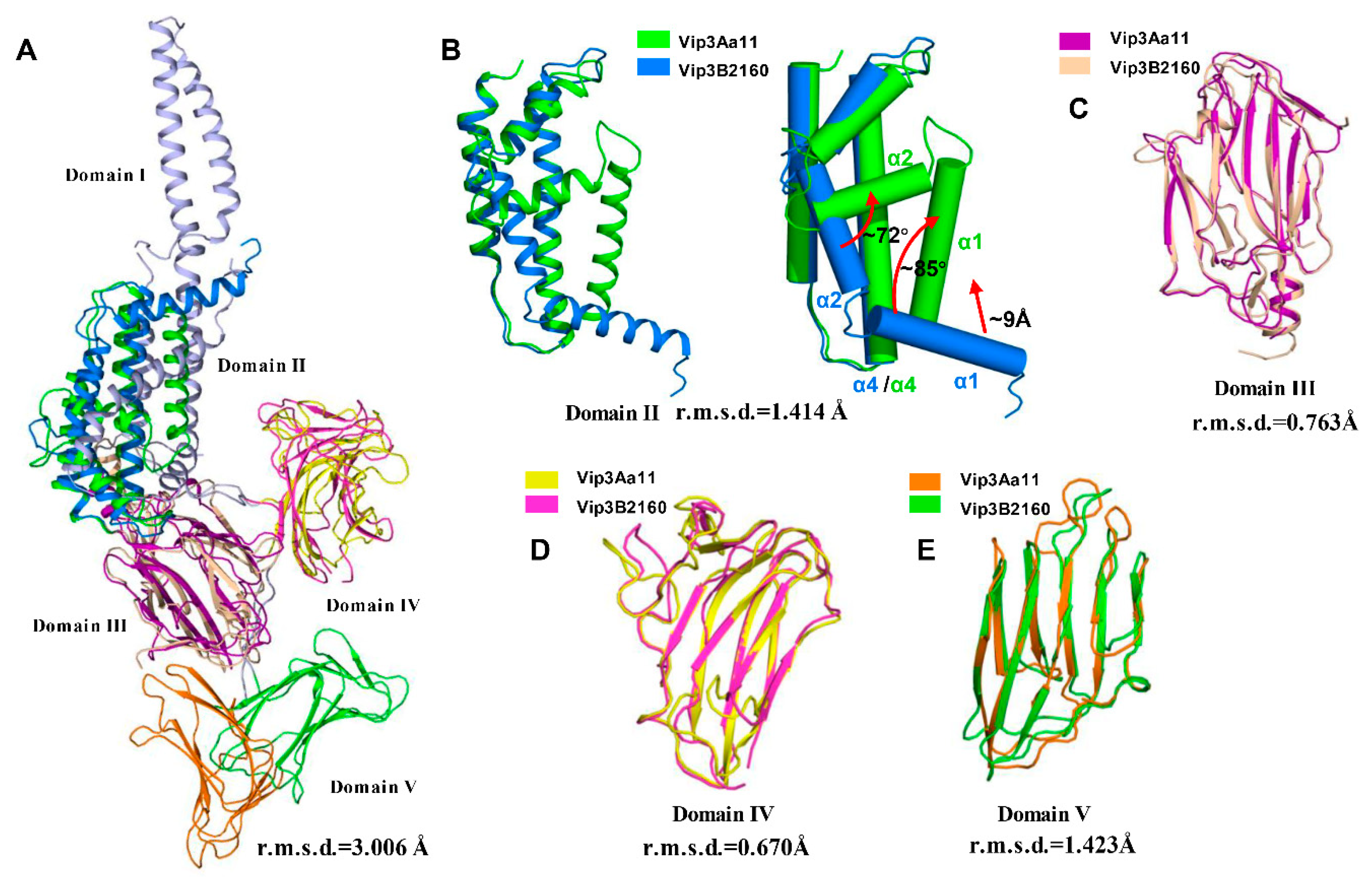
2.1. Overall Structure of Vip3Aa11200–end
2.2. Domain II Contains a Conserved Hydrophobic Architecture
2.3. Domain III Is Involved in Cell Binding of Vip3A Toxin
2.4. Domains IV and V Are Glycan Binding Motifs
2.5. Purified Vip3Aa11200–end Has no Insecticidal Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Cell Lines and Plasmids
4.2. Protein Expression and Purification
4.3. Crystallization, Data Collection and Structural Determination
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.6. Bioassay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
4.8. Data Availability
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Carrière, Y. Surge in insect resistance to transgenic crops and prospects for sustainability. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouzani, G.S.; Valijanian, E.; Sharafi, R. Bacillus thuringiensis: A successful insecticide with new environmental features and tidings. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2017, 101, 2691–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-López, L.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal three-domain Cry toxins: Mode of action, insect resistance and consequences for crop protection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adang, M.N.; Crickmore, N.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L. Diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxins and mechanism of action. In Advances in Insect Physiology 2014, Volume 47: Insect Midgut and Insecticidal Proteins; Dhadialla, T.S.S., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Crickmore, N. Specificity determinants for Cry insecticidal proteins: Insights from their mode of action. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 142, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida Melo, A.L.; Soccol, V.T.; Soccol, C.R. Bacillus thuringiensis: Mechanism of action, resistance, and new applications: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Carrière, Y. Global patterns of resistance to Bt crops highlighting Pink Bollworm in the United States, China, and India. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2513–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroun, M.; Banyuls, N.; Bel, Y.; Escriche, B.; Ferré, J. Bacterial vegetative insecticidal proteins (Vip) from entomopathogenic bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crickmore, N.; Baum, J.; Bravo, A.; Lereclus, D.; Narva, K.; Sampson, K.; Schnepf, E.; Sun, M.; Zeigler, D.R. Bacillus Thuringiensis Toxin Nomenclature. 2018. Available online: http://www.btnomenclature.info/ (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- Jiang, K.; Hou, X.; Han, L.; Tan, T.; Cao, Z.; Cai, J. Fibroblast growth factor receptor, a novel receptor for vegetative insecticidal protein Vip3Aa. Toxins 2018, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Hou, X.-Y.; Tan, T.-T.; Cao, Z.-L.; Mei, S.-Q.; Yan, B.; Chang, J.; Han, L.; Zhao, D.; Cai, J. Scavenger receptor-C acts as a receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein Vip3Aa and mediates the internalization of Vip3Aa via endocytosis. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Walters, F.S.; Hart, H.; Palekar, N.; Chen, J.S. Mode of action of the Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein Vip3A differs from that of Cry1Ab delta-endotoxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4648–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, J.A.D.; Sara Hernández-Rodríguez, C.; Ferré, J. Interaction of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1 and Vip3A proteins with Spodoptera frugiperda midgut binding sites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2236–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, R.W.; McCaffery, A.; O’Reilly, D. Insect resistance management for Syngenta’s VipCot (TM) transgenic cotton. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2007, 95, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, R.E.; Marcus, M.A.; Gould, F.; Bradley, J.R., Jr.; Van Duyn, J.W. Cross-resistance responses of Cry1Ac-selected Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to the Bacillus thuringiensis protein Vip3A. J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-B.; Lu, G.-Q.; Cheng, H.-M.; Liu, C.-X.; Xiao, Y.-T.; Xu, C.; Shen, Z.-C.; Wu, K.-M. Transgenic cotton coexpressing Vip3A and Cry1Ac has a broad insecticidal spectrum against lepidopteran pests. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 149, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Pacheco, S.; Gomez, I.; Song, F.; Soberón, M.; Zhang, J.; Bravo, A. Specific binding between Bacillus thuringiensis Cry9Aa and Vip3Aa toxins synergizes their toxicity against Asiatic rice borer (Chilo suppressalis). J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 11447–11458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wu, K. Recent progress on the interaction between insects and Bacillus thuringiensis crops. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2019, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pan, Z.-Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Niu, L.Y.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Chen, Q.-X. Proteolytic activation of Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3Aa protein by Spodoptera exigua midgut protease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, L.; Scott, D.J.; Harris, G.; Din, S.-U.; Williams, T.L.; Roberts, O.J.; Young, M.T.; Caballero, P.; Berry, C. The Vip3Ag4 insecticidal protoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis adopts a tetrameric configuration that is maintained on proteolysis. Toxins 2017, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel, Y.; Banyuls, N.; Chakroun, M.; Escriche, B.; Ferré, J. Insights into the structure of the Vip3Aa insecticidal protein by protease digestion analysis. Toxins 2017, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunthic, T.; Surya, W.; Promdonkoy, B.; Torres, J.; Boonserm, P. Conditions for homogeneous preparation of stable monomeric and oligomeric forms of activated Vip3A toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis. Eur. Biophys. J. Biophy. 2017, 46, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Ferré, J. Structural domains of the Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3Af protein unraveled by tryptic digestion of alanine mutants. Toxins 2019, 11, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, J.J.; Warren, G.W.; Mullins, M.A.; Nye, G.J.; Craig, J.A.; Koziel, M.G. Vip3A, a novel Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein with a wide spectrum of activities against lepidopteran insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5389–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Mei, S.-Q.; Wang, T.-T.; Pan, J.-H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Cai, J. Vip3Aa induces apoptosis in cultured Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) cells. Toxicon 2016, 120, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Martínez, P.; Gomis-Cebolla, J.; Ferré, J.; Escriche, B. Changes in gene expression and apoptotic response in Spodoptera exigua larvae exposed to sublethal concentrations of Vip3 insecticidal proteins. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Han, L.; An, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Cai, X.; Yan, B.; Cai, J. Mitochondria and lysosomes participate in Vip3Aa-induced Spodoptera frugiperda Sf9 cell apoptosis. Toxins 2020, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyuls, N.; Hernández-Martínez, C.S.; Van Rie, J.; Ferré, J. Critical amino acids for the insecticidal activity of Vip3Af from Bacillus thuringiensis: Inference on structural aspects. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, S.; Jemli, S.; Abdelmalek, N.; Cherif, M.; Abdelkefi-Mesrati, L.; Tounsi, S.; Jamoussi, K. A novel Vip3Aa16-Cry1Ac chimera toxin: Enhancement of toxicity against Ephestia kuehniella, structural study and molecular docking. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Evdokimov, A.G.; Moshiri, F.; Lowder, C.; Haas, J. Crystal structure of a Vip3B family insecticidal protein reveals a new fold and a unique tetrameric assembly. Protein. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krissinel, E.; Henrick, K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, L. Benchmarking Fold Detection by DaliLite v.5. In Bioinformatics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; Volume 35, pp. 5326–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Sachdev, B.; Sharma, N.; Seth, R.; Bhatnagar, R.K. Interaction of Bacillus thuringiensis Vegetative insecticidal protein with ribosomal S2 protein triggers larvicidal activity in Spodoptera frugiperda. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7202–7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, B.; Ohene-Adjei, S.; Kocherginskaya, S.; Mackie, R.I.; Spies, M.A.; Cann, I.K.O.; Nair, S.K. Molecular basis for the selectivity and specificity of ligand recognition by the family 16 carbohydrate-binding modules from Thermoanaerobacterium polysaccharolyticum ManA. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 12415–12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochulski, P.; Masson, L.; Borisova, S.; Pusztaicarey, M.; Schwartz, J.L.; Brousseau, R.; Cygler, M. Bacillus thuringiensis cryla(a) insecticidal toxin-crystal-structure and channel formation. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 254, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maagd, R.A.; Bakker, P.L.; Masson, L.; Adang, M.J.; Sangadala, S.; Stiekema, W.; Bosch, D. Domain III of the Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin Cry1Ac is involved in binding to Manduca sexta brush border membranes and to its purified aminopeptidase N. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 31, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.L.; Lee, M.K.; Valaitis, A.P.; Curtiss, A.; Dean, D.H. Bivalent sequential binding model of a Bacillus thuringiensis toxin to gypsy moth aminopeptidase N receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 14423–14431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Adang, M.J. Characterization of a Cry1Ac-receptor alkaline phosphatase in susceptible and resistant Heliothis virescens larvae. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 3127–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, E.; Zhang, A.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, X.; Sha, L.; Guan, X.; Wang, P.; Huang, Z. Oligomer formation and insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3Aa toxin. Toxins 2020, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zack, M.D.; Sopko, M.S.; Frey, M.L.; Wang, X.; Tan, S.Y.; Arruda, J.M.; Letherer, T.T.; Narva, K.E. Functional characterization of Vip3Ab1 and Vip3Bc1: Two novel insecticidal proteins with differential activity against lepidopteran pests. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomis-Cebolla, J.; Ferreira dos Santos, R.; Wang, Y.; Caballero, J.; Caballero, P.; He, K.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Ferré, J. Domain shuffling between Vip3Aa and Vip3Ca: Chimera stability and insecticidal activity against European, American, African, and Asian Pests. Toxins 2020, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.G.; Young, L.; Chuang, R.-Y.; Venter, J.C.; Hutchison, C.A.; Smith, H.O. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Macromol. Crystallogr. 1997, 276, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, D.S. Crystal structures of MBP fusion proteins. Protein. Sci. 2016, 25, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aver, N.; Skeletonisation, S.K. Cowtan, Joint CCP4 and ESF-EACBM Newsletter on Protein. Crystallography 1994, 31, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkoczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.-W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta. Crystallogr. D 2010, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, D.; Cai, J.; Gao, X. Structural and Functional Insights into the C-terminal Fragment of Insecticidal Vip3A Toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. Toxins 2020, 12, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070438
Jiang K, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Wu D, Cai J, Gao X. Structural and Functional Insights into the C-terminal Fragment of Insecticidal Vip3A Toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. Toxins. 2020; 12(7):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070438
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Kun, Yan Zhang, Zhe Chen, Dalei Wu, Jun Cai, and Xiang Gao. 2020. "Structural and Functional Insights into the C-terminal Fragment of Insecticidal Vip3A Toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis" Toxins 12, no. 7: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070438
APA StyleJiang, K., Zhang, Y., Chen, Z., Wu, D., Cai, J., & Gao, X. (2020). Structural and Functional Insights into the C-terminal Fragment of Insecticidal Vip3A Toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. Toxins, 12(7), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070438




