A Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail to Prevent Pulmonary Ricin Intoxication
Abstract
1. Introduction
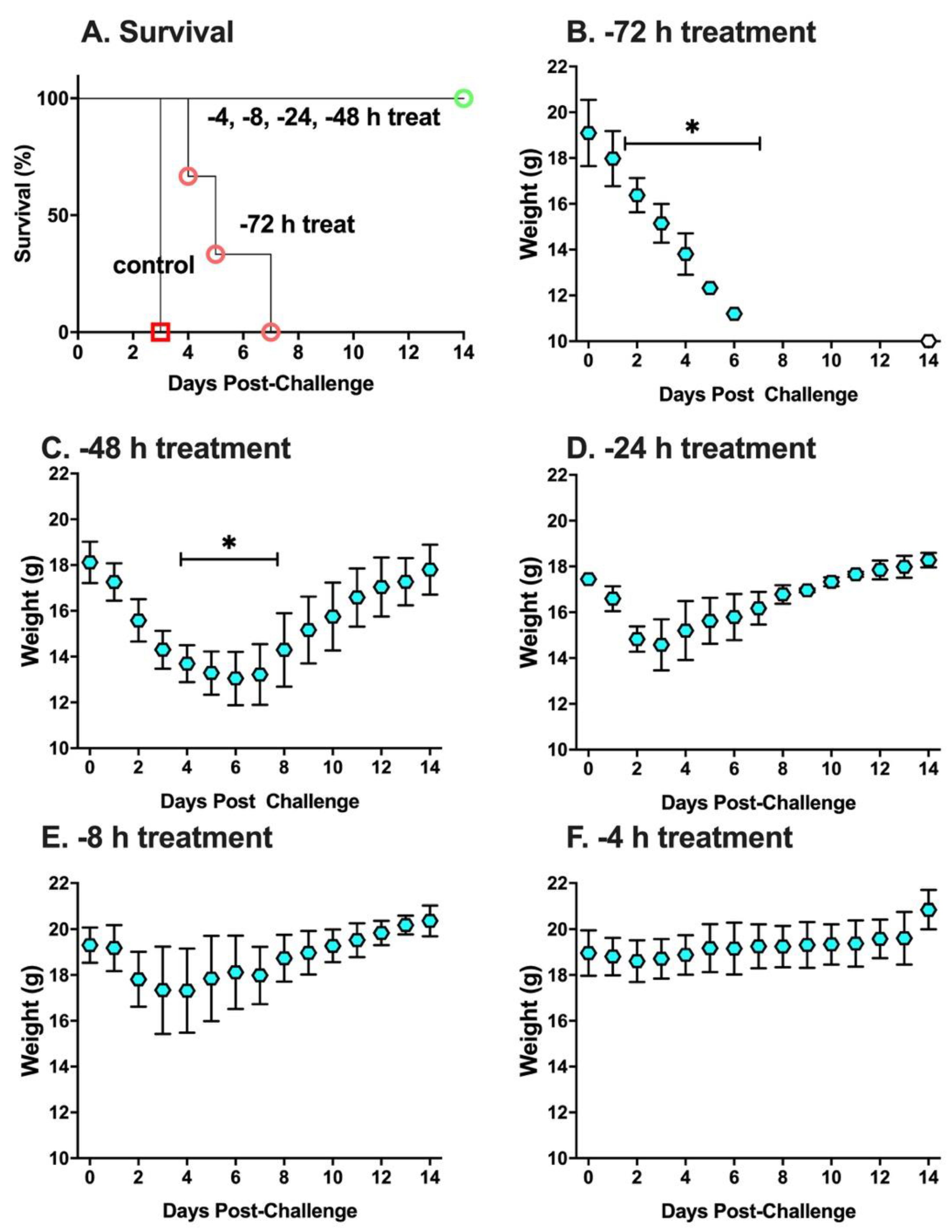
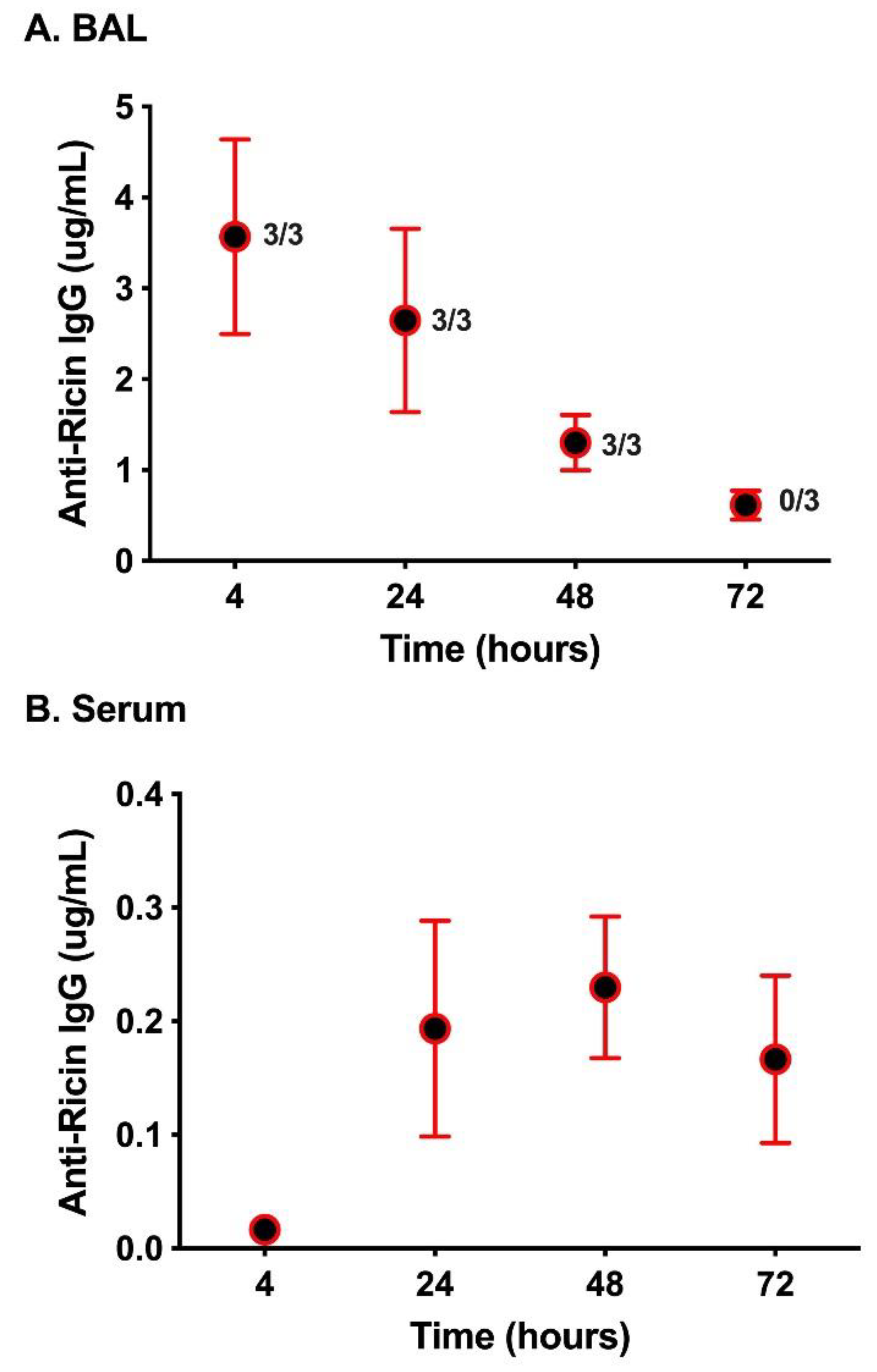
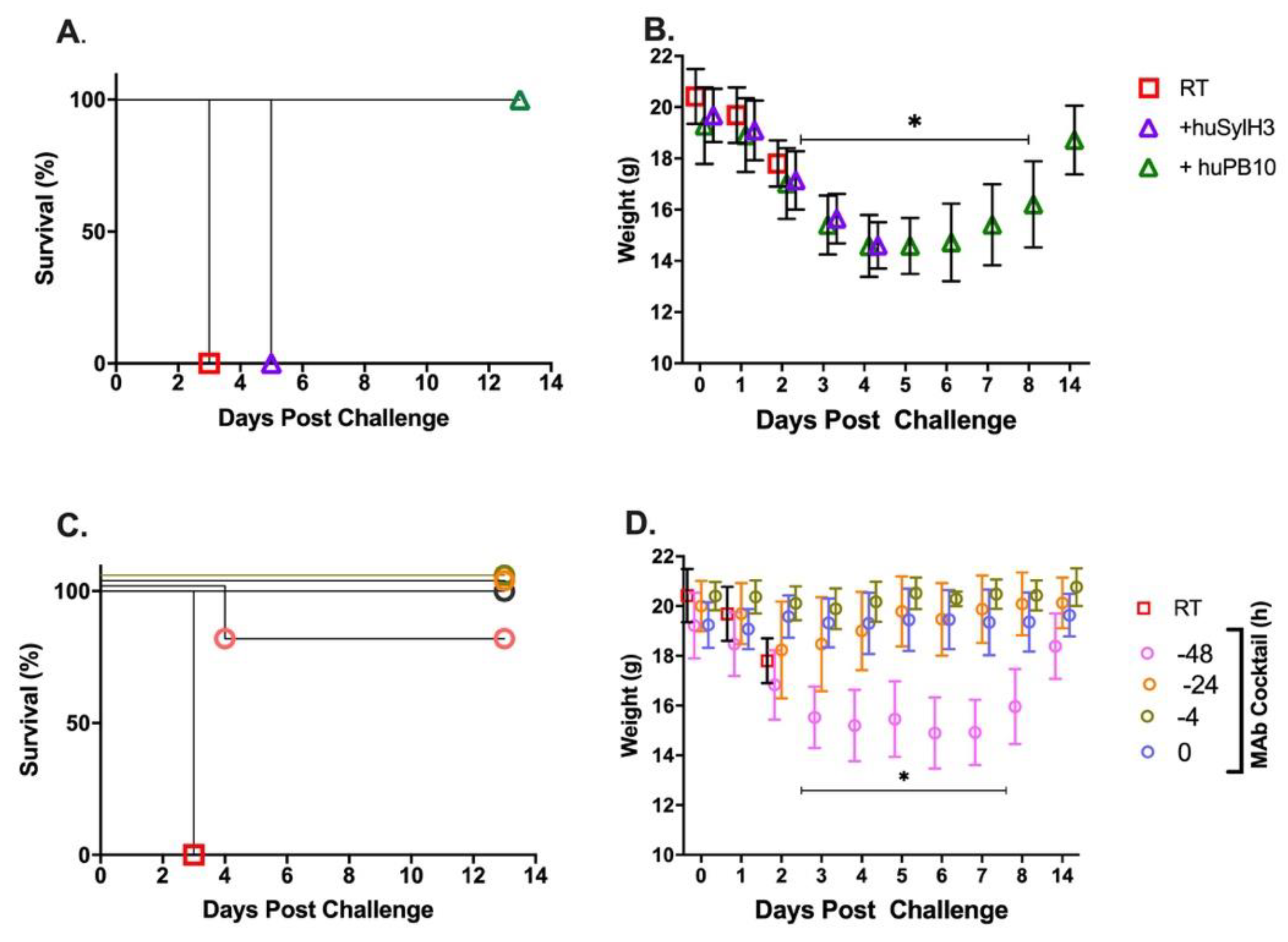
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Biological Reagents
4.2. Monoclonal Antibodies (MAbs)
4.3. Ethics Statement for Studies Involving Mice
4.4. Experimental Design of Animal Studies
4.5. Vero Cell Cytotoxicity Assays
4.6. ELISA Methodology
4.7. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
4.8. Humanization of SylH3
4.9. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cieslak, T.J.; Kortepeter, M.G.; Wojtyk, R.J.; Jansen, H.J.; Reyes, R.A.; Smith, J.O.; NATO Biological Medical Advisory Panel. Beyond the Dirty Dozen: A Proposed Methodology for Assessing Future Bioweapon Threats. Mil. Med. 2018, 183, e59–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smallshaw, J.E.; Richardson, J.A.; Vitetta, E.S. RiVax, a recombinant ricin subunit vaccine, protects mice against ricin delivered by gavage or aerosol. Vaccine 2007, 25, 7459–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, S.H.; Bhaskaran, M.; Brey, R.N., 3rd; Didier, P.J.; Doyle-Meyers, L.A.; Roy, C.J. Clinical and Pathological Findings Associated with Aerosol Exposure of Macaques to Ricin Toxin. Toxins 2015, 7, 2121–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, M.; Didier, P.J.; Sivasubramani, S.K.; Doyle, L.A.; Holley, J.; Roy, C.J. Pathology of lethal and sublethal doses of aerosolized ricin in rhesus macaques. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 42, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal, Y.; Mazor, O.; Falach, R.; Sapoznikov, A.; Kronman, C.; Sabo, T. Treatments for Pulmonary Ricin Intoxication: Current Aspects and Future Prospects. Toxins 2017, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katalan, S.; Falach, R.; Rosner, A.; Goldvaser, M.; Brosh-Nissimov, T.; Dvir, A.; Mizrachi, A.; Goren, O.; Cohen, B.; Gal, Y.; et al. A novel swine model of ricin-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Dis. Model Mech. 2017, 10, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.F.; White, D.E. Ultrastructure of rat lung following inhalation of ricin aerosol. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 1997, 78, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindauer, M.L.; Wong, J.; Iwakura, Y.; Magun, B.E. Pulmonary inflammation triggered by ricin toxin requires macrophages and IL-1 signaling. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Westfall, J.; Ehrbar, D.; LaRocca, T.; Mantis, N.J. TRAIL (CD253) Sensitizes Human Airway Epithelial Cells to Toxin-Induced Cell Death. mSphere 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Torres-Velez, F.J.; Ehrbar, D.; Doering, J.; Song, R.; Mantis, N.J. An intranasally administered monoclonal antibody cocktail abrogates ricin toxin-induced pulmonary tissue damage and inflammation. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Korcheva, V.; Jacoby, D.B.; Magun, B. Intrapulmonary delivery of ricin at high dosage triggers a systemic inflammatory response and glomerular damage. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1497–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, C.J.; Ehrbar, D.J.; Bohorova, N.; Bohorov, O.; Kim, D.; Pauly, M.; Whaley, K.; Rong, Y.; Torres-Velez, F.J.; Vitetta, E.S.; et al. Rescue of rhesus macaques from the lethality of aerosolized ricin toxin. JCI Insight 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, C.J.; Van Slyke, G.; Ehrbar, D.; Bornholdt, Z.A.; Brennan, M.B.; Campbell, L.; Chen, M.; Kim, D.; Mlakar, N.; Whaley, K.J.; et al. Passive immunization with an extended half-life monoclonal antibody protects Rhesus macaques against aerosolized ricin toxin. NPJ Vaccin. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, R.T.I.; Angalakurthi, S.K.; Van Slyke, G.; Vance, D.J.; Hickey, J.M.; Joshi, S.B.; Middaugh, C.R.; Volkin, D.B.; Weis, D.D.; Mantis, N.J. High-Definition Mapping of Four Spatially Distinct Neutralizing Epitope Clusters on RiVax, a Candidate Ricin Toxin Subunit Vaccine. Clin. Vaccin. Immunol. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yermakova, A.; Klokk, T.I.; O’Hara, J.M.; Cole, R.; Sandvig, K.; Mantis, N.J. Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies against Disparate Epitopes on Ricin Toxin’s Enzymatic Subunit Interfere with Intracellular Toxin Transport. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Slyke, G.; Sully, E.K.; Bohorova, N.; Bohorov, O.; Kim, D.; Pauly, M.H.; Whaley, K.J.; Zeitlin, L.; Mantis, N.J. Humanized Monoclonal Antibody That Passively Protects Mice against Systemic and Intranasal Ricin Toxin Challenge. Clin. Vaccin. Immunol. 2016, 23, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whaley, K.J.; Hiatt, A.; Zeitlin, L. Emerging antibody products and Nicotiana manufacturing. Hum. Vaccin. 2011, 7, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poli, M.A.; Rivera, V.R.; Pitt, M.L.; Vogel, P. Aerosolized specific antibody protects mice from lung injury associated with aerosolized ricin exposure. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Respaud, R.; Marchand, D.; Pelat, T.; Tchou-Wong, K.M.; Roy, C.J.; Parent, C.; Cabrera, M.; Guillemain, J.; Mac Loughlin, R.; Levacher, E.; et al. Development of a drug delivery system for efficient alveolar delivery of a neutralizing monoclonal antibody to treat pulmonary intoxication to ricin. J. Control. Release 2016, 234, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, D.J.; Tremblay, J.M.; Rong, Y.; Angalakurthi, S.K.; Volkin, D.B.; Middaugh, C.R.; Weis, D.D.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Mantis, N.J. High-Resolution Epitope Positioning of a Large Collection of Neutralizing and Nonneutralizing Single-Domain Antibodies on the Enzymatic and Binding Subunits of Ricin Toxin. Clin. Vaccin. Immunol. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, D.J.; Tremblay, J.M.; Mantis, N.J.; Shoemaker, C.B. Stepwise engineering of heterodimeric single domain camelid VHH antibodies that passively protect mice from ricin toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 36538–36547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sully, E.K.; Whaley, K.J.; Bohorova, N.; Bohorov, O.; Goodman, C.; Kim, D.H.; Pauly, M.H.; Velasco, J.; Hiatt, E.; Morton, J.; et al. Chimeric plantibody passively protects mice against aerosolized ricin challenge. Clin. Vaccin. Immunol. 2014, 21, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, B.; Torres-Velez, F.J.; Doering, J.; Ehrbar, D.J.; Mantis, N.J. Sensitivity of Kupffer cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells to ricin toxin and ricin toxin-Ab complexes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, Y.; Tsurugi, K. The RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. The characteristics of the enzymatic activity of ricin A-chain with ribosomes and with rRNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 8735–8739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sapoznikov, A.; Falach, R.; Mazor, O.; Alcalay, R.; Gal, Y.; Seliger, N.; Sabo, T.; Kronman, C. Diverse profiles of ricin-cell interactions in the lung following intranasal exposure to ricin. Toxins 2015, 7, 4817–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, A.L.; Kempen, C.G.; McCaig, W.D.; Parker, C.A.; Mantis, N.J.; LaRocca, T.J. TNF Family Cytokines Induce Distinct Cell Death Modalities in the A549 Human Lung Epithelial Cell Line when Administered in Combination with Ricin Toxin. Toxins 2019, 11, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilleminault, L.; Azzopardi, N.; Arnoult, C.; Sobilo, J.; Herve, V.; Montharu, J.; Guillon, A.; Andres, C.; Herault, O.; Le Pape, A.; et al. Fate of inhaled monoclonal antibodies after the deposition of aerosolized particles in the respiratory system. J. Control. Release 2014, 196, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koussoroplis, S.J.; Paulissen, G.; Tyteca, D.; Goldansaz, H.; Todoroff, J.; Barilly, C.; Uyttenhove, C.; Van Snick, J.; Cataldo, D.; Vanbever, R.; et al. PEGylation of antibody fragments greatly increases their local residence time following delivery to the respiratory tract. J. Control. Release 2014, 187, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, A.; Guilleminault, L.; Lemarie, E.; Lerondel, S.; Azzopardi, N.; Montharu, J.; Congy-Jolivet, N.; Reverdiau, P.; Legrain, B.; Parent, C.; et al. The airways, a novel route for delivering monoclonal antibodies to treat lung tumors. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Pfarr, D.S.; Johnson, S.; Brewah, Y.A.; Woods, R.M.; Patel, N.K.; White, W.I.; Young, J.F.; Kiener, P.A. Development of motavizumab, an ultra-potent antibody for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection in the upper and lower respiratory tract. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 368, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Van Slyke, G.; Vance, D.J.; Westfall, J.; Ehrbar, D.; Mantis, N.J. Spatial location of neutralizing and non-neutralizing B cell epitopes on domain 1 of ricin toxin’s binding subunit. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yermakova, A.; Klokk, T.I.; Cole, R.; Sandvig, K.; Mantis, N.J. Antibody-mediated inhibition of ricin toxin retrograde transport. mBio 2014, 5, e00995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Schaefer, A.; Wang, Y.Y.; McCallen, J.; Lee, P.; Newby, J.M.; Arora, H.; Kumar, P.A.; Zeitlin, L.; Whaley, K.J.; et al. ZMappTM Reinforces the Airway Mucosal Barrier Against Ebola Virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemley, P.V.; Amanatides, P.; Wright, D.C. Identification and characterization of a monoclonal antibody that neutralizes ricin toxicity in vitro and in vivo. Hybridoma 1994, 13, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.W.; Shen, B.F.; Feng, J.N.; Sun, Y.X.; Yu, M.; Hu, M.R. A novel neutralizing monoclonal antibody against cell-binding polypeptide of ricin. Hybridoma 2005, 24, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, C.R.; Mantis, N.J. Characterization of a novel high-affinity monoclonal immunoglobulin G antibody against the ricin B subunit. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3463–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, T.S.; Pincus, S.H.; Hale, M.L.; Moreira, A.L.; Roy, C.J.; Tchou-Wong, K.M. Oropharyngeal aspiration of ricin as a lung challenge model for evaluation of the therapeutic index of antibodies against ricin A-chain for post-exposure treatment. Exp. Lung Res. 2007, 33, 459–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, J.M.; Neal, L.M.; McCarthy, E.A.; Kasten-Jolly, J.A.; Brey, R.N., 3rd; Mantis, N.J. Folding domains within the ricin toxin A subunit as targets of protective antibodies. Vaccine 2010, 28, 7035–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermakova, A.; Mantis, N.J. Protective immunity to ricin toxin conferred by antibodies against the toxin’s binding subunit (RTB). Vaccine 2011, 29, 7925–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.G.; Yin, J.; Chau, D.; Hu, C.C.; Lillico, D.; Yu, J.; Negrych, L.M.; Cherwonogrodzky, J.W. Conformation-dependent high-affinity potent ricin-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy-Porat, T.; Rosenfeld, R.; Ariel, N.; Epstein, E.; Alcalay, R.; Zvi, A.; Kronman, C.; Ordentlich, A.; Mazor, O. Isolation of Anti-Ricin Protective Antibodies Exhibiting High Affinity from Immunized Non-Human Primates. Toxins 2016, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddaloni, M.; Cooke, C.; Wilkinson, R.; Stout, A.V.; Eng, L.; Pincus, S.H. Immunological characteristics associated with the protective efficacy of antibodies to ricin. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6221–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambour, J.; Naranjo-Gomez, M.; Piechaczyk, M.; Pelegrin, M. Converting monoclonal antibody-based immunotherapies from passive to active: Bringing immune complexes into play. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2016, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, L.M.; O’Hara, J.; Brey, R.N., 3rd; Mantis, N.J. A monoclonal immunoglobulin G antibody directed against an immunodominant linear epitope on the ricin a chain confers systemic and mucosal immunity to ricin. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahome, P.G.; Mantis, N.J. High-throughput, cell-based screens to identify small-molecule inhibitors of ricin toxin and related category b ribosome inactivating proteins (RIPs). Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.K.; Labute, P. Assessment of fully automated antibody homology modeling protocols in molecular operating environment. Proteins 2014, 82, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennamsetty, N.; Quan, Y.; Nashine, V.; Sadineni, V.; Lyngberg, O.; Krystek, S. Modeling the oxidation of methionine residues by peroxides in proteins. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, N.E.; Robinson, A.B. Prediction of protein deamidation rates from primary and three-dimensional structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4367–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydow, J.F.; Lipsmeier, F.; Larraillet, V.; Hilger, M.; Mautz, B.; Molhoj, M.; Kuentzer, J.; Klostermann, S.; Schoch, J.; Voelger, H.R.; et al. Structure-based prediction of asparagine and aspartate degradation sites in antibody variable regions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckert, P.; Brunak, S.; Blom, N. Prediction of proprotein convertase cleavage sites. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2004, 17, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Hu Variant | ka (1/Ms) | kd (1/s) | KD (M) a | EC50b | IC50c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1008 | 1.25 × 106 | 6.78 × 10−5 | 5.42 × 10−11 | 0.15 | 2 |
| 0403 | 1.33 × 106 | 7.3 × 10−5 | 5.45 × 10−11 | 0.078 | 1 |
| 0703 | 1.35 × 106 | 7.79 × 10−5 | 5.74 × 10−11 | 0.019 | 1 |
| 0107 | 1.59 × 106 | 3.81 × 10−5 | 2.39 × 10−11 | 0.078 | 2 |
| 0206 | 1.41 × 106 | 1.37 × 10−4 | 9.96 × 10−11 | 0.039 | 1 |
| 0908 | 1.34 × 106 | 7.29 × 10−5 | 5.43 × 10−11 | 0.039 | 1 |
| 0801 | 1.46 × 106 | 7.45 × 10−5 | 5.07 × 10−11 | 0.039 | 1 |
| 0209 | 1.40 × 106 | 1.35 × 10−4 | 9.62 × 10−11 | 0.019 | 1 |
| Score | Clinical Signs |
|---|---|
| 0 | Normal |
| 1 | Ruffled Fur |
| 2 | Hunching, ataxia, distended abdomen, diarrhea, solitary nesting, |
| 3 | Severe weakness, tremors, circling, head tilt, seizures, eyes closed |
| 4 | Paralyzed limb(s) |
| 5 | Morbid, non-responsive |
| 6 | Dead |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rong, Y.; Pauly, M.; Guthals, A.; Pham, H.; Ehrbar, D.; Zeitlin, L.; Mantis, N.J. A Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail to Prevent Pulmonary Ricin Intoxication. Toxins 2020, 12, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040215
Rong Y, Pauly M, Guthals A, Pham H, Ehrbar D, Zeitlin L, Mantis NJ. A Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail to Prevent Pulmonary Ricin Intoxication. Toxins. 2020; 12(4):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040215
Chicago/Turabian StyleRong, Yinghui, Michael Pauly, Adrian Guthals, Henry Pham, Dylan Ehrbar, Larry Zeitlin, and Nicholas J. Mantis. 2020. "A Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail to Prevent Pulmonary Ricin Intoxication" Toxins 12, no. 4: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040215
APA StyleRong, Y., Pauly, M., Guthals, A., Pham, H., Ehrbar, D., Zeitlin, L., & Mantis, N. J. (2020). A Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail to Prevent Pulmonary Ricin Intoxication. Toxins, 12(4), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040215





